Peripheral Mechanisms Underlying Bacillus Calmette–Guerin-Induced Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Bladder Cancer
1.2. BCG Immunotherapy for NMIBC
1.3. Adverse Effects of BCG Immunotherapy
2. Mechanisms Underlying the Development of LUTSs During BCG Immunotherapy
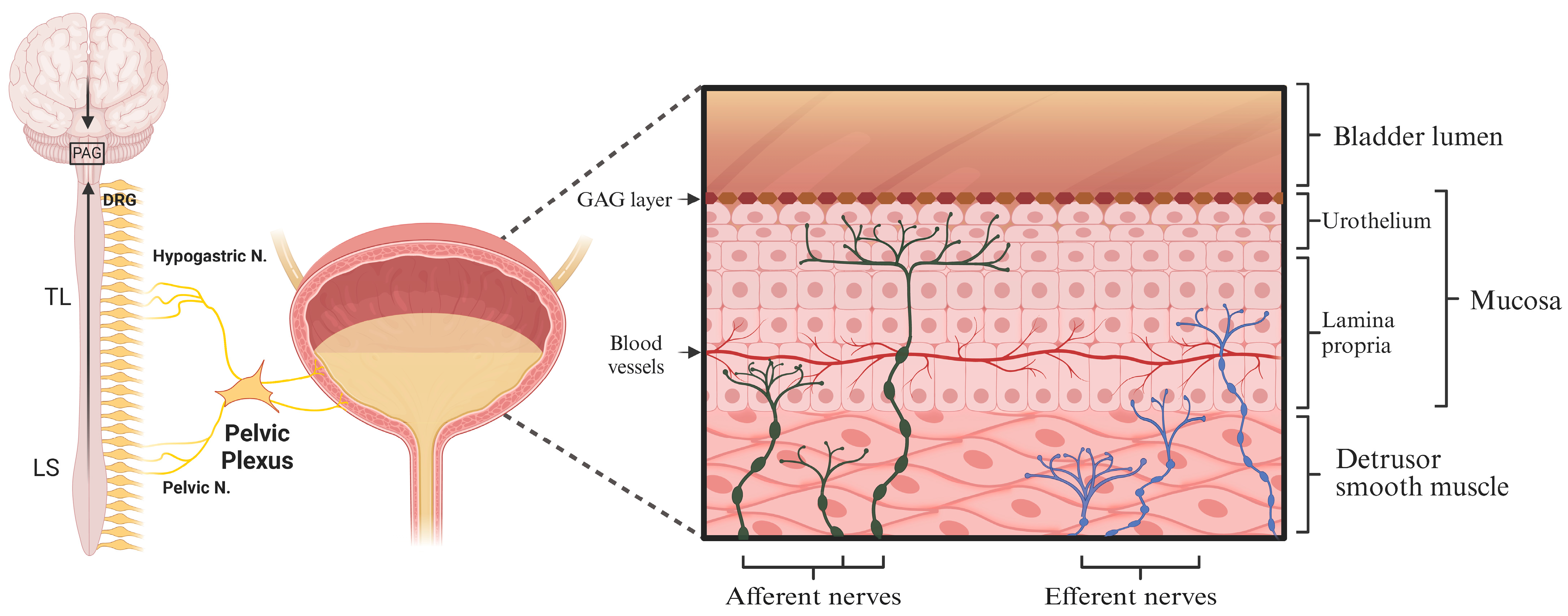
2.1. Neural Control of Bladder Sensation and Function
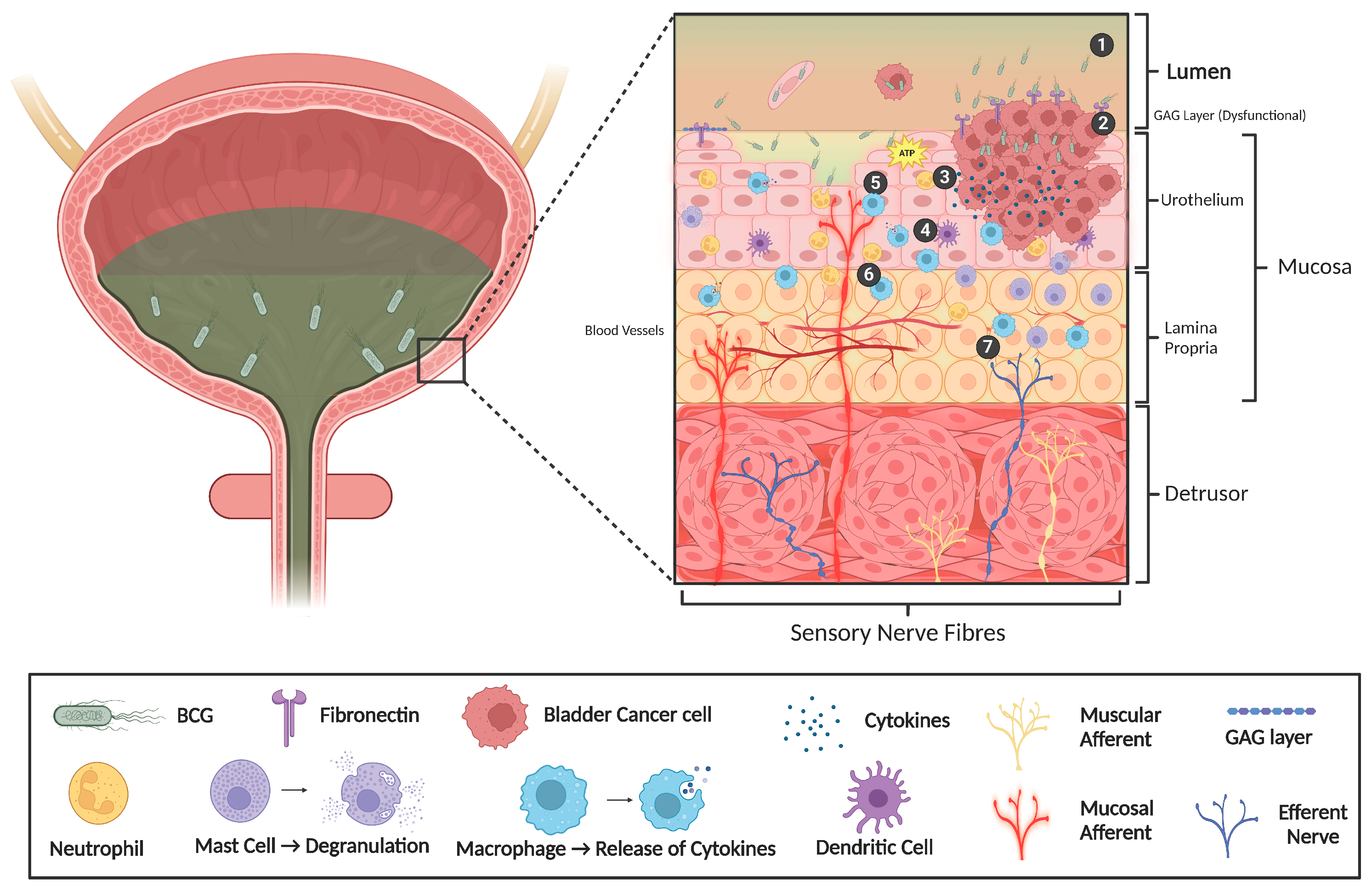
2.2. Sensitisation of Bladder Afferent Nerves During Inflammation
2.3. Altered Urothelial Permeability
2.4. Altered Urothelial Neurotransmission
2.5. Altered Bladder Contractility
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pettenati, C.; Ingersoll, M.A. Mechanisms of BCG immunotherapy and its outlook for bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadis, A.; de Reijke, T.M. Best practice in the treatment of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2012, 4, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, N.D.; Silverman, D.T.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Abnet, C.C. Association between smoking and risk of bladder cancer among men and women. JAMA 2011, 306, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanic, C.; Kogevinas, M.; Dosemeci, M.; Malats, N.; Real, F.X.; Garcia-Closas, M.; Serra, C.; Carrato, A.; García-Closas, R.; Sala, M.; et al. Smoking and bladder cancer in Spain: Effects of tobacco type, timing, environmental tobacco smoke, and gender. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Ulbright, T.; Reuter, V. Tumours of the urinary tract. In WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs; IARC: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nargund, V.H.; Tanabalan, C.K.; Kabir, M.N. Management of non-muscle-invasive (superficial) bladder cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2012, 39, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.; Kitchen, M.O.; Mathias, S.-J.; Khanim, F.L.; Bryan, R.T. Novel intravesical therapeutics in the treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: Horizon scanning. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 912438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyavihally, Y.B.; Dev, P.; Waigankar, S.; Pednekar, A.; Athikari, N.; Raut, A.; Khandekar, A.; Badlani, N.; Asari, A. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) in treating non-muscle invasive bladder cancer-analysis of adverse effects and effectiveness of two strains of BCG (Danish 1331 and Moscow-I). Asian J. Urol. 2022, 9, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babjuk, M.; Böhle, A.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Compérat, E.M.; Hernández, V.; Kaasinen, E.; Palou, J.; Rouprêt, M.; et al. EAU guidelines on non–muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: Update 2016. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, N.; Brooks, N.A.; Zlotta, A.R.; Cirillo, J.D.; Boorjian, S.; Black, P.C.; Meeks, J.J.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Gontero, P.; Steinberg, G.D.; et al. 100 years of Bacillus Calmette–Guérin immunotherapy: From cattle to COVID-19. Nature Reviews Urology 2021, 18, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q. Mechanisms of BCG in the treatment of bladder cancer-current understanding and the prospect. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvester, R.J.; van der Meijden, A.P.; Lamm, D.L. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin reduces the risk of progression in patients with superficial bladder cancer: A meta-analysis of the published results of randomized clinical trials. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhle, A.; Bock, P. Intravesical bacille Calmette-Guerin versus mitomycin C in superficial bladder cancer: Formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on tumor progression. Urology 2004, 63, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redelman-Sidi, G.; Glickman, M.S.; Bochner, B.H. The mechanism of action of BCG therapy for bladder cancer—A current perspective. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitropoulos, D.N. Novel insights into the mechanism of action of intravesical immunomodulators. In Vivo 2005, 19, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jallad, S.; Goubet, S.; Symes, A.; Larner, T.; Thomas, P. Prognostic value of inflammation or granuloma after intravesival BCG in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2014, 113, E22–E27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, E.C.; De Jong, W.H.; Van Der Meijden, A.P.; Steerenberg, P.A.; Witjes, J.A.; Vegt, P.D.J.; Debruyne, F.M.J.; Ruitenberg, E.J. Presence of activated lymphocytes in the urine of patients with superficial bladder cancer after intravesical immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1991, 33, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, E.C.; De Jong, W.H.; Steerenberg, P.A.; Aarden, L.A.; Tetteroo, E.; De Groot, E.R.; Van der Meijden, A.P.M.; Vegt, P.D.J.; Debruyne, F.M.J.; Ruitenberg, E.J. Induction of urinary interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-6, and tumour necrosis factor during intravesical immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette-Guérin in superficial bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1992, 34, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisiaux, A.; Thiounn, N.; Timsit, M.O.; Eladaoui, A.; Chang, H.H.; Mapes, J.; Mogenet, A.; Bresson, J.-L.; Prié, D.; Béchet, S.; et al. Molecular analyte profiling of the early events and tissue conditioning following intravesical bacillus calmette-guerin therapy in patients with superficial bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.B.; Kawashima, A.; Menias, C.O.; Tanaka, T.; Redelman-Sidi, G.; Bhalla, S.; Shah, R.; King, B.F. Complications of Intravesical BCG Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer. RadioGraphics 2019, 39, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naudžiūnas, A.; Juškaitė, R.; Žiaugrytė, I.; Unikauskas, A.; Varanauskienė, E.; Mašanauskienė, E. Tuberculosis complications after BCG treatment for urinary bladder cancer. Medicina 2012, 48, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, D.L.; van der Meijden, P.M.; Morales, A.; Brosman, S.A.; Catalona, W.J.; Herr, H.W.; Soloway, M.S.; Steg, A.; Debruyne, F.M. Incidence and treatment of complications of bacillus Calmette-Guerin intravesical therapy in superficial bladder cancer. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brausi, M.; Oddens, J.; Sylvester, R.; Bono, A.; van de Beek, C.; van Andel, G.; Gontero, P.; Turkeri, L.; Marreaud, S.; Collette, S.; et al. Side effects of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) in the treatment of intermediate-; high-risk Ta T1 papillary carcinoma of the bladder: Results of the EORTC genito-urinary cancers group randomised phase 3 study comparing one-third dose with full dose 1 year with 3 years of maintenance, B.C.G. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuen, J.W.; Wu, R.W.; Ching, S.S.; Ng, C.-F. Impact of Effective Intravesical Therapies on Quality of Life in Patients with Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, G.; Malmström, P.-U.; Jahnson, S.; Wijkström, H.; Nyberg, T.; Thulin, H. Bladder health in patients treated with BCG instillations for T1G2-G3 bladder cancer—A follow-up five years after the start of treatment. Scand. J. Urol. 2018, 52, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouhaud, F.X.; Rigaud, J.; Saint, F.; Colombel, M.; Irani, J.; Soulie, M.; Pfister, C. Final results of the phase III URO-BCG 4 multicenter study: Efficacy and tolerance of one-third dose BCG maintenance in nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2017, 28, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperus, J.M.; Busman, R.D.; Kuipers, S.K.; Broekhuizen, H.T.; Noyes, S.L.; Brede, C.M.; Tobert, C.M.; Lane, B.R. Comparison of side effects and tolerability between intravesical bacillus calmette-guerin, reduced-dose BCG and gemcitabine for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Urology 2021, 156, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibutani, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Mori, N. Uncommon but Clinically Significant: Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Infection of the Urinary Tract and its Impact on Quality of