Abstract
Background: Navigated repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a promising tool for neuromodulation. In previous studies it has been shown that the activity of the default mode network (DMN) areas, particularly of its key region—the angular gyrus—is positively correlated with the level of consciousness. Our study aimed to explore the effect of rTMS of the angular gyrus as a new approach for disorders of consciousness (DOC) treatment; Methods: A 10-session 2-week high-frequency rTMS protocol was delivered over the left angular gyrus in 38 DOC patients with repeated neurobehavioral assessments obtained at baseline and in 2 days after the stimulation course was complete; Results: 20 Hz-rTMS over left angular gyrus improved the coma recovery scale revised (CRS-R) total score in minimally conscious state (MCS) patients. We observed no effects in vegetative state (VS) patients; and Conclusions: The left angular gyrus is likely to be effective target for rTMS in patients with present signs of consciousness.
1. Introduction
Some patients who have survived prolonged coma after severe brain damage and regained wakefulness develop disorders of consciousness (DOC). Depending on the presence of observable signs of consciousness, these states can be divided into the vegetative state (VS, also called the unresponsiveness wakefulness syndrome, UWS) and the minimally conscious state (MCS). While MCS patients have minimal but persistent reproducible behavioral evidence of self-awareness and reactivity, VS patients completely lack any apparent signs of cognitive activity.
Chronic DOC is clinically challenging as prognosis for functional recovery is poor for the majority of patients, and effective pharmacologic therapy is currently lacking [1,2]. Neurostimulation techniques have been recognized as promising experimental approaches to DOC treatment. Nowadays non-invasive brain stimulation methods (NIBS), such as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), prove themselves as promising tools. Few studies have addressed the application of NIBS, with conflicting results [3]. Thibaut et al. in 2014 observed transiently improved signs of consciousness in 13 of 30 MCS patients following severe brain damage as measured by changes in the CRS-R total scores after a single session of tDCS over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), while no effect was seen in VS/UWS subjects [4]. Similar results were obtained in another study using a five-day course of anodal tDCS in MCS patients [5]. Finally, the recently reported results of a study of prolonged home-based tDCS also demonstrated an improvement of signs of consciousness in MCS patients [6]. Stimulation of the right DLPFC with rTMS resulted in some behavioral gain in one posttraumatic VS patient and transient improvement in three of 10 post-anoxic UWS patients; improvement in the levels of consciousness and behavior was also reported by Xie et al. in a set of UWS, MCS and comatose patients [7,8]. When applied over the left DLPFC, rTMS resulted in a notable clinical improvement in MCS subjects in contrast to VS patients in a study by Xia et al. [9]. Piccione et al. in 2011 reported that 20Hz rTMS delivered on the left primary motor cortex (M1) had improved awareness and arousal in an MCS patient [10]. On the other hand, no effects of rTMS of the motor cortex in VS patients were reported by a randomized, sham-controlled study; similar findings were obtained in a set of VS and MCS patients by Liu et al. [9,11]. Protocols of stimulation in the abovementioned studies varied widely which also may be the reason for inconclusive results. Overall, the results of NIBS studies suggest that neuromodulation of certain regions involved in the networks supporting consciousness is worth further investigation as a safe and potentially effective approach for facilitating recovery in chronic DOC patients.
A key question is the choice of a brain area may potentially produce clinically significant behavioral improvement in DOC patients and is suitable for non-invasive stimulation. The structural architecture and functional interactions supporting consciousness are poorly understood, however, there are evidences that functional and structural connectivity within the default mode network (DMN) correlate with the level of behavioral responsiveness in DOC patients [12,13,14]. Perhaps due to the close connection of DMN regions to introspective cognition and memory—visual imagery is linked to activation of supramodal and frontoparietal areas associated with attention and cognitive control and visual cortical regions most strongly activated by visual perception itself and [15,16,17]. Furthermore, connectivity within DMN may have prognostic value for the recovery of consciousness [18,19]. Several areas of DMN, namely posterior cingulate cortex and precuneus, may be the subject of special attention as intrinsic connectivity within these brain areas significantly correlated with consciousness level and recovery [18]. The decreases of connectivity and metabolism in these regions of the DMN are observed as a key marker of the impairment of consciousness [12,13,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
Based on these studies we aimed to choose those DMN regions, stimulation of which may potentially affect consciousness-related brain networks and that are technically feasible for transcranial magnetic stimulation. We particularly suggest left angular gyrus as a target for TMS due to its significant relations to other regions of the brain involved in a number of processes such as language, number processing and spatial cognition, memory retrieval and attention (Brodmann area 39). The angular gyrus occupies a central location from a neuroanatomical perspective to act as a multimodal convergence hub within the DMN. It receives inputs from the primary sensory cortices and integrates sensory information of different modalities [28,29,30]. These mechanisms may extend the role of the angular gyrus into post-sensory processes such as memory retrieval [31,32]. All these facts demonstrate the multimodal integrative functions of the angular gyrus and reflect its possible role in the process of consciousness. In contrast to the cingulate cortex, the angular gyrus is located on the convexital surface of the brain and is easily accessible for transcranial stimulation.
Therefore, we aimed to verify whether repeated sessions of rTMS navigated to the left angular gyrus may produce clinical behavioral improvements (assessed by CRS-R) in DOC patients.
2. Materials and Methods
We developed an open non-randomized study protocol that was approved by the local ethics committee of the Research Center of Neurology. All patients’ legal representatives signed an informed consent form approved by the local ethics committee before enrollment.
