Stimulation of Dopamine D4 Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Increases Palatable Food Intake in Satiated Male Rats: Modulation by NMDA and AMPA Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Diet
2.3. Drugs
2.4. Stereotaxic Surgery
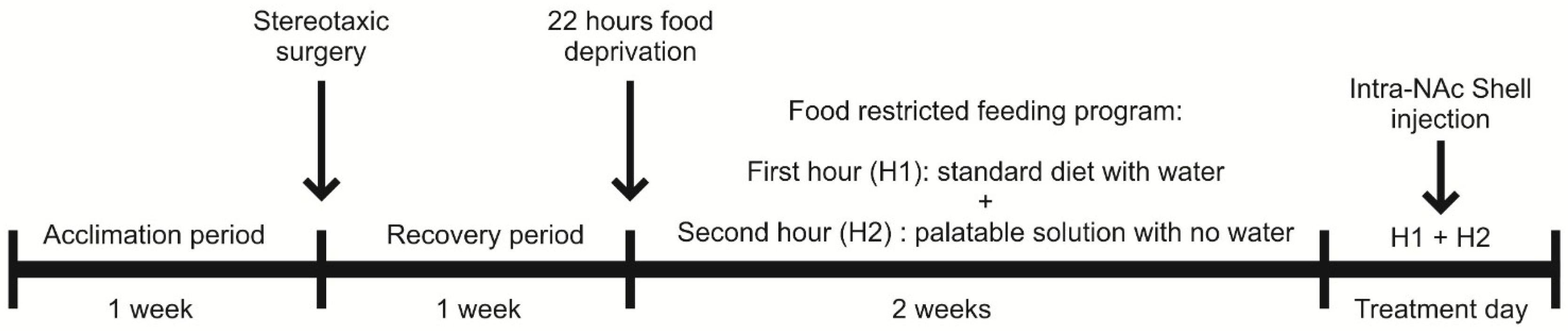
2.5. Feeding Paradigm
2.6. Experimental Procedure
2.7. Experimental Design to Evaluate the Modulation of Palatable Solution Consumption by NAc Shell D4R Activation and the Potential Contribution of NMDARs and AMPARs
2.8. Histology
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
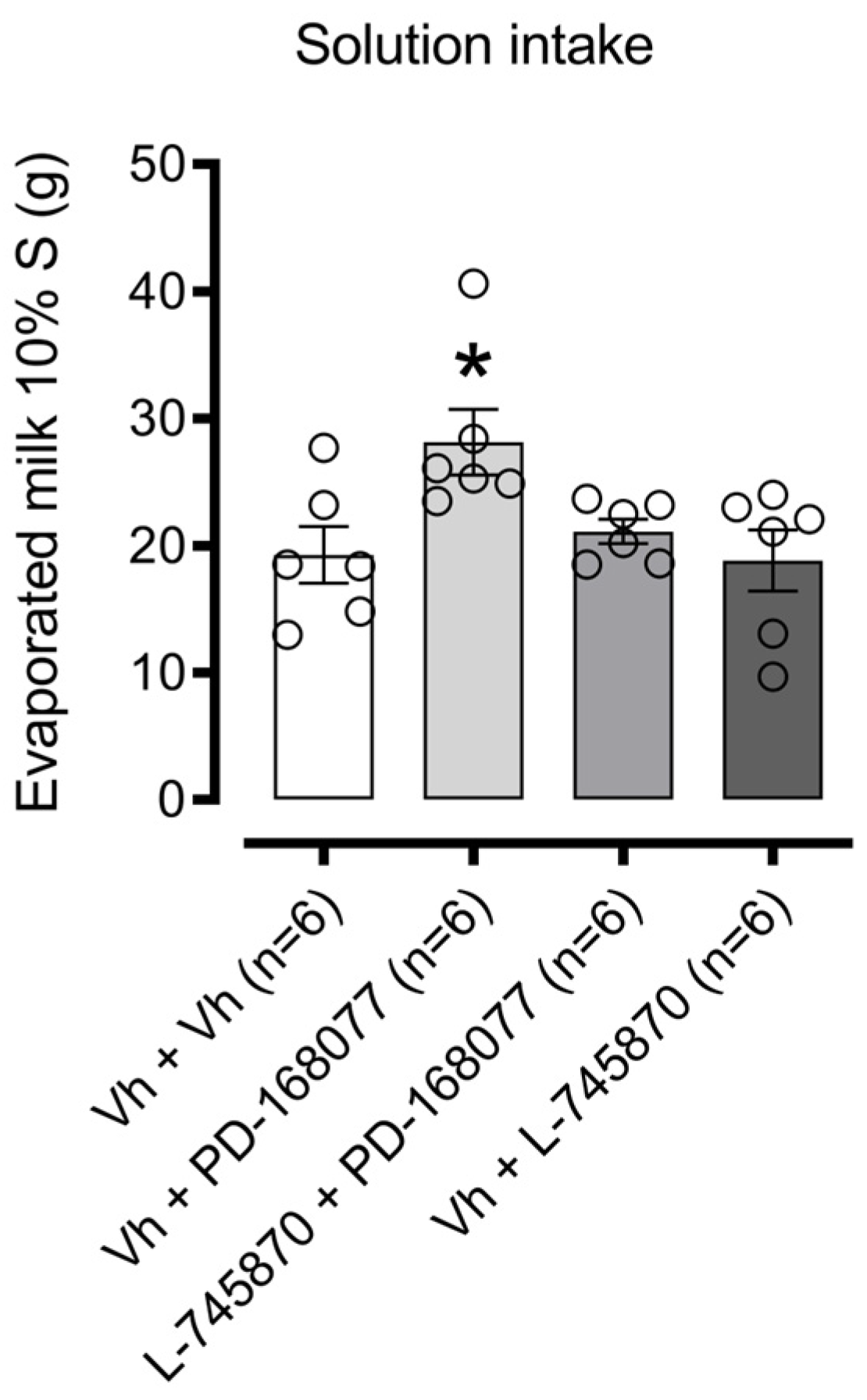
3.1. NAc Shell D4R Modulates Palatable Solution Consumption
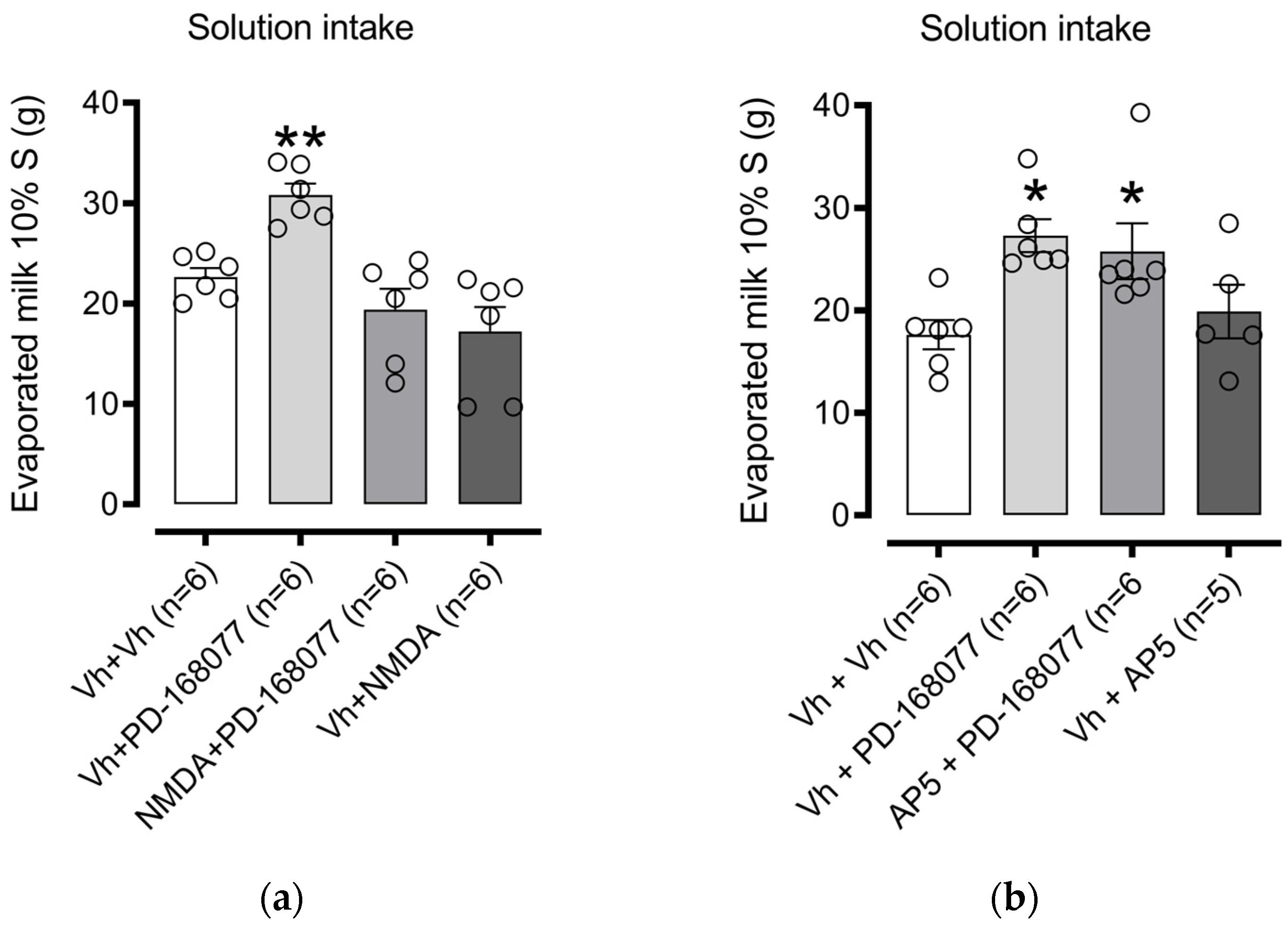
3.1.1. NAc Shell NMDAR Receptor Activation Prevents D4R Effects on Palatable Solution Consumption. The Blockade Did Not Modify Consumption
3.1.2. NAc Shell AMPAR Receptor Activation Prevents D4R Effects on Palatable Solution Consumption. The Blockade Modify Consumption
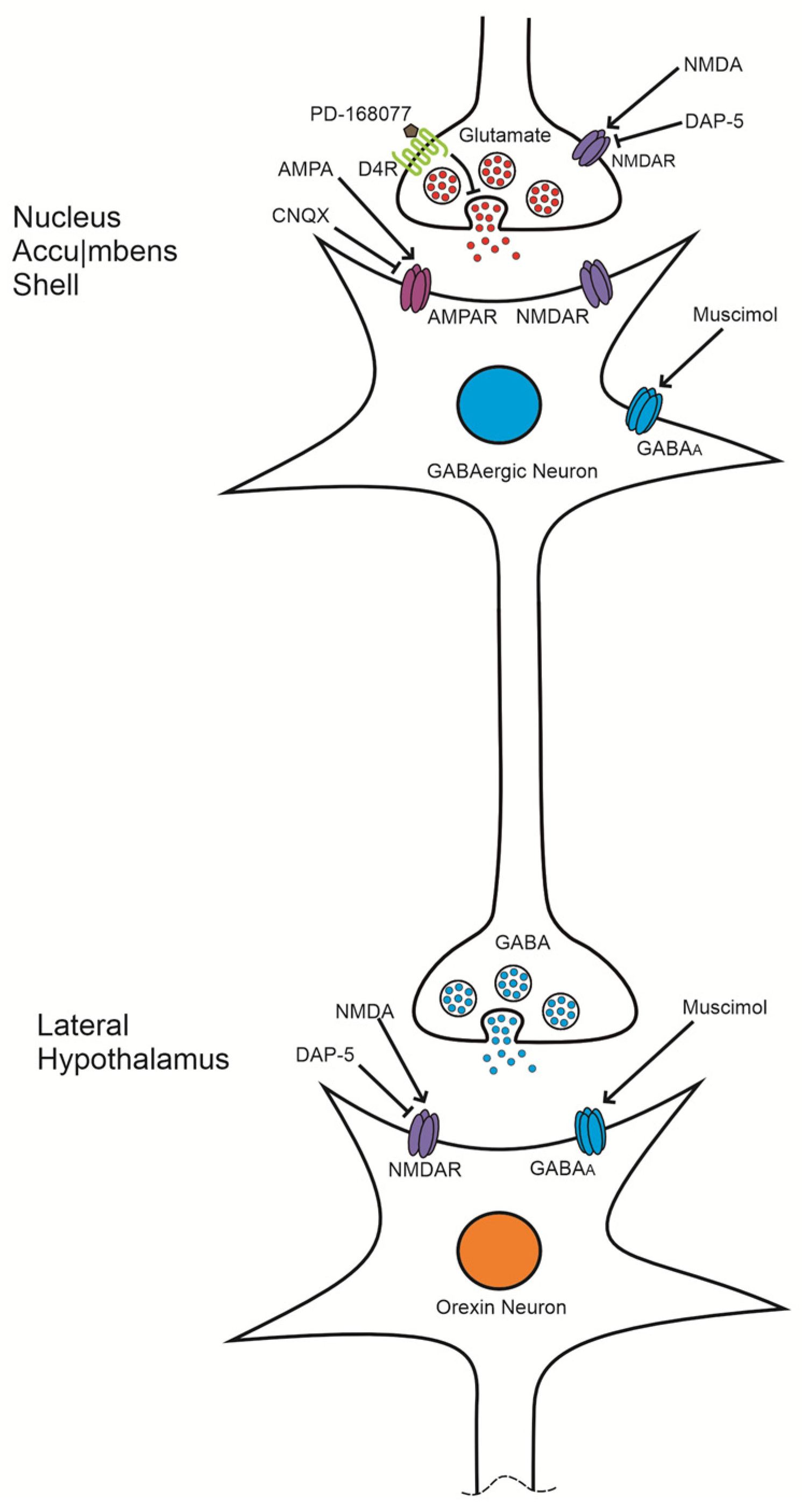
4. Discussion
4.1. The Activation of D4R in the NAc Shell Increases the Consumption of the Sweet Solution
4.2. NMDA Reverses the Effect of D4R Activation but Not by the Antagonist AP-5
4.3. The Effect of D4R Activation Is Reversed by AMPA but Not by the Antagonist CNQX
5. Conclusions
Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baik, J.H. Dopaminergic Control of the Feeding Circuit. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Baler, R.D. Reward, Dopamine and the Control of Food Intake: Implications for Obesity. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; German, P.W.; Taha, S.A.; Fields, H.L. A Pause in Nucleus Accumbens Neuron Firing Is Required to Initiate and Maintain Feeding. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4746–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetterly, T.L.; Catalfio, A.M.; Ferrario, C.R. Effects of Junk-Food on Food-Motivated Behavior and Nucleus Accumbens Glutamate Plasticity; Insights into the Mechanism of Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptor Recruitment. Neuropharmacology 2024, 242, 109772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ciano, P.; Grandy, D.K.; Le Foll, B. Dopamine D4 Receptors in Psychostimulant Addiction. In Advances in Pharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 69. [Google Scholar]
- Mietlicki-Baase, E.G.; Ortinski, P.I.; Reiner, D.J.; Sinon, C.G.; McCutcheon, J.E.; Pierce, R.C.; Roitman, M.F.; Hayes, M.R. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation in the Nucleus Accumbens Core Suppresses Feeding by Increasing Glutamatergic AMPA/Kainate Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6985–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondou, P.; Haegeman, G.; Van Craenenbroeck, K. The Dopamine D4 Receptor: Biochemical and Signalling Properties. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2010, 67, 1971–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, P.; Avena, N.M.; Hoebel, B.G. Daily Bingeing on Sugar Repeatedly Releases Dopamine in the Accumbens Shell. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Michaelides, M.; Baler, R. The Neuroscience of Drug Reward and Addiction. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 2115–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak, J.N.; Oldenhof, J.; Van Tol, H.H.M. The Dopamine D4 Receptor: One Decade of Research. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 405, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundar, B.; Perez, C.I.; Luna, A.; Solorio, J.; Moreno, M.G.; Elias, D.; Simon, S.A.; Gutierrez, R. D1 and D2 Antagonists Reverse the Effects of Appetite Suppressants on Weight Loss, Food Intake, Locomotion, and Rebalance Spiking Inhibition in the Rat NAc Shell. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 114, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Yoon, Y.R.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Shin, S.W.; An, J.J.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Sun, W.; et al. Enhanced Hypothalamic Leptin Signaling in Mice Lacking Dopamine D2 Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8905–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.M.; Kenny, P.J. Dopamine D2 Receptors in Addiction-like Reward Dysfunction and Compulsive Eating in Obese Rats. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botticelli, L.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Del Bello, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Romano, A.; Quaglia, W.; Cifani, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V. Underlying Susceptibility to Eating Disorders and Drug Abuse: Genetic and Pharmacological Aspects of Dopamine D4 Receptors. Nutrients 2020, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Kulkarni, S.K. Studies on Modulation of Feeding Behavior by Atypical Antipsychotics in Female Mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 26, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D.; Clifton, P.G. Meal Patterns of Free Feeding Rats Treated with Clozapine, Olanzapine, or Haloperidol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 71, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Trujillo, R.; Tejas-Juárez, J.G.; Mancilla-Díaz, J.M.; Escartín Pérez, R.E. Evaluación Del Bloqueo de Los Receptores Dopaminérgicos D4 En El Núcleo Accumbens Sobre La Motivación Por El Alimento Palatable. Espacio I+ D Innovación más desarrollo 2020, 9, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Alonso, V.E.; Hernández-Correa, S.; Escobar, C.; Escartín-Pérez, R.E.; Mancilla-Díaz, J.M.; Díaz-Urbina, D. The Central Blockade of the Dopamine DR4 Receptor Decreases Sucrose Consumption by Modifying the Microstructure of Drinking Behavior in Male Rats. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Trujillo, R.; Avalos-Fuentes, A.; Rangel-Barajas, C.; Paz-Bermúdez, F.; Sierra, A.; Escartín-Perez, E.; Aceves, J.; Erlij, D.; Florán, B. D3 Dopamine Receptors Interact with Dopamine D1 but Not D4 Receptors in the GABAergic Terminals of the SNr of the Rat. Neuropharmacology 2013, 67, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S.; Rangel-Barajas, C.; Peper, M.; Lorenzo, R.; Moreno, E.; Ciruela, F.; Borycz, J.; Ortiz, J.; Lluís, C.; Franco, R.; et al. Dopamine D 4 Receptor, but Not the ADHD-Associated D 4.7 Variant, Forms Functional Heteromers with the Dopamine D 2S Receptor in the Brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.; Gutiérrez, A.; Martín, R.; Peñafiel, A.; Rivera, A.; De La Calle, A. Differential Regional and Cellular Distribution of Dopamine D2-like Receptors: An Immunocytochemical Study of Subtype-Specific Antibodies in Rat and Human Brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 402, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, K.D. Homeostatic Regulation of Reward via Synaptic Insertion of Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors in Nucleus Accumbens. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 219, 112850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Li, S.; Kirouac, G.J. Collateralization of Projections from the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus to the Nucleus Accumbens, Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis, and Central Nucleus of the Amygdala. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 3927–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuber, G.D.; Sparta, D.R.; Stamatakis, A.M.; Van Leeuwen, W.A.; Hardjoprajitno, J.E.; Cho, S.; Tye, K.M.; Kempadoo, K.A.; Zhang, F.; Deisseroth, K.; et al. Excitatory Transmission from the Amygdala to Nucleus Accumbens Facilitates Reward Seeking. Nature 2011, 475, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, A.E.; Baldo, B.A.; Pratt, W.E.; Will, M.J. Corticostriatal-Hypothalamic Circuitry and Food Motivation: Integration of Energy, Action and Reward. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 86, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-lrizarry, C.S.; Swanson, C.J.; Kelley, A.E. Glutamate Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Control Feeding Behavior via the Lateral Hypothalamus. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6779–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, J.D.; Selleck, R.A.; Baldo, B.A. Mu-Opioid Stimulation in Rat Prefrontal Cortex Engages Hypothalamic Orexin/Hypocretin-Containing Neurons, and Reveals Dissociable Roles of Nucleus Accumbens and Hypothalamus in Cortically Driven Feeding. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18540–18552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratford, T.R.; Swanson, C.J.; Kelley, A. Specific Changes in Food Intake Elicited by Blockade or Activation of Glutamate Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 93, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, J.; Quiroz, C.; Cai, N.S.; Rubinstein, M.; Tanda, G.; Ferré, S. Key Role of the Dopamine D4 Receptor in the Modulation of Corticostriatal Glutamatergic Neurotransmission. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, S.; Belcher, A.M.; Bonaventura, J.; Quiroz, C.; Sánchez-Soto, M.; Casadó-Anguera, V.; Cai, N.S.; Moreno, E.; Boateng, C.A.; Keck, T.M.; et al. Functional and Pharmacological Role of the Dopamine D4 Receptor and Its Polymorphic Variants. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1014678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Salazar, F.; Suárez Ortíz, J.O.; Cendejas Trejo, N.M.; Mancilla-Díaz, J.M.; López-Alonso, V.E.; Escartín-Pérez, R.E. Effects of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Activation in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell on Feeding Behavior. Acta Colomb. Psicol. 2014, 17, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Salazar, F.; Mancilla-Díaz, J.M.; López-Alonso, V.E.; González-Hernández, B.; Escartín-Pérez, R.E. Relationship between CB1 Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell and the Hedonic Value of Food. In Recent Hispanic Psychological Research on Feeding Behavior and HIV Patients; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, P.C.; Kenny, P.J. Food Addiction: A Valid Concept? Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, C.; Vitolo, M.R.; Campagnolo, P.D.B.; Mattevi, V.S.; Genro, J.P.; Almeida, S. DRD4 and SLC6A3 Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Food Intake and Nutritional Status in Children in Early Stages of Development. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.C.; Berridge, K.C. Opioid Hedonic Hotspot in Nucleus Accumbens Shell: Mu, Delta, and Kappa Maps for Enhancement of Sweetness “Liking” and “Wanting”. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4239–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durst, M.; Könczöl, K.; Balázsa, T.; Eyre, M.D.; Tóth, Z.E. Reward-Representing D1-Type Neurons in the Medial Shell of the Accumbens Nucleus Regulate Palatable Food Intake. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Kool, T.; Diepenbroek, C.; Koekkoek, L.L.; Eggels, L.; Kalsbeek, A.; Mul, J.D.; Barrot, M.; la Fleur, S.E. Dopamine D1 Receptor Signalling in the Lateral Shell of the Nucleus Accumbens Controls Dietary Fat Intake in Male Rats. Appetite 2021, 167, 105597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundar, B.; Perez, C.I.; Arroyo, B.; Moreno, M.G.; Gutierrez, R. The Appetite Suppressant D-Norpseudoephedrine (Cathine) Acts via D1/D2-Like Dopamine Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 572328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, N.T.; Hajnal, A. Acute Methylphenidate Treatments Reduce Sucrose Intake in Restricted-Fed Bingeing Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 70, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgioni, G.; Del Bello, F.; Pavletić, P.; Quaglia, W.; Botticelli, L.; Cifani, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Piergentili, A. Recent Findings Leading to the Discovery of Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Ligands