Involvement of Antioxidant and Prevention of Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect and Anti-Apoptotic Effect: Betaine Ameliorates Haloperidol-Induced Orofacial Dyskinesia in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
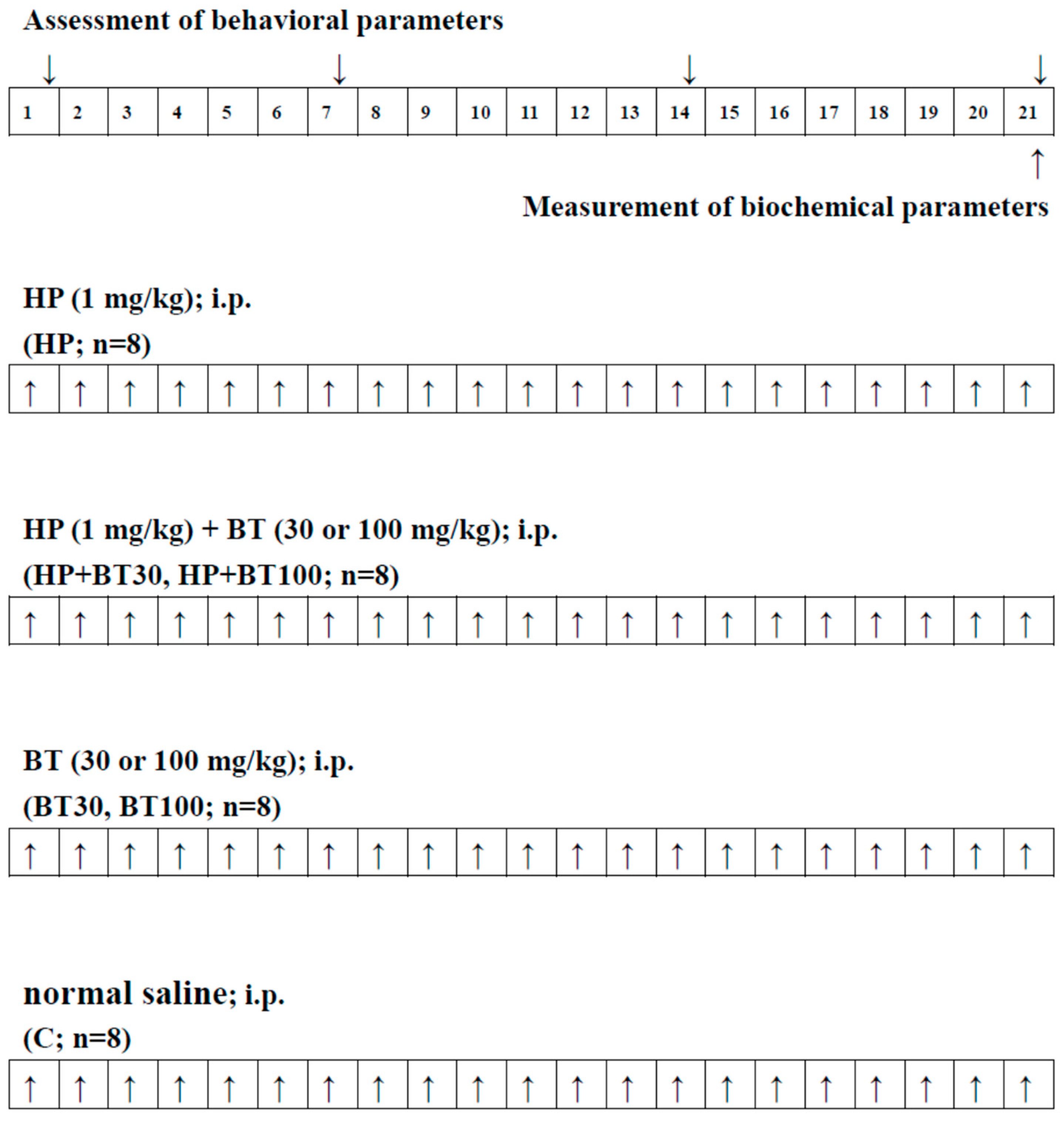
2.3. Experimental Groups and Drug Treatment
- HP treatment group (HP): HP (1 mg/kg i.p.) for 21 days;
- HP + BT 30 mg/kg treatment group (HP + BT30): HP (1 mg/kg i.p.) + BT (30 mg/kg, i.p.) for 21 days;
- HP + BT 100 mg/kg treatment group (HP + BT100): HP (1 mg/kg i.p.) + BT (100 mg/kg, i.p.) for 21 days;
- BT 30 mg/kg treatment group (BT30): BT (30 mg/kg, i.p.) for 21 days;
- BT 100 mg/kg treatment group (BT100): BT (100 mg/kg, i.p.) for 21 daysl
- Control group (C): Normal saline (i.p.) for 21 days.
