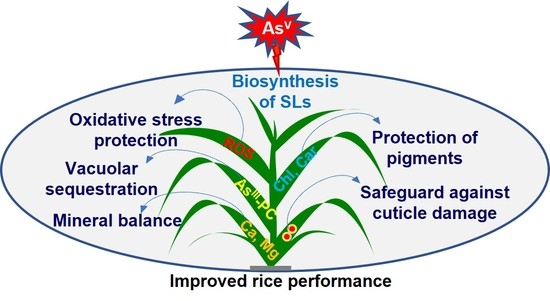
Strigolactones Modulate Cellular Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms to Mitigate Arsenate Toxicity in Rice Shoots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Plant Cultivation and Stress Treatments
2.2. Assessment of Shoot Phenotypes, Shoot Height, Shoot Dry Weight, Photosynthetic Pigment Contents, Electrolyte Leakage and Water Status
2.3. Quantification of the Levels of Arsenic, Phosphorous and Other Minerals in Rice Shoots
2.4. Histochemical Staining of ROS and Cuticle Damage in Rice Leaves
2.5. Estimation of H2O2 and Malondialdehyde Contents in Rice Shoots
2.6. Extraction and Estimation of Total GSH, Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Total Soluble Protein Contents
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
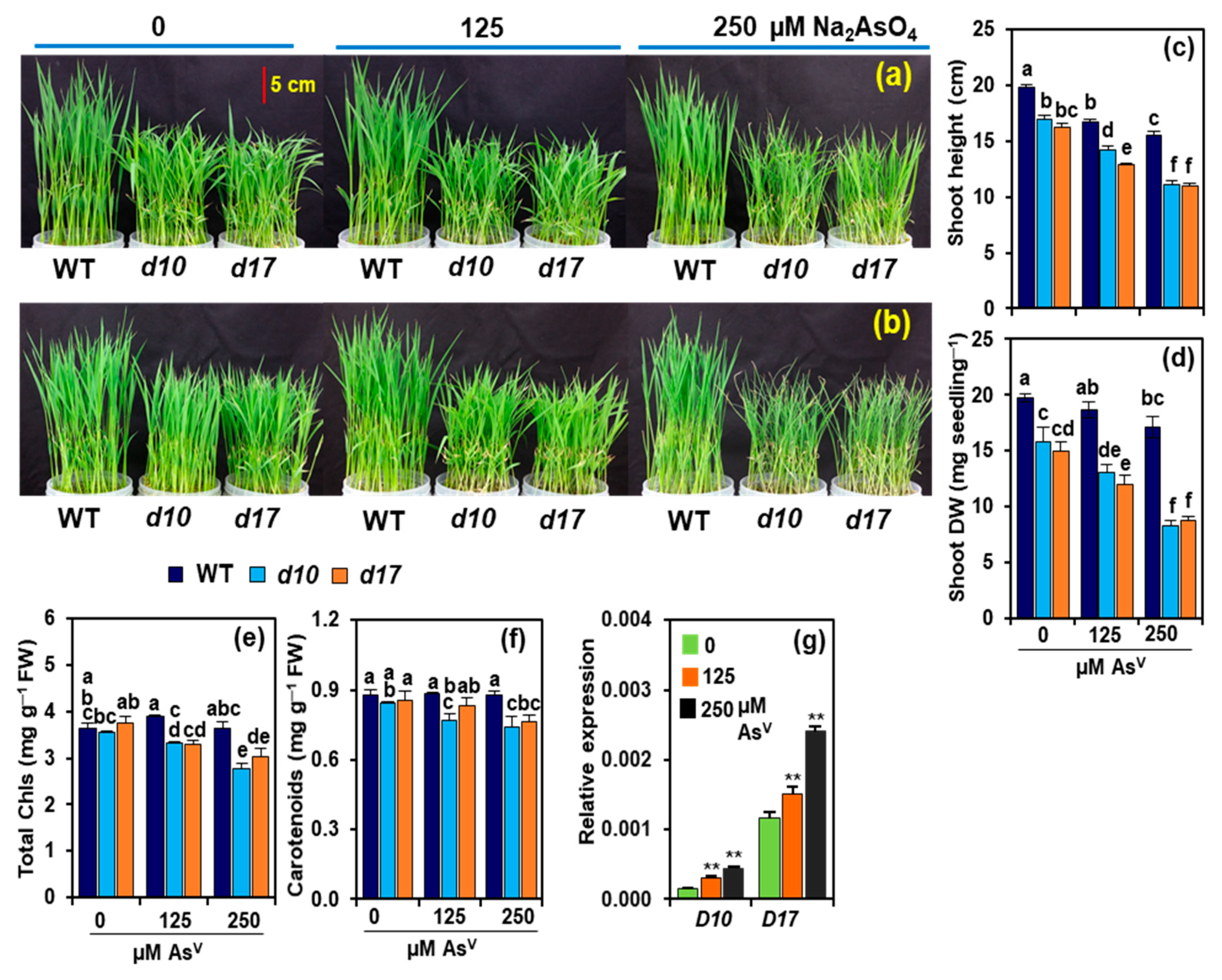
3.1. SL Deficiency Leads to Severe Arsenic Stress on Rice Growth and Biomass Production
3.2. Arsenic Induces the Expression of D10 and D17 in the Shoots of WT Plants
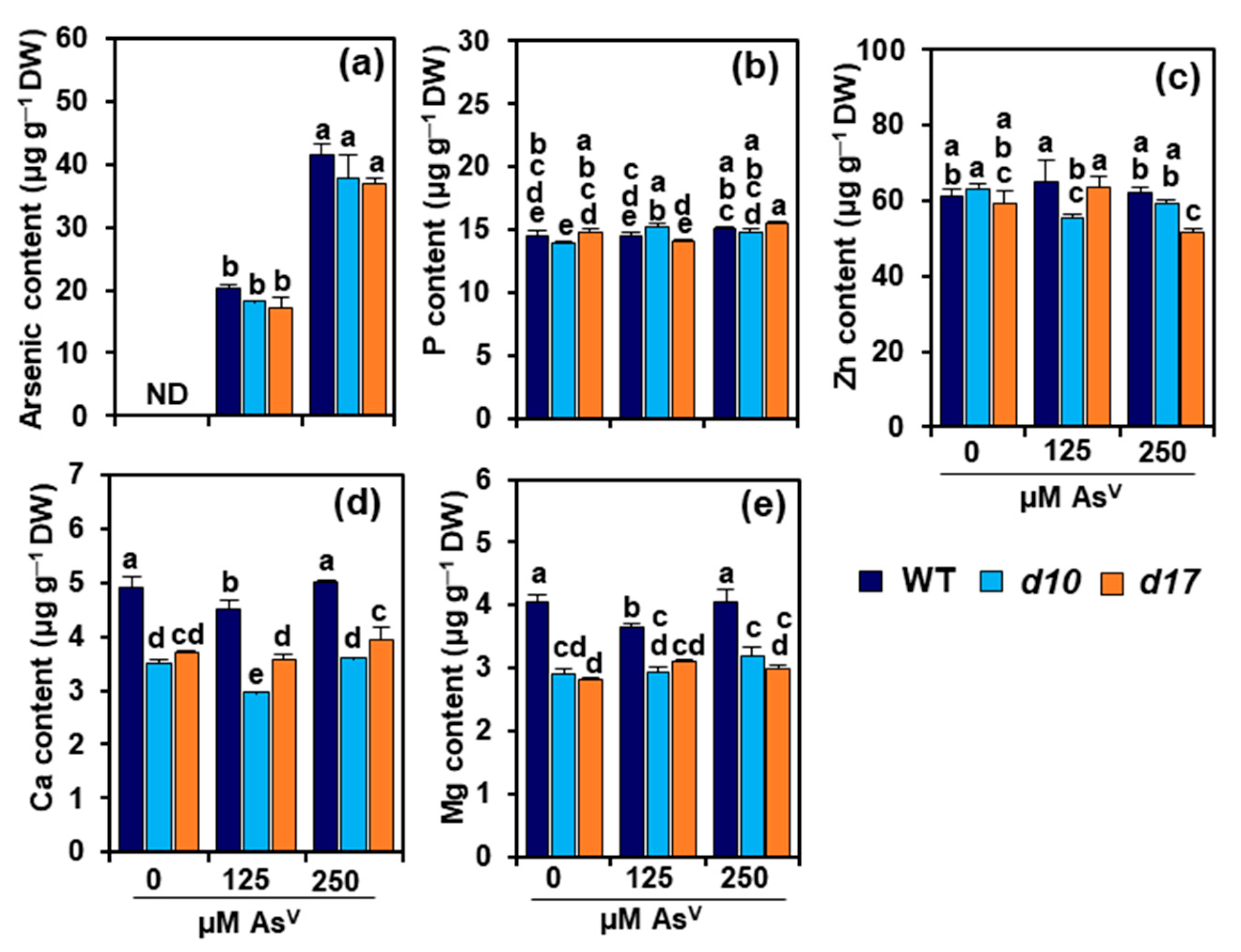
3.3. SL Deficiency Does Not Alter Arsenic, P and Zn Levels in Rice Shoots
3.4. SL Deficiency Alters Ca and Mg Contents in Rice Shoots
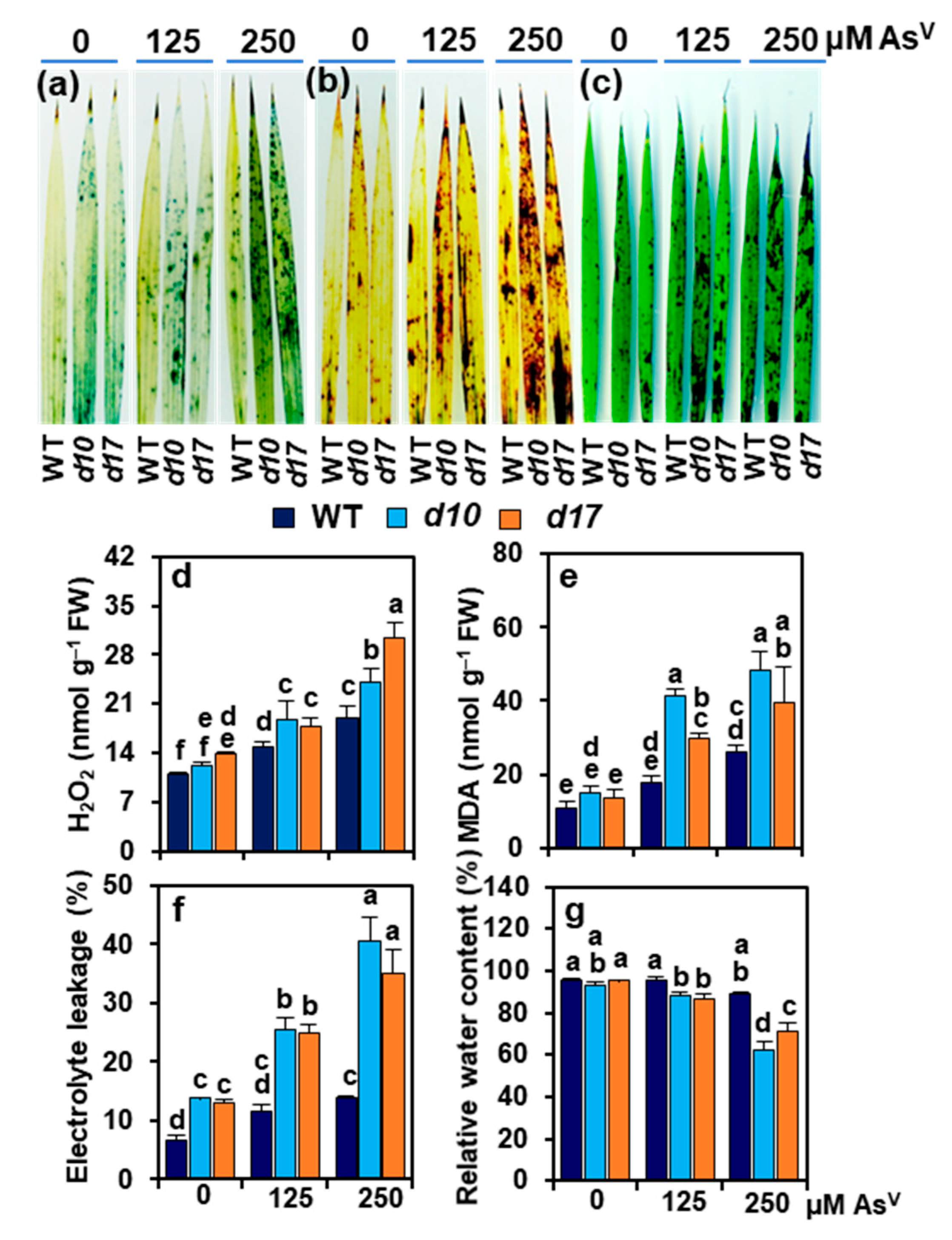
3.5. SL Deficiency Evokes Arsenic-Induced Oxidative Stress, Cuticle Damage, Electrolyte Leakage and Water Loss
3.6. SL Deficiency Compromises Antioxidant Defense System under AsV Stress
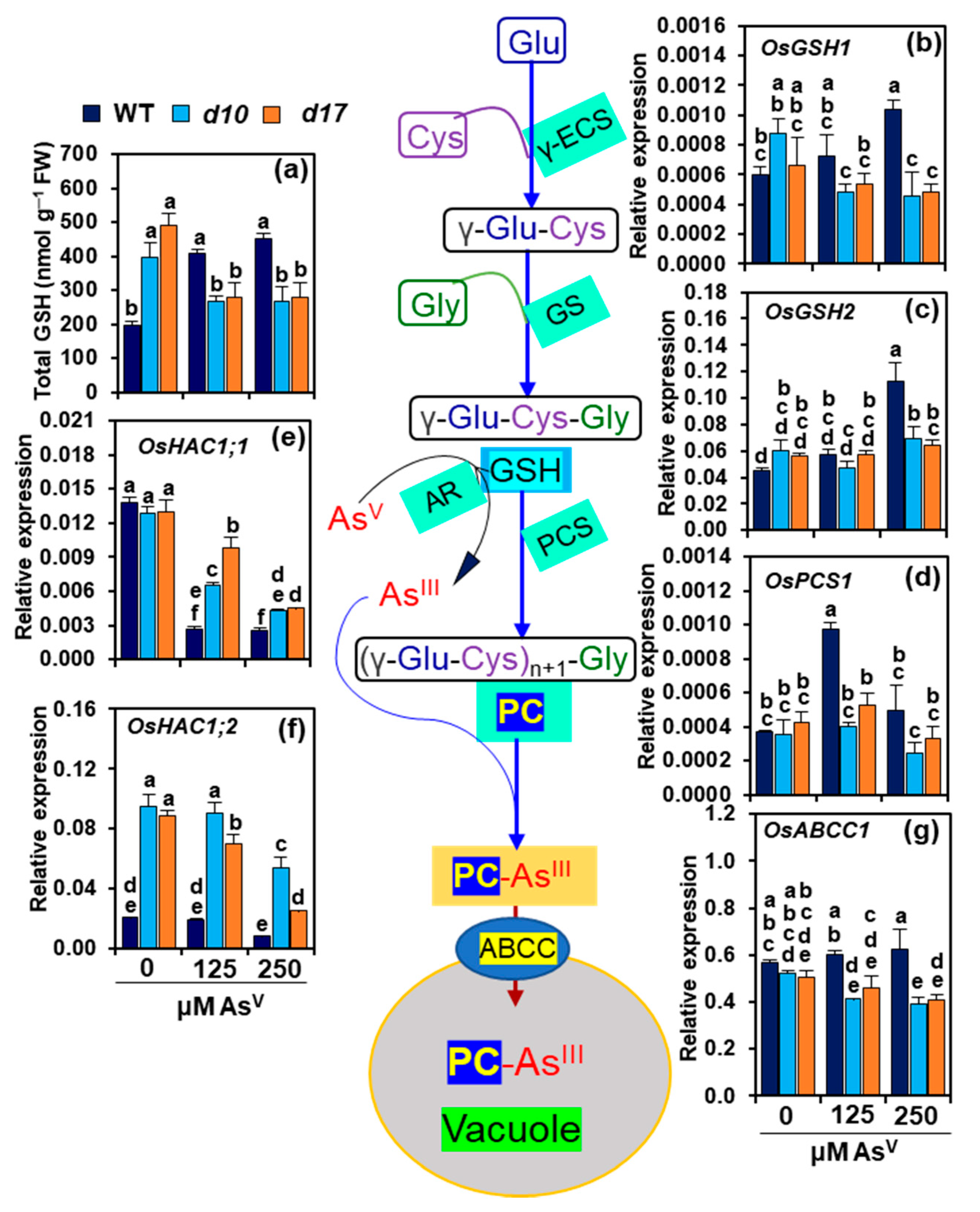
3.7. SL Deficiency Negatively Affects GSH-Assisted Arsenic Detoxification
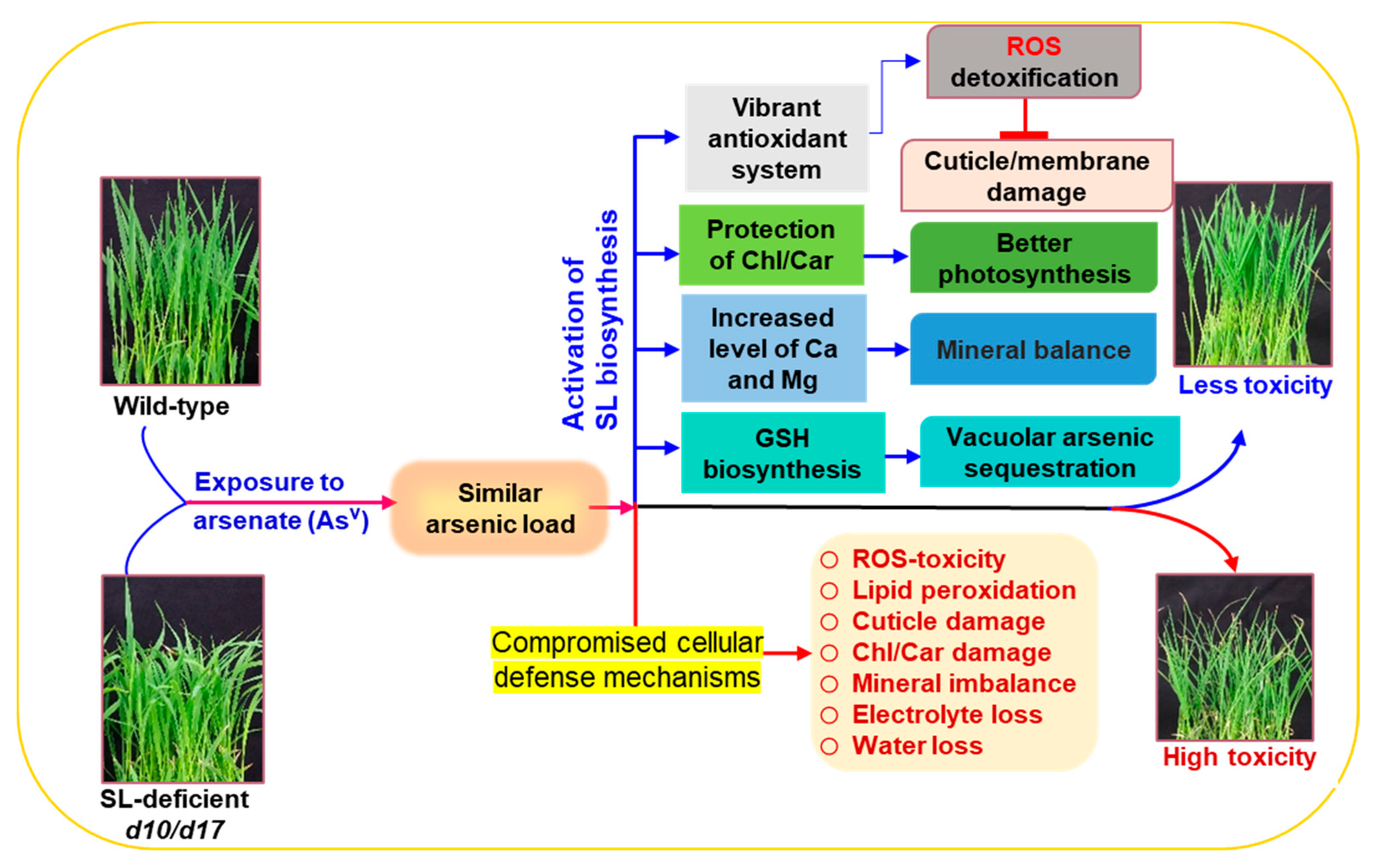
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mostofa, M.G.; Li, W.; Nguyen, K.H.; Fujita, M.; Tran, L.-S.P. Strigolactones in plant adaptation to abiotic stresses: An emerging avenue of plant research. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2227–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sinha, R.; Fernandes, J.L.; Abdelrahman, M.; Burritt, D.J.; Tran, L.-S.P. Phytohormones regulate convergent and divergent responses between individual and combined drought and pathogen infection. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 320–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, M.T.; Gutjahr, C.; Bennett, T.; Nelson, D.C. Strigolactone signaling and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 291–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Babili, S.; Bouwmeester, H.J. Strigolactones, a novel carotenoid-derived plant hormone. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, A.; Jamil, M.; Marzorati, M.; Bruno, M.; Vermathen, M.; Bigler, P. The path from beta-carotene to carlactone, a strigolactone-like plant hormone. Science 2012, 335, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.X.; van Dijk, A.D.J.; Scaffidi, A.; Flematti, G.R.; Hofmann, M.; Charnikhova, T. Rice cytochrome P450 MAX1 homologs catalyze distinct steps in strigolactone biosynthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesterfield, R.J.; Vickers, C.E.; Beveridge, C.A. Translation of strigolactones from plant hormone to agriculture: Achievements, future perspectives, and challenges. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Lin, Q.B.; Zhu, L.H.; Ren, Y.L.; Zhou, K.N.; Shabek, N. D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling. Nature 2013, 504, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Ráez, J.A.; Shirasu, K.; Foo, E. Strigolactones in plant interactions with beneficial and detrimental organisms: The Yin and Yang. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.W.; Hu, Y.; Beyyoudh, L.; Yildiz, D.H.; Kunert, K.; Beveridge, C.A. Strigolactones positively regulate chilling tolerance in pea and in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.-W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.-H.; Mao, W.; Wu, F. Strigolactone GR24 improves cadmium tolerance by regulating cadmium uptake, nitric oxide signaling and antioxidant metabolism in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, M.; Emam, Y.; Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A.; Hazrati, S.; Lovisolo, C.; Visentin, I. The potential of the synthetic strigolactone analogue GR24 for the maintenance of photosynthesis and yield in winter wheat under drought: Investigations on the mechanisms of action and delivery modes. Plants 2021, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, C.V.; Leyva-González, M.A.; Osakabe, Y.; Tran, U.T.; Nishiyama, R.; Watanabe, Y. Positive regulatory role of strigolactone in plant responses to drought and salt stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; He, H.; Vitali, M.; Visentin, I.; Charnikhova, T.; Haider, I. Osmotic stress represses strigolactone biosynthesis in Lotus japonicus roots: Exploring the interaction between strigolactones and ABA under abiotic stress. Planta 2015, 241, 1435–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, I.; Andreo-Jimenez, B.; Bruno, M.; Bimbo, A.; Floková, K.; Abuauf, H. The interaction of strigolactones with abscisic acid during the drought response in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2403–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, I.; Vitali, M.; Ferrero, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ruyter-Spira, C.; Novák, O. Low levels of strigolactones in roots as a component of the systemic signal of drought stress in tomato. New Phytol. 2016, 212, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, F.; Su, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cui, J.; He, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Effects of strigolactone on photosynthetic and physiological characteristics in salt-stressed rice seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Chai, L.; Jiang, W. Photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress from low-light stress with exogenous GR24 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffidi, A.; Waters, M.T.; Sun, Y.K.; Skelton, B.W.; Dixon, K.W.; Ghisalberti, E.L. Strigolactone hormones and their stereoisomers signal through two related receptor proteins to induce different physiological responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbas, G.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Khan, M.I.; Amjad, M. Arsenic uptake, toxicity, detoxification, and speciation in plants: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Awan, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L. Arsenic behavior in soil-plant system and its detoxification mechanisms in plants: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhao, F.