Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol) Metabolism and Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Disease-Specific Changes to Vitamin E Status and Metabolism in CKD
2.1. Vitamin E Deficiency and Lipotoxicity in CKD
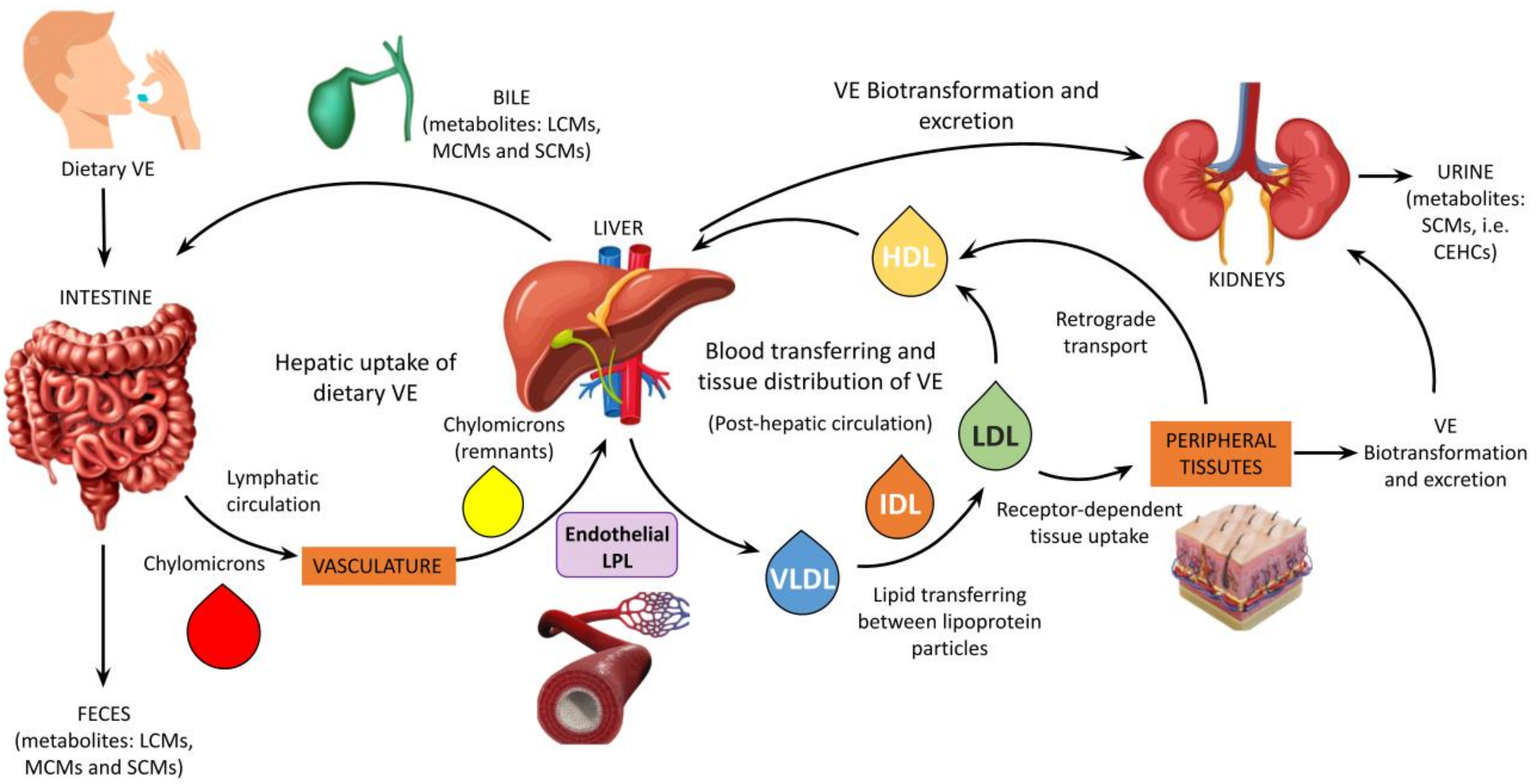
2.2. The Vitamin E Metabolome and Its Alterations in CKD
2.3. Vitamin E Supplementation and Therapy in CKD
2.3.1. Oral Supplements
2.3.2. Vitamin E-Coated Dialyzers
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, H.M.; Burr, G.O. The Anti-Sterility Vitamine Fat Soluble E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1925, 11, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, H.M.; ScottBishop, K. On the Existence of a Hitherto Unrecognized Dietary Factor Essential for Reproduction. Science 1922, 56, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernholz, E. On the Constitution of α-Tocopherol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Azzi, A.; Birringer, M.; Cook-Mills, J.M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Frank, J.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; Özer, N.K. Vitamin E: Emerging Aspects and New Directions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birringer, M.S.; Siems, K.; Maxones, A.; Frank, J.; Lorkowski, S. Natural 6-Hydroxy-Chromanols and -Chromenols: Structural Diversity, Biosynthetic Pathways and Health Implications. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4803–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A. Tocopherols, tocotrienols and tocomonoenols: Many similar molecules but only one vitamin E. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinello, F.; Fardin, P.; Ottina, M.; Ricchieri, G.L.; Koenig, M.; Cavalier, L.; Trevisan, C.P. Supplemental Therapy in Isolated Vitamin E Deficiency Improves the Peripheral Neuropathy and Prevents the Progression of Ataxia. J. Neurol. Sci. 1998, 156, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlschutter, A.; Finckh, B.; Nickel, M.; Bley, A.; Hübner, C. First Recognized Patient with Genetic Vitamin e Deficiency Stable after 36 Years of Controlled Supplement Therapy. Neurodegener. Dis. 2020, 20, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulatowski, L.M.; Manor, D. Vitamin E and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 84, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Galli, F. Vitamin E: A vitamin still awaiting the detection of its biological function. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius-Flohe, R. Vitamin E research: Past, now and future. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 177, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Traber, M.G.; Atkinson, J. Vitamin E, antioxidant and nothing more. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattill, H.A. The Oxidative Destruction of Vitamins A and E: And the Protective Action of Certain Vegetable Oils. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1927, 89, 1505–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M.J.; Mattill, H.A. The Auto-Oxidation of Fats with Reference to Their Destructive Effect on Vitamin E. J. Nutr. 1931, 3, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, K.; Rawat, A. Vitamin E Market Size by Product (Synthetic Vitamin E, Natural Vitamin E [Tocopherol, Tocotrienols]), by Application (Animal Nutrition, Human Nutrition/Dietary Supplements, Functional Food & Beverages, Cosmetics), Industry Analysis Report, Regional Outlook, Growth Potential, Price Trend, Competitive Market Share & Forecast, 2020–2026. 2020. Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/vitamin-e-market (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Zingg, J.-M.; Azzi, A. Non-Antioxidant Activities of Vitamin E. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 11, 1113–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, J.M. Vitamin E: Regulatory Role on Signal Transduction. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 456–478. [Google Scholar]