2.1. Eligibility Criteria and Clinical Assessment
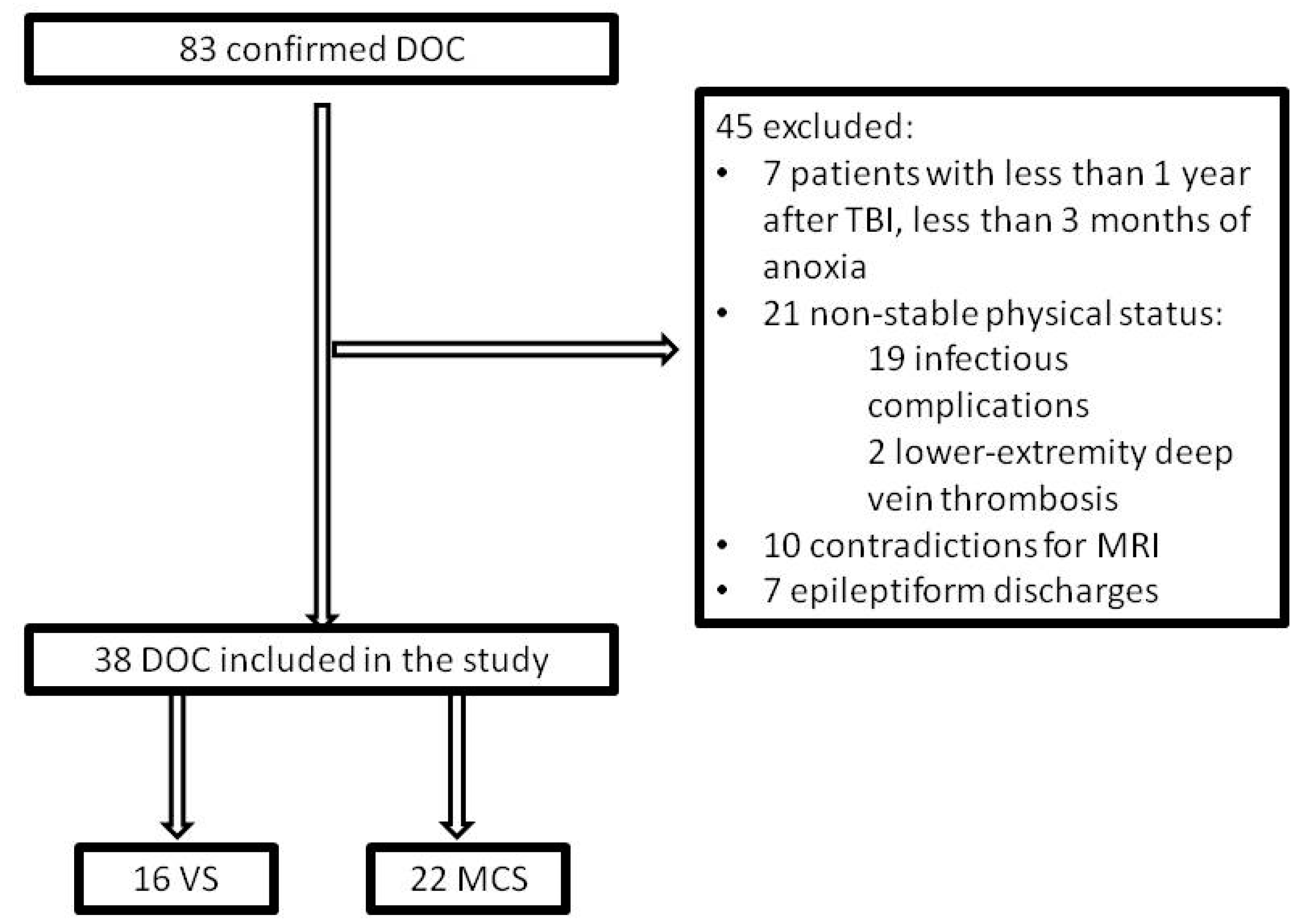
Inclusion criteria were a history of traumatic or anoxic brain injury and verified DOC status. Participants were excluded if they were in non-stable clinical status (e.g., acute myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis, or episodes of pulmonary embolism, acute infections, sepsis, severe anemia, etc.) or had implanted medical devices such as cerebral shunt, cardiac pacemaker, intracardiac catheter, or electronic pump, metal plates closing skull defects, metallic staples or vascular sutures. Patients who showed epileptiform discharges on EEG screening were also excluded due to safety issues (see Figure 1).
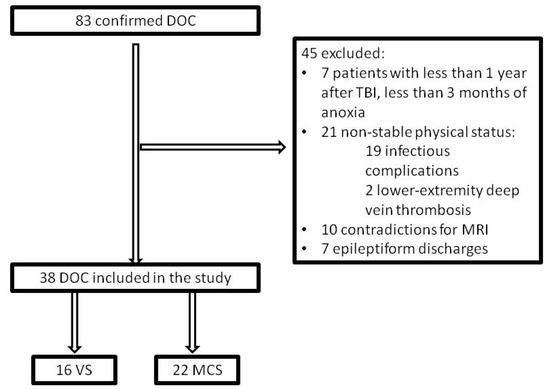
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram. DOC: disorders of consciousness; TBI: traumatic brain injury; VS: vegetative state; MCS: minimally conscious state.
Clinical assessment was performed by trained and experienced clinicians using the validated Russian version of the CRS-R score [33]. We applied internationally established criteria for diagnosing VS and MCS. CRS-R assessment was performed at baseline (before the stimulation) and in two days after the stimulation course was completed [34,35,36]. Changes from baseline in the total score of the CRS-R and in the scores of the six CRS-R subscales addressing auditory, visual, motor, oromotor/verbal, communication, and arousal processes were tested with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Statistical analyses were performed using Matlab (2017a, MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA).
2.2. Structural MRI
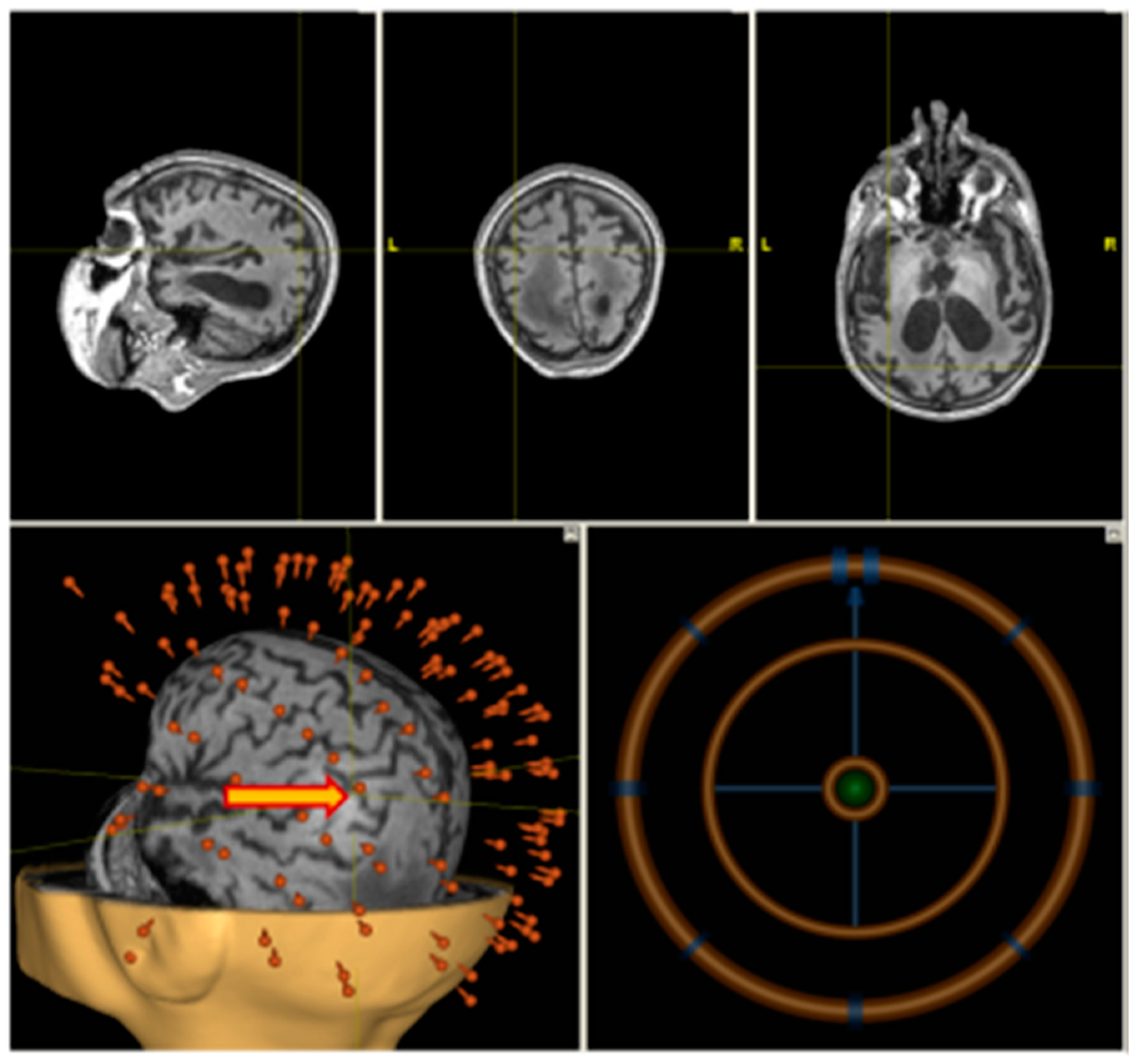
A high-resolution T1-weighted anatomical scan (MP–RAGE or SPGR) was obtained using Siemens MAGNETOM Verio 3T (Siemens AG, Muenchen, Germany) clinical scanner. A total of 176 sagittal slices were acquired to cover the whole brain. Anatomical imaging was co-registered with a patient’s head in the neuronavigation system (Nexstim Ltd., Helsinki, Finland). The stimulation point corresponding to the anatomical location over the angular gyrus was chosen individually using the T1 scan (Figure 2).
