Characterization of Cortical and Subcortical Structural Brain Asymmetry in Adults with and without Dyslexia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Lateralization of Subcortical Structures Involved in Reading
1.2. Lateralization of Cortical Structures Involved in Reading
1.3. Summary
- Are there differences between skilled and dyslexic adult readers in the structural properties of the cortical and subcortical structures?
- Are there relationships between reading behavior and subcortical structure asymmetry?
- Are there relationships between the cortical and subcortical regions?
2. Methods
2.1. Behavioral Data Collection
2.2. MRI Acquisition
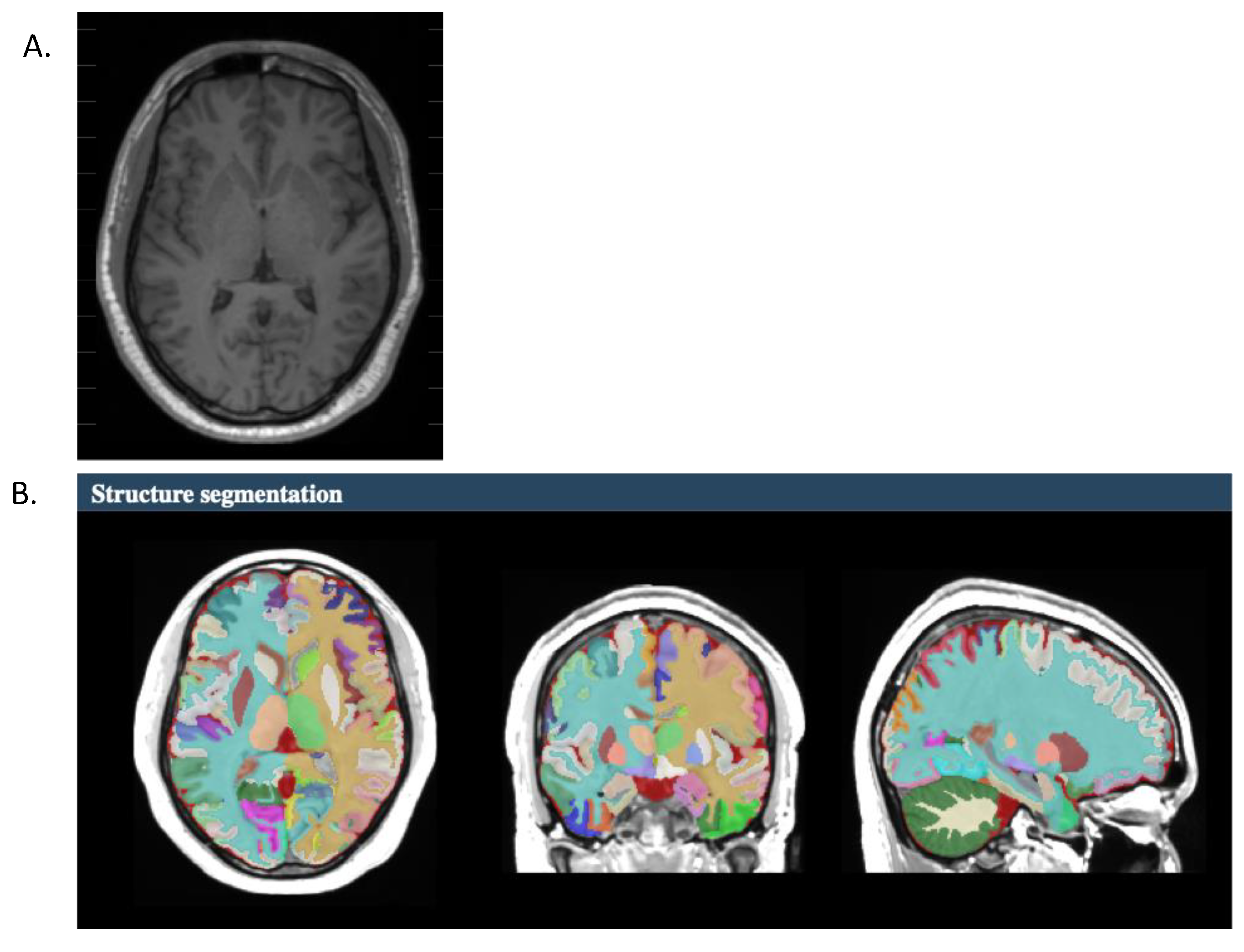
2.3. Segmentation Measurements
2.4. Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Structural Asymmetry and Reading Performance: Brain–Behavior Relationships
4.2. Asymmetry of Structure
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janacsek, K.; Evans, T.M.; Kiss, M.; Shah, L.; Blumenfeld, H.; Ullman, M.T. Subcortical cognition: The fruit below the rind. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 45, 361–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohland, J.W.; Bullock, D.; Guenther, F.H. Neural representations and mechanisms for the performance of simple speech sequences. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 1504–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, W.R. Cortico-basal ganglia circuitry: A review of key research and implications for functional connectivity studies of mood and anxiety disorders. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 215, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.J. A review and synthesis of the first 20 years of PET and fMRI studies of heard speech, spoken language and reading. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 816–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrink, C.; Vogt, K.; Kastrup, A.; Müller, H.P.; Juengling, F.D.; Kassubek, J.; Riecker, A. The contribution of white and gray matter differences to developmental dyslexia: Insights from DTI and VBM at 3.0 T. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 3170–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourville, J.A.; Reilly, K.J.; Guenther, F.H. Neural mechanisms underlying auditory feedback control of speech. NeuroImage 2008, 39, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fondas, A.L.; Cindass, R., Jr.; Mock, J.R.; Corey, D.M. Atypical caudate anatomy in children who stutter. Sage J. 2013, 116, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chen, C.; Ning, N.; Ding, G.; Guo, T.; Peng, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, K.; Lin, C. The neural substrates for atypical planning and execution of word production in stuttering. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 221, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, K.; Lantz, N.; Cummine, J. Exploring the role of subcortical structures in developmental reading impairments: Evidence for subgroups differentiated by caudate activity. NeuroReport 2018, 29, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafnick, A.J.; Flowers, D.L.; Napoliello, E.M.; Eden, G.F. Gray matter volume changes following reading intervention in dyslexic children. NeuroImage 2011, 57, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, D.S.; Gracco, V.L.; Brettschneider, J.; Kroll, R.M.; De Nil, L.F. A voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis of regional grey and white matter volume abnormalities within the speech production network of children who stutter. Cortex 2013, 49, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Peng, D.; Chen, C.; Ning, N.; Ding, G.; Li, K.; Yang, Y.; Lin, C. Altered effective connectivity and anomalous anatomy in the basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuit of stuttering speakers. Cortex 2010, 46, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, N.; Fan, Q.; Compton, D.L.; Fuchs, D.; Fuchs, L.S.; Cutting, L.E.; Gore, J.C.; Anderson, A.W. Influences of neural pathway integrity on children’s response to reading instruction. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, M.S.; Molfese, P.J.; Milham, M.P.; Mencl, W.E.; Pugh, K.R. Thalamus is a common locus of reading, arithmetic, and IQ: Analysis of local intrinsic functional properties. Brain Lang. 2020, 209, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barquero, L.A.; Davis, N.; Cutting, L.E. Neuroimaging of reading intervention: A systematic review and activation likelihood estimate meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, M.V.; Mahaffy, K.; Vlahcevic, K.; Wolfman, E.; Erbeli, F.; Richlan, F.; Landi, N. Reading intervention and neuroplasticity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of brain changes associated with reading intervention. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 465–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richlan, F.; Kronbichler, M.; Wimmer, H. Structural abnormalities in the dyslexic brain: A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, M.A.; Berninger, V.W.; Vaden, K.I., Jr.; Gebregziabher, M.; Tsu, L. Gray Matter Features of Reading Disability: A Combined Meta-Analytic and Direct Analysis Approach(1,2,3,4). eNeuro 2016, 3, ENEURO.0103–15.2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braid, J.; Richlan, F. The Functional Neuroanatomy of Reading Intervention. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 921931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, A.M.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Cognitive Neuroscience of Dyslexia. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2018, 49, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujala, T.; Sihvonen, A.J.; Thiede, A.; Palo-Oja, P.; Virtala, P.; Numminen, J.; Laasonen, M. Voxel and surface based whole brain analysis shows reading skill associated grey matter abnormalities in dyslexia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkersdörfer, J.; Lonnemann, J.; Lindberg, S.; Hasselhorn, M.; Fiebach, C.J. Grey matter alterations co-localize with functional abnormalities in developmental dyslexia: An ALE meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, L.M.; Stoodley, C.J. Are there shared neural correlates between dyslexia and ADHD? A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2019, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Ferrer, M.; Martínez, E.P. A review of the neurobiological basis of dyslexia in the adult population. Neurología 2017, 32, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Hui, Y.; Li, H. The roles of decoding and vocabulary in Chinese reading development: Evidence from a 3-year longitudinal study. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2021, 91, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, K.; Ostevik, A.V.; Westover, L.; Hodgetts, W.E.; Cummine, J. Resting-state networks and reading in adults with and without reading impairments. J. Neurolinguist. 2021, 60, 101016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, K.; Hodgetts, W.E.; Cummine, J. Is the letter ‘t’in the word ‘gourmet’? Disruption in task-evoked connectivity networks in adults with impaired literacy skills. NeuroSci 2021, 2, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullum, A.; Hodgetts, W.E.; Milburn, T.F.; Cummine, J. Cerebellar activation during reading tasks: Exploring the dichotomy between motor vs. language functions in adults of varying reading proficiency. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 688–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manis, F.R.; Seidenberg, M.S.; Doi, L.M.; McBride-Chang, C.; Petersen, A. On the bases of two subtypes of development dyslexia. Cognition 1996, 58, 157–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowling, M.; Dawes, P.; Nash, H.; Hulme, C. Validity of a protocol for adult self-report of dyslexia and related difficulties. Dyslexia 2012, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgeson, J.K.; Wagner, R.K.; Rashotte, C.A. Test Review: Test of Word Reading Efficiency (TOWRE); PRO-ED Inc.: Austin, TX, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Manjón, J.V.; Coupé, P. volBrain: An online MRI brain volumetry system. Front. Neuroinform. 2016, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjón, J.V.; Romero, J.E.; Vivo-Hernando, R.; Rubio, G.; Aparici, F.; de la Iglesia-Vaya, M.; Coupé, P. vol2Brain: A new online Pipeline for whole Brain MRI analysis. Front. Neuroinform. 2022, 16, 862805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrabaszcz, A.; Wang, D.; Lipski, W.J.; Bush, A.; Crammond, D.J.; Shaiman, S.; Dickey, M.W.; Holt, L.L.; Turner, R.S.; Fiez, J.A.; et al. Simultaneously recorded subthalamic and cortical LFPs reveal different lexicality effects during reading aloud. J. Neurolinguist. 