The Role of Ketone Bodies in Treatment Individualization of Glioblastoma Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aims and Scope
2.2. Patients
2.3. Parameters Measured
2.4. Assessment of the Clinical Condition
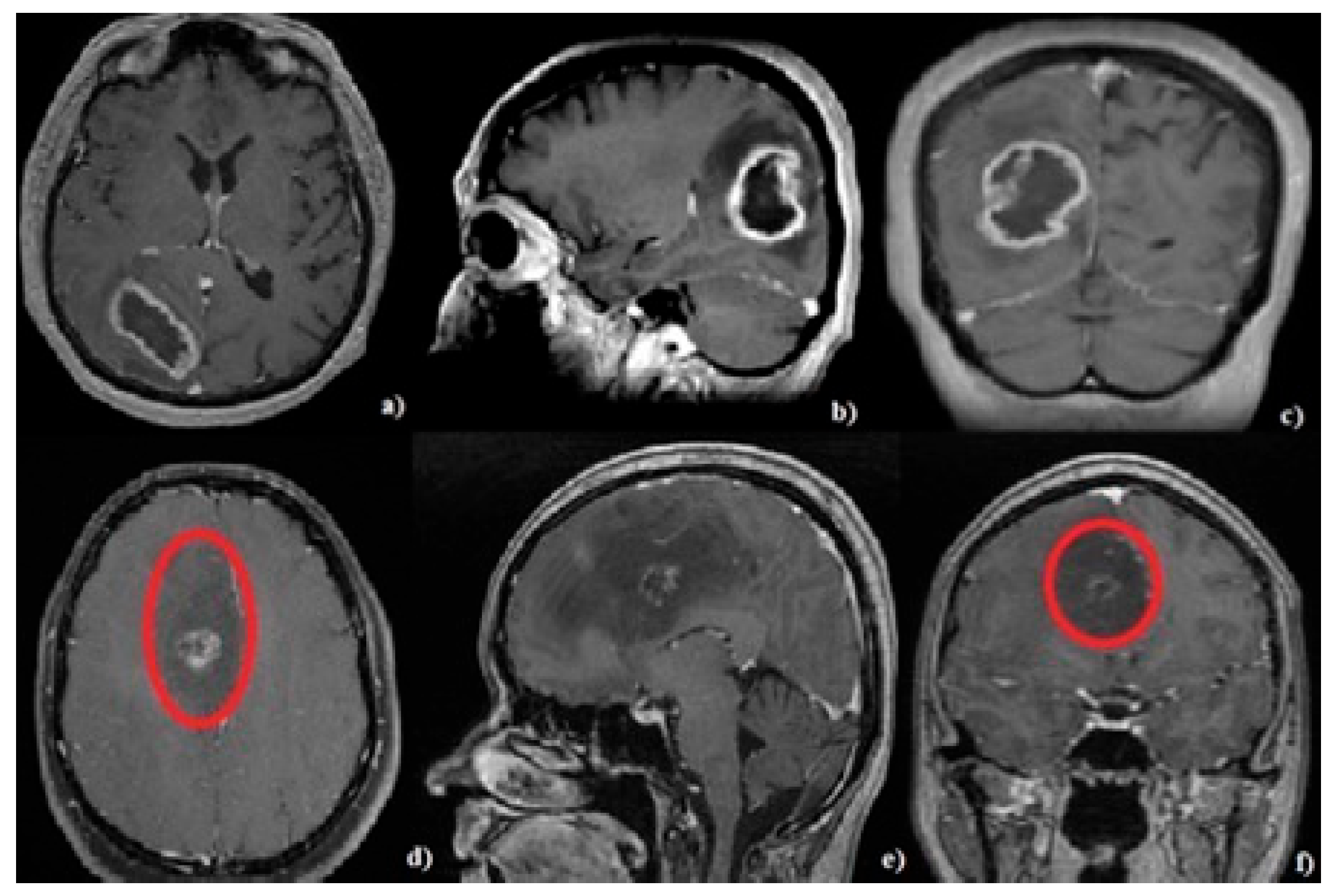
2.5. Neuroimaging Evaluation
2.6. Specific Medical Management
2.7. Surgical Management
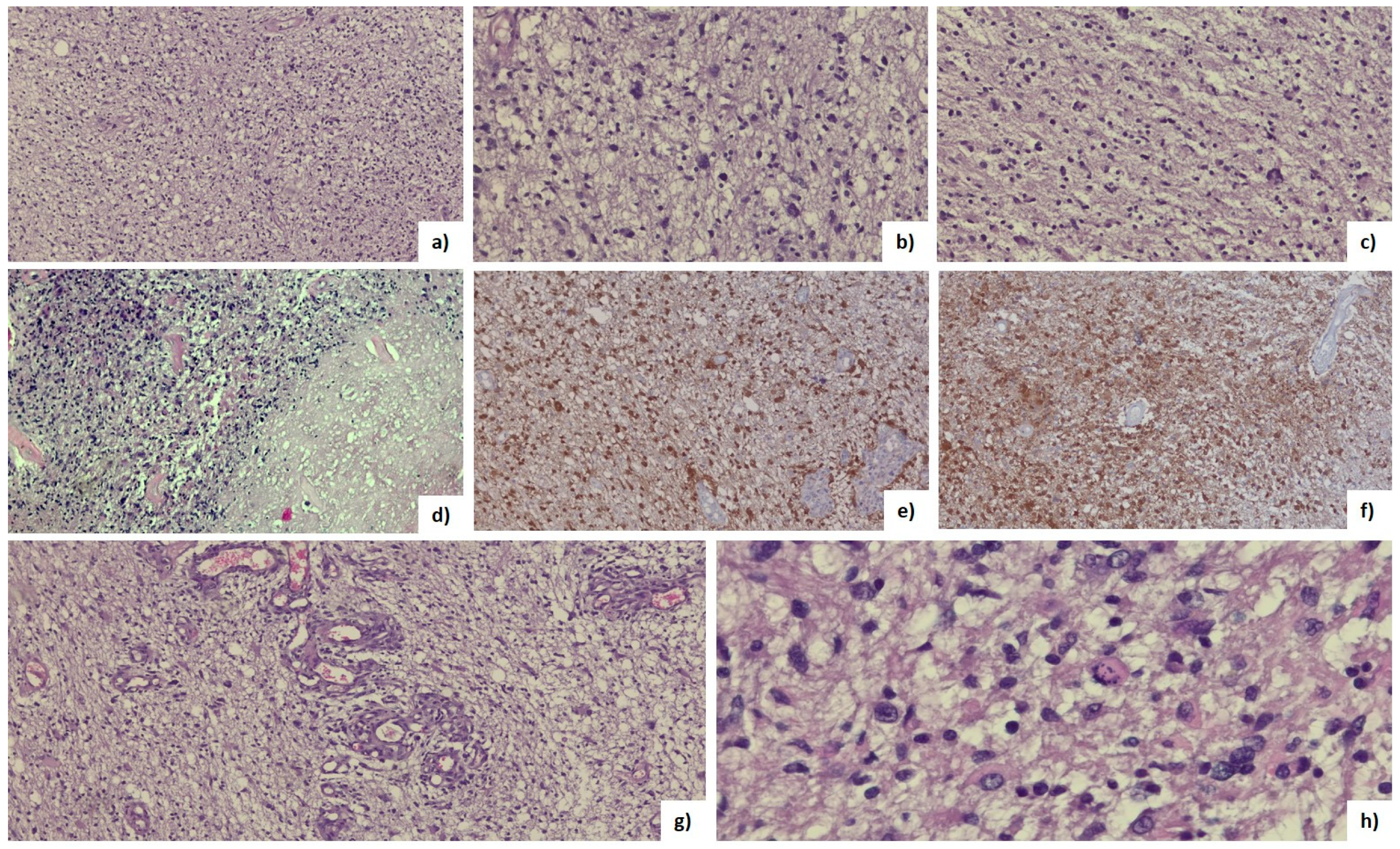
2.8. Histopathological Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Clinical Features
3.2. Specific Clinical Features
3.3. Tumor Characteristics
3.4. Histopathological Features
3.5. Postoperative Death
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Sizoo, E.M.; Bottomley, A. Review on Quality of Life Issues in Patients with Primary Brain Tumors. Oncologist 2010, 15, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Song, K.; Wu, S.; Hameed, N.U.F.; Kudulaiti, N.; Xu, H.; Wu, J.S.; Qin, Z.Y. The prognosis of glioblastoma: A large, multifactorial study. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 35, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwens van der Vlis, T.A.M.; Kros, J.M.; Mustafa, D.A.M.; van Wijck, R.T.A.; Ackermans, L.; van Hagen, P.M.; van der Spek, P.J. The complement system in glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroon, J.; Seyfried, T.; Donohue, J.; Bost, J. The role of metabolic therapy in treating glioblastoma multiforme. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Flores, R.; Poff, A.M.; D’Agostino, D.P.; Mukherjee, P. Metabolic therapy: A new paradigm for managing malignant brain cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Farah, P.; Ondracek, A.; Chen, Y.; Wolinsky, Y.; Stroup, N.E.; Kruchko, C.; Jill, S.B.S. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro-oncology 2013, 15, ii1–ii56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, A.; Henshaw, D.L.; Lamburn, G.; O’Carroll, M.J. Brain tumours: Rise in glioblastoma multiforme incidence in England 1995–2015 Suggests an Adverse Environmental or Lifestyle Factor. J. Environ. Public Health 2018, 2018, 7910754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodbelt, A.; Greenberg, D.; Winters, T.; Williams, M.; Vernon, S.; Collins, V.P. Glioblastoma in England: 2007–2011. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsakka, A.M.A.; Bary, M.A.; Abdelzaher, E.; Elnaggar, M.; Kalamian, M.; Mukherjee, P.; Seyfried, T.N. Management of Glioblastoma Multiforme in a Patient Treated With Ketogenic Metabolic Therapy and Modified Standard of Care: A 24-Month Follow-Up. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Pradhan, S.; Srivastava, T. Recent advances in targeted therapy for glioblastoma. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Hiroko, O.; Otmar, D.W.; Paul, K.; David, W.E. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cynthia, H.; Ng, H.K.; Stefan, M.P.; Guido, R.; et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Neuro-oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gooijer, M.C.; Guillén Navarro, M.; Bernards, R.; Wurdinger, T.; van Tellingen, O. An Experimenter’s Guide to Glioblastoma Invasion Pathways. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 763–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencheva, N.; de Gooijer, M.C.; Vis, D.J.; Wessels, L.F.A.; Würdinger, T.; van Tellingen, O.; Rene, B. Identification of a Druggable Pathway Controlling Glioblastoma Invasiveness. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalma, S.; Turpault, S.; Balandre, A.C.; De Boisvilliers, M.; Gaillard, A.; Chadéneau, C.; Jean, M.M. PKA at a Cross-Road of Signaling Pathways Involved in the Regulation of Glioblastoma Migration and Invasion by the Neuropeptides VIP and PACAP. Cancers 2019, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.; Stoll, E.A. Metabolic Reprogramming in Glioma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 26, 5–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Zadeh, G. Metabolic reprogramming in glioblastoma: The influence of cancer metabolism on epigenetics and unanswered questions. Neuro-oncology 2016, 18, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, K.; Onizuka, H.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mischel, P.S.; Shibata, N. Metabolic reprogramming in the pathogenesis of glioma: Update. Neuropathology 2019, 39, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.; Kong, G.; Gong, N.; Kwon, S.H.; Park, J. Revisiting the Warburg Effect: Diet-Based Strategies for Cancer Prevention. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 4, 8105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, E.C.; Syed, N.; Scheck, A.C. Tumor metabolism, the ketogenic diet and β-hydroxybutyrate: Novel approaches to adjuvant brain tumor therapy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, C. The role of OXCT1 in the pathogenesis of cancer as a rate-limiting enzyme of ketone body metabolism. Life Sci. 2017, 183, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duma, M.N.; Oszfolk, N.I.; Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Oechsner, M.; Zimmer, C.; Meyer, B.; Paul, T.P.; Stephanie, E.C. Positive correlation between blood glucose and radiotherapy doses to the central gustatory system in Glioblastoma Multiforme patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, C.; Ricci, C.; Meier, C.R.; Bodmer, M.; Jick, S.S.; Bogdahn, U.; Peter, U.; Michael, F.L. Diabetes, use of antidiabetic drugs, and the risk of glioma. Neuro-oncology 2016, 18, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caniglia, J.L.; Jalasutram, A.; Asuthkar, S.; Sahagun, J.; Park, S.; Ravindra, A.; Andrew, J.T.; Guda, M.R.; Kiran, K.V. Beyond glucose: Alternative sources of energy in glioblastoma. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, C.J.; Tran, A.N.; Scott, S.E.; Griguer, C.; Hjelmeland, A.B. The pro-tumorigenic effects of metabolic alterations in glioblastoma including brain tumor initiating cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2018, 1869, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.T.; Olson, L.K.; Schwartz, K.A. Ketolytic and glycolytic enzymatic expression profiles in malignant gliomas: Implication for ketogenic diet therapy. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Patel, S.; Affleck, V.S.; Wilson, I.; Turnbull, D.M.; Joshi, A.R.; Ross, M.; Elizabeth, A.S. Fatty acid oxidation is required for the respiration and proliferation of malignant glioma cells. Neuro-oncology 2017, 19, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, J.; Condro, M.C.; Guo, L.; Braas, D.; Vanderveer-Harris, N.; Kim, K.K.O.; Whitney, B.P.; Ajit, D.; Albert, L.; Heather, C.; et al. Glioblastoma Utilizes Fatty Acids and Ketone Bodies for Growth Allowing Progression during Ketogenic Diet Therapy. iScience 2020, 23, 101453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, F.A.; Shah, S.S.; de Cordoba, N.; Walters, W.M.; Prince, J.; Khatib, Z.; Ricardo, J.K.; Steven, V.; Regina, M.G. The contribution of ketone bodies to glycolytic inhibition for the treatment of adult and pediatric glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzalin, A.; Brambilla, F.; Arbustini, E.; Basello, K.; Speciani, A.; Mauri, P.; Paola, B.; Lorenzo, M. A New Pathway Promotes Adaptation of Human Glioblastoma Cells to Glucose Starvation. Cells 2020, 9, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Shivane, A.G.; Kalamian, M.; Maroon, J.C.; Mukherjee, P.; Zuccoli, G. Ketogenic Metabolic Therapy, Without Chemo or Radiation, for the Long-Term Management of IDH1-Mutant Glioblastoma: An 80-Month Follow-Up Case Report. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 682243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, M.G.; Fenton, K.E.; Preul, M.C.; Rho, J.M.; Lynch, A.; Stafford, P.; Adrienne, C.S. The ketogenic diet is an effective adjuvant to radiation therapy for the treatment of malignant glioma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönfeld, P.; Reiser, G. Why does brain metabolism not favor burning of fatty acids to provide energy? Reflections on disadvantages of the use of free fatty acids as fuel for brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friendlander, A.H.; Ettinger, R.L. Karnofsky performance status scale. Spec. Care Dent. 2009, 4, 147–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meidenbauer, J.J.; Mukherjee, P.; Seyfried, T.N. The glucose ketone index calculator: A simple tool to monitor therapeutic efficacy for metabolic management of brain cancer. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewen, S.C.; Anderson, B.A. Reliability of the Modified Motor Assessment Scale and the Barthel Index. Phys. Ther. 1988, 68, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodien, Y.G.; Barra, A.; Temkin, N.R.; Barber, J.; Foreman, B.; Vassar, M.; Claudia, R.; Sabrina, R.T.; Amy, J.M.; Geoffrey, T.M.; et al. Diagnosing Level of Consciousness: The Limits of the Glasgow Coma Scale Total Score. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 3295–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, R.U.; Brott, T.; Broderick, J.P.; Barsan, W.G.; Sauerbeck, L.R.; Zuccarello, M.; Khoury, J. The ABCs of measuring intracerebral hemorrhage volumes. Stroke 1996, 27, 1304–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Karl, B.; Alba, A.B.; Christine, M.; Ulrich, B.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetzler, R.F.; Sanai, N. The quiet revolution: Retractorless surgery for complex vascular and skull base lesions. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 116, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.; Kharbanda, S.; Pope, W.B.; Tran, A.; Solis, O.E.; Peale, F.; William, F.F.; Kanan, P.; Jose, A.C.; Ajay, P.; et al. Evidence for sequenced molecular evolution of IDH1 mutant glioblastoma from a distinct cell of origin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4482–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Xue, Q.; Liu, K.; Ge, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.-Y.; Cai, D.; et al. Dimethylaminomicheliolide (DMAMCL) Suppresses the Proliferation of Glioblastoma Cells via Targeting Pyruvate Kinase 2 (PKM2) and Rewiring Aerobic Glycolysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, J.; Bähr, O.; Maurer, G.D.; Hattingen, E.; Franz, K.; Brucker, D.; Stefan, W.; Ulrike, K.; Johannes, F.C.; Michael, W.; et al. ERGO: A pilot study of ketogenic diet in recurrent glioblastoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanzey, M.; Abdul Rahim, S.A.; Oudin, A.; Dirkse, A.; Kaoma, T.; Vallar, L.; Christel, H.M.; Rolf, B.; Anna, G.; Simone, P.N. Comprehensive analysis of glycolytic enzymes as therapeutic targets in the treatment of glioblastoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanke, K.M.; Wilson, C.; Kidambi, S. High Expression of Glycolytic Genes in Clinical Glioblastoma Patients Correlates With Lower Survival. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 752404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, K.; Dey, T.; Ashish, S.; Mishra, P.; Pandey, U. Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Cancer: The Role of PKM2 in Promoting Tumorigenesis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffel, L. Ketone bodies: A review of physiology, pathophysiology and application of monitoring to diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 1999, 15, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, K.J.; Wagner, M.; Harter, P.N.; Franz, K.; Bojunga, J.; Fokas, E.; Detlef, I.; Claus, R.; Johannes, R.; Elke, H.; et al. Maintenance of energy homeostasis during calorically restricted ketogenic diet and fasting-MR-spectroscopic insights from the ergo2 trial. Cancers 2020, 12, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakomy, R.; Kazda, T.; Selingerova, I.; Poprach, A.; Pospisil, P.; Belanova, R.; Pavel, F.; Vaclav, V.; Martin, S.; Radim, J.; et al. Real-World Evidence in Glioblastoma: Stupp’s Regimen After a Decade. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; De Sanctis, V.; Muni, R.; Filippone, F.; Bozzao, A.; Valeriani, M.; Osti, M.F.; Paula, U.D.; Lanzetta, G.; Tombolini, V.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma in elderly patients. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 88, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.M.; Lhermitte, B.; Steven, T.; Ahmed, I.; Manmeet, S.A.; Karen, F.; et al. Effect of tumor-treating fields plus maintenance temozolomide vs maintenance temozolomide alone on survival in patients with glioblastoma a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofatteh, M.; Mashayekhi, M.S.; Arfaie, S.; Chen, Y.; Malhotra, A.K.; Alvi, M.A.; Sader, N.; Antonick, V.; Fatehi Hassanabad, M.; Mansouri, A.; et al. Suicidal ideation and attempts in brain tumor patients and survivors: A systematic review. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2023, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, K.; Kajimoto, K.; Osaga, S.; Nagai, N.; Eku, S.; Hideyuki, N.; Hitomi, S.; Mai, N.; Mariko, T.; Hideaki, K.; et al. Promising Effect of a New Ketogenic Diet Regimen in Patients with Adanced Cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhans, C.M.; Gresham, G.; Amaral, J.L.; Hu, J. Exploring the Feasibility and Effects of a Ketogenic Diet in Patients With CNS Malignancies: A Retrospective Case Series. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.G.; Bhatia, S.K.; Anderson, C.M.; Eichenberger-Gilmore, J.M.; Sibenaller, Z.A.; Mapuskar, K.A.; Joshua, D.S.; John, M.B.; Douglas, R.S.; Melissa, A.F. Ketogenic diets as an adjuvant cancer therapy: History and potential mechanism. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.; Leloup, C. Mens Sana in corpore Sano: Does the glycemic index have a role to play? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.H.; Jain, S.; Aghi, M.K. Metabolic Drivers of Invasion in Glioblastoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 683276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Da Silva, E.; Mercier, M.C.; Etienne-Selloum, N.; Dontenwill, M.; Choulier, L. A Systematic Review of Glioblastoma-Targeted Therapies in Phases II, III, IV Clinical Trials. Cancers 2021, 13, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feyter, H.M.; Behar, K.L.; Rao, J.U.; Madden-Hennessey, K.; Ip, K.L.; Hyder, F.; Lester, R.D.; Jean-Francois, G.; Robin, A.G.; Douglas, R. A ketogenic diet increases transport and oxidation of ketone bodies in RG2 and 9L gliomas without affecting tumor growth. Neuro-oncology 2016, 18, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, M.; Giorgi, A.; Gentile, M.C.; d’Erme, M.; Morano, S.; Maras, B.; Tiziana, F. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Ji, F.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Zhao, H. A Novel Glucose Metabolism-Related Gene Signature for Overall Survival Prediction in Patients with Glioblastoma. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 22, 8872977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargaço, B.; Oliveira, P.A.; Antunes, M.L.; Moreira, A.C. Effects of the Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Gliomas: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzbaum, J.; Edlinger, M.; Zigmont, V.; Stattin, P.; Rempala, G.A.; Nagel, G.; Nikas, H.; Hanno, U.; Bernhard, F.; Goran, W.; et al. Associations between prediagnostic blood glucose levels, diabetes, and glioma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieu, M.T.; Lovblom, L.E.; McNamara, M.G.; Mason, W.; Laperriere, N.; Millar, B.A.; Cunthia, M.; Tim, R.K.; Bruce, A.P.; Caroline, C. Impact of glycemia on survival of glioblastoma patients treated with radiation and temozolomide. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliger, C.; Genbrugge, E.; Gorlia, T.; Chinot, O.; Stupp, R.; Nabors, B.; Michael, W.; Peter, H. Use of metformin and outcome of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Pooled analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shen, Y.; Huang, T.; Sun, Y.; Alolga, R.N.; Zhang, G.; Ge, Y. The Prognostic Effect of Dexamethasone on Patients With Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 727707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M. Neurosurgery and artificial intelligence. AIMS Neurosci. 2021, 8, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tumor Group | Standard Deviation | Control Group | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Characteristics | |||||||
| ASTRO G4 | GBM | Tumor group | Control group | ||||
| Gender % (N) | Male | 66.7 (4) | 56.3 (9) | 59.1 (13) | |||
| Female | 33.3 (2) | 43.7 (7) | 40.9 (9) | ||||
| Years | Average age | 48.1 | 55.6 | 53.9 | 0.512 | ||
| Age range | 34–66 | 44–78 | 56.09 ± 12.33 | 53.45 ± 14.10 | 36–78 | ||
