Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Waste Bentonite to Produce Functional Antioxidant Excipients for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Waste-to-Market Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
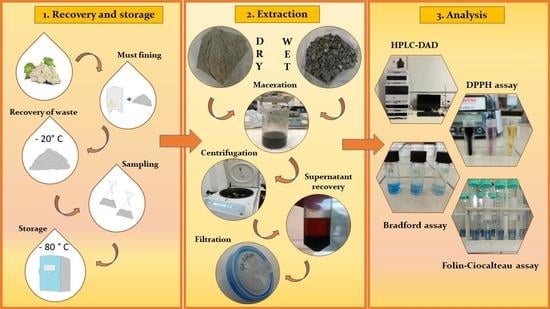
2.2. Waste Bentonite Recovery and Storage
2.3. Pre-Treatment of Waste Bentonite
2.4. Freeze Drying and Evaluation of the Water Content
2.5. Extracts Preparation
2.6. Density Evaluation
2.7. pH Evaluation after Water Dilution
2.8. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Power with a DPPH Assay
2.9. Quantitative Evaluation of Some Representative Polyphenols with HPLC-DAD
2.10. Determination of the Total Phenolic Content with a Folin–Ciocalteu Assay
2.11. Determination of the Total Protein Content with a Bradford Assay
2.12. Cell Viability Assay
2.13. Stability Studies
2.14. Control Group
2.15. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Waste Recovery, Extracts Preparation and Preliminary Evaluations
