Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Potential of the Essential Oil Pistacia lentiscus var. chia and Its Major Components Myrcene and α-Pinene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Essential Oil and Monoterpenes
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. DPPH and ABTS Assays
2.4. Plasmid DNA Protection Assay
2.5. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.6. SRB Assay
2.7. Real-Time Polymerase Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Wound Healing—Scratch Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell-Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Mastic Essential Oil and Its Major Components, Myrcene and α-Pinene
3.2. Antioxidant Capacity of Mastic Essential Oil, Myrcene, and α-Pinene as Monitored by Plasmid DNA Protection Assay
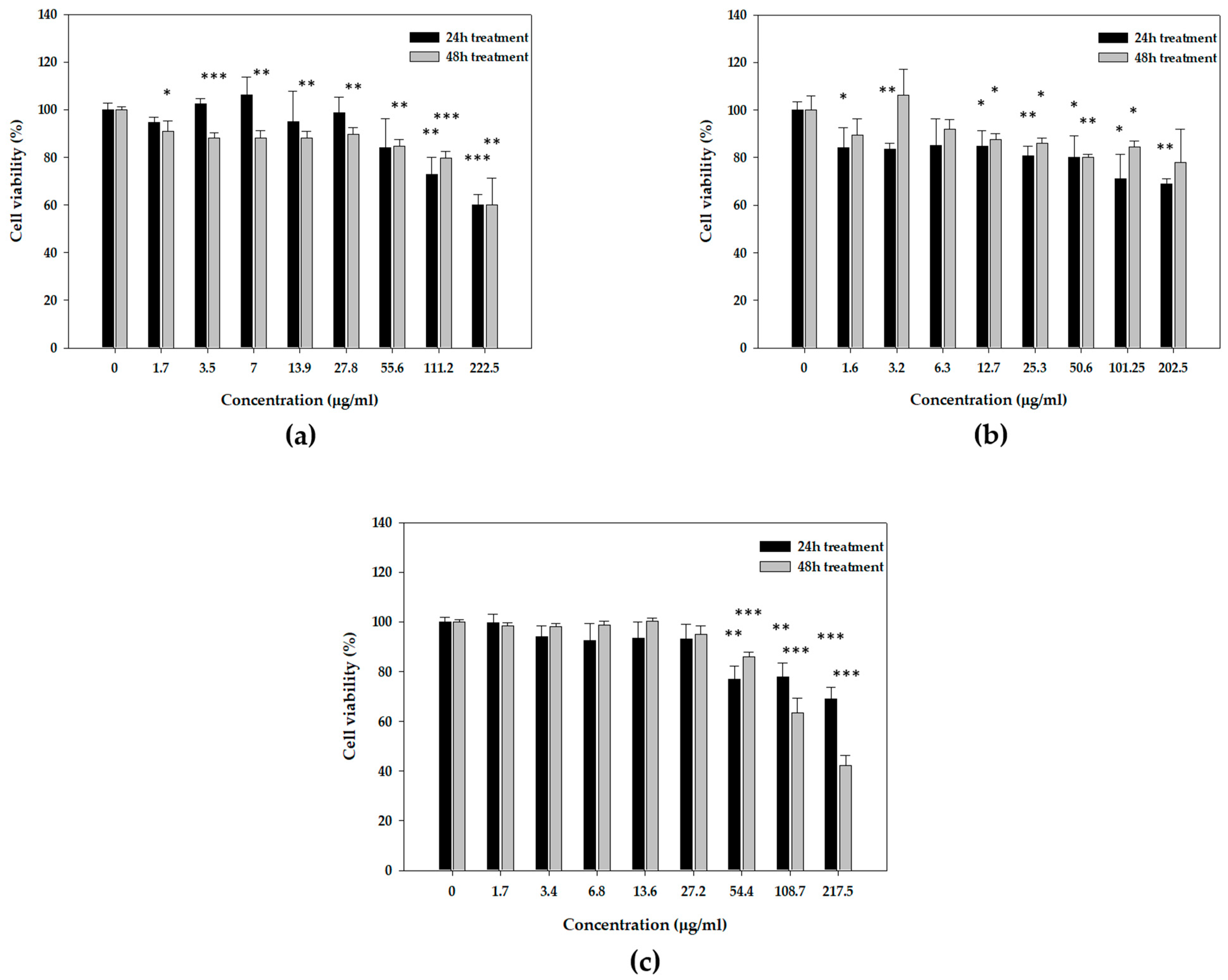
3.3. Cytotoxicity Profiles of Mastic Essential Oil, Myrcene, and α-Pinene in Human Epidermal Keratinocyte (HaCaT) Cells
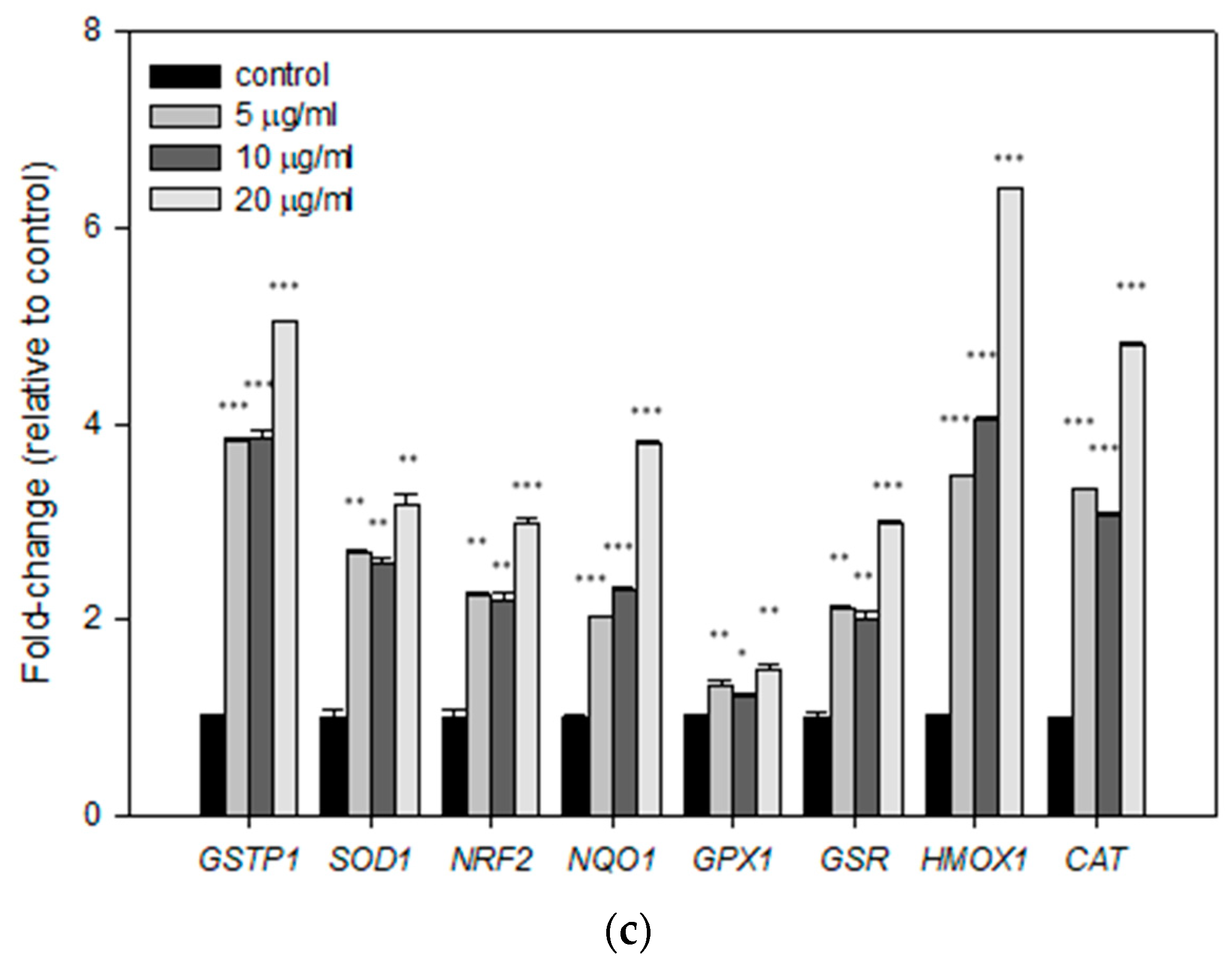
3.4. Effects of Mastic Essential Oil and Its Major Components, Myrcene and α-Pinene, on the Expression Levels of Antioxidant Response Genes
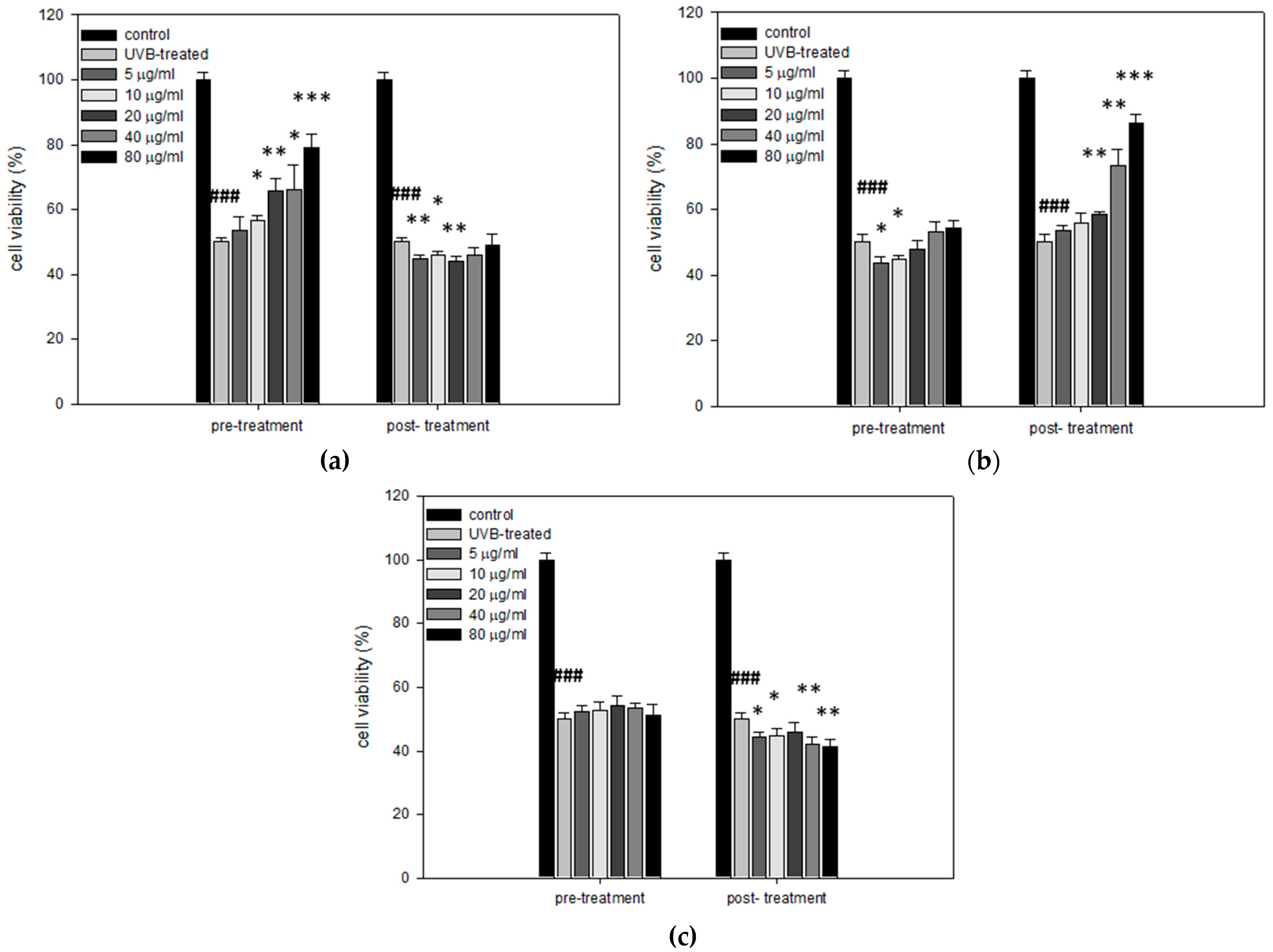
3.5. Cytoprotective and Regenerative Effects of Mastic Oil and Its Major Components on HaCaT Cells after UVB Irradiation
3.6. Cytoprotective Effects of Mastic Essential Oil, Myrcene, and α-Pinene against H2O2 Cytotoxicity in HaCaT Cells
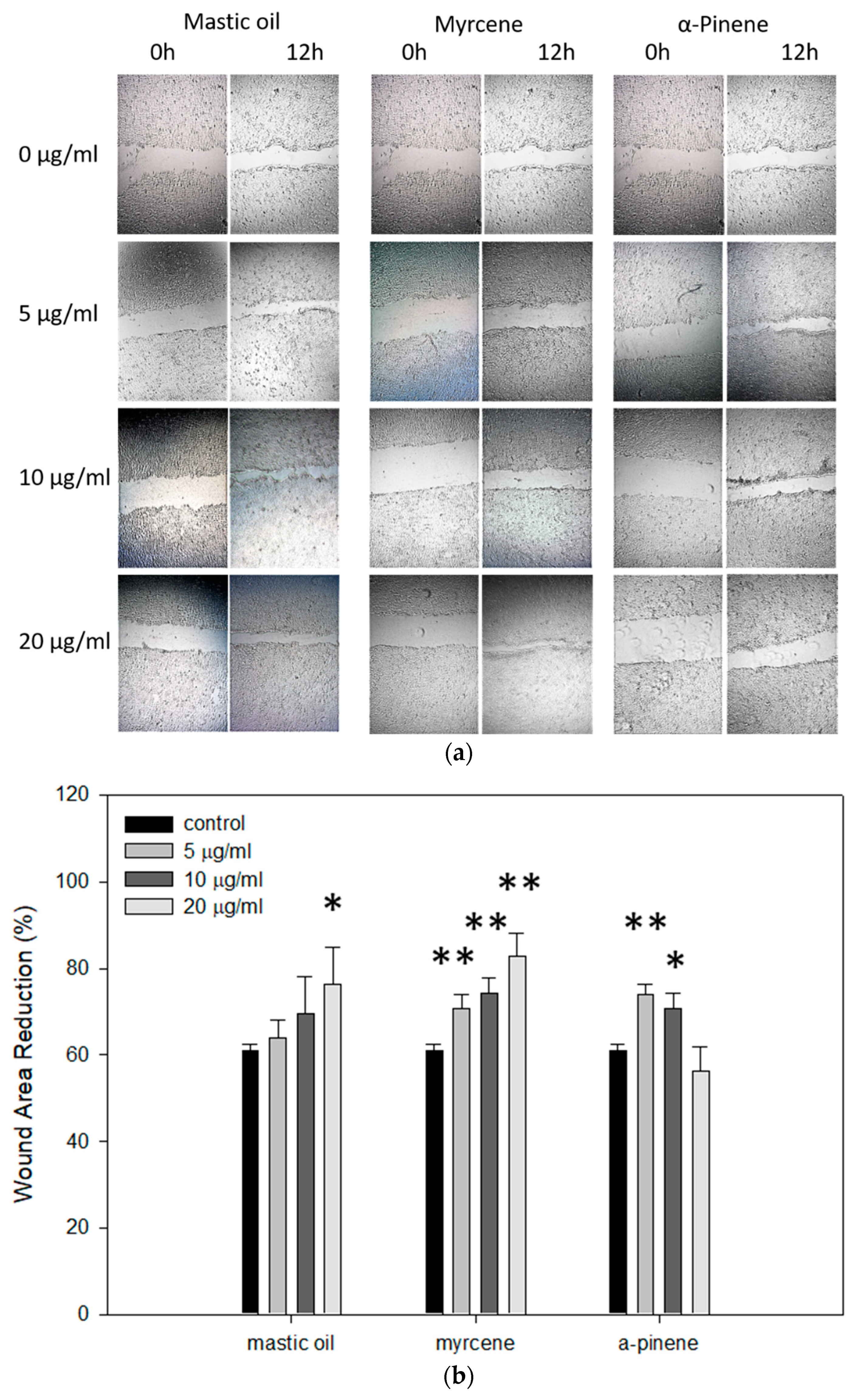
3.7. Effects of Mastic Essential Oil and Its Major Components, Myrcene or α-Pinene, on Migration and Regeneration of HaCaT Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological Effects of Essential Oils—A Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, A.; Abbas, T.; Ali, T.M.; Hasnain, A. Essential Oils: Brief Background and Uses. Ann. Short Rep. 2018, 1, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Dillard, C.J.; German, J.B. Phytochemicals: Nutraceuticals and Human Health. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1744–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Sureda, A.; Tenore, G.; Daglia, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Valussi, M.; Tundis, R.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Loizzo, M.; Ademiluyi, A.; et al. Biological Activities of Essential Oils: From Plant Chemoecology to Traditional Healing Systems. Molecules 2017, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential Oils, Part I: Introduction. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.; Mehdizadeh, L. Chemistry of Essential Oils and Factors Influencing Their Constituents. In Soft Chemistry and Food Fermentation. Handbook of Food Bioengineering; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 379–419. ISBN 978-0-12-811412-4. [Google Scholar]
