Electroacupuncture Alleviates Depressive-like Behavior by Modulating the Expression of P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β of Prefrontal Cortex and Liver in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals and Group Allocation
2.2. CUMS Procedure
2.3. EA Group
2.4. Behavioral Tests
2.4.1. Sucrose Preference Test
2.4.2. Open Field Test
2.4.3. Forced Swimming Test
2.5. Sample Collection
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. HE Staining
2.8. Nissl Staining
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Western Blotting
3. Statistical Analyses
4. Results
4.1. Behavior
4.1.1. Sucrose Preference and Body Weight
4.1.2. OFT and FST
4.2. Effects of EA on the PFC
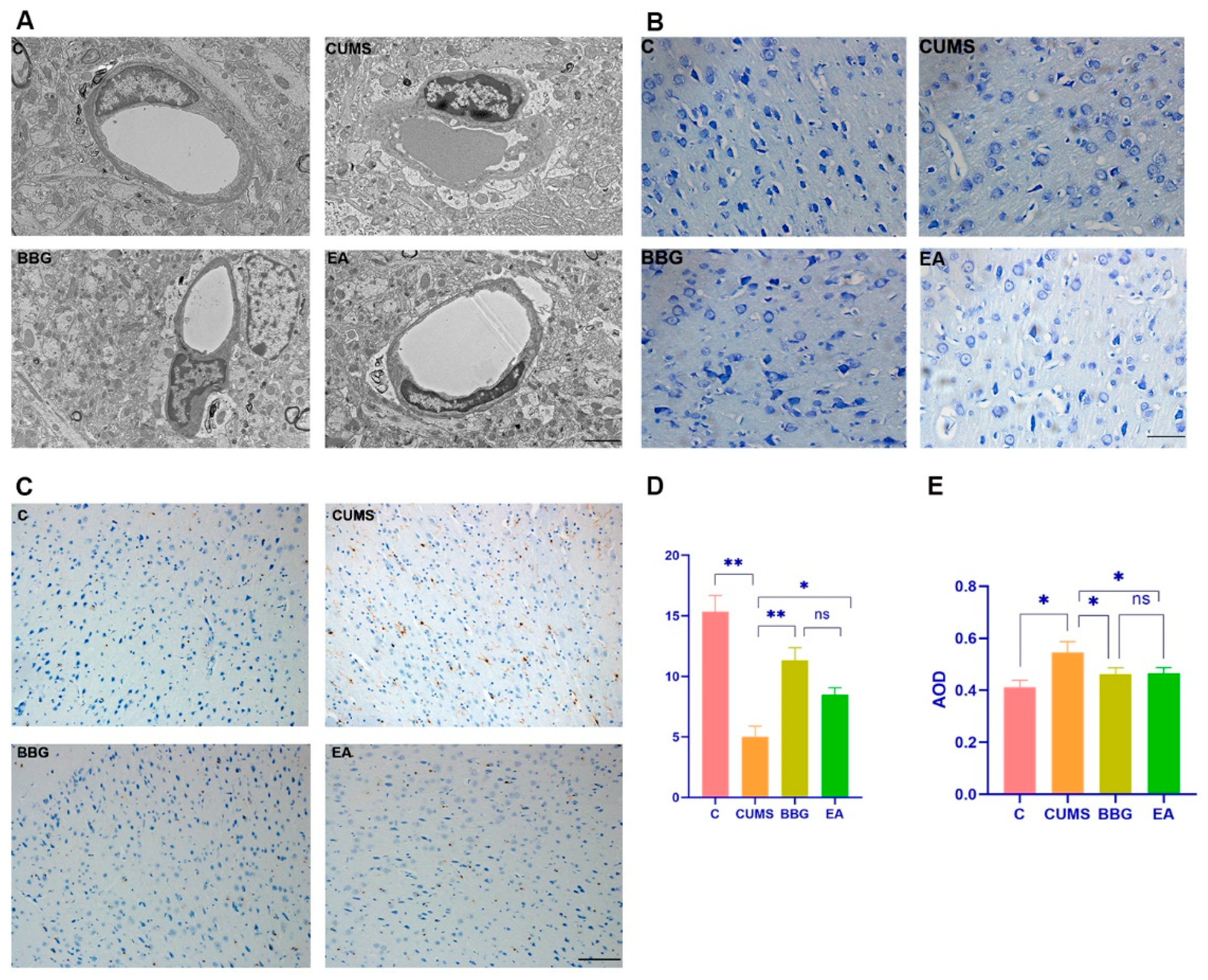
4.2.1. Microglial Morphology of PFC
4.2.2. Nissl Staining of PFC
4.2.3. Iba1 Expression in PFC
4.2.4. Effects of EA on the Expression of P2X7R, NLRP3, and IL-1β Related Protein in PFC
4.3. Effects of EA on the Liver
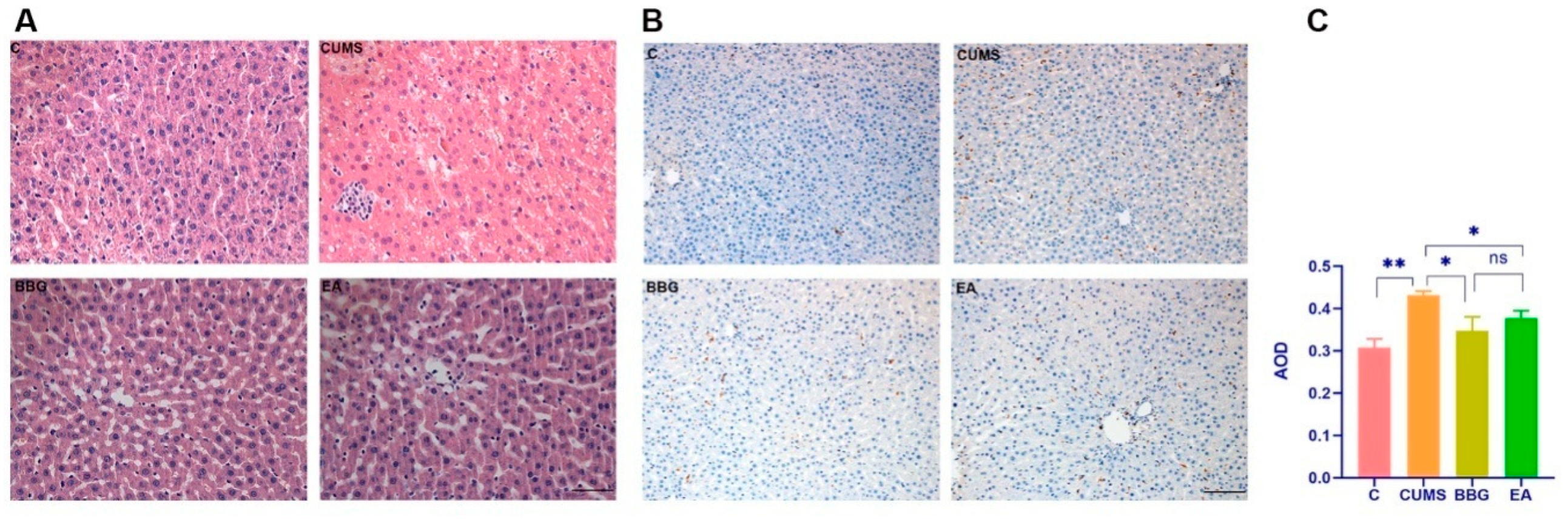
4.3.1. HE Staining of Liver
4.3.2. CD68 Expression in Right Liver Lobe
4.3.3. Effects of EA on the Expression of P2X7R, NLRP3, and IL-1β Related Protein in Liver
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malhi, G.S.; Mann, J.J. Depression. Lancet 2018, 392, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroquín, B. Interpersonal emotion regulation as a mechanism of social support in depression. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 31, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Cardellicchio, P.; Di Fazio, C.; Nazzi, C.; Fracasso, A.; Borgomaneri, S. Stopping in (e)motion: Reactive action inhibition when facing valence-independent emotional stimuli. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 998714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Serio, G.; Scarpazza, C.; D’Ausilio, A.; Borgomaneri, S. Frozen in (e)motion: How reactive motor inhibition is influenced by the emotional content of stimuli in healthy and psychiatric populations. Behav. Res. Ther. 2021, 146, 103963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennin, D.S.; Fresco, D.M. Emotion regulation as an integrative framework for understanding and treating psychopathology. In Emotion Regulation and Psychopathology: A Transdiagnostic Approach to Etiology and Treatment; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, M.L.; Thiruchselvam, R.; Todd, R.; Christoff, K. Emotion and the prefrontal cortex: An integrative review. Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 1033–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleau, E.L.; Treadway, M.T.; Pizzagalli, D.A. The Impact of Stress and Major Depressive Disorder on Hippocampal and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Morphology. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 85, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzagalli, D.A.; Roberts, A.C. Prefrontal cortex and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 47, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Spekker, E.; Polyák, H.; Tóth, F.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondrial Impairment: A Common Motif in Neuropsychiatric Presentation? The Link to the Tryptophan–Kynurenine Metabolic System. Cells 2022, 11, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.