2021, 60, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Green, D.W.; Kherif, F.; Devlin, J.T.; Price, C.J. The role of the left head of caudate in suppressing irrelevant words. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 2369–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Structure | Skilled | Dyslexic | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subcortical | Caudate Total (cm3) + Asymmetry (%) | 7.87 (0.94) −0.36 (2.85) | 7.63 (1.10) 0.91 (2.96) | 0.640 0.067 |
| Putamen Total (cm3) + Asymmetry (%) | 9.07 (0.93) −0.42 (2.41) | 8.69 (1.08) −0.18 (2.47) | 0.537 0.681 | |
| Thalamus Total (cm3) + Asymmetry (%) | 12.89 (1.13) 0.79 (3.40) | 12.44 (1.31) 1.58 (2.74) | 0.645 0.288 | |
| Cortical | Fusiform Gyrus Total (cm3) + Asymmetry (%) | 16.9 (2.50) −3.21 (12.1) | 16.9 (3.08) −1.67 (10.6) | 0.797 0.575 |
| Supramarginal Gyrus Total (cm3) + Asymmetry (%) | 18.2 (1.99) 1.42 (9.5) | 18.1 (3.24) −0.61 (10.9) | 0.800 0.400 | |
| Planum Temporale Total (cm3) + Asymmetry (%) | 4.23 (0.81) −16.8 (22.7) | 4.15 (1.08) −13.3 (22.6) | 0.712 0.518 |
| Caudate | Putamen | Thalamus | Fusiform Gyrus | Planum Temporale | Supramarginal Gyrus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOWRE SWE | −0.220 (0.063) | 0.019 (0.875) | −0.129 (0.280) | −0.132 (0.269) | −0.058 (0.627) | 0.140 (0.241) |
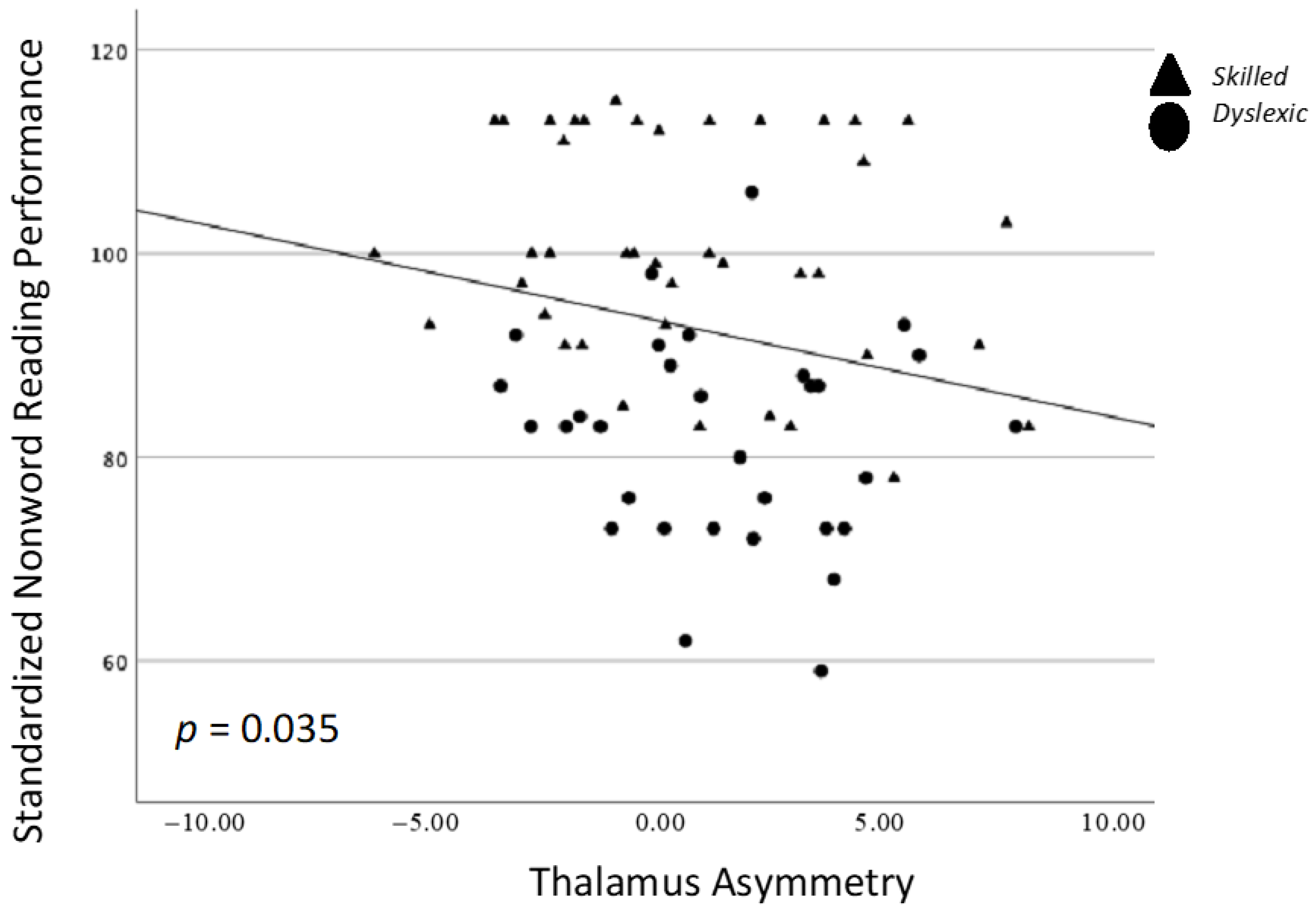
| TOWRE PDE | −0.213 (0.072) | −0.018 (0.880) | −0.249 (0.035) * | −0.095 (0.430) | 0.014 (0.905) | 0.025 (0.837) |
| Caudate | Putamen | Thalamus | Fusiform Gyrus | Planum Temporale | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caudate | - | ||||
| Putamen | −0.131 (0.272) | - | |||
| Thalamus | 0.311 * (0.008) | −0.046 (0.700) | - | ||
| Fusiform Gyrus | 0.183 (0.123) | 0.096 (0.422) | −0.068 (0.571) | - | |
| Planum Temporale | −0.016 (0.895) | −0.038 (0.750) | −0.055 (0.645) | −0.229 (0.053) | - |
| Supramarginal Gyrus | 0.003 (0.982) | 0.025 (0.832) | 0.037 (0.759) | 0.108 (0.367) | −0.318 * (0.006) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cummine, J.; Ngo, T.; Nisbet, K. Characterization of Cortical and Subcortical Structural Brain Asymmetry in Adults with and without Dyslexia. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121622
Cummine J, Ngo T, Nisbet K. Characterization of Cortical and Subcortical Structural Brain Asymmetry in Adults with and without Dyslexia. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(12):1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121622
Chicago/Turabian StyleCummine, Jacqueline, Tiffany Ngo, and Kelly Nisbet. 2023. "Characterization of Cortical and Subcortical Structural Brain Asymmetry in Adults with and without Dyslexia" Brain Sciences 13, no. 12: 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121622
APA StyleCummine, J., Ngo, T., & Nisbet, K. (2023). Characterization of Cortical and Subcortical Structural Brain Asymmetry in Adults with and without Dyslexia. Brain Sciences, 13(12), 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121622





