Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Newborn Mice through Modulation of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Neonatal Hyperoxic Exposure and Recovery
2.3. Immunohistochemistry of Retinal Vessels
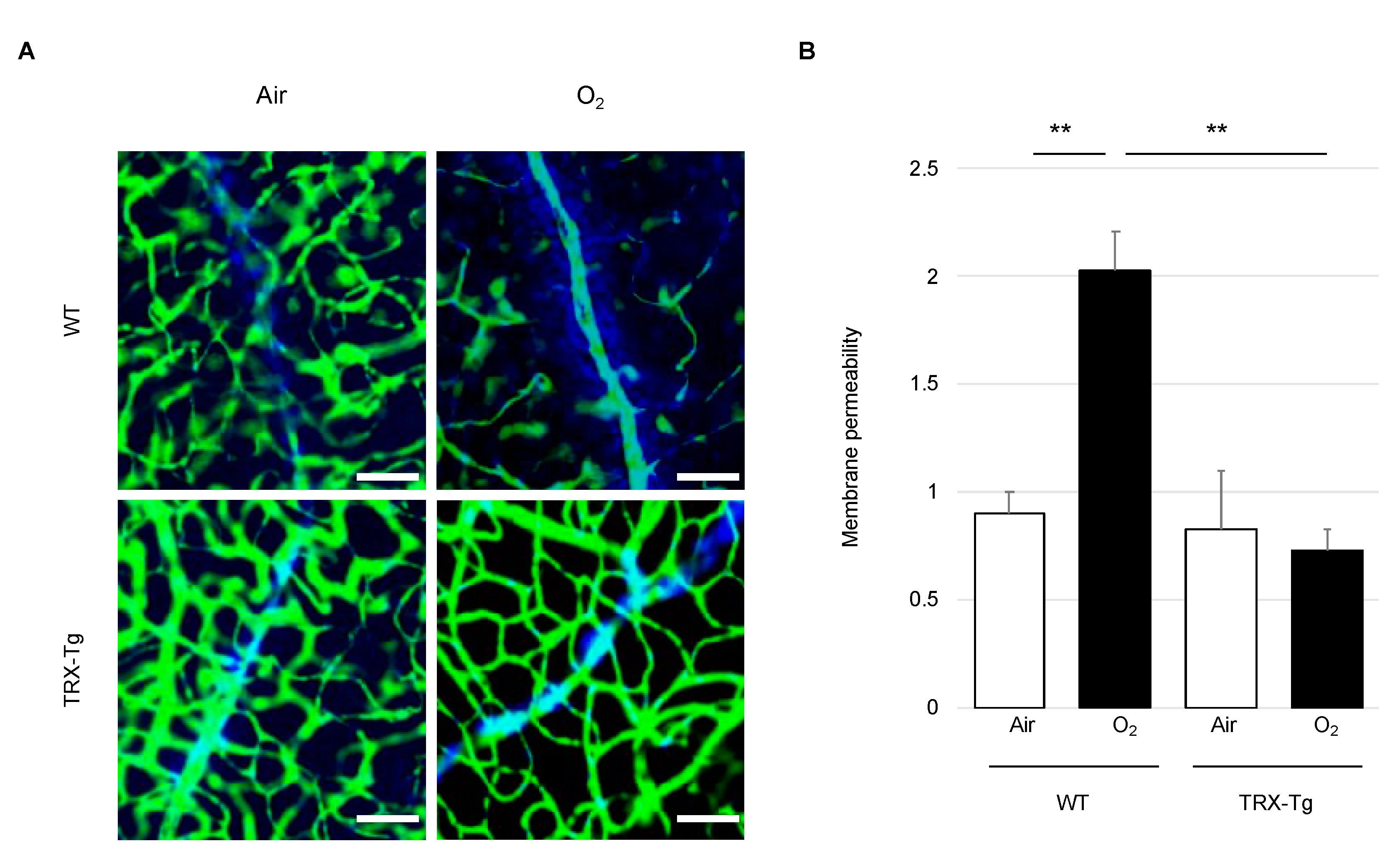
2.4. Retinal Vascular Permeability
2.5. Western Blot Analysis of the Retina
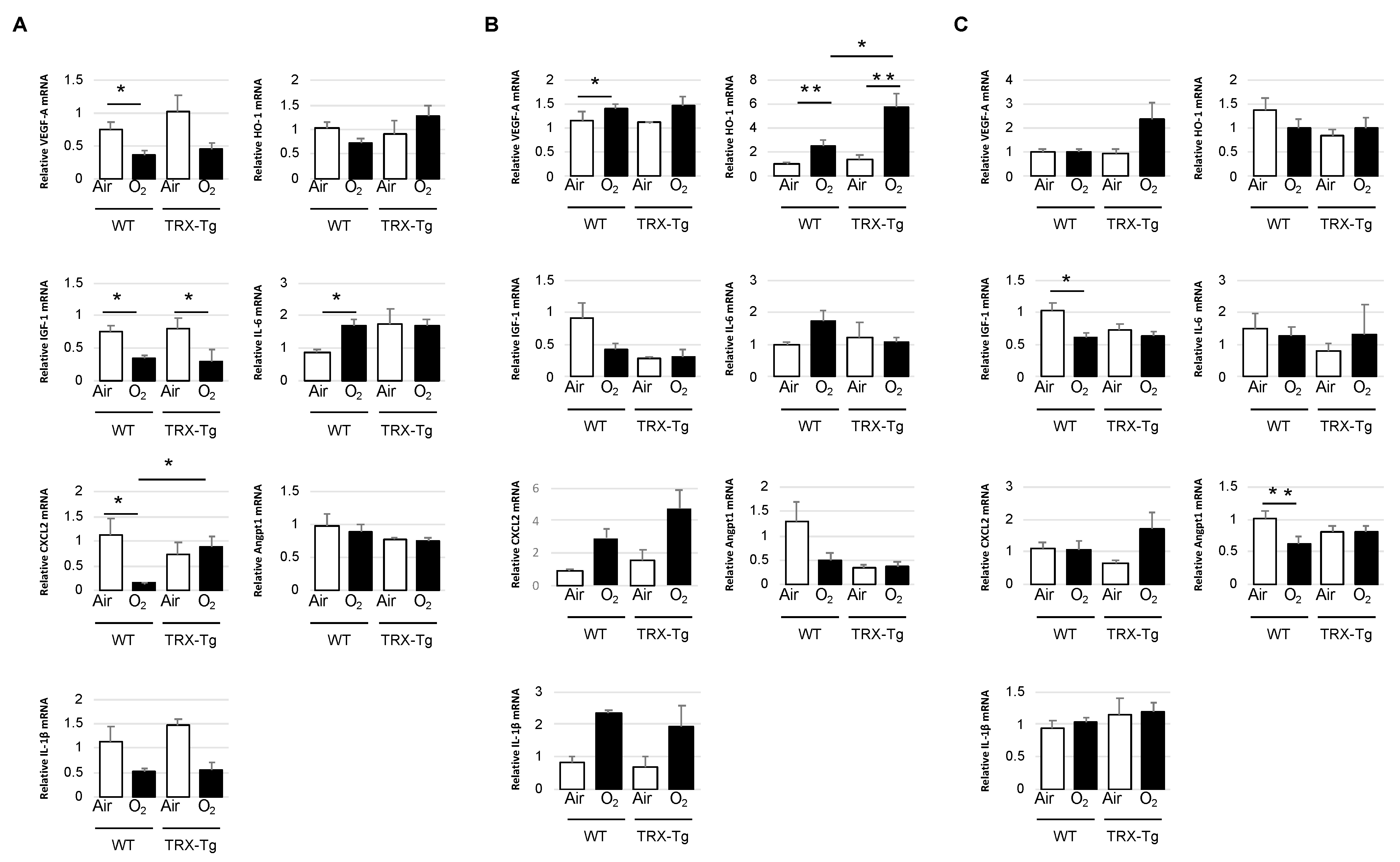
2.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis in the Retina
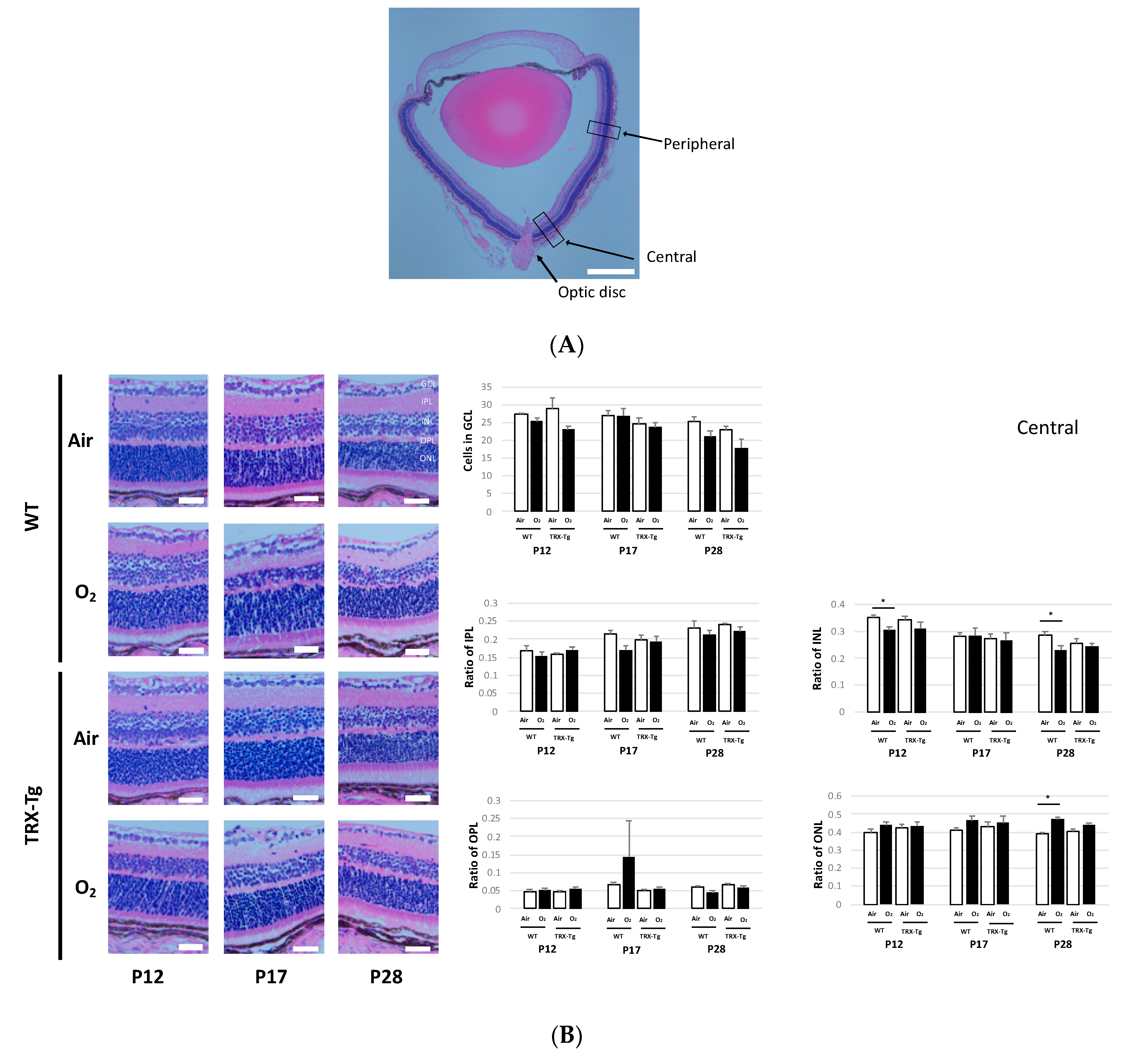
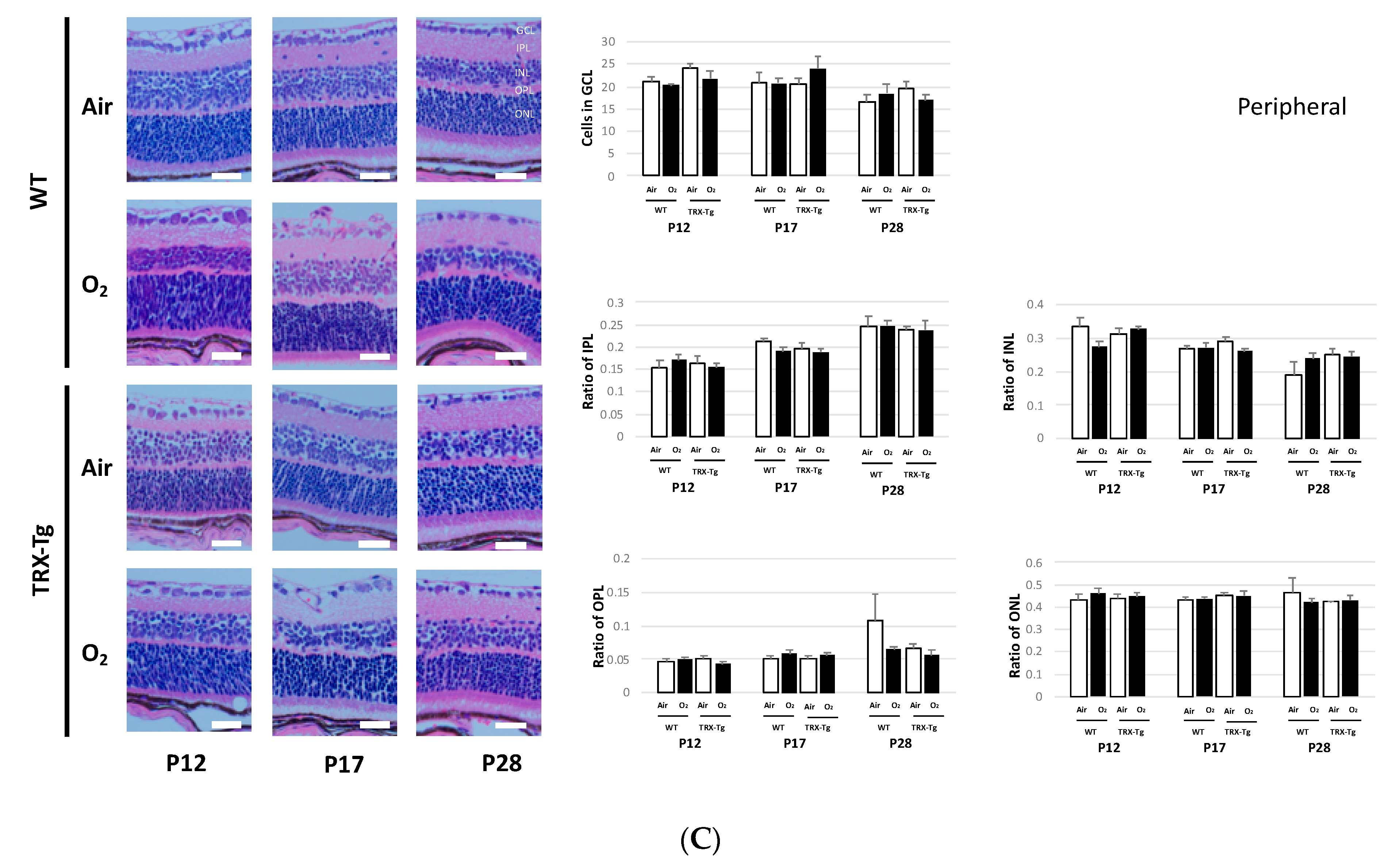
2.7. Retinal Membrane Histological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Immunohistochemistry of Retinal Vessels
3.1.1. Retinal Avascular Area
3.1.2. Retinal Neovascular Area
3.1.3. Morphological Difference in Retinal Arteries and Veins
3.2. Retinal Vascular Permeability
3.3. Expression Levels of Tight Junction Proteins
3.4. Retinal mRNA Expression Levels of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors
3.5. Retinal Membrane Histology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hellström, A.; Smith, L.E.; Dammann, O. Retinopathy of prematurity. Lancet 2013, 382, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartnett, M.E. Pathophysiology and mechanisms of severe retinopathy of prematurity. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashinsky, A.L. Retinopathy of prematurity. N. C. Med. J. 2017, 78, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brion, L.P.; Bell, E.F.; Raghuveer, T.S. Vitamin E supplementation for prevention of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, 2003, CD003665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.N.; Langenberg, P.; Bhutani, V.; Quinn, G.E. Vitamin E prophylaxis to reduce retinopathy of prematurity: A reappraisal of published trials. J. Pediatrics 1997, 131, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soghier, L.M.; Brion, L.P. Cysteine, cystine or N-acetylcysteine supplementation in parenterally fed neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, CD004869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.M.; Stefanovic, N.; Tan, G.