-K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angela, C. Prefrontal Regulation of Threat-Elicited Behaviors: A Pathway to Translation. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2020, 71, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolschijn, P.C.M.; van Haren, N.E.; Lensvelt-Mulders, G.J.; Pol, H.H.; Kahn, R.S. Brain volume abnormalities in major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 3719–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, T.; Radua, J.; Via, E.; Cardoner, N.; Abe, O.; Adams, T.M.; Amico, F.; Cheng, Y.; Cole, J.H.; de Azevedo Marques Périco, C.; et al. Common and distinct patterns of grey-matter volume alteration in major depression and bipolar disorder: Evidence from voxel-based meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maren, S.; Quirk, G.J. Neuronal signalling of fear memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullana, M.; Harrison, B.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Vervliet, B.; Cardoner, N.; Àvila-Parcet, A.; Radua, J. Neural signatures of human fear conditioning: An updated and extended meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 21, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Battaglia, S. Neurobiological advances of learned fear in humans. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 31, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, C. The Flavonoid Quercetin Induces AP-1 Activation in FRTL-5 Thyroid Cells. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Troubat, R.; Barone, P.; Leman, S.; DeSmidt, T.; Cressant, A.; Atanasova, B.; Brizard, B.; El Hage, W.; Surget, A.; Belzung, C.; et al. Neuroinflammation and depression: A review. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, E.; Wilson, A.A.; Mizrahi, R.; Rusjan, P.; Miler, L.; Rajkowska, G.; Suridjan, I.; Kennedy, J.L.; Rekkas, P.V.; Houle, S.; et al. Role of Translocator Protein Density, a Marker of Neuroinflammation, in the Brain During Major Depressive Episodes. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, S.B.; Williams, J.V.; Lavorato, D.H.; Modgill, G.; Jetté, N.; Eliasziw, M. Major depression as a risk factor for chronic disease incidence: Longitudinal analyses in a general population cohort. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2008, 30, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, T.; Castelló, R.; Toussaint, L.L.; Montesó-Curto, P. Depression as a Risk Factor of Organic Diseases: An International Integrative Review. J. Nurs. Sch. 2017, 49, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y. Depression and Chronic Liver Diseases: Are There Shared Underlying Mechanisms? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janik, M.K.; Wunsch, E.; Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J.; Krawczyk, M.; Milkiewicz, P. Depression: An Overlooked Villain in Autoimmune Hepatitis? Hepatology 2019, 70, 2232–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russ, T.C.; Kivimäki, M.; Morling, J.R.; Starr, J.M.; Stamatakis, E.; Batty, G.D. Association between Psychological Distress and Liver Disease Mortality: A Meta-analysis of Individual Study Participants. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kronsten, V.T.; Tranah, T.H.; Pariante, C.; Shawcross, D.L. Gut-derived systemic inflammation as a driver of depression in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, G.; Baune, B.T. Microglia: An Interface between the Loss of Neuroplasticity and Depression. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, S.-L.; Chen, J.-G.; Wang, F. Microglia: A Central Player in Depression. Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawonn, A.M.; Fritz, M.; Castany, S.; Pignatelli, M.; Canal, C.; Similä, F.; Tejeda, H.A.; Levinsson, J.; Jaarola, M.; Jakobsson, J.; et al. Microglial activation elicits a negative affective state through prostaglandin-mediated modulation of striatal neurons. Immunity 2021, 54, 225–234.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, L.E.B.; Mello, P.D.A.; Figliuolo, V.R.; Almeida, T.F.D.A.; Santana, P.T.; Oliveira, S.D.; Silva, C.L.; Feldbrügge, L.; Csizmadia, E.; Minshall, R.D.; et al. CD39 limits P2X7 receptor inflammatory signaling and attenuates sepsis-induced liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira-Souza, A.; Almeida-Da-Silva, C.L.C.; Rangel, T.P.; Rocha, G.D.C.; Bellio, M.; Zamboni, D.; Vommaro, R.C.; Coutinho-Silva, R. The P2X7 Receptor Mediates Toxoplasma gondii Control in Macrophages through Canonical NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemoli, M.; Curti, A.; Idzko, M.; Pizzirani, C.; Adinolfi, E. The P2X7 Receptor: A Key Player in IL-1 Processing and Release. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3877–3883. [Google Scholar]
- Wree, A.; Eguchi, A.; McGeough, M.D.; Pena, C.A.; Johnson, C.D.; Canbay, A.; Hoffman, H.M.; Feldstein, A.E. NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in hepatocyte pyroptosis, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2013, 59, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Shen, X.-L.; Wu, T.-Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.-X.; Jiang, C.-L. NLRP3 Inflammasome Mediates Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression in Mice via Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 18, pyv006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Hernández, M.; Díez-Zaera, M.; Sánchez-Nogueiro, J.; Gómez-Villafuertes, R.; Canals, J.M.; Alberch, J.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Lucas, J.J. Altered P2X7-receptor level and function in mouse models of Huntington’s disease and therapeutic efficacy of antagonist administration. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1893–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.H.; Mackenzie, A.B.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Brilliant blue G selectively blocks ATP-gated rat P2X(7) receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Cotrina, M.L.; Han, X.; Yu, H.; Bekar, L.; Blum, L.; Takano, T.; Tian, G.-F.; Goldman, S.A.; Nedergaard, M. Systemic administration of an antagonist of the ATP-sensitive receptor P2X7 improves recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12489–12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antoniuk, S.; Bijata, M.; Ponimaskin, E.; Wlodarczyk, J. Chronic unpredictable mild stress for modeling depression in rodents: Meta-analysis of model reliability. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 99, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strekalova, T.; Liu, Y.; Kiselev, D.; Khairuddin, S.; Chiu, J.L.Y.; Lam, J.; Chan, Y.