Electroencephalogram-Based ConvMixer Architecture for Recognizing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Proposing ConvMixer-ECA, a novel deep learning architecture that combines ConvMixer with ECA blocks for the accurate EEG-based diagnosis of ADHD.
- Conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the performance of ConvMixer-ECA and demonstrate its superior accuracy compared to state-of-the-art deep learning models.
- Investigate the impact of different attentional mechanisms, in particular ECA, on the performance of ConvMixer and highlight the effectiveness of ECA in improving categorization performance.
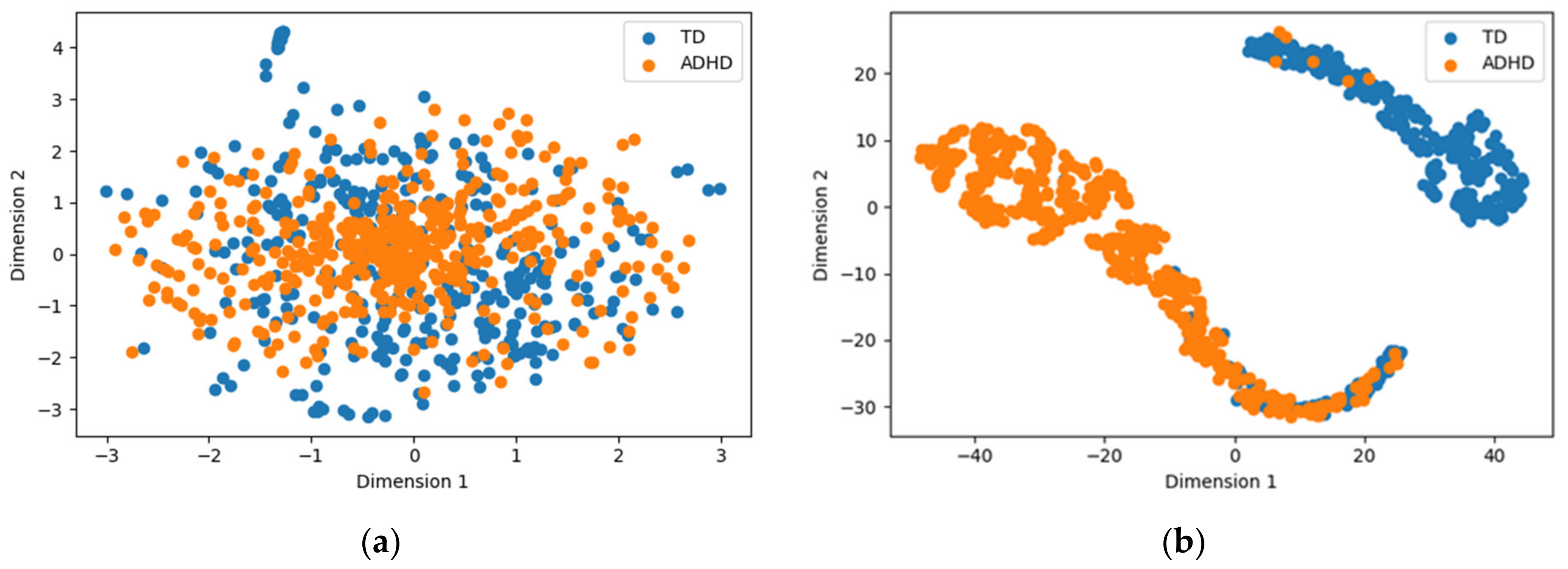
- Insights into the feature learning process of ConvMixer-ECA are provided through t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) visualization, validating its ability to capture discriminative patterns in EEG data for ADHD diagnosis.
