Protective Effect of Curcumin against Sodium Salicylate-Induced Oxidative Kidney Damage, Nuclear Factor-Kappa Dysregulation, and Apoptotic Consequences in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Compounds and Chemicals
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Hematological Analysis
2.5. Serum Biochemical Analysis
2.5.1. Measurement of Some Kidney Function Tests
2.5.2. Protein Profile
2.6. Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Parameters in Kidney Tissue
2.7. Histopathological Investigations
2.8. Immunohistochemical Investigation of Caspase-3 and NF-κB Activity in the Kidney Tissues
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects on Relative Kidney Weights and Hematological Indicators
3.2. Effects on Protein Fractions
3.3. Effects on Kidney Function Indicators
3.4. Effects on Serum Electrolytes Levels
3.5. Effects on Oxidative Kidney Damage
3.6. Effects on Apoptotic Indicators in Kidney Tissues
3.7. Histopathological Findings
3.8. Immunohistochemical Findings
3.9. Correlation Analysis by Principal Components Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.T.; Luo, B.; Huang, Y.N.; Zhou, K.Q.; Chen, L. Sodium salicylate suppresses serotonin-induced enhancement of GABAergic spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents in rat inferior colliculus in vitro. Hear. Res. 2008, 236, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Xia, C.; Wu, C.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, Y. Aberrant expression of Nav1.6 in the cochlear nucleus correlates with salicylate-induced tinnitus in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.N.; Sumner, C.J.; Berger, J.I.; McNaughton, P.A.; Palmer, A.R. Salicylate decreases the spontaneous firing rate of guinea pig auditory nerve fibres. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 747, 135705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Abdel-Motal, S.M.; Malhat, S.M.; Mostafa, H.I.; Moselhy, A.A.; Beheiry, R.R.; Said, E.N. Curcumin mitigates neurotoxic and neurobehavioral changes of gentamicin and sodium salicylate in rats by adjusting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, T.F.; Stefanski, S.A.; Wilson, R.E.; Blair, P.C.; Clark, A.-M.; Birnbaum, L.S. Comparative acute nephrotoxicity of salicylic acid, 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and 2, 5-dihydroxybenzoic acid in young and middle aged Fischer 344 rats. Toxicology 1991, 66, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, G.; Moreno, J.; Franch, M.; Queralt, J. N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) and alanine aminopeptidase (AAP) excretion after acute administration of acetaminophen, salsalate and aspirin in rats. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1993, 81, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Tsimihodimos, V.; Psychogios, N.; Kakaidi, V.; Bairaktari, E.; Elisaf, M. Salicylate-induced proximal tubular dysfunction. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 50, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runde, T.J.; Nappe, T.M. Salicylates Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, T.K.; Moharana, A.K.; Swain, R.P.; Subudhi, B.B. Coamorphisation of acetyl salicylic acid and curcumin for enhancing dissolution, anti-inflammatory effect and minimizing gastro toxicity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Ghoneim, M.H.; Ebraheim, L.L.; Imam, T.S. Taurine and hesperidin rescues carbon tetrachloride-triggered testicular and kidney damage in rats via modulating oxidative stress and inflammation. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Mohamed, W.A.; Bohi, K.M.E.; Ali, H.A.; Mahmoud, F.A.; Saber, T.M. Prevention of melamine-induced hepatorenal impairment by an ethanolic extract of Moringa oleifera: Changes in KIM-1, TIMP-1, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation-related genes. Gene 2021, 764, 145083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behairy, A.; Mohamed, W.A.; Ebraheim, L.L.; Soliman, M.M.; Abd EL-Hakim, Y.M.; El-Sharkawy, N.I.; Saber, T.M.; El Deib, M.M. Boldenone undecylenate mediated hepatorenal impairment by oxidative damage and dysregulation of heat shock protein 90 and androgen receptors expressions: Vitamin C preventive role. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, M.A.; Shoeeb, S.B.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Mohamed, W.A. The antitumor activity of Arthrospira platensis and/or cisplatin in a murine model of Ehrlich ascites carcinoma with hematinic and hepato-renal protective action. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Harikumar, K.B. Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 40–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Momtazi, A.A.; Sahebkar, A. Difluorinated Curcumin: A Promising Curcumin Analogue with Improved Anti-Tumor Activity and Pharmacokinetic Profile. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4386–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivari, F.; Mingione, A.; Brasacchio, C.; Soldati, L. Curcumin and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevention and Treatment. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jalali, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Mosallanezhad, Z.; Jalali, R.; Imanieh, M.H.; Moosavian, S.P. The effects of curcumin supplementation on liver function, metabolic profile and body composition in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 48, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Kariznavi, E.; Jannati, M.; Elyasi, S.; Tayarani-Najaran, Z. Curcumin as a preventive or therapeutic measure for chemotherapy and radiotherapy induced adverse reaction: A comprehensive review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.K.; McClure, D.; Jimenez, L.A.; Megson, I.L.; Rahman, I. Curcumin induces glutathione biosynthesis and inhibits NF-κB activation and interleukin-8 release in alveolar epithelial cells: Mechanism of free radical scavenging activity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, T.M.; Abo-Elmaaty, A.M.A.; Abdel-Ghany, H.M. Curcumin mitigates mancozeb-induced hepatotoxicity and genotoxicity in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, P.M.; Lal, N. Prospective of curcumin, a pleiotropic signalling molecule from Curcuma longa in the treatment of Glioblastoma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, L.A.; Sordillo, P.P.; Helson, L. Curcumin for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 6373–6378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mollazadeh, H.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Blesso, C.N.; Pirro, M.; Majeed, M.; Sahebkar, A. Immune modulation by curcumin: The role of interleukin-10. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Ghasemi, F.; Barreto, G.E.; Rafiee, R.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of curcumin on mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases. Biofactors (Oxf. Engl.) 2020, 46, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.H.; Abdelrahman, A.; Al Suleimani, Y.; Manoj, P.; Ali, H.; Nemmar, A.; Al Za’abi, M. Effect of concomitant treatment of curcumin and melatonin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edrees, N.E.; Galal, A.A.A.; Abdel Monaem, A.R.; Beheiry, R.R.; Metwally, M.M.M. Curcumin alleviates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 294, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejo, J. Chapter 45—Curcumin, antioxidant activity, and paracetamol toxicity. In Toxicology; Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Morón, E.; Calderón-Montaño, J.M.; Salvador, J.; Robles, A.; López-Lázaro, M. The dark side of curcumin. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaji, N.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Derag, M.N.G.; Naderi, R.; Hassanlouei, E.A. Combination effect of ecstasy and curcumin on hematological parameters and serum immunoglobulin levels in early and late phase in male rats. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 24, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Lim, H.