C-Reactive Protein Levels and Cognitive Decline following Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies and Quality Assessments
3.3. CRP Level at Baseline of Stroke and Cognitive Impairment
3.3.1. Meta-Analysis
3.3.2. Meta-Regression
3.3.3. Subgroup Analysis
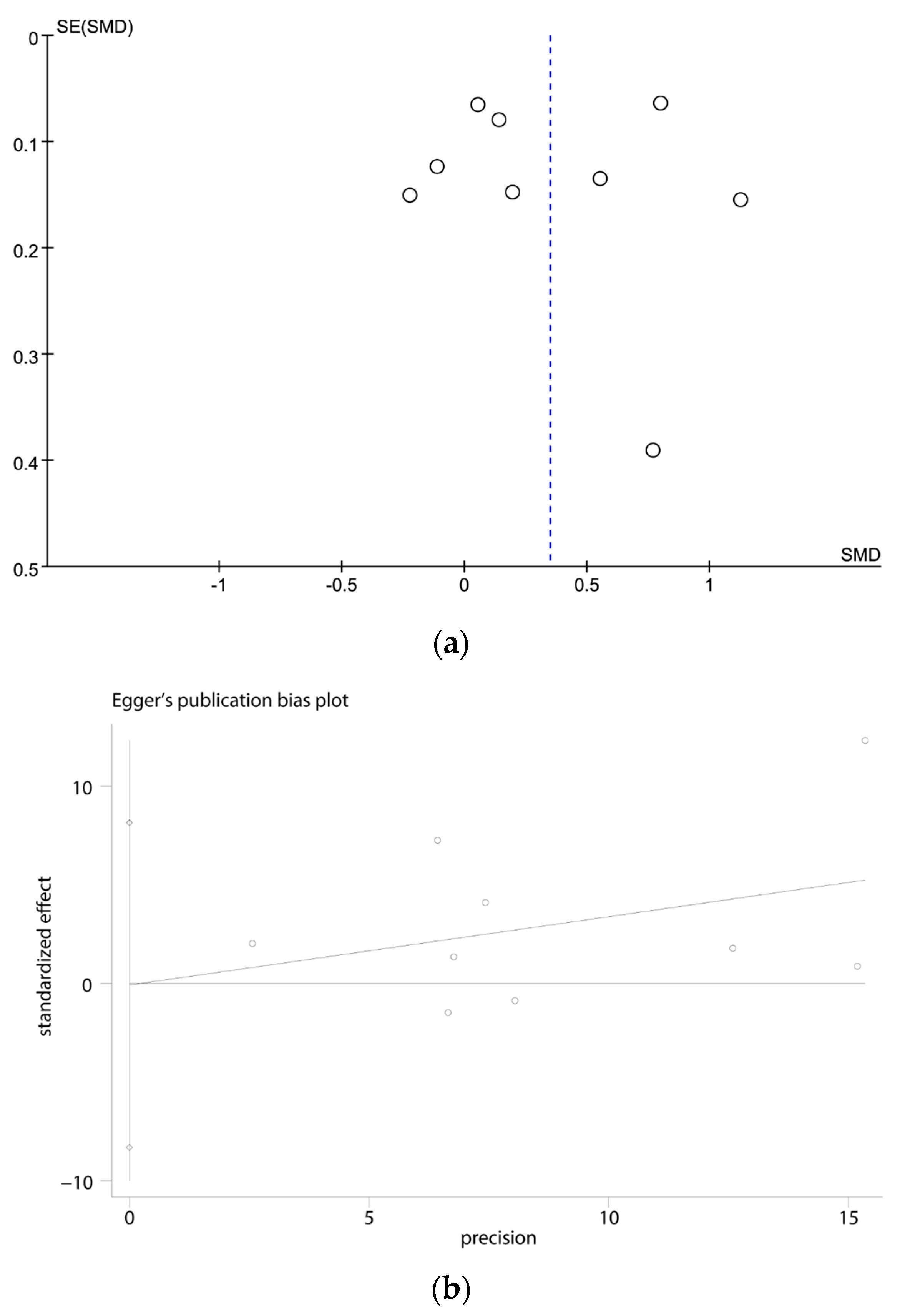
3.4. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mok, V.C.; Lam, B.Y.; Wong, A.; Ko, H.; Markus, H.S.; Wong, L.K. Early-onset and delayed-onset poststroke dementia-revisiting the mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Chan, B.P.; Sharma, V.K.; Slavin, M.J.; Collinson, S.L.; Sachdev, P.; Chan, Y.H.; Chen, C.L. Brief screening tests during acute admission in patients with mild stroke are predictive of vascular cognitive impairment 3-6 months after stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendlebury, S.T.; Rothwell, P.M. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.Y.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.L.; Fang, C.Q.; Deng, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.Q.; Zhou, H.D.; Wang, Y.J. Association of dementia with death after ischemic stroke: A two-year prospective study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1765–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Wan, L.; Gao, Y.; Huang, M.; Zha, F.; Long, J.; Li, D.; Nie, G.; Wang, Y. A novel Longshi Scale measured activity of daily living disability in elderly patients affected by neurological diseases: A multi-center cross-sectional study in China. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhou, L.; Deng, B. Association Between Early Cognitive Impairment and Midterm Functional Outcomes Among Chinese Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Longitudinal Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withiel, T.D.; Stolwyk, R.J.; Ponsford, J.L.; Cadilhac, D.A.; Wong, D. Effectiveness of a manualised group training intervention for memory dysfunction following stroke: A series of single case studies. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 3033–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelouei, T.; Abbasifard, M.; Imani, D.; Aslani, S.; Razi, B.; Fasihi, M.; Shafiekhani, S.; Mohammadi, K.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Reiner, Ž.; et al. Effect of Statins on Serum level of hs-CRP and CRP in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 8732360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fan, C.; Pan, L.; Xie, M.; He, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, S. C-reactive protein plays a marginal role in cognitive decline: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2015, 30, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek-Bal, A.; Jedrzejowska-Szypulka, H.; Student, S.; Warsz-Wianecka, A.; Zareba, K.; Puz, P.; Bal, W.; Pawletko, K.; Lewin-Kowalik, J. The importance of selected markers of inflammation and blood-brain barrier damage for short-term ischemic stroke prognosis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, G.; Baboolal, N.; Nayak, S.; McRae, A. Sialic acid, homocysteine and CRP: Potential markers for dementia. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 465, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, F.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Serum Uric Acid and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein as Predictors of Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cerebral Infarction. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2020, 49, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Li, G.; Lv, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Kang, J.; Zhan, C. Association of plasma trimethylamine-N-oxide levels with post-stroke cognitive impairment: A 1-year longitudinal study. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Chen, X.H.; Zhuang, J.H.