2. Principles and Methodology
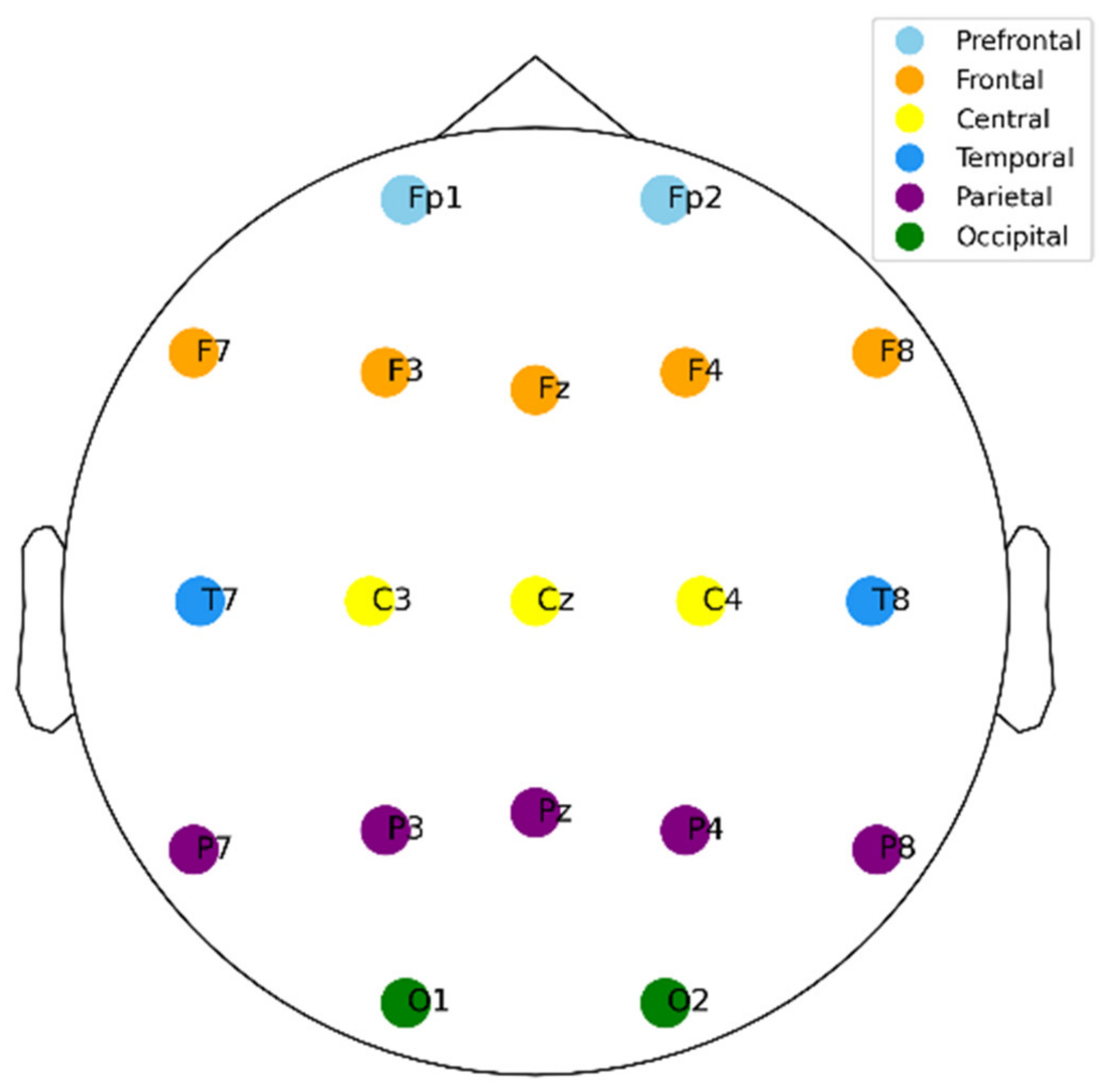
2.1. Participants and Data Preprocessing
2.2. ConvMixer Architecture
2.3. ECA Mechanism
2.4. Implementation of ConvMixer-ECA
3. Experiments and Results
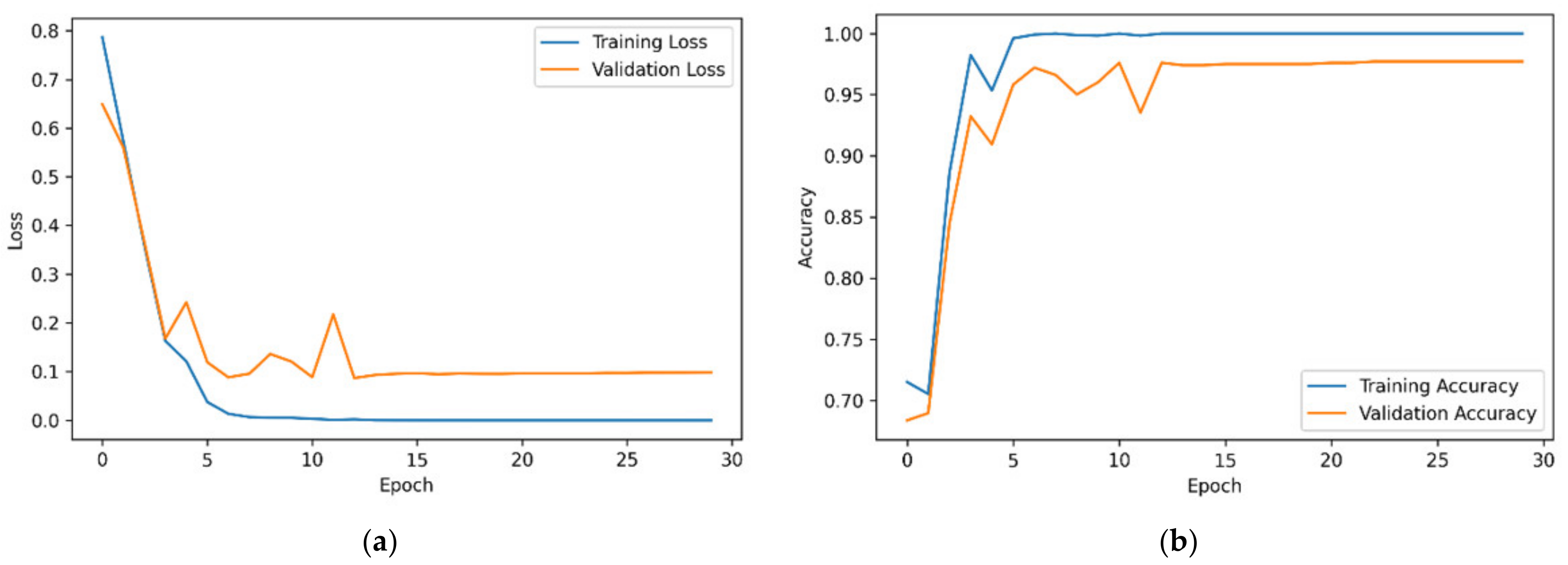
3.1. Training ConvMixer-ECA
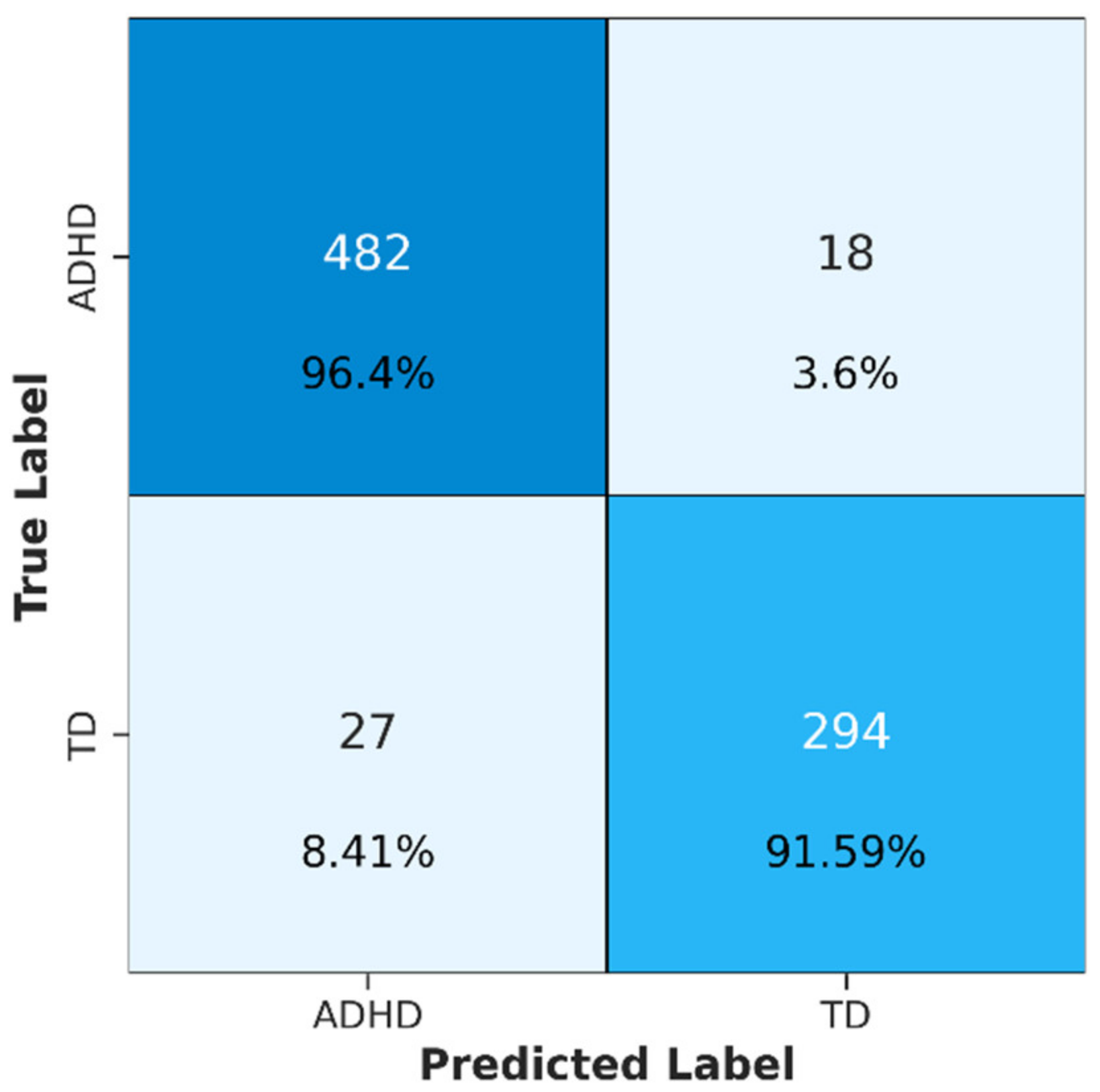
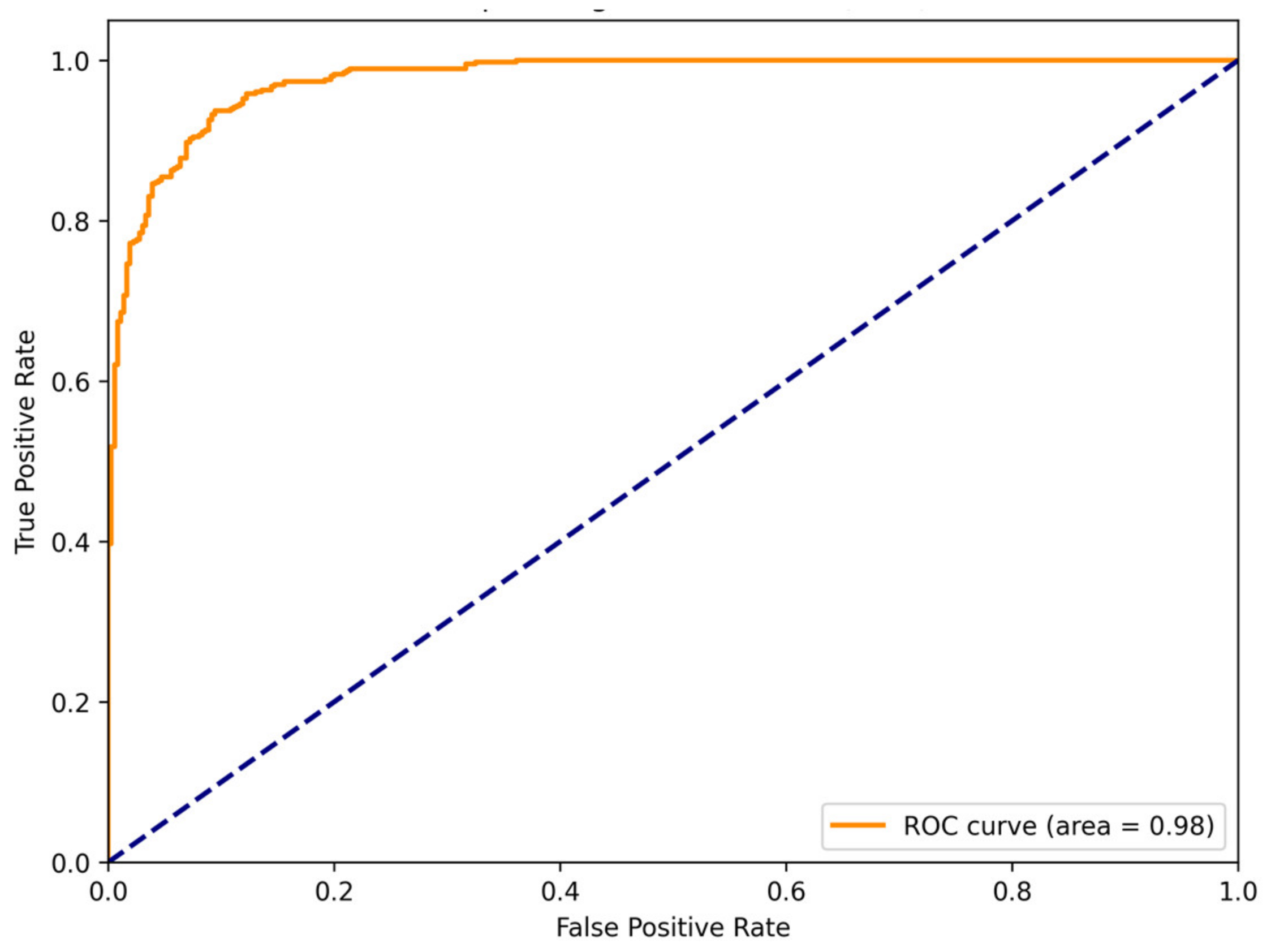
3.2. Results and Analysis
3.3. The Impact of Attention Mechanisms on ConvMixer Performance
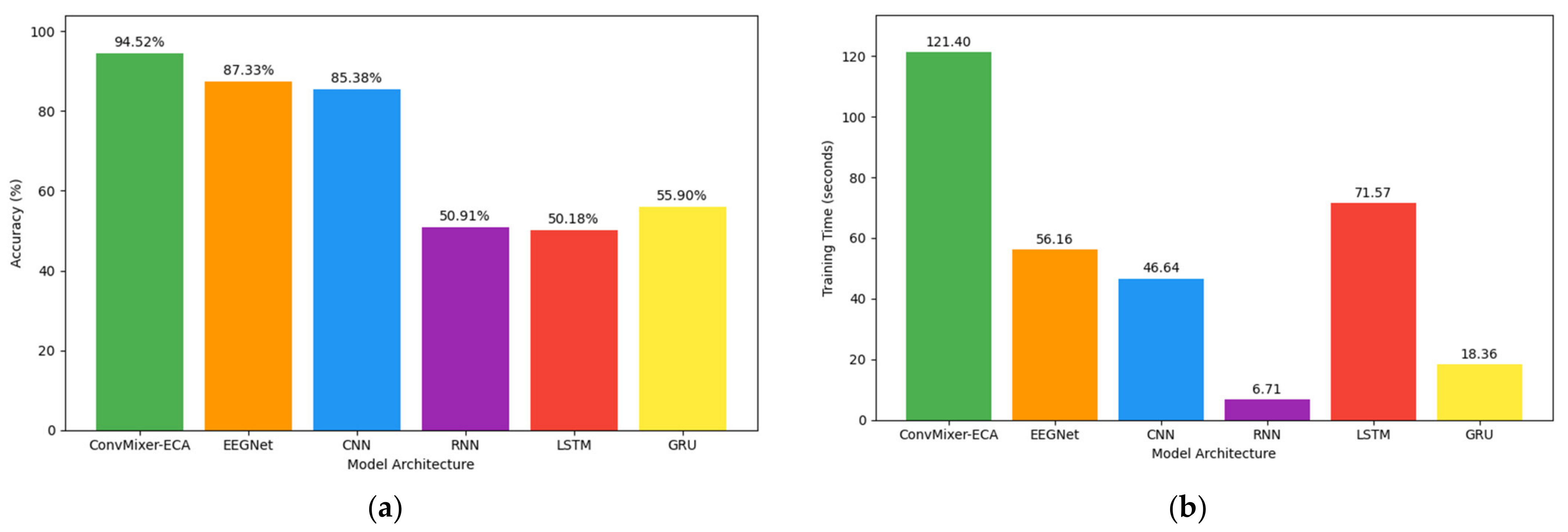
3.4. Comparative Evaluation of Recognition Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- ConvMixer-ECA performed well in detecting ADHD with an accuracy of 94.52%. This highlights its effectiveness in recognizing discriminative features and accurately classifying ADHD individuals from TD individuals.
- (2)
- The integration of attentional mechanisms, especially ECA, significantly improved the performance of the ConvMixer model. It outperformed other attention-based variants, highlighting the importance of incorporating attentional mechanisms in EEG-based recognition tasks.
- (3)
- ConvMixer-ECA outperformed existing state-of-the-art deep learning models including EEGNet, CNN, RNN, LSTM, and GRU, establishing ConvMixer-ECA as an accurate EEG-based ADHD detection method.
- (4)
- The t-SNE visualization of the output of the ConvMixer-ECA layer confirmed the model’s ability to learn to distinguish between the intrinsic patterns and features of individuals with ADHD and those with TD through hierarchical feature learning.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kollins, S.H.; DeLoss, D.J.; Cañadas, E.; Lutz, J.G.; Findling, R.L.; Keefe, R.S.; Epstein, J.N.; Cutler, A.J.; Faraone, S.V. A Novel Digital Intervention for Actively Reducing Severity of Paediatric Adhd (Stars-Adhd): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e168–e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapar, A.; Livingston, L.A.; Eyre, O.; Riglin, L. Practitioner Review: Attention-deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder—The Importance of Depression. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2022, 64, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuermaier, A.B.M.; Hüpen, P.; de Vries, S.M.; Müller, M.; Kok, F.M.; Koerts, J.; Heutink, J.; Tucha, L.; Gerlach, M.; Tucha, O. Perception in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2017, 10, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhan, Y.; Kessi, M.; Chen, S.; Xiong, J.; Deng, X.; Yang, L.; Peng, J.; Yin, F.; He, F. Urine Organic Acids as Metabolic Indicators for Global Developmental Delay/Intellectual Disability in Chinese Children. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 792319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Strathearn, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, B.; Bao, W. Twenty-Year Trends in Diagnosed Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder among Us Children and Adolescents, 1997–2016. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e181471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Xu, J.; Zhai, M.; Wu, Q.; Chu, K.; Xie, L.; Luo, R.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Xu, X.; et al. Behavior Management Training for Parents of Children with Preschool ADHD Based on Parent-Child Interactions: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled, Follow-Up Study. Behav. Neurol. 2023, 2023, 3735634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.L.; Valentine, A.; Groom, M.J.; Walker, G.; Sayal, K.; Daley, D.; Hollis, C. The Clinical Utility of the Continuous Performance Test and Objective Measures of Activity for Diagnosing and Monitoring Adhd in Children: A Systematic Review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 25, 677–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenartowicz, A.; Loo, S.K. Use of Eeg to Diagnose Adhd. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2014, 16, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Xu, J. Detection of ASD Children through Deep-Learning Application of fMRI. Children 2023, 10, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.; Chang, C.; Chang, Y.; Lin, D.; Lin, C.; Ko, L. Neural Dynamics for Facilitating Adhd Diagnosis in Preschoolers: Central and Parietal Delta Synchronization in the Kiddie Continuous Performance Test. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, R.C.; George, S.T.; Rajan, A.A.; Subathra, M.S.P.; Sairamya, N.J.; Prasanna, J.; Mohammed, M.A.; Al-Waisy, A.S.; Jaber, M.M.; Al-Andoli, M.N. Detection and Classification of Adhd from Eeg Signals Using Tunable Q-Factor Wavelet Transform. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 3590973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, S.K.; Makeig, S. Clinical Utility of Eeg in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Research Update. Neurotherapeutics 2012, 9, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, A.; Bluschke, A.; Roessner, V.; Stober, S.; Beste, C. Deep Learning Based on Event-Related Eeg Differentiates Children with Adhd from Healthy Controls. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Stevenson, C.; Chen, I.; Lin, D.; Ko, L. Neurological State Changes Indicative of Adhd in Children Learned via Eeg-Based Lstm Networks. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 016021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil-Vall, L.; Ruffini, G.; Camprodon, J.A. Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks Discriminate Adult ADHD from Healthy Individuals on the Basis of Event-Related Spectral EEG. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 515034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, M. Effects of Spectral Features of EEG Signals Recorded with Different Channels and Recording Statuses on ADHD Classification with Deep Learning. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2021, 44, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Rani, R.; Kalra, N. Prediction of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Using Machine Learning Techniques Based on Classification of EEG Signal. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 25–26 March 2022; Volume 1, pp. 782–786. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Li, X. Use of Deep Learning to Detect Personalized Spatial-Frequency Abnormalities in EEGs of Children with ADHD. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 066046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Kazemi, K.; Kuc, K.; Cybulska-Kłosowicz, A.; Helfroush, M.S.; Aarabi, A. Resting State Dynamic Functional Connectivity in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 0460d1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Singh, B.K. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Detection in Children Using Multivariate Empirical Eeg Decomposition Approaches: A Comprehensive Analytical Study. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanus, C.; Miladinović, A.; De Dea, F.; Skabar, A.; Stecca, M.; Ajčević, M.; Accardo, A.; Carrozzi, M. Sleep Spindle-Related Eeg Connectivity in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: An Exploratory Study. Entropy 2023, 25, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Park, E.; Han, J. A Deep Learning Model for Detecting Mental Illness from User Content on Social Media. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.S.; Galatzer-Levy, I.R.; Bigio, B.; Nasca, C.; Zhang, Y. Modern Views of Machine Learning for Precision Psychiatry. Patterns 2022, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Xie, H.; Fonzo, G.A.; Zhao, K.; Satterthwaite, T.D.; Carlisle, N.B.; Zhang, Y. Symptom Dimensions of Resting-State Electroencephalographic Functional Connectivity in Autism. Nat. Ment. Health 2024, 2, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trockman, A.; Kolter, J.Z. Patches Are All You Need? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.09792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W. CMAT: Integrating Convolution Mixer and Self-Attention for Visual Tracking. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Pan, J.; Tang, J. Shufflemixer: An Efficient Convnet for Image Super-Resolution. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 17314–17326. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Azzam, R.; Javed, S.; Gan, D.; Seneviratne, L.; Abdelqader, A.; Zweiri, Y. Cm-Unet: Convmixer Unet for Segmentation of Unknown Objects in Cluttered Scenes. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 123622–123633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. Eca-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Vaichole, T.S.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Yadav, O.; Khan, F. Eff2Net: An Efficient Channel Attention-Based Convolutional Neural Network for Skin Disease Classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 73, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, A.M.; Allahverdy, A.; Samavati, M.; Mohammadi, M.R. EEG Data for ADHD/Control Children. IEEE Dataport 2020, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Zhai, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Huang, Y.; Ke, X. Kindergarten-Based Screening of ADHD in Preschool Children. J. Nanjing Med. Univ. 2022, 42, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, M.; Lubar, J.F.; Joffe, D. Low-Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography Neurofeedback. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2004, 12, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyari, M.; Mirzaei, S. ADHD Detection Using Dynamic Connectivity Patterns of EEG Data and ConvLSTM with Attention Framework. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 76, 103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafi, M.; Radfar, S. High Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network for EEG Connectivity-Based Diagnosis of ADHD. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2022, 12, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, X. Detection of Concrete Structural Defects Using Impact Echo Based on Deep Networks. J. Test. Eval. 2021, 49, 20190801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: A Compact Convolutional Neural Network for EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenev, A.; Markovska-Simoska, S.; Kocarev, L.; Pop-Jordanov, J.; Müller, A.; Candrian, G. Machine Learning Approach for Classification of ADHD Adults. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 93, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnoud, S.; Shamsi, M.; Nazari, M.A. Non-Linear EEG Analysis in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder during the Rest Condition. In Proceedings of the 2015 22nd Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME), Tehran, Iran, 22–27 November 2015; pp. 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, M.R.; Khaleghi, A.; Nasrabadi, A.M.; Rafieivand, S.; Begol, M.; Zarafshan, H. EEG Classification of ADHD and Normal Children Using Non-Linear Features and Neural Network. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2016, 6, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, J.; Lim, M.H.; Kim, K.M. Comparison of Quantitative Electroencephalography between Tic Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2021, 19, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, P.; Cueli, M.; Cañamero, L.M.; Castro, P.G. A Case Study in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: An Innovative Neurofeedback-Based Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpelli, S.; Gorgoni, M.; D’Atri, A.; Reda, F.; Gennaro, L.D. Advances in Understanding the Relationship between Sleep and Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder (Adhd). J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosch, K.S.; Mostofsky, S.H.; Nebel, M.B. Adhd-Related Sex Differences in Fronto-Subcortical Intrinsic Functional Connectivity and Associations with Delay Discounting. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2018, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fold | Fold 1 | Fold 2 | Fold 3 | Fold 4 | Fold 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.9245 | 0.9038 | 0.9567 | 0.9245 | 0.9354 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConvMixer | 0.9160 | 0.9016 | 0.9544 | 0.9273 |
