Blink Reflex Examination in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Compared to Diseases Affecting the Peripheral Nervous System and Healthy Controls
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Data
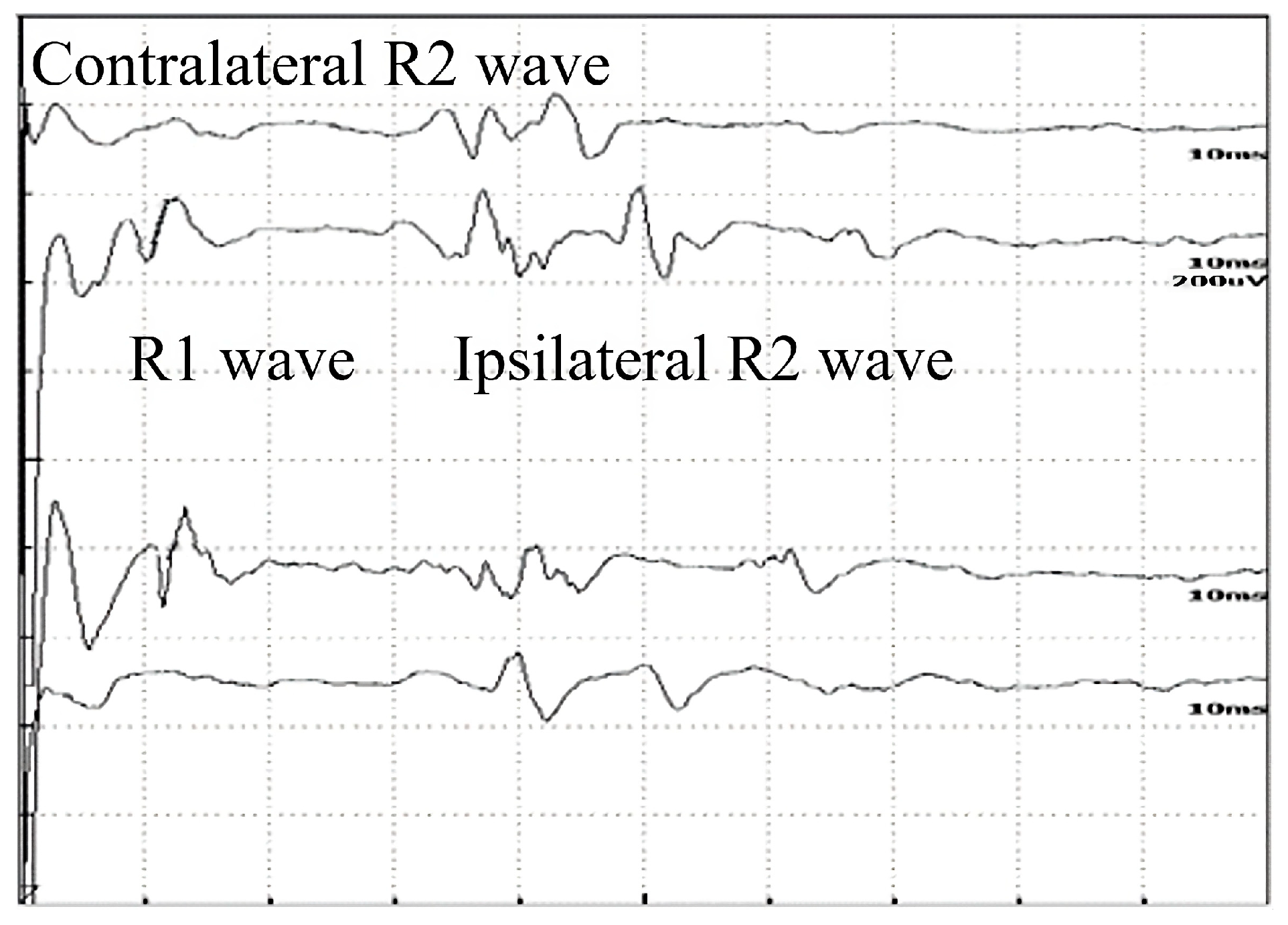
2.2. Blink Reflex
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Blink Reflex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| ALSFRS-R | ALS Functional Rating Scale—Revised |
| BR | Blink reflex |
| EDC | Extensor digitorum communis muscle |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| LMN | Lower motor neuron |
| MND | Motor neuron disease |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| TMS | Transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| UMN | Upper motor neuron |
References
- Gowland, A.; Opie-Martin, S.; Scott, K.M.; Jones, A.R.; Mehta, P.R.; Batts, C.J.; Ellis, C.M.; Leigh, P.N.; Shaw, C.E.; Sreedharan, J.; et al. Predicting the future of ALS: The impact of demographic change and potential new treatments on the prevalence of ALS in the United Kingdom, 2020–2116. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 20, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.G.; Jackson, C.E.; Kasarskis, E.J.; England, J.D.; Forshew, D.; Johnston, W.; Kalra, S.; Katz, J.S.; Mitsumoto, H.; Rosenfeld, J.; et al. Practice Parameter update: The care of the patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Multidisciplinary care, symptom management, and cognitive/behavioral impairment (an evidence-based review): Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2009, 73, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carelli, L.; Solca, F.; Faini, A.; Madotto, F.; Lafronza, A.; Monti, A.; Zago, S.; Doretti, A.; Ciammola, A.; Ticozzi, N.; et al. The Complex Interplay between Depression/Anxiety and Executive Functioning: Insights from the ECAS in a Large ALS Population. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, K.C.; Calvo, A.; Price, T.R.; Geiger, J.T.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B.J. Projected increase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from 2015 to 2040. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londral, A.; Pinto, A.; Pinto, S.; Azevedo, L.; De Carvalho, M. Quality of life in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients and caregivers: Impact of assistive communication from early stages. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, T.; Galvin, M.; Pinto-Grau, M.; Lonergan, K.; Madden, C.; Mays, I.; Carney, S.; Hardiman, O.; Pender, N. Caregivers of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Investigating quality of life, caregiver burden, service engagement, and patient survival. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.M. Neuroepidemiology: From Principles to Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 162–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, M.; Swash, M. Awaji diagnostic algorithm increases sensitivity of El Escorial criteria for ALS diagnosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekestein, W.A.; Kleine, B.U.; Hageman, G.; Schelhaas, H.J.; Zwarts, M.J. Sensitivity and specificity of the ‘Awaji’ electrodiagnostic criteria for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Retrospective comparison of the Awaji and revised El Escorial criteria for ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmidt-Sałkowska, E.; Rowińska-Marcińska, K. Blink reflex in motor neuron disease. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 45, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Podikoglou, D.G.; Avramidis, T.G.; Papadimitriou, A.L. Blink reflex in primary lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1064–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.B.B.; Jardim, M.R.; Papais-Alvarenga, R.M.; Fragoso, Y.D. Time Parameters of the Blink Reflex in Normal Subjects. Neurophysiology 2014, 46, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, L.A.; Syrovegin, A.V.; Avakyan, G.N.; Gnezdilov, A.V.; Zagorulko, O.I. Methods for Studying the Blink Reflex and Its Normative Parameters. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2012, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, M.; Agostino, R.; Gregori, B.; Belvisi, D.; Manfredi, M.; Berardelli, A. Metaplasticity of the human trigeminal blink reflex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramideh, M.; De Visser, B.O. Brainstem reflexes: Electrodiagnostic techniques, physiology, normative data, and clinical applications. Muscle Nerve 2002, 26, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruccu, G.; Iannetti, G.D.; Marx, J.J.; Thoemke, F.; Truini, A.; Fitzek, S.; Galeotti, F.; Urban, P.P.; Romaniello, A.; Stoeter, P.; et al. Brainstem reflex circuits revisited. Brain 2005, 128, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, J.; Powers, J.M.; Van Allen, M.W. Reflex response of the orbicularis oculi muscle to supraorbital nerve stimulation: Study in normal subjects and in peripheral facial paresis. Trans. Am. Neurol. Assoc. 1969, 94, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzek, S.; Fitzek, C.; Marx, J.; Speckter, H.; Urban, P.P.; Thomke, F.; Stoeter, P.; Hopf, H.C. Blink reflex R2 changes and localisation of lesions in the lower brainstem (Wallenberg’s syndrome): An electrophysiological and MRI study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 67, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazhel, B.; Irkeç, C.; Koçer, B. The roles of blink reflex and sympathetic skin response in multiple sclerosis diagnosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2002, 8, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grbelja, L.D.; Mikula, I.; Ćorić, L.; Stojić, M.; Demarin, V. The Value of Blink Reflex in Early Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Acta Clin. Croat. 2021, 60., 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostino, R.; Berardelli, A.; Cruccu, G.; Stocchi, F.; Manfredi, M. Corneal and blink reflexes in Parkinson’s disease with “on-off” fluctuations. Mov. Disord. 1987, 2, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weise, D.; Pargac, C.; Pelz, J.O.; Rumpf, J.-J.; Fricke, C.; Classen, J. Assessing blink reflex circuits by three different afferent routes in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, L.; Anzellotti, F.; Varanese, S.; Thomas, A.; Manzoli, L.; Onofrj, M. Delayed blink reflex in dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddireddy, A.; Wang, K.; Svensson, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Blink reflexes in chronic tension-type headache patients and healthy controls. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Okada, A.; Nakashima, K.; Takahashi, K. Electrically induced blink reflex and clinical blinking ability in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1995, 92, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunohara, N.; Mukoyama, M.; Funamoto, H.; Kamei, N.; Tomi, H.; Satoyoshi, E. Supranuclear paralysis preventing lid closure in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Jpn. J. Med. 1989, 28, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengiz, B.; Ercan, M.B.; Iskender, M.; Kuruoğlu, H.R. Brainstem reflex excitability changes in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedarbaum, J.M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E.; Fuller, C.; Hilt, D.; Thurmond, B.; Nakanishi, A. The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 169, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štětkářová, I.; Ehler, E. Diagnostics of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Up to Date. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, N.; Macklin, E.A.; Sinani, E.; Sherman, A.; Weber, M.; the Pooled Resource Open-Access ALS Clinical Trials Consortium. The revised El Escorial criteria “clinically probable laboratory supported ALS”—Once a promising now a superfluous category? Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 21, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, E.J. The Electrophysiology of the Motor Neuron Diseases. Neurol. Clin. 2012, 30, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swash, M.; de Carvalho, M. The Neurophysiological Index in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2004, 5, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, A. A neurophysiological approach to brainstem reflexes. Blink reflex. Neurophysiol. Clin. 1999, 29, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewelyn, J.G. The Diabetic Neuropathies: Types, Diagnosis and Management. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74 (Suppl. S2), ii15–ii19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, M.S.; Kiernan, M.C.; Heggie, S.; McCombe, P.A.; Henderson, R.D. Study of motor asymmetry in ALS indicates an effect of limb dominance on onset and spread of weakness, and an important role for upper motor neurons. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2014, 15, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramideh, M.; de Visser, B.W.O.; Koelman, J.H.; Majoie, C.B.; Holstege, G. The late blink reflex response abnormality due to lesion of the lateral tegmental field. Brain 1997, 120, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongerboer de Visser, B.W.; Kuypers, H.G.J.M. Late blink reflex changes in lateral medullary lesions: An electrophysiological and neuro-anatomical study of Wallenberg’s syndrome. Brain 1978, 101, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Tsujimoto, T. Pathway of the blink reflex in the brainstem of the cat: Interneurons between the trigeminal nuclei and the facial nucleus. Brain Res. 1986, 380, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiò, A.; Logroscino, G.; Hardiman, O.; Swingler, R.; Mitchell, D.; Beghi, E.; Traynor, B.G. On Behalf of the Eurals Consortium Prognostic factors in ALS: A critical review. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharova, M.N.; Abramova, A. Lower and upper motor neuron involvement and their impact on disease prognosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiri, K.; Zareh, M.; Khosravi, S. Blink Reflex as a Complementary Test to MRI in Early Detection of Brainstem Infarctions: Comparison of Blink Reflex Abnormalities in Anterior Versus Posterior Circulation Strokes. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2004, 4, 162–167. [Google Scholar]








| All Patients | |
|---|---|
| Patient number | 29 |
| Female/male (number) | 12/17 |
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 67.86 ± 10.21 |
| Disease duration (months) (mean ± SD) | 8.21 ± 3.93 |