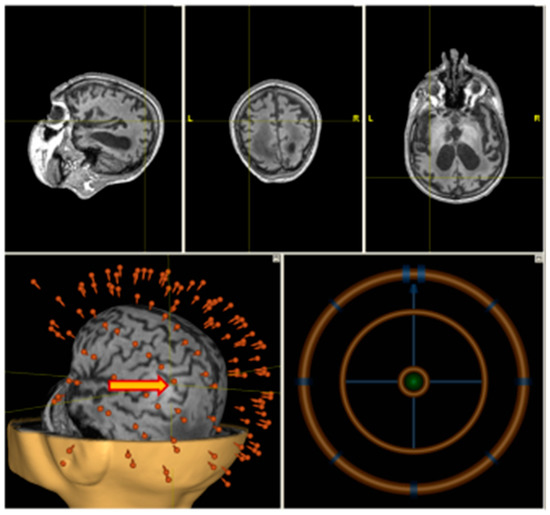
Figure 2.
Individual navigation (Nexstim) on left angular gyrus.
2.3. rTMS
High frequency rTMS was delivered on a non-navigated Neurosoft stimulator (Neurosoft ltd., Ivanovo, Russia) (see Figure 2) with figure-eight coil.
We used the target transfer method allowing us to mark the desired sites of stimulation using the neuronavigated system to continue the therapeutic protocol on a non-navigated system in the intensive care unit to avoid transportation difficulties, and the stimulation point was marked on an individual skull-cap. All patients received an rTMS course consisting of 10 sessions, scheduled five times a week over two consecutive weeks. Stimulation intensity was determined individually as 80% of the resting motor threshold (RMT). RMT was defined as the lowest stimulation intensity which produced a visible hand muscle twitch in five out of 10 trials. In four patients RMT estimation was impossible since no twitch was evoked even with the maximum stimulator intensity. In these patients 40% of the maximum stimulator intensity was used. Each rTMS session consisted of 3200 stimuli applied with 20 Hz frequency (stimulation train duration—4 s, inter-train interval—26 s) for 20 minutes.
During the rehabilitation all patients received a course of 10 physical therapy sessions, each lasting 45–55 minutes, as well as robotic verticalization, scheduled five times a week for two consecutive weeks. The physical therapy focused on passive joint movements and the prevention of contractures with consideration of each patient’s individual limitations.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for testing the effect of the therapy. We employed nonparametric methods because they do not assume normality of the data, and the distribution of CRS-R score changes between sessions was neither known from the literature nor could be reliably derived using the present data, because distribution tests typically require considerably larger samples for good power [37]. The test was applied to the CRS-R total score as a comprehensive measure of behavioral signs of consciousness.
3. Results
Eighty-three patients with confirmed DOC diagnosis were screened for the study at the Research Center of Neurology (Moscow, Russia). To minimize the probability of confounding effect by spontaneous recovery, we excluded anoxic patients less than three months post-incident and traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients at less than 12 months since insult (seven patients excluded in total). Twenty-one patients were excluded because of their unstable clinical status due to severe anemia, acute myocardial infarction, episodes of pulmonary embolism, vein thrombosis, infections complications, decubitus ulcers, etc. Ten patients had contraindications to MRI, such as implanted medical devices, e.g., cerebral shunt, cardiostimulator, intracardiac catheter, electronic pump, or metal plates closing skull defects, metallic staples or vascular sutures. The remaining 45 patients underwent EEG monitoring, which identified epileptiform signs in seven patients, who were excluded.
We assigned thirty-eight patients (16 women, mean age 36.42, range 18–67 years) to receive rTMS delivered over the left angular gyrus. The group demographic data is performed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Group demographic data.
All patients were divided into two subgroups according to their DOC status (VS or MCS). VS patients (n = 16) had a mean age of 36.25 (min: 19; max: 59); seven were women; 15 were post-anoxic, mean interval since awakening after coma was 1 year 7 months (min 3 months, max 3 years and 3 months), and 1 was traumatic (interval since emergence from coma was 2 years and 3 months). MCS patients (n = 22) had a mean age 36.54 (min: 18; max: 67); nine of them were women; proportions of anoxic and post-traumatic patients were equal (11/11). Mean interval since arousal after coma in group with anoxia was 1 year and 4 months (min 3 months; max 2 years and 6 months) and in traumatic patients—1 year 9 months (min 1 year; max 3 years and 1 month). There were no significant differences in age between VS and MCS groups (p = 1, Mann–Whitney test. The individual findings are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Individual findings in coma recovery scale revised (CRS-R) before and after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) course.
All patients completed the course of rTMS. No adverse events related to stimulation were reported.
The behavioral improvement after the rTMS course was assessed by means of the validated Russian version of the CRS-R scale. The baseline mean score was 5 (min: 4; max: 7) in VS and 14 (min: 7; max: 21) in MCS (see Table 2). Subclinical changes are surely fluctuating in MCS patients, but the use of a standardized clinical approach such as CRS-R scale reduces the possibility of establishing an incorrect diagnosis.