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L.; de Haan, J.B. Lack of the antioxidant glutathione peroxidase-1 (GPx1) exacerbates retinopathy of prematurity in mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1985, 54, 237–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 13963–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Bai, J.; Araya, S.; Kondo, N.; Nishinaka, Y.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Yodoi, J. Circulating thioredoxin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil chemotaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15143–15148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, H.; Tamura, S.; Watanabe, I.; Iwasaki, T.; Yodoi, J. Enhanced resistancy of thioredoxin-transgenic mice against influenza virus-induced pneumonia. Immunol. Lett. 2002, 82, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimul Ahsan, M.; Nakamura, H.; Tanito, M.; Yamada, K.; Utsumi, H.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-1 suppresses lung injury and apoptosis induced by diesel exhaust particles (DEP) by scavenging reactive oxygen species and by inhibiting DEP-induced downregulation of Akt. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Nakamura, H.; Okamoto, M.; Kato, S.; Araya, S.; Nomiyama, K.; Oizumi, K.; Young, H.A.; Aizawa, H.; Yodoi, J. Redox-active protein thioredoxin prevents proinflammatory cytokine- or bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohashi, S.; Nishio, A.; Nakamura, H.; Asada, M.; Tamaki, H.; Kawasaki, K.; Fukui, T.; Yodoi, J.; Chiba, T. Overexpression of redox-active protein thioredoxin-1 prevents development of chronic pancreatitis in mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, S.; Nishio, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kido, M.; Ueno, S.; Uza, N.; Inoue, S.; Kitamura, H.; Kiriya, K.; Asada, M.; et al. Protective roles of redox-active protein thioredoxin-1 for severe acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G772–G781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shioji, K.; Nakamura, H.; Masutani, H.; Yodoi, J. Redox regulation by thioredoxin in cardiovascular diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2003, 5, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Hoshino, Y.; Hara, T.; Muro, S.; Nakamura, H.; Mishima, M.