How Functional Connectivity Measures Affect the Outcomes of Global Neuronal Network Characteristics in Patients with Schizophrenia Compared to Healthy Controls
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1).
- Establishing whether and to what extent the graph theory network parameters (e.g., path length) show independence from the input data (FC measures) in terms of the range and direction of difference between patients and healthy controls regarding a given graph parameter;
- (2).
- If it proved that selected graph-theory indicators are independent of the exact measure of connectivity strength, it would be possible to determine which FC parameter used as an element of the global network computation differentiates patients and controls to the greatest extent. Indicating such FC measures may guide future research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. EEG Recording Acquisition
2.3. Functional Connectivity Indicators: PLI and PLV
2.4. Global Neuronal Network Reconstruction: Application of the Minimum Spanning Tree
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Studied Groups
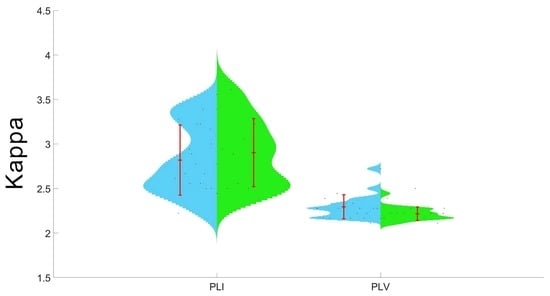
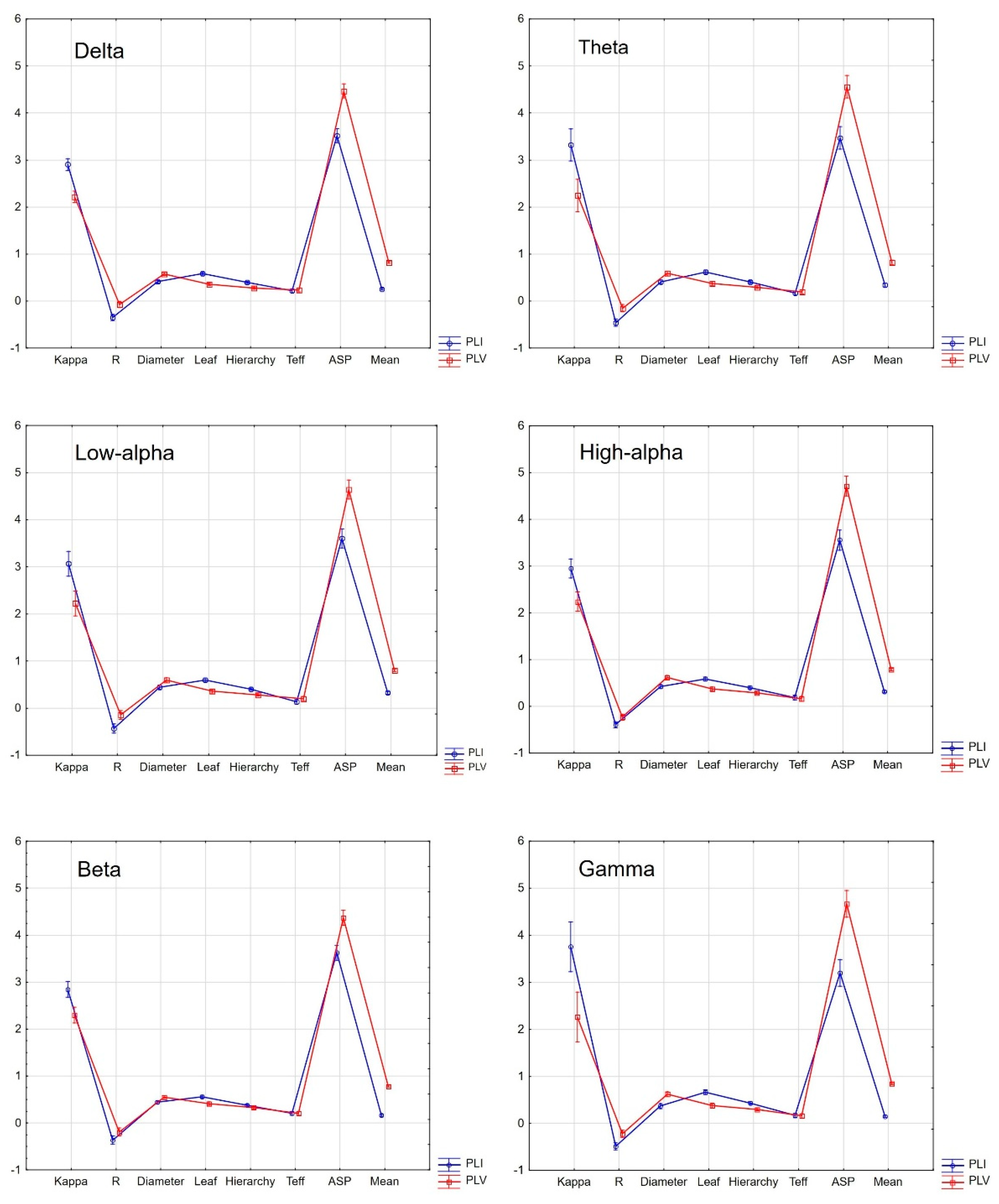
3.2. Between-Group Comparison of MST Outcomes Calculated on the Basis of PLI and PLV
3.3. Within-Group Comparisons of PLI and PLV-Based MST Indicators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Frequency | Network Measure | PLI/PLV | HC | SCH | t | p | d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | ||||||
| Delta | Kappa | PLI | 2.819 | 0.394 | 2.902 | 0.382 | −0.677 | 0.502 | 0.21 |
| PLV | 2.294 | 0.134 | 2.216 | 0.076 | 2.244 | 0.030 | 0.71 | ||
| R | PLI | −0.321 | 0.225 | −0.349 | 0.147 | 0.454 | 0.652 | 0.15 | |
| PLV | −0.174 | 0.211 | −0.072 | 0.146 | −1.780 | 0.082 | 0.56 | ||
| Diameter | PLI | 0.422 | 0.077 | 0.410 | 0.077 | 0.455 | 0.651 | 0.16 | |
| PLV | 0.563 | 0.085 | 0.575 | 0.060 | −0.483 | 0.631 | 0.16 | ||
| Leaf | PLI | 0.558 | 0.102 | 0.583 | 0.077 | −0.867 | 0.391 | 0.28 | |
| PLV | 0.394 | 0.071 | 0.361 | 0.052 | 1.677 | 0.101 | 0.53 | ||
| Hierarchy | PLI | 0.385 | 0.072 | 0.396 | 0.049 | −0.546 | 0.587 | 0.18 | |
| PLV | 0.298 | 0.054 | 0.276 | 0.042 | 1.417 | 0.164 | 0.45 | ||
| Teff | PLI | 0.229 | 0.095 | 0.219 | 0.104 | 0.297 | 0.767 | 0.10 | |
| PLV | 0.212 | 0.091 | 0.232 | 0.075 | −0.740 | 0.463 | 0.24 | ||
| ASP | PLI | 3.591 | 0.424 | 3.517 | 0.399 | 0.568 | 0.572 | 0.18 | |
| PLV | 4.412 | 0.383 | 4.469 | 0.237 | −0.562 | 0.576 | 0.18 | ||
| Mean | PLI | 0.272 | 0.045 | 0.253 | 0.059 | 1.157 | 0.254 | 0.36 | |
| PLV | 0.639 | 0.046 | 0.823 | 0.031 | −14.650 | <0.0001 | 4.69 | ||
| Theta | Kappa | PLI | 3.055 | 0.765 | 3.319 | 1.068 | −0.897 | 0.375 | 0.28 |
| PLV | 2.336 | 0.150 | 2.247 | 0.105 | 2.162 | 0.036 | 0.69 | ||
| R | PLI | −0.438 | 0.154 | −0.459 | 0.164 | 0.414 | 0.681 | 0.13 | |
| PLV | −0.273 | 0.191 | −0.152 | 0.178 | −2.081 | 0.044 | 0.66 | ||
| Diameter | PLI | 0.424 | 0.117 | 0.405 | 0.098 | 0.566 | 0.574 | 0.18 | |
| PLV | 0.591 | 0.118 | 0.594 | 0.074 | −0.091 | 0.927 | 0.03 | ||
