α-Synuclein and Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epigenetic Regulation of α-Synuclein
3. α-Synuclein as a Genetic Modulator
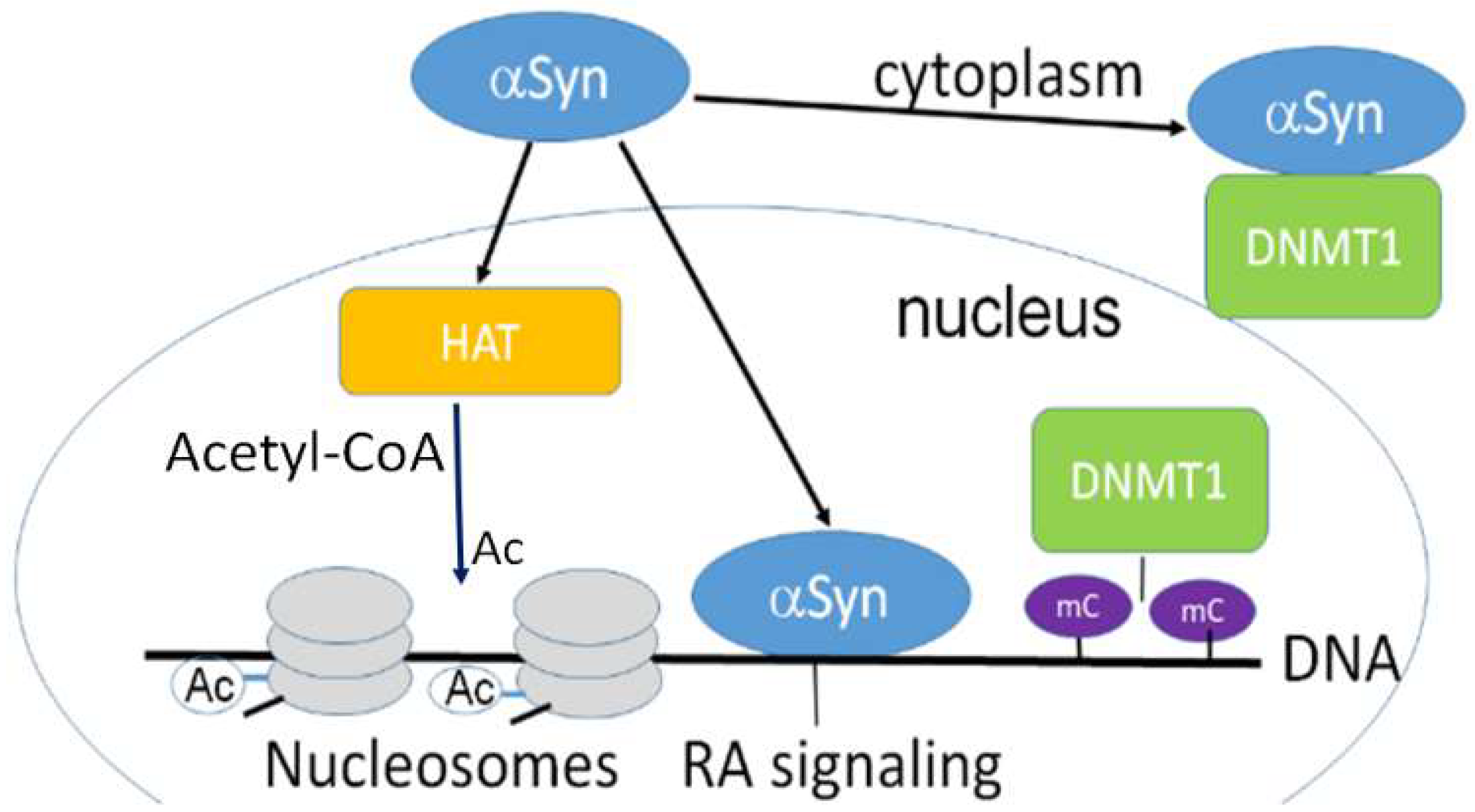
3.1. Nuclear Localization of α-Synuclein and DNA Binding
3.2. Nuclear α-Synuclein Regulates Histone Modifications
3.3. α-Synuclein Mediated Histone Modification Regulates Transcription
3.4. α-Synuclein and Chromatin Remodeling
4. Non-Coding RNAs Regulate α-Synuclein Expression
5. Epigenetic-Based Approaches for Treatment and Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases
6. Conclusions and Further Developments
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Park, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Yi, S.-J. The role of histone modifications: From neurodevelopment to neurodiseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Morales, E.; Meier, K.; Sandoval-Carrillo, A.; Salas-Pacheco, J.; Vázquez-Cárdenas, P.; Arias-Carrión, O. Implications of DNA methylation in parkinson’s disease. Front. Mol. NeuroSci. 2017, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.S.; Birla, H.; Singh, S.S.; Zahra, W.; Dilnashin, H.; Singh, R.; Keshri, P.K.; Singh, S.P. Epigenetic Modulation in Parkinson’s Disease and Potential Treatment Therapies. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surguchov, A. Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. In Neuro degenerative Diseases Biomarkers; Part of the Neuromethods book series; Peplow, P.V., Martinez, B., Gennarelli, T.A., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 173, pp. 155–180. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner, S.L.; Kobor, M.S. DNA methylation as a mediator of genetic and environmental influences on Parkinson’s disease susceptibility: Impacts of alpha-Synuclein, physical activity, and pesticide exposure on the epigenome. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 971298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surguchov, A.; Bernal, L.; Surguchev, A.A. Phytochemicals as Regulators of Genes Involved in Synucleinopathies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington, C.H. Canalization of development and the inheritance of acquired characters. Nature 1942, 150, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.D.; Jones, M.J.; Meaney, M.J.; Turecki, G.; Kobor, M.S. BECon: A tool for interpreting DNA methylation findings from blood in the context of brain. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, L.; Takuma, H.; Tamaoka, A.; Kurisaki, H.; Date, H.; Tsuji, S.; Iwata, A. CpG Demethylation Enhances Alpha-Synuclein Expression and Affects the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüllner, U.; Kaut, O.; Deboni, L.; Piston, D.; Schmitt, I. DNA methylation in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, S.; Costa, B.; Pietrobono, D.; Giacomelli, C.; Iofrida, C.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Fusi, J.; Franzoni, F.; Martini, C. Epigenetic Modifications of the α-Synuclein Gene and Relative Protein Content Are Affected by Ageing and Physical Exercise in Blood from Healthy Subjects. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 3740345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desplats, P.; Spencer, B.; Coffee, E.; Patel, P.; Michael, S.; Patrick, C.; Adame, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E. α-Synuclein Sequesters Dnmt1 from the Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9031–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffner, S.L.; Wassouf, Z.; Lazaro, D.F.; Xylaki, M.; Gladish, N.; Lin, D.T.S.; MacIsaac, J.; Ramadori, K.; Hentrich, T.; Schulze-Hentrich, J.M.; et al. Alpha-synuclein overexpression induces epigenomic dysregulation of glutamate signaling and locomotor pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 3694–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, S.-X.; Xu, Q.; Hu, Y.-C.; Song, C.-Y.; Guo, J.-F.; Shen, L.; Wang, C.-R.; Yu, R.-L.; Yan, X.-X.; Tang, B.