Modulation Effects of Repeated Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation at the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: A Pulsed Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
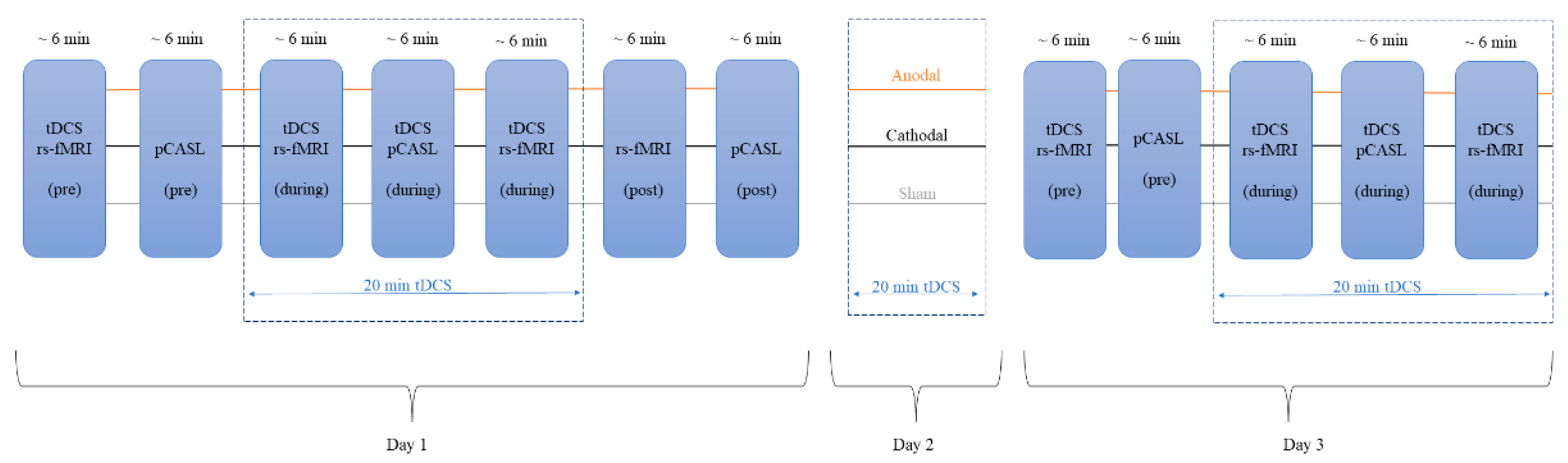
2.2. tDCS Modes
2.3. MRI Acquisition
2.4. MRI Preprocessing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Within-Group Arterial Spin Labeling Analysis Results
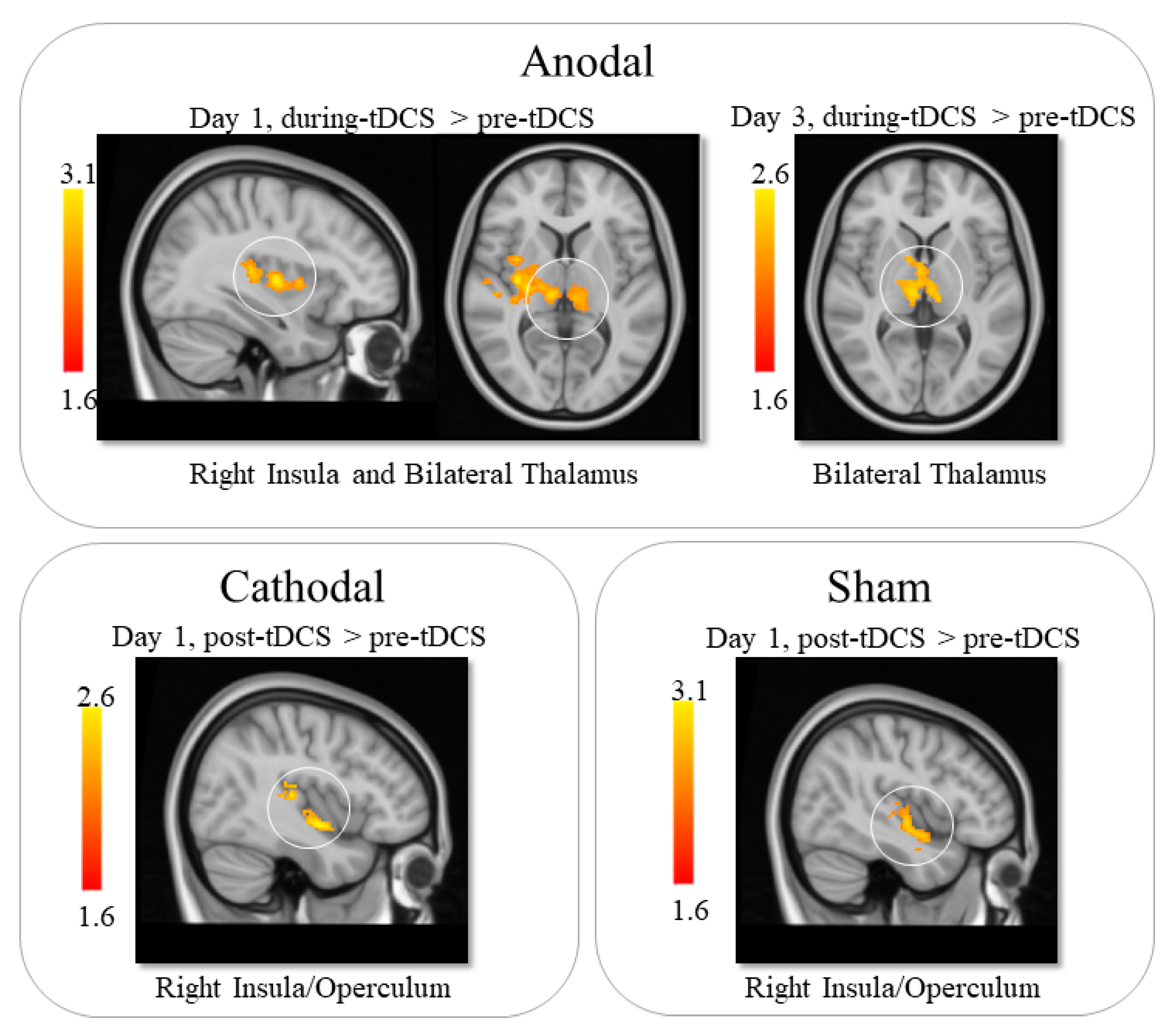
3.2.1. Anodal tDCS
3.2.2. Cathodal tDCS
3.2.3. Sham tDCS
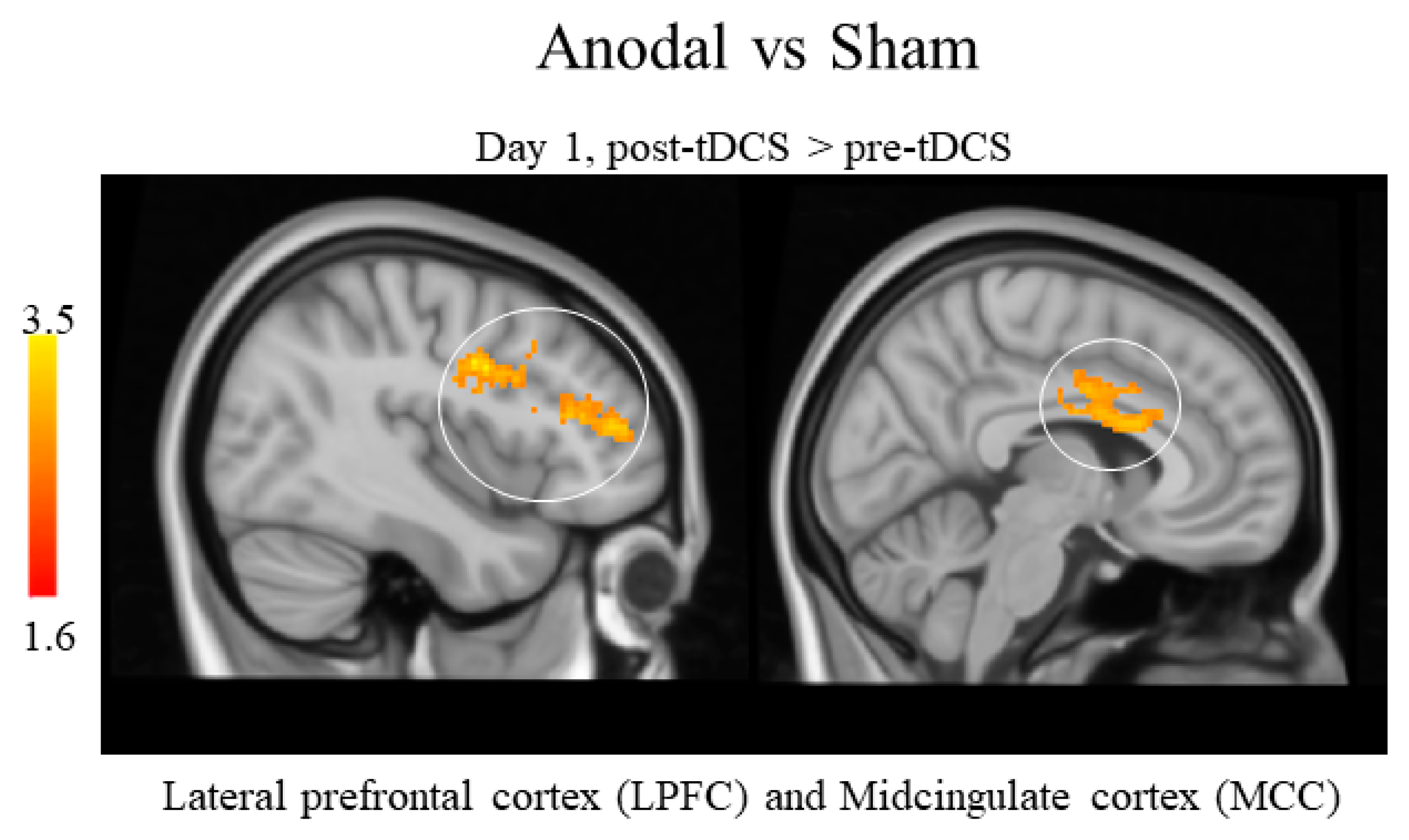
3.2.4. Between-Groups Arterial Spin Labeling Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Name | Abbreviation |
| Blood-Oxygen-Level-Dependent | BOLD |
| Cerebral Blood Flow | CBF |
| Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex | DLPFC |
| Lateral Prefrontal Cortex | LPFC |
| Magnetic Resonance | MR |
| Midcingulate Cortex | MCC |
| Pulsed Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling | pCASL |
| Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation | tDCS |
References
- Bindman, L.J.; Lippold, O.C.J.; Redfearn, J.W.T. The Action of Brief Polarizing Currents on the Cerebral Cortex of the Rat (I) during Current Flow and (2) in the Production of Long-Lasting After-Effects. J. Physiol. 1964, 172, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Alsop, D.C.; Schlaug, G. Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) on Human Regional Cerebral Blood Flow. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stagg, C.J.; Best, J.G.; Stephenson, M.C.; O’Shea, J.; Wylezinska, M.; Kineses, Z.T.; Morris, P.G.; Matthews, P.M.; Johansen-Berg, H. Polarity-Sensitive Modulation of Cortical Neurotransmitters by Transcranial Stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 5202–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Priori, A.; Berardelli, A.; Rona, S.; Accornero, N.; Manfredi, M. Polarization of the Human Motor Cortex through the Scalp. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 2257–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Paulus, W. Excitability Changes Induced in the Human Motor Cortex by Weak Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. J. Physiol. 2000, 527, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaug, G.; Renga, V. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: A Noninvasive Tool to Facilitate Stroke Recovery. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2008, 5, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalu, U.G.; Sexton, C.E.; Loo, C.K.; Ebmeier, K.P. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in the Treatment of Major Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2012, 42, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, C.J.; Lin, R.L.; Mezue, M.; Segerdahl, A.; Kong, Y.; Xie, J.; Tracey, I. Widespread Modulation of Cerebral Perfusion Induced during and after Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Applied to the Left Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 11425–11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, A.B.; Lerud, K.D.; Munsch, F.; Alsop, D.C.; Schlaug, G. Effects of TDCS