The Association Between Traumatic Brain Injury and the Risk of Cognitive Decline: An Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
- Meta-analyses or large cohort studies reporting the association between TBI and dementia or AD.
- Studies reporting effect sizes (such as odds ratios (ORs) or relative risks (RRs)) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
- Studies including data on TBI severity, categorized as mild, moderate, or severe.
- Studies with at least 500 participants to ensure the robustness of the findings.
- They focused on other neurological disorders not related to dementia or AD.
- They were case reports, reviews, or commentaries without original data.
2.4. Data Extraction
- Study characteristics: Author, year of publication, study design, and sample size.
- Effect sizes: ORs or RRs, alongside their 95% CIs.
- Outcome: Whether the study focused on dementia or AD.
- TBI severity: Classification of TBI as mild, moderate, severe, or mixed.
- Number of cases and controls.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Outcome Measures
3. Results
3.1. Selection Process (PRISMA Guidelines)
3.2. Umbrella Systematic Review
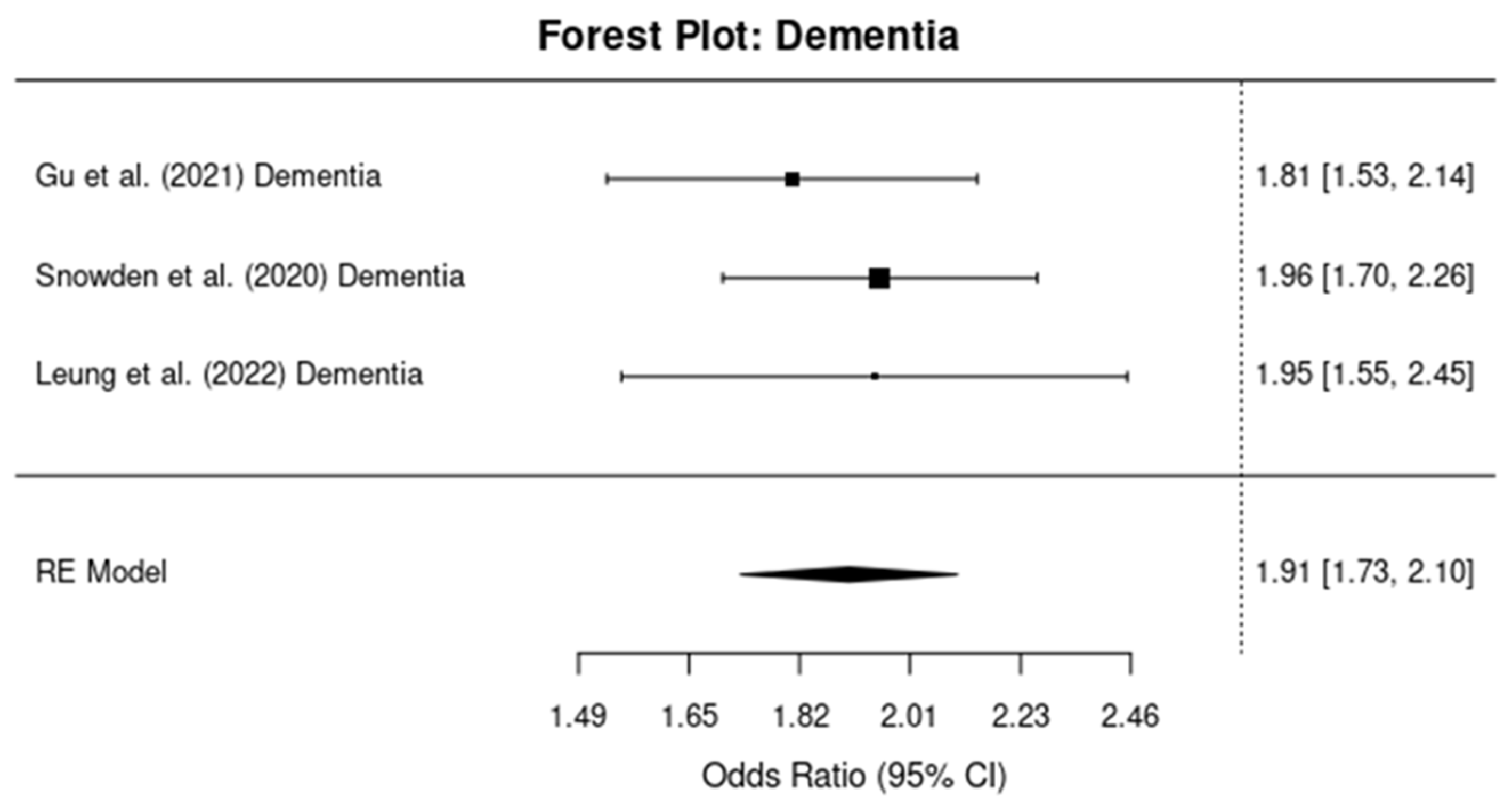
3.2.1. Dementia Risk
3.2.2. Alzheimer’s Disease Risk
3.2.3. The Impact of TBI Severity
3.2.4. TBI and Dementia Subtypes
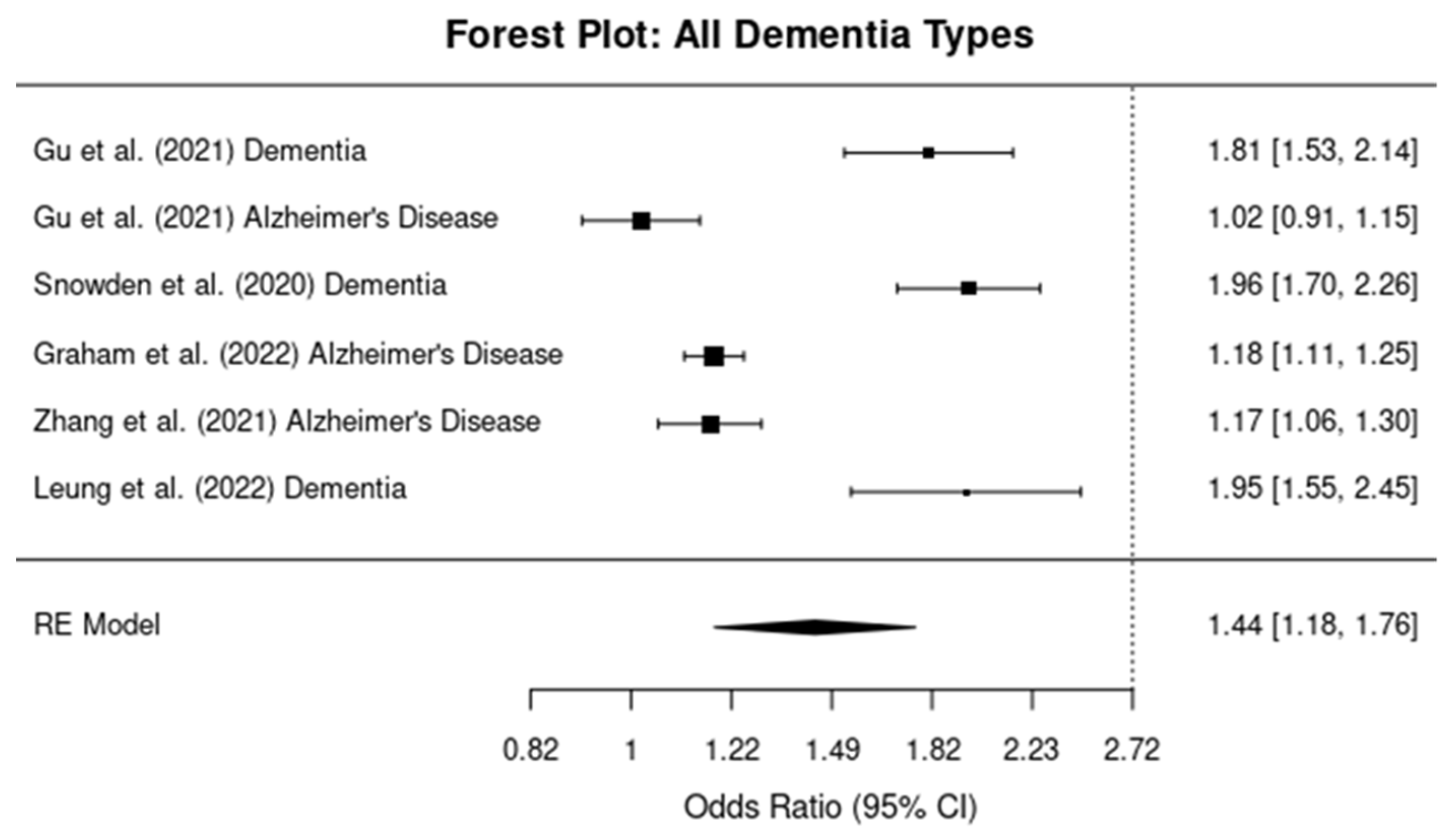
3.3. Umbrella Meta-Analysis of TBI and Dementia Risk
Overall Meta-Analysis for All Dementia Types
3.4. Subgroup Analysis: Alzheimer’s Disease vs. Dementia
3.4.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.4.2. Dementia (Other Than AD)
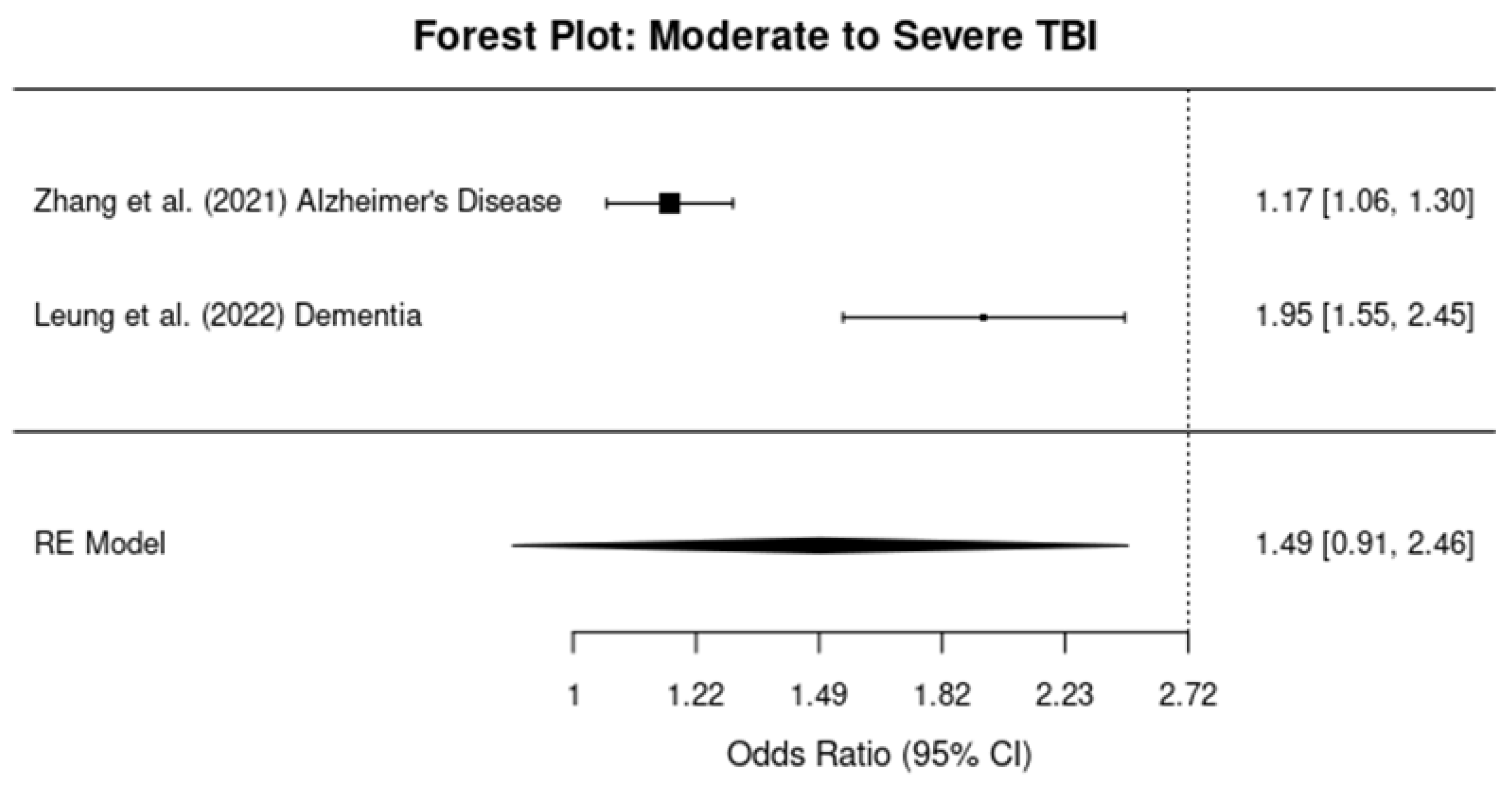