-S. Hypomethylation of SNCA in blood of patients with sporadic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 337, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlou, M.A.S.; Outeiro, T.F. Epigenetics in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroepigenomics Aging Dis. 2017, 978, 363–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlstrøm, L.; Berge, V.; Rengmark, A.; Toft, M. Parkinson’s disease correlates with promoter methylation in the α-synuclein gene. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Piperi, C. Environmental Impact on the Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis: A Narrative Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.-H.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, D.; Kang, S.-J.; et al. Dynamic Transcriptome, DNA Methylome, and DNA Hydroxymethylome Networks During T-Cell Lineage Commitment. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroteaux, L.; Campanelli, J.T.; Scheller, R.H. Synuclein: A neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherny, D.; Hoyer, W.; Subramaniam, V.; Jovin, T.M. Double-stranded DNA Stimulates the Fibrillation of α-Synuclein in vitro and is Associated with the Mature Fibrils: An Electron Microscopy Study. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 344, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, M.L.; Rao, K.S. DNA induces folding in alpha-synuclein: Understanding the mechanism using chaperone property of osmolytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 464, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidhar, L.H.; Hegde, M.L.; Vasudevaraju, P.; Rao, K.J. DNA induced folding/fibrillation of alpha-synuclein: New insights in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Biosci. 2010, 15, 418–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Guerrero, E.; Collen, T.B.; Vasudevaraju, P.; Hegde, M.L.; Britton, G.B. New evidence on α-synuclein and Tau binding to conformation and sequence specific GCFNx01 rich DNA: Relevance to neurological disorders. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaser, A.J.; Osterberg, V.R.; Dent, S.E.; Stackhouse, T.L.; Wakeham, C.M.; Boutros, S.W.; Weston, L.J.; Owen, N.; Weissman, T.A.; Luna, E.; et al. Alpha-synuclein is a DNA binding protein that modulates DNA repair with implications for Lewy body disorders. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, B.; Wang, D.; Patz, C.; Akkermann, D.; Lazaro, D.F.; Galka, D.; Kolog Gulko, M.; Bohnsack, M.T.; Mobius, W.; Bohnsack, K.E.; et al. DEAD-box RNA helicase Dbp4/DDX10 is an enhancer of α-synuclein toxicity and oligomerization. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, S.E.; King, D.P.; Osterberg, V.R.; Adams, E.K.; Mackiewicz, M.R.; Weissman, T.A.; Unni, V.K. Phosphorylation of the aggregate-forming protein alpha-synuclein on serine-129 inhibits its DNA-bending properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 298, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Khurana, V.; Yi, S.; Sahni, N.; Loh, K.H.; Auluck, P.K.; Baru, V.; Udeshi, N.D.; Freyzon, Y.; Carr, S.A.; et al. In Situ Peroxidase Labeling and Mass-Spectrometry Connects Alpha-Synuclein Directly to Endocytic Trafficking and mRNA Metabolism in Neurons. Cell Syst. 2017, 4, 242–250.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.M.; Moon, J.; Choi, H.J. Alpha-synuclein interferes with cAMP/PKA-dependent upregulation of dopamine β-hydroxylase and is associated with abnormal adaptive responses to immobilization stress. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 252, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Rocha, S.; Kumar, R.; Westerlund, F.