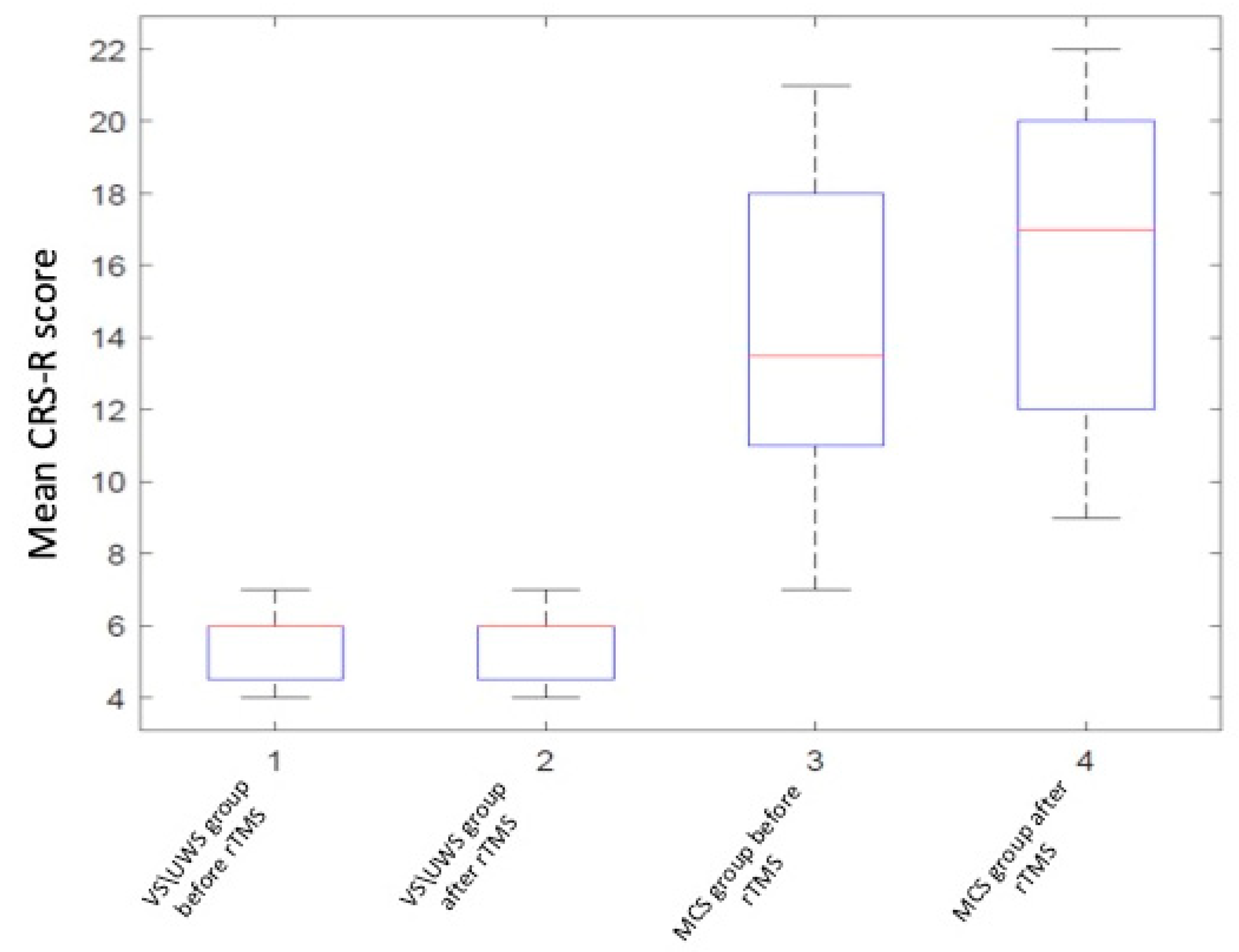
The CRS-R total score significantly increased after stimulation in the MCS subgroup (p = 0.0001, two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test); in the VS subgroup no significant differences were found (p > 0.05) (see Table 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
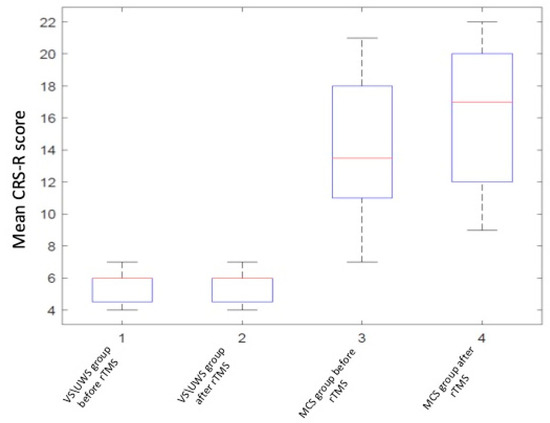
Figure 3.
Coma recovery scale revised (CRS-R) score changes in group analysis.
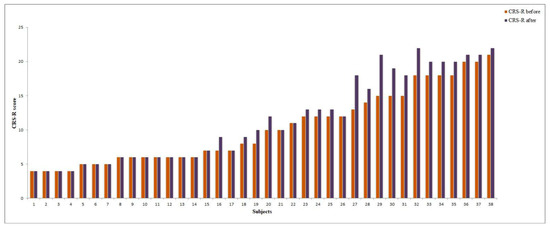
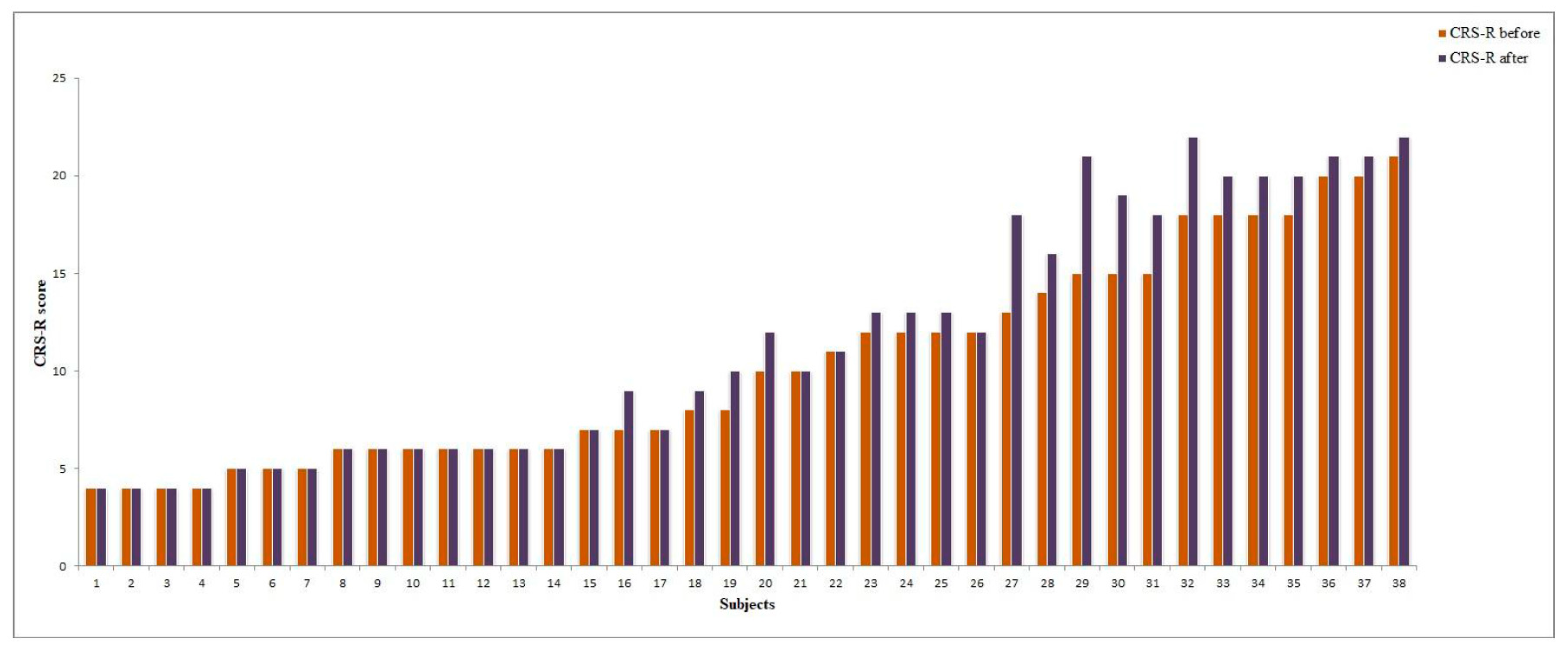
Figure 4.