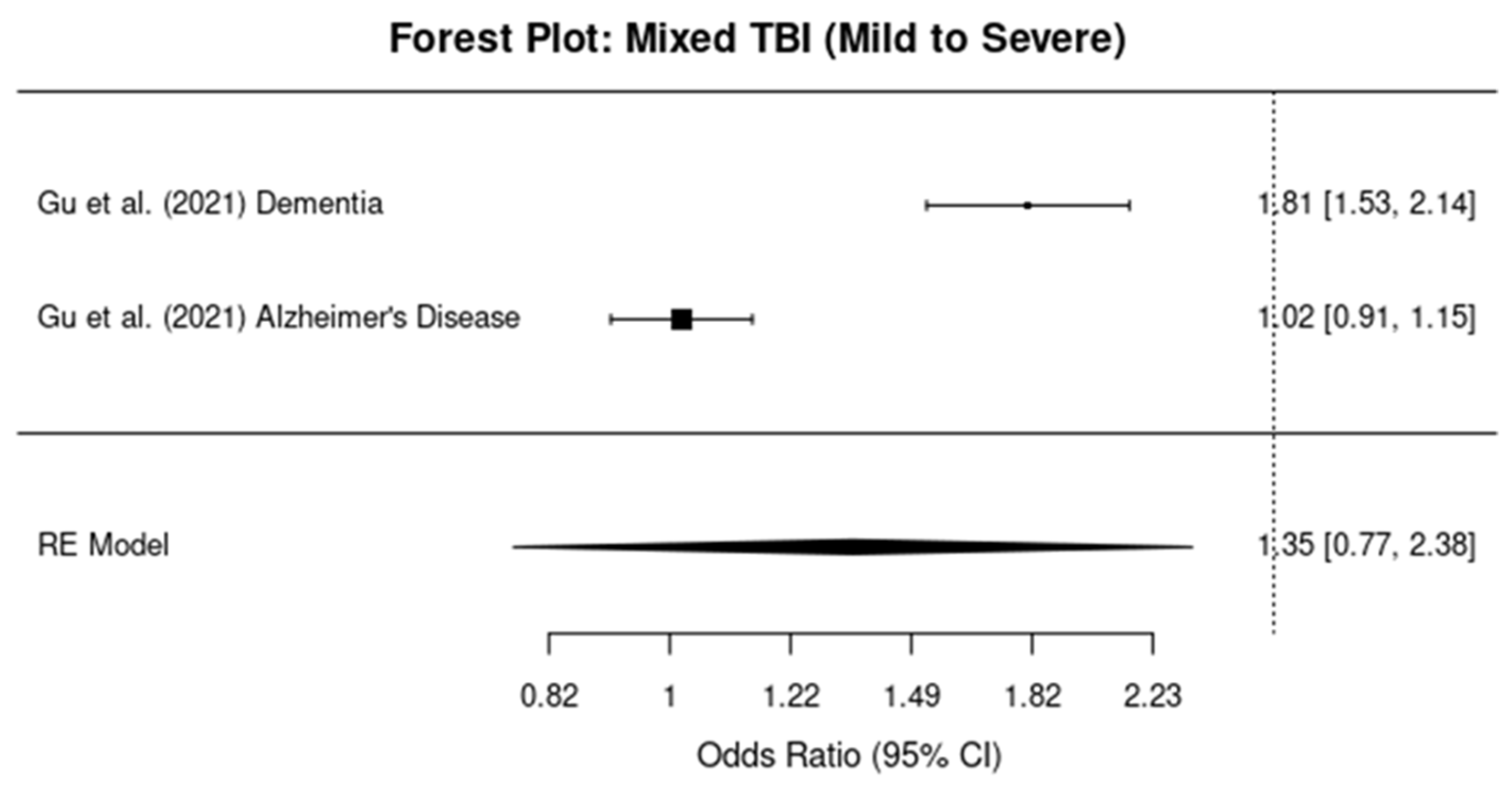
3.5. Subgroup Analysis by TBI Severity
3.5.1. Mild TBI
3.5.2. Moderate-To-Severe TBI
3.5.3. Mixed TBI Severity
3.5.4. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mavroudis, I.; Kazis, D.; Chowdhury, R.; Petridis, F.; Costa, V.; Balmus, I.M.; Ciobica, A.; Luca, A.C.; Radu, I.; Dobrin, R.P.; et al. Post-Concussion Syndrome and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy: Narrative Review on the Neuropathology, Neuroimaging and Fluid Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussman, E.S.; Pendharkar, A.V.; Ho, A.L.; Ghajar, J. Mild traumatic brain injury and concussion: Terminology and classification. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 158, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroudis, I.; Ciobica, A.; Bejenariu, A.C.; Dobrin, R.P.; Apostu, M.; Dobrin, I.; Balmus, I.M. Cognitive Impairment following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI): A Review. Medicina 2024, 60, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, B.L.; Gardner, R.C.; Godbout, J.; Dams-O’Connor, K.; Keene, C.D. Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Neurodegenerative Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Itallie, T.B. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) in collision sports: Possible mechanisms of transformation into chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Metabolism 2019, 100S, 153943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Cejudo, J.; Wisniewski, T.; Marmar, C.