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. C-terminal truncation of α-synuclein alters DNA structure from extension to compaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 568, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopoulos, E.; Parvin, J.D.; Feany, M.B. Alpha-synuclein acts in the nucleus to inhibit histone acetylation and promote neurotoxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 3012–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, R.; Paiva, I.; Jerčić, K.G.; Fonseca-Ornelas, L.; Gerhardt, E.; Fahlbusch, C.; Esparcia, P.G.; Kerimoglu, C.; Pavlou, M.A.S.; Villar-Piqué, A.; et al. Nuclear localization and phosphorylation modulate pathological effects of alpha-synuclein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, P.; Ghosh, D.; Yarramala, D.S.; Das, S.; Maji, S.K.; Kumar, A. Differential copper binding to alpha-synuclein and its disease-associated mutants affect the aggregation and amyloid formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2016, 1861, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez, V.; Mitra, J.; Wang, H.; Hegde, P.M.; Rao, K.; Hegde, M.L. A multi-faceted genotoxic network of alpha-synuclein in the nucleus and mitochondria of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease: Emerging concepts and challenges. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 185, 101729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Fukushima, H.; Masliah, E.; Xia, Y.; Iwai, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Otero, D.A.; Kondo, J.; Ihara, Y.; Saitoh, T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Iwai, A.; Kang, D.; Otero, D.A.; Xia, Y.; Saitoh, T. NACP, the precursor protein of the non-amyloid beta/A4 protein (A beta) component of Alzheimer disease amyloid, binds A beta and stimulates A beta aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9141–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.; Thrush, R.J.; Castellana-Cruz, M.; Oeller, M.; Staats, R.; Nene, A.; Flagmeier, P.; Xu, C.K.; Satapathy, S.; Galvagnion, C.; et al. N-Terminal Acetylation of α-Synuclein Slows down Its Aggregation Process and Alters the Morphology of the Resulting Aggregates. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.; Castellana-Cruz, M.; Nene, A.; Thrush, R.J.; Xu, C.K.; Kumita, J.R.; Vendruscolo, M. Effects of N-terminal Acetylation on the Aggregation of Disease-related α-synuclein Variants. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 435, 167825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma A, Liu H, Tobar-Tosse F, Noll A, Dakal TC, Li H, Holz FG, Loeffler K, Herwig-Carl MC Genome organization in proximity to the BAP1 locus appears to play a pivotal role in a variety of cancers. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1385–1391. [CrossRef]
- Goers, J.; Manning-Bog, A.B.; McCormack, A.L.; Millett, I.S.; Doniach, S.; Di Monte, D.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Nuclear Localization of alpha-Synuclein and Its Interaction with Histones. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 8465–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeno, N.; Jäckel, S.; Voigt, A.; Wassouf, Z.; Schulze-Hentrich, J.; Kahle, P.J. alpha-Synuclein enhances histone H3 lysine-9 dimethylation and H3K9me2-dependent transcriptional responses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Fujigasaki, J.; Fujigasaki, H. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 4 involvement in both Lewy and Marinesco bodies. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2006, 32, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, L. Nuclear Accumulation of Histone Deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) Exerts Neurotoxicity in Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6970–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günaydın, C.; Çelik, Z.B.; Bilge, S.S. CIITA expression is regulated by histone deacetylase enzymes and has a role in α-synuclein pre-formed fibril-induced antigen presentation in murine microglial cell line. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2022, 44, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Neumann, M.; Kahle, P. Nuclear and neuritic distribution of serine-129 phosphorylated α-synuclein in transgenic mice. Neuroscience 2009, 160, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surguchov, A. Chapter Four—Intracellular Dynamics of Synucleins: “Here, There and Everywhere”. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 320, 103–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surguchev, A.A.; Surguchov, A. Synucleins and Gene Expression: Ramblers in a Crowd or Cops Regulating Traffic? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Baek, I.; Liew, H. Sumoylated α-synuclein translocates into the nucleus by karyopherin α6. Mol. Cell Toxicol. 2019, 15, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, H.; Jo, A.; Khang, R.; Park, C.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Kwag, E.; Shin, J.-H. α-Synuclein A53T Binds to Transcriptional Adapter 2-Alpha and Blocks Histone H3 Acetylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Xiao, M.; Ma, F.; Yao, Y.; Ye, M.; et al. Attenuation of epigenetic regulator SMARCA4 and ERK-ETS signaling suppresses aging-related dopaminergic degeneration. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-Y.; Kuo, H.-C. Functional roles and networks of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigno, E.; Magagnoli, C.; Pierce, M.; Iglesias, P. Lubricating ability of two phosphonium-based ionic liquids as additives of a bio-oil for use in wind turbines gearboxes. Wear 2011, 21, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Oe, S.; Kimura, T. Regulatory non-coding RNAs in nervous system development and disease. Front. Biosci. 2019, 24, 1203–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Cai, H.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes α-synuclein aggregation and apoptosis of SH-SY5Y cells by regulating miR-221-3p in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 417, 113132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Z. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 mediates the toxic of Parkinson’s disease induced by MPTP/MPP+ via regulation of gene expression. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, K.; Chen, Y.; Jing, X.; Liang, Y.; Bu, L.; Peng, S.; Zeng, S.; Asakawa, T.; et al. Exploration of the α-syn/T199678/miR-519–3p/KLF9 pathway in a PD-related α-syn pathology. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 186, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.-L.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Lin, D.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Jing, X.-N.; Liang, Y.-R.; Peng, S.-D.; Huang, K.-X.; Tao, E.-X. LncRNA-T199678 Mitigates α-Synuclein-Induced Dopaminergic Neuron Injury via miR-101-3p. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 599246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, L.; Xie, J. Commentary: LncRNA-T199678 Mitigates α-Synuclein-Induced Dopaminergic Neuron Injury via miR-101-3p. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 650840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, M.; Meng, Y.; Song, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, D.; Bi, J.; Xu, S. Long Non-coding RNAs in Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 719247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Cai, H.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J. NEAT1 Decreasing Suppresses Parkinson’s Disease Progression via Acting as miR-1301-3p Sponge. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.E.; Park, H.-J.; He, L.; Skibiel, C.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. The Parkinson’s disease gene product DJ-1 modulates miR-221 to promote neuronal survival against oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2018, 19, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, M. Long non-coding RNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript promotes 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion-induced neuronal inflammation and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease through regulating microRNA-221-3p/ transforming growth factor /nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.; Jin, Z.; Xi, Z.; Wei, J. Downregulation of lncRNA BACE1-AS improves dopamine-dependent oxidative stress in rats with Parkinson’s disease by upregulating microRNA-34b-5p and downregulating BACE1. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1158–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-M.; Wang, M.-H.; Yang, H.-C.; Tian, T.; Sun, G.-F.; Ji, Y.-F.; Hu, W.-T.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.-P.; Lu, H. Dopaminergic neuron injury in Parkinson’s disease is mitigated by interfering lncRNA SNHG14 expression to regulate the miR-133b/ α-synuclein pathway. Aging 2019, 11, 9264–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, E.; Urbanke, H.; Ramachandran, B.; Barth, J.; Halder, R.; Awasthi, A.; Jain, G.; Capece, V.; Burkhardt, S.; Navarro-Sala, M.; et al. HDAC inhibitor–dependent transcriptome and memory reinstatement in cognitive decline models. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3572–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grääff, J.; Tsai, L.H. Histone acetylation: Molecular mnemonics on the chromatin. Nat. Rev. Urosci. 2013, 14, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.; Dent, P. Simultaneous Interruption of Signal Transduction and Cell Cycle Regulatory Pathways: Implications for New Approaches to the Treatment of Childhood Leukemias. Curr. Drug Targets 2007, 8, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, F.; Mercurio, C. Towards Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase Isoforms: What Has Been Achieved, Where We Are and What Will Be Next. Chemmedchem 2014, 9, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräff, J.; Joseph, N.F.; Horn, M.E.; Samiei, A.; Meng, J.; Seo, J.; Rei, D.; Bero, A.W.; Phan, T.X.; Wagner, F.; et al. Epigenetic Priming of Memory Updating during Reconsolidation to Attenuate Remote Fear Memories. Cell 2014, 156, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, A.-E.; Gomes, L.C.; Halder, R.; Jain, G.; Maass, F.; Tönges, L.; Tatenhorst, L.; Bähr, M.; Fischer, A.; Lingor, P. miR-182-5p and miR-183-5p Act as GDNF Mimics in Dopaminergic Midbrain Neurons. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.; Liang, J.; Wang, C.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z. Epigenetic Regulation of Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.G. Targeting Huntington’s disease through histone deacetylases. Clin. Epigenetics 2011, 2, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kundu, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, S. Understanding the role of histone deacetylase and their inhibitors in neurodegenerative disorders: Current targets and future perspective. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 158–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlstrøm, L.; Shireby, G.; Geut, H.; Henriksen, S.P.; Rozemuller, A.J.M.; Tunold, J.-A.; Hannon, E.; Francis, P.; Thomas, A.J.; Love, S.; et al. Epigenome-wide association study of human frontal cortex identifies differential methylation in Lewy body pathology. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surguchov, A.; Surguchev, A. Synucleins: New Data on Misfolding, Aggregation and Role in Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wan, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Q.; Gan, L. LncRNA NEAT1 promoted MPP+-induced ferroptosis via regulating miR-150-5p/BAP1 pathway in SK-N-SH cells. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2022, 82, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surguchov, A. α-Synuclein and Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010150
Surguchov A. α-Synuclein and Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurguchov, Andrei. 2023. "α-Synuclein and Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010150
APA StyleSurguchov, A. (2023). α-Synuclein and Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010150





