Effects of Route Complexity and Lighting on Route Following in Alzheimer’s Disease and Posterior Cortical Atrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ethical Approvals and Consent
2.3. Background Neuropsychology
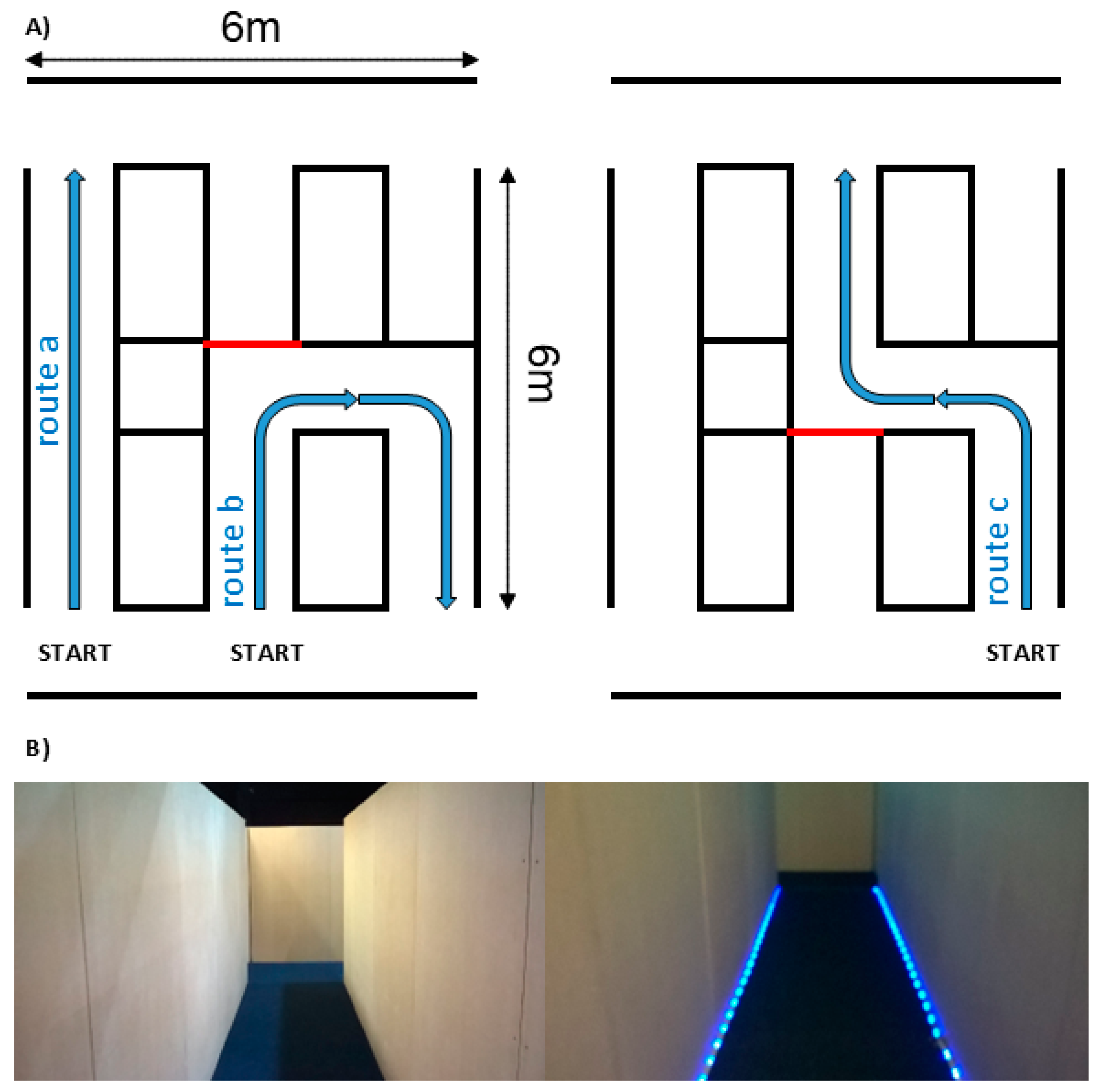
2.4. Built Environment
2.5. Route Complexity
2.6. Lighting Level
2.7. Dynamic LED Visual Cue
2.8. Procedure and Apparatus
2.9. Data Analysis
2.9.1. Completion Time
2.9.2. Kinematic Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Completion Time
3.2. Effect of Route
3.3. Kinematic Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frisoni, G.B.; Fox, N.C.; Jack, C.R.; Scheltens, P.; Thompson, P.M. The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 67–77. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrneurol.2009.215 (accessed on 17 May 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.F.; Mendez, M.A.; Martin, R.; Smyth, K.A.; Whitehouse, P.J. Complex visual disturbances in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1990, 40, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.F.; Cherrier, M.M.; Meadows, R.S. Depth Perception in Alzheimer’s Disease. Percept. Mot. Skills 1996, 83, 987–995. Available online: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.2466/pms.1996.83.3.987 (accessed on 9 August 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendola, A.; Cronin-Golomb, S.; Corkin, J.G. Prevalence of Visual Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease.pdf. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1995, 72, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, R.; Greenwood, P.M.; Alexander, G.E. Alzheimer disease constricts the dynamic range of spatial attention in visual search. Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetewsky, S.J.; Duffy, C.J.; Duffy, C.J. Visual loss and getting lost in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1999, 52, 958–965. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10102412 (accessed on 20 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- Firth, N.C.; Primativo, S.; Marinescu, R.V.; Shakespeare, T.J.; Suarez-Gonzalez, A.; Lehmann, M.; Carton, A.; Ocal, D.; Pavisic, I.; Paterson, R.W.; et al. Longitudinal neuroanatomical and cognitive progression of posterior cortical atrophy. Brain 2019, 142, 2082–2095. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/brain/article-abstract/142/7/2082/5521045 (accessed on 17 April 2020). [CrossRef]
- Paxton, J.L.; Peavy, G.M.; Jenkins, C.; Rice, V.A.; Heindel, W.C.; Salmon, D.P. Deterioration of visual-perceptual organization ability in Alzheimer’s disease. Cortex 2007, 43, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutch, S.J.; Schott, J.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Murray, M.; Snowden, J.S.; van der Flier, W.M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Vandenberghe, R.; Ahmed, S.; Bak, T.H.; et al. Consensus classification of posterior cortical atrophy. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 870–884. Available online: https://alz-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.01.014 (accessed on 3 August 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, K.X.X.; Graff-Radford, J.; Ahmed, S.; Chapleau, M.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Putcha, D.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Suarez-Gonzalez, A.; Schott, J.M.; Crutch, S.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Posterior Cortical Atrophy. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2023, 25, 23–43. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36820004 (accessed on 24 April 2017). [CrossRef]