- PEG200: it is a synthetic, highly water soluble, inert polymer widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and other consumer care products. It could be considered a hydrophilic, stable, non-toxic solvent that also displays humectants properties. Additionally, it was extensively reported to possess good solvent properties towards polyphenols. Particularly, PEG200 was selected after preliminary studies, which displayed that the use or PEGs with higher molecular weight (e.g., PEG400 and PEG600) reduces the solvent power towards polyphenols and, consequently, the efficiency of the extraction process [11,43,44].
- Propylene Glycol: it is a hydrophilic polar solvent characterized by humectants and antimicrobial activities. It is frequently employed in the cosmetic field as a moisturizer and skin conditioner due to its hygroscopic nature playing a role for stratum corneum hydration [45]. Moreover, it is also well-known in the pharmaceutic field due to its plasticizer and penetration enhancer properties. Additionally, it was already reported to possess good solvent properties towards polyphenols [11,14,46,47].
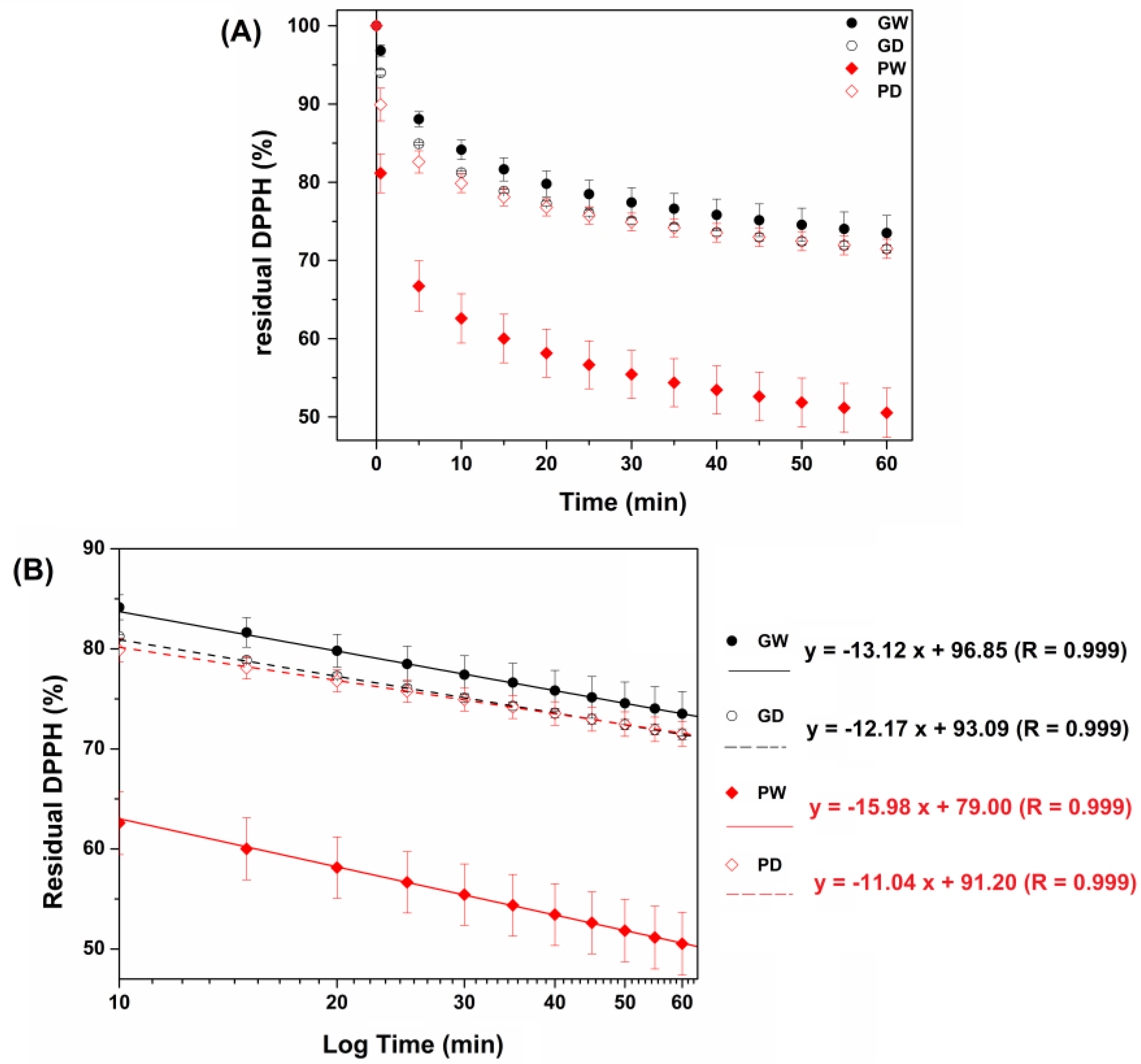
3.2. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Power of the Extracts with a DPPH Assay
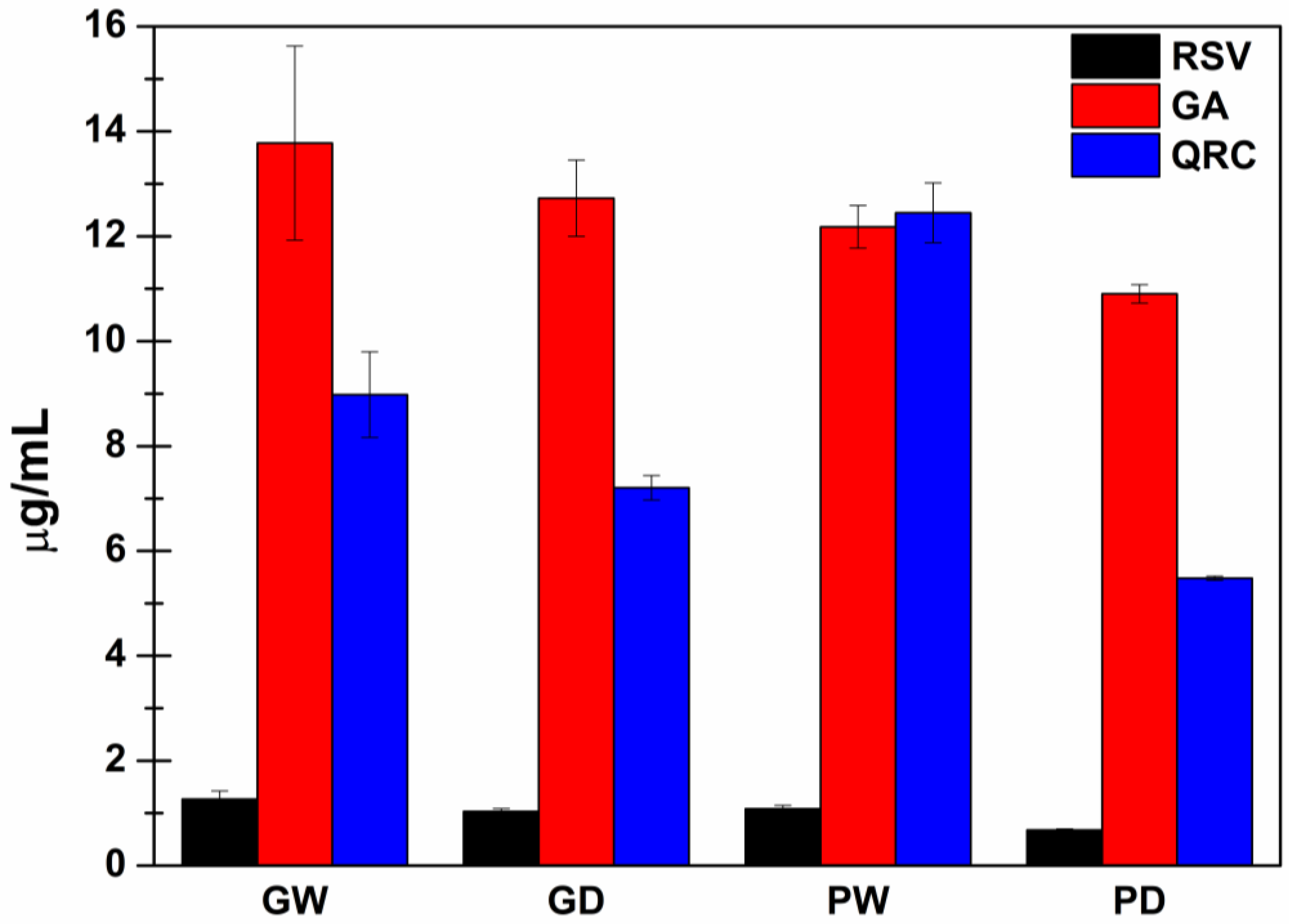
3.3. Quantification of RSV, GA and QRC with HPLC-DAD Analyses
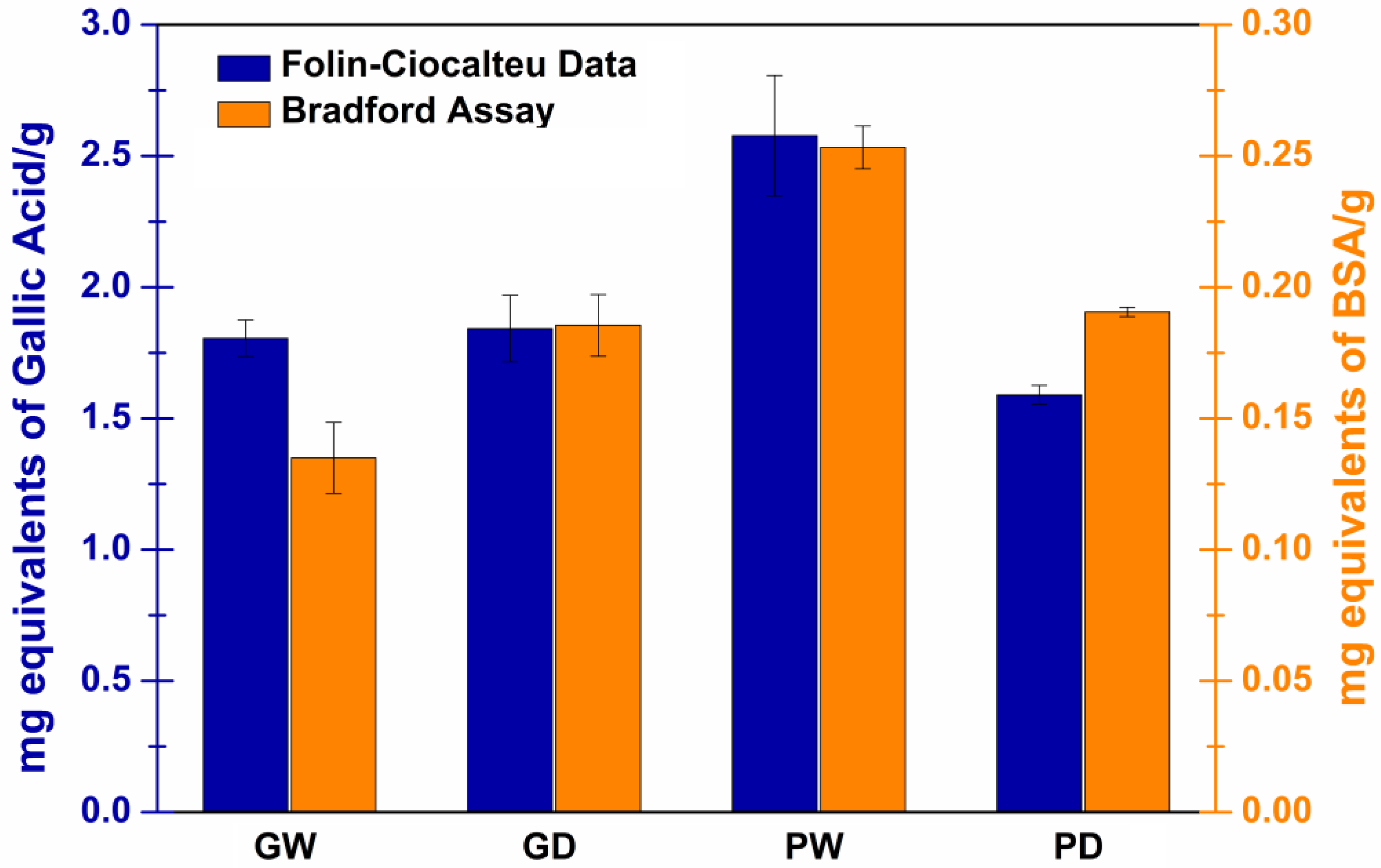
3.4. Determination of the Total Phenolic Content with Folin–Ciocalteu Assay
3.5. Determination of the Total Protein Content with a Bradford Assay
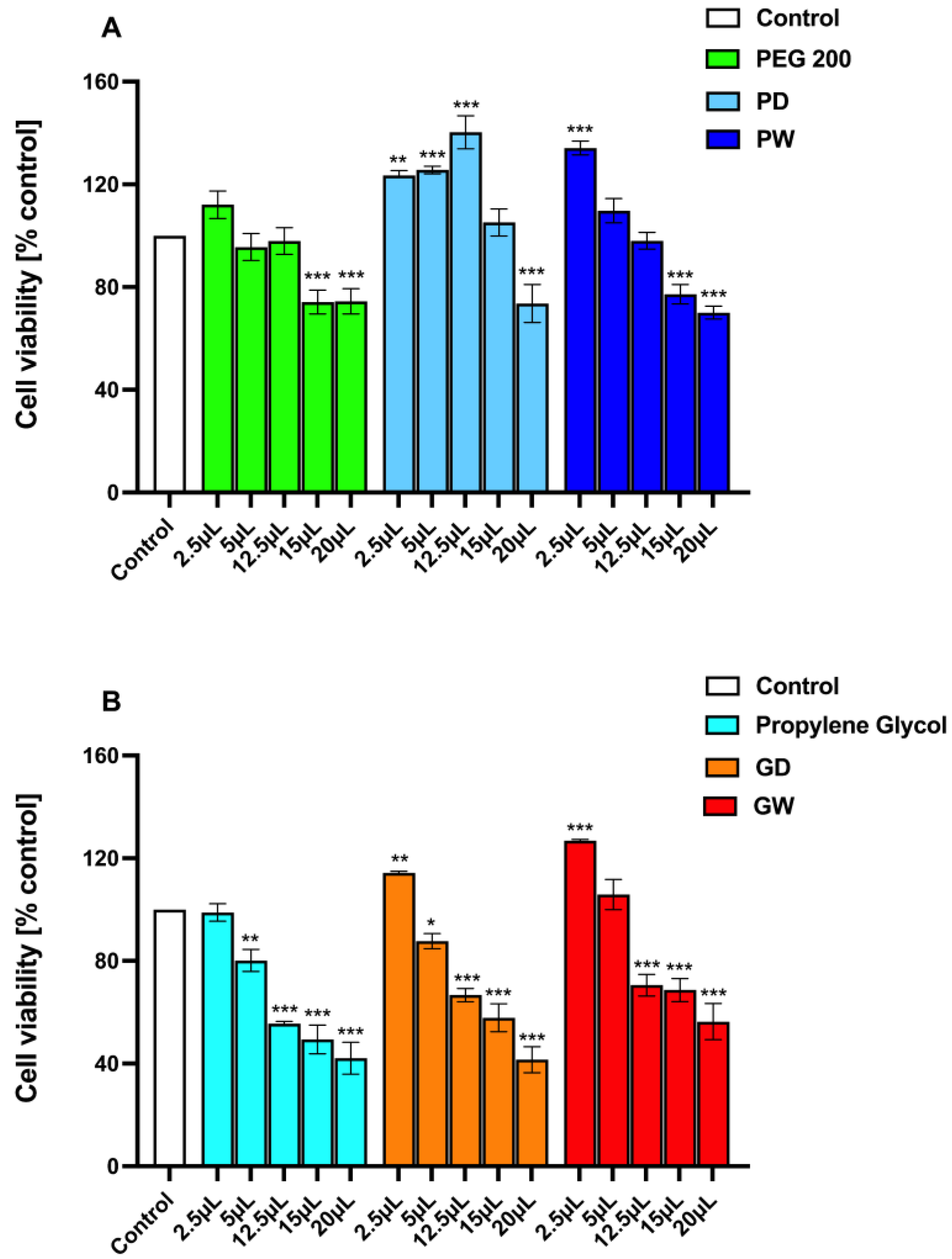
3.6. Evaluation of Extracts Safety with a Cytotoxicity Assay
- The fresh extraction solvents under the employed experimental conditions could result in cytotoxic (cell viability % <80%) products in a concentration-dependent manner. This is much more evident when observing the propylene glycol behavior (Figure 5B). However, it should be considered that both PEG200 and propylene glycol are well-known and extensively used cosmetic and pharmaceutic excipients [43,57].
- Generally, all the prepared extracts, at any concentration tested, resulted in less cytotoxic products than the related fresh extraction solvent.
- The extracts displayed a dual behavior. At the lower concentrations tested, they exert proliferative effects while at the higher concentrations evaluated, they caused a decrease in cell viability. These effects might well be attributable to the dual action of the extracted functional polyphenols. Indeed, the literature fully reports that polyphenols could exhibit either proliferative and wound healing or anti-proliferative and anticancer effects depending on their concentration [58,59,60,61,62,63,64].
- The glycol-based extracts (Figure 5B) resulted in a cytotoxic behavior even at low concentrations (≥12.5 µL mL−1). Additionally, the GD and GW samples gave comparable results.
- The PEG-based extracts (Figure 5A) resulted in a modest cytotoxicity as even the lower observed cell viability % values were around the 80%. Furthermore, the PD sample exerts a proliferative effect higher than the PW extract. This could be attributable to the already reported highly different content in functional polyphenols, resulting in different in vitro performances.