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.C.; Ma, Y.J.; He, B.; Yin, Y. Relationship between β-amyloid protein 1-42, thyroid hormone levels and the risk of cognitive impairment after ischemic stroke. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, S.; Zhao, X.; Steele, R.; Thombs, B.D.; Benedetti, A. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from commonly reported quantiles in meta-analysis. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2020, 29, 2520–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, T.; Kawamoto, M.; Meguro, M.; Shibata, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Furuhata, T.; Sonoda, T.; Hirata, K. Laparoscopic hepatectomy: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and power analysis. Surg. Today 2011, 41, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muncer, S.; Taylor, S.; Craigie, M. Power dressing and meta-analysis: Incorporating power analysis into meta-analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2002, 38, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, M. Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase as a predictor of cognitive impairment in patients with acute ischaemic stroke: A retrospective cohort study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 89, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrova, M.L.; Danovska, M.P. Cognitive impairment one year after ischemic stroke: Predictorsand dynamics of significant determinants. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Ding, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Zou, C.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, D. Serum Retinoic Acid Level and The Risk of Poststroke Cognitive Impairment in Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhong, C.; Guo, D.; Bu, X.; Xu, T.; Guo, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Multiple biomarkers covering several pathways improve predictive ability for cognitive impairment among ischemic stroke patients with elevated blood pressure. Atherosclerosis 2019, 287, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.S.; Liang, J.H.; Yang, M.J.; Ren, Y.R.; Cheng, D.H.; Wu, Q.H.; He, Y.; Yin, J. Low Serum Superoxide Dismutase Is Associated With a High Risk of Cognitive Impairment After Mild Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 834114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Su, W.; Fang, J.; Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; He, L. Elevated CRP at admission predicts post-stroke cognitive impairment in Han Chinese patients with intracranial arterial stenosis. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihle-Hansen, H.; Thommessen, B.; Wyller, T.B.; Engedal, K.; Øksengård, A.R.; Stenset, V.; Løken, K.; Aaberg, M.; Fure, B. Incidence and subtypes of MCI and dementia 1 year after first-ever stroke in patients without pre-existing cognitive impairment. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2011, 32, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Ding, B.; Yang, X.; Bai, S.; Tu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Tao, J.; Jin, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. The current situation on vascular cognitive impairment after ischemic stroke in Changsha. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 58, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, C.; Ji, Y.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, W. Association between Systemic Immune Inflammation Index and Cognitive Impairment after Acute Ischemic Stroke. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Biesbroek, J.M.; Shi, L.; Liu, W.; Kuijf, H.J.; Chu, W.W.; Abrigo, J.M.; Lee, R.K.; Leung, T.W.; Lau, A.Y.; et al. Strategic infarct location for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A multivariate lesion-symptom mapping study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falck, R.S.; Best, J.R.; Davis, J.C.; Eng, J.J.; Middleton, L.E.; Hall, P.A.; Liu-Ambrose, T. Sleep and cognitive function in chronic stroke: A comparative cross-sectional study. Sleep 2019, 42, zsz040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichgans, M.; Leys, D. Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Bi, X. Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: A Review Focusing on Molecular Biomarkers. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijajlović, M.D.; Pavlović, A.; Brainin, M.; Heiss, W.D.; Quinn, T.J.; Ihle-Hansen, H.B.; Hermann, D.M.; Assayag, E.B.; Richard, E.; Thiel, A.; et al. Post-stroke dementia—A comprehensive review. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhalu, K.; Lee, J.; Leong, Y.L.; Ma, L.; De Silva, D.A.; Wong, M.C.; Chang, H.M.; Chen, C. Inflammatory markers and their association with post stroke cognitive decline. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaka, T.P.; Hombach, V.; Torzewski, J. C-reactive protein-mediated low density lipoprotein uptake by macrophages: Implications for atherosclerosis. Circulation 2001, 103, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Li, S.H.; Weisel, R.D.; Fedak, P.W.; Dumont, A.S.; Szmitko, P.; Li, R.K.; Mickle, D.A.; Verma, S. C-reactive protein upregulates angiotensin type 1 receptors in vascular smooth muscle. Circulation 2003, 107, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.K.; Yen, C.J.; Chang, C.H.; Kuo, C.K.; Chen, J.H.; Sorond, F. Relation of C-reactive protein to stroke, cognitive disorders, and depression in the general population: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, Z.; He, F.; Lin, C.; Topatana, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Evaluation of the Mini-Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment for Predicting Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment During the Acute Phase in Chinese Minor Stroke Patients. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Chen, X.; Li, Z. Diagnostic test accuracy of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment in the detection of post-stroke cognitive impairment under different stages and cutoffs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoops, S.; Nazem, S.; Siderowf, A.D.; Duda, J.E.; Xie, S.X.; Stern, M.B.; Weintraub, D. Validity of the MoCA and MMSE in the detection of MCI and dementia in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2009, 73, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.C.C.; Machado, L.; Bulgacov, T.M.; Rodrigues-Júnior, A.L.; Costa, M.L.G.; Ximenes, R.C.C.; Sougey, E.B. Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) screening superior to the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in the detection of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) in the elderly? Int. Psychogeriatr. 2019, 31, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, X. Plasma C-reactive protein is related to cognitive deterioration and dementia in patients with mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 284, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jing, J.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.; Yan, H.; Meng, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Wang, D.Z.; et al. Association of elevated hs-CRP and multiple infarctions with outcomes of minor stroke or TIA: Subgroup analysis of CHANCE randomised clinical trial. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2021, 6, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CD | Non-CD | CRP Level (Mean ± SD, mg/dL) | Hs-CRP Level (Mean ± SD, mg/dL) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Year | Ref. | Country | Research Type | Numbers (n) | Numbers (n) | Total Numbers (n) | Male Sex, n (%) | CD | Non-CD | CD | Non-CD | Cognitive Evaluation Time | Scale | Source of CRP | Sample Collection Time | NOS |
