The Impact of Dexamphetamine Treatment for Obesity on Executive Function: A Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale—Short Form (BDEFS-SF)
2.3.2. Stop-Signal Task (SST)
2.4. Data Analyses
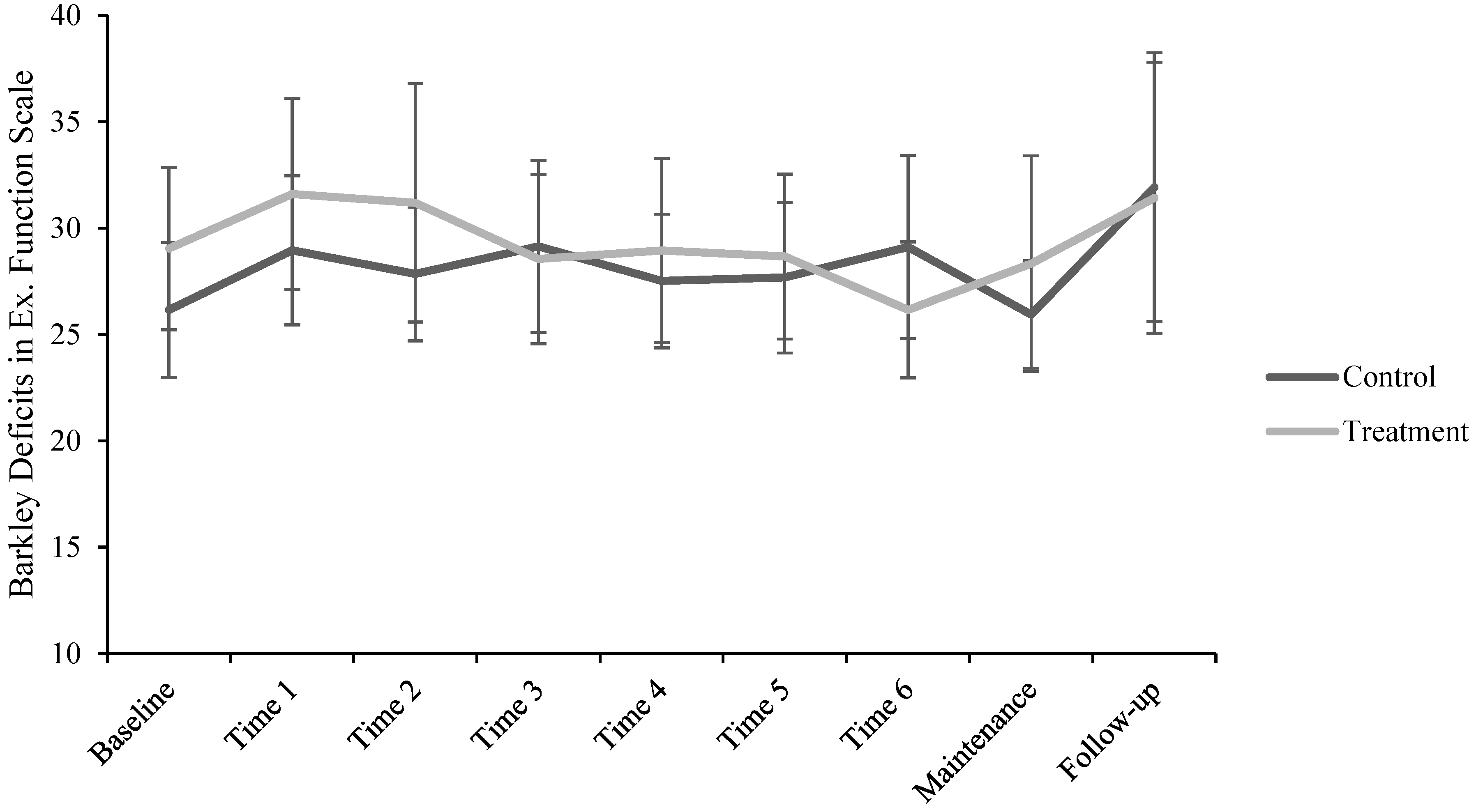
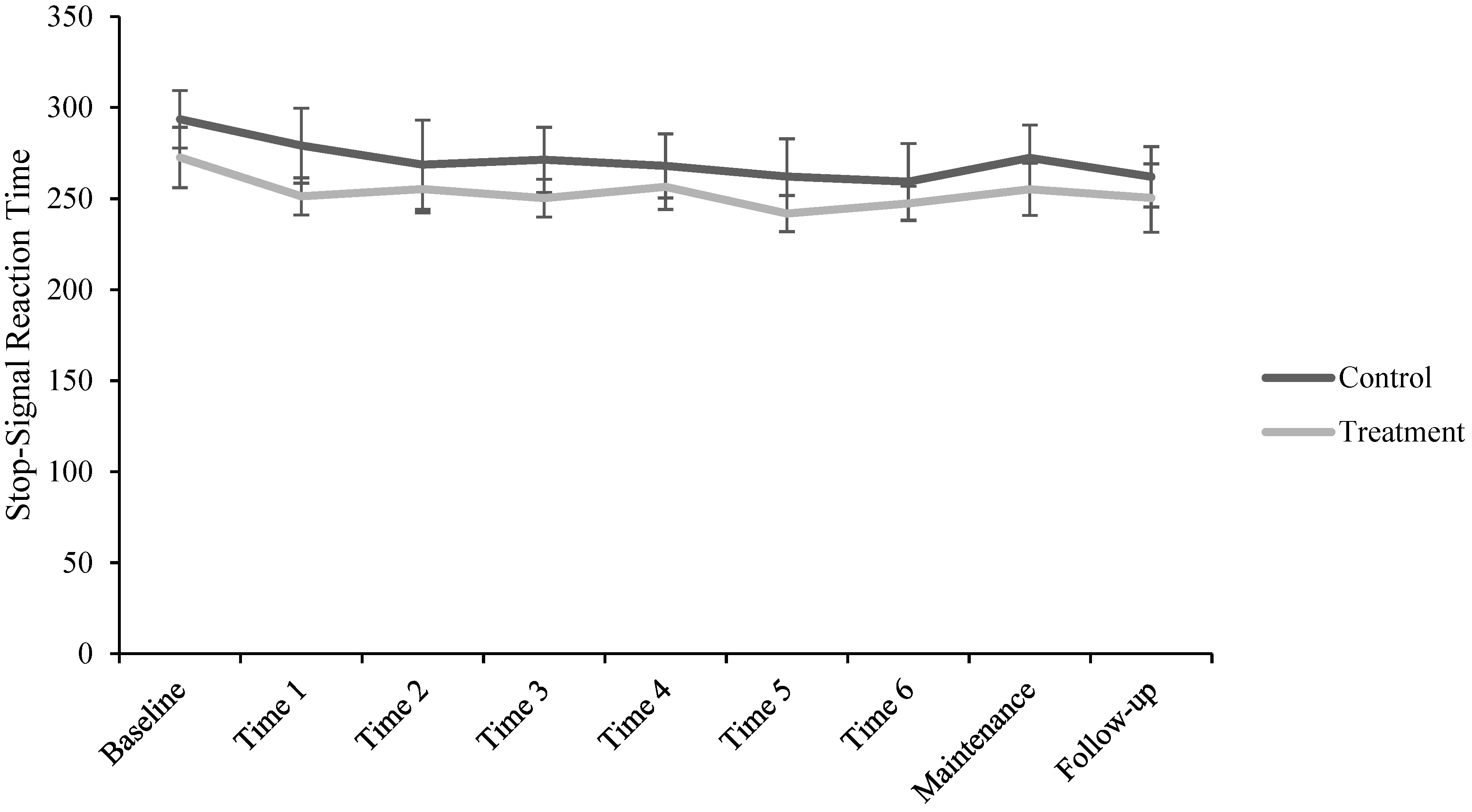
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sitte, H.H.; Freissmuth, M. Amphetamines, New Psychoactive Drugs and the Monoamine Transporter Cycle. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heal, D.J.; Smith, S.L.; Gosden, J.; Nutt, D.J. Amphetamine, Past and Present—A Pharmacological and Clinical Perspective. J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleckenstein, A.E.; Volz, T.J.; Riddle, E.L.; Gibb, J.W.; Hanson, G.R. New Insights into the Mechanism of Action of Amphetamines. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKetin, R.; Leung, J.; Stockings, E.; Huo, Y.; Foulds, J.; Lappin, J.M.; Cumming, C.; Arunogiri, S.; Young, J.T.; Sara, G.; et al. Mental Health Outcomes Associated with of the Use of Amphetamines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2019, 16, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Parada, M.; Iturriaga-Vasquez, P.; Cassels, B.K. Amphetamine Derivatives as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshen, A.; Bartel, S.; Frank, G.K.W.; Svedlund, N.E.; Nunes, A.; Dixon, L.; Ali, S.I.; Kaplan, A.S.; Hay, P.; Touyz, S.; et al. The Potential Role of Stimulants in Treating Eating Disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 55, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.I.; McElroy, S.L.; Ferreira-Cornwell, M.C.; Radewonuk, J.; Gasior, M. Efficacy of Lisdexamfetamine in Adults with Moderate to Severe Binge-Eating Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, S.L.; Hudson, J.; Ferreira-Cornwell, M.C.; Radewonuk, J.; Whitaker, T.; Gasior, M. Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate for Adults with Moderate to Severe Binge Eating Disorder: Results of Two Pivotal Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trials. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janofski, J. The Dopamine Dilemma—Part II: Could Stimulants Cause Tolerance, Dependence, and Paradoxical Decompensation? Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 8, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhan, S.E.; Kirchgessner, A. Prescription Stimulants in Individuals with and without Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Misuse, Cognitive Impact, and Adverse Effects. Brain Behav. 