Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Physician’s Guide to the Clinical Spectrum Diagnosis and Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. What Is Autoimmune Encephalitis?
3. History of Autoimmune Encephalitis
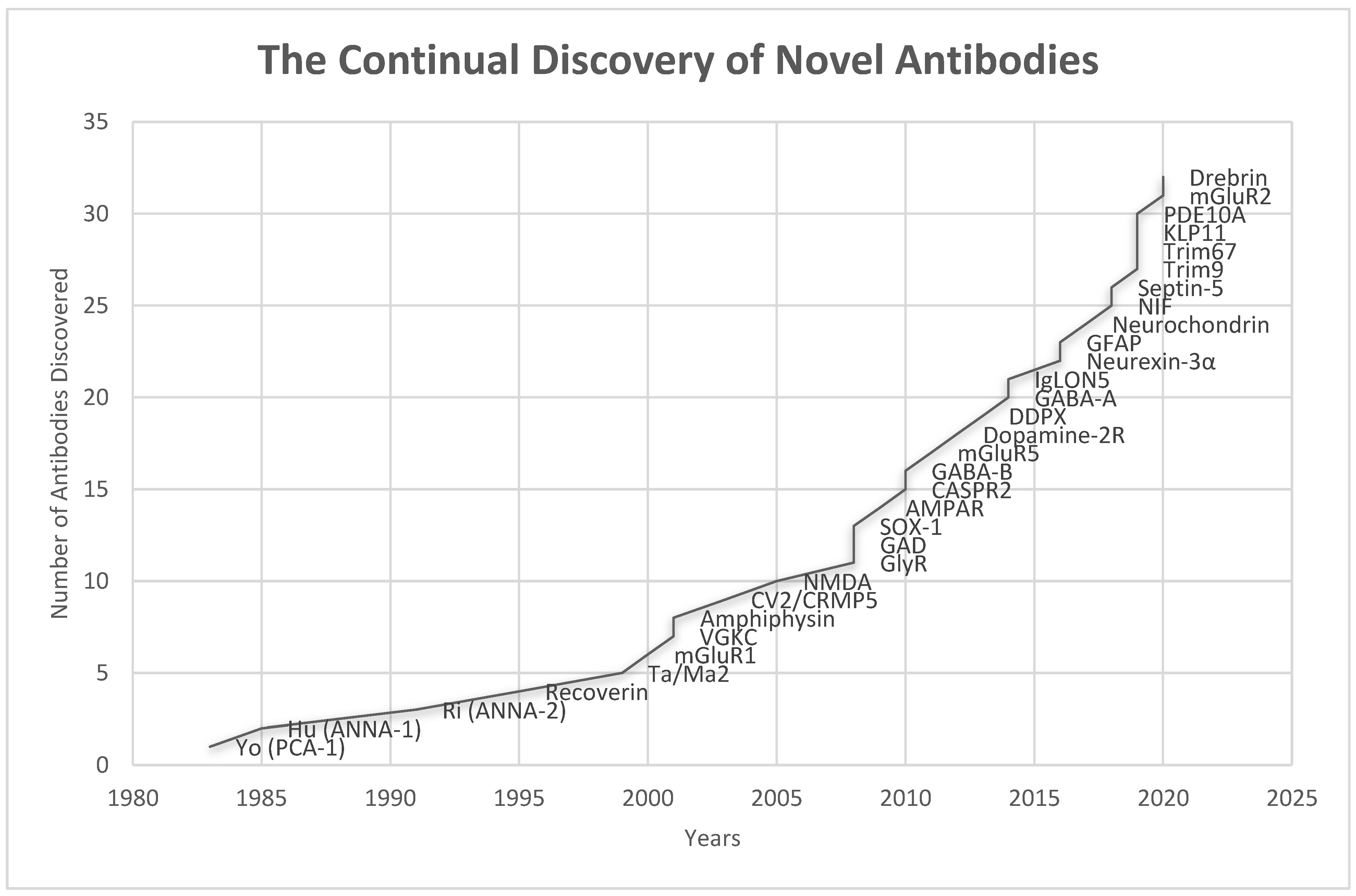
4. Pathophysiology and Immune Triggers of Autoimmune Encephalitis
5. Clinical Spectrum
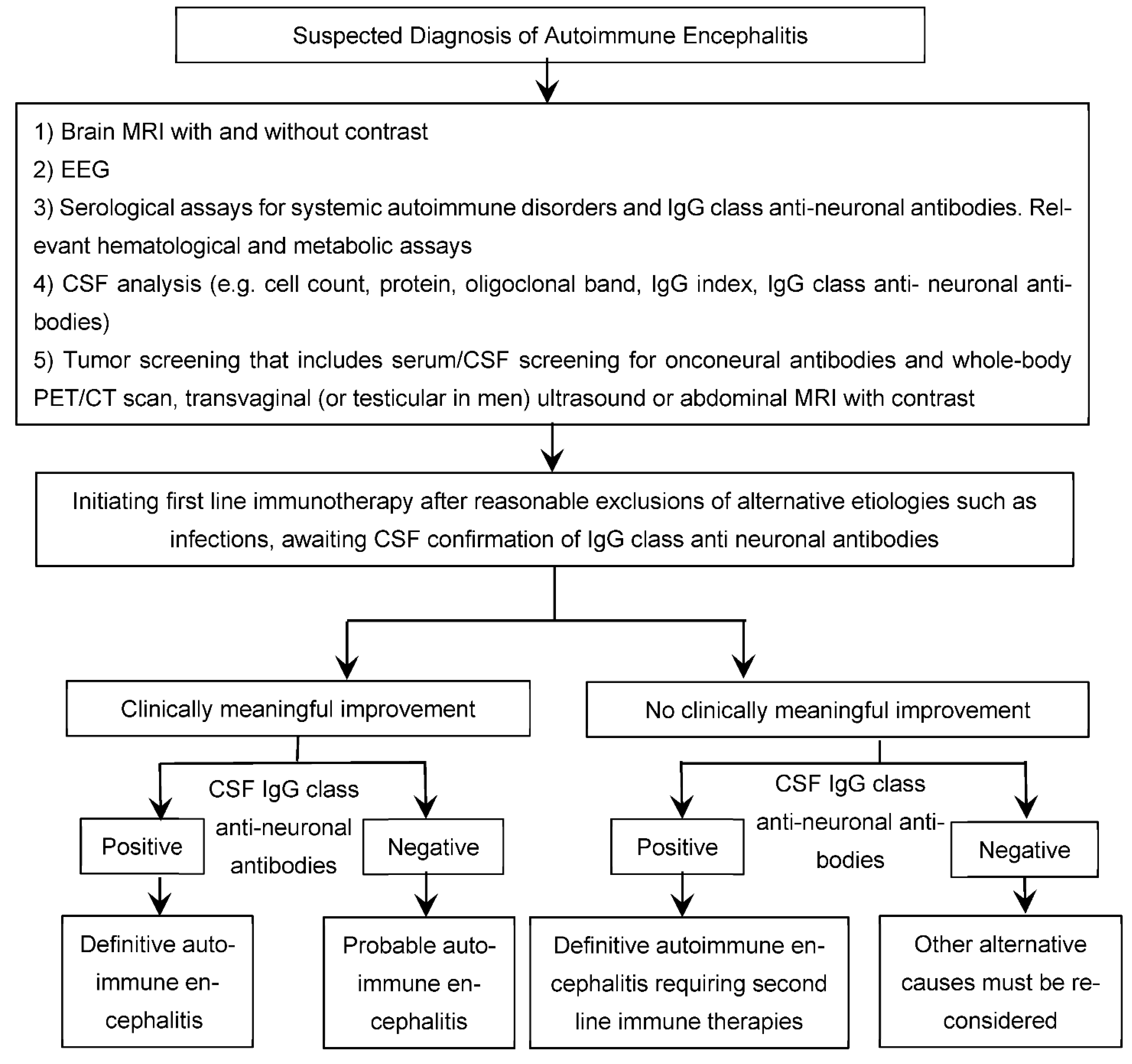
6. Diagnosis
7. Management
| Immunomodulator | Dosing Regimen |
|---|---|
| First line immunomodulators | |
| 1000 mg IV daily for 5 consecutive days |
| 2 g/kg bodyweight IV infusion typically divided over 5 days |
| 1 session every other day for an average of 5–7 sessions, based on response and tolerance |
| Second line immunomodulators | |
| Two 1000 mg doses separated by 2 weeks or weekly 375 mg/m2 infusions for 4 weeks |
| 750–800 mg/m2 monthly for 3–6 months |
| Third line immunomodulators | |
| Initially 4 mg/kg, followed by an increase to 8 mg/kg monthly based on clinical response (maximum dose: 800 mg) |
| 10–12 mg weekly for 3–4 weeks |
| Maintenance therapy | |
| (Doses, frequency, and duration of treatment vary based on the symptom’s severity, relapse risk, and tolerance) |
| |
| |
| |
|
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Autoimmune Encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Pittock, S.J.; Kelly, C.R.; McKeon, A.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Lennon, V.A.; Gadoth, A.; Smith, C.Y.; Bryant, S.C.; Klein, C.J.; et al. Autoimmune Encephalitis Epidemiology and a Comparison to Infectious Encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.; Sotoca, J.; Gandhi, S.; Yeshokumar, A.K.; Gordon-Lipkin, E.; Geocadin, R.G.; Frick, K.D.; Probasco, J.C.; Venkatesan, A. Autoimmune Encephalitis. Neurology 2019, 92, e964–e972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, A. How Do We Fix the Shortage of Neurologists? Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 502–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messacar, K.; Fischer, M.; Dominguez, S.R.; Tyler, K.L.; Abzug, M.J. Encephalitis in US Children. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.; Michael, B.D.; Probasco, J.C.; Geocadin, R.G.; Solomon, T. Acute Encephalitis in Immunocompetent Adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss, H. Postviral Autoimmune Encephalitis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Geis, C.; Graus, F. Autoantibodies to Synaptic Receptors and Neuronal Cell Surface Proteins in Autoimmune Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 839–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignolet, B.S.; Gebauer, C.M.; Liblau, R.S. Immunopathogenesis of Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes Associated with Anti-Hu Antibodies. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e27384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, C.; Pignolet, B.; Yshii, L.; Mauré, E.; Bauer, J.; Liblau, R. CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells Are Both Needed to Induce Paraneoplastic Neurological Disease in a Mouse Model. Oncoimmunology 2016, 6, e1260212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilli, D.; Zou, A.; Tea, F.; Dale, R.C.; Brilot, F. Expanding Role of T Cells in Human Autoimmune Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Antibody-Mediated Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-W.; Lee, S.-T.; Park, K.-I.; Jung, K.-H.; Jung, K.-Y.; Lee, S.K.; Chu, K. Treatment Strategies for Autoimmune Encephalitis. Adv. Neurol. Diso. 2017, 11, 175628561772234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manto, M.; Honnorat, J.; Hampe, C.S.; Guerra-Narbona, R.; López-Ramos, J.C.; Delgado-García, J.M.; Saitow, F.; Suzuki, H.; Yanagawa, Y.; Mizusawa, H.; et al. Disease-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Glutamate Decarboxylase Impair GABAergic Neurotransmission and Affect Motor Learning and Behavioral Functions. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorstad, G.; Hestvik, A.L.K.; Vartdal, F.; Holmøy, T. Cerebrospinal Fluid T Cell Responses against Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase 65 in Patients with Stiff Person Syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 32, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, E.; Dalmau, J. Neuronal Autoantigens—Pathogenesis, Associated Disorders and Antibody Testing. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, B.; Biemond, A. Les Affections Parachymateuses Du Cervelet et Leur Signification Du Point de Vue de l’anatomie et La Physiologie de Cet Organe. 1938, 38, 691–757. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.M.S. Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis. Eur. Neurol. 2005, 53, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsellis, J.A.; Goldberg, G.J.; Norton, A.R. “Limbic Encephalitis” and Its Association with Carcinoma. Brain 1968, 91, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A. John Newsom-Davis: Clinician-Scientist and so Much More. Brain 2011, 134, 3755–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Lee, S.-T. The Laboratory Diagnosis of Autoimmune Encephalitis. J. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 6, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furneaux, H.F.; Reich, L.; Posner, J.B. Autoantibody Synthesis in the Central Nervous System of Patients with Paraneoplastic Syndromes. Neurology 1990, 40, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, C.; Oger, J.; Clover, L.; Tüzün, E.; Carpenter, K.; Jackson, M.; Vincent, A. Potassium Channel Antibodies in Two Patients with Reversible Limbic Encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, R.; Vincent, A.; Clover, L.; Avoni, P.; Plazzi, G.; Cortelli, P.; Baruzzi, A.; Carey, T.; Gambetti, P.; Lugaresi, E.; et al. Morvan’s Syndrome: Peripheral and Central Nervous System and Cardiac Involvement with Antibodies to Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Brain 2001, 124, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitaliani, R.; Mason, W.; Ances, B.; Zwerdling, T.; Jiang, Z.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic Encephalitis, Psychiatric Symptoms, and Hypoventilation in Ovarian Teratoma. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansing, L.H.; Tüzün, E.; Ko, M.W.; Baccon, J.; Lynch, D.R.; Dalmau, J. A Patient with Encephalitis Associated with NMDA Receptor Antibodies. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2007, 3, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Tüzün, E.; Wu, H.; Masjuan, J.; Rossi, J.E.; Voloschin, A.; Baehring, J.M.; Shimazaki, H.; Koide, R.; King, D.; et al. Paraneoplastic Anti–N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Encephalitis Associated with Ovarian Teratoma. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, S.; Pearlman, D.; Devinsky, O.; Najjar, A.; Nadkarni, S.; Butler, T.; Zagzag, D. Neuropsychiatric Autoimmune Encephalitis without VGKC-Complex, NMDAR, and GAD Autoantibodies: Case Report and Literature Review. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2013, 26, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, S.; Pearlman, D.; Zagzag, D.; Devinsky, O. Spontaneously Resolving Seronegative Autoimmune Limbic Encephalitis. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2011, 24, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armangue, T.; Moris, G.; Cantarín-Extremera, V.; Conde, C.E.; Rostasy, K.; Erro, M.E.; Portilla-Cuenca, J.C.; Turón-Viñas, E.; Málaga, I.; Muñoz-Cabello, B.; et al. Autoimmune Post–Herpes Simplex Encephalitis of Adults and Teenagers. Neurology 2015, 85, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.J.; Benavides, D.R.; Patrice, K.-A.; Dalmau, J.O.; de Ávila, A.L.R.; Le, D.T.; Lipson, E.J.; Probasco, J.C.; Mowry, E.M. Association of Autoimmune Encephalitis With Combined Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment for Metastatic Cancer. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee, J.E.; Brashear, H.R. Antibodies to Cerebellar Purkinje Cells in Patients with Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration and Ovarian Carcinoma. Ann. Neurol. 1983, 14, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Posner, J.B. Neuronal Antinuclear Antibody in Sensory Neuronopathy from Lung Cancer. Neurology 1985, 35, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero, D.; Barnadas, A.; Codina, M.; Fueyo, J.; Graus, F. Anti-Ri-Associated Paraneoplastic Neurologic Disorder without Opsoclonus in a Patient with Breast Cancer. Neurology 1993, 43, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, V.A.; Kryzer, T.J.; Griesmann, G.E.; O’Suilleabhain, P.E.; Windebank, A.J.; Woppmann, A.; Miljanich, G.P.; Lambert, E.H. Calcium-Channel Antibodies in the Lambert-Eaton Syndrome and Other Paraneoplastic Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smitt, P.S.; Kinoshita, A.; Leeuw, B.D.; Moll, W.; Coesmans, M.; Jaarsma, D.; Henzen-Logmans, S.; Vecht, C.; Zeeuw, C.D.; Sekiyama, N.; et al. Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Ataxia Due to Autoantibodies against a Glutamate Receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polans, A.S.; Witkowska, D.; Haley, T.L.; Amundson, D.; Baizer, L.; Adamus, G. Recoverin, a Photoreceptor-Specific Calcium-Binding Protein, Is Expressed by the Tumor of a Patient with Cancer-Associated Retinopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9176–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Dalmau, J.; Valldeoriola, F.; Ferrer, I.; Reñe, R.; Marin, C.; Vecht, C.J.; Arbizu, T.; Targa, C.; Moll, J.W. Immunological Characterization of a Neuronal Antibody (Anti-Tr) Associated with Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration and Hodgkin’s Disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 74, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorresteijn, L.D.A.; Kappelle, A.C.; Renier, W.O.; Gijtenbeck, J.M.M. Anti-Amphiphysin Associated Limbic Encephalitis: A Paraneoplastic Presentation of Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 1307–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinirons, P.; Fulton, A.; Keoghan, M.; Brennan, P.; Farrell, M.A.; Moroney, J.T. Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis (PLE) and Chorea Associated with CRMP-5 Neuronal Antibody. Neurology 2003, 61, 1623–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, L.; Titulaer, M.; Saiz, A.; Verschuuren, J.; Gure, A.O.; Graus, F. SOX1 Antibodies Are Markers of Paraneoplastic Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome. Neurology 2007, 70, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.; Waters, P.; McHugh, J.; Gorman, G.; O’Riordan, S.; Connolly, S.; Hager, H.; Yu, P.; Becker, C.