Life. Am. J. Case Rep. 2023, 24, e940375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, G.E.; Smelser, W.W.; Chang, S.S. Side Effects of Intravesical BCG and Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer: What They Are and How to Manage Them. Urology 2021, 149, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steg, A.; Adjiman, S.; Debre, B. BCG therapy in superficial bladder tumours--complications and precautions. Eur. Urol. 1992, 21 (Suppl. S2), 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Palou, J.; Soloway, M.; Lamm, D.; Brausi, M.; Spermon, J.R.; Persad, R.; Buckley, R.; Akaza, H.; Colombel, M.; et al. Clinical practice recommendations for the prevention and management of intravesical therapy–associated adverse events. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2008, 7, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, W.; Matuszewski, M.; Poletajew, S.; Grzegrzółka, J.; Zdrojowy, R.; Kołodziej, A. Are There Differences in Toxicity and Efficacy between Various Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Strains in Bladder Cancer Patients? Analysis of 844 Patients. Urol. Int. 2018, 101, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebacle, C.; Loriot, Y.; Irani, J. BCG-unresponsive high-grade non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: What does the practicing urologist need to know? World, J. Urol. 2021, 39, 4037–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotta, A.R.; Fleshner, N.E.; Jewett, M.A. The management of BCG failure in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: An update. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2009, 3 (Suppl. S4), S199–S205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maibom, S.L.; Joensen, U.N.; Poulsen, A.M.; Kehlet, H.; Brasso, K.; Røder, M.A. Short-term morbidity and mortality following radical cystectomy: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e043266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Park, J.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Tae, B.S. Health-related quality of life after radical cystectomy. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, I.P.; Lichtbroun, B.; Singer, E.A.; Ghodoussipour, S. Pharmacologic Therapies for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Current and Future Treatments. Arch. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 4, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Balar, A.V.; Kamat, A.M.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Uchio, E.M.; Boormans, J.L.; Roumiguié, M.; Krieger, L.E.M.; A Singer, E.; Bajorin, D.F.; Grivas, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab monotherapy for the treatment of high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer unresponsive to BCG (KEYNOTE-057): An open-label, single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchenko, I.V.; Trushina, D.B. Local Drug Delivery in Bladder Cancer: Advances of Nano/Micro/Macro-Scale Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wang, L.; Peng, J.; Lyu, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, D.; Zhang, W.; Wei, G.; Li, T.; Niu, Y.; et al. Drug-Loaded Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Bacteria for Immuno-Chemo Combo Therapy in Bladder Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2310735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, L.; Erickson, A.; Brierley, S.M. Visceral Pain. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chlebicki, M.P. Urinary tract infections in adults. Singap. Med. J. 2016, 57, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, L.; Caldwell, A.; Brierley, S.M. Mechanisms Underlying Overactive Bladder and Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chess-Williams, R.; Sellers, D.J. Pathophysiological Mechanisms Involved in Overactive Bladder/Detrusor Overactivity. Curr. Bladder Dysfunct. Rep. 2023, 18, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.-E. Bladder activation: Afferent mechanisms. Urology 2002, 59 (Suppl. S1), 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, C.J.; Griffiths, D.; de Groat, W.C. The neural control of micturition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groat, W.C.; Griffiths, D.; Yoshimura, N. Neural control of the lower urinary tract. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 327–396. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.; Kyloh, M.; Brookes, S.J.H.; Costa, M.; Spencer, N.J.; Zagorodnyuk, V.P. Morphological and neurochemical characterisation of anterogradely labelled spinal sensory and autonomic nerve endings in the mouse bladder. Auton. Neurosci. 2020, 227, 102697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Anttila, C.J.A.; Morrison, V.; Keast, J.R. Spatiotemporal mapping of sensory and motor innervation of the embryonic and postnatal mouse urinary bladder. Dev. Biol. 2021, 476, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagorodnyuk, V.P.; Costa, M.; Brookes, S.J. Major classes of sensory neurons to the urinary bladder. Auton. Neurosci. 2006, 126–127, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, L.; Harrington, A.M.; Caldwell, A.; Castro, J.; Staikopoulos, V.; Zagorodnyuk, V.P.; Brookes, S.J.; Spencer, N.J.; Brierley, S.M. Translating peripheral bladder afferent mechanosensitivity to neuronal activation within the lumbosacral spinal cord of mice. Pain 2019, 160, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, L.; Wyndaele, J.J.; Hashitani, H.; Vahabi, B.; Wein, A.; Abrams, P.; Chakrabarty, B.; Fry, C.H. How does the lower urinary tract contribute to bladder sensation? ICI-RS 2023. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2024, 43, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groat, W.C.; Yoshimura, N. Afferent nerve regulation of bladder function in health and disease. In Sensory Nerves; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 91–138. [Google Scholar]
- Meerschaert, K.A.; Adelman, P.C.; Friedman, R.L.; Albers, K.M.; Koerber, H.R.; Davis, B.M. Unique Molecular Characteristics of Visceral Afferents Arising from Different Levels of the Neuraxis: Location of Afferent Somata Predicts Function and Stimulus Detection Modalities. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 7216–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, N.; Kaiho, Y.; Miyazato, M.; Yunoki, T.; Tai, C.; Chancellor, M.B.; Tyagi, P. Therapeutic receptor targets for lower urinary tract dysfunction. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2008, 377, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, A.; Andersson, K.-E. Bladder Afferent Signaling: Recent Findings. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Inflammation 2010: New adventures of an old flame. Cell 2010, 140, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baral, P.; Udit, S.; Chiu, I.M. Pain and immunity: Implications for host defence. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, M.F.; Loh, Y.C.; Tan, C.S.; Khadijah Adam, S.; Abdul Manan, N.; Basir, R. General Pathways of Pain Sensation and the Major Neurotransmitters Involved in Pain Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.-F.; Lu, Z.Y.; Massart, C.; Levon, K. Dynamic Immune/Inflammation Precision Medicine: The Good and the Bad Inflammation in Infection and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 595722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, C.; Grundy, L. Animal models of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1232017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julius, D.; Basbaum, A.I. Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature 2001, 413, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, B.L.; Urban, L.A. Mechanisms of inflammatory pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2001, 87, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, A. Inflammatory mediators of pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 1995, 75, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.J.; Jung, H.; Bhangoo, S.K.; White, F.A. Cytokine and chemokine regulation of sensory neuron function. In Sensory Nerves; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 417–449. [Google Scholar]