-S.; Pavlov, D.; Proshin, A.; Lesch, K.-P.; et al. Chronic mild stress paradigm as a rat model of depression: Facts, artifacts, and future perspectives. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 663–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, P.; Towell, A.; Sampson, D.; Sophokleous, S.; Muscat, R. Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology 1987, 93, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyza, A.; Sahin, O.C.; Tugce, B.; Erdem, T.; Cansu, K.; Serap, S.; Ismail, K.C.; Tijen, U. Antidepressant-like Effects Induced by Chronic Blockade of the Purinergic 2X7 Receptor through Inhibition of Non-like Receptor Protein 1 Inflammasome in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model of Depression in Rats. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. Off. Sci. J. Korean Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 17, 261. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrazoli, E.G.; De Souza, H.D.N.; Nascimento, I.C.; Oliveira-Giacomelli, Á.; Schwindt, T.T.; Britto, L.R.; Ulrich, H. Brilliant Blue-G but not Fenofibrate Treatment Reverts Hemiparkinsonian Behavior and Restores Dopamine Levels in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matisz, C.E.; Badenhorst, C.A.; Gruber, A.J. Chronic unpredictable stress shifts rat behavior from exploration to exploitation. Stress 2021, 24, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Guo, J.; Tu, Y. Acupuncture inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the prefrontal cortex of a chronic stress rat model of depression. Anat. Rec. 2021, 304, 2470–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Lai, M.; Fu, W.; Wang, M.; Thi, T.T.M.; Ning, B.; Fu, W. Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Depressive-Like State and Synaptic Deficits Induced by Hyper-Cholinergic Tone During Chronic Stress in Rats. Med. Sci. Monitor. 2021, 27, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. The Bidirectional Relationship between Body Weight and Depression across Gender: A Simultaneous Equation Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.-R.; Zhu, X.-X.; Kong, M.-W.; Zou, X.-J.; Ma, Q.-Y.; Li, X.-J.; Chen, J.-X. Xiaoyaosan Exerts Antidepressant-Like Effect by Regulating Autophagy Involves the Expression of GLUT4 in the Mice Hypothalamic Neurons. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 873646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, A.M.; Kelly, J.P.; Leonard, B.E. Behavioural and neurochemical effects of dizocilpine in the olfactory bulbectomized rat model of depression. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 58, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankelevitch-Yahav, R.; Franko, M.; Huly, A.; Doron, R. The Forced Swim Test as a Model of Depressive-like Behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 2, e52587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogdanova, O.V.; Kanekar, S.; D’Anci, K.E.; Renshaw, P.F. Factors influencing behavior in the forced swim test. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 118, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, K.-K.; Pan, S.-M.; Ding, H.; Liu, J.-H.; Zheng, Y.-J.; Wang, S.-J.; Pan, Y.; Kong, L.