Prolonged Zaleplon Treatment Increases the Expression of Proteins Involved in GABAergic and Glutamatergic Signaling in the Rat Hippocampus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
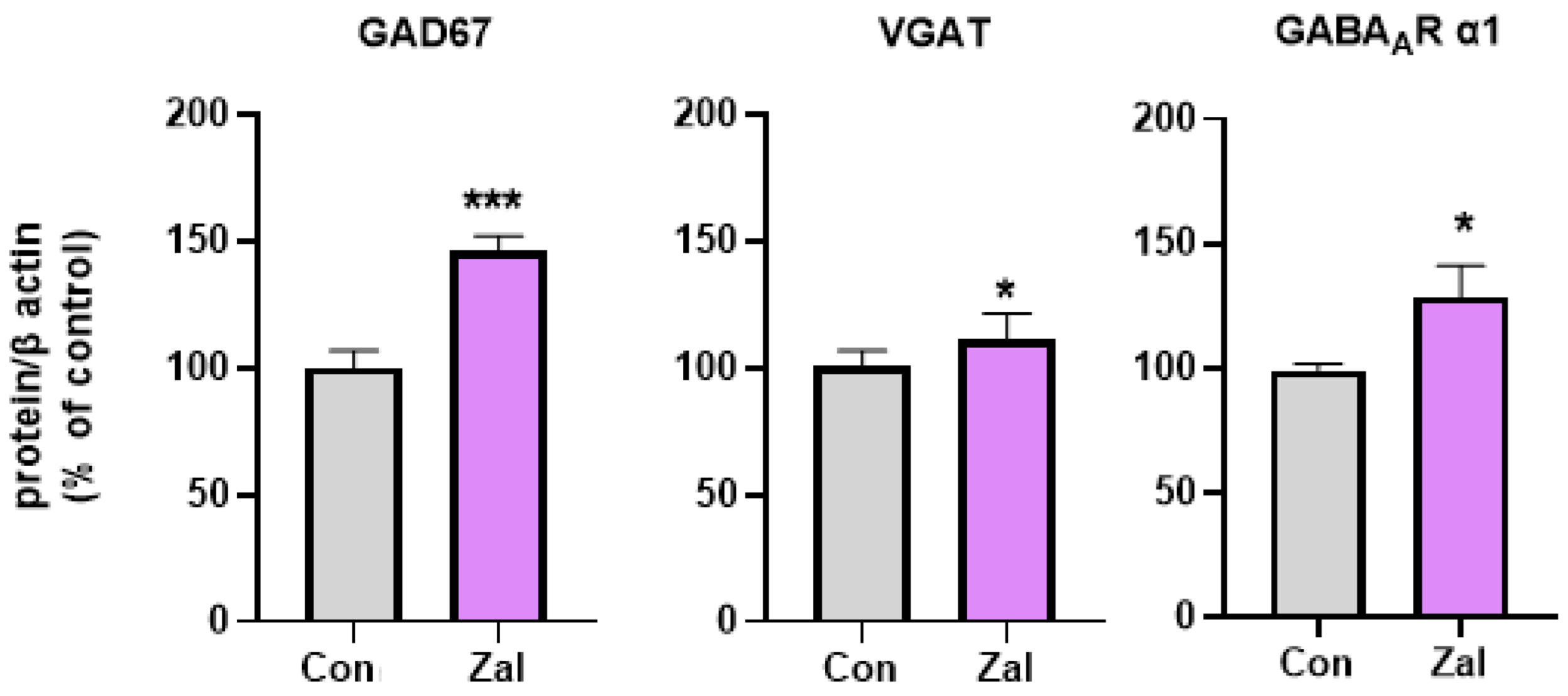
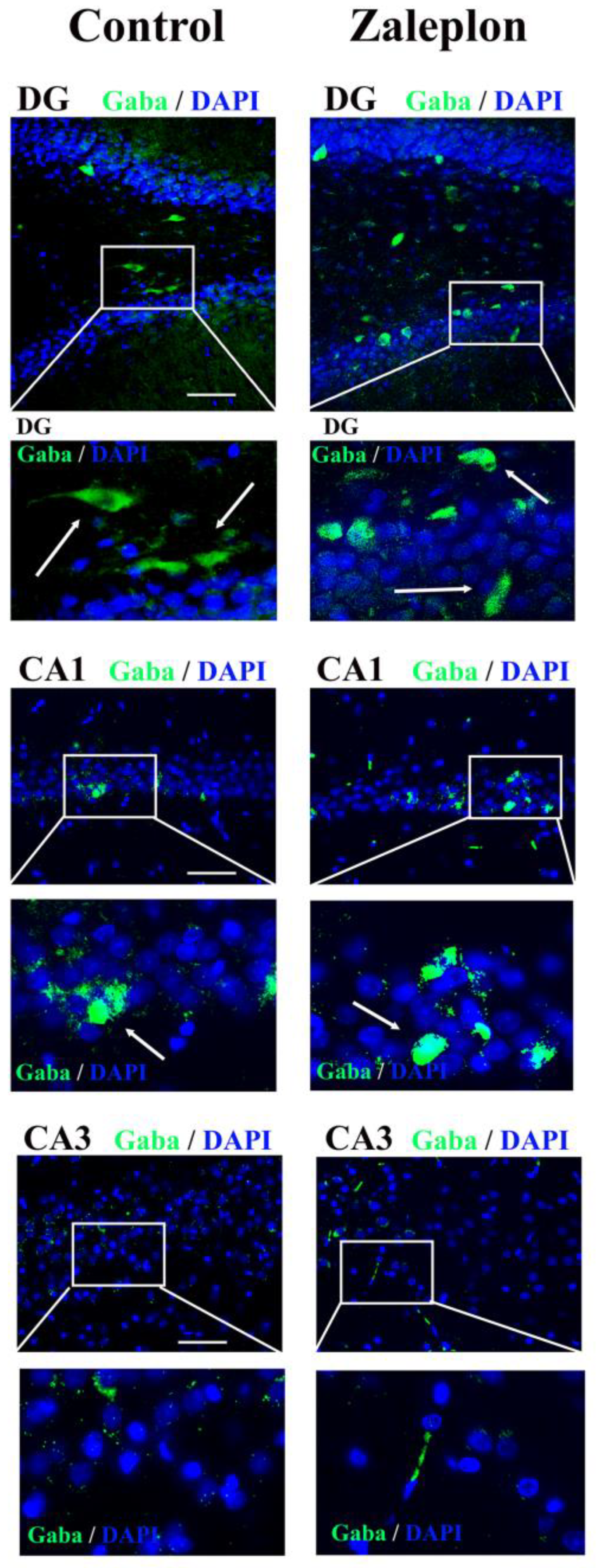
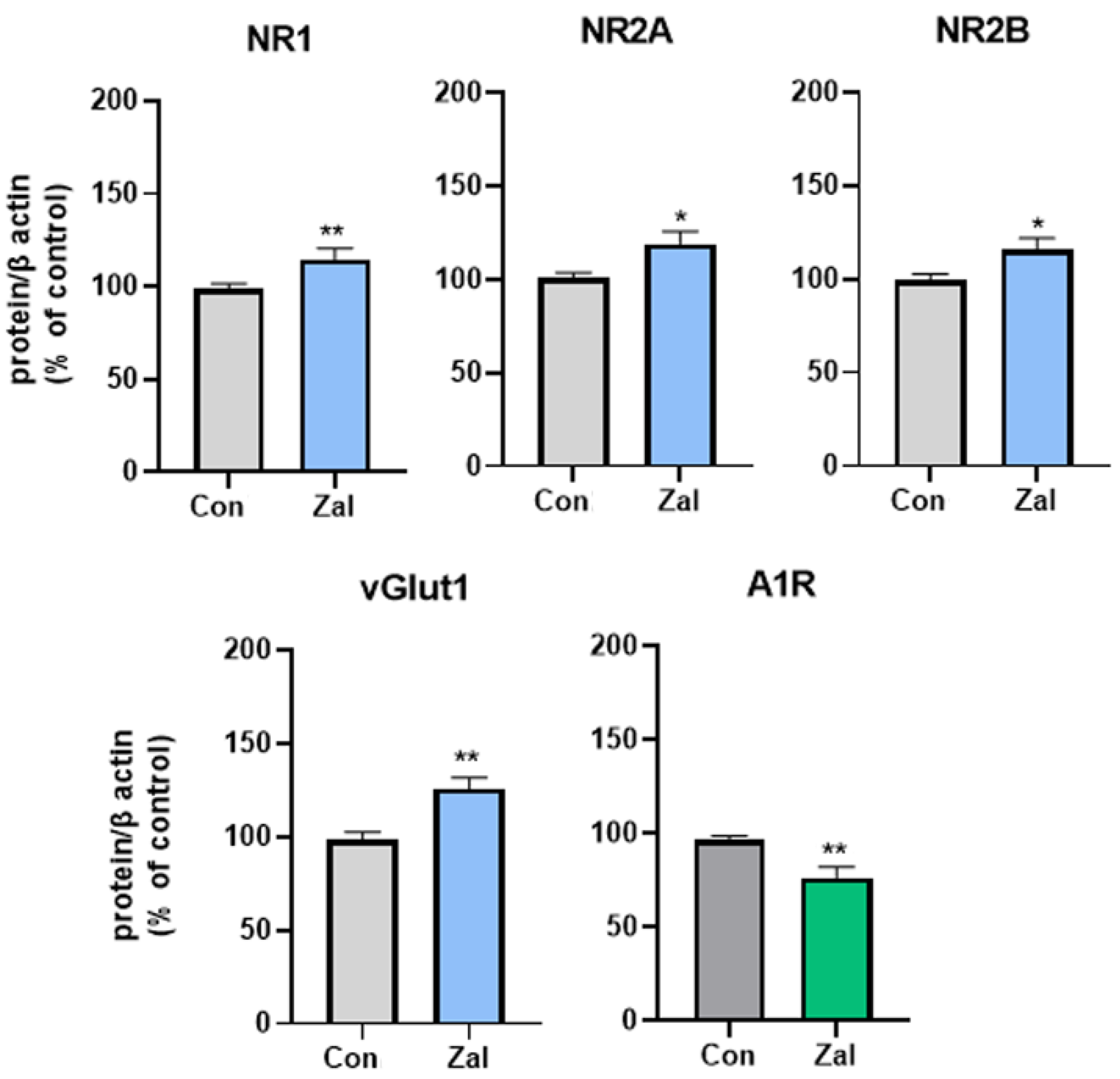
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
6. Authors’ Considerations and Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S.; Corkery, J.M.; Guirguis, A. An Insight into Z-Drug Abuse and Dependence: An Examination of Reports to the European Medicines Agency Database of Suspected Adverse Drug Reactions. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palagini, L.; Bianchini, C. Pharmacotherapeutic management of insomnia and effects on sleep processes, neural plasticity, and brain systems modulating stress: A narrative review. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 893015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghit, A.; Assal, D.; Al-Shami, A.S.; Hussein, D.E.E. GABAA receptors: Structure, function, pharmacology, and related disorders. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, T.; Comai, S.; Gobbi, G. Drugs for Insomnia beyond Benzodiazepines: Pharmacology, Clinical Applications, and Discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 197–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Kitazumi, K.; Mori, M.; Shiba, T. Effect of zaleplon on learning and memory in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2002, 366, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, S.M.; Lucki, I.; Unruh, M.A.; Cevallos, W.H.; Leister, C.A.; Martin, P.T.; Furlan, P.M.; Mangano, R. Comparison of the effects of zaleplon, zolpidem, and triazolam on memory, learning, and psychomotor performance. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2000, 20, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verster, J.C.; Volkerts, E.R.; Schreuder, A.H.C.M.L.; Eijken, E.J.E.; van Heuckelum, J.H.G.; Veldhuijzen, D.S.; Verbaten, M.N.; Paty, I.; Darwish, M.; Danjou, P.; et al. Residual Effects of Middle-of-the-Night Administration of Zaleplon and Zolpidem on Driving Ability, Memory Functions, and Psychomotor Performance. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2002, 22, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Yi, L.; Zhang, W.; Bian, Z.-J.; Zhang, Y.-B. Association between Z Drugs Use and Risk of Cognitive Impairment in Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Chronic Insomnia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 775144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B.; Fuller, P.M. Wake–sleep circuitry: An overview. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 44, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardzic, J.; Jadzic, D.; Hencic, B.; Jancic, J.; Strac, D.S. Introductory Chapter: GABA/Glutamate Balance: A Key for Normal Brain Functioning. In GABA and Glutamate—New Developments in Neurotransmission Research; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/state.item.id (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Xiang, T.; Liao, J.; Cai, Y.; Fan, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Pan, J. Impairment of GABA inhibition in insomnia disorders: Evidence from the peripheral blood system. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1134434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Y.; Chu, S.; Peng, Y.; Chen, N. Research progress on adenosine in central nervous system diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkees, S.A.; Price, S.L.; Zhou, F.C. Immunohistochemical detection of A1 adenosine receptors in rat brain with emphasis on localization in the hippocampal formation, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. Brain Res. 1995, 677, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebola, N.; Pinheiro, P.C.; Oliveira, C.R.; Malva, J.O.; Cunha, R.A. Subcellular localization of adenosine A(1) receptors in nerve terminals and synapses of the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2003, 987, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombo, D.M.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Sebastião, A.M. Hippocampal GABAergic transmission: A new target for adenosine control of excitability. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 1056–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Terunuma, M.; Fellin, T.; Moss, S.J.; Haydon, P.G. Astrocytic activation of A1 receptors regulates the surface expression of NMDA receptors through a src kinase dependent pathway. Glia 2011, 59, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.W.; McIver, S.R.; Hinton, D.J.; Thakkar, M.M.; Sari, Y.; Parkinson, F.E.; Haydon, P.G.; Choi, D.-S. Adenosine and Glutamate Signaling in Neuron-Glial interactions: Implications in Alcoholism and Sleep Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samardzic, J.; Zekovic, J.; Hencic, B.; Vucevic, D.; Jancic, J.; Švob Štrac, D. ACNP 58th Annual Meeting: Poster Session III. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 385–538. [Google Scholar]
- Zaric Kontic, M.; Dragic, M.; Martinovic, J.; Mihajlovic, K.; Brkic, Z.; Mitrovic, N.; Grkovic, I. Prolonged Alprazolam Treatment Alters Components of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats-The Neuroadaptive Changes following Long-Term Benzodiazepine (Mis)Use. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanò, G.; Weber, F.D.; Pizzamiglio, G.; McCormick, C.; Miller, T.D.; Rosenthal, C.R.; Edgin, J.O.; Maguire, E.A. Sleeping with Hippocampal Damage. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 523–529.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avchalumov, Y.; Mandyam, C.D. Plasticity in the Hippocampus, Neurogenesis and Drugs of Abuse. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaric, M.; Drakulic, D.; Stojanovic, I.G.; Mitrovic, N.; Grkovic, I.; Martinovic, J. Regional-specific effects of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion and dehydroepiandrosterone on synaptic NMDAR/PSD-95 complex in male Wistar rats. Brain Res. 2018, 1688, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwell, M.A.; Haas, S.M.; Bieber, L.L.; Tolbert, N.E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 87, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepsomali, P.; Groeger, J.A.; Nishihira, J.; Scholey, A. Effects of Oral Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Administration on Stress and Sleep in Humans: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesmann, C. GABA mechanisms and sleep. Neuroscience 2002, 111, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kang, I.; Edden, R.A.E.; Namgung, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Shorter sleep duration is associated with lower GABA levels in the anterior cingulate cortex. Sleep Med. 2020, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante, D.T.; Jensen, J.E.; Schoerning, L.; Winkelman, J.W. Reduced γ-aminobutyric acid in occipital and anterior cingulate cortices in primary insomnia: A link to major depressive disorder? Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelman, J.W.; Buxton, O.M.; Jensen, J.E.; Benson, K.L.; O’Connor, S.P.; Wang, W.; Renshaw, P.F. Reduced brain GABA in primary insomnia: Preliminary data from 4T proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). Sleep 2008, 31, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.M. Pharmacological modulation of brain levels of glutamate and GABA in rats exposed to total sleep deprivation. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elrasheed, E.; Nageeb El-Helaly, S.; EL-Ashmoony, M.M.; Salah, S. Brain-targeted intranasal zaleplon solid dispersion in hydrophilic carrier system; 23 full-factorial design and in vivo determination of GABA neurotransmitter. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; El-Fayoumi, H.M.; El-Maraghy, N.N.; El-Eraky, W.I.; El-Shenawy, S.M. Toxicological study of Zaleplon (Anxiolytic drug) in experimental animals. Zagazig J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 23, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, Y.; Michels, G.; Armstrong-Gold, C.; Haydon, P.G.; Lindstrom, J.; Pangalos, M.; Moss, S.J. Synaptic GABAA receptors are directly recruited from their extrasynaptic counterparts. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4381–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Smalley, J.L.; Lemons, A.H.S.; Ren, Q.; Bope, C.E.; Dengler, J.S.; Davies, P.A.; Moss, S.J. Analyzing the mechanisms that facilitate the subtype-specific assembly of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1017404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, X.; Qu, S. Glutamate, Glutamate Transporters, and Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders in Neurodegenerative Diseases. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, B.M.; Mitchell, T.R.; Galloway, M.P.; Prevost, K.E.; Fang, J.; Moore, G.J.; Uhde, T.W. Region-specific alteration in brain glutamate: Possible relationship to risk-taking behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 99, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhoff, D.J.; Mon, A.; Metzler, T.; Neylan, T.C. Cortical Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Glutamate in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Their Relationships to Self-Reported Sleep Quality. Sleep 2014, 37, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pan, D.-X.; Wang, D.; Wan, P.; Qiu, D.-L.; Jin, Q.-H. Nitric oxide facilitates active avoidance learning via enhancement of glutamate levels in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 271, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrabi, S.M.; Sharma, N.S.; Karan, A.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; Cordon, B.; Ma, B.; Xie, J. Nitric Oxide: Physiological Functions, Delivery, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2303259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossenza, M.; Socodato, R.; Portugal, C.C.; Domith, I.C.L.; Gladulich, L.F.H.; Encarnação, T.G.; Calaza, K.C.; Mendonça, H.R.; Campello-Costa, P.; Paes-de-Carvalho, R. Chapter Five—Nitric Oxide in the Nervous System: Biochemical, Developmental, and Neurobiological Aspects. In Vitamins & Hormones; Litwack, G., Ed.; Nitric Oxide; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 96, pp. 79–125. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128002544000052 (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Reichert, C.F.; Deboer, T.; Landolt, H.-P. Adenosine, caffeine, and sleep–wake regulation: State of the science and perspectives. J. Sleep Res. 2022, 31, e13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, M.; Oishi, Y.; Bjorness, T.E.; Greene, R.W. Gating and the Need for Sleep: Dissociable Effects of Adenosine A1 and A2A Receptors. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmenhorst, D.; Meyer, P.T.; Winz, O.H.; Matusch, A.; Ermert, J.; Coenen, H.H.; Basheer, R.; Haas, H.L.; Zilles, K.; Bauer, A. Sleep Deprivation Increases A1 Adenosine Receptor Binding in the Human Brain: A Positron Emission Tomography Study. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2410–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmenhorst, D.; Elmenhorst, E.-M.; Hennecke, E.; Kroll, T.; Matusch, A.; Aeschbach, D.; Bauer, A. Recovery sleep after extended wakefulness restores elevated A1 adenosine receptor availability in the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4243–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmenhorst, D.; Basheer, R.; McCarley, R.W.; Bauer, A. Sleep deprivation increases A1 adenosine receptor density in the rat brain. Brain Res. 2009, 1258, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Ye, C.; Ge, W.