CRS-R score change after rTMS in vegetative state (VS) and minimally conscious state (MCS) patients (individual data).
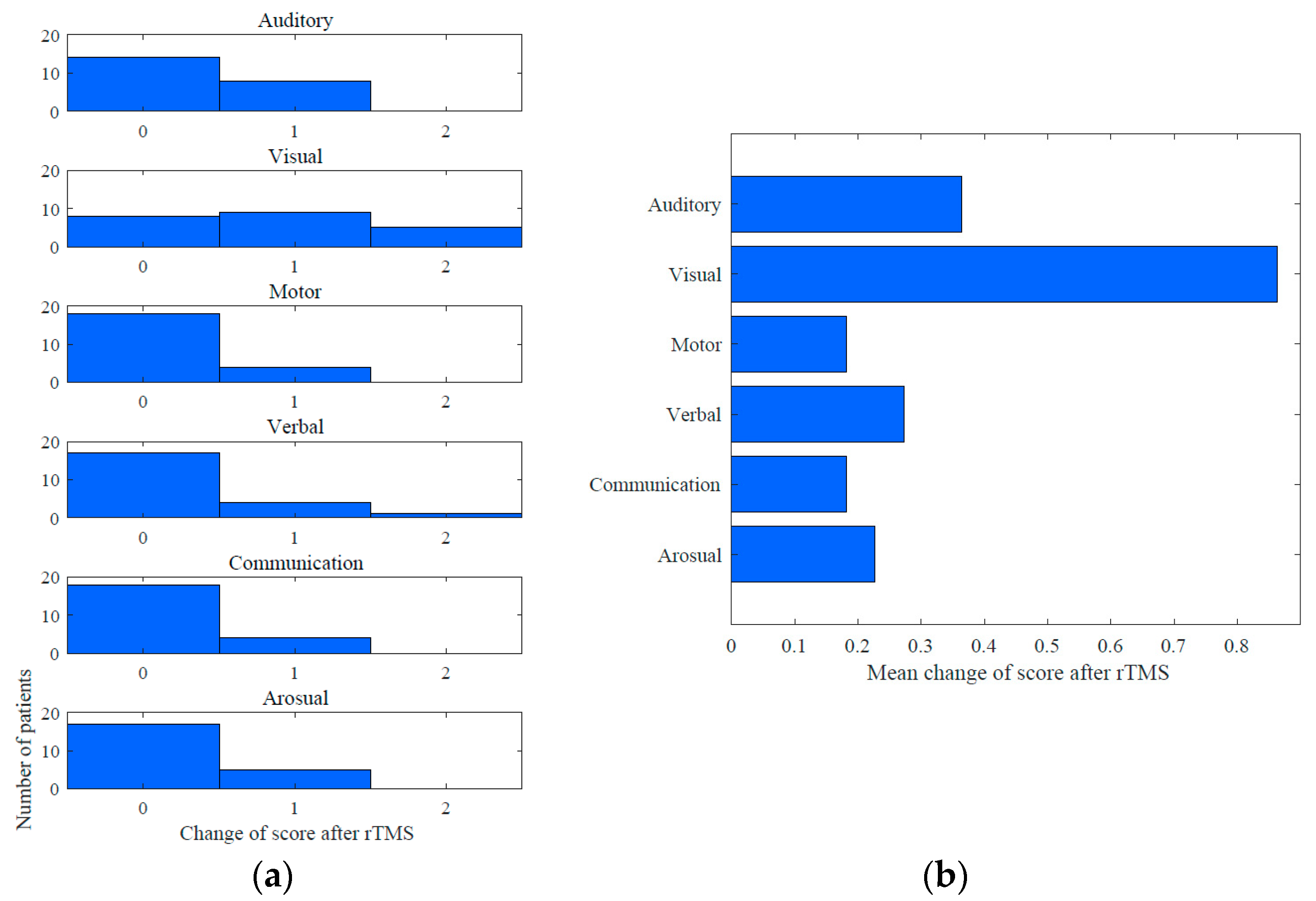
Improvements in the CRS-R score after the rTMS course were observed in 19/22 (86.3%) MCS patients (Figure 4). The mean increase in the CRS-R total score was 2,1. Among the CRS-R subscales, the largest improvements were observed in the visual (mean change 0.86), auditory (0.36) and verbal (0.27) scores (see Figure 5).
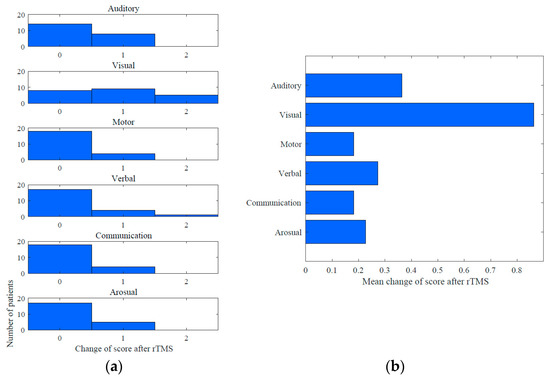
Figure 5.
Mean changes in CRS-R score subscales in MCS group: (a) mean change into CRS-R subscales after rTMS course; (b) improvements were observed in subscores.
In three traumatic MCS patients, object recognition was observed after rTMS, whereas at baseline they had only shown visual pursuit. In two anoxic MCS patients the visual function changed from fixation to object reaching after the stimulation course. In one case of MCS there was a dramatic improvement in verbal signs. The patient progressed from oral reflexive movement to articulation with yes/no answers, attempts to pronounce her name, etc. This case represented how the subclinical changes improved the DOC diagnosis quality to emergence from minimally conscious state (EMCS) by means of CRS-R scoring. In other cases of MCS the diagnosis remain the same despite positive CRS-R changes. No significant effect of etiology on CRS-R improvement within the MCS subgroup was found (p = 0.3, two-sided Mann–Whitney test). Figure 5 shows the CRS-R subscale score changes for MCS patients.
4. Discussion
The present study is the first application of 20 Hz-rTMS over the left angular gyrus at 80% of the individual RMT for 10 sessions in DOC patients. Each session lasted 20 minutes and did not cause any side-effects. We observed significant improvement in the CRS-R total score in the MCS subgroup, whereas in the VS/UWS subgroup there was no significant effect.