| ALSFRS-R (mean ± SD) | 33.13 ± 6.72 |
| (A) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALS | Bell’s Paresis, Left Side | Bell’s Paresis, Right Side | Myasthenia Gravis, Ocular | Myasthenia Gravis, Generalized | Diabetic PNP | Healthy Controls | ||||||||||||||
| Patient number | 29 | 12 | 15 | 4 | 5 | 25 | 50 | |||||||||||||
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 67.86 ± 10.21 | 54 ± 13.65 | 52.53 ± 15.42 | 53.5 ± 13.6 | 63 ± 18.53 | 68.24 ± 10.64 | 52.94 ± 17.74 | |||||||||||||
| Left side | R1 | 12.17 ± 0.4 | 15.63 ± 1.1 | 12.01 ± 0.1 | 13.1 ± 0.47 | 12.76 ± 0.78 | 12.23 ± 0.15 | 12.07 ± 0.14 | ||||||||||||
| R2i | 41.93 ± 2.05 | 46.58 ± 2.62 +3 absent | 35.37 ± 0.99 | 40.35 ± 0.6 | 37.04 ± 0.93 | 36.08 ± 1.34 | 35.49 ± 0.66 | |||||||||||||
| R2c | 42.76 ± 2.41 +2 absent | 35.65 ± 0.68 | 47.54 ± 1.58 +5 absent | 40.63 ± 1.05 | 37.44 ± 0.81 | 36.86 ± 1.73 | 35.41 ± 0.8 | |||||||||||||
| Right side | R1 | 12.0 ± 0.26 | 12.06 ± 0.17 | 15.14 ± 0.94 +5 absent | 13.18 ± 0.31 | 12.76 ± 0.35 | 12.23 ± 0.15 | 12.06 ± 0.13 | ||||||||||||
| R2i | 41.63 ± 2.25 | 35.69 ± 0.51 | 45.59 ± 2.03 +5 absent | 40.18 ± 0.69 | 37.4 ± 0.65 | 38.42 ± 1.6 | 35.48 ± 0.53 | |||||||||||||
| R2c | 42.78 ± 1.3 +4 absent | 45.56 ± 1.4 +3 absent | 35.14 ± 0.92 | 40.38 ± 0.68 | 37.94 ± 1.67 | 38.1 ± 1.75 | 35.55 ± 1.03 | |||||||||||||
| (B) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ALS | Diabetic Polyneuropathy | Myasthenia Gravis, Generalized | Myasthenia Gravis, Ocular | Bell’s Paresis, Right Side | Bell’s Paresis, Left Side | |||||||||||||||
| Healthy controls | R1 left | 0.12 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.13 | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||
| R2i left | <0.0001 | 0.01 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.59 | <0.0001 | ||||||||||||||
| R2c left | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.34 | ||||||||||||||
| R1 right | 0.18 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||||
| R2i right | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.22 | ||||||||||||||
| R2c right | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.17 | <0.0001 | ||||||||||||||
| (C) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Diabetic Polyneuropathy | Myasthenia Gravis, Generalized | Myasthenia Gravis, Ocular | Bell’s Paresis, Right Side | Bell’s Paresis, Left Side | ||||||||||||||||
| ALS | R1 left | 0.48 * | 0.01 * | 0.0001 * | 0.13 | <0.0001 * | ||||||||||||||
| R2i left | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.14 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 * | |||||||||||||||
| R2c left | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.096 | <0.0001 * | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| R1 right | 0.0003 * | <0.0001 * | <0.0001 * | <0.0001 * | 0.47 * | |||||||||||||||
| R2i right | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.21 | <0.0001 * | <0.0001 | |||||||||||||||
| R2c right | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0013 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 * | |||||||||||||||
| Bulbar Onset | p (b-l) | p (b-s) | Limb Onset | p (l-s) | Severe Cases | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient number | 6 | 19 | 4 | ||||
| Female/male (number) | 4/2 | 6/13 | 2/2 | ||||
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 57.5 ± 13.91 | 0.004 | 0.099 | 70.32 ± 6.98 | 0.72 | 71.75 ± 9.25 | |
| Disease duration (months) (mean ± SD) | 7 ± 0.89 | 0.82 | <0.0001 | 6.79 ± 2.2 | <0.0001 | 16.75 ± 0.96 | |