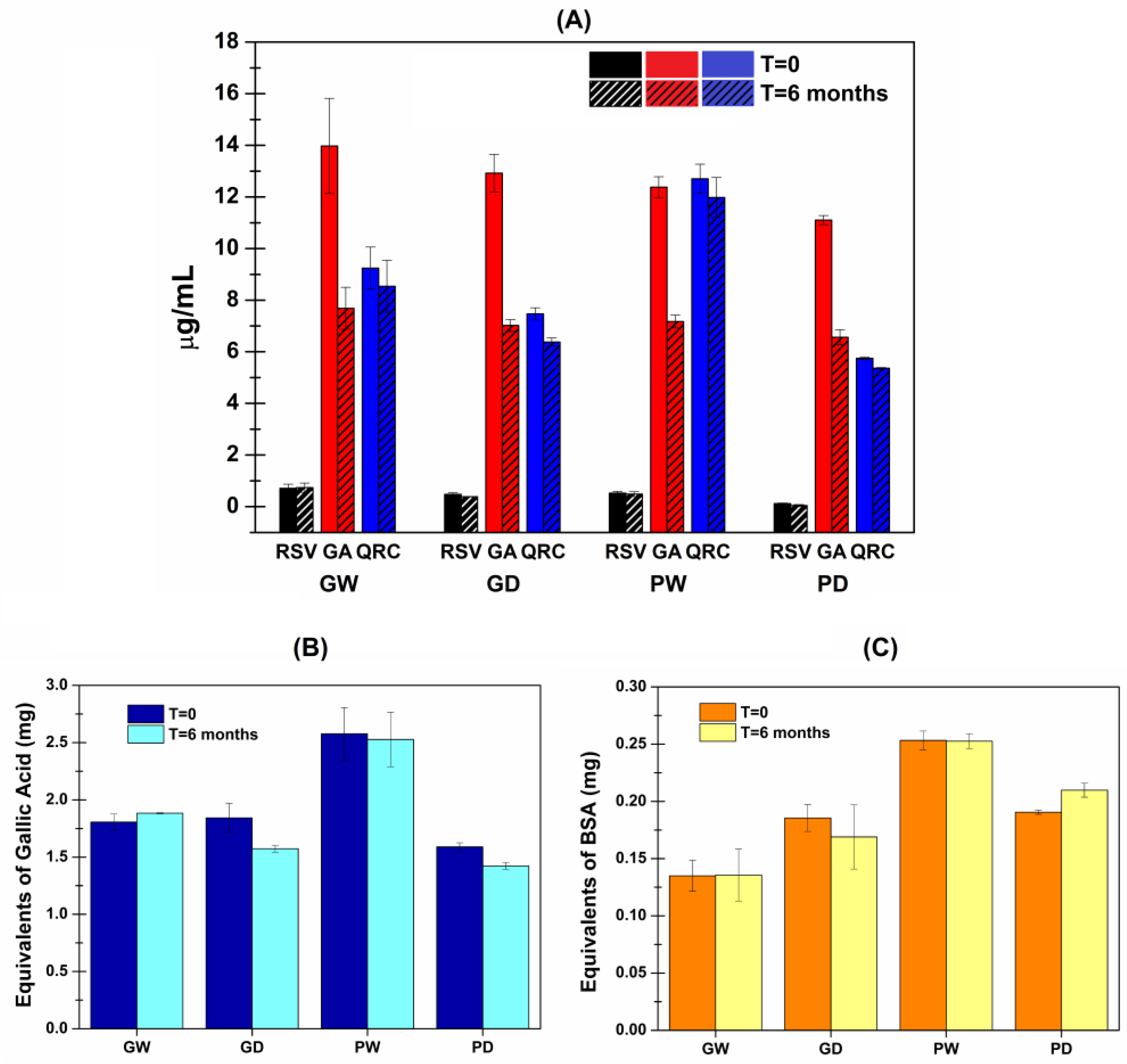
3.7. Stability Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per L’alimentazione e L’agricoltura; International Organisation of Vine and Wine. Table and Dried Grapes; 2016. Available online: https://www.oiv.int/public/medias/5268/fao-oiv-focus-2016.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Sinab. Bio in Cifre 2019. Available online: https://www.sinab.it/sites/default/files/share/BIO%20IN%20CIFRE%202019%20-%20Rapporto%20completo.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- European Environment Agency. Circular Economy in Europe Developing the Knowledge Base; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hoss, I.; Rajha, H.N.; El Khoury, R.; Youssef, S.; Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Louka, N.; Maroun, R.G. Valorization of Wine-Making By-Products’ Extracts in Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kantar, S.; Rajha, H.N.; Boussetta, N.; Vorobiev, E.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N. Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Grapefruit Peels Using High Voltage Electrical Discharges, Deep Eutectic Solvents and Aqueous Glycerol. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi-Khattar, A.M.; Rajha, H.N.; Abdel-Massih, R.M.; Habchi, R.; Maroun, R.G.; Debs, E.; Louka, N. “Intensification of Vaporization by Decompression to the Vacuum” (IVDV), a Novel Technology Applied as a Pretreatment to Improve Polyphenols Extraction from Olive Leaves. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajha, H.N.; El Kantar, S.; Afif, C.; Boussetta, N.; Louka, N.; Maroun, R.G.; Vorobiev, E. Selective Multistage Extraction Process of Biomolecules from Vine Shoots by a Combination of Biological, Chemical, and Physical Treatments. C. R. Chim. 2018, 21, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Darra, N.; Rajha, H.N.; Debs, E.; Saleh, F.; El-Ghazzawi, I.; Louka, N.; Maroun, R.G. Comparative Study between Ethanolic and β-Cyclodextrin Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Peach Pomace. Int. J. Food Sci. 2018, 2018, 9491681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajha, H.N.; Mhanna, T.; El Kantar, S.; El Khoury, A.; Louka, N.; Maroun, R.G. Innovative Process of Polyphenol Recovery from Pomegranate Peels by Combining Green Deep Eutectic Solvents and a New Infrared Technology. LWT 2019, 111, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daayf, F.; El Hadrami, A.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Henriquez, M.A.; Yao, Z.; Derksen, H.; El-Hadrami, I.; Adam, L.R. Phenolic Compounds in Plant Defense and Pathogen Counter-Defense Mechanisms. Recent Adv. Polyphen. Res. 2012, 3, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prima, G.; Angellotti, G.; Scarpaci, A.G.; Murgia, D.; D’agostino, F.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Improvement of Resveratrol Permeation through Sublingual Mucosa: Chemical Permeation Enhancers versus Spray Drying Technique to Obtain Fast-Disintegrating Sublingual Mini-Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, D.; Angellotti, G.; Conigliaro, A.; Pavia, F.C.; D’agostino, F.; Contardi, M.; Mauceri, R.; Alessandro, R.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Development of a Multifunctional Bioerodible Nanocomposite Containing Metronidazole and Curcumin to Apply on L-PRF Clot to Promote Tissue Regeneration in Dentistry. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angellotti, G.; Murgia, D.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Quercetin-Based Nanocomposites as a Tool to Improve Dental Disease Management. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angellotti, G.; Presentato, A.; Murgia, D.; Di Prima, G.; D’Agostino, F.; Scarpaci, A.G.; D’Oca, M.C.; Alduina, R.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Lipid Nanocarriers-Loaded Nanocomposite as a Suitable Platform to Release Antibacterial and Antioxidant Agents for Immediate Dental Implant Placement Restorative Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angellotti, G.; Murgia, D.; Presentato, A.; D’Oca, M.C.; Scarpaci, A.G.; Alduina, R.; Raimondi, M.V.; De Caro, V. Antibacterial PEGylated Solid Lipid Microparticles for Cosmeceutical Purpose: Formulation, Characterization, and Efficacy Evaluation. Materials 2020, 13, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, D.; Angellotti, G.; D’Agostino, F.; De Caro, V. Bioadhesive Matrix Tablets Loaded with Lipophilic Nanoparticles as Vehicles for Drugs for Periodontitis Treatment: Development and Characterization. Polymers 2019, 11, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murgia, D.; Mauceri, R.