Bimodal Transformer with Regional EEG Data for Accurate Gameplay Regularity Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
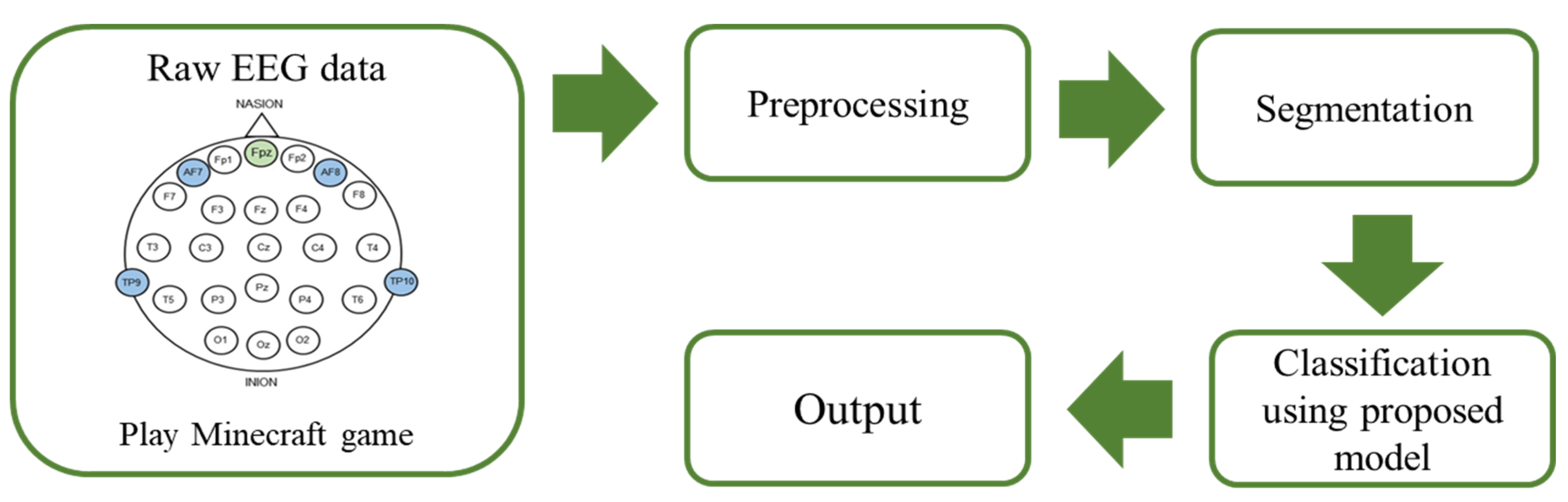
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. EEG Dataset
2.2. Preprocessing
2.3. Bimodal Transformer Structure Featuring AF and TP Channels of EEG Data
2.3.1. AF and TP Channel Convolution
2.3.2. Self-Attention and Cross-Attention Mechanisms
3. Results
3.1. Classification Results of the Proposed Model Comparing to Existing Models
- Ravindran et al. [29] is designed with separate spatial and temporal convolutions.
- EEGNet [36] features a compact and efficient CNN architecture with depthwise separable convolutions.
- BPR-STNet [37] is a neural architecture designed for the identification and classification of EEG data. It employs depthwise separable convolutions for efficient and effective feature extraction from spatiotemporal signals.
- CoSleepNet [38] introduces a cutting-edge hybrid architecture that combines CNN and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, specifically designed for the automatic classification of EEG sleep stages.
