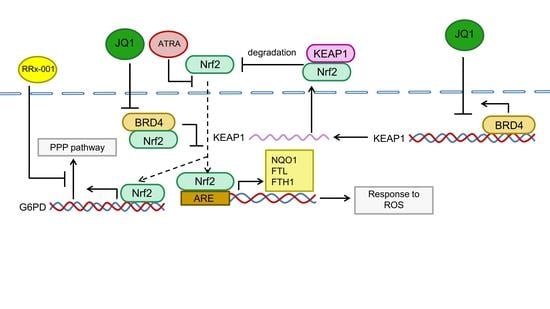
BRD4 Targets the KEAP1-Nrf2-G6PD Axis and Suppresses Redox Metabolism in Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Small Compounds
2.2. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.3. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation and PCR
2.4. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
2.5. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
- BRD4-F: 5′-ACCTCCAACCCTAACAAGCC-3′;
- BRD4-R: 5′-TTTCCATAGTGTCTTGAGCACC-3′;
- β-actin-F: 5′-TGTATGCCTCTGGTCGTACC-3′;
- β-actin–R: 5′-CAGGTCCAGACGCAGGATG-3′;
- G6PD-F: 5′-CCGGAAACGGTCGTACACTT-3′;
- G6PD-R: 5′-ATGACGCTGTCTGCGCTT-3′;
- KEAP1-F: 5′-TGGCCAAGCAAGAGGAGTTC-3′;
- KEAP1-R: 5′-GGCTGATGAGGGTCACCAGTT-3′;
- NQO1-F: 5′-CCTGCCATTCTGAAAGGCTGGT-3′;
- NQO1-R: 5′- GTGGTGTGTGGAAAGCACTGCCT-3′;
- FTL-F: 5′-CACCTACCTCTCTGGGCT-3′;
- FTL-R: 5′-CAATTCGCGGAAGAAGTGGC-3′;
- FTH1-F: 5′-CCAGAACTACCACCAGGACTC-3′;
- FTH1-R: 5′-GTAAGTAGCTGGGCAGAGGCAA-3′.
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Preparation of Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Extracts Assay
2.8. Transcription Factor Prediction
2.9. Multi-Omics Data Analysis
2.10. Analysis of Expression Data
2.11. RNA Interference
2.12. SCLC Xenograft Mouse Models
3. Results
3.1. KEAP1 Is UpRegulated and Correlated with Prognosis in Various Cancer Types
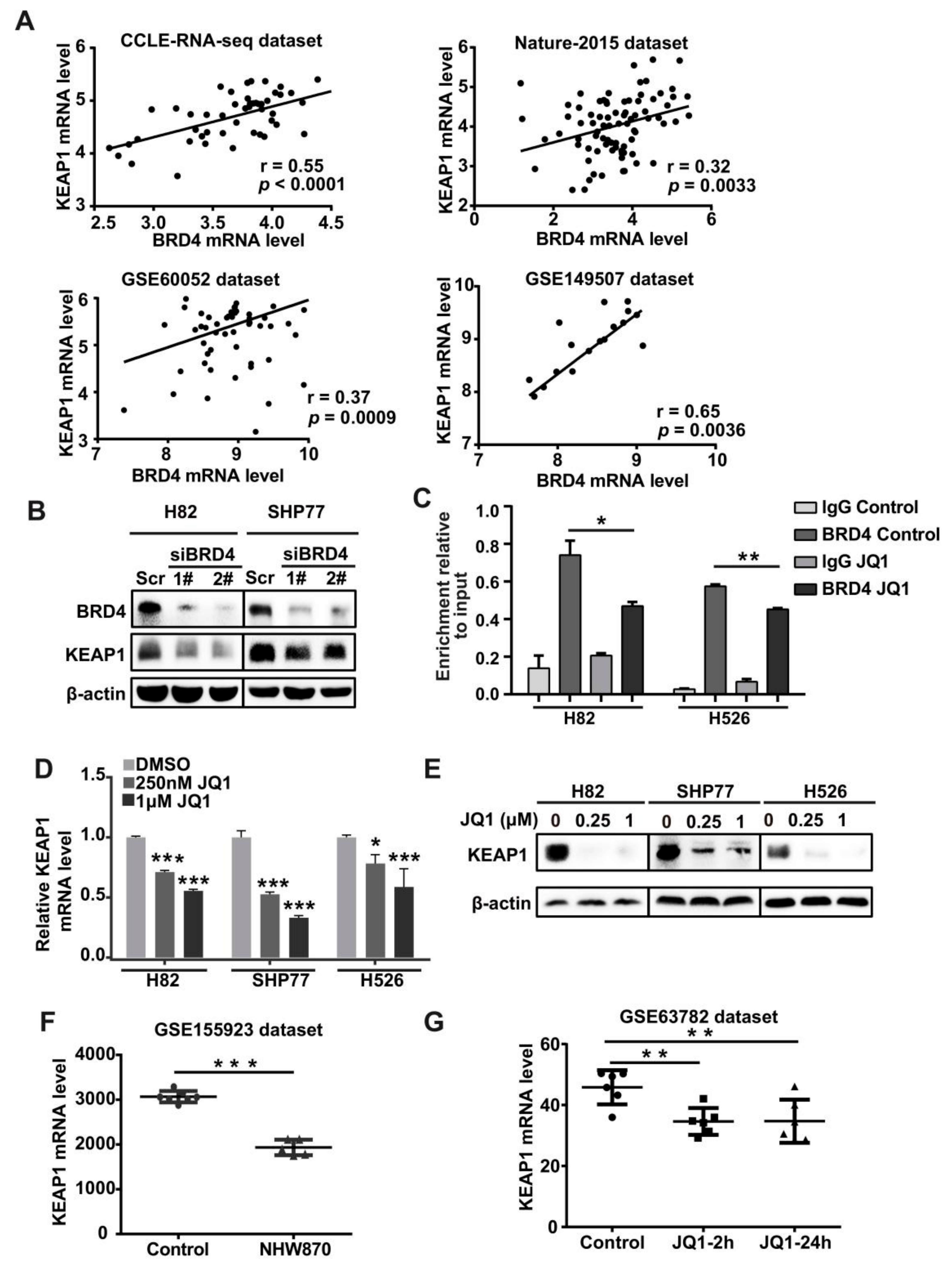
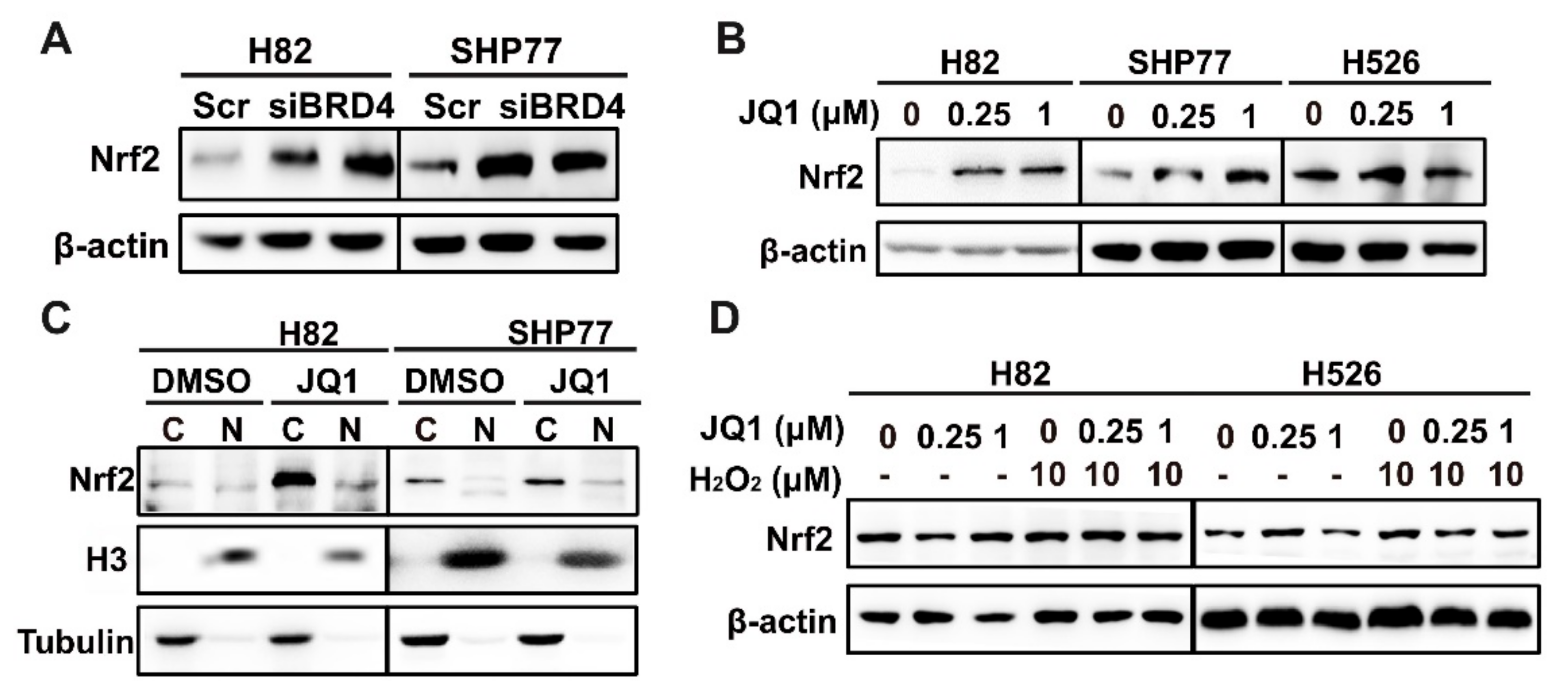
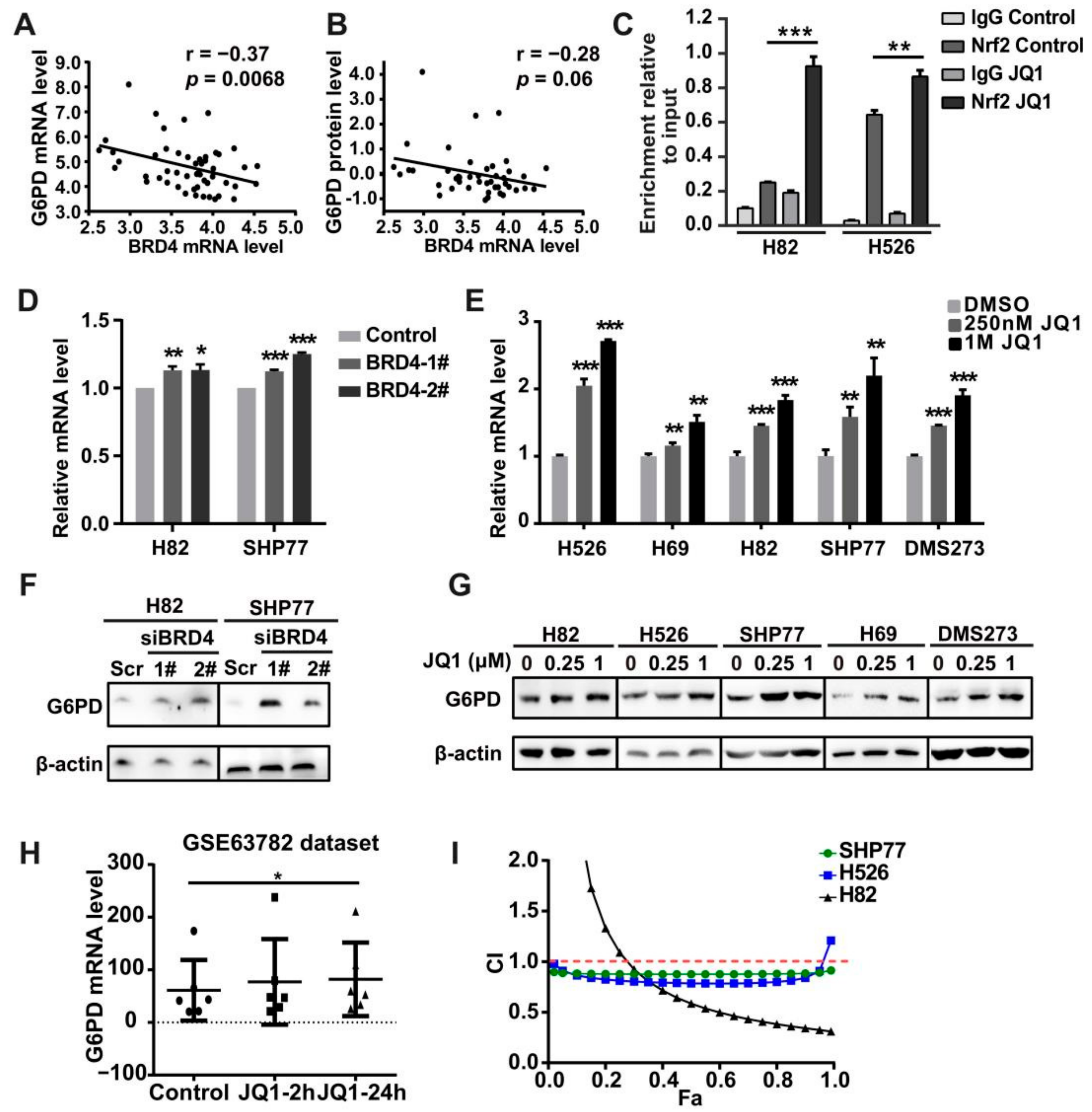
3.2. BRD4 Targets the KEAP1 Promoter and Regulates KEAP1 Expression in Lung Cancer
3.3. The Positive Association between KEAP1 and BRD4 in SCLC
3.4. BETi and Nrf2i Synergistically Inhibit SCLC Cell Proliferation
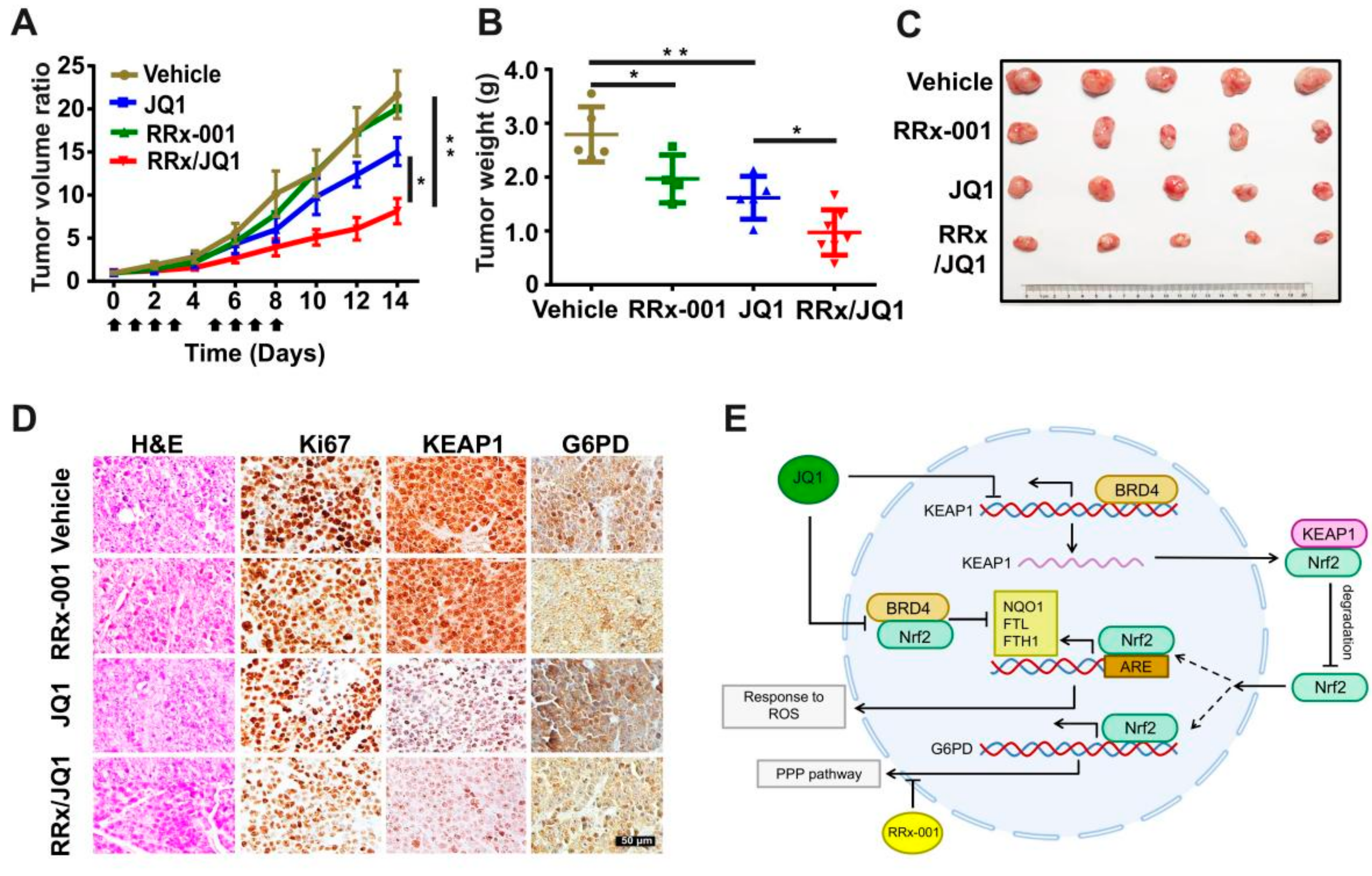