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, C.; Poo, M.; Duan, S. ATP released by astrocytes mediates glutamatergic activity-dependent heterosynaptic suppression. Neuron 2003, 40, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antigen | Manufacturer/Catalog No. | Species/Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| GABAAR α1 | Sigma Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA, G4416 | rabbit polyclonal, 1:5000 |
| vGlut1 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK, 134283 | mouse monoclonal, 1:4000 |
| NR1 | Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA, # 5704 | rabbit polyclonal, 1:1000 |
| NR2A | Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA, # 07-632 | rabbit polyclonal, 1:1000 |
| NR2B | Abcam, Cambridge, UK, 93610 | mouse monoclonal, 1:4000 |
| GAD67 | Millipore, Burlington, MA, MAB5406 | mouse monoclonal, 1:1000 |
| VGAT | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA, sc-393373 | mouse monoclonal, 1:1000 |
| A1R | Alomone labs, Jerusalem, Israel | rabbit polyclonal, 1:1000 |
| β-actin | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA; PA1-21167 | rabbit polyclonal, 1:5000 |
| mouse IgG | R&D systems, bio-techne, Minneapolis, MN, USA; HAF007 | goat polyclonal, 1:10,000 |
| rabbit IgG | Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA; # 31460 | goat polyclonal, 1:10,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinovic, J.; Samardzic, J.; Zaric Kontic, M.; Ivkovic, S.; Dacic, S.; Major, T.; Radosavljevic, M.; Svob Strac, D. Prolonged Zaleplon Treatment Increases the Expression of Proteins Involved in GABAergic and Glutamatergic Signaling in the Rat Hippocampus. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121707
Martinovic J, Samardzic J, Zaric Kontic M, Ivkovic S, Dacic S, Major T, Radosavljevic M, Svob Strac D. Prolonged Zaleplon Treatment Increases the Expression of Proteins Involved in GABAergic and Glutamatergic Signaling in the Rat Hippocampus. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(12):1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121707
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinovic, Jelena, Janko Samardzic, Marina Zaric Kontic, Sanja Ivkovic, Sanja Dacic, Tamara Major, Milica Radosavljevic, and Dubravka Svob Strac. 2023. "Prolonged Zaleplon Treatment Increases the Expression of Proteins Involved in GABAergic and Glutamatergic Signaling in the Rat Hippocampus" Brain Sciences 13, no. 12: 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121707
APA StyleMartinovic, J., Samardzic, J., Zaric Kontic, M., Ivkovic, S., Dacic, S., Major, T., Radosavljevic, M., & Svob Strac, D. (2023). Prolonged Zaleplon Treatment Increases the Expression of Proteins Involved in GABAergic and Glutamatergic Signaling in the Rat Hippocampus. Brain Sciences, 13(12), 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121707