Statistical Analysis according to the Classification Results
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathews, C.L.; Morrell, H.E.R.; Molle, J.E. Video game addiction, ADHD symptomatology, and video game reinforcement. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2019, 45, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.M.; Saeed, S.M.U.; Majid, M.; Usman, S.; Mehmood, C.A.; Liu, W. A game player expertise level classification system using electroencephalography (EEG). Appl. Sci. 2017, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, A.E.; Wolbrink, T.A. Serious gaming in medical education: A proposed structured framework for game development. Simul. Healthc. 2017, 12, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.A.; Connolly, T.M.; Hainey, T.; Boyle, J.M. Engagement in digital entertainment games: A systematic review. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2012, 28, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, T.; Umar Saeed, S.M.; Arsalan, A.; Anwar, S.M.; Ashraf, M.U.; Alsubhi, K. EEG in game user analysis: A framework for expertise classification during gameplay. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaarani, B.; Ortigara, J.; Yuan, D.; Loso, H.; Potter, A.; Garavan, H.P. Association of video gaming with cognitive performance among children. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2235721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioulac, S.; Lallemand, S.; Fabrigoule, C.; Thoumy, A.L.; Philip, P.; Bouvard, M.P. Video game performances are preserved in ADHD children compared with controls. J. Atten. Disord. 2014, 18, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguera, J.A.; Boccanfuso, J.; Rintoul, J.L.; Al-Hashimi, O.; Faraji, F.; Janowich, J.; Kong, E.; Larraburo, Y.; Rolle, C.; Johnston, E.; et al. Video game training enhances cognitive control in older adults. Nature 2013, 501, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Sasaki, Y.; Watanabe, T. Real-time strategy video game experience and visual perceptual learning. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 10485–10492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, R.A. Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, A.M. Computer and Video Game Addiction—A Comparison between Game Users and Non-Game Users. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2010, 36, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, L.; Kringelbach, M.L.; Vuust, P. Ever-changing cycles of musical pleasure: The role of dopamine and anticipation. Psychomusicol. Music Mind Brain 2012, 22, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiri, L.; Mas-Herrero, E.; Zatorre, R.J.; Ripollés, P.; Gomez-Andres, A.; Alicart, H.; Olivé, G.; Marco-Pallarés, J.; Antonijoan, R.M.; Valle, A.; et al. Dopamine modulates the reward experiences elicited by music. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3793–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Dong, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Du, X.; Potenza, M.N. Dorsal and ventral striatal functional connectivity shifts play a potential role in internet gaming disorder. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepp, M.J.; Gunn, R.N.; Lawrence, A.D.; Cunningham, V.J.; Dagher, A.; Jones, T.; Grasby, P.M. Evidence for striatal dopamine release during a video game. Nature 1998, 393, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previc, F.H. Prenatal influences on brain dopamine and their relevance to the rising incidence of autism. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 68, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comings, D.E.; Wu, S.; Chiu, C.; Ring, R.H.; Gade, R.; Ahn, C.; Muhleman, D. Polygenic inheritance of Tourette syndrome, stuttering, attention deficit hyperactivity, conduct, and oppositional defiant disorder: The additive and subtractive effect of the three dopaminergic genes—DRD2, DβH, and DAT1. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996, 67, 264–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Mosa, A.H.; Al Machot, F.; Kyamakya, K. EEG-based emotion recognition approach for e-healthcare applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eighth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Vienna, Austria, 5–8 July 2016; pp. 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Boss, J.A.; Meas, P. Playing in the virtual sandbox: Students’ collaborative practices in Minecraft. Int. J. Game Based Learn. 2018, 8, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzan, N.; Sophian Shminan, A.; James Anak Binit, A.J.A. The effects of Minecraft videogame on creativity. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, W.R.; Kramer, A.F.; Simons, D.J.; Fabiani, M.; Gratton, G. The effects of video game playing on attention, memory, and executive control. Acta Psychol. 2008, 129, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, A.D.; Pratt, J.; Drummond, E. The effects of action video game experience on the time course of inhibition of return and the efficiency of visual search. Acta Psychol. 2005, 119, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, S.; Gleich, T.; Lorenz, R.C.; Lindenberger, U.; Gallinat, J. Playing Super Mario induces structural brain plasticity: Gray matter changes resulting from training with a commercial video game. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Action video game modifies visual selective attention. Nature 2003, 423, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemenson, G.D.; Henningfield, C.M.; Stark, C.E.L. Improving hippocampal memory through the experience of a rich Minecraft environment. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.; Rustad, M. Using Minecraft as an educational tool for supporting collaboration as a 21st century skill. Comput. Educ. Open 2022, 3, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.N.; Koo, I. Mixed-input deep learning approach to sleep/wake state classification by using EEG signals. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondrou, C.; Caridakis, G. Affective, natural interaction using EEG: Sensors, application and future directions. In Artificial Intelligence: Theories and Applications, Proceedings of the 7: 7th Hellenic Conference on AI, SETN 2012, Lamia, Greece, 28–31 May 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.S.; Mobiny, A.; Cruz-Garza, J.G.; Paek, A.; Kopteva, A.; Vidal, J.L.C. Assaying neural activity of children during video game play in public spaces: A deep learning approach. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 036028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, E.; Shahbakhti, M. Adaptive wavelet technique for EEG de-noising. In Proceedings of the 8th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–27 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraclough, D.J.; Conroy, M.L.; Lee, D. Prefrontal cortex and decision making in a mixed-strategy game. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeranki, Y.R.; Kumar, H.; Ganapathy, N.; Natarajan, B.; Swaminathan, R. A systematic review of sensing and differentiating dichotomous emotional states using audio-visual stimuli. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 124434–124451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayer, C.; Freedman, M. Frontal lobe functions. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2001, 1, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campitelli, G.; Gobet, F.; Head, K.; Buckley, M.; Parker, A. Brain localization of memory chunks in chessplayers. Int. J. Neurosci. 2007, 117, 1641–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.M.C.; Yip, J.T.H.; Jones-Gotman, M. Memory deficits after resection from left or right anterior temporal lobe in humans: A meta-analytic review. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: A compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Li, P.; Wang, Q.; Bai, B.; Cui, R.; Yu, Z.; Gao, D.; Zhang, Y. An EEG-based cross-subject interpretable CNN for game player expertise level classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, E.; Ozsen, S. CoSleepNet: Automated sleep staging using a hybrid CNN-LSTM network on imbalanced EEG-EOG datasets. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, H.; Al-Ahmadi, S.; Muhammad, F. Optimizing 1D-CNN-Based Emotion Recognition Process through Channel and Feature Selection from EEG Signals. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Putten, M.J.; Olbrich, S.; Arns, M. Predicting sex from brain rhythms with deep learning. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeranki, Y.R.; McNaboe, R.; Posada-Quintero, H.F. EEG-Based Seizure Detection Using Variable-Frequency Complex Demodulation and Convolutional Neural Networks. Signals 2023, 4, 816–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Information of the EEG Dataset for Our Experiments | |
|---|---|
| Number of participants | 86 |
| Number of males | 66 |
| Number of females | 20 |
| Age of participants | 8.8 ± 2.40 |
| Class | Played game often/sometimes |
| EEG device | Muse EEG headband |
| Recording EEG channel | TP9, AF7, AF8, TP10 (4 channel) |
| Sampling rate | 220 Hz |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed model | 88.86 | 85.81 | 86.03 | 87.67 |
| Ravindran et al. [29] | 81.83 | 78.81 | 77.48 | 80.64 |
| EEGNet [36] | 76.60 | 73.01 | 73.02 | 73.00 |
| BPR-STNet [37] | 79.32 | 73.53 | 74.41 | 73.91 |
| CoSleepNet [38] | 78.75 | 72.86 | 71.23 | 76.25 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed model | 85.11 | 83.29 | 81.75 | 84.89 |
| Ravindran et al. [29] | 77.63 | 74.63 | 74.01 | 75.27 |
| EEGNet [36] | 75.80 | 72.24 | 72.45 | 72.03 |
| BPR-STNet [37] | 76.16 | 72.75 | 72.71 | 72.78 |
| CoSleepNet [38] | 75.53 | 74.08 | 69.02 | 79.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Han, J.-H. Bimodal Transformer with Regional EEG Data for Accurate Gameplay Regularity Classification. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030282
Lee J, Han J-H. Bimodal Transformer with Regional EEG Data for Accurate Gameplay Regularity Classification. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(3):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030282
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jinui, and Jae-Ho Han. 2024. "Bimodal Transformer with Regional EEG Data for Accurate Gameplay Regularity Classification" Brain Sciences 14, no. 3: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030282
APA StyleLee, J., & Han, J.-H. (2024). Bimodal Transformer with Regional EEG Data for Accurate Gameplay Regularity Classification. Brain Sciences, 14(3), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030282