-D. Chaihu-shugan san inhibits inflammatory response to improve insulin signaling in liver and prefrontal cortex of CUMS rats with glucose intolerance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, L.; Yue, C.; Qian, M.; Xie, M. Changes in gonadal function at different stages of chronic restraint stress-induced depression animals. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 210, 112656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianliang, P.Z. Effects of regulating gut microbiota on the serotonin metabolism in the chronic unpredictable mild stress rat model. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13677. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.D.; Crean, A.J.; Senior, A.M. Obesogenic diets induce anxiety in rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2021, 23, e13399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, J.W.G. Depression and anxiety. Med. J. Aust. 2012, 1, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartt, A.N.; Mariani, M.B.; Hen, R.; Mann, J.J.; Boldrini, M. Dysregulation of adult hippocampal neuroplasticity in major depression: Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahar, I.; Bambico, F.R.; Mechawar, N.; Nobrega, J.N. Stress, serotonin, and hippocampal neurogenesis in relation to depression and antidepressant effects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 38, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemogne, C.; Delaveau, P.; Freton, M.; Guionnet, S.; Fossati, P. Medial prefrontal cortex and the self in major depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 136, e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Kong, L.-D. Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates IL-1β-related inflammation in prefrontal cortex of depressive rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 41, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-H.; Song, E.-M.; Do, Y.-H.; Ahn, S.; Oh, J.-Y.; Hwang, T.-Y.; Ryu, Y.; Jeon, S.; Song, M.-Y.; Park, H.-J. Acupuncture alleviates chronic pain and comorbid conditions in a mouse model of neuropathic pain: The involvement of DNA methylation in the prefrontal cortex. Pain 2021, 162, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.; Choe, I.-H.; Noort, M.V.D.; Bosch, P.; Jahng, G.-H.; Rosen, B.; Kim, S.-H.; Lim, S. Acupuncture on GB34 activates the precentral gyrus and prefrontal cortex in Parkinson’s disease. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calovi, S.; Mut-Arbona, P.; Tod, P.; Iring, A.; Nicke, A.; Mato, S.; Vizi, E.S.; Tønnesen, J.; Sperlagh, B. P2X7 Receptor-Dependent Layer-Specific Changes in Neuron-Microglia Reactivity in the Prefrontal Cortex of a Phencyclidine Induced Mouse Model of Schizophrenia. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 566251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Verkhratsky, A.; Tang, Y. Pathological ATPergic Signaling in Major Depression and Bipolar Disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuijpers, P.; Vogelzangs, N.; Twisk, J.; Kleiboer, A.; Li, J.; Penninx, B.W. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Excess Mortality in Depression in the General Community Versus Patients with Specific Illnesses. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bot, M.; Milaneschi, Y.; Al-Shehri, T.; Amin, N.; Garmaeva, S.; Onderwater, G.L.; Pool, R.; Thesing, C.S.