| Specific Characteristics (average) | |||||||
| Wight (kg) | 80 | 89.6 | 85.00 ± 12.72 | 82.23 ± 16.70 | 82.2 | 0.538 | |
| Height (cm) | 169.8 | 175 | 173.6 ± 7.681 | 171.2 ± 10.13 | 171.2 | 0.379 | |
| BMI | 27.8 | 28.3 | 28.15 ± 3.867 | 28.02 ± 4.136 | 28.0 | 0.914 | |
| Ketone Bodies (mM) | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.227 ± 0.2004 | 0.0773 ± 0.0812 | 0.08 | 0.0061 | |
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 138.5 | 129.6 | 132.0 ± 39.43 | 96.73 ± 11.78 | 96.7 | 0.0003 | |
| GKI (mM) | 63.7 | 29.3 | 38.68 ± 29.80 | 16.85 ± 21.37 | 18.0 | 0.0080 | |
| Clinical debut (weeks) | 12.7 | 2.9 | 85.00 ± 12.72 | 82.23 ± 16.70 | 82.2 | 0.538 | |
| % | Headache | 83.3 | 93.7 | ||||
| Motor deficit | 33.3 | 56.3 | |||||
| Confusion | 16.7 | 50 | |||||
| Seizures | 16.7 | 25 | |||||
| Aphasia | 16.7 | 12.5 | |||||
| ASTRO G4 (%) | GBM (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor location | Frontal | 50 | 50 |
| Temporal | 33.3 | 31.2 | |
| Parietal | 16.7 | 37.5 | |
| Occipital | 16.7 | 31.2 | |
| Insular | 0.0 | 12.5 | |
| Cerebral hemisphere | Left | 33.3 | 37.5 |
| Right | 66.7 | 62.5 | |
| Tumor size (mm) | 40.1/30.2 | 48.4/39.6 | |
| Size of the perilesional edema (mm) | 23.6/3.5 | 23/2.4 | |
| Ki-67 index | ≤15 | 50 | 18.7 |
| 15–30 | 16.7 | 37.5 | |
| ≥30 | 33.3 | 43.8 | |
| P53 + | 83.3 | 50 | |
| Ketone Bodies | Tumor Group | Control Group (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTRO G4 (%) | GBM (%) | |||
| ≤0.2 mM | 100 | 56.25 | 100 | |
| >0.2 mM | 0.0 | 43.75 | 0.0 | |
| MORTALITY AT 3 MONTHS | ≤0.2 mM | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 0.2–0.5 mM | 0.0 | 85.7 | ||
| ≥0.5 mM | 0.0 | 100 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamas, C.; Tamas, F.; Kovecsi, A.; Serban, G.; Boeriu, C.; Balasa, A. The Role of Ketone Bodies in Treatment Individualization of Glioblastoma Patients. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091307
Tamas C, Tamas F, Kovecsi A, Serban G, Boeriu C, Balasa A. The Role of Ketone Bodies in Treatment Individualization of Glioblastoma Patients. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(9):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091307
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamas, Corina, Flaviu Tamas, Attila Kovecsi, Georgiana Serban, Cristian Boeriu, and Adrian Balasa. 2023. "The Role of Ketone Bodies in Treatment Individualization of Glioblastoma Patients" Brain Sciences 13, no. 9: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091307
APA StyleTamas, C., Tamas, F., Kovecsi, A., Serban, G., Boeriu, C., & Balasa, A. (2023). The Role of Ketone Bodies in Treatment Individualization of Glioblastoma Patients. Brain Sciences, 13(9), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091307