- Graff-Radford, J.; Yong, K.X.X.; Apostolova, L.G.; Bouwman, F.H.; Carrillo, M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Schott, J.M.; Jones, D.T.; Murray, M.E.; et al. New insights into atypical Alzheimer’s disease in the era of biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 222–234. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1474442220304403 (accessed on 1 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.J.; Hodges, J.R. Attention and executive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease A critical review. Brain 1999, 122, 383–404. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/brain/article-abstract/122/3/383/527986 (accessed on 23 August 2018). [CrossRef]
- Harding, E.; Sullivan, M.P.; Woodbridge, R.; Yong, K.X.; McIntyre, A.; Gilhooly, M.L.; Gilhooly, K.J.; Crutch, S.J. “Because my brain isn’t as active as it should be, my eyes don’t always see”: A qualitative exploration of the stress process for those living with posterior cortical atrophy. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e018663. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29439072 (accessed on 30 March 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, K.X.X.; McCarthy, I.D.; Poole, T.; Suzuki, T.; Yang, B.; Carton, A.M.; Holloway, C.; Papadosifos, N.; Boampong, D.; Langham, J.; et al. Navigational cue effects in Alzheimer’s disease and posterior cortical atrophy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 697–709. Available online: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/acn3.566 (accessed on 9 May 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namazi, K.H.; Johnson, B.D. Physical environmental cues to reduce the problems of incontinence in Alzheimer’s disease units. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Dement. 1991, 6, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakespeare, T.J.; Yong, K.X.X.; Foxe, D.; Hodges, J.; Crutch, S.J. Pronounced Impairment of Everyday Skills and Self-Care in Posterior Cortical Atrophy. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 43, 381–384. Available online: https://content.iospress.com/download/journal-of-alzheimers-disease/jad141071?id=journal-of-alzheimers-disease%2Fjad141071 (accessed on 9 May 2018). [CrossRef]
- Fleming, R.; Purandare, N. Long-Term Care for People with Dementia: Environmental Design Guidelines. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2010, 22, pp. 1084–1096. [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, M.; Innes, A.; Wiener, J.M. Decreasing spatial disorientation in care-home settings: How psychology can guide the development of dementia friendly design guidelines. Dementia 2017, 16, 315–328. Available online: http://dem.sagepub.com/cgi/doi/10.1177/1471301215591334 (accessed on 9 August 2017). [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, G.; Laczó, J.; Hort, J.; Hornberger, M. Spatial Navigation Deficits-Overlooked Cognitive Marker for Preclinical Alzheimer Disease? Clinical Feasibility of Spatial Navigation as a Diagnostic Tool for Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease View Project Basal Forebrain Atrophy Contributes to Allocentric. Epub 2018. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326233339 (accessed on 23 July 2019).