| Leaf | PLI | 0.586 | 0.119 | 0.616 | 0.118 | −0.816 | 0.419 | 0.25 | |
| PLV | 0.405 | 0.076 | 0.374 | 0.059 | 1.409 | 0.166 | 0.46 | ||
| Hierarchy | PLI | 0.398 | 0.067 | 0.404 | 0.065 | −0.275 | 0.784 | 0.09 | |
| PLV | 0.309 | 0.050 | 0.297 | 0.047 | 0.769 | 0.446 | 0.25 | ||
| Teff | PLI | 0.189 | 0.111 | 0.173 | 0.112 | 0.457 | 0.650 | 0.14 | |
| PLV | 0.165 | 0.109 | 0.193 | 0.065 | −0.994 | 0.326 | 0.31 | ||
| ASP | PLI | 3.602 | 0.640 | 3.467 | 0.617 | 0.679 | 0.500 | 0.21 | |
| PLV | 4.522 | 0.596 | 4.556 | 0.424 | −0.211 | 0.833 | 0.07 | ||
| Mean | PLI | 0.341 | 0.113 | 0.339 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.974 | 0.02 | |
| PLV | 0.721 | 0.093 | 0.824 | 0.037 | −4.571 | <0.0001 | 1.46 | ||
| Low Alpha | Kappa | PLI | 2.886 | 0.479 | 3.066 | 0.820 | −0.849 | 0.401 | 0.27 |
| PLV | 2.333 | 0.115 | 2.222 | 0.082 | 3.503 | 0.001 | 1.11 | ||
| R | PLI | −0.342 | 0.187 | −0.431 | 0.162 | 1.602 | 0.117 | 0.51 | |
| PLV | −0.344 | 0.153 | −0.143 | 0.242 | −3.127 | 0.003 | 0.99 | ||
| Diameter | PLI | 0.466 | 0.081 | 0.441 | 0.104 | 0.840 | 0.406 | 0.27 | |
| PLV | 0.580 | 0.107 | 0.600 | 0.077 | −0.658 | 0.514 | 0.21 | ||
| Leaf | PLI | 0.538 | 0.067 | 0.597 | 0.110 | −2.009 | 0.051 | 0.65 | |
| PLV | 0.422 | 0.075 | 0.358 | 0.055 | 3.058 | 0.004 | 0.97 | ||
| Hierarchy | PLI | 0.360 | 0.058 | 0.405 | 0.061 | −2.381 | 0.022 | 0.76 | |
| PLV | 0.321 | 0.062 | 0.281 | 0.047 | 2.278 | 0.028 | 0.73 | ||
| Teff | PLI | 0.184 | 0.104 | 0.136 | 0.115 | 1.380 | 0.175 | 0.44 | |
| PLV | 0.160 | 0.097 | 0.202 | 0.089 | −1.392 | 0.171 | 0.45 | ||
| ASP | PLI | 3.705 | 0.443 | 3.602 | 0.525 | 0.673 | 0.504 | 0.21 | |
| PLV | 4.443 | 0.466 | 4.638 | 0.360 | −1.472 | 0.149 | 0.47 | ||
| Mean | PLI | 0.308 | 0.033 | 0.326 | 0.077 | −0.938 | 0.354 | 0.30 | |
| PLV | 0.623 | 0.079 | 0.801 | 0.041 | −8.937 | <0.0001 | 2.83 | ||
| High Alpha | Kappa | PLI | 2.741 | 0.518 | 2.949 | 0.638 | −1.132 | 0.264 | 0.36 |
| PLV | 2.341 | 0.144 | 2.241 | 0.111 | 2.450 | 0.018 | 0.78 | ||
| R | PLI | −0.341 | 0.154 | −0.392 | 0.146 | 1.062 | 0.294 | 0.34 | |
| PLV | −0.261 | 0.236 | −0.231 | 0.135 | −0.487 | 0.628 | 0.16 | ||
| Diameter | PLI | 0.458 | 0.078 | 0.422 | 0.088 | 1.363 | 0.180 | 0.43 | |
| PLV | 0.561 | 0.082 | 0.616 | 0.101 | −1.896 | 0.065 | 0.60 | ||
| Leaf | PLI | 0.533 | 0.083 | 0.588 | 0.108 | −1.808 | 0.078 | 0.57 | |
| PLV | 0.419 | 0.083 | 0.374 | 0.076 | 1.767 | 0.085 | 0.57 | ||
| Hierarchy | PLI | 0.370 | 0.056 | 0.402 | 0.074 | −1.545 | 0.130 | 0.49 | |
| PLV | 0.324 | 0.066 | 0.293 | 0.065 | 1.527 | 0.134 | 0.47 | ||
| Teff | PLI | 0.205 | 0.079 | 0.187 | 0.095 | 0.627 | 0.534 | 0.21 | |
| PLV | 0.185 | 0.101 | 0.161 | 0.113 | 0.716 | 0.477 | 0.22 | ||
| ASP | PLI | 3.800 | 0.426 | 3.556 | 0.478 | 1.695 | 0.098 | 0.54 | |
| PLV | 4.400 | 0.408 | 4.713 | 0.461 | −2.276 | 0.028 | 0.72 | ||
| Mean | PLI | 0.321 | 0.051 | 0.316 | 0.054 | 0.328 | 0.744 | 0.10 | |
| PLV | 0.607 | 0.074 | 0.788 | 0.055 | −8.664 | <0.0001 | 2.78 | ||
| Beta | Kappa | PLI | 2.616 | 0.313 | 2.841 | 0.512 | −1.674 | 0.102 | 0.53 |
| PLV | 2.352 | 0.130 | 2.299 | 0.120 | 1.331 | 0.190 | 0.42 | ||