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Advance on Resveratrol Application in Bone Regeneration: Progress and Perspectives for Use in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Lima Cherubim, D.J.; Buzanello Martins, C.V.; Oliveira Fariña, L.; da Silva de Lucca, R.A. Polyphenols as Natural Antioxidants in Cosmetics Applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morocho-Jácome, A.L.; Freire, T.B.; de Oliveira, A.C.; de Almeida, T.S.; Rosado, C.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Baby, A.R. In Vivo SPF from Multifunctional Sunscreen Systems Developed with Natural Compounds—A Review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, H.; Passarelli, S.; Szeto, J.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. The Role of Polyphenols in Human Health and Food Systems: A Mini-Review. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, I.; Pérez-Gregorio, R.; Soares, S.; Mateus, N.; De Freitas, V.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Feliciano, A.S. Wine Flavonoids in Health and Disease Prevention. Molecules 2017, 22, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, J.; Douglas Kinghorn, A. Development of Anticancer Agents from Plant-Derived Sesquiterpene Lactones. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2397–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, B.; Li, X.; Kong, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. An Overview of Plant Phenolic Compounds and Their Importance in Human Nutrition and Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.; Borges, F. Wine and Grape Polyphenols—A Chemical Perspective. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1844–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez-Escobar, R.; Aliaño-González, M.J.; Cantos-Villar, E. Wine Polyphenol Content and Its Influence on Wine Quality and Properties: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioli, F.; Panaite, S.A.; Tomé-Carneiro, J. Wine’s Phenolic Compounds and Health: A Pythagorean View. Molecules 2020, 25, 4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N.; Siddiqua, S. Stabilization of Silty Sand Using Bentonite-magnesium-Alkalinization: Mechanical, Physicochemical and Microstructural Characterization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 183, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Siddiqua, S. Calcium Bentonite vs Sodium Bentonite: The Potential of Calcium Bentonite for Soil Foundation. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Peinado, R. Enological Chemistry; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, E.J.; Alexander, G.; Muhlack, R.; Pocock, K.F.; Colby, C.; O’Neill, B.K.; Høj, P.B.; Jones, P. Preventing Protein Haze in Bottled White Wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2005, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Brasili, E.; Pasqua, G. Antifungal Activity of Phenolic and Polyphenolic Compounds from Different Matrices of Vitis vinifera L. against Human Pathogens. Molecules 2020, 25, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prima, G.; Scurria, A.; Angellotti, G.; Belfiore, E.; Pagliaro, M.; Meneguzzo, F.; De Caro, V.; Ciriminna, R. Grapefruit IntegroPectin Isolation via Spray Drying and via Freeze Drying: A Comparison. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanzio, A.; D’Anneo, A.; Pappalardo, F.; Bonina, F.P.; Livrea, M.A.; Allegra, M.; Tesoriere, L. Phenolic Composition of Hydrophilic Extract of Manna from Sicilian Fraxinus Angustifolia Vahl and Its Reducing, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity In Vitro. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attanzio, A.; Frazzitta, A.; Busa, R.; Tesoriere, L.; Livrea, M.A.; Allegra, M. Indicaxanthin from Opuntia ficus indica (L. Mill) Inhibits Oxidized LDL-Mediated Human Endothelial Cell Dysfunction through Inhibition of NF-κB Activation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3457846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambri, M.; Dordoni, R.; Giribaldi, M.; Violetta, M.R.; Giuffrida, M.G. Heat-Unstable Protein Removal by Different Bentonite Labels in White Wines. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzi, S.; Marangon, M.; Tolin, S.; Curioni, A. Protein Evolution during the Early Stages of White Winemaking and Its Relations with Wine Stability. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2011, 17, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.L.; Sacks, G.L.; Jeffery, D.W. Grape Must Composition Overview. Underst. Wine Chem. 2016, Chapter 20, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmulo, E.; Ceccantoni, B.; Bellincontro, A.; Mencarelli, F. Use of Water and Ethanol Extracts from Wine Grape Seed Pomace to Prepare an Antioxidant Toothpaste. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5813–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidis, D.; Angelis, A.; Nikolaou, P.E.; Mitakou, S.; Skaltsounis, A.L. Exploitation of Vitis vinifera, Foeniculum vulgare, Cannabis sativa and Punica granatum By-Product Seeds as Dermo-Cosmetic Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, A.; Schäfers, C.; Schröder, C.; Antranikian, G. Towards a Sustainable Biobased Industry—Highlighting the Impact of Extremophiles. New Biotechnol. 2018, 40, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, A.A.; Sarruf, F.D.; Oliveira, C.A.; Neto, A.V.; Fischer, D.C.H.; Kato, E.T.M.; Lourenço, F.R.; Baby, A.R.; Bacchi, E.M. Safety and Photoprotective Efficacy of a Sunscreen System Based on Grape Pomace (Vitis vinifera L.) Phenolics from Winemaking. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarovaya, L.; Waranuch, N.; Wisuitiprot, W.; Khunkitti, W. Effect of Grape Seed Extract on Skin Fibroblasts Exposed to UVA Light and Its Photostability in Sunscreen Formulation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Shin, C.Y.; Kim, K.B. Safety Evaluation of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Compounds for Cosmetic Use. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 105–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyano-Mendez, J.R.; Fabbrocini, G.; De Stefano, D.; Mazzella, C.; Mayol, L.; Scognamiglio, I.; Carnuccio, R.; Ayala, F.; La Rotonda, M.I.; De Rosa, G. Enhanced Antioxidant Effect of Trans-Resveratrol: Potential of Binary Systems with Polyethylene Glycol and Cyclodextrin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnamawati, S.; Indrastuti, N.; Danarti, R.; Saefudin, T. The Role of Moisturizers in Addressing Various Kinds of Dermatitis: A Review. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 15, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Desai, K.G.H.; Mallery, S.R.; Holpuch, A.S.; Phelps, M.P.; Schwendeman, S.P. Mucoadhesive Fenretinide Patches for Site-Specific Chemoprevention of Oral Cancer: Enhancement of Oral Mucosal Permeation of Fenretinide by Coincorporation of Propylene Glycol and Menthol. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazwani, M.; Alam, P.; Alqarni, M.H.; Yusufoglu, H.S.; Shakeel, F. Solubilization of Trans-Resveratrol in Some Mono-Solvents and Various Propylene Glycol + Water Mixtures. Molecules 2021, 26, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirivibulkovit, K.; Nouanthavong, S.; Sameenoi, Y. Paper-Based DPPH Assay for Antioxidant Activity Analysis. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanaida, M.; Hudz, N.; Jasicka-Misiak, I.; Wieczorek, P.P. Polyphenols and Pharmacological Screening of a Monarda fistulosa L. Dry Extract Based on a Hydrodistilled Residue By-Product. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, S.S.; Soni, L.K.; Maheshwari, R.K. Study on Mixed Solvency Concept in Formulation Development of Aqueous Injection of Poorly Water Soluble Drug. J. Pharm. 2013, 2013, 678132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akkol, E.K.; Göger, F.; Koşar, M.; Başer, K.H.C. Phenolic Composition and Biological Activities of Salvia Halophila and Salvia Virgata from Turkey. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Bradford Assay for Determining Protein Concentration. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2020, 2020, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, J.P.D. Measuring Protein Concentration with Absorbance, Lowry, Bradford Coomassie Blue, or the Smith Bicinchoninic Acid Assay before Electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1855, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiume, M.M.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of Propylene Glycol, Tripropylene Glycol, and PPGs as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 245S–260S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiume, M.M.