2012, 2, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulton, A.; Hester, R. Transition to Substance Use Disorders: Impulsivity for Reward and Learning from Reward. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Blanco, C. Substance Use Disorders: A Comprehensive Update of Classification, Epidemiology, Neurobiology, Clinical Aspects, Treatment and Prevention. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A.; Robbins, T.W. Inhibition and Impulsivity: Behavioral and Neural Basis of Response Control. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 108, 44–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wit, H.; Richards, J.B. Dual Determinants of Drug Use in Humans: Reward and Impulsivity. In 50th Nebraska Symposium on Motivation; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.Z.; Volkow, N.D. Dysfunction of the Prefrontal Cortex in Addiction: Neuroimaging Findings and Clinical Implications. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 652–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.L.; Carroll, M.E. The Role of Impulsive Behavior in Drug Abuse. Psychopharmacology 2008, 200, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenza, M.N.; Taylor, J.R. Found in Translation: Understanding Impulsivity and Related Constructs through Integrative Preclinical and Clinical Research. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilverstand, A.; Huang, A.S.; Alia-Klein, N.; Goldstein, R.Z. Neuroimaging Impaired Response Inhibition and Salience Attribution in Human Drug Addiction: A Systematic Review. Neuron 2018, 98, 886–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, W.K.; Jarmolowicz, D.P.; Mueller, E.T.; Gatchalian, K.M.; McClure, S.M. Are Executive Function and Impulsivity Antipodes? A Conceptual Reconstruction with Special Reference to Addiction. Psychopharmacology 2012, 221, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo-García, A.; Lawrence, A.J.; Clark, L. Impulsivity as a Vulnerability Marker for Substance-Use Disorders: Review of Findings from High-Risk Research, Problem Gamblers and Genetic Association Studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 777–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappin, J.M.; Sara, G.E. Psychostimulant Use and the Brain. Addiction 2019, 114, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caye, A.; Swanson, J.M.; Coghill, D.; Rohde, L.A. Treatment Strategies for ADHD: An Evidence-Based Guide to Select Optimal Treatment. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.