| R | PLI | −0.308 | 0.167 | −0.363 | 0.172 | 1.021 | 0.313 | 0.32 | |
| PLV | −0.238 | 0.195 | −0.191 | 0.210 | −0.720 | 0.475 | 0.23 | ||
| Diameter | PLI | 0.469 | 0.073 | 0.438 | 0.067 | 1.372 | 0.177 | 0.44 | |
| PLV | 0.536 | 0.104 | 0.550 | 0.053 | −0.533 | 0.596 | 0.17 | ||
| Leaf | PLI | 0.525 | 0.075 | 0.555 | 0.069 | −1.327 | 0.192 | 0.42 | |
| PLV | 0.424 | 0.065 | 0.413 | 0.079 | 0.480 | 0.633 | 0.15 | ||
| Hierarchy | PLI | 0.369 | 0.047 | 0.377 | 0.051 | −0.531 | 0.598 | 0.16 | |
| PLV | 0.313 | 0.055 | 0.324 | 0.069 | −0.540 | 0.591 | 0.18 | ||
| Teff | PLI | 0.200 | 0.052 | 0.207 | 0.096 | −0.271 | 0.787 | 0.09 | |
| PLV | 0.220 | 0.121 | 0.205 | 0.087 | 0.435 | 0.665 | 0.14 | ||
| ASP | PLI | 3.857 | 0.441 | 3.624 | 0.393 | 1.765 | 0.085 | 0.56 | |
| PLV | 4.284 | 0.504 | 4.369 | 0.302 | −0.645 | 0.522 | 0.20 | ||
| Mean | PLI | 0.188 | 0.034 | 0.161 | 0.039 | 2.270 | 0.028 | 0.74 | |
| PLV | 0.542 | 0.081 | 0.781 | 0.061 | −10.429 | <0.0001 | 3.33 | ||
| Gamma | Kappa | PLI | 2.686 | 0.402 | 3.755 | 1.652 | −2.812 | 0.007 | 0.89 |
| PLV | 2.366 | 0.137 | 2.261 | 0.136 | 2.435 | 0.019 | 0.77 | ||
| R | PLI | −0.320 | 0.226 | −0.491 | 0.180 | 2.646 | 0.011 | 0.84 | |
| PLV | −0.276 | 0.196 | −0.222 | 0.155 | −0.958 | 0.344 | 0.31 | ||
| Diameter | PLI | 0.477 | 0.085 | 0.366 | 0.099 | 3.797 | 0.001 | 1.20 | |
| PLV | 0.527 | 0.089 | 0.619 | 0.127 | −2.627 | 0.012 | 0.84 | ||
| Leaf | PLI | 0.533 | 0.089 | 0.663 | 0.127 | −3.743 | 0.001 | 1.19 | |
| PLV | 0.433 | 0.075 | 0.380 | 0.090 | 2.001 | 0.052 | 0.64 | ||
| Hierarchy | PLI | 0.384 | 0.061 | 0.430 | 0.063 | −2.287 | 0.027 | 0.74 | |
| PLV | 0.313 | 0.057 | 0.296 | 0.059 | 0.931 | 0.357 | 0.29 | ||
| Teff | PLI | 0.171 | 0.096 | 0.167 | 0.104 | 0.127 | 0.899 | 0.04 | |
| PLV | 0.220 | 0.114 | 0.157 | 0.099 | 1.857 | 0.070 | 0.59 | ||
| ASP | PLI | 3.864 | 0.441 | 3.199 | 0.591 | 4.030 | 0.0001 | 1.28 | |
| PLV | 4.260 | 0.441 | 4.663 | 0.657 | −2.273 | 0.028 | 0.72 | ||
| Mean | PLI | 0.221 | 0.037 | 0.144 | 0.028 | 7.321 | <0.0001 | 2.35 | |
| PLV | 0.553 | 0.081 | 0.842 | 0.057 | −12.936 | <0.0001 | 4.13 | ||
References
- Reinert, M.; Nguyen, T.; Fritze, D. The State of Mental Health in America; Mental Health America: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, W.G.; Mohs, R.C.; Johns, C.A.; Small, N.S.; Kendler, K.S.; Horvath, T.B.; Davis, K.L. Positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 1984, 13, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilbronner, U.; Samara, M.; Leucht, S.; Falkai, P.; Schulze, T.G. The Longitudinal Course of Schizophrenia Across the Lifespan: Clinical, Cognitive, and Neurobiological Aspects. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2016, 24, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, M.F.; Horan, W.P.; Lee, J. Nonsocial and social cognition in schizophrenia: Current evidence and future directions. World Psychiatry 2019, 18, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keefe, R.S.E. Why are there no approved treatments for cognitive impairment in schizophrenia? World Psychiatry 2019, 18, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.; Palaniyappan, L.; Li, M.; Kendrick, K.