-J.; Lim, J.S.; Son, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.M.; Chang, S.-C.; Kim, H.S. Curcumin ameliorates cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Allah, E.S.; Gomaa, A.M. Effects of curcumin and captopril on the functions of kidney and nerve in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Role of angiotensin converting enzyme 1. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Chen, W.; Cao, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, J. Protective effect of curcumin on acrylamide-induced hepatic and renal impairment in rats: Involvement of CYP2E1. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20910548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akintunde, J.; Farouk, A.; Mogbojuri, O. Metabolic treatment of syndrome linked with Parkinson’s disease and hypothalamus pituitary gonadal hormones by turmeric curcumin in Bisphenol-A induced neuro-testicular dysfunction of wistar rat. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2019, 17, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-D.; Kermany, M.H.; D’Elia, A.; Ralli, M.; Tanaka, C.; Bielefeld, E.C.; Ding, D.; Henderson, D.; Salvi, R. Too much of a good thing: Long-term treatment with salicylate strengthens outer hair cell function but impairs auditory neural activity. Hear. Res. 2010, 265, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chyka, P.A.; Erdman, A.R.; Christianson, G.; Wax, P.M.; Booze, L.L.; Manoguerra, A.S.; Martin Caravati, E.; Nelson, L.S.; Olson, K.R.; Cobaugh, D.J. Salicylate poisoning: An evidence-based consensus guideline for out-of-hospital management. Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 95–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, B.; Hu, S.; Zuo, C.; Jiao, F.; Lv, J.; Chen, D.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Mei, L.; Wang, X. Effects of long-term salicylate administration on synaptic ultrastructure and metabolic activity in the rat CNS. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coulombe, J.; Favreau, L. A new simple semimicro method for colorimetric determination of urea. Clin. Chem. 1963, 9, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, K. Creatinine assay in the presence of protein with LKB 8600 Reaction Rate Analyser. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1972, 38, 475. [Google Scholar]
- Barham, D.; Trinder, P. Enzymatic determination of uric acid. Analyst 1972, 97, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, G.; Beyer, G.; Klin, Z. Determination of potassium concentration. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1967, 5, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, R.; Cannon, D.; Winkelman, J. Clinical Chemistry Principles and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Haper and Row: Hagerstown, MD, USA, 1974; pp. 411–421. [Google Scholar]
- Tietz, N. Clinical guide to laboratory tests, WB Saunders Company. Phila. USA 1990, 554, 556. [Google Scholar]
- Gindler, E.M.; King, J.D. Rapid colorimetric determination of calcium in biologic fluids with methylthymol blue. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1972, 58, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schales, O.; Schales, S.S. A simple and accurate method for the determination of chloride in biological fluids. J. Biol. Chem. 1941, 140, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Merzabani, M.; El-Aaser, A.; Zakhary, N.I. New Method Determ. Inorg. Phosphorus Serum Deproteinization. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1977, 15, 715–718. [Google Scholar]
- Gornal, A.; Bardawill, C.; David, M. Protein-Biuret colorimetric method. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 177, 751. [Google Scholar]