| Chen Zhu | 2020 | [14] | China | prospective study | 86 | 170 | 256 | 139 (54) | / | / | 6.6 ± 5.1 | 4.2 ± 3.9 | after 1 year | MMSE | plasma | within 24 h after admission | 8 |
| Fang Ran | 2020 | [13] | China | prospective study | 82 | 115 | 197 | 84 (43) | 10.7 ± 5.3 | 6.2 ± 2.7 | NA | MoCA | serum | at admission | 8 | ||
| He Jia | 2020 | [24] | China | retrospective study | 523 | 496 | 1019 | 531 (52) | 6.7 ± 4.6 | 3.2 ± 4.1 | / | / | 3 months poststroke | MMSE | serum | within 24 h of admission | 7 |
| Jian Guo | 2018 | [29] | China | prospective study | 326 | 790 | 1116 | 631 (57) | 21.4 ± 17.2 | 20.4 ± 17.6 | / | / | 6 months after stroke | the Six-Item Screener | Serum | within one week of stroke onset | 9 |
| Le Hou | 2019 | [26] | China | prospective study | 141 | 120 | 261 | 140 (54) | / | / | 5.7 ± 4.6 | 6.3 ± 6.5 | 3 months After the stroke | MoCA | serum | in the morning after admission | 8 |
| Lei Mao | 2020 | [15] | China | prospective study | 72 | 116 | 188 | 117 (62) | / | / | 4.8 ± 4.6 | 6.2 ± 7.1 | 1 year after stroke | MoCA | serum | within 24 h of admission | 8 |
| M.L Alexandrova | 2016 | [25] | Bulgaria | prospective study | 20 | 11 | 31 | 16 (52) | / | / | 17.5 ± 24.5 | 1.9 ± 1.1 | 12 months After the stroke | MMSE | serum | at admission | 7 |
| Mingsi Zhang | 2022 | [28] | China | prospective study | 105 | 82 | 187 | 148 (79) | 1.37 ± 2.48 | 0.9 ± 2.5 | / | / | within 2 weeks | MoCA | serum | at admission | 8 |
| Zhengbao Zhu | 2019 | [27] | China | prospective study | 340 | 298 | 638 | 448 (70) | / | / | 2.6 ± 3.0 | 2.2 ± 2.6 | 3 months after acute ischemic stroke | MMSE | serum | within 24 h of hospital admission | 8 |
| Studies | Comparison Statistics | Heterogeneity | p-Value between Subgroups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMD | 95% CI | Z | p-Value | Q | df | p-Value | I2 (%) | |||
| CD VS non-CD | ||||||||||
| Scales for cognitive assessment | ||||||||||
| MMSE | 4 | 0.54 | 0.13, 0.94 | 2.59 | 0.01 | 41.58 | 3 | <0.01 | 93 | 0.24 |
| Other kinds of scales | 5 | 0.20 | −0.18, 0.58 | 1.05 | 0.29 | 51.39 | 4 | <0.01 | 92 | |
| Detection sensitivity of CRP | ||||||||||
| CRP | 3 | 0.36 | −0.19, 0.90 | 1.29 | 0.20 | 66.86 | 2 | <0.01 | 97 | 0.97 |
| Hs-CRP | 6 | 0.34 | −0.04, 0.72 | 1.77 | 0.08 | 58.27 | 5 | <0.01 | 91 | |
| Research types | ||||||||||
| Prospective study | 8 | 0.27 | 0.02, 0.53 | 2.11 | 0.03 | 62.88 | 7 | <0.01 | 89 | / |
| Retrospective study | 1 | 0.80 | 0.67, 0.93 | 12.30 | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Sample size | ||||||||||
| N < 500 | 6 | 0.36 | −0.07, 0.79 | 1.66 | 0.10 | 56.22 | 5 | <0.01 | 91 | 0.94 |
| N ≥ 500 | 3 | 0.33 | −0.15, 0.82 | 1.36 | 0.17 | 74.62 | 2 | <0.01 | 97 | |
| Source of CRP | ||||||||||
| serum | 8 | 0.32 | 0.00, 0.64 | 1.98 | 0.05 | 129.09 | 7 | <0.01 | 95 | / |
| plasma | 1 | 0.55 | 0.29, 0.82 | 4.10 | / | / | / | / | / | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Pu, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Chen, Q.; Pu, F.; Bai, D. C-Reactive Protein Levels and Cognitive Decline following Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071082
Wang L, Yang L, Liu H, Pu J, Li Y, Tang L, Chen Q, Pu F, Bai D. C-Reactive Protein Levels and Cognitive Decline following Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(7):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071082
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Likun, Lining Yang, Haiyan Liu, Juncai Pu, Yi Li, Lu Tang, Qing Chen, Fang Pu, and Dingqun Bai. 2023. "C-Reactive Protein Levels and Cognitive Decline following Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Brain Sciences 13, no. 7: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071082
APA StyleWang, L., Yang, L., Liu, H., Pu, J., Li, Y., Tang, L., Chen, Q., Pu, F., & Bai, D. (2023). C-Reactive Protein Levels and Cognitive Decline following Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071082