- Grundy, L.; Caldwell, A.; Caraballo, S.G.; Erickson, A.; Schober, G.; Castro, J.; Harrington, A.M.; Brierley, S.M. Histamine induces peripheral and central hypersensitivity to bladder distension via the histamine H(1) receptor and TRPV1. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 318, F298–F314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, S.M.; Goh, K.G.K.; Sullivan, M.J.; Moore, K.H.; Ulett, G.C.; Grundy, L. Innate immune response to bacterial urinary tract infection sensitises high-threshold bladder afferents and recruits silent nociceptors. Pain 2020, 161, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konthapakdee, N.; Grundy, L.; O’Donnell, T.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Brierley, S.M.; Grundy, D.; Daly, D.M. Serotonin exerts a direct modulatory role on bladder afferent firing in mice. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 5247–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, M.C.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Kim, K.B.; Tuttle, J.B.; Steers, W.D. Histological and neurotrophic changes triggered by varying models of bladder inflammation. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, B.W.; Choi, H.W.; Rathore, A.P.; Bao, C.; Shi, J.; Huh, Y.; Kim, M.W.; Mencarelli, A.; Bist, P.; Ng, L.G.; et al. Recurrent infections drive persistent bladder dysfunction and pain via sensory nerve sprouting and mast cell activity. Sci. Immunol. 2024, 9, eadi5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnegelsberg, B.; Sun, T.-T.; Cain, G.; Bhattacharya, A.; Nunn, P.A.; Ford, A.P.D.W.; Vizzard, M.A.; Cockayne, D.A. Overexpression of NGF in mouse urothelium leads to neuronal hyperinnervation, pelvic sensitivity, and changes in urinary bladder function. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R534–R547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, X.; Vivó, M.; Valero-Cabré, A. Neural plasticity after peripheral nerve injury and regeneration. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 82, 163–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ochodnicky, P.; Cruz, C.D.; Yoshimura, N.; Cruz, F. Neurotrophins as regulators of urinary bladder function. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2012, 9, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowell, A.C.; Cobby, E.; Wen, K.; Devall, A.J.; During, V.; Anderson, J.; James, N.D.; Cheng, K.K.; Zeegers, M.P.; Bryan, R.T.; et al. Interleukin-17-positive mast cells influence outcomes from BCG for patients with CIS: Data from a comprehensive characterisation of the immune microenvironment of urothelial bladder cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.W.; Naskar, M.; Seo, H.K.; Lee, H.W. Tumor-Associated Mast Cells in Urothelial Bladder Cancer: Optimizing Immuno-Oncology. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, C.; Karlsson, M.; Codeluppi, S.; Varas-Godoy, M.; Zhang, S.; Louhivuori, L.; Mangsbo, S.; Hosseini, A.; Soltani, N.; Kaba, R.; et al. BCG-induced cytokine release in bladder cancer cells is regulated by Ca(2+) signaling. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saban, M.R.; Simpson, C.; Davis, C.; Wallis, G.; Knowlton, N.; Frank, M.B.; Centola, M.; Gallucci, R.M.; Saban, R. Discriminators of mouse bladder response to intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG). BMC Immunol. 2007, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsekoglu, M.F.; Sinharib, C.; Demirdag, C.; Talat, Z. Efficacy of Urinary Mast Cell Activation Markers in Patients with Primary High-Grade Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Treated with BCG Immunotherapy. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2020, 38, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsekoglu, M.F.; Kaleler, I.; Onal, B.; Demirdag, C.; Citgez, S.; Uslu, E.; Erozenci, A.; Talat, Z. Do urinary mast cell mediators predict immune response to BCG in patients with primary high-grade non-muscle invasive bladder cancer? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenwolf, P.; Southgate, J. Permeability of Differentiated Human Urothelium In Vitro. In Permeability Barrier: Methods and Protocols, Turksen, K., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 207–222. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, N.V.; Rohn, J.L. The urothelium: A multi-faceted barrier against a harsh environment. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, R.M.; Ketterer, B.; Warren, R.C. The ultrastructure and chemistry of the luminal plasma membrane of the mammalian urinary bladder: A structure with low permeability to water and ions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1974, 268, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jost, S.P.; Gosling, J.A.; Dixon, J.S. The morphology of normal human bladder urothelium. J. Anat. 1989, 167, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal, P.; Abraham, S.N.; Apodaca, G. Cell biology and physiology of the uroepithelium. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F1477–F1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodov, G.; Feloney, M.; Gran, C.; Kyker, K.D.; Hurst, R.E.; Culkin, D.J. Abnormal expression of molecular markers for bladder impermeability and differentiation in the urothelium of patients with interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, L.; Caldwell, A.; Lumsden, A.; Mohammadi, E.; Hannig, G.; Greenwood Van-Meervald, B.; Brierley, S.M. Experimentally Induced Bladder Permeability Evokes Bladder Afferent Hypersensitivity in the Absence of Inflammation. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 590871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbetti, N.; Rued, A.C.; Taiclet, S.N.; Birder, L.A.; Kullmann, F.A.; Carattino, M.D. Urothelial Tight Junction Barrier Dysfunction Sensitizes Bladder Afferents. eNeuro 2017, 4, ENEURO.0381-16.2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offiah, I.; Didangelos, A.; O’Reilly, B.A.; McMahon, S.B. Manipulating the extracellular matrix: An animal model of the bladder pain syndrome. Pain 2017, 158, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbetti, N.; Rued, A.C.; Clayton, D.R.; Ruiz, W.G.; Bastacky, S.I.; Prakasam, H.S.; Eaton, A.F.; Kullmann, F.A.; Apodaca, G.; Carattino, M.D.; et al. Increased urothelial paracellular transport promotes cystitis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2015, 309, F1070–F1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keay, S.K.; Birder, L.A.; Chai, T.C. Evidence for Bladder Urothelial Pathophysiology in Functional Bladder Disorders. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 865463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewski, J.E.; Landis, J.R.; Russack, V.; Williams, T.M.; Wang, L.-P.; Hardy, C.; Brensinger, C.; Matthews, Y.L.; Abele, S.T.; Kusek, J.W.; et al. Biopsy features are associated with primary symptoms in interstitial cystitis: Results from the interstitial cystitis database study. Urology 2001, 57, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-T.; Shie, J.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Wang, Y.-S.; Kuo, H.-C. Differences in Mast Cell Infiltration, E-cadherin, and Zonula Occludens-1 Expression Between Patients with Overactive Bladder and Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Urology 2012, 80, 225.e13–225.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, R.E.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Wisniewski, A.B.; VanGordon, S.; Lin, H.; Kropp, B.P.; Towner, R.A. Increased bladder permeability in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saban, M.R.; Hellmich, H.L.; Simpson, C.; Davis, C.A.; Lang, M.L.; Ihnat, M.A.; O’Donnell, M.A.; Wu, X.-R.; Saban, R. Repeated BCG treatment of mouse bladder selectively stimulates small GTPases and HLA antigens and inhibits single-spanning uroplakins. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, P.J.; Bree, K.K.; Brooks, N.; Matulay, J.; Li, R.; Nogueras González, G.M.; Navai, N.; Grossman, H.B.; Dinney, C.P.; Kamat, A.M. Time interval from transurethral resection of bladder tumour to bacille Calmette-Guérin induction does not impact therapeutic response. BJU Int. 2021, 128, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.H.; Kuo, H.C. Higher levels of cell apoptosis and abnormal E-cadherin expression in the urothelium are associated with inflammation in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int. 2011, 108, E136–E141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Jacques, W. Intravesical Therapy for BPS/IC. Curr. Bladder Dysfunct. Rep. 2021, 16, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvach, K.; Rosamilia, A. Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 629–637. [Google Scholar]