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of PEGylated Alkyl Glycerides as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 26S–58S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.E.; Scheman, A.; McGowan, M.A. Propylene Glycol. Dermatitis 2018, 29, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Imran, M.; Butt, M.S.; Nadeem, M.; Peters, D.G.; Mubarak, M.S. Resveratrol as an Anti-Cancer Agent: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1428–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignet, A.L.; Schellnegger, M.; Hecker, A.; Kohlhauser, M.; Kotzbeck, P.; Kamolz, L.P. Resveratrol-Induced Signal Transduction in Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kręgiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, N.‘I.; Wong, S.K.; Mohamed, I.N.; Mohamed, N.; Chin, K.Y.; Ima-Nirwana, S.; Shuid, A.N. Wound Healing Properties of Selected Natural Products. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niedzwiecki, A.; Roomi, M.W.; Kalinovsky, T.; Rath, M. Anticancer Efficacy of Polyphenols and Their Combinations. Nutrients 2016, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ul Islam, B.; Suhail, M.; Khan, M.K.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Alserihi, R.F.; Zaidi, S.K.; Tabrez, S. Polyphenols as Anticancer Agents: Toxicological Concern to Healthy Cells. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6063–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F.; Kochish, I.I.; Fisinin, V.I.; Kidd, M.T. Antioxidant Defence Systems and Oxidative Stress in Poultry Biology: An Update. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formula Code | Bentonite | Solvent |
|---|---|---|
| GW | 2 g of wet bentonite | Propylene Glycol |
| GD | 1 g of freeze-dried bentonite | Propylene Glycol |
| PW | 2 g of wet bentonite | PEG200 |
| PD | 1 g of freeze-dried bentonite | PEG200 |
| Formula Code | Density (g/mL) | pH | Yield % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propylene Glycol | 1.038 ± 0.004 | 6.66 | - |
| GCONTROL | 1.035 ± 0.005 | 6.36 | - |
| GW | 1.053 ± 0.005 | 4.26 | 82.85 ± 4.88 |
| GD | 1.087 ± 0.008 | 4.32 | 61.56 ± 6.69 |
| PEG200 | 1.115 ± 0.005 | 6.39 | - |
| PCONTROL | 1.111 ± 0.007 | 6.92 | - |
| PW | 1.134 ± 0.006 | 4.23 | 69.32 ± 6.32 |
| PD | 1.180 ± 0.009 | 4.44 | 66.31 ± 2.30 |
| Sample | Equivalents mg of GA per 1 g of Extract | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min | 30 min | 60 min | |
| GW | 0.263 ± 0.051 | 0.512 ± 0.069 | 0.608 ± 0.079 |
| GD | 0.375 ± 0.006 | 0.579 ± 0.014 | 0.659 ± 0.018 |
| PW | 1.073 ± 0.121 | 1.225 ± 0.105 | 1.322 ± 0.104 |
| PD | 0.396 ± 0.043 | 0.539 ± 0.037 | 0.606 ± 0.039 |
| Sample | Equivalents mg of GA per 1 g of Extract | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min | 30 min | 60 min | |
| GW | 0.431 ± 0.032 | 0.627 ± 0.013 | 0.707 ± 0.009 |
| GD | 0.361 ± 0.005 | 0.565 ± 0.001 | 0.666 ± 0.008 |
| PW | 0.739 ± 0.034 | 1.034 ± 0.023 | 1.178 ± 0.025 |
| PD | 0.345 ± 0.020 | 0.523 ± 0.026 | 0.589 ± 0.027 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Prima, G.; Belfiore, E.; Migliore, M.; Scarpaci, A.G.; Angellotti, G.; Restivo, I.; Allegra, M.; Arizza, V.; De Caro, V. Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Waste Bentonite to Produce Functional Antioxidant Excipients for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Waste-to-Market Approach. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122493
Di Prima G, Belfiore E, Migliore M, Scarpaci AG, Angellotti G, Restivo I, Allegra M, Arizza V, De Caro V. Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Waste Bentonite to Produce Functional Antioxidant Excipients for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Waste-to-Market Approach. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(12):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122493
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Prima, Giulia, Elena Belfiore, Martina Migliore, Amalia Giulia Scarpaci, Giuseppe Angellotti, Ignazio Restivo, Mario Allegra, Vincenzo Arizza, and Viviana De Caro. 2022. "Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Waste Bentonite to Produce Functional Antioxidant Excipients for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Waste-to-Market Approach" Antioxidants 11, no. 12: 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122493
APA StyleDi Prima, G., Belfiore, E., Migliore, M., Scarpaci, A. G., Angellotti, G., Restivo, I., Allegra, M., Arizza, V., & De Caro, V. (2022). Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Waste Bentonite to Produce Functional Antioxidant Excipients for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Waste-to-Market Approach. Antioxidants, 11(12), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122493