Combining Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Knowledge, Relevance and Future Perspectives
Abstract
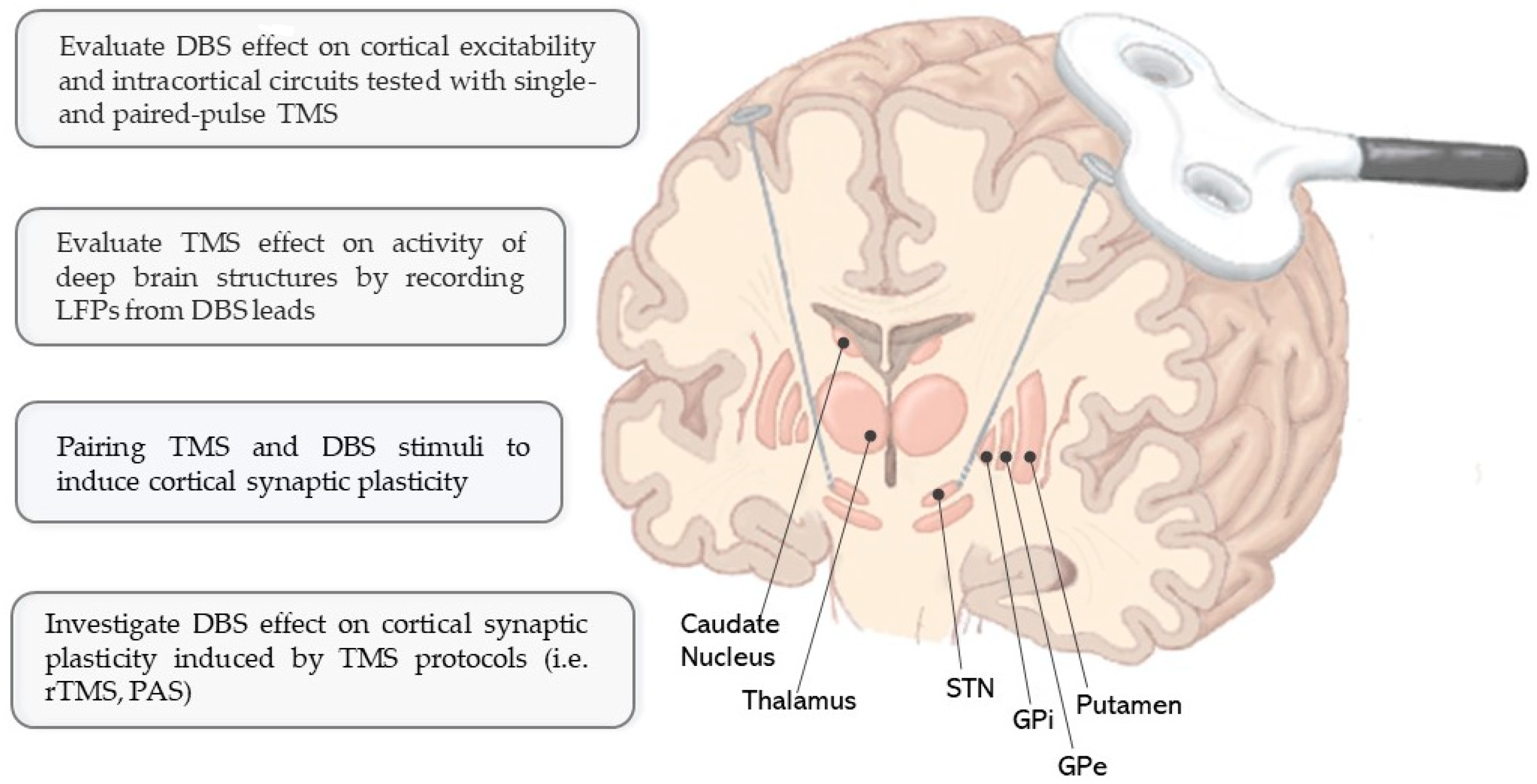
1. Introduction
2. Combined TMS–DBS Application: Current Evidence and Experimental Relevance
2.1. Evaluation of DBS Effects on Cerebral Cortex in Different Neurological Conditions
2.1.1. Parkinson’s Disease
| Reference | Subjects (n °) | DBS Target | Time after DBS | DBS | Medication | TMS Measures (ISI) | Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFF | ON | OFF | ON | ||||||
| Parkinson’s Disease | |||||||||
| Chen et al. 2001 [39] | PD (7) HS (7) | GPi (5 unil *, 2 bil) | 1–5 y– | + | + | usual med ° | MT, SP, I/O curve SICI (2 ms), ICF (10 ms), LICI (50/100/150/200 ms) | - No change in MT, I/O curve, SICI, ICF, and LICI - SP lengthening in DBS-OFF with respect to DBS-ON and HS | |
| Cunic et al. 2002 [40] | PD (9) HS (8) | STN (7 bil, 2 unil *) | 1 mo–2.7 y | + | + | + | MT, SP, I/O curve, SICI (2 ms), ICF (10 ms), LICI (50/200 ms) | - No change in MT, SP, I/O curve, LICI, and ICF - Increased SICI inhibition during DBS-ON | |
| Däuperet al. 2002 [41] | PD (8) HS (10) | STN (bil) | >3 mo | + | + | + | + | RMT, SP, MEP latency, ICI (3 ms), ICF (13 ms) | - No change in RMT, ICF, and MEP latency - Longer SP and increased ICI in DBS-ON/MED-ON with respect to DBS-OFF/MED-OFF |
| Sailer et al. 2007 [42] | PD(7) HS(7) | STN (bil) | ≈6 mo–4 y | + | + | + | + | SAI (23 ms), LAI (200 ms) | - No change in MT - SAI reduced in MED-ON/STIM OFF and increased in DBS-ON/MED-ON. - LAI increased in STIM-ON/MED-ON, reduced in STIM-OFF/MED-ON and in MED-OFF (in both DBS conditions). |
| Hidding et al. 2006 [43] | PD (8) | STN (bil) | Before, 2–3 w after surgery | + | + | + | RMT, I/O curve, MEP latency, maximal M response | - No changes in RMT, I/O curve after surgery - Shortened MEP latencies at rest, but unchanged during muscle activation after surgery | |
| Baümer et al. 2009 [44] | PD (10) | STN (bil) | Before, 4 d after surgery | + | + | + | RMT, SP | - No change in SP and RMT | |
| Kim et al. 2015 [49] | PD (8) HS (9) | STN (bil) | ≈9 mo–9 y | + | + | + | + | MT, SP PAS (21.5 ms) | - No change in MT and SP - MEP size increase in DBS-ON condition - Increased PAS response in PD only in DBS-ON/MED-ON condition. |
| Casula et al. 2016 [50] | PD (6) HS (8) | STN (bil) | 3–10 y | + | + | + | + | RMT, TMS-evoked potentials, TMS-evoked spectral perturbation | -No change in RMT - Modulation of early TMS-evoked activity by DBS stimulation - Additional modulation of later TMS-evoked components induced by DBS stimulation and L-Dopa |
| Dystonia | |||||||||
| Kühn et al. 2003 [51] | DYST(9) HS(20) | GPi (8 bil, 1 unil, 4 with VIM) | 3–11 mo | + | + | Medicated and non-medicated | RMT, SP, ICI (1–7 ms), ICF (10/15 ms), SRC | - No change in ICI and ICF - Higher MT in DBS OFF with respect to DBS-ON - Higher SRC with DBS-ON | |
| Tisch et al. 2007 [52] | DYST(10) HS(10) | GPi (bil) | >6 mo | + | + | Medicated and non-medicated | MT, SRC PAS (25 ms) | - No change in MT - Reduced PAS response in DBS ON | |
| Ruge et al. 2011 [53] | DYT1 DYST(10) HS(10) | GPi (bil) | 4.5–11.5 y | + | + | Not clearly reported ° | MT, I/O curve, SICI (2/3 ms) | - No change in MT, I/O, and SICI - No change in PAS response with DBS - Reduced PAS response in DYST patients | |
| Ruge et al. 2011 [54] | Primary DYST(8) | GPi (bil) | Before and 1–3–6 mo after surgery | + | Not clearly reported ° | MT, I/O curve, SICI (2/3 ms) PAS (25 ms) | - No change in MT and I/O curve -SICI reduced before surgery, then progressively increased after surgery - Increased PAS response before surgery, absent after 1 mo, then increased at 3 and 6 mo | ||
| Wagle Shukla et al. 2018 [55] | Cervical DYST(10) HS(10) | STN (bil) | 1–6 y | + | + | Medicated and non-medicated | RMT, SICI 2/3 ms, ICF 10/15 ms, SAI 20/30 ms, LAI 150/200 ms PAS (25 ms) | - No change in RMT, SICI and ICF, LAI 150 ms - In DBS-ON increased SAI, LAI 200 ms and reduced PAS response with respect to DBS-OFF | |
| Essential tremor | |||||||||