-J. The roles of membrane transporters in arsenic uptake, translocation and detoxification in plants. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 51, 2449–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah; Dahlawi, S.; Naeem, A.; Iqbal, M.; Farooq, M.A.; Bibi, S. Opportunities and challenges in the use of mineral nutrition for minimizing arsenic toxicity and accumulation in rice: A critical review. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Garcia, Y.; Shinde, S.; Natarajan, P.; Lopez-Ortiz, C.; Balagurusamy, N.; Chavez, A.C.D. Arsenic Stress-Related F-Box (ASRF) gene regulates arsenic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezza, M.E.; Luna, D.F.; Agostini, E.; Talano, M.A. Glutathione, a key compound for As accumulation and tolerance in soybean plants treated with AsV and AsIII. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.S.; Sidhu, G.P.S. Arsenic acquisition, toxicity and tolerance in plants-From physiology to remediation: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Rahman, M.M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Li, W.; Watanabe, Y.; Tran, C.D. Strigolactones regulate arsenate uptake, vacuolar-sequestration and antioxidant defense responses to resist arsenic toxicity in rice roots. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, G.; Singh, A.P.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Kumar, S. Reduced arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) shoot involves sulfur mediated improved thiol metabolism, antioxidant system and altered arsenic transporters. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, T.; Khan, S.; Muhammad, S.; Amin, S. Arsenic speciation, mechanisms, and factors affecting rice uptake and potential human health risk: A systematic review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehe, E.M.; Wang, T.; Kerl, C.F.; Planer-Friedrich, B.; Fendorf, S. Rice production threatened by coupled stresses of climate and soil arsenic. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Rahman, M.M.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Fujita, M.; Tran, L.-S.P. Salicylic acid antagonizes selenium phytotoxicity in rice: Selenium homeostasis, oxidative stress metabolism and methylglyoxal detoxification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Maekawa, M.; Arite, T.; Onishi, K.; Takamure, I.; Kyozuka, J. Suppression of tiller bud activity in tillering dwarf mutants of rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Fujita, M. Salicylic acid alleviates copper toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by up-regulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Hossain, M.A.; Fujita, M. Trehalose pretreatment induces salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings: Oxidative damage and co-induction of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Protoplasma 2015, 252, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itouga, M.; Kato, Y.; Sakakibara, H. Phenotypic plasticity and mineral nutrient uptake of the moss Polymeric commune Hew. during acclimation to a change in light intensity. Hikobia 2014, 16, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, H.; Machida, C.; Watanabe, M.; Machida, Y. A new method for rapid visualization of defects in leaf cuticle reveals five intrinsic patterns of surface defects in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004, 37, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.H.; Mostofa, M.G.; Watanabe, Y.; Tran, C.D.; Rahman, M.M.; Tran, L.-S.P. Overexpression of GmNAC085 enhances drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by regulating glutathione biosynthesis, redox balance and glutathione-dependent detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, O.W. Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 106, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawi, H.; Kumar, B.; Kaul, T.; Reddy, M.K.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Sopory, S.K. Redox homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and methylglyoxal detoxification as markers for salt tolerance in Pokkali rice. Protoplasma 2010, 245, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 867–880. [Google Scholar]