- Imperatore, V.; Creta, M.; Di Meo, S.; Buonopane, R.; Longo, N.; Fusco, F.; Spirito, L.; Imbimbo, C.; Mirone, V. Intravesical administration of combined hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate can improve symptoms in patients with refractory bacillus Calmette-Guerin-induced chemical cystitis: Preliminary experience with one-year follow-up. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2018, 90, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletajew, S.; Krajewski, W.; Adamowicz, J.; Radziszewski, P. A systematic review of preventive and therapeutic options for symptoms of cystitis in patients with bladder cancer receiving intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy. Anticancer. Drugs 2019, 30, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topazio, L.; Miano, R.; Maurelli, V.; Gaziev, G.; Gacci, M.; Iacovelli, V.; Finazzi-Agrò, E. Could hyaluronic acid (HA) reduce Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) local side effects? Results of a pilot study. BMC Urol. 2014, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, R.; Stäblein, J.; Mari, A.; Afferi, L.; D’Andrea, D.; Marcq, G.; del Giudice, F.; Soria, F.; Caño-Velasco, J.; Subiela, J.D.; et al. Treating BCG-Induced Cystitis with Combined Chondroitin and Hyaluronic Acid Instillations in Bladder Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birder, L.; Andersson, K.-E. Urothelial signaling. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 653–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.J.; Merrill, L.; Vizzard, M.A. Bladder sensory physiology: Neuroactive compounds and receptors, sensory transducers, and target-derived growth factors as targets to improve function. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 306, R869–R878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signalling in the lower urinary tract. Acta Physiol. 2013, 207, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chai, T.C. Augmented extracellular ATP signaling in bladder urothelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C27–C34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Keay, S.; De Deyne, P.G.; Chai, T.C. Augmented stretch activated adenosine triphosphate release from bladder uroepithelial cells in patients with interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Qi, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Urinary ATP may be a biomarker of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and its severity. Biomol. Biomed. 2024, 24, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Park, E.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Seo, S.I.; Park, Y.H.; Hwangtk, T.K. Changes of urinary nerve growth factor and prostaglandins in male patients with overactive bladder symptom. Int. J. Urol. 2005, 12, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birder, L.; Barrick, S.; Roppolo, J.; Kanai, A.; De Groat, W.; Kiss, S.; Buffington, C.A. Feline interstitial cystitis results in mechanical hypersensitivity and altered ATP release from bladder urothelium. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2003, 285, F423–F429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, B.; Barrick, S.R.; Meyers, S.; Beckel, J.M.; Zeidel, M.L.; Ford, A.P.D.W.; De Groat, W.C.; Birder, L.A. Expression and function of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors in normal and inflamed rat urinary bladder urothelium. J. Physiol. 2005, 562, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, B.M.; Wolf-Johnston, A.; Braas, K.M.; Birder, L.A.; May, V.; Vizzard, M.A. PACAP-mediated ATP release from rat urothelium and regulation of PACAP/VIP and receptor mRNA in micturition pathways after cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 36, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signalling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S172–S181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.