-M.; Vincent, A. Progressive Encephalomyelitis, Rigidity, and Myoclonus: A Novel Glycine Receptor Antibody. Neurology 2008, 71, 1291–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiz, A.; Blanco, Y.; Sabater, L.; González, F.; Bataller, L.; Casamitjana, R.; Ramió-Torrentà, L.; Graus, F. Spectrum of Neurological Syndromes Associated with Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Antibodies: Diagnostic Clues for This Association. Brain 2008, 131, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spatola, M.; Stojanova, V.; Prior, J.O.; Dalmau, J.; Rossetti, A.O. Serial Brain 18FDG-PET in Anti-AMPA Receptor Limbic Encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 271, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, E.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Boulos, M.; Weaver, S.; Antoine, J.-C.; Liebers, E.; Kornblum, C.; Bien, C.G.; Honnorat, J.; et al. Antibodies to Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Ophelia Syndrome. Neurology 2011, 77, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.C.; Merheb, V.; Pillai, S.; Wang, D.; Cantrill, L.; Murphy, T.K.; Ben-Pazi, H.; Varadkar, S.; Aumann, T.D.; Horne, M.K.; et al. Antibodies to Surface Dopamine-2 Receptor in Autoimmune Movement and Psychiatric Disorders. Brain 2012, 135, 3453–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boronat, A.; Gelfand, J.M.; Gresa-Arribas, N.; Jeong, H.-Y.; Walsh, M.; Roberts, K.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Balice-Gordon, R.; Graus, F.; et al. Encephalitis and Antibodies to Dipeptidyl-Peptidase-like Protein-6, a Subunit of Kv4.2 Potassium Channels. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 73, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, L.; Gaig, C.; Gelpi, E.; Bataller, L.; Lewerenz, J.; Torres-Vega, E.; Contreras, A.; Giometto, B.; Compta, Y.; Embid, C.; et al. A Novel Non-Rapid-Eye Movement and Rapid-Eye-Movement Parasomnia with Sleep Breathing Disorder Associated with Antibodies to IgLON5: A Case Series, Characterisation of the Antigen, and Post-Mortem Study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresa-Arribas, N.; Planagumà, J.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Kawachi, I.; Katada, S.; Glaser, C.A.; Simabukuro, M.M.; Armangue, T.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Graus, F.; et al. Human Neurexin-3α Antibodies Associate with Encephalitis and Alter Synapse Development. Neurology 2016, 86, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; McKeon, A.; Hinson, S.R.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Aksamit, A.J.; Lennon, V.A. Autoimmune Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Astrocytopathy: A Novel Meningoencephalomyelitis. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveau, A.; Plog, B.A.; Antila, S.; Alitalo, K.; Nedergaard, M.; Kipnis, J. Understanding the Functions and Relationships of the Glymphatic System and Meningeal Lymphatics. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3210–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.; Restrepo-Jiménez, P.; Monsalve, D.M.; Pacheco, Y.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Leung, P.S.C.; Ansari, A.A.; Gershwin, M.E.; Anaya, J.-M. Molecular Mimicry and Autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 95, 100–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarkiewicz, J.; Pogoda, K.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Pozarowski, P.; Giannopoulos, K. The Role of IL-17 and Th17 Lymphocytes in Autoimmune Diseases. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2015, 63, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, M.P.; Agalliu, D.; Cutforth, T. Hello from the Other Side: How Autoantibodies Circumvent the Blood–Brain Barrier in Autoimmune Encephalitis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Könnecke, H.; Bechmann, I. The Role of Microglia and Matrix Metalloproteinases Involvement in Neuroinflammation and Gliomas. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 914104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Kang, W.; Peng, G.; Yu, D.; Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Dai, F.; et al. Cytokines/Chemokines: Potential Biomarkers for Non-Paraneoplastic Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 582296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bien, C.G.; Vincent, A.; Barnett, M.H.; Becker, A.J.; Blumcke, I.; Graus, F.; Jellinger, K.A.; Reuss, D.E.; Ribalta, T.; Schlegel, J.; et al. Immunopathology of Autoantibody-Associated Encephalitides: Clues for Pathogenesis. Brain 2012, 135, 1622–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.A.; Banks, W.A. Age-Associated Changes in the Immune System and Blood−Brain Barrier Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenreich, H. Autoantibodies against the N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Subunit NR1: Untangling Apparent Inconsistencies for Clinical Practice. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, S.; Steiner, J.; Najjar, A.; Bechter, K. A Clinical Approach to New-Onset Psychosis Associated with Immune Dysregulation: The Concept of Autoimmune Psychosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, T.A.; Lennox, B.R.; Müller, S.; Benros, M.E.; Prüss, H.; Van Elst, L.T.; Klein, H.; Steiner, J.; Frodl, T.; Bogerts, B.; et al. Autoimmune Psychosis: An International Consensus on an Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Psychosis of Suspected Autoimmune Origin. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 7, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N. Long-Term Memory Dysfunction in Limbic Encephalitis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honnorat, J.; Joubert, B. Movement Disorders in Autoimmune Encephalitis and Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 174, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, J. Autoimmune Epilepsy. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 133, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatola, M.; Dalmau, J. Seizures and Risk of Epilepsy in Autoimmune and Other Inflammatory Encephalitis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattner, M.S.; de Bruin, G.S.; Bucelli, R.C.; Day, G.S. Sleep Disturbances Are Common in Patients with Autoimmune Encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, A.M.L.; Britton, J.W.; McKeon, A.; So, E.; Lennon, V.A.; Shin, C.; Klein, C.; Watson, R.E.; Kotsenas, A.L.; Lagerlund, T.D.; et al. Autoimmune Epilepsy: Clinical Characteristics and Response to Immunotherapy. Arch. Neurol-Chic. 2012, 69, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.M.; Day, G.S. Autoimmune Dementia. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J. NMDA Receptor Encephalitis and Other Antibody-Mediated Disorders of the Synapse. Neurology 2016, 87, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Orsi, G.; Martino, T.; Lalla, A.; Claudio, M.T.D.; Carapelle, E.; Avolio, C. Faciobrachial Dystonic Seizures Expressed as Epileptic Spasms, Followed by Focal Seizures in Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis: A Video-Polygraphic Study. Epileptic Disord. 2018, 20, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisher, J.; Richie, M.; Price, R.; Scherer, S.; Dalmau, J.; Lancaster, E. Acquired Neuromyotonia Heralding Recurrent Thymoma in Myasthenia Gravis. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Hughes, E.G.; Peng, X.; Zhou, L.; Gleichman, A.J.; Shu, H.; Matà, S.; Kremens, D.; Vitaliani, R.; Geschwind, M.D.; et al. AMPA Receptor Antibodies in Limbic Encephalitis Alter Synaptic Receptor Location. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, E.; Lai, M.; Peng, X.; Hughes, E.; Constantinescu, R.; Raizer, J.; Friedman, D.; Skeen, M.B.; Grisold, W.; Kimura, A.; et al. Antibodies to the GABA(B) Receptor in Limbic Encephalitis with Seizures: Case Series and Characterisation of the Antigen. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, W.O.; Lennon, V.A.; Komorowski, L.; Probst, C.; Clardy, S.L.; Aksamit, A.J.; Appendino, J.P.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Matsumoto, J.Y.; Pittock, S.J.; et al. DPPX Potassium Channel Antibody: Frequency, Clinical Accompaniments, and Outcomes in 20 Patients. Neurology 2014, 83, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaig, C.; Graus, F.; Compta, Y.; Högl, B.; Bataller, L.; Brüggemann, N.; Giordana, C.; Heidbreder, A.; Kotschet, K.; Lewerenz, J.; et al. Clinical Manifestations of the Anti-IgLON5 Disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Keime-Guibert, F.; Reñe, R.; Benyahia, B.; Ribalta, T.; Ascaso, C.; Escaramis, G.; Delattre, J.Y. Anti-Hu-Associated Paraneoplastic Encephalomyelitis: Analysis of 200 Patients. Brain 2001, 124, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.L.; Dent, S. Anti-Yo Antibody–Mediated Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration Associated with Cognitive Affective Syndrome in a Patient with Breast Cancer: A Case Report and Literature Review. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, e585–e591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Kryzer, T.J.; Griesmann, G.E.; Kim, K.; Benarroch, E.E.; Lennon, V.A. CRMP-5 Neuronal Autoantibody: Marker of Lung Cancer and Thymoma-Related Autoimmunity. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 49, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.A.; Jarius, S.; Pellkofer, H.L.; Schueller, M.; Krumbholz, M.; Koenig, F.; Johannis, W.; La Fougere, C.; Newman, T.; Vincent, A.; et al. Anti-Ma and Anti-Ta Associated Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes: 22 Newly Diagnosed Patients and Review of Previous Cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamus, G. Autoantibody Targets and Their Cancer Relationship in the Pathogenicity of Paraneoplastic Retinopathy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 8, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stich, O.; Klages, E.; Bischler, P.; Jarius, S.; Rasiah, C.; Voltz, R.; Rauer, S. SOX1 Antibodies in Sera from Patients with Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2011, 125, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohid, H. Anti-Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Antibody Positive Neurological Syndromes. Neurosciences 2016, 21, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Fujii, M.; Li, M.; McElroy, B. The Clinical Spectrum of Anti-GAD Antibody-Positive Patients with Stiff-Person Syndrome. Neurology 2000, 55, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Long, Y.; Qiu, W. Autoimmune Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Astrocytopathy: A Review of the Literature. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maat, P.; de Graaff, E.; van Beveren, N.M.; Hulsenboom, E.; Verdijk, R.M.; Koorengevel, K.; van Duijn, M.; Hooijkaas, H.; Hoogenraad, C.; Smitt, P.A.S. Psychiatric Phenomena as Initial Manifestation of Encephalitis by Anti-NMDAR Antibodies. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2013, 25, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Diwani, A.; Handel, A.; Townsend, L.; Pollak, T.; Leite, M.I.; Harrison, P.J.; Lennox, B.R.; Okai, D.; Manohar, S.G.; Irani, S.R. The Psychopathology of NMDAR-Antibody Encephalitis in Adults: A Systematic Review and Phenotypic Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejuste, F.; Thomas, L.; Picard, G.; Desestret, V.; Ducray, F.; Rogemond, V.; Psimaras, D.; Antoine, J.-C.; Delattre, J.-Y.; Groc, L.; et al. Neuroleptic Intolerance in Patients with Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. Advances in Autoimmune Epilepsy Associated with Antibodies, Their Potential Pathogenic Molecular Mechanisms, and Current Recommended Immunotherapies. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.; Irani, S.R. Caspr2 Antibodies in Patients with Thymomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, S277–S280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.E.; Barber, P.A. Limbic Encephalitis—A Review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, J.; Day, G.S.; Steriade, C.; Wennberg, R.A.; Tang-Wai, D.F. Long-Term Cognitive Outcomes in Patients with Autoimmune Encephalitis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. J. Can. Des. Sci. Neurol. 2018, 45, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corallo, F.; Buono, V.L.; Cara, M.D.; Salvo, S.D.; Formica, C.; Morabito, R.; Floridia, D.; Pastura, C.; Rifici, C.; D’Aleo, G.; et al. The Role of Cognitive Rehabilitation in Limbic Encephalitis. Medicine 2018, 97, e13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolle, D.C.M.; Moses, J.L. A Systematic Review of the Neuropsychological Sequelae of People Diagnosed with Anti N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis in the Acute and Chronic Phases. Arch. Clin. Neuropsych. 2018, 33, 964–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranzo, A.; Graus, F.; Clover, L.; Morera, J.; Bruna, J.; Vilar, C.; Martínez-Rodriguez, J.E.; Vincent, A.; Santamaría, J. Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder and Potassium Channel Antibody–Associated Limbic Encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, N.; Kawajiri, M.; Ohyagi, Y.; Minohara, M.; Murai, H.; Kira, J. A Patient with Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis Induced by Breast Cancer Presenting with Hypersomnia. Rinsho Shinkeigaku Clin. Neurol. 2005, 45, 575–578. [Google Scholar]
- Armangue, T.; Leypoldt, F.; Dalmau, J. Autoimmune Encephalitis as Differential Diagnosis of Infectious Encephalitis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2014, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, E.; Kondo, Y.; Kanazawa, N.; Akutsu, T.; Nishiyama, K.; Iizuka, T. Autoimmune Encephalitis as an Extra-Articular Manifestation of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Report. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 1846-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, E. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune Encephalitis. J. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.-T.; Park, S.; Joo, E.Y.; Chung, C.-S.; Lee, M.J. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome as Initial Manifestation of Autoimmune Encephalitis. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2019, 9, e42–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermo, O.P.; Izbudak, I.; Sutter, R.; Venkatesan, A.; Kaplan, P.W.; Probasco, J.C. Autoimmune Encephalitis Mimicking Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2014, 4, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, L.; Jiao, J. Repeated Misdiagnosis of a Relapsed Atypical Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis without an Associated Ovarian Teratoma. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 638, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnoila, J.J.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Dalmau, J. Neuronal Surface Antibody-Mediated Autoimmune Encephalitis. Semin. Neurol. 