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-1 ameliorates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kondo, N.; Tanito, M.; Kwon, Y.W.; Ahsan, M.K.; Matsui, H.; Narita, M.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-1 attenuates indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Namba, F.; Kobayashi-Miura, M.; Goda, T.; Nakura, Y.; Nishiumi, F.; Son, A.; Kubota, A.; Yodoi, J.; Yanagihara, I. Human thioredoxin-1 attenuates the rate of lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm delivery in mice in association with its anti-inflammatory effect. Pediatric Res. 2016, 80, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagano, N.; Tanaka, K.; Ozawa, J.; Watanabe, T.; Miyake, F.; Matsumura, S.; Osada, K.; Matsuoka, K.; Tamura, M.; Namba, F. Attenuation of hyperoxic lung injury in newborn Thioredoxin-1-Overexpressing mice through the suppression of proinflammatory cytokine mRNA expression. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.S.; Geng, W.S.; Chen, L.; Jia, J.J. Thioredoxin as a therapeutic target in cerebral ischemia. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.E.; Wesolowski, E.; McLellan, A.; Kostyk, S.K.; D’Amato, R.; Sullivan, R.; D’Amore, P.A. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Penn, J.S.; Tolman, B.L.; Lowery, L.A. Variable oxygen exposure causes preretinal neovascularization in the newborn rat. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1993, 34, 576–585. [Google Scholar]