| Left side | R1 | 12.31 ± 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 12.04 ± 0.26 | 0.02 | 12.58 ± 0.78 |
| R2i | 44.24 ± 1.88 | <0.0001 | 0.38 | 41.07 ± 0.45 | 0.12 | 42.5 ± 4.04 | |
| R2c | 45.82 ± 2.2 | 0.0001 | 0.005 | 42.03 ± 1.6 | 0.11 | 40.5 ± 2.12 | |
| Right side | R1 | 12.21 ± 0.38 | 0.016 | 0.56 | 11.92 ± 0.18 | 0.13 | 12.08 ± 0.22 |
| R2i | 43.48 ± 0.63 | 0.0002 | 0.4 | 41.05 ± 1.27 | 0.65 | 41.63 ± 5.29 | |
| R2c | 44.48 ± 0.83 | <0.0001 | N/A | 42.25 ± 0.89 | N/A | 0 | |
| ALSFRS-R (mean ± SD) | 33 ± 5.02 | 0.24 | 0.0017 | 35.74 ± 4.83 | <0.0001 | 21.0 ± 0.82 |
| Right Upper Limb | p (ru-lu) | p (ru-rl) | p (ru-ll) | Left Upper Limb | p (lu-rl) | p (lu-ll) | Right Lower Limb | p (rl-ll) | Left Lower Limb | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient number | 7 | 6 | 4 | 2 | |||||||
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 69.14 ± 7.8 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.27 | 70.17 ± 5.46 | 0.83 | 0.24 | 69.25 ± 7.37 | 0.33 | 77 ± 9.9 | |
| Disease duration until examination (months) (mean ± SD) | 5.43 ± 1.72 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.44 | 7 ± 2.61 | 0.35 | 0.88 | 8.5 ± 1.73 | 0.78 | 7.5 ± 0.71 | |
| Left side | R1 | 11.89 ± 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 12.03 ± 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.64 | 12.29 ± 0.26 | 0.46 | 12.13 ± 0.02 |
| R2i | 40.78 ± 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.014 | 0.16 | 41.07 ± 0.4 | 0.14 | 0.72 | 41.54 ± 0.5 | 0.39 | 41.18 ± 0.05 | |
| R2c | 41.03 ± 1.53 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 42.07 ± 1.56 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 43.36 ± 1.27 | 0.55 | 42.73 ± 0.16 | |
| Right side | R1 | 11.81 ± 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 11.92 ± 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.6 | 12.09 ± 0.17 | 0.48 | 11.99 ± 0.01 |
| R2i | 40.29 ± 1.23 | 0.33 | 0.024 | 0.19 | 40.98 ± 1.22 | 0.12 | 0.52 | 42.22 ± 0.91 | 0.42 | 41.6 ± 0.13 | |
| R2c | 41.65 ± 0.79 | 0.18 | 0.015 | 0.18 | 42.29 ± 0.83 | 0.16 | 0.72 | 43.09 ± 0.72 | 0.35 | 42.52 ± 0.13 | |
| ALSFRS-R (mean ± SD) | 38.86 ± 3.8 | 0.25 | 0.013 | N/C | 35.83 ± 5.19 | 0.19 | N/C | 31.5 ± 3.79 | N/C | 33 ± 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rostás, R.; Fekete, I.; Horváth, L.; Fekete, K. Blink Reflex Examination in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Compared to Diseases Affecting the Peripheral Nervous System and Healthy Controls. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101384
Rostás R, Fekete I, Horváth L, Fekete K. Blink Reflex Examination in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Compared to Diseases Affecting the Peripheral Nervous System and Healthy Controls. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(10):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101384
Chicago/Turabian StyleRostás, Róbert, István Fekete, László Horváth, and Klára Fekete. 2023. "Blink Reflex Examination in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Compared to Diseases Affecting the Peripheral Nervous System and Healthy Controls" Brain Sciences 13, no. 10: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101384
APA StyleRostás, R., Fekete, I., Horváth, L., & Fekete, K. (2023). Blink Reflex Examination in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Compared to Diseases Affecting the Peripheral Nervous System and Healthy Controls. Brain Sciences, 13(10), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101384