-J.; Newcorn, J.; Telang, F.; Solanto, M.V.; Fowler, J.S.; Logan, J.; Ma, Y.; Schulz, K.; Pradhan, K.; et al. Depressed Dopamine Activity in Caudate and Preliminary Evidence of Limbic Involvement in Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.-J.; Kollins, S.H.; Wigal, T.L.; Newcorn, J.H.; Telang, F.; Fowler, J.S.; Zhu, W.; Logan, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. Evaluating Dopamine Reward Pathway in ADHD: Clinical Implications. JAMA 2009, 302, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.; Pedersen, M.L.; Mowinckel, A.M.; Biele, G. Modelling ADHD: A Review of ADHD Theories through Their Predictions for Computational Models of Decision-Making and Reinforcement Learning. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 633–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanarik, M.; Grimm, O.; Mota, N.R.; Reif, A.; Harro, J. ADHD Co-Morbidities: A Review of Implication of Gene × Environment Effects with Dopamine-Related Genes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 139, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, C.R.M.; Cortese, S.; Caye, A.; Deakin, T.K.; Polanczyk, G.V.; Polanczyk, C.A.; Rohde, L.A.P. Long-Term Efficacy of Methylphenidate Immediate-Release for the Treatment of Childhood ADHD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Atten. Disord. 2017, 21, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilder, R.M.; Loo, S.K.; McGough, J.J.; Whelan, F.; Hellemann, G.; Sugar, C.; Del’Homme, M.; Sturm, A.; Cowen, J.; Hanada, G.; et al. Cognitive Effects of Stimulant, Guanfacine, and Combined Treatment in Child and Adolescent Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 55, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Faraone, S.V. The Pharmacology of Amphetamine and Methylphenidate: Relevance to the Neurobiology of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Other Psychiatric Comorbidities. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 87, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, G.K.W.; Shott, M.E.; Stoddard, J.; Swindle, S.; Pryor, T.L. Association of Brain Reward Response with Body Mass Index and Ventral Striatal-Hypothalamic Circuitry among Young Women with Eating Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.C.; Cole, S.L.; Berridge, K.C. Lateral Hypothalamus, Nucleus Accumbens, and Ventral Pallidum Roles in Eating and Hunger: Interactions between Homeostatic and Reward Circuitry. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, S.L.; Mitchell, J.E.; Wilfley, D.; Gasior, M.; Ferreira-Cornwell, M.C.; McKay, M.; Wang, J.; Whitaker, T.; Hudson, J.I. Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Effects on Binge Eating Behaviour and Obsessive-Compulsive and Impulsive Features in Adults with Binge Eating Disorder. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2016, 24, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.M.; Hutson, P.H.; Herman, B.K.; Potenza, M.N. The Neurobiological Basis of Binge-Eating Disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 63, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, K.S.; Stice, E. Variability in Reward Responsivity and Obesity: Evidence from Brain Imaging Studies. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2011, 4, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Serralta, M.; Ciscar, S.; Blasco, L.; Oltra-Cucarella, J.; Roncero, M.; Espert, R.; Elvira, V.; Pinedo-Esteban, R.; Perpiñá, C. Contribution of Executive Functions to Eating Behaviours in Obesity and Eating Disorders. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2020, 48, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnino, L.; Arnone, D.; Cao, B.; Soares, J.C.; Selvaraj, S. Inhibitory Control in Obesity and Binge Eating Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Neurocognitive and Neuroimaging Studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Marsa, M.; Pemau, A.; de la Torre-Luque, A.; Vaz-Leal, F.; Rojo-Moreno, L.; Beato-Fernandez, L.; Graell, M.; Carrasco-Diaz, A.; Carrasco, J.L. Executive Dysfunction in Eating Disorders: Relationship with Clinical Features. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 120, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.; Priefer, R. Anti-Obesity Weight Loss Medications: Short-Term and Long-Term Use. Life Sci. 2022, 306, 120825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, K.R.; Aparício, L.; Braund, T.A.; Yang, J.; Harvie, G.; Harris, A.; Hay, P.J.; Touyz, S.; Kohn, M.R. Impulsivity and Its Relationship with Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Treatment in Binge Eating Disorder. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 716010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, R.A. Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale: Children and Adolescents (BDEFS-CA); The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Clauss, K.; Witte, T.K.; Bardeen, J.R. Examining the Factor Structure and Incremental Validity of the Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale–Short Form in a Community Sample. J. Pers. Assess. 2021, 103, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inquisit 4.0.10.0 Lab; Millisecond Software: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2013.