| ConvMixer-CBA | 0.9196 | 0.9022 | 0.9610 | 0.9307 |
| ConvMixer-SEA | 0.9318 | 0.9299 | 0.9501 | 0.9399 |
| ConvMixer-NLA | 0.9415 | 0.9460 | 0.9501 | 0.9481 |
| ConvMixer-ECA | 0.9452 | 0.9469 | 0.9640 | 0.9554 |
| Author | Year | Dataset | Method | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenev et al. [38] | 2014 | 50 healthy, 67 ADHD | SVM and voting | 82.3 |
| Khoshnoud et al. [39] | 2015 | 10 healthy, 12 ADHD | LLE, ApEn, PNN | 87.5 |
| Mohammadi et al. [40] | 2016 | 30 healthy, 31 ADHD | MLP neural network | 93.65 |
| Chen et al. [18] | 2019 | 57 healthy, 50 ADHD | Deep CNN | 90.29 |
| Dubreuil-Vall et al. [15] | 2020 | 20 healthy, 20 ADHD | Spectrogram and CNN | 88.0 |
| Tosun [16] | 2021 | 16 subject | Data augmentation, PSD, SE, and LSTM | 92.15 |
| Saini et al. [17] | 2022 | 80 healthy, 77 ADHD | PCA, KNN | 86.0 |
| Our proposed approach | 2024 | 60 healthy, 61 ADHD | ConvMixer with ECA | 94.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, M.; Xu, J. Electroencephalogram-Based ConvMixer Architecture for Recognizing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050469
Feng M, Xu J. Electroencephalogram-Based ConvMixer Architecture for Recognizing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(5):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050469
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Min, and Juncai Xu. 2024. "Electroencephalogram-Based ConvMixer Architecture for Recognizing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children" Brain Sciences 14, no. 5: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050469
APA StyleFeng, M., & Xu, J. (2024). Electroencephalogram-Based ConvMixer Architecture for Recognizing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children. Brain Sciences, 14(5), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050469