- de Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential Oils, Part III: Chemical Composition. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heghes, S.C.; Filip, L.; Vostinaru, O.; Mogosan, C.; Miere, D.; Iuga, C.A.; Moldovan, M. Essential Oil-Bearing Plants from Balkan Peninsula: Promising Sources for New Drug Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachi, V.K.; Mikropoulou, E.V.; Gkiouvetidis, P.; Siafakas, K.; Argyropoulou, A.; Angelis, A.; Mitakou, S.; Halabalaki, M. Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Chios Mastic Gum (Pistacia lentiscus var. chia, Anacardiaceae): A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xynos, N.; Termentzi, A.; Fokialakis, N.; Skaltsounis, L.A.; Aligiannis, N. Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Mastic Gum and Chemical Characterization of Bioactive Fractions Using LC-HRMS/MS and GC–MS. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 133, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschos, S. Phytochemical and Pharmacological Study of Chios Mastic Gum. Ph.D. Thesis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoudaki, C.; Krsek, M.; Rodger, A. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of the Essential Oil and the Gum of Pistacia lentiscus Var. chia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7681–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiatis, P.; Melliou, E.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Chinou, I.B.; Mitaku, S. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oils of Pistacia lentiscus var. chia. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, V.P.; Mellidis, A.S.; Argyriadou, N. The Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil of Mastic Gum. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1991, 3, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimas, K.S.; Pantazis, P.; Ramanujam, R. Review: Chios Mastic Gum: A Plant-Produced Resin Exhibiting Numerous Diverse Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Properties. In Vivo 2012, 26, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paraschos, S.; Mitakou, S.; Skaltsounis, A.