for the Treatment of Widespread Diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 212, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, C.W.; Hopkins, C.R. Return of D4 Dopamine Receptor Antagonists in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7233–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, P.P.; Portella, A.K.; Kennedy, J.L.; Gaudreau, H.; Davis, C.; Steiner, M.; Soares, C.N.; Matthews, S.G.; Sokolowski, M.B.; Dubé, L.; et al. Association between the Seven-Repeat Allele of the Dopamine-4 Receptor Gene (DRD4) and Spontaneous Food Intake in Pre-School Children. Appetite 2014, 73, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejas-Juárez, J.G.; Cruz-Martínez, A.M.; López-Alonso, V.E.; García-Iglesias, B.; Mancilla-Díaz, J.M.; Florán-Garduño, B.; Escartín-Pérez, R.E. Stimulation of Dopamine D4 Receptors in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus of Male Rats Induces Hyperphagia: Involvement of Glutamate. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 133, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yager, L.M.; Garcia, A.F.; Wunsch, A.M.; Ferguson, S.M. The Ins and Outs of the Striatum: Role in Drug Addiction. Neuroscience 2015, 301, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svingos, A.L.; Periasamy, S.; Pickel, V.M. Presynaptic Dopamine D4 Receptor Localization in the Rat Nucleus Accumbens Shell. Synapse 2000, 36, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, G.; Brown, N.A.; McAllister, G.; Milligan, G.; Seabrook, G.R. Human D2 and D4 Dopamine Receptors Couple through Βγ G-Protein Subunits to Inwardly Rectifying K+ Channels (GIRK1) in a Xenopus Oocyte Expression System: Selective Antagonism by L-741,626 and L-745,870 Respectively. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, C.; Goutman, J.D.; Avale, M.E.; Franchini, L.F.; Rubinstein, M.; Calvo, D.J. Functional Activation by Central Monoamines of Human Dopamine D4 Receptor Polymorphic Variants Coupled to GIRK Channels in Xenopus Oocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 562, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratford, T.R.; Kelley, A.E. GABA in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Participates in the Central Regulation of Feeding Behavior. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4434–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, L.; Luis-Islas, J.; Sandoval, O.I.; Puron, L.; Gil, M.M.; Luna, A.; Arias-García, M.A.; Galarraga, E.; Simon, S.A.; Gutierrez, R. Activation of Glutamatergic Fibers in the Anterior NAc Shell Modulates Reward Activity in the aNAcSh, the Lateral Hypothalamus, and Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Transiently Stops Feeding. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 12511–12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, R.D.; Jansen, P.; Wendland, B.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Silveira, P.P.; Kennedy, J.L.; Atkinson, L.; Fleming, A.; Sokolowski, M.; et al. A DRD4 Gene by Maternal Sensitivity Interaction Predicts Risk for Overweight or Obesity in Two Independent Cohorts of Preschool Children. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2017, 58, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Rao, R.R.; Velázquez-Sánchez, C.; Valenza, M.; Giuliano, C.; Everitt, B.J.; Sabino, V.; Cottone, P. The Uncompetitive N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Antagonist Memantine Reduces Binge-Like Eating, Food-Seeking Behavior, and Compulsive Eating: Role of the Nucleus Accumbens Shell. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echo, J.A.; Lamonte, N.; Christian, G.; Znamensky, V.; Ackerman, T.F.; Bodnar, R.J. Excitatory Amino Acid Receptor Subtype Agonists Induce Feeding in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell in Rats: Opioid Antagonist Actions and Interactions with μ-Opioid Agonists. Brain Res. 2001, 921, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, P.; Gu, Z.; Yan, Z. Regulation of NMDA Receptors by Dopamine D4 Signaling in Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 9852–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Liu, W.; Ma, K.; Wei, J.; Zhong, P.; Cho, K.; Yan, Z. The ADHD-Linked Human Dopamine D4 Receptor Variant D4.7 Induces over-Suppression of NMDA Receptor Function in Prefrontal Cortex. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 95, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gracy, K.N.; Svingos, A.L.; Pickel, V.M. Dual Ultrastructural Localization of μ-Opioid Receptors and NMDA-Type Glutamate Receptors in the Shell of the Rat Nucleus Accumbens. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4839–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazi, F.I.; Campbell, A.; Yeghiayan, S.K.; Baldessarini, R.J. Localization of Dopamine Receptor Subtypes in Corpus Striatum and Nucleus Accumbens Septi of Rat Brain: Comparison of D1-, D2- and D4-like Receptors. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, A.; Reynolds, S.M.; Richard, J.M.; Berridge, K.C. Mesolimbic Dopamine in Desire and Dread: Enabling Motivation to Be Generated by Localized Glutamate Disruptions in Nucleus Accumbens. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 7184–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, S.M.; Berridge, K.C. Emotional Environments Retune the Valence of Appetitive versus Fearful Functions in Nucleus Accumbens. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, S.M.; Berridge, K.C. Glutamate Motivational Ensembles in Nucleus Accumbens: Rostrocaudal Shell Gradients of Fear and Feeding. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 2187–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urstadt, K.R.; Coop, S.H.; Banuelos, B.D.; Stanley, B.G. Behaviorally Specific versus Non-Specific Suppression of Accumbens Shell-Mediated Feeding by Ipsilateral versus Bilateral Inhibition of the Lateral Hypothalamus. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 257, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratford, T.R.; Kelley, A.E. Evidence of a Functional Relationship between the Nucleus Accumbens Shell and Lateral Hypothalamus Subserving the Control Oil Feeding Behavior. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 11040–11048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, N.M.; Laviolette, S.R. Dopamine D 4-Receptor Modulation of Cortical Neuronal Network Activity and Emotional Processing: Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Leighton, C.; Little, M.R.; Grace, M.; Billington, C.; Kotz, C.M. Orexin Signaling in Rostral Lateral Hypothalamus and Nucleus Accumbens Shell in the Control of Spontaneous Physical Activity in High- and Low-Activity Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 312, R338–R346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, B.A.; Gual-Bonilla, L.; Sijapati, K.; Daniel, R.A.; Landry, C.F.; Kelley, A.E. Activation of a Subpopulation of Orexin/Hypocretin-Containing Hypothalamic Neurons by GABAA Receptor-Mediated Inhibition of the Nucleus Accumbens Shell, but Not by Exposure to a Novel Environment. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Corkern, M.; Stoyanova, I.; Patterson, L.M.; Tian, R.; Berthoud, H.R. Appetite-Inducing Accumbens Manipulation Activates Hypothalamic Orexin Neurons and Inhibits POMC Neurons. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R1436–R1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barson, J.R.; Leibowitz, S.F. Orexin/Hypocretin System: Role in Food and Drug Overconsumption. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 136. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, A.J.; Mullett, M.A.; Wang, C.; Kotz, C.M. Regional, Metabolic, and Circadian Specificity of Lateral Hypothalamic Orexin A Feeding Stimulation. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R1409–R1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperatore, R.; Palomba, L.; Cristino, L. Role of Orexin-A in Hypertension and Obesity. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urstadt, K.R.; Berridge, K.C. Optogenetic Mapping of Feeding and Self-Stimulation within the Lateral Hypothalamus of the Rat. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0224301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duva, M.A.; Tomkins, E.M.; Moranda, L.M.; Kaplan, R.; Sukhaseum, A.; Stanley, B.G. Origins of Lateral Hypothalamic Afferents Associated with N-Methyl-d-Aspartic Acid-Elicited Eating Studied Using Reverse Microdialysis of NMDA and Fluorogold. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 52, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Carcea, I.; Schiavo, J.K.; Jones, K.T.; Rabinowitsch, A.; Kolaric, R.; Cabeza de Vaca, S.; Froemke, R.C.; Carr, K.D. Food Restriction Induces Synaptic Incorporation of Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors in Nucleus Accumbens. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, F.; Laricchiuta, D.; Natale, G.; Marino, G.; Calabrese, V.; Picconi, B.; Petrosini, L.; Calabresi, P.; Ghiglieri, V. Long-Term Shaping of Corticostriatal Synaptic Activity by Acute Fasting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 1. DR4 Treatments | 2. NMDAR Agonist + D4R Agonist | 3. NMDAR Antagonist + D4R Agonist | 4. AMPAR Agonist + DR4 Agonist | 5. AMPAR Antagonist + DR4 Agonist |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saline + Saline | Saline + Saline | Saline + Saline | Saline + Saline | Saline + Saline |
| Saline + PD-168077 | Saline + PD-168077 | Saline + PD-168077 | Saline + PD-168077 | Saline + PD-168077 |
| Saline + L-745870 | NMDA + PD-168077 | AP5 + PD-168077 | AMPA + PD-168077 | CNQX + PD-168077 |
| L-745870+ PD-168077 | Saline + NMDA | Saline + AP5 | Saline + AMPA | Saline + CNQX |
| Intra NAc shell administration of the D4R agonist, PD-168077, stimulates the intake of a sweet solution. Intra NAc shell co-administration of NMDA, but not of AP5, reverts the PD-16877-induced sweet solution intake. Intra NAc shell co-administration of AMPA, but not CNQX, reverts the PD-16977-induced sweet solution intake. Intra NAc shell administration of AMPA alone inhibits the intake of a sweet solution. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Trujillo, R.; Díaz-Urbina, D.; Díaz-Gandarilla, J.A.; Vidal-López, D.G.; Escartín-Pérez, R.E.; Mancilla-Diaz, J.M.; Florán, B.; Tejas-Juárez, J.G. Stimulation of Dopamine D4 Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Increases Palatable Food Intake in Satiated Male Rats: Modulation by NMDA and AMPA Receptors. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14111103
Cruz-Trujillo R, Díaz-Urbina D, Díaz-Gandarilla JA, Vidal-López DG, Escartín-Pérez RE, Mancilla-Diaz JM, Florán B, Tejas-Juárez JG. Stimulation of Dopamine D4 Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Increases Palatable Food Intake in Satiated Male Rats: Modulation by NMDA and AMPA Receptors. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(11):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14111103
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Trujillo, Refugio, Daniel Díaz-Urbina, José Alfredo Díaz-Gandarilla, Dolores Guadalupe Vidal-López, Rodrigo Erick Escartín-Pérez, Juan Manuel Mancilla-Diaz, Benjamín Florán, and Juan Gabriel Tejas-Juárez. 2024. "Stimulation of Dopamine D4 Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Increases Palatable Food Intake in Satiated Male Rats: Modulation by NMDA and AMPA Receptors" Brain Sciences 14, no. 11: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14111103
APA StyleCruz-Trujillo, R., Díaz-Urbina, D., Díaz-Gandarilla, J. A., Vidal-López, D. G., Escartín-Pérez, R. E., Mancilla-Diaz, J. M., Florán, B., & Tejas-Juárez, J. G. (2024). Stimulation of Dopamine D4 Receptors in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Increases Palatable Food Intake in Satiated Male Rats: Modulation by NMDA and AMPA Receptors. Brain Sciences, 14(11), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14111103