- Verbruggen, F.; Aron, A.R.; Band, G.; Beste, C.; Bissett, P.; Brockett, A.T.; Brown, J.W.; Chamberlain, S.; Chambers, C.; Colonius, H.; et al. A Consensus Guide to Capturing the Ability to Inhibit Actions and Impulsive Behaviours in the Stop-Signal Task. Elife 2019, 8, e46323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellgrove, M.A.; Hester, R.; Garavan, H. The Functional Neuroanatomical Correlates of Response Variability: Evidence from a Response Inhibition Task. Neuropsychologia 2004, 42, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, G.D.; Schachar, R.J.; Tannock, R. Impulsivity and Inhibitory Control. Psychol. Sci. 1997, 8, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, F.; Logan, G.D.; Stevens, M.A. STOP-IT: Windows Executable Software for the Stop-Signal Paradigm. Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulton, A.; Chen, L.P.E.; Dali, G.; Fox, M.; Hester, R. Web-Based Independent versus Laboratory-Based Stop-Signal Task Performance: Within-Subjects Counterbalanced Comparison Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e32922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congdon, E.; Mumford, J.A.; Cohen, J.R.; Galvan, A.; Canli, T.; Poldrack, R.A. Measurement and Reliability of Response Inhibition. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, R.E. Practical Significance: A Concept Whose Time Has Come. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1996, 56, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltman, H.J. Experimental Design and Analysis; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Detry, M.A.; Ma, Y. Analyzing Repeated Measurements Using Mixed Models. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meteyard, L.; Davies, R.A.I. Best Practice Guidance for Linear Mixed-Effects Models in Psychological Science. J. Mem. Lang. 2020, 112, 104092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. A General and Simple Method for Obtaining R2 from Generalized Linear Mixed-Effects Models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchetti, E.; Sparrow, S.A. Developing Criteria for Establishing Interrater Reliability of Specific Items: Applications to Assessment of Adaptive Behavior. Am. J. Ment. Defic. 1981, 86, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattingly, G.W.; Wilson, J.; Ugarte, L.; Glaser, P. Individualization of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Treatment: Pharmacotherapy Considerations by Age and Co-Occurring Conditions. CNS Spectr. 2021, 26, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKillop, J.; Weafer, J.; Gray, C.J.; Oshri, A.; Palmer, A.; de Wit, H. The Latent Structure of Impulsivity: Impulsive Choice, Impulsive Action, and Impulsive Personality Traits. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemiri, L.; Brynte, C.; Konstenius, M.; Guterstam, J.; Rosendahl, I.; Franck, J.; Jayaram-Lindström, N. Self-Rated Impulsivity in Healthy Individuals, Substance Use Disorder and ADHD: Psychometric Properties of the Swedish Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.; Milich, R.; Fillmore, M.T. The Effects of Preresponse Cues on Inhibitory Control and Response Time in Adults With ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2016, 20, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Pimenta, M.; Gruhnert, R.K.; Fuermaier, A.B.M.; Groen, Y. The Role of Executive Functions in Mediating the Relationship between Adult ADHD Symptoms and Hyperfocus in University Students. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2024, 144, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstorf, D.; Siedlecki, K.L.; Tucker-Drob, E.M.; Salthouse, T.A. Executive Dysfunctions across Adulthood: Measurement Properties and Correlates of the DEX Self-Report Questionnaire. Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2008, 15, 424–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weafer, J.; Baggott, M.J.; de Wit, H. Test-Retest Reliability of Behavioral Measures of Impulsive Choice, Impulsive Action, and Inattention. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 21, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dali, G.; Poulton, A.; Chen, L.P.E.; Hester, R. Extended Ambulatory Assessment of Executive Function: Within-Person Reliability of Working Memory and Inhibitory Control Tasks. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2024, 46, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulton, A.; Eastwood, O.; Bruns, L.R.; Sinnott, R.O.; Hester, R. Addressing Methodological Issues in a Study of Impulsivity and Vulnerability for Transition to Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 46, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.L.; Mattick, R.P.; Jamadar, S.D.; Iredale, J.M. Deficits in Behavioural Inhibition in Substance Abuse and Addiction: A Meta-Analysis. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2014, 145, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical Power Analyses Using G*Power 3.1: Tests for Correlation and Regression Analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelides, A.; Mitchell, E.S.; Behr, H.; Ho, A.S.; Hanada, G.; Lee, J.; McPartland, S. Executive Function-Related Improvements on a Commercial CBT-Based Weight Management Intervention: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, E.; Higgs, S.; Dourish, C.T. Lisdexamfetamine and Binge-Eating Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Preclinical and Clinical Data with a Focus on Mechanism of Drug Action in Treating the Disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 53, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Treatment for Stimulant Use Disorders: Treatment Improvement Protocol 33; Center for Substance Abuse Treatment: Rockville, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
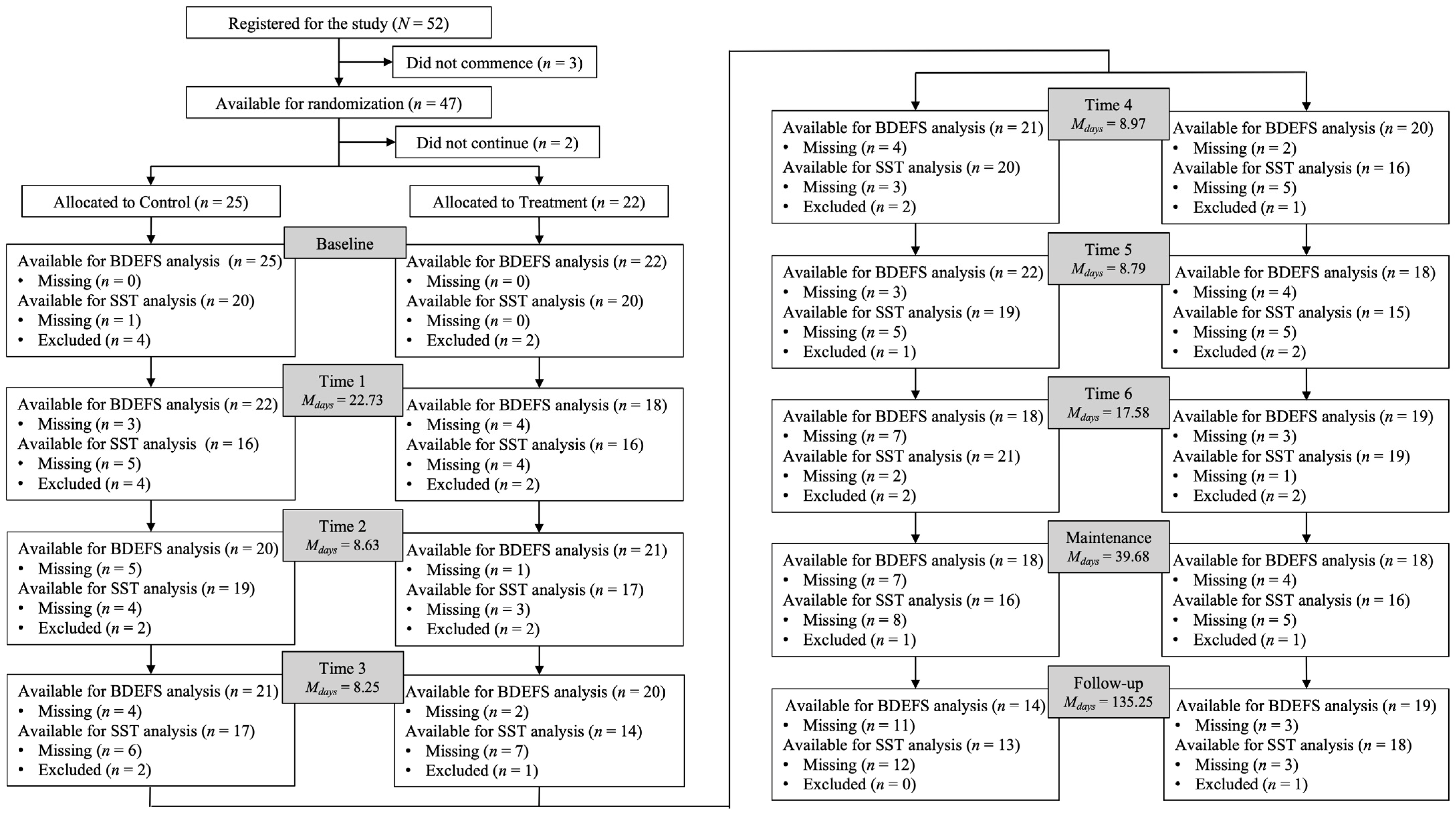
| Baseline (n = 47) | Time 1 (n = 40) | Time 2 (n = 41) | Time 3 (n = 41) | Time 4 (n = 41) | Time 5 (n = 40) | Time 6 (n = 37) | Maintenance (n = 36) | Follow-up (n = 33) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | |
| BDEFS-SF * | 27.51 (7.05) | 30.15 (7.97) | 29.56 (9.19) | 28.85 (7.93) | 28.22 (7.48) | 28.13 (7.31) | 27.60 (7.59) | 27.14 (7.98) | 31.64 (12.51) |