- Doumas, B.T.; Bayse, D.D.; Carter, R.J.; Peters, T.; Schaffer, R. A candidate reference method for determination of total protein in serum. I. Development and validation. Clin. Chem. 1981, 27, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumas, B.; Biggs, H. Determination of Serum Globulin in: Standerd Methods of Clinical Chemistry; Cooper, Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ornstein, L. Disc electrophoresis-i background and theory. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1964, 121, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikimi, M.; Rao, N.A.; Yagi, K. The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1972, 46, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, D.E.; Valentine, W.N. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1967, 70, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, K.S.; Layton, C.; Bancroft, J.D. Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Kiupel, M.; Baszler, T.; Bliven, L.; Brodersen, B.; Chelack, B.; West, K.; Czub, S.; Del Piero, F.; Dial, S. Suggested guidelines for immunohistochemical techniques in veterinary diagnostic laboratories. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amann, R.; Peskar, B.A. Anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin and sodium salicylate. Eur. J. Pharm. 2002, 447, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, D.J.; Capodanno, D. Aspirin for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in the 21st Century: A Review of the Evidence. Am. J. Cardiol. 2021, 144, S15–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcumin Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Application (Pharmaceutical, Food, Cosmetics), By Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Central & South America, Middle East & Africa), And Segment Forecasts, 2020–2027. 2020. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/turmeric-extract-curcumin-market?utm_source=pressrelease&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=PRN_Sep03_Curcumin_RD2&utm_content=Content (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- Oetari, S.; Sudibyo, M.; Commandeur, J.N.; Samhoedi, R.; Vermeulen, N.P. Effects of curcumin on cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah-Opong, R.; Commandeur, J.N.; van Vugt-Lussenburg, B.; Vermeulen, N.P. Inhibition of human recombinant cytochrome P450s by curcumin and curcumin decomposition products. Toxicology 2007, 235, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapliyal, R.; Maru, G. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 isozymes by curcumins in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, C.; Barone, E. Curcumin in clinical practice: Myth or reality? Update 2009, 30, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmin, S.F.; Giroux, M.C.; Vachon, P.; Beaudry, F. In vitro metabolism of specific CYP2D and CYP3A opioid substrates using rat liver S9 fractions and mass spectrometry reveal a severe metabolic impairment with increasing age. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauthier, V.; Verbeeck, R.-K.; Buc Calderon, P. The effect of ageing on cytochrome p450 enzymes: Consequences for drug biotransformation in the elderly. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, K.; Blackshear, P.E.; Lobenhofer, E.K.; Parker, J.S.; Orzech, D.P.; Roycroft, J.H.; Walker, K.L.; Johnson, K.A.; Marsh, T.A.; Irwin, R.D. Hepatic transcript levels for genes coding for enzymes associated with xenobiotic metabolism are altered with age. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-F.; Hu, A.-L.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.-J.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J. Age-associated changes of cytochrome P450 and related phase-2 gene/proteins in livers of rats. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrasciotta, Y.; Sultana, J.; Giorgianni, F.; Menditto, E.; Scuteri, A.; Tari, M.; Tari, D.U.; Basile, G.; Trifiro, G. Analgesic drug use in elderly persons: A population-based study in Southern Italy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Souza, C.; Silva, T.; Gomes, I.; Brito, G.; Araújo, A.; Lyra Jr, D.; Silva, W.; Silva, F. Use of Herbal Medicines by Elderly Patients: A Systematic Review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Wilkinson IV, J.; Di, X.; Wang, W.; Hatcher, H.; Kock, N.D.; D’Agostino Jr, R.; Knovich, M.A.