| Molnar et al. 2005 [56] | ET(7) HS(11) | VIM (unil) | 3.1–7.5 y | + | + | Non-medicated | MT, SP, I/O curve, SICI (2 ms), ICF (10 ms), LICI (50/100/150/200 ms) | - No change in MT, SP, SICI, ICF, and LICI - Increased MEP amplitude during DBS-ON for TMS intensities >130% RMT (I/O curve) | |
| Molnar et al. 2004 [57] | ET(6) HS(9) | VIM (unil) | 1.2–7.5 y | + | + | Non-medicated | Paired cerebellar and M1 TMS stimulation (from 3 to 7 ms) | - No change in MEP amplitude with DBS - With paired stimulation reduced MEP amplitudes in DBS-ON at ISIs of 6–7 ms. | |
| Epilepsy | |||||||||
| Molnar et al. 2006 [58] | Epilepsy(5) HS(9) | ANT (bil) | Not clearly reported | + | + | AED | MT, SP, I/O curve, SICI (2 ms), ICF (10 ms), LICI (50/100/150/200 ms) | - No change in MT, SP, I/O curve, ICF, and LICI - Reduced SICI with DBS-ON (similar to HS) | |
2.1.2. Dystonia
2.1.3. Essential Tremor
2.1.4. Epilepsy
2.1.5. Overview
2.2. Modulation of Cortical Synaptic Plasticity
2.2.1. Induction of Cortical Plasticity with TMS in Patients with DBS
2.2.2. Pairing of TMS and DBS Stimuli to Induce Cortical Synaptic Plasticity
2.3. Evaluation of TMS-Induced Changes in Deep Brain Structures
3. Safety Issues
4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossini, P.M.; Barker, A.T.; Berardelli, A.; Caramia, M.D.; Caruso, G.; Cracco, R.Q.; Dimitrijević, M.R.; Hallett, M.; Katayama, Y.; Lücking, C.H.; et al. Non-Invasive Electrical and Magnetic Stimulation of the Brain, Spinal Cord and Roots: Basic Principles and Procedures for Routine Clinical Application. Report of an IFCN Committee. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1994, 91, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Burke, D.; Chen, R.; Cohen, L.G.; Daskalakis, Z.; Di Iorio, R.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Ferreri, F.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; George, M.S.; et al. Non-Invasive Electrical and Magnetic Stimulation of the Brain, Spinal Cord, Roots and Peripheral Nerves: Basic Principles and Procedures for Routine Clinical and Research Application. An Updated Report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1071–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and the Human Brain. Nature 2000, 406, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: A Primer. Neuron 2007, 55, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberra, A.S.; Wang, B.; Grill, W.M.; Peterchev, A.V. Simulation of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Head Model with Morphologically-Realistic Cortical Neurons. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardelli, A.; Abbruzzese, G.; Chen, R.; Orth, M.; Ridding, M.C.; Stinear, C.; Suppa, A.; Trompetto, C.; Thompson, P.D. Consensus Paper on Short-Interval Intracortical Inhibition and Other Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Intracortical Paradigms in Movement Disorders. Brain Stimul. 2008, 1, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokimura, H.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Tokimura, Y.; Oliviero, A.; Profice, P.; Insola, A.; Mazzone, P.; Tonali, P.; Rothwell, J.C. Short Latency Inhibition of Human Hand Motor Cortex by Somatosensory Input from the Hand. J. Physiol. 2000, 523, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, F.; Ponzo, D.; Hukkanen, T.; Mervaala, E.; Könönen, M.; Pasqualetti, P.; Vecchio, F.; Rossini, P.M.; Määttä, S. Human Brain Cortical Correlates of Short-Latency Afferent Inhibition: A Combined EEG–TMS Study. J. Neurophysiol. 2012, 108, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, C.V.; El-Sayes, J.; Savoie, M.J.; Fassett, H.J.; Locke, M.B.; Nelson, A.J. Short- and Long-Latency Afferent Inhibition; Uses, Mechanisms and Influencing Factors. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Z.; Edwards, M.J.; Rounis, E.; Bhatia, K.P.; Rothwell, J.C. Theta Burst Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex. Neuron 2005, 45, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A. Safety of TMS Consensus Group Safety, Ethical Considerations, and Application Guidelines for the Use of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Clinical Practice and Research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 2008–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestmann, S.; Baudewig, J.; Siebner, H.R.; Rothwell, J.C.; Frahm, J. Functional MRI of the Immediate Impact of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Cortical and Subcortical Motor Circuits. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1950–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, F.; Rossini, P.M. TMS and TMS-EEG Techniques in the Study of the Excitability, Connectivity, and Plasticity of the Human Motor Cortex. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 24, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, T.O.; Varatheeswaran, R.; Hanlon, C.A.; Madsen, K.H.; Thielscher, A.; Siebner, H.R. Concurrent TMS-FMRI for Causal Network Perturbation and Proof of Target Engagement. NeuroImage 2021, 237, 118093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Di Iorio, R.; Bentivoglio, M.; Bertini, G.; Ferreri, F.; Gerloff, C.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Miraglia, F.; Nitsche, M.A.; Pestilli, F.; et al. Methods for Analysis of Brain Connectivity: An IFCN-Sponsored Review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1833–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krack, P.; Volkmann, J.; Tinkhauser, G.; Deuschl, G. Deep Brain Stimulation in Movement Disorders: From Experimental Surgery to Evidence-Based Therapy. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1795–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetkas, A.; Fomenko, A.; Germann, J.; Sarica, C.; Iorio-Morin, C.; Samuel, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Milano, V.; Cheyuo, C.; Zemmar, A.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation Targets in Epilepsy: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Anterior and Centromedian Thalamic Nuclei and Hippocampus. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangiabadi, N.; Ladino, L.D.; Sina, F.; Orozco-Hernández, J.P.; Carter, A.; Téllez-Zenteno, J.F. Deep Brain Stimulation and Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Review of the Literature. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N.; Bergman, H.; Brown, P.; Chabardes, S.; Chang, J.W.; Matthews, K.; McIntyre, C.C.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Schulder, M.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Challenges and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Williams, D. Basal Ganglia Local Field Potential Activity: Character and Functional Significance in the Human. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Schroeder, C.E. How Local Is the Local Field Potential? Neuron 2011, 72, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.A.; Wang, J.; Nebeck, S.D.; Zhang, J.; Johnson, M.D.; Vitek, J.L. Direct Activation of Primary Motor Cortex during Subthalamic But Not Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 2166–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ke, Y.; Chan, D.C.W.; Qian, Z.-M.; Yung, K.K.L.; Ko, H.; Arbuthnott, G.W.; Yung, W.-H. Therapeutic Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinsonian Rats Directly Influences Motor Cortex. Neuron 2012, 76, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, A.; Gwun, D.; Chow, C.T.; Boutet, A.; Tasserie, J.; Germann, J.; Santyr, B.; Elias, G.; Yamamoto, K.; Sarica, C.; et al. Probing Responses to Deep Brain Stimulation with Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenger, V.M.; Kahan, J.; Foltynie, T.; Friston, K.; Aziz, T.Z.; Green, A.L.; van Hartevelt, T.J.; Cabral, J.; Stevner, A.B.A.; Fernandes, H.M.; et al. Uncovering the Underlying Mechanisms and Whole-Brain Dynamics of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.; Udupa, K.; Hallett, M.; Chen, R. Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation on the Primary Motor Cortex: Insights from Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Studies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Kim, S.J.; Phielipp, N.; Ghosh, S.; Udupa, K.; Gunraj, C.A.; Saha, U.; Hodaie, M.; Kalia, S.K.; Lozano, A.M.; et al. Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation Modulates Cortical Excitability and Plasticity: Pallidal DBS. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Chen, R. Exploring the Connections between Basal Ganglia and Cortex Revealed by Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Evoked Potential and Deep Brain Stimulation in Dystonia. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2022, 36, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Antal, A.; Bestmann, S.; Bikson, M.; Brewer, C.; Brockmöller, J.; Carpenter, L.L.; Cincotta, M.; Chen, R.; Daskalakis, J.D.; et al. Safety and Recommendations for TMS Use in Healthy Subjects and Patient Populations, with Updates on Training, Ethical and Regulatory Issues: Expert Guidelines. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 269–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N. Probing and Regulating Dysfunctional Circuits Using Deep Brain Stimulation. Neuron 2013, 77, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, K.; Chen, R. The Mechanisms of Action of Deep Brain Stimulation and Ideas for the Future Development. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 133, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limousin, P.; Foltynie, T. Long-Term Outcomes of Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridding, M.C.; Rothwell, J.C.; Inzelberg, R. Changes in Excitability of Motor Cortical Circuitry in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 37, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, A.; Suppa, A.; D’Onofrio, V.; Di Stasio, F.; Asci, F.; Fabbrini, G.; Berardelli, A. Abnormal Cortical Facilitation and L-Dopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, C.F.; Parr-Brownlie, L.C. Primary Motor Cortex in Parkinson’s Disease: Functional Changes and Opportunities for Neurostimulation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 147, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, M.; Paparella, G.; Fasano, A.; Hallett, M.; Berardelli, A. Evolving Concepts on Bradykinesia. Brain 2020, 143, 727–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bologna, M.; Guerra, A.; Paparella, G.; Giordo, L.; Alunni Fegatelli, D.; Vestri, A.R.; Rothwell, J.C.; Berardelli, A. Neurophysiological Correlates of Bradykinesia in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2018, 141, 2432–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, K.; Chen, R. Motor Cortical Circuits in Parkinson Disease and Dystonia. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 161, pp. 167–186. ISBN 978-0-444-64142-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Garg, R.R.; Lozano, A.M.; Lang, A.E. Effects of Internal Globus Pallidus Stimulation on Motor Cortex Excitability. Neurology 2001, 56, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunic, D.; Roshan, L.; Khan, F.I.; Lozano, A.M.; Lang, A.E.; Chen, R. Effects of Subthalamic Nucleus Stimulation on Motor Cortex Excitability in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurology 2002, 58, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauper, J.; Peschel, T.; Schrader, C.; Kohlmetz, C.; Joppich, G.; Nager, W.; Dengler, R.; Rollnik, J.D. Effects of Subthalamic Nucleus (STN) Stimulation on Motor Cortex Excitability. Neurology 2002, 59, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailer, A.; Cunic, D.I.; Paradiso, G.O.; Gunraj, C.A.; Wagle-Shukla, A.; Moro, E.; Lozano, A.M.; Lang, A.E.; Chen, R. Subthalamic Nucleus Stimulation Modulates Afferent Inhibition in Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2007, 68, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidding, U.; Bäumer, T.; Siebner, H.R.; Demiralay, C.; Buhmann, C.; Weyh, T.; Moll, C.; Hamel, W.; Münchau, A. MEP Latency Shift after Implantation of Deep Brain Stimulation Systems in the Subthalamic Nucleus in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumer, T.; Hidding, U.; Hamel, W.; Buhmann, C.; Moll, C.K.E.; Gerloff, C.; Orth, M.; Siebner, H.R.; Münchau, A. Effects of DBS, Premotor RTMS, and Levodopa on Motor Function and Silent Period in Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantello, R.; Gianelli, M.; Civardi, C.; Mutani, R. Magnetic Brain Stimulation: The Silent Period after the Motor Evoked Potential. Neurology 1992, 42, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeugin, D.; Ionta, S. Anatomo-Functional Origins of the Cortical Silent Period: Spotlight on the Basal Ganglia. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantello, R.; Tarletti, R.; Varrasi, C.; Cecchin, M.; Monaco, F. Cortical Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease: New Insights from Early, Untreated Patients. Neuroscience 2007, 150, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojovic, M.; Bologna, M.; Kassavetis, P.; Murase, N.; Palomar, F.J.; Berardelli, A.; Rothwell, J.C.; Edwards, M.J.; Bhatia, K.P. Functional Reorganization of Sensorimotor Cortex in Early Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2012, 78, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Udupa, K.; Ni, Z.; Moro, E.; Gunraj, C.; Mazzella, F.; Lozano, A.M.; Hodaie, M.; Lang, A.E.; Chen, R. Effects of Subthalamic Nucleus Stimulation on Motor Cortex Plasticity in Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, E.P.; Stampanoni Bassi, M.; Pellicciari, M.C.; Ponzo, V.; Veniero, D.; Peppe, A.; Brusa, L.; Stanzione, P.; Caltagirone, C.; Stefani, A.; et al. Subthalamic Stimulation and Levodopa Modulate Cortical Reactivity in Parkinson’s Patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 34, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, A.A.; Meyer, B.-U.; Trottenberg, T.; Brandt, S.A.; Schneider, G.H.; Kupsch, A. Modulation of Motor Cortex Excitability by Pallidal Stimulation in Patients with Severe Dystonia. Neurology 2003, 60, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisch, S.; Rothwell, J.C.; Bhatia, K.P.; Quinn, N.; Zrinzo, L.; Jahanshahi, M.; Ashkan, K.; Hariz, M.; Limousin, P. Pallidal Stimulation Modifies After-Effects of Paired Associative Stimulation on Motor Cortex Excitability in Primary Generalised Dystonia. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 206, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruge, D.; Cif, L.; Limousin, P.; Gonzalez, V.; Vasques, X.; Hariz, M.I.; Coubes, P.; Rothwell, J.C. Shaping Reversibility? Long-Term Deep Brain Stimulation in Dystonia: The Relationship between Effects on Electrophysiology and Clinical Symptoms. Brain 2011, 134, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruge, D.; Tisch, S.; Hariz, M.I.; Zrinzo, L.; Bhatia, K.P.; Quinn, N.P.; Jahanshahi, M.; Limousin, P.; Rothwell, J.C. Deep Brain Stimulation Effects in Dystonia: Time Course of Electrophysiological Changes in Early Treatment. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle Shukla, A.; Ostrem, J.L.; Vaillancourt, D.E.; Chen, R.; Foote, K.D.; Okun, M.S. Physiological Effects of Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery in Cervical Dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, G.F.; Sailer, A.; Gunraj, C.A.; Cunic, D.I.; Lang, A.E.; Lozano, A.M.; Moro, E.; Chen, R. Changes in Cortical Excitability with Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation. Neurology 2005, 64, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, G.F.; Sailer, A.; Gunraj, C.A.; Lang, A.E.; Lozano, A.M.; Chen, R. Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation Activates the Cerebellothalamocortical Pathway. Neurology 2004, 63, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, G.F.; Sailer, A.; Gunraj, C.A.; Cunic, D.I.; Wennberg, R.A.; Lozano, A.M.; Chen, R. Changes in Motor Cortex Excitability with Stimulation of Anterior Thalamus in Epilepsy. Neurology 2006, 66, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujirai, T.; Caramia, M.D.; Rothwell, J.C.; Day, B.L.; Thompson, P.D.; Ferbert, A.; Wroe, S.; Asselman, P.; Marsden, C.D. Corticocortical Inhibition in Human Motor Cortex. J. Physiol. 1993, 471, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U. TMS and Drugs. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, C.D.; Gilley, E.A.; Weis-McNulty, A.; Simuni, T. Pathways Mediating Abnormal Intracortical Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraix, V.; Pollak, P.; Vercueil, L.; Benabid, A.-L.; Mauguière, F. Effects of Subthalamic Nucleus Stimulation on Motor Cortex Excitability in Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriakose, R.; Saha, U.; Castillo, G.; Udupa, K.; Ni, Z.; Gunraj, C.; Mazzella, F.; Hamani, C.; Lang, A.E.; Moro, E.; et al. The Nature and Time Course of Cortical Activation Following Subthalamic Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisch, S.; Limousin, P. Neurophysiological Insights in Dystonia and Its Response to Deep Brain Stimulation Treatment. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridding, M.C.; Sheean, G.; Rothwell, J.C.; Inzelberg, R.; Kujirai, T. Changes in the Balance between Motor Cortical Excitation and Inhibition in Focal, Task Specific Dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 59, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rona, S.; Berardelli, A.; Vacca, L.; Inghilleri, M.; Manfredi, M. Alterations of Motor Cortical Inhibition in Patients with Dystonia. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilio, F. Abnormalities of Motor Cortex Excitability Preceding Movement in Patients with Dystonia. Brain 2003, 126, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, A.; Joseph, T.; Velayudhan, B.; Popa, T.; Meunier, S. Early, Severe and Bilateral Loss of LTP and LTD-like Plasticity in Motor Cortex (M1) in de Novo Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, K.; Chen, R. Motor Cortical Plasticity in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.A.; Sejnowski, T.J.; Poizner, H. Convergent Evidence for Abnormal Striatal Synaptic Plasticity in Dystonia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgante, F.; Espay, A.J.; Gunraj, C.; Lang, A.E.; Chen, R. Motor Cortex Plasticity in Parkinson’s Disease and Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias. Brain 2006, 129, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppa, A.; Asci, F.; Guerra, A. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation as a Tool to Induce and Explore Plasticity in Humans. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 184, pp. 73–89. ISBN 978-0-12-819410-2. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-Z.; Lu, M.-K.; Antal, A.; Classen, J.; Nitsche, M.; Ziemann, U.; Ridding, M.; Hamada, M.; Ugawa, Y.; Jaberzadeh, S.; et al. Plasticity Induced by Non-Invasive Transcranial Brain Stimulation: A Position Paper. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, K. Induction of Plasticity in the Human Motor Cortex by Paired Associative Stimulation. Brain 2000, 123, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Collingridge, G.L. A Synaptic Model of Memory: Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Classen, J.; Wolters, A.; Stefan, K.; Wycislo, M.; Sandbrink, F.; Schmidt, A.; Kunesch, E. Chapter 59 Paired Associative Stimulation. In Supplements to Clinical Neurophysiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 57, pp. 563–569. ISBN 978-0-444-51439-4. [Google Scholar]
- van Hartevelt, T.J.; Cabral, J.; Deco, G.; Møller, A.; Green, A.L.; Aziz, T.Z.; Kringelbach, M.L. Neural Plasticity in Human Brain Connectivity: The Effects of Long Term Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus in Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kricheldorff, J.; Göke, K.; Kiebs, M.; Kasten, F.H.; Herrmann, C.S.; Witt, K.; Hurlemann, R. Evidence of Neuroplastic Changes after Transcranial Magnetic, Electric, and Deep Brain Stimulation. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneberg, D.; Plettig, P.; Schneider, G.-H.; Kühn, A.A. Motor Cortical Plasticity Relates to Symptom Severity and Clinical Benefit From Deep Brain Stimulation in Cervical Dystonia. Neuromodul. Technol. Neural Interface 2018, 21, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, J.-P.; Desbeaumes Jodoin, V.; Fournier-Gosselin, M.