- Buonocore, G.; Perrone, S.; Longini, M.; Vezzosi, P.; Marzocchi, B.; Paffetti, P.; Bracci, R. Oxidative stress in preterm neonates at birth and on the seventh day of life. Pediatric Res. 2002, 52, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.E.; Gu, X.; Samuel, S.; Marcus, D.M.; Bartoli, M.; Huang, P.L.; Caldwell, R.B. Reduced severity of oxygen-induced retinopathy in eNOS-deficient mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, Y.; Mitsui, A.; Nishiyama, A.; Nozaki, K.; Sono, H.; Gon, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Yodoi, J. Overexpression of thioredoxin in transgenic mice attenuates focal ischemic brain damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4131–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connor, K.M.; Krah, N.M.; Dennison, R.J.; Aderman, C.M.; Chen, J.; Guerin, K.I.; Sapieha, P.; Stahl, A.; Willett, K.L.; Smith, L.E.H. Quantification of oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse: A model of vessel loss, vessel regrowth and pathological angiogenesis. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, A.; Sawada, S.; Mori, A.; Arima, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Nagamitsu, T.; Nakahara, T. Establishment of an abnormal vascular patterning model in the mouse retina. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 136, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikaraishi, Y.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. New quantitative analysis, using high-resolution images, of oxygen-induced retinal neovascularization in mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 84, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Imai, S.; Ogishima, H.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Morphological and functional changes in the retina after chronic oxygen-induced retinopathy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gariano, R.F.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; Hendrickson, A.E. Vascular development in primate retina: Comparison of laminar plexus formation in monkey and human. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 3442–3455. [Google Scholar]