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Curcumin, a cancer chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agent, is a biologically active iron chelator. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2009, 113, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srichairatanakool, S.; Thephinlap, C.; Phisalaphong, C.; Porter, J.; Fucharoen, S. Curcumin contributes to in vitro removal of non-transferrin bound iron by deferiprone and desferrioxamine in thalassemic plasma. Med. Chem. 2007, 3, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means Jr, R.T. Ironing out complementary medicine. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2009, 113, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciejka, M.; Nguyen, K.; Bluth, M.H.; Dubey, E. Drug toxicities of common analgesic medications in the emergency department. Clin. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgalaleh, A.; Mahmudi, M.; Tabibian, S.; Khatib, Z.K.; Tamaddon, G.H.; Moghaddam, E.S.; Bamedi, T.; Alizadeh, S.; Moradi, E. Anemia and thrombocytopenia in acute and chronic renal failure. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 7, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalaji, N.; Dindarian, S.; Hazeghi-Rad, A.A.; Baba Hasanzadeh, S.; Asghari, S. The Role of Curcumin on Reduced Leukocyte and Platelet Counts in Rats After Exposure to Ultraviolet Light from Compact Fluorescent Lamps: A Morphological Study. Shiraz E Med. J. 2019, 20, e85196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyle, M.E.; Kocsis, J.J. The effect of age on salicylate-induced nephrotoxicity in male rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1985, 81, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, M.E.; Kocsis, J.J. The effect of mixed function oxidase induction and inhibition on salicylate-induced nephrotoxicity in male rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1986, 84, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Beulaja, M.; Thiagarajan, R.; Priyadarsini, A.; Saravanan, R.; Arumugam, M. Ameliorative effects of curcumin against renal injuries mediated by inducible nitric oxide synthase and nuclear factor kappa B during gentamicin-induced toxicity in Wistar rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, M.; Ueno, M.; Morishita, J.; Maekawa, N. Curcumin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting renal inflammation in mice. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 115, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.K.; Stricklett, P.K.; Padilla, E.; Kohan, D.E. Effect of reactive oxygen species on endothelin-1 production by human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haller, C. Hypoalbuminemia in renal failure: Pathogenesis and therapeutic considerations. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2005, 28, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, T.; Horita, T.J.; Kasravi, B. Understanding and interpreting the serum protein electrophoresis. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 71, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yousef, M.I.; Omar, S.A.; El-Guendi, M.I.; Abdelmegid, L.A. Potential protective effects of quercetin and curcumin on paracetamol-induced histological changes, oxidative stress, impaired liver and kidney functions and haematotoxicity in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3246–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.; Farrar, F.C. Kidney Influence on Fluid and Electrolyte Balance. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 53, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inker, L.A.; Perrone, R.D. Assessment of Kidney Function. 2014. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/assessment-of-kidney-function (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- Arroyo, R.A. Electrolyte and acid-base balance disorders in advanced chronic kidney disease. Nefrol. Publ. Off. Soc. Esp. Nefrol. 2008, 28, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolova, M.; Leont’ev, V.; Semenova, O.; Khrustaleva, R. Potassium distribution in rat tissues in relation to its concentration in the blood. Fiziol. Zhurnal SSSR Im. IM Sechenova 1990, 76, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar]