As there are no pharmacological treatments that provide clear evidence on improvement of restoration of consciousness in chronic DOC patients, alternative strategies of rehabilitation, that involve external modulation of cortico-cortical and corticothalamic neural loops, increasingly attract attention. Currently, several techniques of stimulation are proposed, including non-invasive (tDCS and rTMS) and invasive (DBS) approaches, both showing some effectiveness in the recovery of consciousness [28]. In this protocol technically feasible non-invasive rTMS approach was selected. rTMS is known to depolarize neurons under the stimulating coil and indirectly affect on areas related to cognition and behavior and its application in the high-frequency protocols may induce an increased release of dopamine which may modulate the neuronal activity [38].
Positive effects of rTMS over DLPFC or M1 area in chronic DOC setting were seen in several studies, while others did not demonstrate significant improvement [7,9,10,11,39,40,41]. However, not only the site of stimulation but the frequency and exposure to rTMS varied across these studies, and currently there is no unified protocol for rTMS in DOC patients. Based on the aforementioned results, we decided to apply protocol with high-frequency stimulation aimed at the restoration of impaired neuronal connectivity within DMN pathways [42]. Seizures are often seen in patients with VS/UWS or MCS, and to ensure safety of the high-frequency stimulation we excluded patients with epileptic discharges revealed at screening EEG [43,44]. Previous studies showed that effects of a single session of rTMS varied and even if the effect is present, it is transient [10,39,41]. Thus a single session may not be enough to provide a significant effect. As prolonged exposure to rTMS is assumed to increase its possible efficacy, our protocol included repeated stimulation for a total of 10 sessions.
The choice of the target for stimulation was based on recent studies that explored the role of the left angular gyrus in the framework of neural correlates of consciousness. From a neuroanatomical perspective, this area lies at the confluence of brain regions supporting episodic memory, language, attentional, semantic, numerical, and social cognitive processes [28,29]. It also receives visual, auditory, and visuomotor input from primary sensory cortices and sensory association areas [28,30,45]. Due to its location, the angular gyrus has a role of a multimodal convergence hub. It is placed to integrate incoming sensory and cognitive information to create unified representations [29,46]. Moreover, being a node of the default mode network it also connects with the frontoparietal control network, which is implicated into executive control during cognitive processing [47]. Activation in the angular gyrus remains blind to the modality of the recollected content and the type of episodic retrieval task, which indicates its multimodal processing role [48,49]. The angular gyrus is also connected with the precuneus and the mid-cingulate cortex. This area was proposed to mediate different aspects of memory function, including memory retrieval tasks [50]. It also responds to familiarity of stimuli during learning and memory as a part of the “parietal memory network” [50,51,52]. Moreover, in a meta-analysis of the attention and memory systems, it was stated that the inferior parietal cortex, which includes the supramarginal gyrus and the angular gyrus, is part of an attentional subsystem that mediates the automatic allocation of attention to task-relevant information, particularly in attending to retrieved memories [53,54]. One of our aims in the application of rTMS over the angular gyrus was to describe this area as the hub-modulator of the integration mechanism inside the process of consciousness. This state is supported by clinical heterogeneous changes in MCS patients group with the dramatic improvement in verbal and visual signs. In particular, the visual signs improvement can be also linked to imagery domain—the activation of visual regions are strongly associated with memory processing (hippocampus, parahippocampal cortex) and the posterior cingulate/precuneus (BA 31) that correlates with the vividness ratings of autobiographical memory [17,55,56].
Mild effect of rTMS in our study was seen only in MCS patients, which is in line with the studies of tDCS by Thibaut and rTMS over left DLPFC by Xia [9]. No improvement was observed in VS/UWS group, and this might be related to the poor capacity for neural plasticity in VS/UWS patients [57]. Of note, the majority of VS/UWS patients (15/1) in our study were of anoxic etiology, and clinical inefficacy of rTMS in this category of subjects may be related to a complete (or almost complete) derangement of cortical connectivity. This may have resulted in the absence of neural networks capable to act as an efficient substrate for the long-term effects of rTMS. However, at present there is no evidence that other cortical targets of stimulation may produce behavioral effects in VS/UWS patients with both non-traumatic and traumatic etiologies, neither using rTMS nor tDCS [4,7,11,39,40]. In the MCS group there was no significant difference in the results between the traumatic and non-traumatic subgroups. Thus, we assume that the heterogeneous etiology of our VS/UWS group did not affect the results of the stimulation. However, the question of the possible dependence of the rTMS effect on the etiology needs further study.
MCS patients seem to react behaviorally to the rTMS of the angular gyrus, and the largest function improvements were observed in the visual, auditory and verbal behavioral measures. This may be explained by a spread of the modulation effect from the angular gyrus to all the areas connected to it. We suggest that the absence of effect in three MCS patients might be associated with partial disconnections and lesions of the brain. In the case of the EMCS patient the dramatic subclinical improvement might be spontaneous but due to the timing of impaired consciousness is rather improbable.
Thus, rTMS may also be useful in identifying subgroups of MCS patients who could benefit from more invasive and potentially more effective stimulation strategies such as DBS. Cortical plasticity and changes in connectivity are central to the recovery of consciousness in DOC patients. We assume that neuromodulation, such as NIBS, applied to an area within a given neural network (e.g., the angular gyrus in the DMN) can lead to the activation of the whole network. Our hypothesis was supported by plenty of studies using fMRI and PET connectivity in DOC patients [12,20,24]. It has been shown that there is a significant difference in connectivity between DOC patients and healthy subjects. DOC patients have decreased glucose standardized uptake value in the thalamus, precuneus/posterior parietal cortex, inferior parietal, mesiofrontal cortex, as well as decreased DMN connectivity, compared with healthy subjects [14,19,58,59]. Graph theory also shows reduced modularity in VS/UWS and MCS compared with healthy subjects [60]. However, the contrast between the MCS and VS/UWS patients is more subtle and harder to pinpoint at the level of the overall connectivity. The DMN functional connectivity strength is able to differentiate MCS from VS/UWS patients [14]. Significant differences were found in the patterns of strong positive connections using node-specific whole-brain measures of connectome disruption [61].
We conclude that therapeutic brain stimulation techniques enhanced by neuroimaging-based target selection constitute a promising approach to the extremely challenging problem of DOC treatment.
There are some limitations in our study. The absence of a placebo group, which was due to the small number of patients eligible for the study, was partially compensated by selecting patients at sufficiently long intervals since anoxia/injury to avoid confounding by spontaneous recovery. However, in the future it is necessary to confirm the effect in controlled studies. Another limitation of the study is that the evaluation of the clinical effect was presented only once (2 days after the stimulation course), however it is planned to do a follow-up evaluation of the long-term effects.
Results added, in this study we employed only behavioral measure of rTMS effect, and future studies should include established instrumental approaches for the assessment of chronic DOC patients, such as EEG, TMS-EEG and fMRI that may promote further understanding of mechanisms underlying neuromodulation.
It is important to note, that in four cases the RMT could not be determined due to the absence of muscle twitches in response to TMS. We note that no adverse effects were observed in these patients. At the same time, the lack of data on the threshold could have led to an underestimation of the required simulation intensity, which may potentially have affected the effectiveness. Generally, it is also unclear how closely the motor threshold corresponds to the intensity of angular gyrus stimulation. Thus, there is a need for new methods of intensity selection in this group of patients (for example, based on TMS-EEG data).
