The Effect of Situational Experiment Conditions on Hasty Decision Making in the ‘Beads Task’
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aims
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Ethics
2.2. Materials: The Beads Task(s)
2.2.1. Abstract ‘Draws to Decision’ Variant
2.2.2. Cover-Story Combined Variant
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Analysis
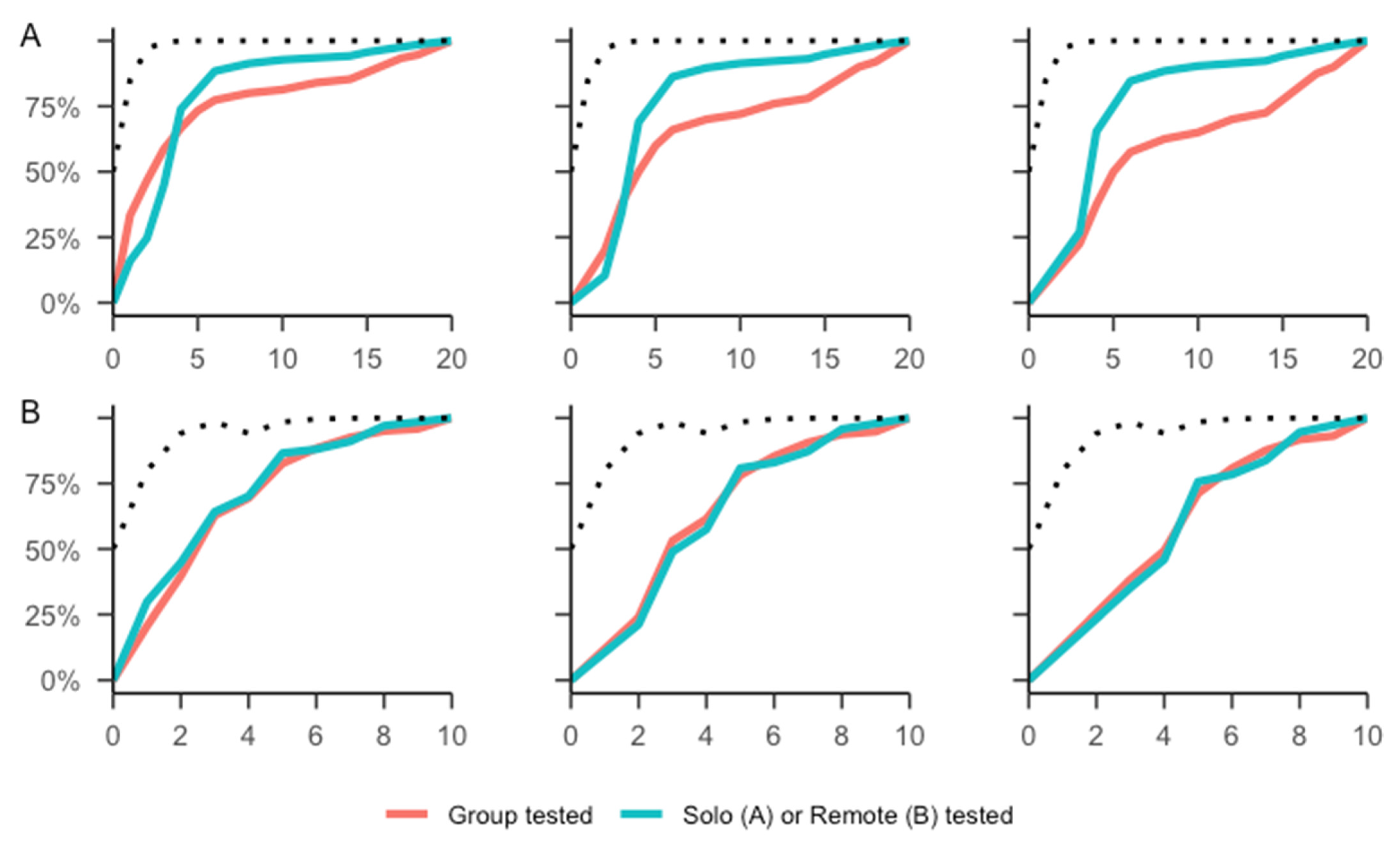
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashinoff, B.K.; Singletary, N.M.; Baker, S.C.; Horga, G. Rethinking delusions: A selective review of delusion research through a computational lens. Schizophr. Res. 2021, 245, S0920996421000657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, R.E.J.; John, C.H.; Young, A.W.; Over, D.E. Normal and abnormal reasoning in people with delusions. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 1997, 36, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garety, P.A.; Freeman, D. Cognitive approaches to delusions: A critical review of theories and evidence. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 1999, 38, 113–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garety, P.A.; Hemsley, D.R.; Wessely, S. Reasoning in Deluded Schizophrenic and Paranoid Patients: Biases in Performance on a Probabilistic Inference Task. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1991, 179, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, S.F.; Garety, P.A.; Hemsley, D.R. Probabilistic Judgements in Deluded and Non-Deluded Subjects. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. Sect. A 1988, 40, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, L.D.; Edwards, W. Conservatism in a simple probability inference task. J. Exp. Psychol. 1966, 72, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, R.; Taylor, P.; Wickham, S.; Hutton, P. Psychosis, Delusions and the “Jumping to Conclusions” Reasoning Bias: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 42, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, C.; Gardner, M.; Craigie, J.; Gold, I. Hopping, skipping or jumping to conclusions? Clarifying the role of the JTC bias in delusions. Cogn. Neuropsychiatry 2007, 12, 46–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, B.F.; Mattiske, J.K.; Balzan, R.P. Association of the Jumping to Conclusions and Evidence Integration Biases with Delusions in Psychosis: A Detailed Meta-analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 43, sbw056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.M.; McKay, R.; Coltheart, M.; Langdon, R. Jumping to Conclusions About the Beads Task? A Meta-analysis of Delusional Ideation and Data-Gathering. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, S.H.; Siu, N.Y.; Wong, H.; Chan, W.; Garety, P.A. “Jumping to conclusions” data-gathering bias in psychosis and other psychiatric disorders—Two meta-analyses of comparisons between patients and healthy individuals. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 46, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, O.; Doyen, S.; Leys, C.; Magalhães de Saldanha da Gama, P.A.; Miller, S.; Questienne, L.; Cleeremans, A. Low Hopes, High Expectations: Expectancy Effects and the Replicability of Behavioral Experiments. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2012, 7, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garety, P.A.; Freeman, D.; Jolley, S.; Dunn, G.; Bebbington, P.E.; Fowler, D.G.; Kuipers, E.; Dudley, R. Reasoning, emotions, and delusional conviction in psychosis. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2005, 114, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, S.; Woodward, T.S. Jumping to conclusions in delusional and non-delusional schizophrenic patients. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 44, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzan, R.P.; Delfabbro, P.H.; Galletly, C.A.; Woodward, T.S. Overadjustment or miscomprehension? A re-examination of the jumping to conclusions bias. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2012, 46, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirce, J.; Gray, J.R.; Simpson, S.; MacAskill, M.; Höchenberger, R.; Sogo, H.; Kastman, E.; Lindeløv, J.K. PsychoPy2: Experiments in behavior made easy. Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 51, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speechley, W. The contribution of hypersalience to the “jumping to conclusions” bias associated with delusions in schizophrenia. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2010, 35, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, P.B. Group Influence on Individual Task Performance. In Basic Group Processes; Paulus, P.B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, T.S.; Munz, M.; LeClerc, C.; Lecomte, T. Change in delusions is associated with change in “jumping to conclusions”. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 170, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, S.; Göritz, A.S.; Balzan, R.P.; Gawęda, Łukasz, Kulagin, S. C.; Andreou, C. A new paradigm to measure probabilistic reasoning and a possible answer to the question why psychosis-prone individuals jump to conclusions. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2017, 126, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltz, C.J.; Miller, G.E. An Asymptotic Test for The Equality of Coefficients of Variation from K Populations. Stat. Med. 1996, 15, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedge, C.; Powell, G.; Sumner, P. The reliability paradox: Why robust cognitive tasks do not produce reliable individual differences. Behav. Res. Methods 2018, 50, 1166–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfuhl, G. A Bayesian perspective on delusions: Suggestions for modifying two reasoning tasks. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2017, 56, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, A.O.; Gileadi, N.; Knolle, F.; Justicia, A.; Anderson, R.; Fletcher, P.C.; Moutoussis, M.; Murray, G.K. Cost Evaluation During Decision-Making in Patients at Early Stages of Psychosis. Comput. Psychiatry 2019, 3, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann-Thürig, D.; Läge, D. Sequential evidence accumulation in decision making: The individual desired level of confidence can explain the extent of information acquisition. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2008, 3, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutoussis, M.; Bentall, R.P.; El-Deredy, W.; Dayan, P. Bayesian modelling of Jumping-to-Conclusions bias in delusional patients. Cogn. Neuropsychiatry 2011, 16, 422–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Participants (Valid) | Mean (Median) | SD (CoV) | Min/Max | DtD1 | DtD1-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abstract–Individual Abstract–Group | 70 (69) | 4.49 (4) | 3.98 (0.89) | 1/20 | 16% | 25% |
| 75 (75) | 5.31 (3) | 5.90 (1.11) | 1/20 | 33% | 47% | |
| Cover–Group Cover–Remote | 124 (121) | 3.53 (3) | 2.35 (0.66) | 1/10 | 21% | 40% |
| 67 (67) | 3.31 (3) | 2.37 (0.71) | 1/10 | 30% | 45% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klevjer, K.; Pfuhl, G. The Effect of Situational Experiment Conditions on Hasty Decision Making in the ‘Beads Task’. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020359
Klevjer K, Pfuhl G. The Effect of Situational Experiment Conditions on Hasty Decision Making in the ‘Beads Task’. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(2):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020359
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlevjer, Kristoffer, and Gerit Pfuhl. 2023. "The Effect of Situational Experiment Conditions on Hasty Decision Making in the ‘Beads Task’" Brain Sciences 13, no. 2: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020359
APA StyleKlevjer, K., & Pfuhl, G. (2023). The Effect of Situational Experiment Conditions on Hasty Decision Making in the ‘Beads Task’. Brain Sciences, 13(2), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020359