- de Araujo, M.; Helou, C.M.d.B.; Seguro, A.C. Renal potassium handling in aging rats. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 1998, 21, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, S.C.; Spyres, M.B. Salicylates. In Critical Care Toxicology: Diagnosis and Management of the Critically Poisoned Patient; Brent, J., Burkhart, K., Dargan, P., Hatten, B., Megarbane, B., Palmer, R., White, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1251–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Un, H.; Ugan, R.A.; Gurbuz, M.A.; Bayir, Y.; Kahramanlar, A.; Kaya, G.; Cadirci, E.; Halici, Z. Phloretin and phloridzin guard against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice through inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vysakh, A.; Abhilash, S.; Kuriakose, J.; Midhun, S.J.; Jyothis, M.; Latha, M.S. Protective effect of Rotula aquatica Lour against gentamicin induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, S.; Ashafaq, M.; Hussain, S.; Mohammed, M.; Sultan, M.; Jali, A.M.; Siddiqui, R.; Islam, F. Renoprotective effects of cinnamon oil against APAP-Induced nephrotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation in rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, Z.; Moaiedi, M.Z.; Gorji, A.V.; Mansouri, E. P-Coumaric acid mitigates doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity through suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannakopoulou, E.C.; Tiligada, E. Protective effect of salicylates against hydrogen peroxide stress in yeast. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, W.A.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Ismail, S.A. Involvement of the anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-secretory activity of bee venom in its therapeutic effects on acetylsalicylic acid-induced gastric ulceration in rats. Toxicology 2019, 419, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Park, M.J.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, M.Y.; Han, S.I.; Park, H.G.; Kang, H.S. Implication of reactive oxygen species, ERK1/2, and p38MAPK in sodium salicylate-induced heat shock protein 72 expression in C6 glioma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Ding, D.; Su, J.; Manohar, S.; Salvi, R. Salicylate selectively kills cochlear spiral ganglion neurons by paradoxically up-regulating superoxide. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 24, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Park, H.G.; Kang, H.S. Sodium salicylate induces apoptosis in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells through activation of p38MAPK. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 23, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokaç, M.; Taner, G.; Aydın, S.; Özkardeş, A.B.; Dündar, H.Z.; Taşlıpınar, M.Y.; Arıkök, A.T.; Kılıç, M.; Başaran, A.A.; Basaran, N. Protective effects of curcumin against oxidative stress parameters and DNA damage in the livers and kidneys of rats with biliary obstruction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 61, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu-Tarladacalisir, Y.; Sapmaz-Metin, M.; Karaca, T. Curcumin counteracts cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by preventing renal tubular cell apoptosis. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unnikrishnan, M.; Rao, M. Curcumin inhibits nitrogen dioxide induced oxidation of hemoglobin. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1995, 146, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M. Curcuminoids as potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, T.; Maekawa, T.; Hidaka, K.; Bando, H.; Takeda, Y.; Yamaguchi, H. Chemical studies on antioxidant mechanism of curcumin: Analysis of oxidative coupling products from curcumin and linoleate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.; Sumitra, M.; Aishwarya, S.; Manohar, B.M.; Lokanadam, B.; Puvanakrishnan, R. Curcumin modulates free radical quenching in myocardial ischaemia in rats. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, P.; Telang, A.G.; Manimaran, A. Protective effect of curcumin on cypermethrin-induced oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droge, W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, A.; O’Neill, L.A. Oxidative stress and nuclear factor-κB activation: A reassessment of the evidence in the light of recent discoveries. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Omelchenko, I.; Shi, X.; Nuttall, A.L. The influence of NF-κB signal-transduction pathways on the murine inner ear by acoustic overstimulation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1832–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, P.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, U.; Mayachari, A.; Sangli, G.; Singh, S. Protective effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra supplementation against methotrexate-induced hepato-renal damage in rats: An experimental approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, H.; Abraham, P.; Isaac, B.; Selvakumar, D. Role for NF-κB inflammatory signalling pathway in tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) induced renal damage in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppstädter, J.; Hachenthal, N.; Valbuena-Perez, J.V.; Lampe, S.; Astanina, K.; Kunze, M.M.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C.; Schmid, T.; Diesel, B. Induction of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) contributes to anti-inflammatory effects of the natural product curcumin in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22949–22960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granato, D.; Santos, J.S.; Escher, G.B.; Ferreira, B.L.; Maggio, R.M. Use of principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) for multivariate association between bioactive compounds and functional properties in foods: A critical perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.E.; Adel, M.; Helal, G.; El-Shafey, M. Role of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Autophagy in Cadmium-induced Renal Injury in Rats: Renoprotective Effect of Ghrelin. Bull. Egypt. Soc. Physiol. Sci. 2019, 39, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, G.P.; Chandrashekar, K.; Juncos, L.A. Molecular Interactions Between Reactive Oxygen Species and Autophagy in Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
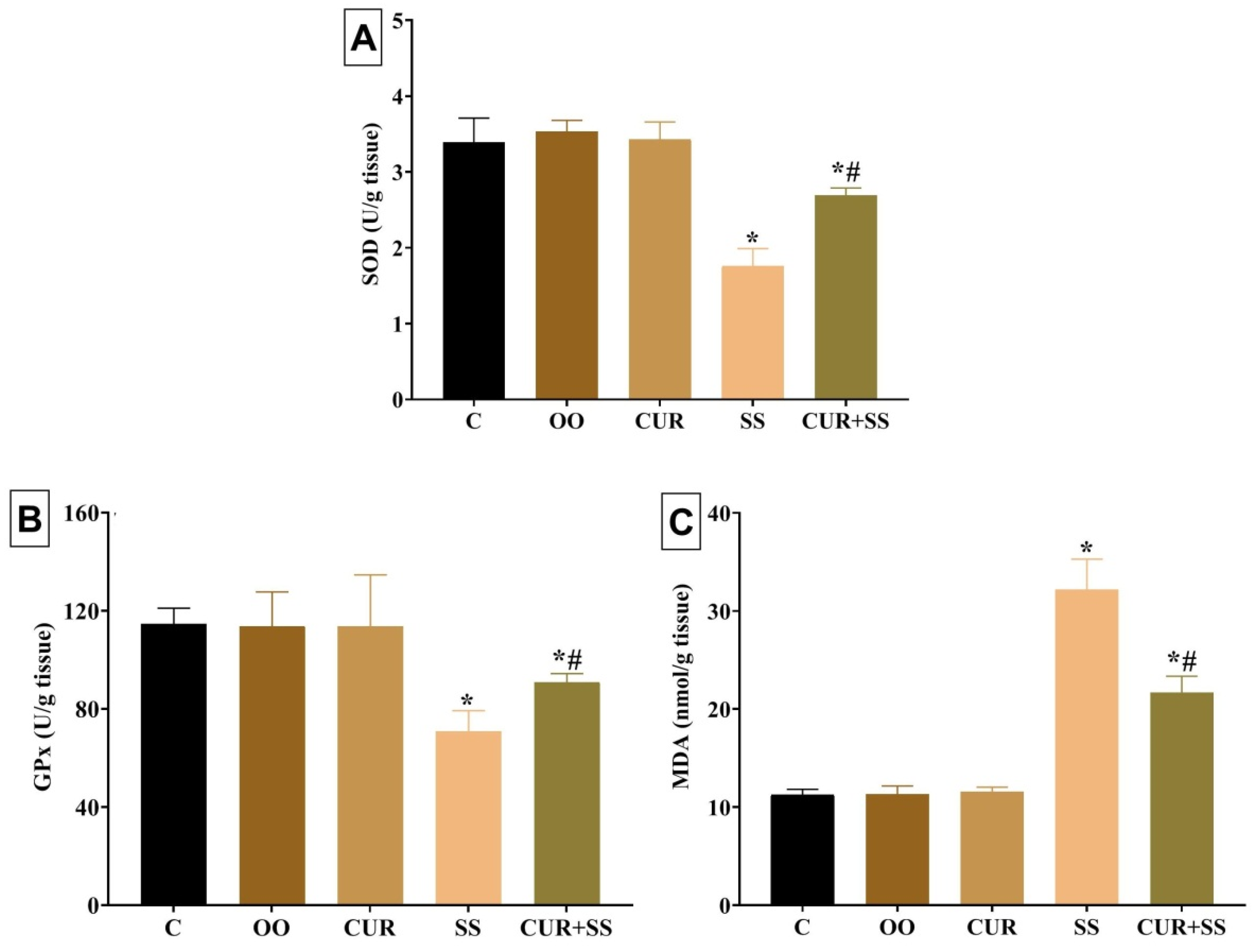
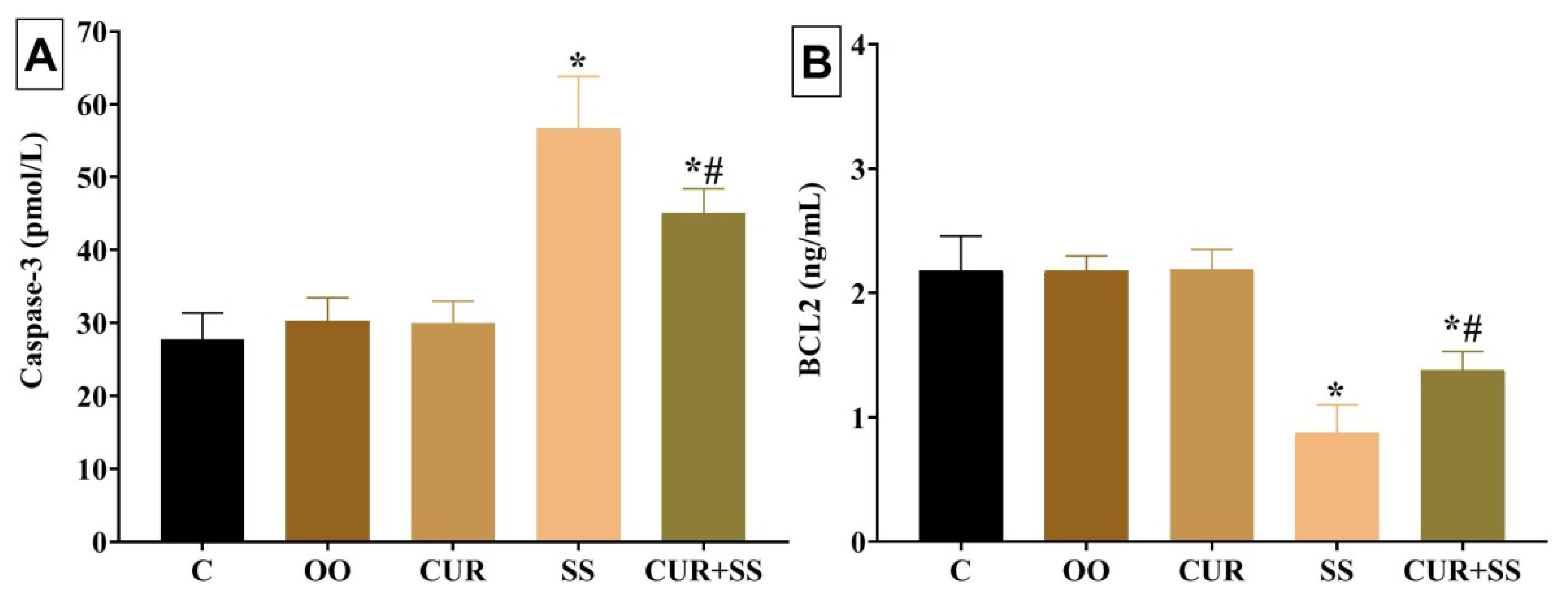
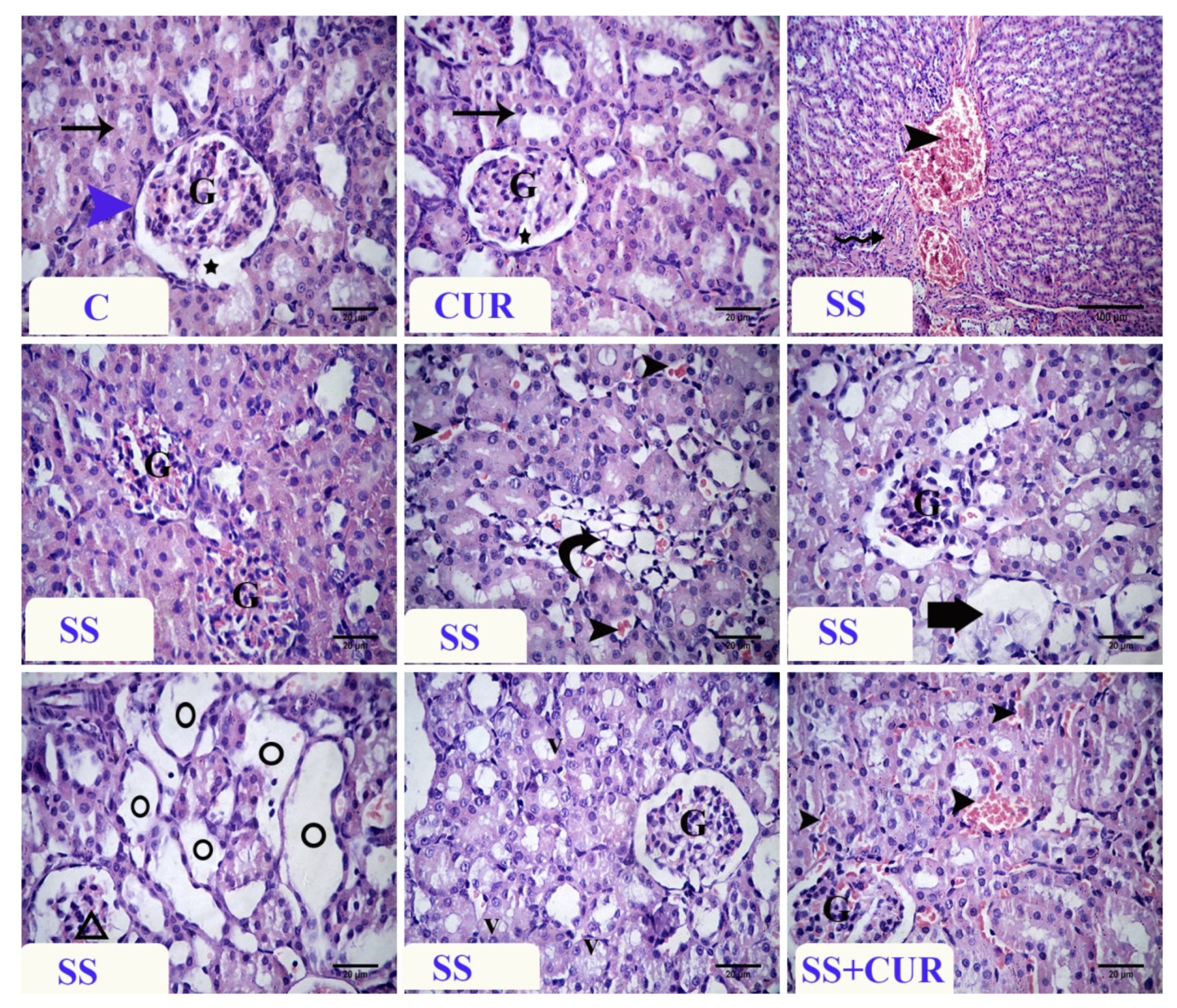
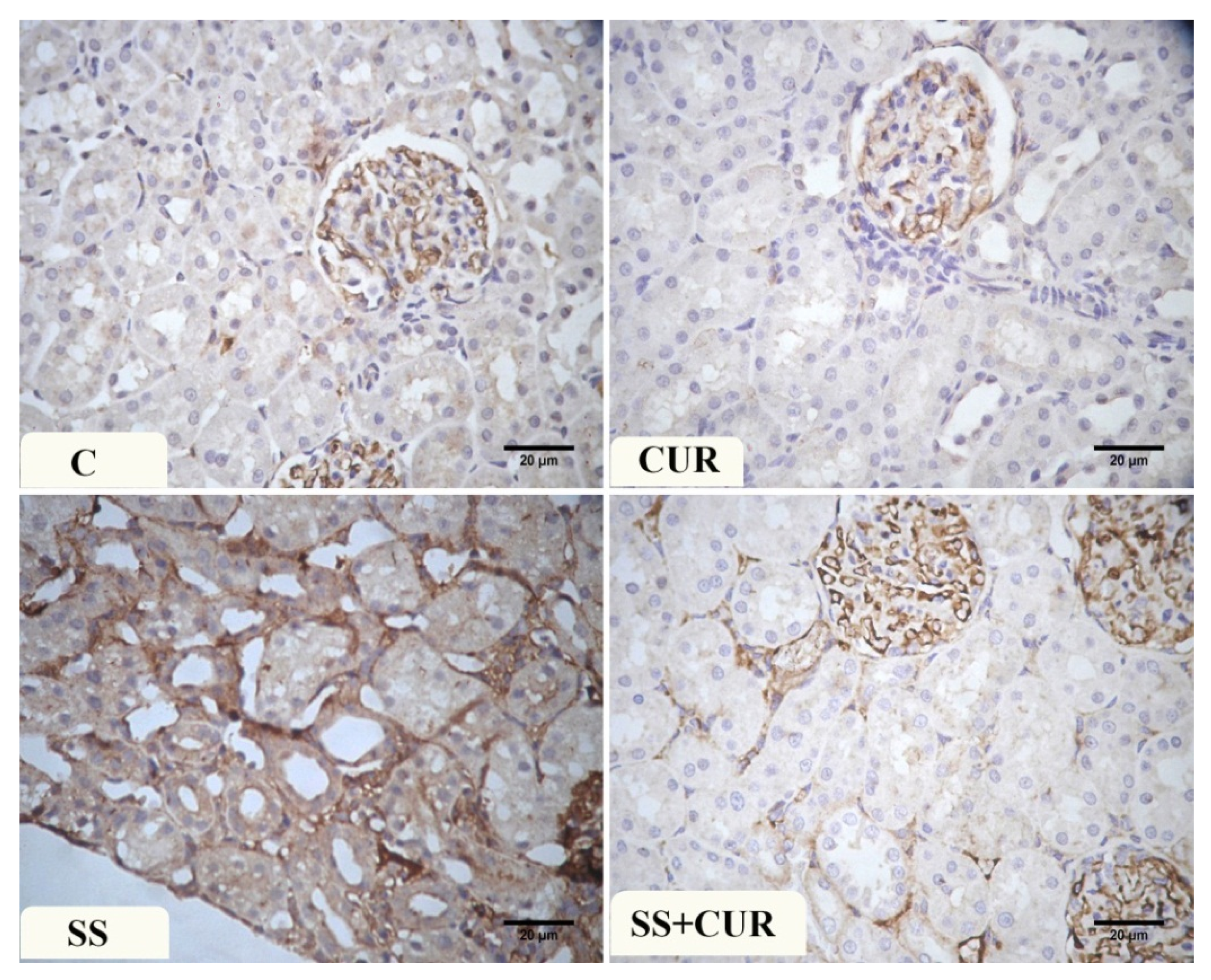


| Parameters | Control | OO | CUR | SS | CUR+SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative right kidney weight | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 0.51 ± 0.04 | 0.46 ± 0.05 | 0.41 ± 0.10 | 0.42 ± 0.10 |
| Left relative kidney weight | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 0.48 ± 0.08 | 0.44 ± 0.09 | 0.44 ± 0.01 |
| Erythrogram | |||||
| RBCs (106/mm3) | 4.35 ± 0.23 | 4.41 ± 0.65 | 4.53 ± 0.30 | 4.40 ± 0.47 | 2.67 *# ± 0.04 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 10.87 ± 0.12 | 11.47 ± 1.10 | 11.73 ± 1.47 | 10.23 ± 1.41 | 7.20 *# ± 0.14 |
| PCV (%) | 23.07 ± 3.36 | 22.73 ± 2.82 | 24.87 ± 2.98 | 24.47 ± 3.31 | 14.23 *# ± 0.34 |
| MCV(fl) | 52.93 ± 1.89 | 52.97 ± 1.54 | 55.40 ± 0.51 | 55.47 ± 3.14 | 54.07 ± 0.95 |
| MCH (%) | 26.63 ± 0.58 | 26.70 ± 1.42 | 25.90 ± 2.01 | 23.23 * ± 1.00 | 27.37 # ± 0.37 |
| MCHC (%) | 45.63 ± 2.95 | 47.57 ± 2.40 | 43.23 ± 1.84 | 45.23 ± 3.87 | 47.93 ± 3.69 |
| Platelets (103/mm3) | 314.33 ± 23.33 | 315.33 ± 53.94 | 565.00 *# ± 134.35 | 376.67 *± 8.81 | 534.67 *# ± 66.78 |
| Leukogram | |||||
| WBCs (103/mm3) | 5.10 ± 0.22 | 5.33 ± 0.21 | 5.37 ± 0.56 | 9.40 * ± 0.22 | 5.23 # ± 0.53 |