- Nestor, P.J.; Caine, D.; Fryer, T.D.; Clarke, J.; Hodges, J.R. The topography of metabolic deficits in posterior cortical atrophy (the visual variant of Alzheimer’s disease) with FDG-PET. J. Neurol. Neurosurgery Psychiatry 2003, 74, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmståhl, S.; Annerstedt, L.; Åhlund, O. How should a group living unit for demented elderly be designed to decrease psychiatric symptoms? Alzheimer Dis. Assoc Disord. 1997, 11, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, A.; Dawson, A.; Greasley-adams, C.; McCabe, L. Developing best practice guidelines for designing living environments for people with dementia and sight loss. Ageing Soc. 2018, 38, 900–925. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0144686X16001409/type/journal_article (accessed on 23 July 2018). [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, G.; Schmieg, P. Dementia-friendly architecture: Environments that facilitate wayfinding in nursing homes. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2009, 24, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, T.E.; Neargarder, S.A.; Cipolloni, P.B.; Cronin-Golomb, A. Visual contrast enhances food and liquid intake in advanced Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 533–538. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261561403002103 (accessed on 24 April 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutch, S.J. Seeing why they cannot see: Understanding the syndrome and causes of posterior cortical atrophy. J. Neuropsychol. 2014, 8, 157–170. Available online: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/jnp.12011 (accessed on 24 April 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midorikawa, A.; Nakamura, K.; Nagao, T.; Kawamura, M. Residual perception of moving objects: Dissociation of moving and static objects in a case of posterior cortical atrophy. Eur. Neurol. 2008, 59, 152–158. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18285689 (accessed on 24 April 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantzartzis, E.; Price, A.D.F.; Pascale, F. A built environment response to the rising costs of dementia. J. Financ. Manag. Prop. Constr. 2016, 21, 160–187. Available online: http://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/10.1108/JFMPC-06-2015-0019 (accessed on 14 June 2018). [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.F.; Ghajaraniad, M.; Perryman, K.M. Posterior Cortical Atrophy: Clinical Characteristics and Differences Compared to Alzheimer’ s Disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2002, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang-Wai, D.F.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Parisi, J.E.; Crook, R.; Caselli, R.J.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C. Clinical, genetic, and neuropathologic characteristics of posterior cortical atrophy. Neurology 2004, 63, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1552526011001014 (accessed on 24 April 2017).
- Utton, D. The design of housing for people with dementia. J. Care Manag. Serv. 2009, 3, 380–390. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/04b8/2a30da957edf5be1dbd78085c2bfb0489ea0.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2017). [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, I.; Yong, K.; Carton, A.; Yang, B.; Boampong, D.; Holloway, C.; Tyler, N.; Carton, A.; Crutch, S. Infrastructureless Pedestrian Navigation to Assess the Response of Alzheimer’s Patients to Visual Cues. In IET International Conference on Technologies for Active and Assisted Living; IET: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1–5. Available online: http://digital-library.theiet.org/content/conferences/10.1049/ic.2015.0134 (accessed on 24 April 2017).