3.5. Co-Targeting BRD4 and G6PD Suppresses SCLC In Vitro and In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kansanen, E.; Kuosmanen, S.M.; Leinonen, H.; Levonen, A.L. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: Mechanisms of activation and dysregulation in cancer. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Network CGAR. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Nature 2012, 491, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.K.; Singh, A.; Biswal, S.; Askin, F.; Gabrielson, E. KEAP1 gene mutations and NRF2 activation are common in pulmonary papillary adenocarcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 56, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchouague, M.; Grondin, M.; Glory, A.; Averill-Bates, D. Heat shock induces the cellular antioxidant defenses peroxiredoxin, glutathione and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase through Nrf2. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 310, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, E.; Okuda, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Watabe, K. Metabolic genes in cancer: Their roles in tumor progression and clinical implications. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2010, 1805, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, S.A.; De Souza, D.P.; Kersbergen, A.; Policheni, A.N.; Dayalan, S.; Tull, D.; Rathi, V.; Gray, D.H.; Ritchie, M.E.; McConville, M.J.; et al. Synergy between the KEAP1/NRF2 and PI3K Pathways Drives Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with an Altered Immune Microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuishi, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Kawatani, Y.; Shibata, T.; Nukiwa, T.; Aburatani, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Motohashi, H. Nrf2 Redirects Glucose and Glutamine into Anabolic Pathways in Metabolic Reprogramming. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Oishi, H.; Matteson, E.L.; Tian, L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Restoring oxidant signaling suppresses proarthritogenic T cell effector functions in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 331ra338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathagen-Buhmann, A.; Schulte, A.; Weller, J.; Holz, M.; Herold-Mende, C.; Glass, R.; Lamszus, K. Glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway are differentially associated with the dichotomous regulation of glioblastoma cell migration versus proliferation. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 18, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S.; Zhang, Z.G.; Du, G.Y.; Sun, H.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, X.M.; Wu, X.H.; Yu, X.Y.; Huang, Y.H. Nrf2 promotes breast cancer cell migration via up-regulation of G6PD/HIF-1 alpha/Notch1 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3451–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.; Namani, A.; Elshaer, M.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. “NRF2 addiction” in lung cancer cells and its impact on cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 467, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Happel, C.; Manna, S.K.; Acquaah-Mensah, G.; Carrerero, J.; Kumar, S.; Nasipuri, P.; Krausz, K.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Dewi, R.; et al. Transcription factor NRF2 regulates miR-1 and miR-206 to drive tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2921–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.E.; Fenger, J.M.; Carson, W.E.,3rd. Emerging roles of and therapeutic strategies targeting BRD4 in cancer. Cell Immunol. 2019, 337, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Long, X.; Zhu, S.Q.; Jin, C.; Xu, J.J.; Ding, J.Y. High level of BRD4 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9491–9500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, N.P.; Alsarraj, J.; Lukes, L.; Walker, R.C.; Officewala, J.S.; Yang, H.H.; Lee, M.P.; Ozato, K.; Hunter, K.W. Bromodomain 4 activation predicts breast cancer survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6380–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussong, M.; Borno, S.T.; Kerick, M.; Wunderlich, A.; Franz, A.; Sultmann, H.; Timmermann, B.; Lehrach, H.; Hirsch-Kauffmann, M.; Schweiger, M.R. The bromodomain protein BRD4 regulates the KEAP1/NRF2-dependent oxidative stress response. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, J.M.; Stancill, J.S.; Smith, B.C.; Girotti, A.W. Nitric oxide antagonism to glioblastoma photodynamic therapy and mitigation thereof by BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 5345–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniguez, A.B.; Alexe, G.; Wang, E.J.; Roti, G.; Patel, S.; Chen, L.; Kitara, S.; Conway, A.; Robichaud, A.L.; Stolte, B.; et al. Resistance to Epigenetic-Targeted Therapy Engenders Tumor Cell Vulnerabilities Associated with Enhancer Remodeling. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 922.e927–938.e927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hong, B.; Li, X.; Deng, K.; Li, H.; Yan Lui, V.W.; Lin, W. JQ1 synergizes with the Bcl-2 inhibitor ABT-263 against MYCN-amplified small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86312–86324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W.B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E.M.; Keates, T.; Hickman, T.T.; Felletar, I.; et al. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.Y.; Gilan, O.; Lam, E.Y.; Rubin, A.F.; Ftouni, S.; Tyler, D.; Stanley, K.; Sinha, D.; Yeh, P.; Morison, J.; et al. BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells. Nature 2015, 525, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandarlapaty, S.; Sawai, A.; Scaltriti, M.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.; Grbovic-Huezo, O.; Serra, V.; Majumder, P.K.; Baselga, J.; Rosen, N. AKT inhibition relieves feedback suppression of receptor tyrosine kinase expression and activity. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Hobor, S.; Bertotti, A.; Zecchin, D.; Huang, S.; Galimi, F.; Cottino, F.; Prahallad, A.; Grernrum, W.; Tzani, A.; et al. Intrinsic resistance to MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant lung and colon cancer through transcriptional induction of ERBB3. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, L.A.; Rudin, C.M. Small cell lung cancer: Where do we go from here? Cancer 2015, 121, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lichtenberg, T.; Hoadley, K.A.; Poisson, L.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Cherniack, A.D.; Kovatich, A.J.; Benz, C.C.; Levine, D.A.; Lee, A.V.; et al. An Integrated TCGA Pan-Cancer Clinical Data Resource to Drive High-Quality Survival Outcome Analytics. Cell 2018, 173, 400.e411–416.e411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.W.; Fan, J.Y.; Wang, B.B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.M.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, E108–E110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.C.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretic, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Hsiao, J.R.; Jiang, S.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chu, P.Y.; Liu, K.J.; Fang, H.L.; Lin, L.M.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, Y.W.; et al. C-MYC-directed NRF2 drives malignant progression of head and neck cancer via glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and transketolase activation. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5232–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Wang, D.J.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, S.C.; Gao, K.; Ye, Z.Q.; Wang, S.Q.; Pan, C.W.; Zhu, Y.S.; Yan, Y.Q.; et al. Intrinsic BET inhibitor resistance in SPOP-mutated prostate cancer is mediated by BET protein stabilization and AKT-mTORC1 activation. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurimchak, A.M.; Shelton, C.; Duncan, K.E.; Johnson, K.J.; Brown, J.; O’Brien, S.; Gabbasov, R.; Fink, L.S.; Li, Y.S.; Lounsbury, N.; et al. Resistance to BET Bromodomain Inhibitors Is Mediated by Kinome Reprogramming in Ovarian Cancer. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oronsky, B.; Reid, T.R.; Larson, C.; Caroen, S.; Quinn, M.; Burbano, E.; Varner, G.; Thilagar, B.; Brown, B.; Coyle, A.; et al. REPLATINUM Phase III randomized study: RRx-001+platinum doublet versus platinum doublet in third-line small cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 3427–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oronsky, B.; Reid, T.R.; Oronsky, A.; Caroen, S.; Carter, C.A.; Cabrales, P. Brief report: RRx-001 is a c-Myc inhibitor that targets cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 23439–23442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhang, J.; Cao, G.; Xu, C.; Zhang, B.; Lin, W. BRD4 Targets the KEAP1-Nrf2-G6PD Axis and Suppresses Redox Metabolism in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040661
Lv Y, Lv X, Zhang J, Cao G, Xu C, Zhang B, Lin W. BRD4 Targets the KEAP1-Nrf2-G6PD Axis and Suppresses Redox Metabolism in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(4):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040661
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yang, Xiaotong Lv, Jiahui Zhang, Guozhen Cao, Changzhi Xu, Buchang Zhang, and Wenchu Lin. 2022. "BRD4 Targets the KEAP1-Nrf2-G6PD Axis and Suppresses Redox Metabolism in Small Cell Lung Cancer" Antioxidants 11, no. 4: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040661
APA StyleLv, Y., Lv, X., Zhang, J., Cao, G., Xu, C., Zhang, B., & Lin, W. (2022). BRD4 Targets the KEAP1-Nrf2-G6PD Axis and Suppresses Redox Metabolism in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Antioxidants, 11(4), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040661