- Foyer, C.H.; Halliwell, B. The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: A proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 1976, 133, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Fujita, M. Up-regulation of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems by exogenous glycinebetaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2010, 16, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elia, A.C.; Galarini, R.; Taticchi, M.I.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Mantilacci, L. Antioxidant responses and bioaccumulation in Ictalurus melas under mercury exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 55, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Nishiyama, R.; Watanabe, Y.; Mochida, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Genome-wide expression profiling of soybean two-component system genes in soybean root and shoot tissues under dehydration stress. DNA Res. 2011, 18, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, P.; Srivastava, S.; Patil, T.; Raghuvanshi, R.; Srivastava, A.K.; Suprasanna, P. Tracking the time-dependent and tissue-specific processes of arsenic accumulation and stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Augustine, R.; Panthri, M.; Zia, I.; Bisht, N.C.; Gupta, M. Arsenic affects the production of glucosinolate, thiol and phytochemical compounds: A comparison of two Brassica cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 111, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Khatun, M.A.; Haque, M.N.; Bari, M.A.; Alam, M.F.; Mandal, A. Silicon alleviates arsenic-induced toxicity in wheat through vacuolar sequestration and ROS scavenging. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2018, 20, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.A.; Tanveer, M.; Hussain, S.; Ashraf, U.; Khan, I.; Wang, L. Alteration in growth, leaf gas exchange, and photosynthetic pigments of maize plants under combined cadmium and arsenic stress. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 228, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Jha, A.B.; Misra, A.N.; Sharma, P. Differential responses of growth, photosynthesis, oxidative stress, metals accumulation and NRAMP genes in contrasting Ricinus communis genotypes under arsenic stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31166–31177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Huang, F.; Wu, N.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Xiong, L. Integrative regulation of drought escape through ABA-dependent and -independent pathways in rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tawfik, D.S.; Viola, R.E. Arsenate replacing phosphate: Alternative life chemistries and ion promiscuity. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finnegan, P.M.; Chen, W. Arsenic toxicity: The effects on plant metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farnese, F.S.; Oliveira, J.A.; Paiva, E.A.S.; Menezes-Silva, P.E.; da Silva, A.A.; Campos, F.V. The involvement of nitric oxide in integration of plant physiological and ultrastructural adjustments in response to arsenic. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Rahman, M.M.; Ansary, M.M.U.; Keya, S.S.; Abdelrahman, M.; Miah, M.G. Silicon in mitigation of abiotic stress-induced oxidative damage in plants. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, R.; Lippmann, B.; Holzinger, S.; Bergmann, H. Arsenate toxicity: Effects on oxidative stress response molecules and enzymes in red clover plants. Plant Sci. 2002, 163, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvobgo, G.; LwalabaWaLwalaba, J.; Sagonda, T.; Mutemachani, M.J.; Muhammad, N.; Haider Shamsi, I. Phosphate alleviates arsenate toxicity by altering expression of phosphate transporters in the tolerant barley genotypes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiszár, J.; Horváth, E.; Bela, K.; Gallé, Á. Glutathione-related enzyme system: Glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione transferases (GSTs) and glutathione peroxidases (GPXs). In Redox State as a Central Regulator of Plant-Cell Stress Responses; Gupta, D.K., Palma, J.M., Corpas, F.