| Baseline (n = 40) | Time 1 (n = 32) | Time 2 (n = 36) | Time 3 (n = 31) | Time 4 (n = 36) | Time 5 (n = 34) | Time 6 (n = 40) | Maintenance (n = 32) | Follow-up (n = 31) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | |
| Go accuracy (%) | 98.27 (2.12) | 97.95 (6.27) | 98.13 (5.50) | 98.86 (1.17) | 99.06 (1.51) | 99.32 (0.76) | 97.84 (5.63) | 98.81 (1.49) | 98.79 (2.29) |
| Go RT (ms) | 552.88 (138.19) | 573.95 (151.19) | 618.09 (159.76) | 620.37 (178.08) | 641.98 (160.32) | 638.07 (156.97) | 612.59 (165.08) | 607.86 (178.72) | 641.90 (176.92) |
| Go omissions (%) | 0.81 (1.90) | 1.47 (5.95) | 1.39 (4.70) | 0.75 (0.98) | 0.69 (1.42) | 0.37 (0.68) | 1.54 (5.61) | 0.60 (1.13) | 0.84 (2.02) |
| Go errors (%) | 0.92 (1.15) | 0.57 (0.92) | 0.49 (1.22) | 0.39 (0.81) | 0.25 (0.75) | 0.29 (0.58) | 0.62 (1.45) | 0.60 (1.19) | 0.37 (0.88) |
| Stop accuracy (%) | 49.05 (4.82) | 49.06 (6.15) | 48.37 (4.83) | 48.66 (3.59) | 48.92 (5.14) | 48.72 (5.73) | 49.23 (6.25) | 49.73 (5.00) | 48.18 (5.13) |
| Failed stop RT (ms) | 483.59 (105.67) | 511.68 (130.47) | 553.21 (139.29) | 556.12 (152.27) | 578.76 (148.62) | 568.38 (133.40) | 544.40 (139.21) | 546.94 (151.76) | 573.02 (152.70) |
| SSD * (ms) | 268.37 (147.54) | 308.13 (163.84) | 355.37 (168.18) | 358.26 (183.08) | 378.68 (165.88) | 384.40 (166.90) | 358.27 (167.80) | 343.30 (189.47) | 386.25 (189.78) |
| SSRT ** (ms) | 283.21 (33.70) | 265.24 (35.00) | 262.33 (39.84) | 261.87 (31.29) | 262.93 (31.18) | 253.21 (34.90) | 253.67 (33.27) | 263.78 (33.34) | 255.30 (35.65) |
| Minutes | |
|---|---|
| M (SD) | |
| Baseline | - |
| Time 1 | 169.14 (99.34) |
| Time 2 | 165.56 (92.50) |
| Time 3 | 148.07 (82.81) |
| Time 4 | 190.00 (125.44) |
| Time 5 | 150.94 (68.97) |
| Time 6 | 154.50 (83.70) |
| Maintenance | 167.81 (78.34) |
| Follow-up | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulton, A.; Gauci, N.; Khalifa, H.; Hibbert, E.J.; Poulton, A.S. The Impact of Dexamphetamine Treatment for Obesity on Executive Function: A Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121274
Poulton A, Gauci N, Khalifa H, Hibbert EJ, Poulton AS. The Impact of Dexamphetamine Treatment for Obesity on Executive Function: A Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Pilot Study. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(12):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121274
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulton, Antoinette, Natalie Gauci, Hazer Khalifa, Emily J. Hibbert, and Alison S. Poulton. 2024. "The Impact of Dexamphetamine Treatment for Obesity on Executive Function: A Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Pilot Study" Brain Sciences 14, no. 12: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121274
APA StylePoulton, A., Gauci, N., Khalifa, H., Hibbert, E. J., & Poulton, A. S. (2024). The Impact of Dexamphetamine Treatment for Obesity on Executive Function: A Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Pilot Study. Brain Sciences, 14(12), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14121274