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; de Leon, M.J.; Fossati, S. Traumatic Brain Injury and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Cerebrovascular Link. eBioMedicine 2018, 28, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.H.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Bramlett, H.M.; Keane, R.W.; Dietrich, W.D. Inflammasome activation in traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Res. 2023, 254, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, PBC, Boston, MA. 2020. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Ou, S.; Liu, G. Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2022, 56, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, T.M.; Hinde, A.K.; Reid, H.M.O.; Christie, B.R. Does Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Increase the Risk for Dementia? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 78, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, A.; Livingston, G.; Purnell, L.; Huntley, J. Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries and Future Risk of Developing Alzheimer’s Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 87, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Cao, F. A meta-analysis of cohort studies: Traumatic brain injury and risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.K.; Carr, F.M.; Russell, M.J.; Bremault-Phillips, S.; Triscott, J.A.C. Traumatic brain injuries among veterans and the risk of incident dementia: A systematic review & meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afab194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Lin, C.W.; Lee, Y.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Huang, R.Y.; Tai, Y.C.; Wang, K.W.; Yang, S.N.; Sun, Y.T.; Wang, H.K. Is traumatic brain injury a risk factor for neurodegeneration? A meta-analysis of population-based studies. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Dove, A.; Qi, X.; Pan, K.Y.; Xu, W. Association of life-course traumatic brain injury with dementia risk: A nationwide twin study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharbafshaaer, M. Impacts of cognitive impairment for different levels and causes of traumatic brain injury, and education status in TBI patients. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2018, 12, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Ransom, J.E.; Mandrekar, J.; Turcano, P.; Savica, R.; Brown, A.W. Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias in the Population. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 88, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.C.; Burke, J.F.; Nettiksimmons, J.; Kaup, A.; Barnes, D.E.; Yaffe, K. Dementia Risk After Traumatic Brain Injury vs. Nonbrain Trauma: The Role of Age and Severity. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.E.; Stewart, W.; Arena, J.D.; Smith, D.H. Traumatic Brain Injury as a Trigger of Neurodegeneration. In Neurodegenerative Diseases. Advances in Neurobiology; Beart, P., Robinson, M., Rattray, M., Maragakis, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoBue, C.; Woon, F.L.; Rossetti, H.C.; Hynan, L.S.; Hart, J.; Cullum, C.M. Traumatic brain injury history and progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease. Neuropsychology 2018, 32, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.; Paul, B.D.; Pieper, A.A. Increased Risk of Aging-Related Neurodegenerative Disease after Traumatic Brain Injury. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, L.O.; Martindale-Adams, J.; Seel, R.T.; Zuber, J.K.; Perrin, P.B. Demographics, Clinical Characteristics, and Well-Being of Veterans with TBI and Dementia and Their Caregivers. Geriatrics 2024, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnahan, J.L.; Judge, K.S.; Daggy, J.K.; Slaven, J.E.; Coleman, N.; Fortier, E.L.; Suelzer, C.; Fowler, N.R. Supporting caregivers of veterans with Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2020, 21, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayen, E.; Jourdan, C.; Ghout, I.; Darnoux, E.; Azerad, S.; Vallat-Azouvi, C.; Weiss, J.J.; Aegerter, P.; Pradat-Diehl, P.; Joël, M.E.; et al. Objective and Subjective Burden of Informal Caregivers 4 Years After a Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2016, 31, E59–E67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Study | Outcome | Effect Size (OR/RR) | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | TBI Severity (Factor) | Cases (n) | Controls (n) | Total Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | Dementia | OR = 1.81 | 1.53 | 2.14 | Mixed (Mild to Severe) | 11,487 | 2,820,181 | 2,831,668 |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | OR = 1.02 | 0.91 | 1.15 | Mixed (Mild to Severe) | 11,487 | 2,820,181 | 2,831,668 | |
| [11] | Dementia | OR = 1.96 | 1.70 | 2.26 | Mild | 1710 | 48,500 | 50,210 |
| [12] | Alzheimer’s Disease | RR = 1.18 | 1.11 | 1.25 | Mild | 4500 | 3,145,240 | 3,149,740 |
| [13] | Alzheimer’s Disease | RR = 1.17 | 1.05 | 1.29 | Moderate to Severe | 7000 | 4,282,548 | 4,289,548 |