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Vogelzangs, N.; et al. Metabolomics Profile in Depression: A Pooled Analysis of 230 Metabolic Markers in 5283 Cases with Depression and 10,145 Controls. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahl, K.G.; Stapel, B.; Frieling, H. Link between depression and cardiovascular diseases due to epigenomics and proteomics: Focus on energy metabolism. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 89, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colognesi, M.; Gabbia, D.; De Martin, S. Depression and Cognitive Impairment—Extrahepatic Manifestations of NAFLD and NASH. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntona, S.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Kountouras, J.; Gialamprinou, D.; Kotronis, G.; Boziki, M.; Polyzos, S.A.; Tzitiridou, M.; Chatzopoulos, D.; Thavayogarajah, T.; et al. Impact of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-related metabolic state on depression. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 163, 105484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, D.; Pariante, C.M.; Mondelli, V. Markers of central inflammation in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies examining cerebrospinal fluid, positron emission tomography and post-mortem brain tissue. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Jones, D.N. Emerging role of the P2X7-NLRP3-IL1β pathway in mood disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 98, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Muecke-Heim, I.-A.; Ries, C.; Urbina, L.; Deussing, J.M. P2X7R antagonists in chronic stress-based depression models: A review. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegrin, P. P2X7 receptor and the NLRP3 inflammasome: Partners in crime. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 187, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z. P2X7 receptor mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in depression and diabetes. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Bi, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gong, L.; Qi, N.; Li, D.; Jin, X.; Xu, T.; Shi, B. Electroacupuncture Prevents the Depression-Like Behavior by Inhibiting the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway in Hippocampus of Mice Subjected to Chronic Mild Stress. Neuropsychobiology 2022, 81, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, N.; Li, B.; Yang, L.; Han, Q.-Q.; Huang, H.-J.; Wang, Y.-L.; Wang, J.; Yu, R.; Wu, G.-C.; Liu, Q.; et al. Electro-Acupuncture Alleviates Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depressive- and Anxiety-Like Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroinflammation in Rat Model of Depression. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.Y.H.; Zhao, T.Y.; Sun, S.Y.; Pan, X.F.; Guo, Y. Study on Compatibility Law of Acupoints in Patients with Depression Treated by Acupuncture Based on Data Mining. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Xinxi Zazhi 2021, 28, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, H.; Bao, T.; Wang, Y.; Meng, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P.; Quan, S.; Li, W.; Qi, S.; et al. Acupuncture Ameliorates Depressive Behaviors by Modulating the Expression of Hippocampal Iba-1 and HMGB1 in Rats Exposed to Chronic Restraint Stress. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, K.; Tanahashi, N.; Amagasu, N.; Mizuno, K.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Yi, G.; Ishida, T. Effect of Manual Acupuncture Stimulation at “Bai-Hui” (GV 20) or “Yintáng” (Ex-HN3) on Depressed Rats. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2017, 10, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Ma, W.; Li, Y.-J.; Wang, G.-T.; Yang, H.; Shen, W.-D. Efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture for post-stroke depression: A randomized controlled trial. Acupunct. Med. 2022, 40, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Content | Day |
|---|---|
| cold swimming | D1, D4, D10, D19, D25, D34 |
| water deprivation | D2, D15, D24, D28, D32 |
| food deprivation | D9, D11, D21, D29 |
| continuous illumination | D3, D13, D17, D20, D27, D35 |
| tail clamping | D5, D8, D14, D22, D33 |
| tail suspension | D7, D16, D21, D26, D30 |
| wet bedding | D6, D12, D18, D23, D31 |
| Groups | 0 Week | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 3 Weeks | 4 Weeks | 5 Weeks | 6 Weeks | 7 Weeks | 8 Weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 90.93 ± 1.12 | 90.13 ± 1.16 | 90.48 ± 0.96 | 90.66 ± 0.69 | 90.29 ± 1.26 | 90.68 ± 0.80 | 90.41 ± 1.03 | 90.24 ± 0.90 | 90.08 ± 0.87 |
| CUMS | 90.56 ± 1.14 | 85.93 ± 0.66 ** | 70.52 ± 2.26 | 58.48 ± 1.53 | 56.22 ± 1.18 | 56.30 ± 1.19 ** | 55.91 ± 0.88 ** | 55.94 ± 0.80 ** | 56.17 ± 0.89 ** |
| BBG | 90.60 ± 1.27 | 85.16 ± 0.93 ** | 69.10 ± 2.16 | 59.38 ± 2.52 | 56.69 ± 1.60 | 55.89 ± 1.17 ** | 62.42 ± 1.27 ◊◊ | 72.00 ± 1.32 ◊◊ | 83.49 ± 0.93 ◊◊ |
| EA | 90.55 ± 1.15 | 85.11 ± 0.81 ** | 69.92 ± 1.91 | 59.14 ± 1.48 | 56.85 ± 1.60 | 55.63 ± 1.01 ** | 58.22 ± 2.33 | 62.80 ± 1.65 ◊◊□□ | 72.80 ± 1.63 ◊◊□□ |
| Groups | 0 Week | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 3 Weeks | 4 Weeks | 5 Weeks | 6 Weeks | 7 Weeks | 8 Weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 194.21 ± 14.20 | 214.02 ± 15.63 | 263.72 ± 14.22 | 306.32 ± 6.98 | 323.77 ± 5.51 | 340.52 ± 7.85 | 368.68 ± 14.73 | 391.24 ± 14.58 | 418.02 ± 10.78 |
| CUMS | 195.68 ± 12.85 | 198.6 ± 8.31 | 234.44 ± 5.27 | 256.03 ± 9.28 | 287.72 ± 9.30 | 305.55 ± 15.46 ** | 324.46 ± 13.70 | 341.28 ± 10.76 | 351.44 ± 8.89 |
| BBG | 197.13 ± 4.76 | 195.18 ± 4.80 | 238.90 ± 4.25 | 255.44 ± 4.22 | 280.82 ± 7.43 | 303.52 ± 7.03 ** | 334.86 ± 11.98 | 355.22 ± 11.76 ◊ | 380.27 ± 13.64 ◊◊ |
| EA | 192.94 ± 8.47 | 196,88 ± 5.90 | 234.20 ± 2.60 | 258.20 ± 4.18 | 281.41 ± 19.08 | 307.69 ± 5.57 ** | 330.50 ± 5.18 | 352.08 ± 5.79 | 370.44 ± 8.47 ◊◊ |
| Groups | Total Distance (cm) | Immobility Time (s) | Resting Time Percent (%) | Time in Centre Zone (%) | Average Speed (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 5072.25 ± 527.29 | 6.80 ± 1.36 | 9.33 ± 2.30 | 29.56 ± 9.10 | 13.92 ± 0.77 |
| CUMS | 2849.84 ± 193.97 ** | 42.33 ± 5.08 ** | 41.35 ± 7.26 ** | 2.26 ± 1.93 ** | 6.45 ± 1.31 ** |
| BBG | 3967.77 ± 379.50 **◊◊ | 18.78 ± 5.89 **◊◊ | 20.63 ± 4.26 **◊◊ | 17.77 ± 2.06 **◊◊ | 11.87 ± 1.22 **◊◊ |
| EA | 35342.04 ± 477.89 **◊◊ | 23.89 ± 5.51 **◊◊ | 21.73 ± 2.84 **◊◊ | 13.84 ± 3.74 **◊◊□ | 9.63 ± 0.61 **◊◊□□ |
| Groups | Nissl Body Counts | Iba1 Relative Intensity | CD68 Relative Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 15.33 ± 1.36 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.02 |