- Kermorvant-Duchemin, E.; Sapieha, P.; Sirinyan, M.; Beauchamp, M.; Checchin, D.; Hardy, P.; Sennlaub, F.; Lachapelle, P.; Chemtob, S. Understanding ischemic retinopathies: Emerging concepts from oxygen-induced retinopathy. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2010, 120, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, T.; Hemo, I.; Itin, A.; Pe’er, J.; Stone, J.; Keshet, E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.E. Through the eyes of a child: Understanding retinopathy through ROP the Friedenwald lecture. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 5177–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, S.J.; Bellamy, W.T.; Briehl, M.M.; Powis, G. The redox protein thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) increases hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein expression: Trx-1 overexpression results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor production and enhanced tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5089–5095. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Damdimopoulos, A.E.; Spyrou, G.; Brüne, B. Thioredoxin 1 and thioredoxin 2 have opposed regulatory functions on hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7482–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.E.; Choi, D.K.; Jang, J.Y.; Jung, J.J.; Kiyonari, H.; Shioi, G.; Chang, W.; Suda, T.; Mochizuki, N.; et al. Angiopoietin-1 guides directional angiogenesis through integrin αvβ5 signaling for recovery of ischemic retinopathy. 2013, 5, 203ra127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, H. Toll-like receptor 3 activation drives the inflammatory response in oxygen-induced retinopathy in rats. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 99, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, A.; Kato, N.; Horibe, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Mochizuki, M.; Mitsui, A.; Kawakami, K.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J. Direct association of thioredoxin-1 (TRX) with macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): Regulatory role of TRX on MIF internalization and signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, Y.Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, L. Temporal requirement of RPE-derived VEGF in the development of choroidal vasculature. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suttner, D.M.; Dennery, P.A. Reversal of HO-1 related cytoprotection with increased expression is due to reactive iron. Faseb. J. 1999, 13, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Shimazawa, M.; Ishizuka, F.; Nakamura, S.; Tsuruma, K.; Hara, H. Tissue kallikrein (kallidinogenase) protects against retinal ischemic damage in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, X.; Mao, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Tang, S.; Rizzolo, L.J. Differential expression of claudins in retinas during normal development and the angiogenesis of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7556–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozawa, J.; Tanaka, K.; Arai, Y.; Haga, M.; Miyahara, N.; Miyamoto, A.; Nishimura, E.; Namba, F. Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Newborn Mice through Modulation of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050899
Ozawa J, Tanaka K, Arai Y, Haga M, Miyahara N, Miyamoto A, Nishimura E, Namba F. Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Newborn Mice through Modulation of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(5):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050899
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzawa, Junichi, Kosuke Tanaka, Yukio Arai, Mitsuhiro Haga, Naoyuki Miyahara, Ai Miyamoto, Eri Nishimura, and Fumihiko Namba. 2022. "Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Newborn Mice through Modulation of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors" Antioxidants 11, no. 5: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050899
APA StyleOzawa, J., Tanaka, K., Arai, Y., Haga, M., Miyahara, N., Miyamoto, A., Nishimura, E., & Namba, F. (2022). Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Newborn Mice through Modulation of Proinflammatory and Angiogenic Factors. Antioxidants, 11(5), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050899