-P.; Lespérance, P. Safety of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in an Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Patient With Deep Brain Stimulation: A Case Report. J. ECT 2019, 35, e7–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, N.; Dan, Y. Spike Timing–Dependent Plasticity: A Hebbian Learning Rule. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradinaru, V.; Mogri, M.; Thompson, K.R.; Henderson, J.M.; Deisseroth, K. Optical Deconstruction of Parkinsonian Neural Circuitry. Science 2009, 324, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Arbuthnott, G.W.; Jutras, M.J.; Goldberg, J.A.; Jaeger, D. Resonant Antidromic Cortical Circuit Activation as a Consequence of High-Frequency Subthalamic Deep-Brain Stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 98, 3525–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, P.; Paradiso, G.; Saint-Cyr, J.A.; Chen, R.; Lang, A.E.; Lozano, A.M. Potentials Recorded at the Scalp by Stimulation near the Human Subthalamic Nucleus. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, H.C.; Huang, H.; Gonzalez, C.L.; Bryant, J.E.; Killen, J.; Cutter, G.R.; Knowlton, R.C.; Montgomery, E.B.; Guthrie, B.L.; Watts, R.L. Short Latency Activation of Cortex during Clinically Effective Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, K.; Bahl, N.; Ni, Z.; Gunraj, C.; Mazzella, F.; Moro, E.; Hodaie, M.; Lozano, A.M.; Lang, A.E.; Chen, R. Cortical Plasticity Induction by Pairing Subthalamic Nucleus Deep-Brain Stimulation and Primary Motor Cortical Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, F.; Pasqualetti, P.; Määttä, S.; Ponzo, D.; Ferrarelli, F.; Tononi, G.; Mervaala, E.; Miniussi, C.; Rossini, P.M. Human Brain Connectivity during Single and Paired Pulse Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, T.O.; Karabanov, A.; Hartwigsen, G.; Thielscher, A.; Siebner, H.R. Combining Non-Invasive Transcranial Brain Stimulation with Neuroimaging and Electrophysiology: Current Approaches and Future Perspectives. NeuroImage 2016, 140, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebner, H.R.; Funke, K.; Aberra, A.S.; Antal, A.; Bestmann, S.; Chen, R.; Classen, J.; Davare, M.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Fox, P.T.; et al. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Brain: What Is Stimulated?—A Consensus and Critical Position Paper. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 140, 59–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magsood, H.; Syeda, F.; Holloway, K.; Carmona, I.C.; Hadimani, R.L. Safety Study of Combination Treatment: Deep Brain Stimulation and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojima, Y.; Morita, H.; Nishikawa, N.; Kodaira, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Ikeda, S. The Safety of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation with Deep Brain Stimulation Instruments. Park. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.-D.; Lisanby, S.H.; Peterchev, A.V. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in the Presence of Deep Brain Stimulation Implants: Induced Electrode Currents. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 6821–6824. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Chen, R.; Ashby, P. Safety of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Patients with Implanted Deep Brain Stimulators. Mov. Disord. 1999, 14, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phielipp, N.M.; Saha, U.; Sankar, T.; Yugeta, A.; Chen, R. Safety of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Patients with Implanted Cortical Electrodes. An Ex-Vivo Study and Report of a Case. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, E.M. Longlasting Antalgic Effects of Daily Sessions of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Central and Peripheral Neuropathic Pain. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, N.S.; Carpenter, S.L.; Carpenter, L.L. Safe Use of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Patients with Implanted Vagus Nerve Stimulators. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauss, J.K.; Lipsman, N.; Aziz, T.; Boutet, A.; Brown, P.; Chang, J.W.; Davidson, B.; Grill, W.M.; Hariz, M.I.; Horn, A.; et al. Technology of Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Status and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, L.K.; Lofredi, R.; Neumann, W.