| CUMS | 5.00 ± 0.89 ** | 0.55 ± 0.04 * | 0.43 ± 0.01 ** |
| BBG | 11.33 ± 1.03 ◊◊ | 0.46 ± 0.02 ◊ | 0.34 ± 0.03 ◊ |
| EA | 8.5 ± 0.54 ◊ | 0.46 ± 0.02 ◊ | 0.38 ± 0.02 ◊ |
| Groups | NLRP3/β-Actin | P2X7R/β-Actin | Pro-Caspase-1/β-Actin | Cleaved-Caspase-1/β-Actin | Pro-IL-1β/β-Actin | Cleaved-IL-1β/β-Actin | ASC/ β-Actin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 0.31 ± 0.18 | 0.34 ± 0.11 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.47 ± 0.06 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.16 | 0.39 ± 0.04 |
| CUMS | 0.81 ± 0.25 * | 0.68 ± 0.04 ** | 0.54 ± 0.04 ** | 0.74 ± 0.06 ** | 0.52 ± 0.05 * | 0.89 ± 0.06 ** | 0.80 ± 0.15 ** |
| BBG | 0.53 ± 0.18 ◊ | 0.40 ± 0.10 ◊◊ | 0.40 ± 0.12 ◊ | 0.59 ± 0.05 ◊ | 0.26 ± 0.04 ◊ | 0.41 ± 0.10 ◊ | 0.69 ± 0.11 |
| EA | 0.58 ± 0.16 ◊ | 0.45 ± 0.07 ◊ | 0.45 ± 0.04 ◊ | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.28 ± 0.01 ◊ | 0.47 ± 0.05 ◊ | 0.76 ± 0.15 |
| Groups | NLRP3/β-Actin | P2X7R/β-Actin | Pro-Caspase-1/β-Actin | Cleaved-Caspase-1/β-Actin | Pro-IL-1β/β-Actin | Cleaved-IL-1β/Β-Actin | ASC/ β-Actin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 0.31 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 0.07 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 0.54 ± 0.09 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 0.14 |
| CUMS | 0.64 ± 0.07 ** | 0.72 ± 0.12 ** | 0.63 ± 0.07 ** | 0.79 ± 0.16 * | 0.75 ± 0.09 * | 0.73 ± 0.14 * | 0.72 ± 0.14 ** |
| BBG | 0.44 ± 0.06 ◊ | 0.55 ± 0.10 ◊ | 0.43 ± 0.10 ◊ | 0.51 ± 0.28 ◊ | 0.64 ± 0.02 ◊ | 0.58 ± 0.10 ◊ | 0.55 ± 0.13 ◊ |
| EA | 0.47 ± 0.04 ◊ | 0.55 ± 0.04 ◊ | 0.48 ± 0.05 ◊ | 0.61 ± 0.13 | 0.70 ± 0.10 | 0.57 ± 0.07 ◊ | 0.66 ± 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, F.; Yang, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liao, D.; Guo, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Tang, C. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Depressive-like Behavior by Modulating the Expression of P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β of Prefrontal Cortex and Liver in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030436
Pang F, Yang Y, Huang S, Yang Z, Zhu Z, Liao D, Guo X, Zhou M, Li Y, Tang C. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Depressive-like Behavior by Modulating the Expression of P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β of Prefrontal Cortex and Liver in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030436
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Fang, Yunhao Yang, Siqin Huang, Zhixue Yang, Zhengwei Zhu, Dongmei Liao, Xiao Guo, Min Zhou, Yi Li, and Chenglin Tang. 2023. "Electroacupuncture Alleviates Depressive-like Behavior by Modulating the Expression of P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β of Prefrontal Cortex and Liver in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030436
APA StylePang, F., Yang, Y., Huang, S., Yang, Z., Zhu, Z., Liao, D., Guo, X., Zhou, M., Li, Y., & Tang, C. (2023). Electroacupuncture Alleviates Depressive-like Behavior by Modulating the Expression of P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β of Prefrontal Cortex and Liver in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030436