2014, 34, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leypoldt, F.; Germany, P.; Doctoral, R.F.; Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies (ICREA); August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS), Barcelona, Spain; Junior Attending Physician, Department of Neurology, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf; Wandinger, K. -P.; Germany, A.P.; Institute of Clinical Chemistry; Attending Physician, Department of Neurology, University Medical-Centre Schleswig-Holstein Campus Lübeck; et al. Barcelona, Autoimmune Encephalitis. Eur. Neurol. Rev. 2012, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, L.; Zhang, J.; Greene, M.; Crivaro, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Kamoun, M.; Lancaster, E. Improving the Antibody-Based Evaluation of Autoimmune Encephalitis. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermetter, C.; Fazekas, F.; Hochmeister, S. Systematic Review: Syndromes, Early Diagnosis, and Treatment in Autoimmune Encephalitis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, X. Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis: A Severe, Potentially Reversible Autoimmune Encephalitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Hoffmann, L.; Clover, L.; Vincent, A.; Voltz, R. CSF Findings in Patients with Voltage Gated Potassium Channel Antibody Associated Limbic Encephalitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 268, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, B.P.; Patel, S.C.; Marin, H.L.; Corrigan, J.J.; Mitsias, P.D.; Griffith, B. Autoimmune Encephalitis: Pathophysiology and Imaging Review of an Overlooked Diagnosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, M.; Prüss, H.; Ben-Dayan, I.; Paul, F.; Arzy, S.; Finke, C. Functional Connectivity of Large-Scale Brain Networks in Patients with Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis: An Observational Study. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probasco, J.C.; Solnes, L.; Nalluri, A.; Cohen, J.; Jones, K.M.; Zan, E.; Javadi, M.S.; Venkatesan, A. Abnormal Brain Metabolism on FDG-PET/CT Is a Common Early Finding in Autoimmune Encephalitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, J.; Prüss, H.; Bartsch, T.; Ploner, C.J.; Paul, F.; Finke, C. Imaging of Autoimmune Encephalitis—Relevance for Clinical Practice and Hippocampal Function. Neuroscience 2015, 309, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbelli, S.; Djekidel, M.; Hesse, S.; Pagani, M.; Barthel, H.; Neuroimaging Committee of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM); Brain Imaging Council of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI). Role of 18F-FDG-PET Imaging in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Seki, M.; Dalmau, J.; Shinohara, Y. Perfusion IMP-SPECT Shows Reversible Abnormalities in GABA(B) Receptor Antibody Associated Encephalitis with Normal MRI. Brain Behav. 2011, 1, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, T.A.; Moran, N. Emergence of New-Onset Psychotic Disorder Following Recovery from LGI1 Antibody-Associated Limbic Encephalitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2016218328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Dalmau, J. Role of 18F-FDG-PET Imaging in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Encephalitis—Authors’ Reply. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspard, N.; Foreman, B.P.; Alvarez, V.; Kang, C.C.; Probasco, J.C.; Jongeling, A.C.; Meyers, E.; Espinera, A.; Haas, K.F.; Schmitt, S.E.; et al. New-Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus. Neurology 2015, 85, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probasco, J.C.; Benavides, D.R.; Ciarallo, A.; Sanin, B.W.; Wabulya, A.; Bergey, G.K.; Kaplan, P.W. Electroencephalographic and Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography Correlates in Anti-N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Autoimmune Encephalitis. Epilepsy Behav. Case Rep. 2014, 2, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herken, J.; Prüss, H. Red Flags: Clinical Signs for Identifying Autoimmune Encephalitis in Psychiatric Patients. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.E.; Pargeon, K.; Frechette, E.S.; Hirsch, L.J.; Dalmau, J.; Friedman, D. Extreme Delta Brush: A Unique EEG Pattern in Adults with Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis. Neurology 2012, 79, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaki, S.; Gardner, T.; Khanlou, N.; Yong, W.H.; Salamon, N.; Vinters, H.V. Brain Biopsy in Neurologic Decline of Unknown Etiology. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, L.; Nosadini, M.; Gastaldi, M.; Spatola, M.; Iorio, R.; Zoccarato, M.; Mariotto, S.; Gaspari, P.D.; Perini, F.; Ferrari, S.; et al. Management of Antibody-Mediated Autoimmune Encephalitis in Adults and Children: Literature Review and Consensus-Based Practical Recommendations. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randell, R.L.; Adams, A.V.; Mater, H.V. Tocilizumab in Refractory Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Series of Pediatric Cases. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 86, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-Z.; Zhu, H.-D.; Ren, H.-T.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Peng, B.; Cui, L.-Y.; Guan, H.-Z. Utility and Safety of Intrathecal Methotrexate Treatment in Severe Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis: A Pilot Study. Chin. Med. J.