2.4. Behavioral Assessment of Orofacial Dyskinesia
2.5. Biochemical Measurement
2.6. Determination of Nitrites Concentration
2.7. Assessment of Lipid Peroxidative Indices
2.8. Measurement of Glutathione
2.9. Measurement of Superoxide Dismutase Activity
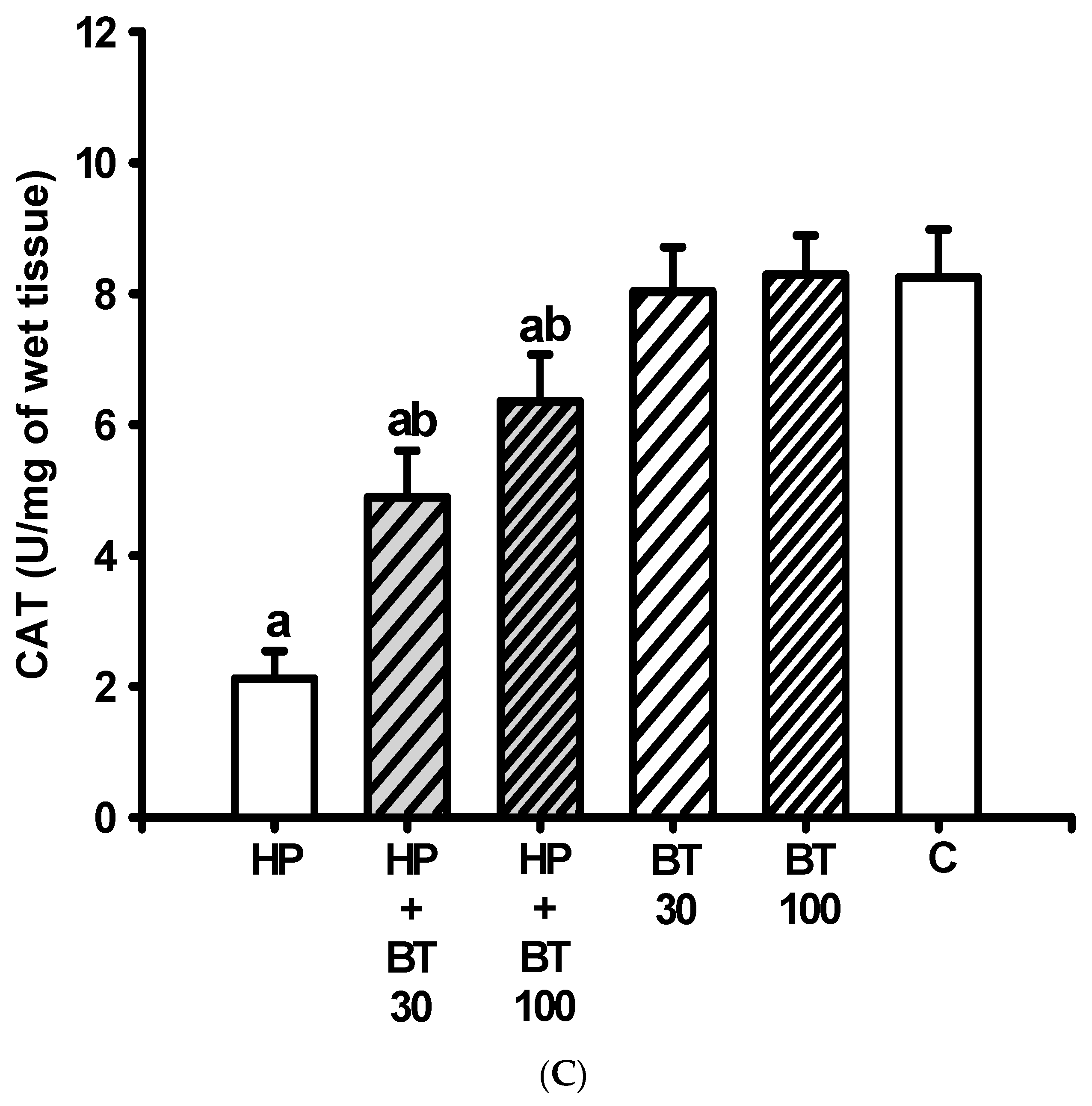
2.10. Measurement of Catalase Activity
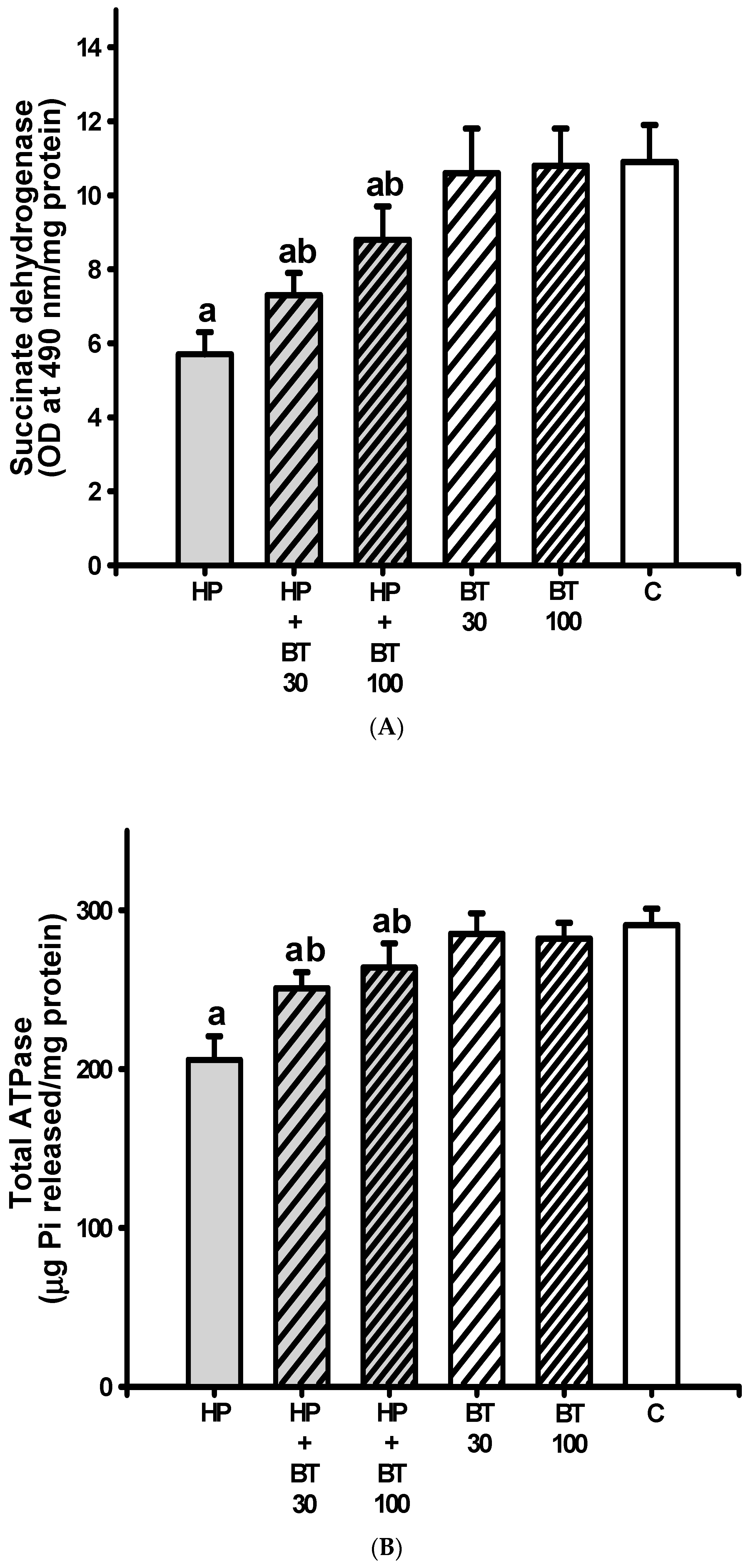
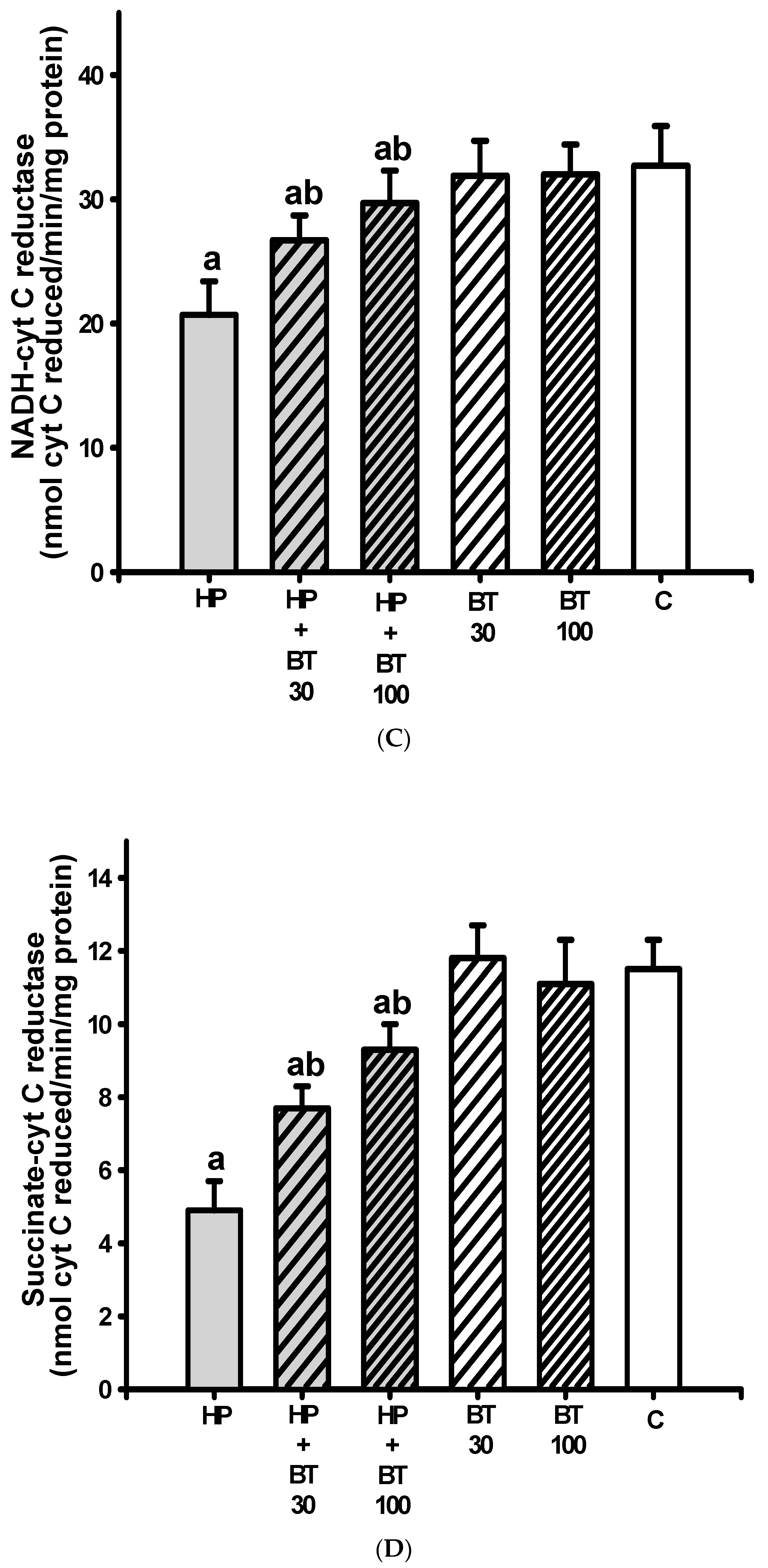
2.11. Measurement of Mitochondrial Function
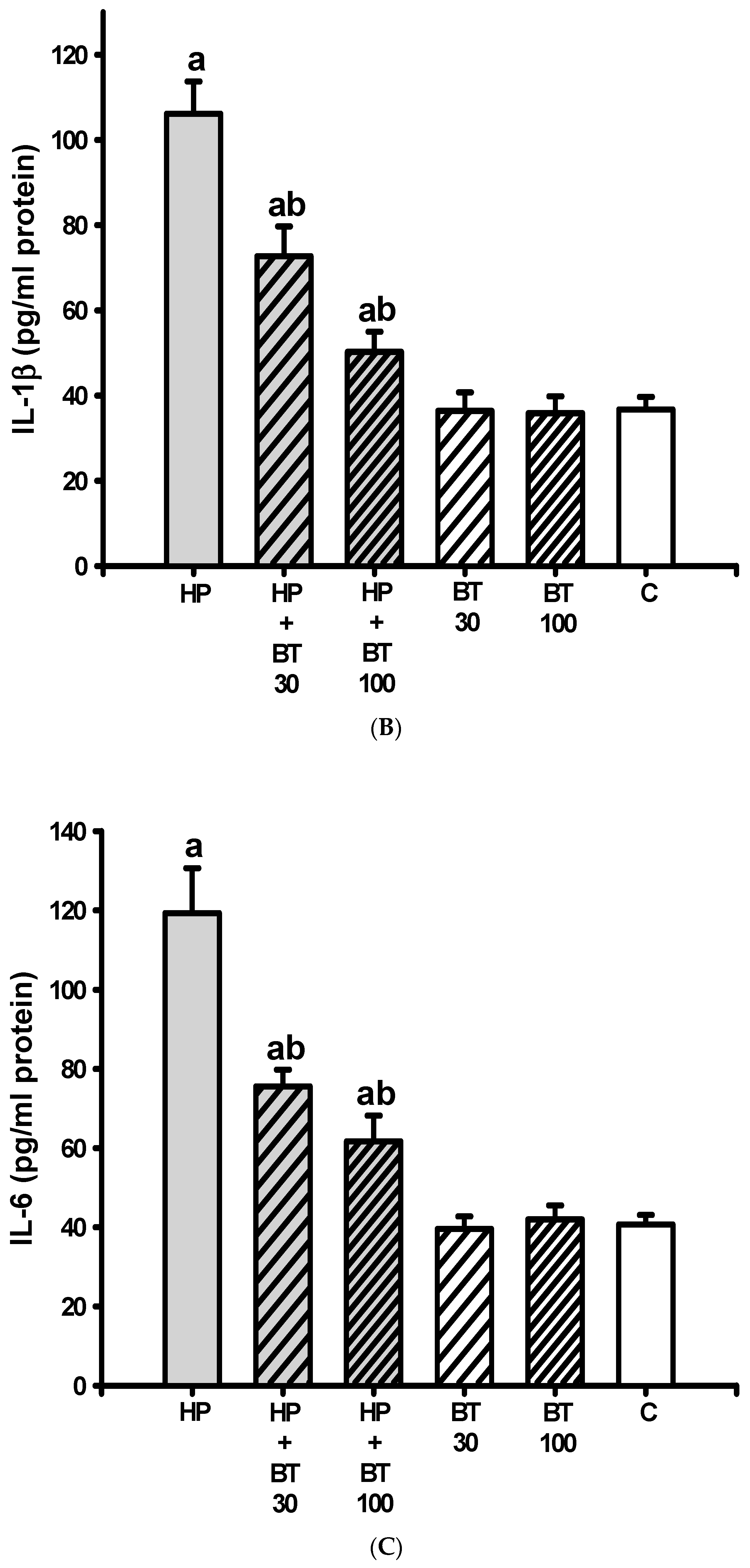
2.12. Measurement of Neuroinflammatory Markers
2.13. Measurement of the Apoptotic Marker Caspase-3
2.14. Determination of Protein Content
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
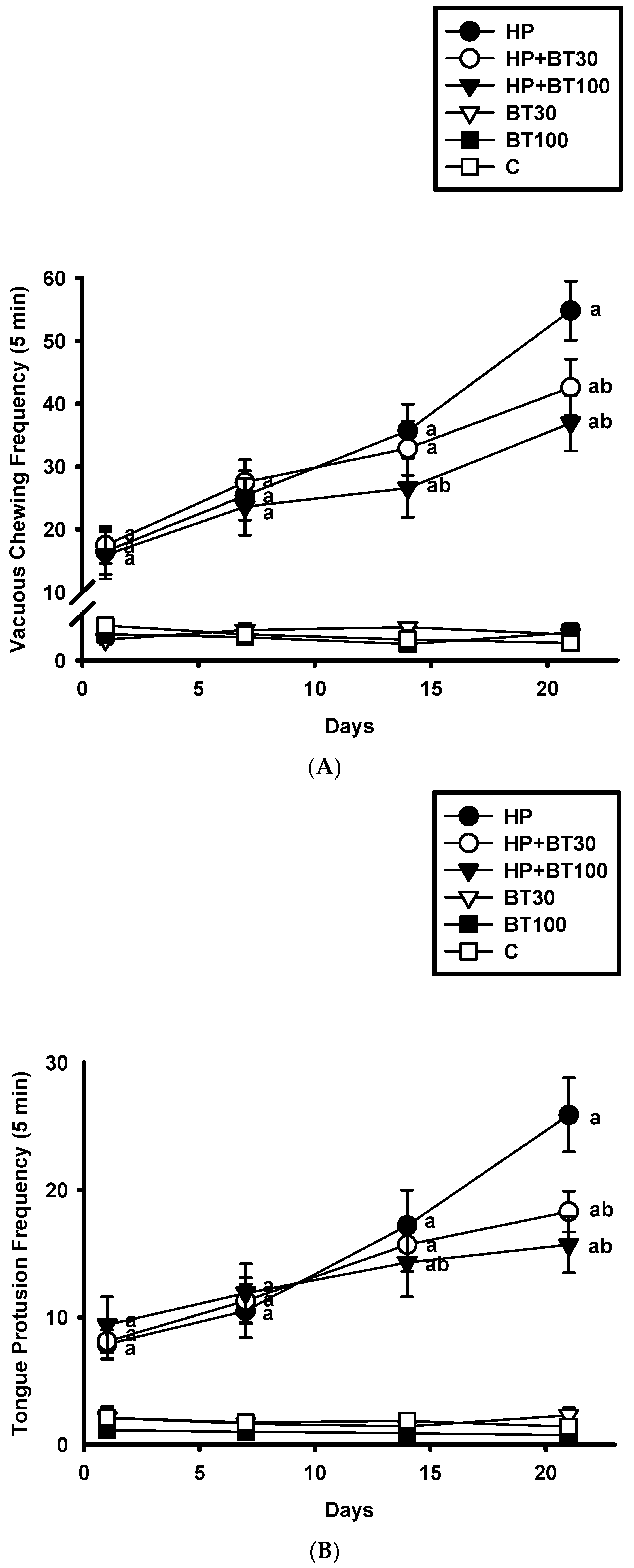
3.1. Effect of BT on the HP-Induced Increases in the Frequency of VCM and TP
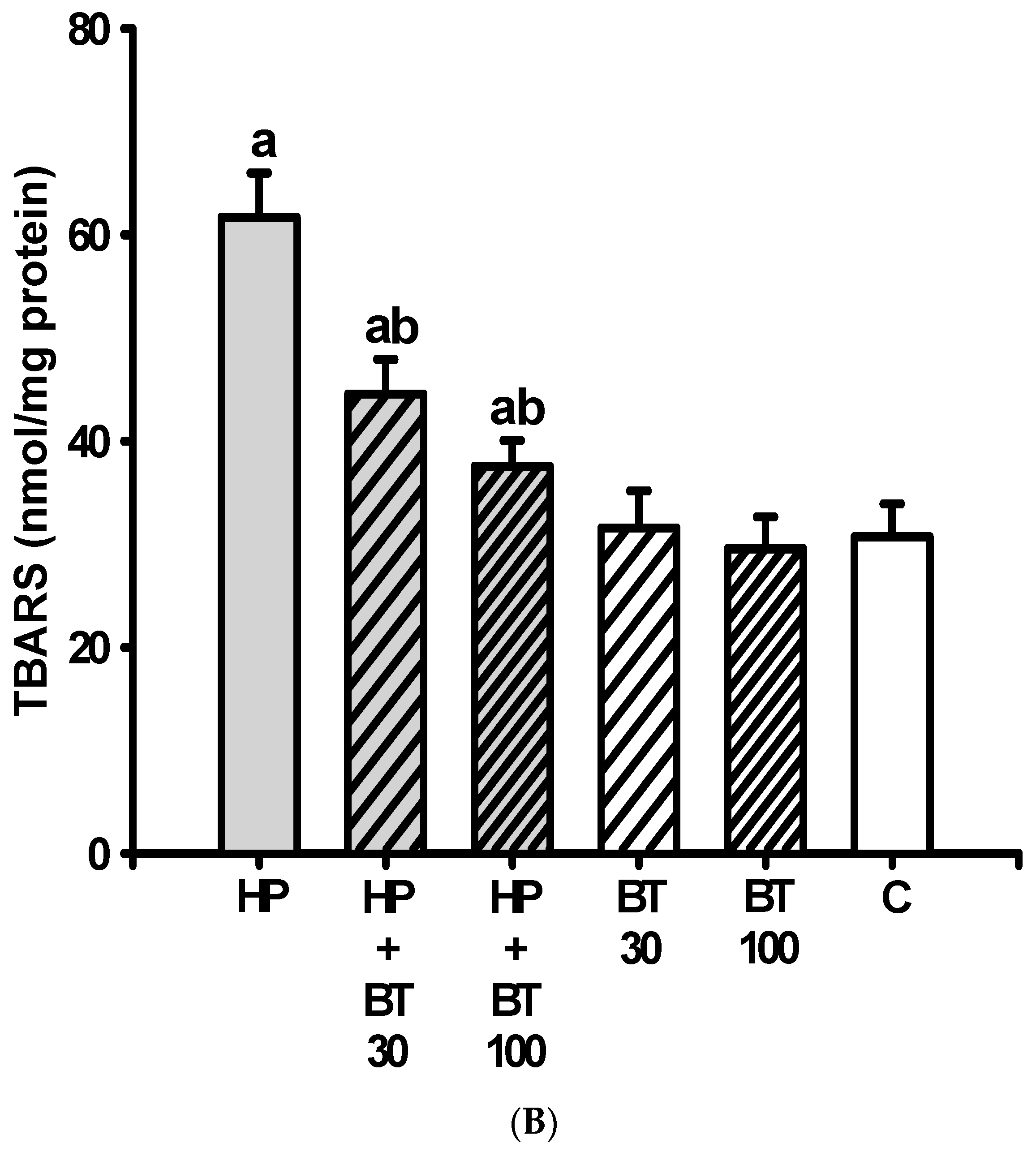
3.2. Effect of BT on the HP-Induced Increases in Striatal Nitric Oxide and Lipid Peroxide Production
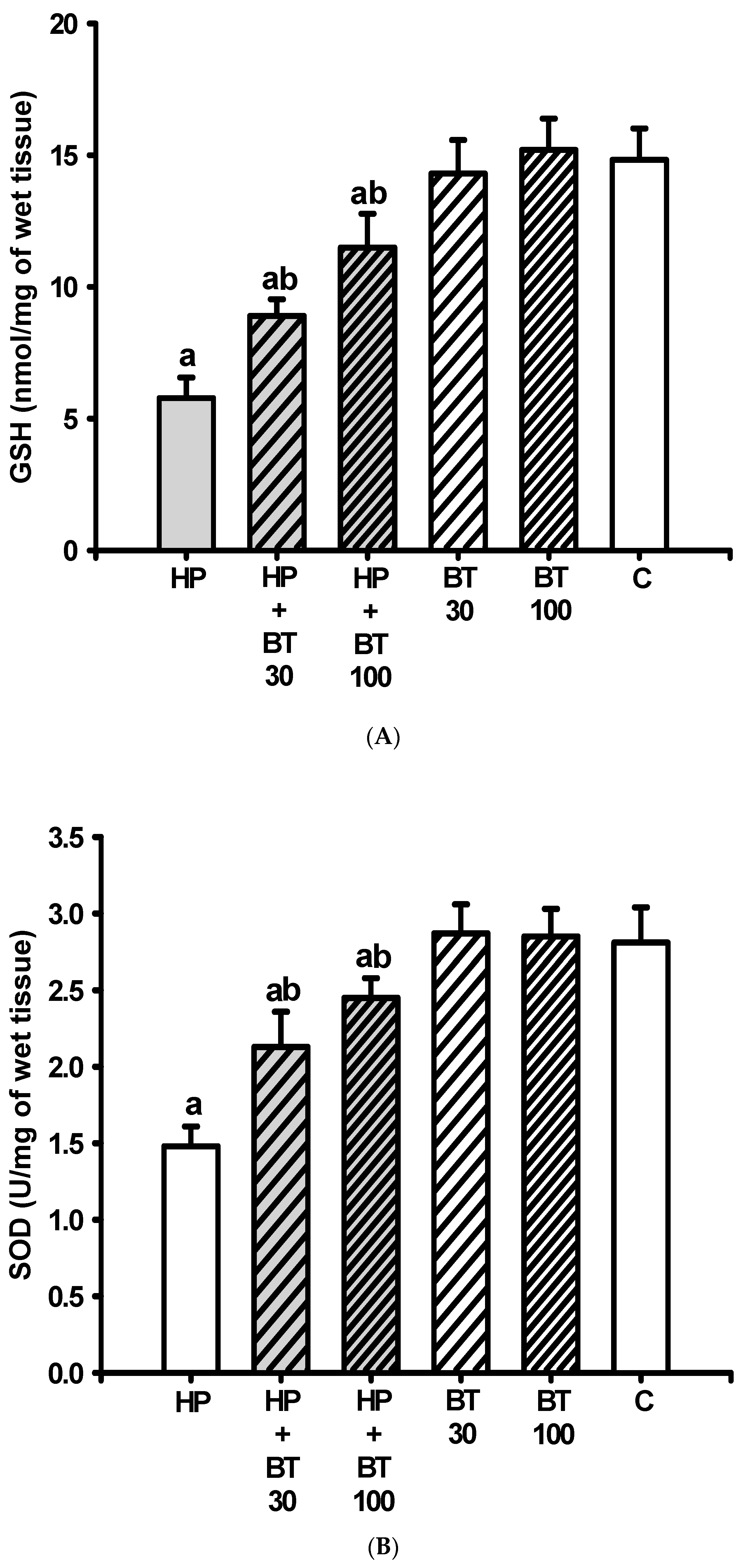
3.3. Effect of BT on the HP-Induced Decreases in Striatal Antioxidation Power
3.4. Effect of BT on the HP-Induced Striatal Mitochondrial Dysfunction
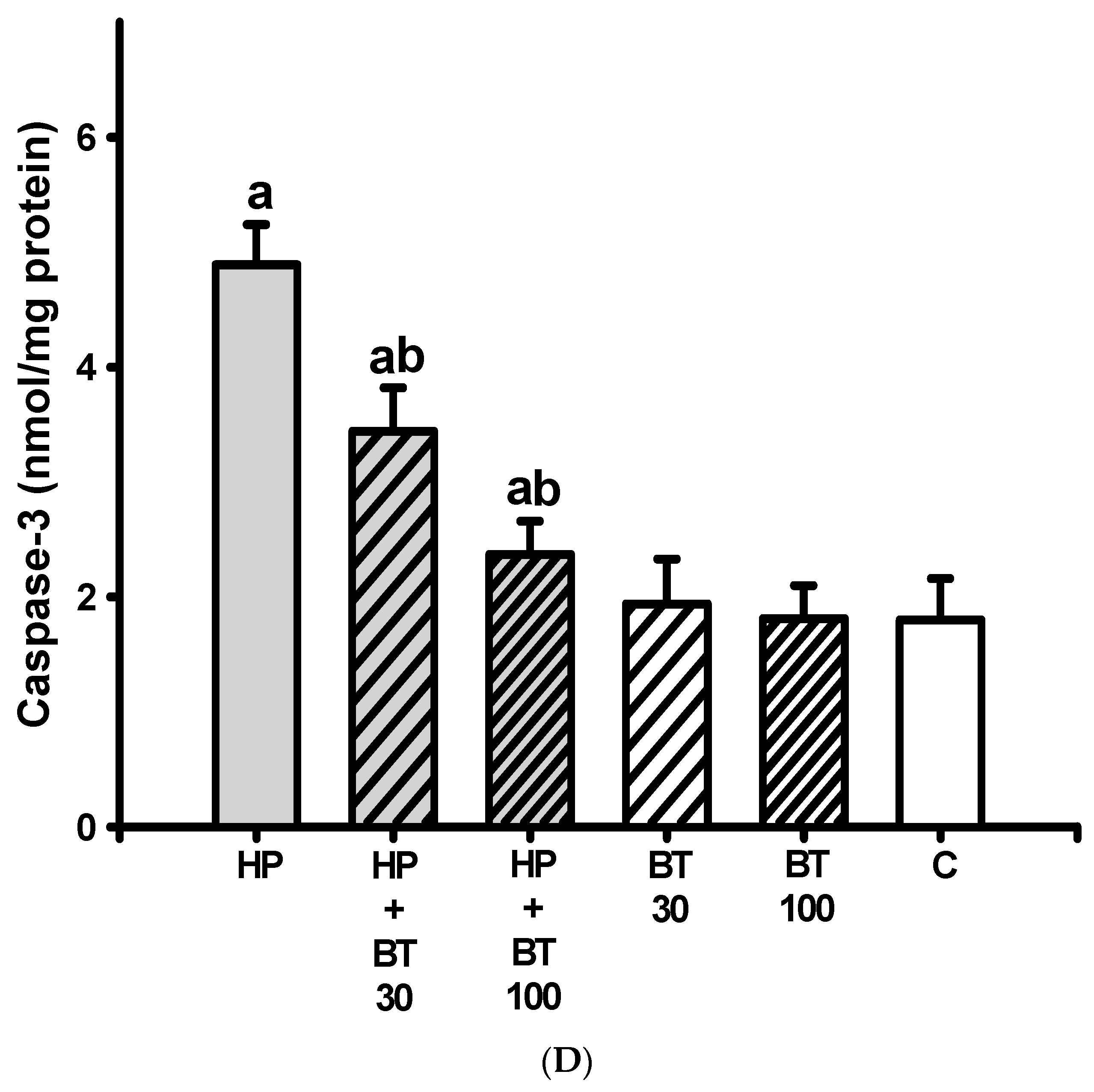
3.5. Effect of BT on the HP-Induced Increases in Striatal Neuroinflammatory and Apoptotic Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasan, S.; Padhy, R.K. Tardive Dyskinesia. In StatPearls; Disclosure: Ranjit Padhy Declares No Relevant Financial Relationships with Ineligible Companies; Ineligible Companies: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Stegmayer, K.; Walther, S.; van Harten, P. Tardive Dyskinesia Associated with Atypical Antipsychotics: Prevalence, Mechanisms and Management Strategies. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzen, F.P.; Cavalcanti, J.; Cavalcanti, D.; de Sales, L.G.P.; da Silva, M.S.M.; da Silva, A.N.A.; Pinheiro, F.I.; de Araujo, D.P. Haloperidol-Induced Preclinical Tardive Dyskinesia Model in Rats. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2019, 88, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, M.; Chopra, K.; Kulkarni, S.K. Activation of striatal inflammatory mediators and caspase-3 is central to haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 590, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.N.; Chang, K.C.; Wang, M.H.; Tseng, H.C.; Soung, H.S. Protective Effect of L-Theanine on Haloperidol-Induced Orofacial. Chin. J. Physiol. 2018, 61, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Jamwal, S.; Deshmukh, R.; Kumar, P. Beneficial effects of lycopene against haloperidol induced orofacial dyskinesia in rats: Possible neurotransmitters and neuroinflammation modulation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 771, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, D.; Goswami, S.; Gahalain, N. Protective effect of hesperetin against haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia and catalepsy in rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, J.J.; Roberts, R.C. Effects of haloperidol on cholinergic striatal interneurons: Relationship to oral dyskinesias. J. Neural Transm. 2004, 111, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, G.; Casu, M.A.; Bartholini, F.; Ruiu, S.; Saba, P.; Gessa, G.L.; Pani, L. Sub-chronic treatment with classical but not atypical antipsychotics produces morphological changes in rat nigro-striatal dopaminergic neurons directly related to “early onset” vacuous chewing. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzomo, N.F.; da Silva Schmitz, I.; de Lima, V.B.; Dorneles, G.P.; Schaffer, L.F.; Boeck, C.R.; Romao, P.R.T.; Peroza, L.R. Reversal of haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia and neuroinflammation by isoflavones. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.C.; Wang, M.H.; Chang, K.C.; Soung, H.S.; Yang, C.C.; Tseng, H.C. Possible nitric oxide mechanism involved in the protective effect of L-theanine on haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia. Chin. J. Physiol. 2019, 62, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Yang, C.C.; Tseng, H.C.; Fang, C.H.; Lin, Y.W.; Soung, H.S. Naringin Ameliorates Haloperidol-Induced Neurotoxicity and Orofacial Dyskinesia in a Rat Model of Human Tardive Dyskinesia. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.K.; Paal, M.C.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Ganesan, M.; Osna, N.A.; Kharbanda, K.K. Beneficial Effects of Betaine: A Comprehensive Review. Biology 2021, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, S.A. Betaine in human nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, M.; Di Iacovo, A.; Romanazzi, T.; Roseti, C.; Bossi, E. Betaine-The dark knight of the brain. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, L.S.; Piibe, Q.; Lambie, I.; Perkins, C.; Yancey, P.H. Betaine in the Brain: Characterization of Betaine Uptake, its Influence on Other Osmolytes and its Potential Role in Neuroprotection from Osmotic Stress. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3490–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Betaine in Inflammation: Mechanistic Aspects and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.; Peng, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, D.; Cao, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, S. Betaine attenuate chronic restraint stress-induced changes in testicular damage and oxidative stress in male mice. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2022, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Rodriguez, J.A.; Valenzuela-Soto, E.M. The glycine betaine role in neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, hepatic, and renal diseases: Insights into disease and dysfunction networks. Life Sci. 2021, 285, 119943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkudelska, K.; Szkudelski, T. The anti-diabetic potential of betaine. Mechanisms of action in rodent models of type 2 diabetes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Lai, F.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Min, T.; Wu, H. Antioxidant Mechanism of Betaine without Free Radical Scavenging Ability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7921–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.L.; Shi, H.; Meng, L.Q.; Quan, H.F.; Yan, L.; Yang, H.F.; Peng, X.D. Betaine Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Hyperactivation and Regulates Microglial M1/M2 Phenotypic Differentiation, Thereby Attenuating Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-Like Behavior. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 9313436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.T.; Hsieh, C.P.; Lee, M.Y.; Chen, L.C.; Huang, C.M.; Chen, H.H.; Chan, M.H. Betaine prevents and reverses the behavioral deficits and synaptic dysfunction induced by repeated ketamine exposure in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramipour, P.; Asghari, A.; Hassanpour, S.; Jahandideh, A. Anti-depressant Effect of Betaine Mediates via Nitrergic and Serotoninergic Systems in Ovariectomized Mice. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 1404–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibi, D.; Kondo, S.; Ohmi, A.; Kojima, Y.; Nakasai, G.; Takaba, R.; Hiramatsu, M. Preventive Effect of Betaine Against Cognitive Impairments in Amyloid beta Peptide-Injected Mice Through Sirtuin1 in Hippocampus. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyhoonabadi, M.; Alimoahmmadi, S.; Hassanpour, S.; Hashemnia, M. Betaine Ameliorates Depressive-Like Behaviors in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Exposed Mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4771–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Qu, M.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Fan, G.; Yang, C. Betaine protects rats against ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced brain damage. J. Neurophysiol. 2022, 127, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, P.; Boz, Z.; Tang, R.; Zheng, K.; Yu, Y.; Huang, X.F. Resveratrol prevents haloperidol-induced mitochondria dysfunction through the induction of autophagy in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurotoxicology 2021, 87, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budantsev, A.; Kisliuk, O.S.; Shul’govskii, V.V.; Rykunov, D.S.; Iarkov, A.V. The brain in stereotaxic coordinates (a textbook for colleges). Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deiatelnosti Imeni IP Pavlova 1993, 43, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Bilska, A.; Dubiel, M.; Sokolowska-Jezewicz, M.; Lorenc-Koci, E.; Wlodek, L. Alpha-lipoic acid differently affects the reserpine-induced oxidative stress in the striatum and prefrontal cortex of rat brain. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1758–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, H.P.; Fridovich, I. The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 3170–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, R.F., Jr.; Sizer, I.W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, R.J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem. J. 1961, 80, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.N.; Muralidhara. Neuroprotective efficacy of eugenol and isoeugenol in acrylamide-induced neuropathy in rats: Behavioral and biochemical evidence. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Gomez, C.; Lopez-Cepero, J.M.; Boveris, A. Beneficial effects of moderate exercise on mice aging: Survival, behavior, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial electron transfer. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 286, R505–R511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Lee, H.J. Oxidative stress and tardive dyskinesia: Pharmacogenetic evidence. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 46, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudenska, M.; Gumulec, J.; Babula, P.; Stracina, T.; Sztalmachova, M.; Polanska, H.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Novakova, M.; Masarik, M. Haloperidol cytotoxicity and its relation to oxidative stress. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cikankova, T.; Fisar, Z.; Bakhouche, Y.; Luptak, M.; Hroudova, J. In vitro effects of antipsychotics on mitochondrial respiration. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rego, A.C.; Oliveira, C.R. Mitochondrial dysfunction and reactive oxygen species in excitotoxicity and apoptosis: Implications for the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2003, 28, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonnum, F.; Lock, E.A. The contributions of excitotoxicity, glutathione depletion and DNA repair in chemically induced injury to neurones: Exemplified with toxic effects on cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korhonen, R.; Lahti, A.