Excellent Interrater Reliability for Manual Segmentation of the Medial Perirhinal Cortex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. Preprocessing of Structural MR Images
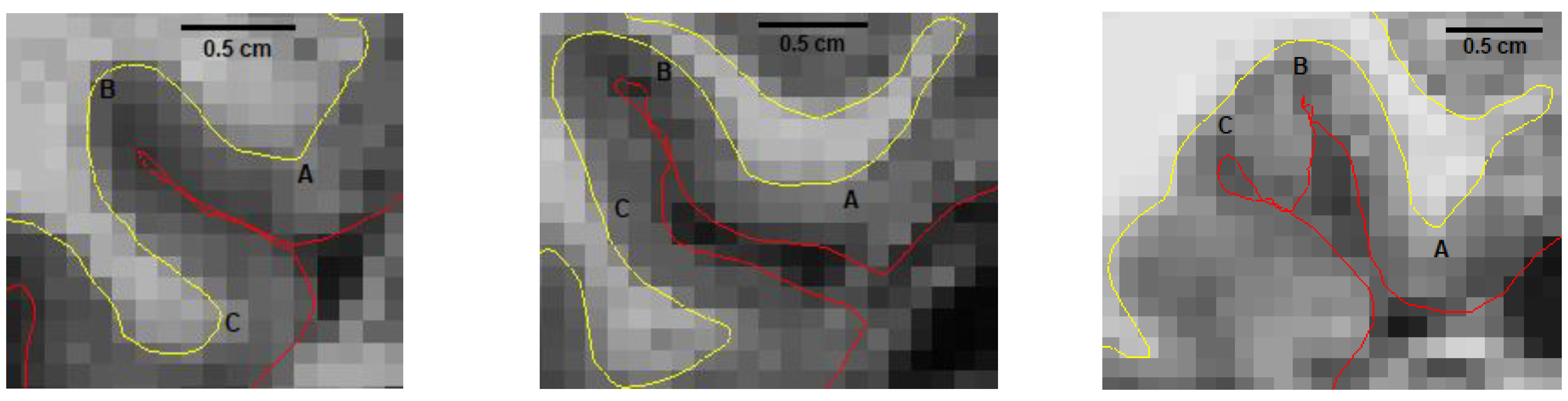
2.4. Manual Segmentation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graham, N.; Emery, T.; Hodges, J. Distinctive cognitive profiles in Alzheimer’s disease and subcortical vascular dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C.; Kimberly, A.; Quaid, K.; Holtzman, D.M.; Kantarci, K.; Kaye, J.; Reiman, E.M.; Klunk, W.E.; Siemers, E.R. Role of biomarkers in studies of presymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2005, 1, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, C.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Alzheimer’s Disease: A Physician’s Guide to Practical Management; Richter, R.W., Richter, B.Z., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillozet, A.L.; Weintraub, S.; Mash, D.C.; Mesulam, M.M. Neurofibrillary Tangles, Amyloid, and Memory in Aging and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A. Tau Proteins and Neurofibrillary Degeneration. Brain Pathol. 1991, 1, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Yamashita, S.; Fukuda, T.; Park, J.-M.; Murayama, M.; Mizoroki, T.; Yoshiike, Y.; Sahara, N.; Takashima, A. Hyperphosphorylated tau in parahippocampal cortex impairs place learning in aged mice expressing wild-type human tau. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 5143–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobinski, M.; Wegiel, J.; Tarnawski, M.; Bobinski, M.; Reisberg, B.; de Leon, M.J.; Miller, D.C.; Wisniewski, H.M. Relationships between Regional Neuronal Loss and Neurofibrillary Changes in the Hippocampal Formation and Duration and Severity of Alzheimer Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Isla, T.; Hollister, R.; West, H.; Mui, S.; Growdon, J.H.; Petersen, R.C.; Parisi, J.E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuronal loss correlates with but exceeds neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 41, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, P.; Jack, C.R. Role of structural MRI in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2010, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, K.I.; Probst, A. Anatomic localization of the transentorhinal region of the perirhinal cortex. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K. Staging of cortical neurofibrillary inclusions of the Alzheimer’s type. In Alzheimer: 100 Years and Beyond; Jucker, M., Beyreuther, K., Haass, C., Nitsch, R.M., Christen, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, D.; Imabayashi, E.; Maikusa, N.; Okamura, N.; Furumoto, S.; Kudo, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Takano, H.; Yokoi, Y.; Sakata, M.; et al. Regional tau deposition and subregion atrophy of medial temporal structures in early Alzheimer’s disease: A combined positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging study. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2017, 9, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talwar, P.; Kushwaha, S.; Chaturvedi, M.; Mahajan, V. Systematic Review of Different Neuroimaging Correlates in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2021, 31, 953–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkirch, S.J.; Traschütz, A.; Müller, A.; Widmann, C.N.; Gielen, G.H.; Heneka, M.T.; Jurcoane, A.; Schild, H.H.; Hattingen, E. The ERICA Score: An MR Imaging–based Visual Scoring System for the Assessment of Entorhinal Cortex Atrophy in Alzheimer Disease. Radiology 2018, 288, 226–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheltens, P.; van de Pol, L. Impact commentaries. Atrophy of medial temporal lobes on MRI in “probable” Alzheimer’s disease and normal ageing: Diagnostic value and neuropsychological correlates. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulason, S.; Tward, D.J.; Brown, T.; Sicat, C.S.; Liu, C.-F.; Ratnanather, J.T.; Younes, L.; Bakker, A.; Gallagher, M.; Albert, M.; et al. Cortical thickness atrophy in the transentorhinal cortex in mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 21, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulason, S.; Xu, E.; Tward, D.J.; Bakker, A.; Albert, M.; Younes, L.; Miller, M.I. Entorhinal and Transentorhinal Atrophy in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, L.; Albert, M.; Miller, M.I. Inferring changepoint times of medial temporal lobe morphometric change in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 5, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krumm, S.; Kivisaari, S.L.; Probst, A.; Monsch, A.U.; Reinhardt, J.; Ulmer, S.; Stippich, C.; Kressig, R.W.; Taylor, K.I. Cortical thinning of parahippocampal subregions in very early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 38, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouri, N.; Murray, M.E.; Hassan, A.; Rademakers, R.; Uitti, R.J.; Boeve, B.F.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Litvan, I.; Josephs, K.A.; et al. Neuropathological features of corticobasal degeneration presenting as corticobasal syndrome or Richardson syndrome. Brain 2011, 134, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustinack, J.C.; Huber, K.E.; Stevens, A.A.; Roy, M.; Frosch, M.P.; van der Kouwe, A.J.W.; Wald, L.L.; Van Leemput, K.; McKee, A.C.; Fischl, B. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Predicting the location of human perirhinal cortex, Brodmann’s area 35, from MRI. NeuroImage 2013, 64, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. On areas of transition between entorhinal allocortex and temporal isocortex in the human brain. Normal morphology and lamina-specific pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1985, 68, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodmann, K.; Garey, L. Brodmann’s Localisation in the Cerebral Cortex: The Principles of Comparative Localisation in the Cerebral Cortex Based on the Cytoarchitectonics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivisaari, S.L.; Probst, A.; Taylor, K.I. The Perirhinal, Entorhinal, and Parahippocampal Cortices and Hippocampus: An Overview of Functional Anatomy and Protocol for Their Segmentation in MR Images. In FMRI: Basics and Clinical Applications; Ulme, S., Jansen, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 239–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisse, L.E.M.; Chételat, G.; Daugherty, A.M.; de Flores, R.; la Joie, R.; Mueller, S.G.; Stark, C.E.L.; Wang, L.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Berron, D.; et al. Hippocampal subfield volumetry from structural isotropic 1 mm3 MRI scans: A note of caution. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussey, T.J.; Saksida, L.M.; Murray, E.A. Perirhinal cortex resolves feature ambiguity in complex visual discriminations. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowell, R.A. Computational models of perirhinal cortex function. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 1952–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimone, R.; Ungerleider, L.G. Multiple visual areas in the caudal superior temporal sulcus of the macaque. J. Comp. Neurol. 1986, 248, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, R.A.; Bussey, T.J.; Saksida, L.M. Components of recognition memory: Dissociable cognitive processes or just differences in representational complexity? Hippocampus 2010, 20, 1245–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, E.A.; Richmond, B.J. Role of perirhinal cortex in object perception, memory, and associations. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, W.L.; Amaral, D.G. Perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices of the macaque monkey: Cortical afferents. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 350, 497–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, M.; Berres, M.; Kivisaari, S.L.; Henzen, N.A.; Monsch, A.U.; Reinhardt, J.; Blatow, M.; Kressig, R.W.; Krumm, S. Can you find it? Novel oddity detection task for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychology, 2022; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.I.; Moss, H.E.; Tyler, L.K. The Conceptual Structure Account: A cognitive model of semantic memory and its neural instantiation. In Neural Basis of Semantic Memory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 265–301. [Google Scholar]
- Hirni, D.I.; Kivisaari, S.L.; Monsch, A.U.; Taylor, K.I. Distinct neuroanatomical bases of episodic and semantic memory performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 2013, 51, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krumm, S.; Berres, M.; Kivisaari, S.L.; Monsch, A.U.; Reinhardt, J.; Blatow, M.; Kressig, R.W.; Taylor, K.I. Cats and Apples: Semantic Fluency Performance for Living Things Identifies Patients with Very Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. Off. J. Natl. Acad. Neuropsychol. 2021, 36, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I. Cortical Surface-Based Analysis: I. Segmentation and Surface Reconstruction. NeuroImage 1999, 9, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I.; Dale, A.M. Cortical Surface-Based Analysis: II: Inflation, Flattening, and a Surface-Based Coordinate System. NeuroImage 1999, 9, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Insausti, R.; Juottonen, K.; Soininen, H.; Insausti, A.M.; Partanen, K.; Vainio, P.; Laakso, M.P.; Pitkänen, A. MR volumetric analysis of the human entorhinal, perirhinal, and temporopolar cortices. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1998, 19, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delis, D.C.; Kramer, J.H.; Kaplan, E.; Ober, B.A. California Verbal Learning Test; Psychological Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Reitan, R.M. Validity of the Trail Making Test as an Indicator of Organic Brain Damage. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1958, 8, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorm, A.F.; Scott, R.; Jacomb, P.A. Assessment of cognitive decline in dementia by informant questionnaire. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1989, 4, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM-IV: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winblad, B.; Palmer, K.; Kivipelto, M.; Jelic, V.; Fratiglioni, L.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Nordberg, A.; Bäckman, L.; Albert, M.; Almkvist, O.; et al. Mild cognitive impairment--beyond controversies, towards a consensus: Report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsch, A.; Kressig, R. Specific care program for the older adults: Memory Clinics. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 1, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. ICD-10: International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems: Tenth Revision; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42980 (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- Galik, E.; Fukudo, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Gidron, Y.; Campbell, T.S.; Johnson, J.A.; Zernicke, K.A.; Pellowski, J.; Garcia, L.I.; Mitchell, J.W.; et al. Geriatric Depression Scale. In Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine; Gellman, M.D., Turner, J.