| Neutrophils (103/mm3) | 19.00 ± 2.45 | 19.00 ± 2.16 | 18.67 ± 2.05 | 24.67 * ± 3.30 | 19.00 # ± 4.55 |
| Lymphocytes (103/mm3) | 69.33 ± 3.86 | 67.00 ± 2.94 | 69.67 ± 5.73 | 69.33 ± 4.03 | 68.67 ± 6.34 |
| Eosinophils (103/mm3) | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.33 ± 0.47 | 1.33 ± 0.47 | 1.33 ± 0.47 | 1.00 ± 0.00 |
| Monocytes (103/mm3) | 11.67 ± 1.25 | 13.33 ± 2.05 | 12.67 ± 2.49 | 11.33 ± 1.25 | 13.00 ± 0.82 |
| Basophils (103/mm3) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Parameters | Control | OO | CUR | SS | CUR+SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total protein (g/L) | 74.70 ± 3.18 | 75.23 ± 2.54 | 74.85 ± 2.96 | 48.63 * ± 4.86 | 59.25 *# ± 0.99 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 40.80 ± 1.06 | 41.05 ± 1.51 | 41.28 ± 1.15 | 23.08* ± 2.88 | 30.70 *# ± 3.10 |
| Total globulin (g/L) | 33.90 ± 3.64 | 34.18 ± 3.12 | 33.58 ± 3.61 | 25.55 * ± 5.03 | 28.55 ± 3.00 |
| α1 globulin (g/L) | 18.98 ± 3.68 | 19.30 ± 3.45 | 18.40 ± 3.81 | 13.03 ± 6.30 | 13.45 ± 3.65 |
| α2 globulin (g/L) | 6.78 ± 0.21 | 6.73 ± 0.45 | 6.90 ± 0.29 | 9.13 * ± 0.57 | 8.20 *# ± 0.34 |
| β globulin (g/L) | 4.97 ± 0.34 | 5.06 ± 0.33 | 5.04 ± 0.12 | 4.82 ± 0.57 | 4.99 ± 0.67 |
| γ globulin (g/L) | 3.20 ± 0.54 | 3.08 ± 0.33 | 3.26 ± 0.46 | 1.42 * ± 0.38 | 2.05 *# ± 0.17 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 9.17 ± 1.61 | 9.39 ± 0.89 | 9.40 ± 1.38 | 16.77 * ± 1.77 | 13.57 *# ± 0.77 |
| Creatinine (umol/L) | 72.33 ± 2.17 | 72.69 ± 3.43 | 72.26 ± 1.88 | 107.83 * ± 7.94 | 90.85 *# ± 3.42 |
| Uric acid (umol/L) | 354.70 ± 9.12 | 355.63 ±9.56 | 355.49 ± 13.00 | 727.24 * ± 59.80 | 544.90 *# ± 14.89 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 144.33 ± 5.56 | 140.58 ± 7.15 | 144.15 ± 11.12 | 93.66 * ± 8.03 | 120.54 *# ± 7.39 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 3.93 ± 0.57 | 4.53 ± 0.55 | 4.28 ± 0.70 | 9.80 * ± 1.14 | 6.89 *# ± 0.85 |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 91.67 ± 7.04 | 93.23 ± 4.93 | 94.87 ± 6.54 | 65.91 * ± 5.02 | 84.16 # ± 6.69 |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 0.86 ± 0.05 | 1.71 * ± 0.15 | 1.15 *# ± 0.11 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 2.46 ± 0.20 | 2.40 ± 0.20 | 2.46 ± 0.11 | 1.14 * ± 0.19 | 1.68 *# ± 0.07 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 1.03 ± 0.07 | 1.03 ± 0.04 | 1.03 ± 0.07 | 0.56 * ± 0.07 | 0.81 *# ± 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Moselhy, A.A.A.; Aldhahrani, A.; Beheiry, R.R.; Mohamed, W.A.M.; Soliman, M.M.; Saffaf, B.A.; M. El Deib, M. Protective Effect of Curcumin against Sodium Salicylate-Induced Oxidative Kidney Damage, Nuclear Factor-Kappa Dysregulation, and Apoptotic Consequences in Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060826
Abd-Elhakim YM, Moselhy AAA, Aldhahrani A, Beheiry RR, Mohamed WAM, Soliman MM, Saffaf BA, M. El Deib M. Protective Effect of Curcumin against Sodium Salicylate-Induced Oxidative Kidney Damage, Nuclear Factor-Kappa Dysregulation, and Apoptotic Consequences in Rats. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(6):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060826
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd-Elhakim, Yasmina M., Attia A. A. Moselhy, Adil Aldhahrani, Rasha R. Beheiry, Wafaa A. M. Mohamed, Mohamed Mohamed Soliman, Bayan A. Saffaf, and Maha M. El Deib. 2021. "Protective Effect of Curcumin against Sodium Salicylate-Induced Oxidative Kidney Damage, Nuclear Factor-Kappa Dysregulation, and Apoptotic Consequences in Rats" Antioxidants 10, no. 6: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060826
APA StyleAbd-Elhakim, Y. M., Moselhy, A. A. A., Aldhahrani, A., Beheiry, R. R., Mohamed, W. A. M., Soliman, M. M., Saffaf, B. A., & M. El Deib, M. (2021). Protective Effect of Curcumin against Sodium Salicylate-Induced Oxidative Kidney Damage, Nuclear Factor-Kappa Dysregulation, and Apoptotic Consequences in Rats. Antioxidants, 10(6), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060826