-E.; Hedlund, P. Pharmacologic perspective on the physiology of the lower urinary tract. Urology 2002, 60, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.P.; Vemulakonda, V.M.; Kiss, S.; Boone, T.B.; Somogyi, G.T. Enhanced ATP release from rat bladder urothelium during chronic bladder inflammation: Effect of botulinum toxin A. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 47, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.F.; Ribeiro, C.M.; Sesma, J.I.; Seminario-Vidal, L.; Abdullah, L.H.; van Heusden, C.; Lazarowski, E.R.; Boucher, R.C. Inflammation promotes airway epithelial ATP release via calcium-dependent vesicular pathways. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leron, E.; Weintraub, A.Y.; Mastrolia, S.A.; Schwarzman, P. Overactive Bladder Syndrome: Evaluation and Management. Curr. Urol. 2018, 11, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Ku, J.H. Treatment strategies for the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2023, 64, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witjes, J.A. Management of BCG Failures in Superficial Bladder Cancer: A Review. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamali, K.; Nikbakht, J.; Ayubi, E.; Nabizadeh, M.; Sarhadi, S. Comparison of the Efficacy of Oxybutynin, Phenazopyridine, Celecoxib, and Placebo in the Treatment of Urinary Tract Symptoms after BCG Therapy in Patients with Bladder Tumors. Urol. J. 2020, 18, 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.H.; Nepple, K.G.; Peck, V.; Trinkaus, K.; Klim, A.; Sandhu, G.S.; Kibel, A.S. Randomized controlled trial of oxybutynin extended release versus placebo for urinary symptoms during intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin treatment. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, E.D. Mirabegron: A Review in Overactive Bladder Syndrome. Drugs 2018, 78, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wang, D.; Wu, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Mirabegron improves the irritative symptoms caused by BCG immunotherapy after transurethral resection of bladder tumors. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 7534–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozhin, A.A.; Pang, K.K.; Bukharaeva, E.; Young, C.; Slater, C.R. Recovery of mouse neuromuscular junctions from single and repeated injections of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 3163–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.-F.; Chiu, H.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Chou, E.C.-L. Botulinum toxin A for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder. Toxins 2016, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Kim, D.K.; Chiang, P.H.; Chancellor, M.B. Bladder botulinum toxin A injection can benefit patients with radiation and chemical cystitis. BJU Int. 2008, 102, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, M.; Gilhooly, P. The use of botulinum neurotoxin type a in a patient with refractory urge incontinence to facilitate the intravesical treatment of bladder carcinoma. Rev. Urol. 2014, 16, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmasri, M.; Clark, A.; Grundy, L. Peripheral Mechanisms Underlying Bacillus Calmette–Guerin-Induced Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS). Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121203
Elmasri M, Clark A, Grundy L. Peripheral Mechanisms Underlying Bacillus Calmette–Guerin-Induced Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS). Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(12):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121203
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmasri, Meera, Aaron Clark, and Luke Grundy. 2024. "Peripheral Mechanisms Underlying Bacillus Calmette–Guerin-Induced Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)" Brain Sciences 14, no. 12: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121203
APA StyleElmasri, M., Clark, A., & Grundy, L. (2024). Peripheral Mechanisms Underlying Bacillus Calmette–Guerin-Induced Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS). Brain Sciences, 14(12), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121203