5. Conclusions
This study is the first evaluation of the efficacy of rTMS applied over the left angular gyrus in disorders of consciousness. We obtained a clinical effect in MCS, but not in VS/UWS. These results provide a motivation for future research into the effectiveness of this new protocol. Additionally, the findings highlight the left angular gyrus as a promising target for therapeutic NIBS in DOC patients, which can help optimize the use of human and financial resources in DOC management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L., A.P., D.S. (Dmitry Sergeev) and N.S.; methodology, E.I., I.B., A.P.; validation, L.L., E.I., D.S. (Dmitry Sergeev), D.S. (Dmitry Sinitsyn); formal analysis, D.S. (Dmitry Sinitsyn); investigation, L.L., E.I., D.L., A.P., E.K., S.M.; resources, Y.R., N.S.; data curation, D.S. (Dmitry Sergeev), D.S. (Dmitry Sinitsyn); writing—original draft preparation, L.L., E.I., D.S. (Dmitry Sinitsyn), I.B.; writing—N.S., D.S. (Dmitry Sergeev); visualization, D.S. (Dmitry Sinitsyn); supervision, N.S.; project administration, M.P.; funding acquisition, M.P.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant NO. 16-15-00274.
Acknowledgments
This paper is dedicated to memory of Alexander Chervyakov, our friend and colleague.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gosseries, O.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Bruno, M.-A.; Demertzi, A.; Schnakers, C.; Boly, M.M.; Maudoux, A.; Moonen, G.; Laureys, S. Disorders of Consciousness: Coma, Vegetative and Minimally Conscious States; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 29–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gosseries, O.; Zasler, N.D.; Laureys, S. Recent advances in disorders of consciousness: Focus on the diagnosis. Brain Inj. 2014, 28, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Bai, Y.; Dang, Y.; Xu, R.; He, J. Current Status of Neuromodulatory Therapies for Disorders of Consciousness. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaut, A.; Bruno, M.-A.; LeDoux, D.; Demertzi, A.; Laureys, S. tDCS in patients with disorders of consciousness: Sham-controlled randomized double-blind study. Neurology 2014, 82, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaut, A.; Wannez, S.; Donneau, A.-F.; Chatelle, C.; Gosseries, O.; Bruno, M.-A.; Laureys, S. Controlled clinical trial of repeated prefrontal tDCS in patients with chronic minimally conscious state. Brain Inj. 2017, 31, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, G.; Lejeune, N.; O’Brien, A.T.; Fregni, F.; Martial, C.; Wannez, S.; Laureys, S.; Thibaut, A.; O’Brien, A.T. Randomized controlled trial of home-based 4-week tDCS in chronic minimally conscious state. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, T.L.-B.; Rosenow, J.; Lewis, G.; Ahmed, G.; Walker, M.; Guernon, A.; Roth, H.; Patil, V. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation-associated neurobehavioral gains during coma recovery. Brain Stimul. 2009, 2, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosseries, O.; Di, H.; Laureys, S.; Boly, M. Measuring Consciousness in Severely Damaged Brains. Annu. Neurosci. 2014, 37, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; He, J. Effects of 10 Hz Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Left Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Disorders of Consciousness. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccione, F.; Cavinato, M.; Manganotti, P.; Formaggio, E.; Storti, S.F.; Battistin, L.; Cagnin, A.; Tonin, P.; Dam, M. Behavioral and neurophysiological effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on the minimally conscious state: A case study. Neurorehabil. Neural. Repair 2011, 25, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincotta, M.; Giovannelli, F.; Chiaramonti, R.; Bianco, G.; Godone, M.; Battista, D.; Cardinali, C.; Borgheresi, A.; Sighinolfi, A.; D’Avanzo, A.M.; et al. No effects of 20 Hz-rTMS of the primary motor cortex in vegetative state: A randomised, sham-controlled study. Cortex 2015, 71, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Noirhomme, Q.; Tshibanda, L.J.F.; Bruno, M.A.; Boveroux, P.; Schnakers, C.; Soddu, A.; Perlbarg, V.; Ledoux, D.; Brichant, J.-F.; et al. Default network connectivity reflects the level of consciousness in non-communicative brain-damaged patients. Brain 2010, 133, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Espejo, D.; Soddu, A.; Cruse, D.; Palacios, E.M.; Junqué, C.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Rivas, E.; Newcombe, V.; Menon, D.K.; Pickard, J.D.; et al. A role for the default mode network in the bases of disorders of consciousness. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosazza, C.; Andronache, A.; Sattin, D.; Bruzzone, M.G.; Marotta, G.; Nigri, A.; Ferraro, S.; Sebastiano, D.R.; Porcu, L.; Bersano, A.; et al. Multimodal study of default-mode network integrity in disorders of consciousness. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvyagintsev, M.; Clemens, B.; Chechko, N.; Mathiak, K.A.; Sack, A.T.; Mathiak, K. Brain networks underlying mental imagery of auditory and visual information. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishai, A.; Ungerleider, L.G.; Haxby, J.V. Distributed neural systems for the generation of visual images. Neuron 2000, 28, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daselaar, S.M.; Porat, Y.; Huijbers, W.; Pennartz, C.M. Modality-specific and modality-independent components of the human imagery system. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Wu, X.; Huang, Z.; Duncan, N.W.; Tang, W.; Wolff, A.; Hu, J.; Gao, L.; Jin, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. How are different neural networks related to consciousness? Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Perri, C.; Bahri, M.A.; Amico, E.; Thibaut, A.; Heine, L.; Antonopoulos, G.; Charland-Verville, V.; Wannez, S.; Gomez, F.; Hustinx, R.; et al. Neural correlates of consciousness in patients who have emerged from a minimally conscious state: A cross-sectional multimodal imaging study. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureys, S.; Goldman, S.; Phillips, C.; Van Bogaert, P.; Aerts, J.; Luxen, A.; Franck, G.; Maquet, P. Impaired Effective Cortical Connectivity in Vegetative State: Preliminary Investigation Using PET. NeuroImage 1999, 9, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureys, S.; Lemaire, C.; Maquet, P.; Phillips, C.; Franck, G. Cerebral metabolism during vegetative state and after recovery to consciousness. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 67, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, J.S.; Bio, B.J.; Vespa, P.M.; Lutkenhoff, E.S.; Monti, M.M. Restoration of thalamo-cortical connectivity after brain injury: Recovery of consciousness, complex behavior, or passage of time? J. Neurosci. 2017, 96, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldenmund, J.P.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Boly, M.; Laureys, S.; Soddu, A. A default mode of brain function in altered states of consciousness. Arch. Ital. Biol. 2012, 150, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stender, J.; Gosseries, O.; Bruno, M.-A.; Charland-Verville, V.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Demertzi, A.; Chatelle, C.; Thonnard, M.; Thibaut, A.; Heine, L.; et al. Diagnostic precision of PET imaging and functional MRI in disorders of consciousness: A clinical validation study. Lancet 2014, 384, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannawi, Y.; Lindquist, M.A.; Caffo, B.S.; Sair, H.I.; Stevens, R.D. Resting brain activity in disorders of consciousness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2015, 84, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demertzi, A.; Antonopoulos, G.; Heine, L.; Voss, H.U.; Crone, J.S.; Angeles, C.D.L.; Bahri, M.A.; Di Perri, C.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Charland-Verville, V.; et al. Intrinsic functional connectivity differentiates minimally conscious from unresponsive patients. Brain 2015, 138, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boly, M.; Massimini, M.; Garrido, M.I.; Gosseries, O.; Noirhomme, Q.; Laureys, S.; Soddu, A. Brain Connectivity in Disorders of Consciousness. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghier, M.L. The angular gyrus: Multiple functions and multiple subdivisions. Neuroscience 2013, 19, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.R.; Desai, R.H. The neurobiology of semantic memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, M.F.; Peelle, J.E.; Cook, P.A.; Grossman, M. Heteromodal conceptual processing in the angular gyrus. NeuroImage 2013, 71, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnici, H.M.; Richter, F.R.; Yazar, Y.; Simons, J.S. Multimodal Feature Integration in the Angular Gyrus during Episodic and Semantic Retrieval. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5462–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazar, Y.; Bergström, Z.M.; Simons, J.S. Reduced multimodal integration of memory features following continuous theta burst stimulation of angular gyrus. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalova, E.G.; Legostaeva, L.A.; Zimin, A.A.; Yusupova, D.G.; Sergeev, D.V.; Ryabinkina, Y.V.; Bodien, Y.; Suponeva, N.A.; Piradov, M.A. The Russian version of Coma Recovery Scale-revised—A standardized method for assessment of patients with disorders of consciousness. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. SS Korsakova 2018, 118, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacino, J.T. The vegetative and minimally conscious states: Consensus-based criteria for establishing diagnosis and prognosis. NeuroRehabilitation 2004, 19, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Howsepian, A.A. The 1994 Multi-Society Task Force consensus statement on the Persistent Vegetative State: A critical analysis. Issues Law Med. 1996, 12, 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gosseries, O.; Bruno, M.-A.; Chatelle, C.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Schnakers, C.; Soddu, A.; Laureys, S. Disorders of consciousness: what’s in a name? NeuroRehabilitation 2011, 28, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Razali, N.M.; Wah, Y.B. Power Comparisons of Shapiro-Wilk, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Lilliefors and Anderson-Darling Tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2011, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Guse, B.; Falkai, P.; Wobrock, T.J. Cognitive effects of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: A systematic review. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naro, A.; Calabrò, R.S.; Russo, M.; Leo, A.; Pollicino, P.; Quartarone, A.; Bramanti, P. Can transcranial direct current stimulation be useful in differentiating unresponsive wakefulness syndrome from minimally conscious state patients? Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2015, 33, 159–176. [Google Scholar]
- Naro, A.; Russo, M.; Leo, A.; Bramanti, P.; Quartarone, A.; Calabrò, R.S. A single session of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in patients with unresponsive wakefulness syndrome: Preliminary results. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganotti, P.; Formaggio, E.; Storti, S.F.; Fiaschi, A.; Battistin, L.; Tonin, P.; Piccione, F.; Cavinato, M. Effect of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Brain Excitability in Severely Brain-Injured Patients in Minimally Conscious or Vegetative State. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdayer, E.; Degardin, A.; Cassim, F.; Bocquillon, P.; Derambure, P.; Devanne, H. The effects of low- and high-frequency repetitive TMS on the input/output properties of the human corticospinal pathway. Exp. Brain 2008, 187, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Safety of TMS Consensus Group. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 2008–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, S.; Boccagni, C.; Galardi, G. Structural epilepsy occurrence in vegetative and minimally conscious states. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 103, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, J.R.; Desai, R.H.; Graves, W.W.; Conant, L.L. Where is the semantic system? A critical review and meta-analysis of 120 functional neuroimaging studies. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 2767–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, A.P. Episodic retrieval and the cortical binding of relational activity. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 11, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Kahn, I.; Snyder, A.Z.; Raichle, M.E.; Buckner, R.L. Evidence for a Frontoparietal Control System Revealed by Intrinsic Functional Connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 3328–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, S.A.; Miller, M.B. Lateralization of the parietal old/new effect: An event-related fMRI study comparing recognition memory for words and faces. NeuroImage 2009, 44, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, K.B.; Szpunar, K.K.; Christ, S.E. Laboratory-based and autobiographical retrieval tasks differ substantially in their neural substrates. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, A.W.; Nelson, S.M.; McDermott, K.B. A parietal memory network revealed by multiple MRI methods. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2015, 19, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestieri, C.; Shulman, G.L.; Corbetta, M. The contribution of the human posterior parietal cortex to episodic memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, P.P.; Madore, K.P.; Schacter, D.L. A role for the left angular gyrus in episodic simulation and memory. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaramelli, E.; Grady, C.L.; Moscovitch, M. Top-down and bottom-up attention to memory: A hypothesis (AtoM) on the role of the posterior parietal cortex in memory retrieval. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 1828–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, R.; Ciaramelli, E.; Olson, I.R.; Moscovitch, M. The parietal cortex and episodic memory: An attentional account. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, A.; Winocur, G.; Grady, C.L.; Hevenor, S.J.; Moscovitch, M. Remembering our past: Functional neuroanatomy of recollection of recent and very remote personal events. Cerebral Cortex. 2004, 14, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addis, D.R.; Moscovitch, M.; Crawley, A.P.; McAndrews, M.P. Recollective qualities modulate hippocampal activation during autobiographical memory retrieval. Hippocampus 2004, 14, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosanova, M.; Gosseries, O.; Casarotto, S.; Boly, M.; Casali, A.G.; Bruno, M.-A.; Mariotti, M.; Boveroux, P.; Tononi, G.; Laureys, S.; et al. Recovery of cortical effective connectivity and recovery of consciousness in vegetative patients. Brain 2012, 135, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annen, J.; Heine, L.; Ziegler, E.; Frasso, G.; Bahri, M.; Di Perri, C.; Stender, J.; Martial, C.; Wannez, S.; D’Ostilio, K.; et al. Function-structure connectivity in patients with severe brain injury as measured by MRI-DWI and FDG-PET. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaut, A.; Bruno, M.; Chatelle, C.; Gosseries, O.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Demertzi, A.; Schnakers, C.; Thonnard, M.; Charland-Verville, V.; Bernard, C.; et al. Metabolic activity in external and internal awareness networks in severely brain-damaged patients. J. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 44, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, J.S.; Schurz, M.; Höller, Y.; Bergmann, J.; Monti, M.M.; Schmid, E.; Trinka, E.; Kronbichler, M. Impaired consciousness is linked to changes in effective connectivity of the posterior cingulate cortex within the default mode network. NeuroImage 2015, 110, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinitsyn, D.O.; Legostaeva, L.A.; Kremneva, E.I.; Morozova, S.N.; Poydasheva, A.G.; Mochalova, E.G.; Chervyakova, O.G.; Ryabinkina, J.V.; Suponeva, N.A.; Piradov, M.A. Degrees of functional connectome abnormality in disorders of consciousness. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 2929–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).