| [14] | Dementia | HR = 1.95 | 1.55 | 2.45 | Moderate to Severe | 155,000 | 6,945,000 | 7,100,000 |
| [15] | Dementia | OR = 1.93 | 1.47 | 2.55 | Mixed (Mild to Severe) | Not reported | Not reported | 3,263,207 |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | OR = 1.03 | 0.06 | 16.33 | Mixed (Mild to Severe) | Not reported | Not reported | 3,263,207 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavroudis, I.; Kazis, D.; Petridis, F.E.; Balmus, I.-M.; Papaliagkas, V.; Ciobica, A. The Association Between Traumatic Brain Injury and the Risk of Cognitive Decline: An Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121188
Mavroudis I, Kazis D, Petridis FE, Balmus I-M, Papaliagkas V, Ciobica A. The Association Between Traumatic Brain Injury and the Risk of Cognitive Decline: An Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(12):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121188
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavroudis, Ioannis, Dimitrios Kazis, Foivos Efstratios Petridis, Ioana-Miruna Balmus, Vasileios Papaliagkas, and Alin Ciobica. 2024. "The Association Between Traumatic Brain Injury and the Risk of Cognitive Decline: An Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Brain Sciences 14, no. 12: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121188
APA StyleMavroudis, I., Kazis, D., Petridis, F. E., Balmus, I.-M., Papaliagkas, V., & Ciobica, A. (2024). The Association Between Traumatic Brain Injury and the Risk of Cognitive Decline: An Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences, 14(12), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121188