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yu, R.; Deng, W.; Wang, Q.; et al. Voxel-based, brain-wide association study of aberrant functional connectivity in schizophrenia implicates thalamocortical circuitry. npj Schizophr. 2015, 1, 15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, D.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X.; Luo, C.; Yao, D. Dysfunction of large-scale brain networks in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friston, K.J. Functional and effective connectivity in neuroimaging: A synthesis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1994, 2, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, M.; Mesulam, M. What is a disconnection syndrome? Cortex 2008, 44, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vico Fallani, F.; Richiardi, J.; Chavez, M.; Achard, S. Graph analysis of functional brain networks: Practical issues in translational neuroscience. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindriks, R. Relation between the phase-lag index and lagged coherence for assessing interactions EEG and MEG data. Neuroimage Rep. 2021, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, O.; Zanin, M.; Papo, D. Principles and open questions in functional brain network reconstruction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 3680–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelis, C.; Yücel, M.; Bora, E.; Fornito, A.; Testa, R.; Brewer, W.J.; Velakoulis, D.; Wood, S.J. Neurobiological markers of illness onset in psychosis and schizophrenia: The search for a moving target. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2009, 19, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dellen, E.; Sommer, I.E.; Bohlken, M.; Tewarie, P.; Draaisma, L.; Zalesky, A.; Di Biase, M.; Brown, J.A.; Douw, L.; Otte, W.M.; et al. Minimum spanning tree analysis of the human connectome. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 2455–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tewarie, P.; van Dellen, E.; Hillebrand, A.; Stam, C.J. The minimum spanning tree: An unbiased method for brain network analysis. Neuroimage 2015, 104, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.; Chen, Y.H. The wiring economy principle: Connectivity determines anatomy in the human brain. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, M.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; Hao, Y.; Song, M.; Yu, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, T. Disrupted small-world networks in schizophrenia. Brain 2008, 131 Pt 4, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open-source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stam, C.J.; Nolte, G.; Daffertshofer, A. Phase lag index: Assessment of functional connectivity from multi-channel EEG and MEG with diminished bias from common sources. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaux, J.P.; Rodriguez, E.; Martinerie, J.; Varela, F.J. Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1999, 8, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruña, R.; Maestú, F.; Pereda, E. Phase locking value revisited: Teaching new tricks to an old dog. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, C.J. BrainWave: A Java Based Application for Functional Connectivity and Network Analysis. Available online: http://home.kpn.nl/stam7883/brainwave.html. (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Barrenas, F.; Chavali, S.; Holme, P.; Mobini, R.; Benson, M. Network Properties of Complex Human Disease Genes Identified through Genome-Wide Association Studies. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, K.E.; Friston, K.J.; Frith, C.D. Dysconnection in schizophrenia: From abnormal synaptic plasticity to failures of self-monitoring. Schizophr Bull. 2009, 35, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Heuvel, M.P.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Exploring the brain network: A review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufe, S.; Nikulin, V.V.; Müller, K.R.; Nolte, G. A critical assessment of connectivity measures for EEG data: A simulation study. Neuroimage 2013, 64, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nentwich, M.; Ai, L.; Madsen, J.; Telesford, Q.K.; Haufe, S.; Milham, M.P.; Parra, L.C. Functional connectivity of EEG is subject-specific, associated with phenotype, and different from fMRI. Neuroimage 2020, 218, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.E.; Bénar, C.G.; Quilichini, P.P.; Friston, K.J.; Jirsa, V.K.; Bernard, C. A systematic framework for functional connectivity measures. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshayesh, H.; Fitzgibbon, S.P.; Janani, A.S.; Grummett, T.S.; Pope, K.J. Detecting synchrony in EEG: A comparative study of functional connectivity measures. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 105, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshinaga, K.; Matsuhashi, M.; Mima, T.; Fukuyama, H.; Takahashi, R.; Hanakawa, T.; Ikeda, A. Comparison of Phase Synchronization Measures for Identifying Stimulus-Induced Functional Connectivity in Human Magnetoencephalographic and Simulated Data. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, X.; Wei, H.L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Erkoyuncu, J.A.; Sarrigiannis, P.G. Brain functional and effective connectivity based on electroencephalography recordings: A review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomsma, N.; de Rooy, B.; Gerritse, F.; van der Spek, R.; Tewarie, P.; Hillebrand, A.; Otte, W.M.; Stam, C.J.; van Dellen, E. Minimum spanning tree analysis of brain networks: A systematic review of network size effects, sensitivity for neuropsychiatric pathology, and disorder specificity. Netw. Neurosci. 2022, 6, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wei, M.; Guo, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Fan, H. A novel index of functional connectivity: Phase lag based on Wilcoxon signed rank test. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2022, 15, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizkallah, J.; Amoud, H.; Wendling, F.; Hassan, M. Effect of connectivity measures on the identification of brain functional core network at rest. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 6426–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraepelin, E. Dementia praecox. In The Clinical Roots of the Schizophrenia Concept: Translations of Seminal European Contributions on Schizophrenia; Cutting, J., Shepherd, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kambeitz, J.; Kambeitz-Ilankovic, L.; Cabral, C.; Dwyer, D.B.; Calhoun, V.D.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; Falkai, P.; Koutsouleris, N.; Malchow, B. Aberrant Functional Whole-Brain Network Architecture in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull. 2016, 42 (Suppl. S1), S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krukow, P.; Jonak, K.; Karpiński, R.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H. Abnormalities in hubs location and nodes centrality predict cognitive slowing and increased performance variability in first-episode schizophrenia patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| HC n = 20 M (SD) | SCH n = 20 M (SD) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 21.10 (1.80) | 21.20 (1.96) | 0.867 a |
| Male/female | 10/10 | 10/10 | 0.999 b |
| Education (years) | 13.10 (1.29) | 12.90 (1.16) | 0.610 a |
| Duration of illness (months) | 19.50 (4.96) | ||
| Duration of untreated psychosis (months) | 5.60 (3.10) | ||
| Risperidone equivalents | 4.82 (0.93) | ||
| PANSS c positive subscale | 14.20 (3.52) | ||
| PANSS negative subscale | 17.40 (4.89) | ||
| PANSS general subscale | 32.60 (10.93) | ||
| PANSS total | 64.20 (10.18) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jonak, K.; Marchewka, M.; Podkowiński, A.; Siejka, A.; Plechawska-Wójcik, M.; Karpiński, R.; Krukow, P. How Functional Connectivity Measures Affect the Outcomes of Global Neuronal Network Characteristics in Patients with Schizophrenia Compared to Healthy Controls. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010138
Jonak K, Marchewka M, Podkowiński A, Siejka A, Plechawska-Wójcik M, Karpiński R, Krukow P. How Functional Connectivity Measures Affect the Outcomes of Global Neuronal Network Characteristics in Patients with Schizophrenia Compared to Healthy Controls. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010138
Chicago/Turabian StyleJonak, Kamil, Magdalena Marchewka, Arkadiusz Podkowiński, Agata Siejka, Małgorzata Plechawska-Wójcik, Robert Karpiński, and Paweł Krukow. 2023. "How Functional Connectivity Measures Affect the Outcomes of Global Neuronal Network Characteristics in Patients with Schizophrenia Compared to Healthy Controls" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010138
APA StyleJonak, K., Marchewka, M., Podkowiński, A., Siejka, A., Plechawska-Wójcik, M., Karpiński, R., & Krukow, P. (2023). How Functional Connectivity Measures Affect the Outcomes of Global Neuronal Network Characteristics in Patients with Schizophrenia Compared to Healthy Controls. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010138