Dose and Electrode Montage on Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Motor Behavior. Neuroimage 2021, 237, 118144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Cao, J.; Guler, S.; Chai-Zhang, T.; Camprodon, J.A.; Vangel, M.; Gollub, R.L.; Dougherty, D.D.; Kong, J. Perturbing FMRI Brain Dynamics Using Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. Neuroimage 2021, 237, 118100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Batsikadze, G.; Kuo, H.I.; Meesen, R.L.J.; Dechent, P.; Paulus, W.; Nitsche, M.A. Current Intensity- and Polarity-Specific Online and Aftereffects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: An FMRI Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 1644–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosayebi-Samani, M.; Jamil, A.; Salvador, R.; Ruffini, G.; Haueisen, J.; Nitsche, M.A. The Impact of Individual Electrical Fields and Anatomical Factors on the Neurophysiological Outcomes of TDCS: A TMS-MEP and MRI Study. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, A.; Hinson, E.; Stagg, C.J. TDCS and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Clinical Principles and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 127–158. [Google Scholar]
- Jog, M.V.; Wang, D.J.J.; Narr, K.L. A Review of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) for the Individualized Treatment of Depressive Symptoms. Pers. Med. Psychiatry 2019, 17–18, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fregni, F.; Gimenes, R.; Valle, A.C.; Ferreira, M.J.L.; Rocha, R.R.; Natalle, L.; Bravo, R.; Rigonatti, S.P.; Freedman, S.D.; Nitsche, M.A.; et al. A Randomized, Sham-Controlled, Proof of Principle Study of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for the Treatment of Pain in Fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3988–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggio, P.S.; Rigonatti, S.P.; Ribeiro, R.B.; Myczkowski, M.L.; Nitsche, M.A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Fregni, F. A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial on the Efficacy of Cortical Direct Current Stimulation for the Treatment of Major Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 11, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, Y.; Wilson, G.; Camprodon, J.; Dougherty, D.D.; Vangel, M.; Benedetti, F.; Kaptchuk, T.J.; Gollub, R.L.; Kong, J. Manipulating Placebo Analgesia and Nocebo Hyperalgesia by Changing Brain Excitability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101273118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, S.; Zaharchuk, G.; Thomas, D.L.; Lovblad, K.O.; Barkhof, F.; Golay, X. Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion of the Brain: Emerging Clinical Applications. Radiology 2016, 281, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, W.; Garcia, D.; de Bazelaire, C.; Alsop, D.C. Continuous Flow-Driven Inversion for Arterial Spin Labeling Using Pulsed Radio Frequency and Gradient Fields. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved Optimization for the Robust and Accurate Linear Registration and Motion Correction of Brain Images. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M. Fast Robust Automated Brain Extraction. Hum Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antal, A.; Alekseichuk, I.; Bikson, M.; Brockmöller, J.; Brunoni, A.R.; Chen, R.; Cohen, L.G.; Dowthwaite, G.; Ellrich, J.; Flöel, A.; et al. Low Intensity Transcranial Electric Stimulation: Safety, Ethical, Legal Regulatory and Application Guidelines. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1774–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, X.; Tang, W.; Cai, Y.; Shi, S.; Luo, Q. Connectivity between the Anterior Insula and Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Links Early Symptom Improvement to Treatment Response. J. Affect Disord. 2020, 260, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Long, Z.; Luo, Q.; Xu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Du, W.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Du, L. Functional and Structural Connectivity Between the Left Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex and Insula Could Predict the Antidepressant Effects of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 645936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Reste, P.J.; Haegelen, C.; Gibaud, B.; Moreau, T.; Morandi, X. Connections of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex with the Thalamus: A Probabilistic Tractography Study. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2016, 38, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funahashi, S. Thalamic Mediodorsal Nucleus and Its Participation in Spatial Working Memory Processes: Comparison with the Prefrontal Cortex. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Dun, W. Correlation Between Thalamus-Related Functional Connectivity and Serum BDNF Levels During the Periovulatory Phase of Primary Dysmenorrhea. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Leinisch, E.; Gänssbauer, S.; Draganski, B.; Bogdahn, U.; Altmeppen, J.; May, A. Affective Components and Intensity of Pain Correlate with Structural Differences in Gray Matter in Chronic Back Pain Patients. Pain 2006, 125, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, T.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, M.; Meng, F.; Fu, H.; Xie, Y.; Xu, H. Insular Cortex Is Critical for the Perception, Modulation, and Chronification of Pain. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.; Loggia, M.L.; Zyloney, C.; Tu, P.; LaViolette, P.; Gollub, R.L. Exploring the Brain in Pain: Activations, Deactivations and Their Relation. Pain 2010, 148, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shackman, A.J.; Salomons, T.V.; Slagter, H.A.; Fox, A.S.; Winter, J.J.; Davidson, R.J. The Integration of Negative Affect, Pain and Cognitive Control in the Cingulate Cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rushworth, M.F.S. Connectivity-Based Parcellation of Human Cingulate Cortex and Its Relation to Functional Specialization. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, B.A. Cingulate Cortex in the Three Limbic Subsystems. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 166, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apps, M.A.J.; Lockwood, P.L.; Balsters, J.H. The Role of the Midcingulate Cortex in Monitoring Others’ Decisions. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cieslik, E.C.; Zilles, K.; Caspers, S.; Roski, C.; Kellermann, T.S.; Jakobs, O.; Langner, R.; Laird, A.R.; Fox, P.T.; Eickhoff, S.B. Is There One DLPFC in Cognitive Action Control? Evidence for Heterogeneity from Co-Activation-Based Parcellation. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 2677–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, J.M. The Prefrontal Cortex—An update: Time Is of the Essence. Neuron 2001, 30(2), 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefaucheur, J.-P.; Antal, A.; Ahdab, R.; de Andrade, D.C.; Fregni, F.; Khedr, E.M.; Nitsche, M.; Paulus, W. The Use of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (RTMS) and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) to Relieve Pain. Brain Stimul. 2008, 1, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotkova, H.; Soto, E.; Leuschner, Z.; Greenberg, A.; Stock, V.; Das, D.; Cruciani, R. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. J. Pain 2013, 14, S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregni, F.; Freedman, S.; Pascual-Leone, A. Recent Advances in the Treatment of Chronic Pain with Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation Techniques. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.B.; Costa, B.T.; Duarte, D.; Fregni, F. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation as a Therapeutic Tool for Chronic Pain. J. ECT 2018, 34, e36–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Aleman, A.; Baeken, C.; Benninger, D.H.; Brunelin, J.; di Lazzaro, V.; Filipović, S.R.; Grefkes, C.; Hasan, A.; Hummel, F.C.; et al. Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Therapeutic Use of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (RTMS): An Update (2014–2018). Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 474–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krienen, F.M.; Buckner, R.L. Segregated Fronto-Cerebellar Circuits Revealed by Intrinsic Functional Connectivity. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hertrich, I.; Dietrich, S.; Blum, C.; Ackermann, H. The Role of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex for Speech and Language Processing. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 645209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Ralph, M.A.L.; Jackson, R.L. Subregions of DLPFC Display Graded yet Distinct Structural and Functional Connectivity. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Feng, L.; Li, X.; Gu, C.; Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Cheng, H. Dissociation between Conceptual and Perceptual Implicit Memory: Evidence from Patients with Frontal and Occipital Lobe Lesions. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreasen, N.C.; O’Leary, D.S.; Paradiso, S.; Cizadlo, T.; Arndt, S.; Watkins, G.L.; Ponto, L.L.B.; Hichwa, R.D. The Cerebellum Plays a Role in Conscious Episodic Memory Retrieval. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1999, 8, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, G.N. Cognitive Vision, Its Disorders and Differential Diagnosis in Adults and Children: Knowing Where and What Things Are. Eye 2003, 17, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.R.; Hewedi, D.H.; Eissa, A.M.; Moustafa, A.A. The Cerebellum and Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Public Health 2015, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, N. The Cerebellum and Cognition. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2007, 11, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D. Disorders of the Cerebellum: Ataxia, Dysmetria of Thought, and the Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Comparison | Region | Peak MNI Coordinates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||
| Anodal tDCS | ||||
| Day 1—pre vs. during tDCS | Left Thalamus | −10 | −26 | 10 |
| Day 1—pre vs. during tDCS | Right Thalamus | 14 | −26 | 14 |
| Day 1—pre vs. during tDCS | Right Insula | 50 | −24 | 8 |
| Day 1—pre vs. post tDCS | Cerebellum | −8 | −58 | −14 |
| Day 1—pre vs. post tDCS | Occipital Lobe | 18 | −90 | 20 |
| Day 3—pre vs. during tDCS | Bilateral Thalamus | −10 | −22 | 16 |
| Cathodal tDCS | ||||
| Day 1—pre vs. post tDCS | Right Insula | 38 | −22 | 0 |
| Sham tDCS | ||||
| Day 1—pre vs. post tDCS | Right Insula | 50 | −4 | −8 |
| Comparison | Region | Peak MNI Coordinates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||
| Anodal vs. Sham | ||||
| Day 1—pre vs. post tDCS | Bilateral Middle Cingulate Cortex | −12 | 4 | 30 |
| Day 1—pre vs. post tDCS | Bilateral Lateral Prefrontal Cortex | 38 | 34 | 20 |
| Cathodal vs. Sham | ||||
| No significant results were found | ||||
| Anodal vs. Cathodal | ||||
| No significant results were found | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sacca, V.; Maleki, N.; Wen, Y.; Hodges, S.; Kong, J. Modulation Effects of Repeated Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation at the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: A Pulsed Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030395
Sacca V, Maleki N, Wen Y, Hodges S, Kong J. Modulation Effects of Repeated Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation at the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: A Pulsed Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Study. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030395
Chicago/Turabian StyleSacca, Valeria, Nasim Maleki, Ya Wen, Sierra Hodges, and Jian Kong. 2023. "Modulation Effects of Repeated Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation at the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: A Pulsed Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Study" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030395
APA StyleSacca, V., Maleki, N., Wen, Y., Hodges, S., & Kong, J. (2023). Modulation Effects of Repeated Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation at the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: A Pulsed Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling Study. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030395








