Differential Treatment Responses in Pakistani Schizophrenia Samples: Correlation with Sociodemographic Parameters, Drug Addiction, Attitude to the Treatment and Antipsychotic Agents
Abstract
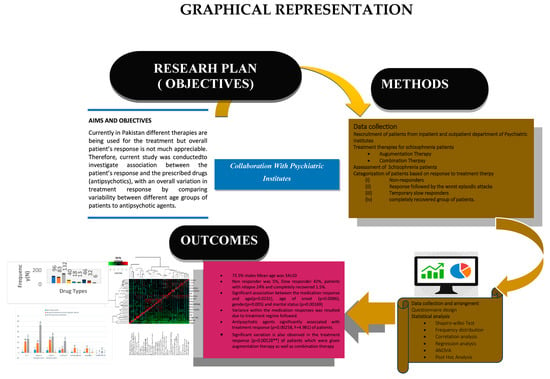
1. Introduction
Aims and Goals
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Assessment Instruments
2.3. Assessment of Therapeutic Approaches
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic and Diagnostic Characteristics
3.2. Correlation between Different Diagnostic and Sociodemographic Variables
3.3. Analysis of Variance in Treatment Responses
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECT | Electro-convulsive therapy |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |
| ICD | International Classification of Diseases |
| PNASs | Positive and Negative Symptoms |
References
- Ansari, I. Mental Health Pakistan: Optimizing Brains. Int. J. Emerg. Ment. Health 2015, 17, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen, P.B.; Pedersen, M.G.; Pedersen, C.B. Psychiatric Family History and Schizophrenia Risk in Denmark: Which Mental Disorders Are Relevant? Psychol. Med. 2010, 40, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciudad, A.; Bobes, J.; Álvarez, E.; San, L.; Novick, D.; Gilaberte, I. Clinical Meaningful Outcomes in Schizophrenia: Remission and Recovery. Rev. Psiquiatr. y SaludMent. (Engl. Ed.) 2011, 4, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; De Almeida, J.M.C.; Irfan, U.M.; Raza, U.A.; Farooq, S. Schizophrenia Diagnosis and Treatment by General Practitioners: A Cross-Sectional Study in District Peshawar, Pakistan. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2015, 65, 937–942. [Google Scholar]
- Gogtay, N.; Vyas, N.S.; Testa, R.; Wood, S.J.; Pantelis, C. Age of Onset of Schizophrenia: Perspectives from Structural Neuroimaging Studies. Schizophr. Bull. 2011, 37, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simona A Stilo, R.M.M. The Epidemiology of Schizophrenia: Replacing Dogma with Knowledge. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 12, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoutová, J.; Janáčková, P.; Šerý, O.; Zeman, T.; Ambroz, P.; Kovalová, M.; Vařechová, K.; Hosák, L.; Jiřík, V.; Janout, V. Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Schizophrenia. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2016, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Scherr, M.; Hamann, M.; Schwerthöffer, D.; Froböse, T.; Vukovich, R.; Pitschel-Walz, G.; Bäuml, J. Environmental Risk Factors and Their Impact on the Age of Onset of Schizophrenia: Comparing Familial to Non-Familial Schizophrenia. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2012, 66, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, J.Y.; Dwiel, L.L.; Henricks, A.M.; Doucette, W.T.; Green, A.I. The Link Between Schizophrenia and Substance Use Disorder: A Unifying Hypothesis. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 194, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.J.; Hei, G.R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.C.; Xiao, J.M.; Long, Y.J.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.P.; Wu, R.R. The Association Between Cognitive Deficits and Clinical Characteristic in First-Episode Drug Naïve Patients With Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 638773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, C.S.; Ballon, J.S.; Bivens, N.M.; Freyberg, Z.; Girgis, R.R.; Lizardi-Ortiz, J.E.; Markx, S.; Lieberman, J.A.; Javitch, J.A. Signaling Pathways in Schizophrenia: Emerging Targets and Therapeutic Strategies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tandon, R.; Gaebel, W.; Barch, D.M.; Bustillo, J.; Gur, R.E.; Heckers, S.; Malaspina, D.; Owen, M.J.; Schultz, S.; Tsuang, M.; et al. Definition and Description of Schizophrenia in the DSM-5. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 150, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, R.; Chiliza, B.; Asmal, L.; Harvey, B.H. The Nature of Relapse in Schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dazzan, P.; Morgan, K.D.; Orr, K.; Hutchinson, G.; Chitnis, X.; Suckling, J.; Fearon, P.; McGuire, P.K.; Mallett, R.M.; Jones, P.B.; et al. Different Effects of Typical and Atypical Antipsychotics on Grey Matter in First Episode Psychosis: The AESOP Study. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.; O’Flaherty, L. Antipsychotic Drugs: Atypical Advantages and Typical Disadvantages. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 2003, 20, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucht, S.; Leucht, C.; Huhn, M.; Chaimani, A.; Mavridis, D.; Helfer, B.; Samara, M.; Rabaioli, M.; Bächer, S.; Cipriani, A.; et al. Sixty Years of Placebo-Controlled Antipsychotic Drug Trials in Acute Schizophrenia: Systematic Review, Bayesian Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression of Efficacy Predictors. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucht, S.; Tardy, M.; Komossa, K.; Heres, S.; Kissling, W.; Davis, J.M. Maintenance Treatment with Antipsychotic Drugs for Schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 8, CD008016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, T.S.; Gray, N. Management of Common Adverse Effects of Antipsychotic Medications. World Psychiatry 2018, 17, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.D. Cognitive Impairment in Schizophrenia: Characteristics, Assessment and Treatment; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, A.; Falkai, P.; Wobrock, T.; Lieberman, J.; Glenthøj, B.; Gattaz, W.F.; Thibaut, F.; Möller, H.J.; Carlo Altamura, A.; Andreasen, N.; et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Schizophrenia—A Short Version for Primary Care. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2017, 21, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, P.M.; Correll, C.U. The Acute Efficacy of Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia: A Review of Recent Meta-Analyses. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 8, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, I.S.; Kumar, K.L.; Reddy, M.P.; Reddy, C.M.P.K. Attitudes toward Medication and Reasons for Non-Compliance in Patients with Schizophrenia. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2014, 36, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schennach, R.; Riedel, M.; Musil, R.; Möller, H.J. Treatment Response in First-Episode Schizophrenia. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2012, 10, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Takeuchi, H.; Fervaha, G.; Sin, G.L.; Foussias, G.; Agid, O.; Farooq, S.; Remington, G. Subtyping Schizophrenia by Treatment Response: Antipsychotic Development and the Central Role of Positive Symptoms. Can. J. Psychiatry 2015, 60, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faden, J.; Citrome, L. Resistance Is Not Futile: Treatment-Refractory Schizophrenia—Overview, Evaluation and Treatment. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Swanson, J.M.; Evins, A.E.; DeLisi, L.E.; Meier, M.H.; Gonzalez, R.; Bloomfield, M.A.P.; Curran, H.V.; Baler, R. Effects of Cannabis Use on Human Behavior, Including Cognition, Motivation, and Psychosis: A Review. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, K.R.; Darlington, N.; Kondel, T.K.; McKenna, P.J.; Jauhar, S. Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Schizophrenia—Outcomes for Functioning, Distress and Quality of Life: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Psychol. 2018, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.; Burudpakdee, C.; Seetasith, A.; Behling, M.; Krasa, H. Evaluation of Patient Support Program and Adherence to Long-Acting Injectable Aripiprazole for Patients Utilizing Injection Local Care Centers. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2019, 35, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potkin, S.G.; Kane, J.M.; Correll, C.U.; Lindenmayer, J.P.; Agid, O.; Marder, S.R.; Olfson, M.; Howes, O.D. The Neurobiology of Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Paths to Antipsychotic Resistance and a Roadmap for Future Research. npjSchizophr. 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pompili, M.; Lester, D.; Dominici, G.; Longo, L.; Marconi, G.; Forte, A.; Serafini, G.; Amore, M.; Girardi, P. Indications for Electroconvulsive Treatment in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Mathur, N.; Malhotra, A.K.; Braga, R.J. Electroconvulsive Therapy and Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review. Complex Psychiatry 2019, 5, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, D.A.; Kuhl, E.A.; Kupfer, D.J. The DSM-5: Classification and Criteria Changes. World Psychiatry 2013, 12, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Yavorsky, C.; Liechti, S.; Opler, M.; Rothman, B.; DiClemente, G.; Lucic, L.; Jovic, S.; Inada, T.; Yang, L. A Rasch Model to Test the Cross-Cultural Validity in the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) across Six Geo-Cultural Groups. BMC Psychol. 2013, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opler, M.G.A.; Yavorsky, C.; Daniel, D.G. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Training: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Directions. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 14, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maglione, J.E.; Thomas, S.E.; Jeste, D.V. Late-Onset Schizophrenia: Do Recent Studies Support Categorizing LOS as a Subtype of Schizophrenia? Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2014, 27, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, M.T.; Leucht, C.; Leeflang, M.M.; Anghelescu, I.G.; Chung, Y.C.; Crespo-Facorro, B.; Elkis, H.; Hatta, K.; Giegling, I.; Kane, J.M.; et al. Early Improvement As a Predictor of Later Response to Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia: A Diagnostic Test Review. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.; Sorensen, H.J.; Maeda, J.; Mortensen, E.L.; Victoroff, J.; Hayashi, K.; Michelsen, N.M.; Ekstrom, M.; Mednick, S. Childhood Motor Coordination and Adult Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.C.Y.; Gadelrab, R.; Ntephe, C.U.; McGuire, P.K.; Demjaha, A. Clinical Course, Neurobiology and Therapeutic Approaches to Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia. Toward an Integrated View. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.S.; Keefe, R.S.E. Schizophrenia Is a Cognitive Illness: Time for a Change in Focus. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, P.F.; Miller, B.J.; Lehrer, D.S.; Castle, D.J. Psychiatric Comorbidities and Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2009, 35, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungvari, G.; Petho, B. High-Dose Haloperidol Therapy: Its Effectiveness and a Comparison with Electroconvulsive Treatment. J. Psychiatr. Treat. Eval. 1982, 4, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, K.R.; Kulhara, P. The Efficacy of Electroconvulsive Therapy in the Treatment of Schizophrenia. A Comparative Study. Br. J. Psychiatry 1987, 151, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janakiramaiah, N.; Channabasavanna, S.M.; Murthy, N.S.N. ECT/Chlorpromazine Combination versus Chlorpromazine Alone in Acutely Schizophrenic Patients. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1982, 66, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Komossa, K.; Rummel-Kluge, C.; Corves, C.; Hunger, H.; Schmid, F.; Lobos, C.A.; Schwarz, S.; Davis, J.M. A Meta-Analysis of Head-to-Head Comparisons of Second-Generation Antipsychotics in the Treatment of Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarita, E.P.; Janakiramaiah, N.; Gangadhar, B.N.; Subbakrishna, D.K.; Rao, K.M.J. Efficacy of Combined ECT after Two Weeks of Neuroleptics in Schizophrenia: A Double BlindControlled Study. NIMHANS J. 1998, 16, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmayer, J.