-L. Chios Gum Mastic: A Review of Its Biological Activities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2292–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridopoulou, K.; Tiptiri-Kourpeti, A.; Lampri, E.; Fitsiou, E.; Vasileiadis, S.; Vamvakias, M.; Bardouki, H.; Goussia, A.; Malamou-Mitsi, V.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; et al. Dietary Mastic Oil Extracted from Pistacia lentiscus var. chia Suppresses Tumor Growth in Experimental Colon Cancer Models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassou, C.C.; Nychas, G.J.E. Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oil of Mastic Gum (Pistacia lentiscus var. chia) on Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria in Broth and in Model Food System. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1995, 36, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutrari, H.; Magkouta, S.; Pyriochou, A.; Koika, V.; Kolisis, F.N.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Roussos, C. Mastic Oil from Pistacia lentiscus var. chia Inhibits Growth and Survival of Human K562 Leukemia Cells and Attenuates Angiogenesis. Nutr. Cancer 2006, 55, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magkouta, S.; Stathopoulos, G.T.; Psallidas, I.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Kolisis, F.N.; Roussos, C.; Loutrari, H. Protective Effects of Mastic Oil from Pistacia Lentiscus Variation Chia against Experimental Growth of Lewis Lung Carcinoma. Nutr. Cancer 2009, 61, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, J.M.C.; Professor Halliwell, B. Invited Review Free Radicals in Disease Processes: A Compilation of Cause and Consequence. Free Radic. Res. 1993, 19, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Boxin, O.U.; Prior, R.L. The Chemistry behind Antioxidant Capacity Assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.D.; Dizdaroglu, M.; Cooke, M.S. Oxidative DNA Damage and Disease: Induction, Repair and Significance. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2004, 567, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, E.N.; German, J.B. Antioxidants in Foods and Health: Problems and Fallacies in the Field. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1999–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Are Polyphenols Antioxidants or Pro-Oxidants? What Do We Learn from Cell Culture and In Vivo Studies? Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 476, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskaug, J.Ø.; Carlsen, H.; Myhrstad, M.C.W.; Blomhoff, R. Polyphenols and Glutathione Synthesis Regulation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 277S–283S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapetsas, A.; Voulgaridou, G.-P.; Konialis, M.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Kynigopoulos, S.; Lambropoulou, M.; Stavropoulou, M.-I.; Stathopoulou, K.; Aligiannis, N.; Bozidis, P.; et al. Propolis Extracts Inhibit UV-Induced Photodamage in Human Experimental In Vitro Skin Models. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anestopoulos, I.; Kavo, A.; Tentes, I.; Kortsaris, A.; Panayiotidis, M.; Lazou, A.; Pappa, A. Silibinin Protects H9c2 Cardiac Cells from Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Phenylephrine-Induced Hypertrophy: Potential Mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, U.; Bhimathati, S.S.R. Evaluation of Antioxidant and DNA Damage Protection Activity of the Hydroalcoholic Extract of Desmostachya bipinnata L. Stapf. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-C.; Park, A.Y.; Guan, J.-L. In Vitro Scratch Assay: A Convenient and Inexpensive Method for Analysis of Cell Migration In Vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, S.N.; Anilakumar, K.R. In Vitro Free Radical Scavenging and DNA Damage Protective Property of Coriandrum sativum L. Leaves Extract. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlastos, D.; Drosopoulou, E.; Efthimiou, I.; Gavriilidis, M.; Panagaki, D.; Mpatziou, K.; Kalamara, P.; Mademtzoglou, D.; Mavragani-Tsipidou, P. Genotoxic and Antigenotoxic Assessment of Chios Mastic Oil by the In Vitro Micronucleus Test on Human Lymphocytes and the In Vivo Wing Somatic Test on Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitić-Culafić, D.; Zegura, B.; Nikolić, B.; Vuković-Gacić, B.; Knezević-Vukcević, J.; Filipic, M. Protective Effect of Linalool, Myrcene and Eucalyptol against t-Butyl Hydroperoxide Induced Genotoxicity in Bacteria and Cultured Human Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzenna, H.; Hfaiedh, N.; Giroux-Metges, M.