DNA Damage in Human Amniotic Cells: Antigenotoxic Potential of Curcumin and α-Lipoic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Exposure Procedure
2.3. Cell Morphology Analysis
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. DNA Polymorphisms and Genomic Template Stability
2.6. DNA Fragmentation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
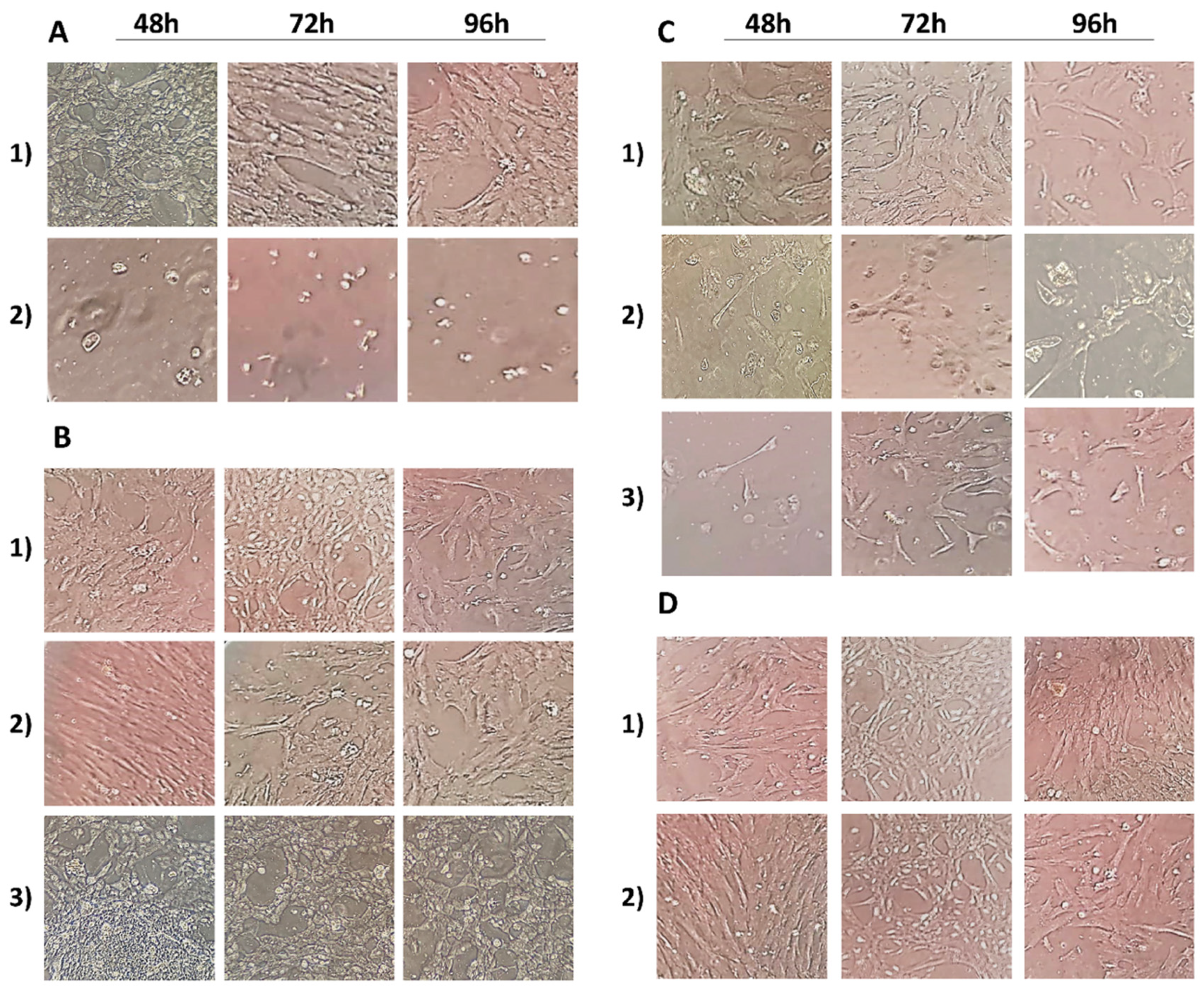
3.1. Cell Morphology Analysis
3.2. Cell Viability
3.3. DNA Polymorphic Profiles
3.4. Genomic Template Stability
3.5. DNA Fragmentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooke, M.S.; Evans, M.D.; Dizdaroglu, M.; Lunec, J. Oxidative DNA damage: Mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1195–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulsen Henrik, E. Oxidative DNA modifications. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2005, 57, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Q.; Zhang, L. Hypoxia and mitochondrial dysfunction in pregnancy complications. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.H.; Burton, G.J. Hypoxia and reoxygenation: A possible mechanism for placental oxidative stress in preeclampsia. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 45, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuffe, J.S.; Xu, Z.C.; Perkins, A.V. Biomarkers of oxidative stress in pregnancy complications. Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkumar, M. Oxidative stress damage as a detrimental factor in preterm birth pathology. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 567. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, I.; Berti, C.; Calabrese, S. Role of micronutrients in the periconceptional period. Hum. Reprod. Update 2010, 16, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conde-Agudelo, A.; Romero, R.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Hassan, S.S. Supplementation with vitamins C and E during pregnancy for the prevention of preeclampsia and other adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 503.e1–503.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Formoso, G.; Baldassarre, M.P.A.; Ginestra, F.; Carlucci, M.A.; Bucci, I.; Consoli, A. Inositol and antioxidant supplementation: Safety and efficacy in pregnancy. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, D.; Guaraldi, C.; Costantino, M.; Bounous, V.E. Acido alfa-lipoico e omega-3 nel trattamento del dolore nel postpartum (Use of alpha-lipoic acid and omega-3 in postpartum pain treatment). Minerva Ginecol. 2015, 67, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, V.; Sahebkar, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Turmeric (Curcuma longa) and its major constituent (curcumin) as nontoxic and safe substances: Review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filardi, T.; Varì, R.; Ferretti, E.; Zicari, A.; Morano, S.; Santangelo, C. Curcumin: Could this compound be useful in pregnancy and pregnancy-related complications? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Miao, H.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Sun, H.; Hou, Y. Curcumin inhibits placental inflammation to ameliorate LPS-induced adverse pregnancy outcomes in mice via upregulation of phosphorylated Akt. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.M.; Kalantar, S.M.; Bahrami, A.R.; Matin, M.M. Human amniocytes: A comprehensive study on morphology, frequency and growth properties of subpopulations from a single clone to the senescence. Cell Tiss. Biol. 2020, 14, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottola, F.; Iovine, C.; Santonastaso, M.; Romeo, M.L.; Pacifico, S.; Cobellis, L.; Rocco, L. NPs-TiO2 and Lincomycin coexposure induces DNA damage in cultured human amniotic cells. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Bai, D.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Deng, H.; Huang, X. Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e021671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unal, F.; Taner, G.; Yuzbasioglu, D.; Yilmaz, S. Antigenotoxic effect of lipoic acid against mitomycin-C in human lymphocyte cultures. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maddux, B.A.; See, W.; Lawrence, J.C.J.; Goldfine, A.L.; Goldfine, I.D.; Evans, J.L. Protection against oxidative stress-induced insulin resistance in rat L6 muscle cells by mircomolar concentrations of alpha-lipoic acid. Diabetes 2001, 50, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miki, T.; Lehmann, T.; Cai, H.; Stolz, D.B.; Strom, S.C. Stem cell characteristics of amniotic epithelial cells. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strober, W. Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2001, 111, A3.B.1–A3.B.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, Y.S.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, L.; Li, P.; Sun, T. Impact assessment of cadmium contamination on rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings at molecular and population levels using multiple biomarkers. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonastaso, M.; Mottola, F.; Iovine, C.; Cesaroni, F.; Colacurci, N.; Rocco, L. In Vitro effects of Titanium Dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) on Cadmium Chloride (CdCl2) Genotoxicity in human sperm cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Iovine, C.; Agarwal, A.; Henkel, R. TUNEL assay-standardized method for testing sperm DNA fragmentation. Andrologia 2021, 53, e13738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottola, F.; Scudiero, N.; Iovine, C.; Santonastaso, M.; Rocco, L. Protective activity of ellagic acid in counteract oxidative stress damage in zebrafish embryonic development. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovine, C.; Mottola, F.; Santonastaso, M.; Finelli, R.; Agarwal, A.; Rocco, L. In vitro ameliorative effects of ellagic acid on vitality, motility and DNA quality in human spermatozoa. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2021, 88, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markesbery, W.R. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, M.T.; Boddie, A.M.; Fisher, A.J.; Macmahon, W.; Saxe, D.; Sullivan, K.M.; Dembure, P.P.; Elsas, L.J. Neural-tube defects are associated with low concentration of cobalamine (vitamin B12) in amniotic fluid. Prenat. Diagn. 1998, 18, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odetti, P.; Valentini, S.; Aragno, I.; Garibaldi, S.; Pronzato, M.A.; Rolandi, E.; Barreca, T. Oxidative stress in subjects affected by celiac disease. Free Radic. Res. 1998, 29, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, W.; Stewart, F.; Nelson, J.; McBreen, G.; McMillan, S.A.; Porter, K.G. Screening for coeliac disease as a possible maternal risk factor for neural tube defect. Clin. Genet. 1996, 49, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotman, C.W.; Head, E.; Muggenburg, B.A.; Zicker, S.; Milgram, N.W. Brain aging in the canine: A diet enriched in antioxidants reduces cognitive dysfunction. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toklu, H.Z.; Hakan, T.; Celik, H.; Biber, N.; Erzik, C.; Ogunc, A.V.; Akakin, D.; Cikler, E.; Cetinel, S.; Ersahin, M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid in experimental spinal cord injury in rats. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2010, 33, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liczbiński, P.; Michałowicz, J.; Bukowska, B. Molecular mechanism of curcumin action in signaling pathways: Review of the latest research. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1992–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Pan, S.T.; Yuan, C.J. Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3 plays a role in hypoxia-induced apoptosis of trophoblast cell line 3A-sub-E. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.H.; Skepper, J.N.; Burton, G.J. In vitro ischemia-reperfusion injury in term human placenta as a model for oxidative stress in pathological pregnancies. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santonastaso, M.; Mottola, F.; Iovine, C.; Colacurci, N.; Rocco, L. Protective effects of Curcumin on the outcome of Cryopreservation in human sperm. Reprod. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Maiorino, M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3289–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, H.S.; Real, C.; Cyrne, L.; Soares, H.; Antunes, F. Hydrogen peroxide sensing, signaling and regulation of transcription factors. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, J.E.; Prahalad, A.K.; Williams, G.M. 8-Oxodeoxyguanosine formation in the DNA of cultured cells after exposure to H2O2 alone or with UVB or UVA irradiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 64, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombino, S.; Serini, S.; Di Nicuolo, F.; Celleno, L.; Andò, S.; Picci, N.; Calviello, G.; Palozza, P. Antioxidant effect of ferulic acid in isolated membranes and intact cells: Synergistic interactions with alpha-tocopherol, beta-carotene, and ascorbic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torricelli, P.; Ricci, P.; Provenzano, B.; Lentini, A.; Tabolacci, C. Synergic effect of α-tocopherol and naringenin in transglutaminase-induced differentiation of human prostate cancer cells. Amino Acids. 2011, 41, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koekkoek, W.A.; van Zanten, A.R. Antioxidant vitamins and trace elements in critical illness. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, I.; de Serna, D.G.; Gutierrez, A.; Schade, D.S. Vitamin E in humans: An explanation of clinical trial failure. Endocr. Pract. 2006, 12, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, K. Novel antioxidative activity of Astaxanthin and its synergistic effect with vitamin E. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65 (Suppl.), S109–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lammer, E.J.; Chen, D.T.; Hoar, R.M.; Agnish, N.D.; Benke, P.J.; Braun, J.T.; Curry, C.J.; Fernhoff, P.M.; Grix, A.W.J.; Lott, I.T.; et al. Retinoic acid embryopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Chan, W.H. Injurious effects of curcumin on maturation of mouse oocytes, fertilization and fetal development via apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4655–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poschner, S.; Maier-Salamon, A.; Thalhammer, T.; Jäger, W. Resveratrol and other dietary polyphenols are inhibitors of estrogen metabolism in human breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squillaro, T.; Schettino, C.; Sampaolo, S.; Galderisi, U.; Di Iorio, G.; Giordano, A.; Melone, M.A.B. Adult-onset brain tumors and neurodegeneration: Are polyphenols protective? J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 3955–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichert, J.; Hermann, R.; Ruus, P.; Preiss, R. Plasma kinetics, metabolism, and urinary excretion of alpha-lipoic acid following oral administration in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 43, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of curcumin: Problems and promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mottola, F.; Santonastaso, M.; Iovine, C.; Rossetti, C.; Ronga, V.; Rocco, L. DNA Damage in Human Amniotic Cells: Antigenotoxic Potential of Curcumin and α-Lipoic Acid. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10071137
Mottola F, Santonastaso M, Iovine C, Rossetti C, Ronga V, Rocco L. DNA Damage in Human Amniotic Cells: Antigenotoxic Potential of Curcumin and α-Lipoic Acid. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(7):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10071137
Chicago/Turabian StyleMottola, Filomena, Marianna Santonastaso, Concetta Iovine, Cristina Rossetti, Valentina Ronga, and Lucia Rocco. 2021. "DNA Damage in Human Amniotic Cells: Antigenotoxic Potential of Curcumin and α-Lipoic Acid" Antioxidants 10, no. 7: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10071137
APA StyleMottola, F., Santonastaso, M., Iovine, C., Rossetti, C., Ronga, V., & Rocco, L. (2021). DNA Damage in Human Amniotic Cells: Antigenotoxic Potential of Curcumin and α-Lipoic Acid. Antioxidants, 10(7), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10071137