-P.; Liu-Seifert, H.; Kulkarni, P.M.; Kinon, B.J.; Stauffer, V.; Edwards, S.E.; Chen, L.; Adams, D.H.; Ascher-Svanum, H.; Buckley, P.F.; et al. Medication Nonadherence and Treatment Outcome in Patients With Schizophrenia or Schizoaffective Disorder With Suboptimal Prior Response. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usall, J.; Suarez, D.; Haro, J.M. Gender Differences in Response to Antipsychotic Treatment in Outpatients with Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2007, 153, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, M.S.; Wong, Y.L.I.; Yang, S.Y.; Ho, P.S.Y.; Mao, W.J.; Li, J.; Chan, C.L.W. Marriage and Outcomes of People with Schizophrenia in Rural China: 14-Year Follow-up Study. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 182, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Gender (N) | Age | Age at Onset (y) | Ethnicity (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Mean ± SD | 15–25 | 26–35 | 36–50 | Unknown | Punjabi | Kashmiri | Pakhtoons | Other Ethnic Groups | Unknown |
| 147 | 53 | 34 ± 10 | 50.5% | 10.5% | 6% | 33% | 42.5% | 15.5% | 11% | 8% | 22% |
| Variables | OR (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.074 (0.0082–0.680) | 0.0231 |
| Age at onset | 0.916 (0.839–1.0008) | 0.00864 |
| Gender | 6.183 (1.695–22.544) | 0.00577 |
| ECT | 1.672 (0.201–13.901) | 0.634 |
| Drug Addiction | 1.407 (0.166–11.905) | 0.7537 |
| Ethnicity | 0.422 (0.1048–1.703) | 0.225 |
| Marital Status | 5.28 (1.4921–18.683) | 0.00169 |
| Variable | B | S. E | T | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of Onset | −1.190× 10−17 | 1.519 × 10−17 | −7.840 × 10−1 | 0.435 |
| Drug Addiction | −2.156 × 10−17 | 2.017 × 10−16 | −1.070 × 10−1 | 0.915 |
| Response to medication | 9.182 × 10−17 | 1.476 × 10−16 | 6.220 × 10−1 | 0.536 |
| Stress | 1.214 × 10−16 | 2.439 × 10−16 | 4.980 × 10−1 | 0.620 |
| Hospitalization | 1.041 × 10−16 | 2.106 × 10−16 | 4.940 × 10−1 | 0.622 |
| AGE | −1.539 × 10−18 | 6.355 × 10−18 | −2.420 × 10−1 | 0.809 |
| Gender | 2.762 × 10−17 | 1.128 × 10−16 | 2.450 × 10−1 | 0.807 |
| Learning Disability | −2.340 × 10−17 | 9.725 × 10−17 | −2.410 × 10−1 | 0.810 |
| Paranoia | −8.181 × 10−17 | 1.177 × 10−16 | −6.950 × 10−1 | 0.489 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habiba, U.; Malik, A.; Raja, G.K.; Memon, M.R.; Nizami, A.T.d.; Ishaq, R.; Ilyas, M.; Valadi, H.; Nawaz, M.; Shaiq, P.A. Differential Treatment Responses in Pakistani Schizophrenia Samples: Correlation with Sociodemographic Parameters, Drug Addiction, Attitude to the Treatment and Antipsychotic Agents. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030407
Habiba U, Malik A, Raja GK, Memon MR, Nizami ATd, Ishaq R, Ilyas M, Valadi H, Nawaz M, Shaiq PA. Differential Treatment Responses in Pakistani Schizophrenia Samples: Correlation with Sociodemographic Parameters, Drug Addiction, Attitude to the Treatment and Antipsychotic Agents. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030407
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabiba, Umme, Aafia Malik, Ghazala Kaukab Raja, Muhammad Raza Memon, Asad Tameezud din Nizami, Rafaqat Ishaq, Muhammad Ilyas, Hadi Valadi, Muhammad Nawaz, and Pakeeza Arzoo Shaiq. 2023. "Differential Treatment Responses in Pakistani Schizophrenia Samples: Correlation with Sociodemographic Parameters, Drug Addiction, Attitude to the Treatment and Antipsychotic Agents" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030407
APA StyleHabiba, U., Malik, A., Raja, G. K., Memon, M. R., Nizami, A. T. d., Ishaq, R., Ilyas, M., Valadi, H., Nawaz, M., & Shaiq, P. A. (2023). Differential Treatment Responses in Pakistani Schizophrenia Samples: Correlation with Sociodemographic Parameters, Drug Addiction, Attitude to the Treatment and Antipsychotic Agents. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030407