-A.; Elfeki, A.; Talarmin, H. Potential Protective Effects of Alpha-Pinene against Cytotoxicity Caused by Aspirin in the IEC-6 Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, M.; Rostami, H. Chemical Composition, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of the Essential Oil of Psammogeton Canescens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, M.; Mondin, A.; Chen, Z.; Miranda, F.M.; do Nascimento, B.B.; Schirato, G.; Pastore, P.; Froldi, G. Radical Scavenging and Antimicrobial Activities of Croton Zehntneri, Pterodon Emarginatus and Schinopsis Brasiliensis Essential Oils and Their Major Constituents: Estragole, Trans-Anethole, β-Caryophyllene and Myrcene. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Bikineyeva, A.; Dikalova, A.; Nazarewicz, R.; Lerakis, S.; Dikalov, S. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Chios Mastic Gum Is Associated with Inhibition of TNF-Alpha Induced Oxidative Stress. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrikopoulos, N.K.; Kaliora, A.C.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Papapeorgiou, V.P. Biological Activity of Some Naturally Occurring Resins, Gums and Pigments Againstin Vitro LDL Oxidation. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikopoulos, N.K.; Kaliora, A.C.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Papageorgiou, V.P. Biological Activity of Saliva against In Vitro LDL Oxidation after Chewing Commercial Chewing Gums. Ital. J. Food Sci. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2002, 14, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Yosr, Z.; Imen, B.H.Y.; Rym, J.; Chokri, M.; Mohamed, B. Sex-Related Differences in Essential Oil Composition, Phenol Contents and Antioxidant Activity of Aerial Parts in Pistacia lentiscus L. during Seasons. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 121, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Chadon Assemian, I.C.; Mouzount, H.; Bourais, I.; Et-Touys, A.; Fellah, H.; Benjouad, A.; Dakka, N.; Bakri, Y. Could Volatile Compounds from Leaves and Fruits of Pistacia Lentiscus Constitute a Novel Source of Anticancer, Antioxidant, Antiparasitic and Antibacterial Drugs? Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 128, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, M.; Racioppi, R. Characterization of the Volatile Fraction of Mastic Oil and Mastic Gum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, N.F.; Lau, A.; Zhang, D.D. Regulation of the Nrf2–Keap1 Antioxidant Response by the Ubiquitin Proteasome System: An Insight into Cullin-Ring Ubiquitin Ligases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.D. Mechanistic Studies of the Nrf2-Keap1 Signaling Pathway. Drug Metab. Rev. 2006, 38, 769–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.D. The Nrf2-Keap1-ARE Signaling Pathway: The Regulation and Dual Function of Nrf2 in Cancer. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1623–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakkoli, A.; Iranshahi, M.; Hasheminezhad, S.H.; Hayes, A.W.; Karimi, G. The Neuroprotective Activities of Natural Products through the Nrf2 Upregulation. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2256–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranshahy, M.; Iranshahi, M.; Abtahi, S.R.; Karimi, G. The Role of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 in Hepatoprotective Activity of Natural Products: A Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, Y.C. Natural Nrf2 Modulators for Skin Protection. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggler, A.L.; Gay, K.A.; Mesecar, A.D. Molecular Mechanisms of Natural Products in Chemoprevention: Induction of Cytoprotective Enzymes by Nrf2. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52 (Suppl. 1), S84–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-0-19-180213-3. [Google Scholar]
- Imlay, J.A.; Linn, S. DNA Damage and Oxygen Radical Toxicity. Science 1988, 240, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, F. Chemical Basis of Reactive Oxygen Species Reactivity and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porres-Martínez, M.; González-Burgos, E.; Carretero, M.E.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. In Vitro Neuroprotective Potential of the Monoterpenes α-Pinene and 1,8-Cineole against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in PC12 Cells. Z. Nat. C J. Biosci. 2016, 71, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serifi, I.; Tzima, E.; Bardouki, H.; Lampri, E.; Papamarcaki, T. Effects of the Essential Oil from Pistacia lentiscus var. chia on the Lateral Line System and the Gene Expression Profile of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Molecules 2019, 24, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhail, G.R.; Selak, L.; Salo, S. Reinforcement of Surgical Adhesive Strips. J. Derm. Surg. Oncol. 1986, 12, 904–905, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhail, G.R.; Selak, L.; Salo, S.; Balle, M.R. The Efficacy of Adhesives in the Application of Wound Dressings. J. Burn Care Rehabil. 