- McCarthy, I.; Suzuki, T.; Holloway, C.; Poole, T.; Frost, C.; Carton, A.; Tyler, N.; Crutch, S.; Yong, K. Detection and localisation of hesitant steps in people with Alzheimer’s disease navigating routes of varying complexity. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 42–47. Available online: https://digital-library.theiet.org/content/journals/10.1049/htl.2018.5034 (accessed on 21 June 2019). [CrossRef]
- Brawley, E.C. Enriching lighting design. NeuroRehabilitation 2009, 25, 189–199. Available online: http://content.iospress.com/download/neurorehabilitation/nre00515?id=neurorehabilitation%2Fnre00515 (accessed on 9 August 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengstberger, F.; Pollard, N.; Sagawa, K.; Bouma, H.; Halonen, L.; Iwai, W.; Werner, J.; Cook, G.; Akashi, Y. CIE Guide to Increasing Accessibility in Light and Lighting; CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2011; Volume 57, Available online: http://www.cie.co.at/index.php?i_ca_id=807 (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Yong, K.X.X.; McCarthy, I.D.; Poole, T.; Ocal, D.; Suzuki, A.; Suzuki, T.; Mengoudi, K.; Papadosifos, N.; Boampong, D.; Tyler, N.; et al. Effects of lighting variability on locomotion in posterior cortical atrophy. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2020, 6, e12077. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/trc2.12077 (accessed on 28 January 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakespeare, T.J.; Crutch, S.J.; Fox, N.C. Posterior cortical atrophy: Advice for diagnosis and implications for management. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2012, 2, 599–607. Available online: http://www.futuremedicine.com/doi/10.2217/nmt.12.61 (accessed on 24 August 2017). [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, A.; Harding, E.; Yong, K.X.X.; Sullivan, M.P.; Gilhooly, M.; Gilhooly, K.; Woodbridge, R.; Crutch, S. Health and social care practitioners’ understanding of the problems of people with dementia-related visual processing impairment. Heal Soc. Care Community 2019, 27, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passini, R.; Pigot, H.; Rainville, C.; Tetreault, M.-H. Wayfinding in a Nursing Home for Advanced Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type. Environ. Behav. 2000, 32, 684–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakespeare, T.J.; Pertzov, Y.; Yong, K.X.X.; Nicholas, J.; Crutch, S.J. Reduced modulation of scanpaths in response to task demands in posterior cortical atrophy. Neuropsychologia 2015, 68, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapstone, M.; Steffenella, T.M.; Duffy, C.J. A visuospatial variant of mild cognitive impairment: Getting lost between aging and, A.D. Neurology 2003, 60, 802–808. Available online: http://n.neurology.org/content/neurology/60/5/802.full.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- Shakespeare, T.J.; Kaski, D.; Yong, K.X.X.; Paterson, R.W.; Slattery, C.F.; Ryan, N.S.; Schott, J.M.; Crutch, S.J. Abnormalities of fixation, saccade and pursuit in posterior cortical atrophy. Brain 2015, 138, 1976–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, G.G.; Basilico, P.; Arighi, A.; Mercurio, M.; Scarioni, M.; Carandini, T.; Colombi, A.; Pietroboni, A.M.; Sacchi, L.; Conte, G.; et al. Parieto-occipital sulcus widening differentiates posterior cortical atrophy from typical Alzheimer disease. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 28, 102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, B.L.; Ocal, D.; Peters, A.; Bancroft, M.J.; Cash, D.; Kaski, D.; Crutch, S.J.; Yong, K.X.X. Altered visual and haptic verticality perception in posterior cortical atrophy and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Physiol. 2021, 1–19. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1113/JP282289 (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Warrington, E.K. The Camden Memory Tests Manual; Psychology Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Warrington, E.K.; McKenna, P.; Orpwood, L. Single word comprehension: A concrete and abstract word synonym test. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 1998, 8, 472. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.; Warrington, E.K. Arithmetic skills in patients with unilateral cerebral lesions. Cortex 1986, 22, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, D.M.; Warrington, E.K. Measuring dysgraphia: A graded-difficulty spelling test. Behav. Neurol. 1994, 7, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrington, E.K.; James, M.; Thames Valley Test Company. The Visual Object and Space Perception Battery; Thames Valley Test Company: Bury St. Edmunds, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, R. What is perception? In Proceedings of the Boston Colloquium for the Philosophy of Science 1966/1968; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1969; pp. 137–173. [Google Scholar]
- Willison, J.R.; Warrington, E.K. Cognitive retardation in a patient with preservation of psychomotor speed. Behav. Neurol. 1992, 5, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrington, E.K.; James, M. Visual apperceptive agnosia: A clinico-anatomical study of three cases. Cortex 1988, 24, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| A | Controls | PCA | tAD |
| Light high/low | 0.980 (0.942, 1.019) | 0.983 (0.871, 1.109) | 0.945 (0.822, 1.087) |
| Cue/no cue | 1.012 (0.997, 1.028) | 1.126 (1.002, 1.267) | 0.995 (0.947, 1.044) |
| Route U/straight | 1.470 (1.409, 1.533) | 1.914 (1.673, 2.189) | 1.741 (1.467, 2.065) |
| Route S/straight | 1.491 (1.443, 1.542) | 1.968 (1.675, 2.312) | 1.690 (1.453, 1.967) |
| Route S/Route U | 1.015 (0.991, 1.039) | 1.028 (0.950, 1.112) | 0.971 (0.926, 1.019) |
| B | Controls | PCA | tAD |
| Light high/low | 1.003 (0.885, 1.136) | 0.965 (0.837, 1.113) | 0.962 (0.810, 1.143) |
| Cue/no cue | 1.113 (0.989, 1.252) | 0.983 (0.935, 1.033) | 0.883 (0.781, 0.998) |
| Route U/straight | 1.303 (1.135, 1.495) | 1.185 (0.966, 1.409) | 0.909 (0.742, 1.115) |
| Route S/straight | 1.319 (1.121, 1.553) | 1.134 (0.972, 1.321) | 0.859 (0.699, 1.056) |
| Route S/Route U | 1.013 (0.935, 1.098) | 0.957 (0.909, 1.007) | 0.945 (0.866, 1.031) |
| Controls | PCA | tAD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Cue | Cue | No Cue | Cue | No Cue | Cue | |
| Low lighting | 1.14% | 0.43% | 1.41% | 4.54% | 1.52% | 1.04% |
| 8/703 | 3/704 | 15/1,067 | 56/1,235 | 14/923 | 9/862 | |
| High lighting | 1.05% | 1.29% | 1.59% | 2.22% | 1.17% | 0.71% |
| 7/669 | 9/699 | 18/1131 | 25/1128 | 10/852 | 6/840 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carton, A.M.; Frost, C.; Poole, T.; Yang, B.; McCarthy, I.D.; Suzuki, T.; Holloway, C.; Serougne, R.; Boampong, D.; Sullivan, M.P.; et al. Effects of Route Complexity and Lighting on Route Following in Alzheimer’s Disease and Posterior Cortical Atrophy. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121217
Carton AM, Frost C, Poole T, Yang B, McCarthy ID, Suzuki T, Holloway C, Serougne R, Boampong D, Sullivan MP, et al. Effects of Route Complexity and Lighting on Route Following in Alzheimer’s Disease and Posterior Cortical Atrophy. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(12):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121217
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarton, Amelia M., Chris Frost, Teresa Poole, Biao Yang, Ian D. McCarthy, Tatsuto Suzuki, Catherine Holloway, Robin Serougne, Derrick Boampong, Mary Pat Sullivan, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Route Complexity and Lighting on Route Following in Alzheimer’s Disease and Posterior Cortical Atrophy" Brain Sciences 14, no. 12: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121217
APA StyleCarton, A. M., Frost, C., Poole, T., Yang, B., McCarthy, I. D., Suzuki, T., Holloway, C., Serougne, R., Boampong, D., Sullivan, M. P., Tyler, N., Crutch, S., & Yong, K. X. X. (2024). Effects of Route Complexity and Lighting on Route Following in Alzheimer’s Disease and Posterior Cortical Atrophy. Brain Sciences, 14(12), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121217