-Peking 2018, 131, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macher, S.; Zimprich, F.; Simoni, D.D.; Höftberger, R.; Rommer, P.S. Management of Autoimmune Encephalitis: An Observational Monocentric Study of 38 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.W.; Rojas, O.L.; Gommerman, J.L. B Cell Depletion Therapies in Autoimmune Disease: Advances and Mechanistic Insights. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosadini, M.; Mohammad, S.S.; Ramanathan, S.; Brilot, F.; Dale, R.C. Immune Therapy in Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Systematic Review. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 1391–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titulaer, M.J.; McCracken, L.; Gabilondo, I.; Armangué, T.; Glaser, C.; Iizuka, T.; Honig, L.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Kawachi, I.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; et al. Treatment and Prognostic Factors for Long-Term Outcome in Patients with Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Lancaster, E.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Balice-Gordon, R. Clinical Experience and Laboratory Investigations in Patients with Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
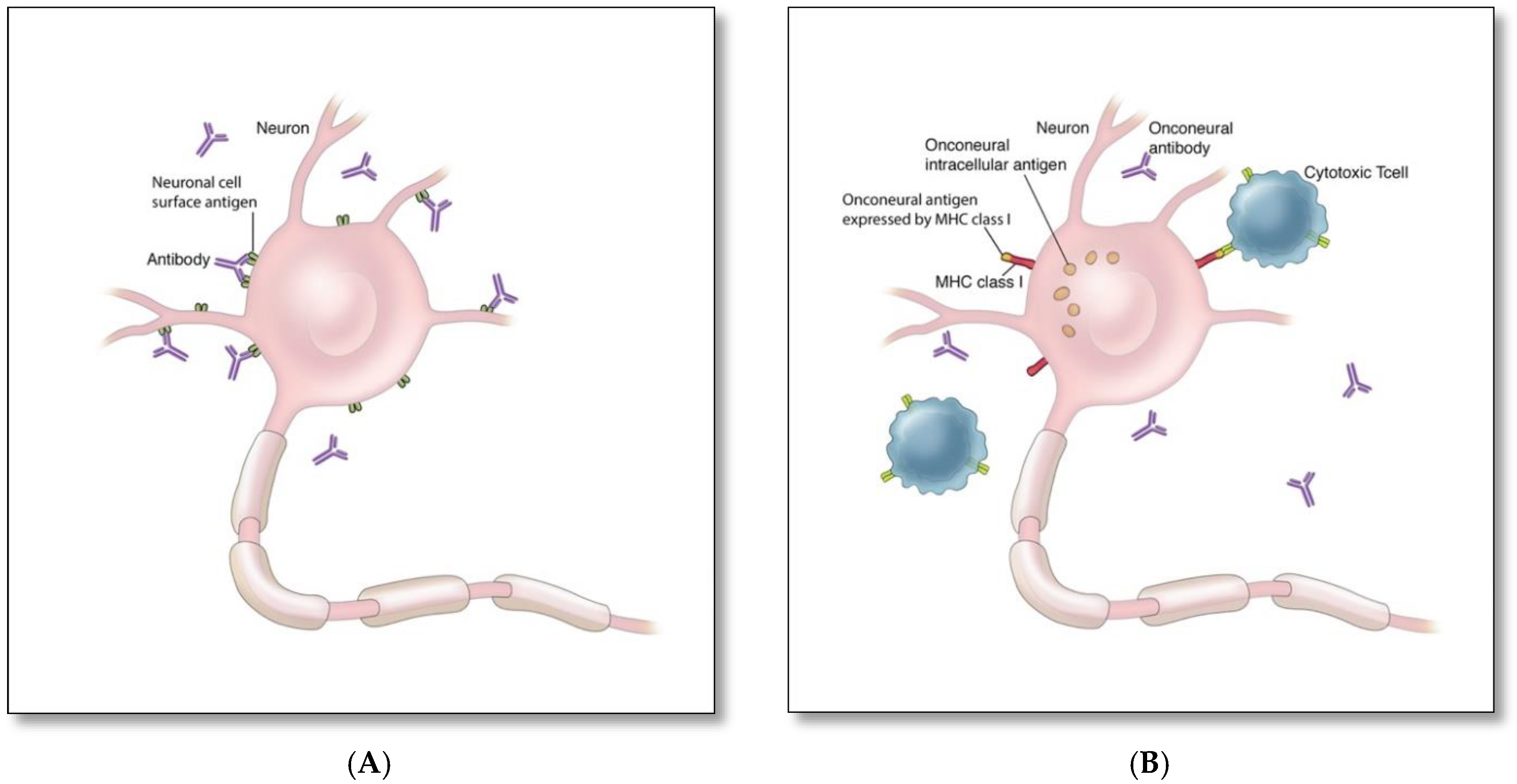
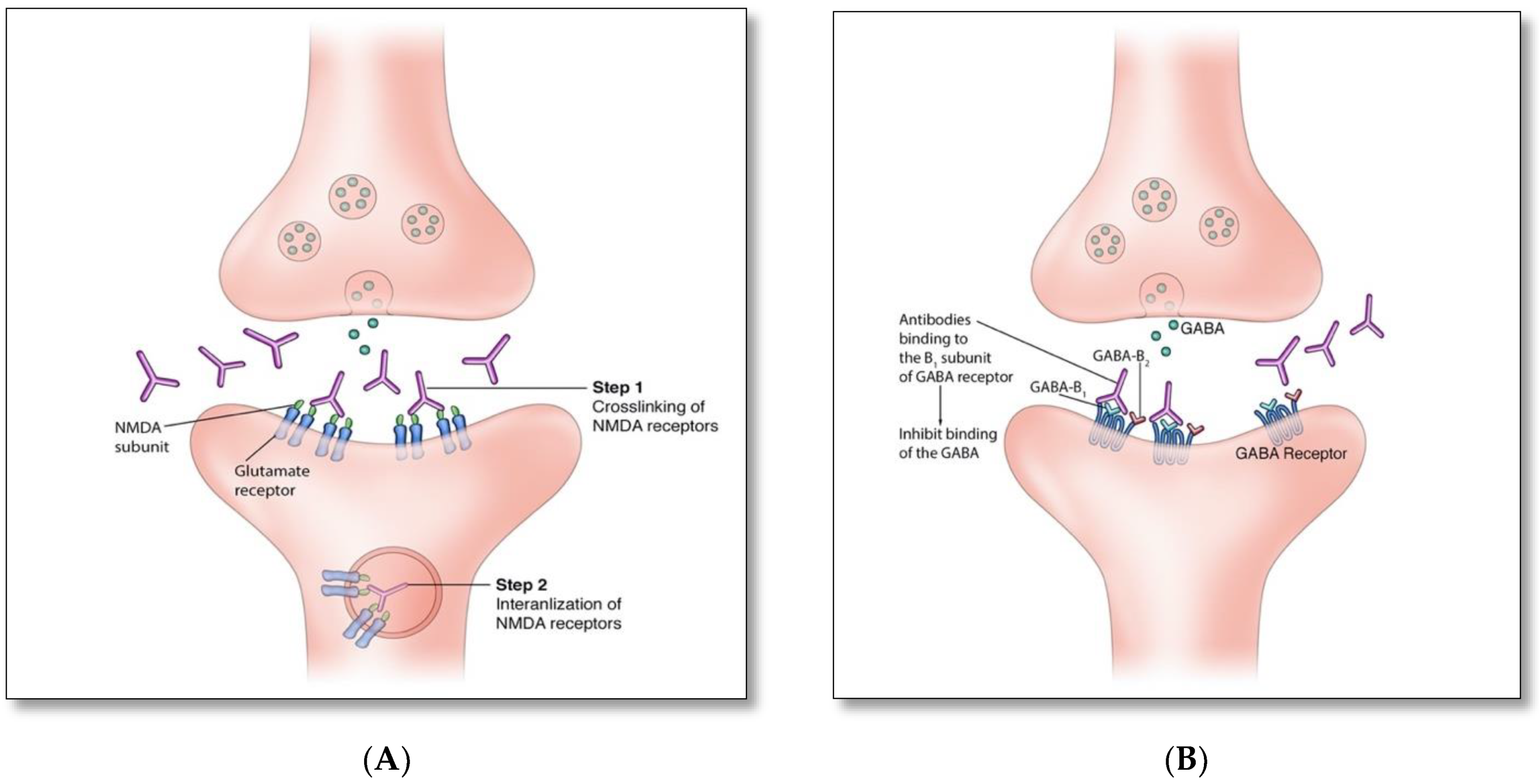
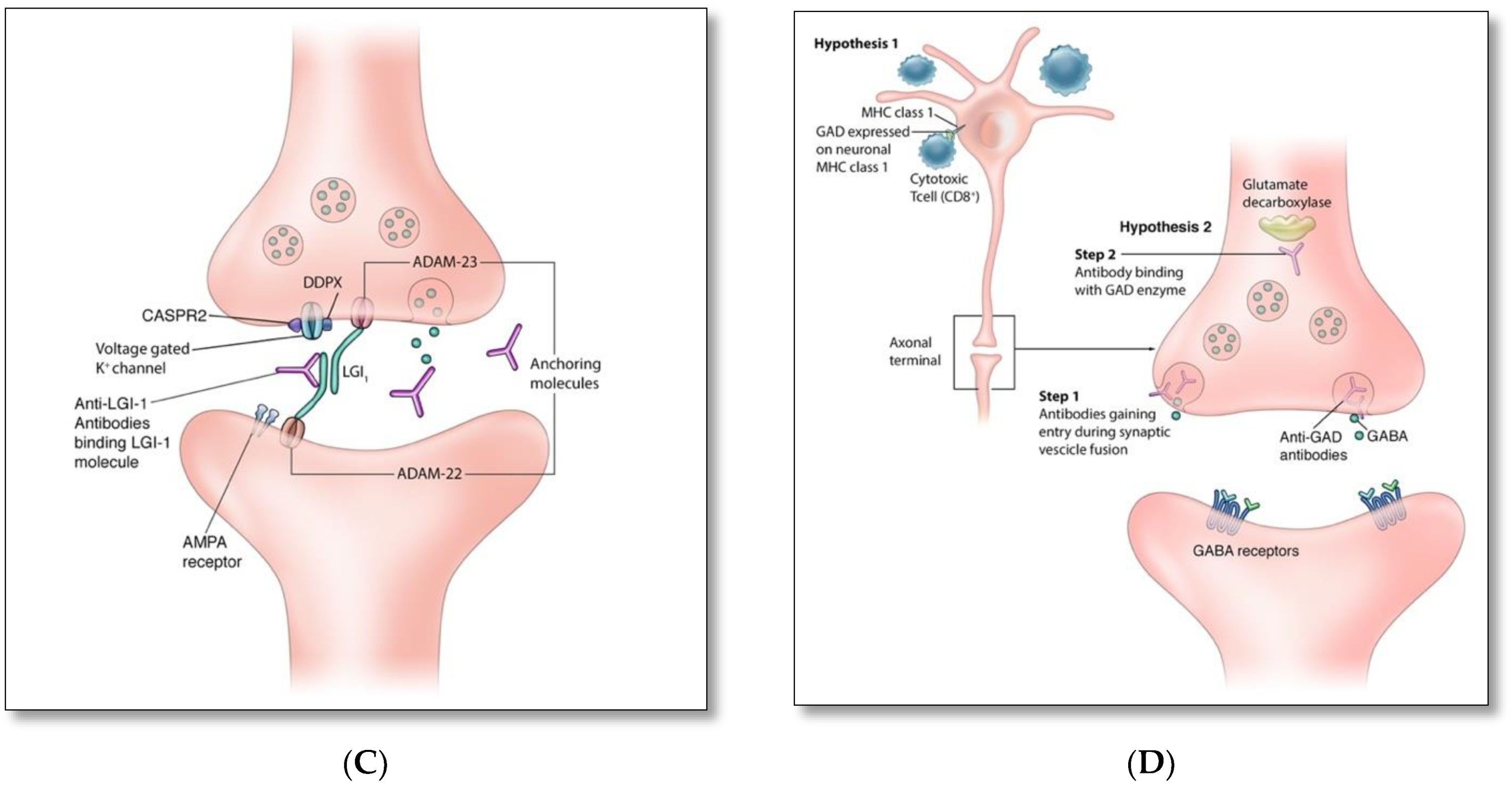
| Targeted Antigens | Antigen Location | Patient Demographics; Median Age (Range); Male: Female Ratio | Frequency and Main Type of Associated Malignancy | Main Neurological and Psychiatric Presentations | Other Clinical Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMDAR [69] | Cell surface (extra-limbic cortices) | Young women and children; 21 yr (2 mo–85 yr); 1:4 | Overall 40%; 58% in women 18–45 yr (teratoma) | Panencephalitis with psychiatric symptoms, behavioral changes; cognitive and short-term memory impairment, seizures, movement disorders (e.g., dyskinesias) | Catatonia, autonomic instability (50% has central hypoventilation) |
| LGI1 [70] | Synaptic (limbic system) | Older men; 64 yr (31–84); 2:1 | 5–10% (thymoma) | Limbic encephalitis with short-term memory loss, seizures (particularly faciobrachial dystonic seizures) | Psychiatric symptoms such as depression, REM sleep behavior disorders, hyponatremia, rarely movement disorders (choreoathetosis, dyskinesia, dystonia) |
| CASPR2 [71] | Synaptic | Older men; 66 yr (25–77); 9:1 | Overall 20% (thymoma); | Morvan syndrome (peripheral nerve hyperexcitability and neuromyotonia), limbic encephalitis, sleep disorder, memory loss, dysautonomia, ataxia, neuropathic pain | Delusions and hallucinations, concurrent immune-mediated disorders (e.g., myasthenia gravis) |
| AMPAR [72] | Cell surface (limbic system) | Middle-aged women; 56 yr (23–81); 1:2.3 | 65% (thymoma, SCLC, or breast cancer) | Limbic encephalitis, encephalopathy with memory loss | Features of limbic encephalitis on MRI in about 67%; history of concurrent auto-immunity in about 50% [63]; psychiatric symptoms (e.g., psychosis and personality changes, confabulation) |
| GABAAR | Cell surface (extra-limbic cortices) | 40 yr (2 mo–88 yr); 1:1 | 25% (thymoma, other) | Limbic encephalitis with encephalopathy and intractable epilepsy | Behavioral and psychiatric features, including catatonia |
| GABABR [73] | Cell surface (limbic system) | Men and women; 61 yr (16–77); 1.5:1 | 50% (SCLC) | Limbic encephalitis with intractable seizures and status epilepticus, short-term memory loss, opsoclonus-myoclonus | Features of limbic encephalitis on MRI in about 45%, psychiatric symptoms (e.g., psychosis and catatonia) |
| DPPX [74] | Cell surface (limbic system) | 52 yr (13–76); 2.3:1 | <10% (B-cell neoplasms) | Limbic encephalitis, encephalopathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, myoclonus, tremors, hyperekplexia | Psychiatric symptoms (e.g., psychosis, depression, delirium), PERM |
| Dopamine-2R [46] | Cell surface (basal ganglia, limbic system, and substantia nigra) | (2–15) | n/k | Basal ganglia encephalitis presenting with diverse movement disorders (e.g., dystonia, chorea, tics, parkinsonian features), psychiatric symptoms (e.g., emotional lability, depression, psychosis) | Gait disturbance, sleep disorders |
| mGluR5 [45] | Cell surface (olfactory bulb, cortex, and hippocampus) | 29 yr (6–75); 1.5:1 | 6 of 11 patients (Hodgkin’s lymphoma) | Ophelia syndrome: limbic encephalitis in association with Hodgkin lymphoma | Psychiatric symptoms, encephalopathy, myoclonus |
| Neurexin-3α [49] | Synaptic (throughout brain) | 44 yr (23–57); 2:4 | n/k | Infectious-like prodrome, encephalopathy, seizures, orofacial dyskinesia, cognitive decline, decrease level of consciousness, central hypoventilation | Psychiatric symptoms (less severe than those associated with NMDAR encephalitis |
| IgLON5 [75] | Cell surface (brainstem and thalamus) | n/k | n/k | Non-REM and REM sleep disorders, brainstem dysfunction (e.g., bulbar symptoms, oculomotor abnormalities), gait impairment, tauopathy-associated cognitive dysfunction | Occasionally associated with severe dementia; can mimic progressive supranuclear palsy |
| DNER (Tr) [38] | Intracellular cytoplasmic (cerebellum) | n/k | >90% (Hodgkin disease) | Gait instability | Cerebellar ataxia |
| P/Q type VGCC [35] | Synaptic (cerebellum) | n/k | >90% (SCLC) | Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, gait instability | Cerebellar ataxia |