1989, 10, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuzer, R.; Kelly, C.; Durrani, N.; Mittal, V.; Jackson, I.T.; Remine, S. Reinforcement of Subcuticular Continuous Suture Closure with Surgical Adhesive Strips and Gum Mastic: Is There Any Additional Strength Provided? Am. J. Surg. 2005, 189, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, P.; Sarada, D.; Ramkumar, K.M. Pharmacological Activation of Nrf2 Promotes Wound Healing. Eur. J. Pharm. 2020, 886, 173395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papada, E.; Gioxari, A.; Brieudes, V.; Amerikanou, C.; Halabalaki, M.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Smyrnioudis, I.; Kaliora, A.C. Bioavailability of Terpenes and Postprandial Effect on Human Antioxidant Potential. An Open-Label Study in Healthy Subjects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papada, E.; Gioxari, A.; Amerikanou, C.; Galanis, N.; Kaliora, A.C. An Absorption and Plasma Kinetics Study of Monoterpenes Present in Mastiha Oil in Humans. Foods 2020, 9, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.; Schaefer, U.; Sporer, F.; Reichling, J. Comparative Study on the In Vitro Human Skin Permeation of Monoterpenes and Phenylpropanoids Applied in Rose Oil and in Form of Neat Single Compounds. Pharmazie 2010, 65, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Q.-D.; Chai, Y.-P.; Zhang, H.; Peng, P.; Yang, X.-X. Natural Terpenes as Penetration Enhancers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Molecules 2016, 21, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitropoulou, G.; Sidira, M.; Skitsa, M.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Pappa, A.; Dimtsoudis, C.; Proestos, C.; Kourkoutas, Y. Assessment of the Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Antiproliferative Potential of Sideritisraeseri Subps. Raeseri Essential Oil. Foods 2020, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano-Garibay, J.D.; Arriaga-Alba, M.; Sánchez-Navarrete, J.; Mendoza-García, M.; Flores-Estrada, J.J.; Moreno-Eutimio, M.A.; Espinosa-Aguirre, J.J.; González-Ávila, M.; Ruiz-Pérez, N.J. Antimutagenic and Antioxidant Activity of the Essential Oils of Citrus Sinensis and Citrus Latifolia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghdoost, F.; Baradaran Mahdavi, M.M.; Zandifar, A.; Sanei, M.H.; Zolfaghari, B.; Javanmard, S.H. Pistacia Atlantica Resin Has a Dose-Dependent Effect on Angiogenesis and Skin Burn Wound Healing in Rat. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 893425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) | Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GCGCGGCTACAGCTTCA | CTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTCC | NM_001101.5 | |