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 857–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T. An Inventory for Measuring Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G. Beck Depression Inventory–II; American Psychological Association: Worcester, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pruessner, J.C.; Köhler, S.; Crane, J.; Pruessner, M.; Lord, C.; Byrne, A.; Kabani, N.; Collins, D.L.; Evans, A.C. Volumetry of temporopolar, perirhinal, entorhinal and parahippocampal cortex from high-resolution MR images: Considering the variability of the collateral sulcus. Cereb. Cortex 2002, 12, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Wisse, L.E.M.; Pluta, J.; Flores, R. de, Piskin, V.; Manjón, J.V.; Wang, H.; Das, S.R.; Ding, S.-L.; Wolk, D.A.; et al. Automated segmentation of medial temporal lobe subregions on in vivo T1-weighted MRI in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 3431–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| NCs (n = 9) | AD (n = 18) | non-AD (n = 9) | MD (n = 8) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (m/f) | 5/4 | 7/11 | 6/3 | 2/6 | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Age (years) | 70.89 | 11.41 | 71.56 | 10.61 | 71.56 | 7.09 | 59.13 | 6.40 |
| Education (years) | 13.33 | 4.03 | 14.50 | 3.24 | 12.89 | 2.42 | 13.63 | 2.88 |
| MMSE score | 29.00 | 1.00 | 26.72 | 2.42 | 25.89 | 1.54 | 29.00 | 1.41 |
| Variable | Cronbach’s Alpha | ICC | 95% Confidence Interval | F Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Value | df1/df2 | p | |||
| mPRC lh | 0.993 | 0.986 | 0.974 | 0.992 | 136.618 | 43/43 | 4.81 × 10−35 |
| mPRC rh | 0.994 | 0.985 | 0.967 | 0.992 | 154.670 | 43/43 | 3.46 × 10−36 |
| lPRC lh | 0.992 | 0.984 | 0.970 | 0.991 | 118.834 | 43/43 | 9.23 × 10−34 |
| lPRC rh | 0.975 | 0.953 | 0.915 | 0.974 | 40.344 | 43/43 | 5.82 × 10−24 |
| ERC lh | 0.984 | 0.969 | 0.944 | 0.983 | 62.657 | 43/43 | 6.44 × 10−28 |
| ERC rh | 0.980 | 0.961 | 0.930 | 0.979 | 49.390 | 43/43 | 9.02 × 10−26 |
| Variable | Cronbach’s Alpha | ICC | 95% Confidence Interval | F Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Value | df1/df2 | p | |||
| mPRC lh | 0.932 | 0.874 | 0.781 | 0.929 | 14.647 | 43/43 | 3.06 × 10−15 |
| mPRC rh | 0.864 | 0.757 | 0.597 | 0.859 | 7.363 | 43/43 | 6.58 × 10−10 |
| lPRC lh | 0.909 | 0.831 | 0.712 | 0.904 | 10.960 | 43/43 | 6.53 × 10−13 |
| lPRC rh | 0.825 | 0.705 | 0.518 | 0.827 | 5.703 | 43/43 | 3.96 × 10−8 |
| ERC lh | 0.978 | 0.948 | 0.887 | 0.974 | 44.603 | 43/43 | 7.40 × 10−25 |
| ERC rh | 0.951 | 0.908 | 0.838 | 0.949 | 20.326 | 43/43 | 5.58 × 10−18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henzen, N.A.; Reinhardt, J.; Blatow, M.; Kressig, R.W.; Krumm, S. Excellent Interrater Reliability for Manual Segmentation of the Medial Perirhinal Cortex. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060850
Henzen NA, Reinhardt J, Blatow M, Kressig RW, Krumm S. Excellent Interrater Reliability for Manual Segmentation of the Medial Perirhinal Cortex. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(6):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060850
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenzen, Nicolas A., Julia Reinhardt, Maria Blatow, Reto W. Kressig, and Sabine Krumm. 2023. "Excellent Interrater Reliability for Manual Segmentation of the Medial Perirhinal Cortex" Brain Sciences 13, no. 6: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060850
APA StyleHenzen, N. A., Reinhardt, J., Blatow, M., Kressig, R. W., & Krumm, S. (2023). Excellent Interrater Reliability for Manual Segmentation of the Medial Perirhinal Cortex. Brain Sciences, 13(6), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060850