-J.; Al-Fatly, B.; Roediger, J.; Bahners, B.H.; Nikolov, P.; Denison, T.; Saryyeva, A.; Krauss, J.K.; et al. Toward Therapeutic Electrophysiology: Beta-Band Suppression as a Biomarker in Chronic Local Field Potential Recordings. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, I.E.; Elias, G.J.B.; Beyn, M.E.; Boutet, A.; Pancholi, A.; Germann, J.; Mansouri, A.; Lozano, C.S.; Lozano, A.M. Clinical Trials for Deep Brain Stimulation: Current State of Affairs. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehmeyer, L.; Schüller, T.; Kiess, J.; Heiden, P.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Baldermann, J.C.; Andrade, P. Target-Specific Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 769275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobisz, D.; Damborská, A. Deep Brain Stimulation Targets for Treating Depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tian, X.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Shu, B.; Hou, W. Deep Brain Stimulation for Alzheimer’s Disease: Stimulation Parameters and Potential Mechanisms of Action. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 619543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, J.; Carr, H.; Kelley, N.; Seneviratne, R.; Reed, C.; Parlatini, V.; Garner, M.; Solmi, M.; Rosson, S.; Cortese, S.; et al. Efficacy of Neurostimulation across Mental Disorders: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 208 Randomized Controlled Trials. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Schüler, A.; Hegner, Y.L.; Friedel, E.; Godde, B. Facilitating Effect of 15-Hz Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Tactile Perceptual Learning. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2006, 18, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, E.M.; Abo El-Fetoh, N.; Ali, A.M.; El-Hammady, D.H.; Khalifa, H.; Atta, H.; Karim, A.A. Dual-Hemisphere Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Rehabilitation of Poststroke Aphasia: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mar-Barrutia, L.; Ibarrondo, O.; Mar, J.; Real, E.; Segalàs, C.; Bertolín, S.; Aparicio, M.A.; Plans, G.; Menchón, J.M.; Alonso, P. Long-Term Comparative Effectiveness of Deep Brain Stimulation in Severe Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Andrade, P.; Mosley, P.E.; Greenberg, B.D.; Schuurman, R.; McLaughlin, N.C.; Voon, V.; Krack, P.; Foote, K.D.; Mayberg, H.S.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder: A Crisis of Access. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Onofrio, V.; Manzo, N.; Guerra, A.; Landi, A.; Baro, V.; Määttä, S.; Weis, L.; Porcaro, C.; Corbetta, M.; Antonini, A.; et al. Combining Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Knowledge, Relevance and Future Perspectives. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020349
D’Onofrio V, Manzo N, Guerra A, Landi A, Baro V, Määttä S, Weis L, Porcaro C, Corbetta M, Antonini A, et al. Combining Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Knowledge, Relevance and Future Perspectives. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(2):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020349
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Onofrio, Valentina, Nicoletta Manzo, Andrea Guerra, Andrea Landi, Valentina Baro, Sara Määttä, Luca Weis, Camillo Porcaro, Maurizio Corbetta, Angelo Antonini, and et al. 2023. "Combining Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Knowledge, Relevance and Future Perspectives" Brain Sciences 13, no. 2: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020349
APA StyleD’Onofrio, V., Manzo, N., Guerra, A., Landi, A., Baro, V., Määttä, S., Weis, L., Porcaro, C., Corbetta, M., Antonini, A., & Ferreri, F. (2023). Combining Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Knowledge, Relevance and Future Perspectives. Brain Sciences, 13(2), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020349