| CAT | ACATCTGAAGGATCCGGACA | ATGCAGAGACTCAGGACGTA | NM_001752.4 | |
| GPX1 | GGCAAGGAGAACGCCAAGA | AGCATGAAGTTGGGCTCGAA | NM_001329455.2 | |
| GSR | GAGGTGCTGAAGTTCTCCCA | TGACTTCCAAGCCCGACAAA | NM_000637.5 | |
| GSTP1 | TGGTGGACATGGTGAATGAC | AGATGTATTTGCAGCGGAGG | NM_000852.4 | |
| HMXO1 | CAGTCAGGCAGAGGGTGATA | CTCCTCAAAGAGCTGGATGTT | NM_002133.3 | |
| NRF2 | CAGCTTTTGGCGCAGACATT | AAGTGACTGAAACGTAGCCGA | NM_006164.5 | |
| NQO1 | CCAGAAAGGACATCACAGGTAA | AGACTCGGCAGGATACTGAA | NM_001025434.2 | |
| SOD1 | GAGACCTGGGCAATGTGACT | GTTTACTGCGCAATCCCAAT | NM_000454.5 | |
| IC50 (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| DPPH | ABTS | |
| Mastic oil | n.d. | n.d. |
| Myrcene | n.d. | n.d. |
| α-Pinene | n.d. | n.d. |
| Ascorbic acid | 26.13 ± 0.16 | 30.71 ± 0.24 |
| Inhibition (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| DPPH | ABTS | |
| Myrcene (40.5 mg/mL) | 29.22 ± 6 | 0 |
| α-Pinene (43.5 mg/mL) | 47.9 ± 2.78 | 49.28 ± 3.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xanthis, V.; Fitsiou, E.; Voulgaridou, G.-P.; Bogadakis, A.; Chlichlia, K.; Galanis, A.; Pappa, A. Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Potential of the Essential Oil Pistacia lentiscus var. chia and Its Major Components Myrcene and α-Pinene. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010127
Xanthis V, Fitsiou E, Voulgaridou G-P, Bogadakis A, Chlichlia K, Galanis A, Pappa A. Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Potential of the Essential Oil Pistacia lentiscus var. chia and Its Major Components Myrcene and α-Pinene. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleXanthis, Vasileios, Eleni Fitsiou, Georgia-Persephoni Voulgaridou, Athanasios Bogadakis, Katerina Chlichlia, Alex Galanis, and Aglaia Pappa. 2021. "Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Potential of the Essential Oil Pistacia lentiscus var. chia and Its Major Components Myrcene and α-Pinene" Antioxidants 10, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010127
APA StyleXanthis, V., Fitsiou, E., Voulgaridou, G.-P., Bogadakis, A., Chlichlia, K., Galanis, A., & Pappa, A. (2021). Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Potential of the Essential Oil Pistacia lentiscus var. chia and Its Major Components Myrcene and α-Pinene. Antioxidants, 10(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010127