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soung, H.S.; Wang, M.H.; Chang, K.C.; Chen, C.N.; Chang, Y.; Yang, C.C.; Tseng, H.C. (L)-Theanine Decreases Orofacial Dyskinesia Induced by Reserpine in Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 34, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, H.-C.; Wang, M.-H.; Fang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-W.; Soung, H.-S. Involvement of Antioxidant and Prevention of Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect and Anti-Apoptotic Effect: Betaine Ameliorates Haloperidol-Induced Orofacial Dyskinesia in Rats. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071064
Tseng H-C, Wang M-H, Fang C-H, Lin Y-W, Soung H-S. Involvement of Antioxidant and Prevention of Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect and Anti-Apoptotic Effect: Betaine Ameliorates Haloperidol-Induced Orofacial Dyskinesia in Rats. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(7):1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071064
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Hsiang-Chien, Mao-Hsien Wang, Chih-Hsiang Fang, Yi-Wen Lin, and Hung-Sheng Soung. 2023. "Involvement of Antioxidant and Prevention of Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect and Anti-Apoptotic Effect: Betaine Ameliorates Haloperidol-Induced Orofacial Dyskinesia in Rats" Brain Sciences 13, no. 7: 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071064
APA StyleTseng, H.-C., Wang, M.-H., Fang, C.-H., Lin, Y.-W., & Soung, H.-S. (2023). Involvement of Antioxidant and Prevention of Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effect and Anti-Apoptotic Effect: Betaine Ameliorates Haloperidol-Induced Orofacial Dyskinesia in Rats. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071064