| mGluR1 | Cell surface (cerebellum) | n/k | A few cases (Hodgkin disease) | Gait instability | Cerebellar ataxia |
| GlyR [42] | Cell surface (brainstem and spinal cord) | 49 yr (1–75); 5:1 adult | <5% (thymoma, lung, Hodgkin) | PERM, stiff-person syndrome, muscle rigidity, spasms, oculomotor disturbance, bulbar symptoms, gait impairment | Pyramidal signs, cerebellar ataxia, autonomic disturbance, excessive startle |
| Amphiphysin [39] | Intracellular synaptic (brain and spinal cord) | Exclusively Female; 60 | >90% (breast cancer, SCLC) | Stiff person syndrome, confusion, memory loss | Encephalomyelitis |
| Hu (ANNA-1) [76] | Intracellular Nuclear (cerebellum and dorsal root ganglia) | 63; 3:1 | 70 % associated with cancer | Limbic encephalitis or encephalomyelitis, painful sensory neuropathy in about 50%, cerebellar degeneration | Brainstem encephalitis (dysphagia, dysarthria, central hypoventilation) |
| Yo (PCA-1) [77] | Intracellular cytoplasmic (cerebellum) | 60; 1:3 | Brest and gynecological tumors | Cerebellar degeneration-associated ataxia | Vertigo, slurred speech, nystagmus, diplopia and oscillopsia |
| CV2/CRMP5 [78] | Intracellular cytoplasmic (cerebellum, dorsal root ganglia, limbic system) | 62; M > F | 70% SCLC, 6% thymoma | Limbic encephalitis, cerebellar ataxia (26%), sensory neuropathy (47%), subacute dementia (25%) | Chorea (11%), optic neuropathy (7%) |
| Ta/Ma2 [79] | Intracellular Nuclear (limbic system) | 36; 4:1 | Germ cell tumors (Testicular tumor) | Limbic encephalitis (64%), short-term memory impairment, REM sleep disorder | Cerebellar and brainstem dysfunction, psychiatric symptoms |
| Recoverin [80] | Intracellular cytoplasmic (retina) | 65; F > M | Lung, Breast, Melanoma | Retinopathy with progressive visual loss | |
| SOX-1 [81] | Synaptic (neuromuscular junction) | 63; M > F | 40% (SCLC) | Lambert Eaton Myasthenic syndrome | Neuropathy, paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration |
| GAD [82,83] | Intracellular synaptic (brain and spinal cord) | 41; F > M | Usually unrelated to tumor | Stiff person syndrome, limbic encephalitis | Cerebellar ataxia, intractable seizure |
| GFAP [50,84] | Astrocytes | Over age 40; slight F > M predominance | 34% (ovarian teratoma among common tumors) | Meningoencephalitis, encephalitis. encephalomyelitis, encephalopathy with short-term memory loss, movement disorders | At times associated with psychiatric symptoms |
| Ri (ANNA-2) [34] | Intracellular Nuclear (cerebellum and dorsal root ganglia) | Over age 50; predominantly in F > M | SCLS, breast cancer | Encephalomyelitis, Cerebellar degeneration, stridor, laryngospasm, jaw dystonia, opsoclonus myoclonus | Sensory neuropathy, vertigo, muscle weakness |
| 1 | New-onset acute psychiatric episodes (acute mania, first episode psychosis, catatonia), particularly in those exhibiting significant adverse response (e.g., neuroleptic malignant syndrome) or resistance to antipsychotics |
| 2 | Rapidly progressive short-term memory and cognitive decline |
| 3 | Unexplained new-onset intractable epilepsy or status epilepticus, particular seizure types such as faciobrachial dystonic seizures |
| 4 | New-onset movement disorders affecting any part of the body (e.g., dyskinesias and dystonia), presentation of unclear etiology, particularly at a young age |
| 5 | Clinically significant autonomic instability |
| 6 | Deterioration, relapse, or emergence of new neurological and/or neuropsychiatric symptoms following confirmed or presumed viral illness, despite adequate treatment |
| 7 | Infectious-like prodromal illness |
| 8 | Strong personal or family history of autoimmune disorders |
| 9 | Recent diagnosis of neoplasm |
| 10 | Extreme delta brush on EEG, unexplained CSF inflammatory changes with or without oligoclonal bands (OCBs), or limbic structural abnormalities on coronal T2- or FLAIR-weighted MR imaging after excluding infectious etiologies |
| Diagnosis can be made when all three of the following criteria have been met: |
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, A.; Meng, Y.; Najjar, A.; Lado, F.; Najjar, S. Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Physician’s Guide to the Clinical Spectrum Diagnosis and Management. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091130
Patel A, Meng Y, Najjar A, Lado F, Najjar S. Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Physician’s Guide to the Clinical Spectrum Diagnosis and Management. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(9):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091130
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Arpan, Yue Meng, Amanda Najjar, Fred Lado, and Souhel Najjar. 2022. "Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Physician’s Guide to the Clinical Spectrum Diagnosis and Management" Brain Sciences 12, no. 9: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091130
APA StylePatel, A., Meng, Y., Najjar, A., Lado, F., & Najjar, S. (2022). Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Physician’s Guide to the Clinical Spectrum Diagnosis and Management. Brain Sciences, 12(9), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091130