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 137–158. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Salt, D.E. OsHAC1;1 and OsHAC1;2 Function as arsenate reductases and regulate arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coelho, D.G.; Marinato, C.S.; de Matos, L.P.; de Andrade, H.M.; da Silva, V.M.; Santos-Neves, P.H. Is arsenite more toxic than arsenate in plants? Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mostofa, M.G.; Ha, C.V.; Rahman, M.M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Keya, S.S.; Watanabe, Y.; Itouga, M.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Fujita, M.; et al. Strigolactones Modulate Cellular Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms to Mitigate Arsenate Toxicity in Rice Shoots. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111815
Mostofa MG, Ha CV, Rahman MM, Nguyen KH, Keya SS, Watanabe Y, Itouga M, Hashem A, Abd_Allah EF, Fujita M, et al. Strigolactones Modulate Cellular Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms to Mitigate Arsenate Toxicity in Rice Shoots. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(11):1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111815
Chicago/Turabian StyleMostofa, Mohammad Golam, Chien Van Ha, Md. Mezanur Rahman, Kien Huu Nguyen, Sanjida Sultana Keya, Yasuko Watanabe, Misao Itouga, Abeer Hashem, Elsayed Fathi Abd_Allah, Masayuki Fujita, and et al. 2021. "Strigolactones Modulate Cellular Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms to Mitigate Arsenate Toxicity in Rice Shoots" Antioxidants 10, no. 11: 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111815
APA StyleMostofa, M. G., Ha, C. V., Rahman, M. M., Nguyen, K. H., Keya, S. S., Watanabe, Y., Itouga, M., Hashem, A., Abd_Allah, E. F., Fujita, M., & Tran, L.-S. P. (2021). Strigolactones Modulate Cellular Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms to Mitigate Arsenate Toxicity in Rice Shoots. Antioxidants, 10(11), 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111815