- Torquato, P.; Marinelli, R.; Bartolini, D.; Giusepponi, D.; Cruciani, G.; Siragusa, L.; Galarini, R.; Sebastiani, B.; Gioiello, A.; Galli, F. Vitamin E: Metabolism and Molecular Aspects. In Molecular Nutrition: Vitamins; Patel, V.B., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 487–518. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, K.; Chojnacka, A.; Górnicka, M. Tocopherols and Tocotrienols-Bioactive Dietary Compounds; What Is Certain, What Is Doubt? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohé, L.; Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Saliou, C.; Traber, M.; Packer, L. Redox Regulation of NF-kappa B Activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Packer, L. Inhibition of NF-kappa B activation by vitamin E derivatives. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 193, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yin, X.; Lill, M.A.; Danielson, M.L.; Freiser, H.; Huang, J. Long-Chain Carboxychromanols, Metabolites of Vitamin E, are Potent Inhibitors of Cyclooxygenases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20464–20469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pein, H.; Ville, A.; Pace, S.; Temml, V.; Garscha, U.; Raasch, M.; Alsabil, K.; Viault, G.; Dinh, C.-P.; Guilet, D.; et al. Endogenous Metabolites of Vitamin E Limit Inflammation by Targeting 5-Lipoxygenase. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.Y.; Nakatsu, C.H.; Jones-Hall, Y.; Kozik, A.; Jiang, Q. Vitamin E Alpha- and Gamma-Tocopherol Mitigate Colitis, Protect Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulate the Gut Microbiota in Mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 163, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Guo, C.; Guo, K.; Hu, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Vitamin E Exerts Neuroprotective Effects in Pentylenetetrazole Kindling Epilepsy via Suppression of Ferroptosis. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinman, A.; Holst, C.R.; Latham, J.C.; Bruegger, J.J.; Ulas, G.; McCusker, K.P.; Amagata, A.; Davis, D.; Hoff, K.G.; Kahn-Kirby, A.H.; et al. Vitamin E Hydroquinone is an Endogenous Regulator of Ferroptosis via Redox Control of 15-Lipoxygenase. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, V.E.; Mao, G.; Qu, F.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Doll, S.; Croix, C.S.; Dar, H.H.; Liu, B.; Tyurin, V.A.; Ritov, V.B.; et al. Oxidized Arachidonic and Adrenic PEs Navigate Cells to Ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascale, M.C.; Bassi, A.M.; Patrone, V.; Villacorta, L.; Azzi, A.; Zingg, J.M. Increased Expression of Transglutaminase-1 and PPARgamma after Vitamin E Treatment in Human Keratinocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 447, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, S.; Rubic, T.; Lorenz, R.L. alpha-Tocopherol disturbs macrophage LXRalpha regulation of ABCA1/G1 and cholesterol handling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 369, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poynter, M.E.; Daynes, R.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha activation modulates cellular redox status, represses nuclear factor-kappaB signaling, and reduces inflammatory cytokine production in aging. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32833–32841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquato, P.; Bartolini, D.; Giusepponi, D.; Saluti, G.; Russo, A.; Barola, C.; Birringer, M.; Galarini, R.; Galli, F. Alpha-13′-Oh Is the Main Product of a-Tocopherol Metabolism and Influences Cyp4f2 and Ppar Gamma Gene Expression in Hepg2 Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 96, S19–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, R.; Torquato, P.; Bartolini, D.; Mas-Bargues, C.; Bellezza, G.; Gioiello, A.; Borras, C.; De, A.L.; Fallarino, F.; Sebastiani, B.; et al. Garcinoic Acid Prevents β-Amyloid (Aβ) Deposition in the Mouse Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 11866–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, S.; Gellrich, L.; Chaikuad, A.; Kluge, S.; Werz, O.; Heering, J.; Knapp, S.; Lorkowski, S.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M.; Merk, D. Endogenous Vitamin E Metabolites Mediate Allosteric PPARγ Activation with Unprecedented Co-Regulatory Interactions. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, P.; Leers-Sucheta, S.; Azhar, S. Suppression of steroidogenesis and activator protein-1 transcription factor activity in rat adrenals by vitamin E deficiency-induced chronic oxidative stress. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.J.; Lin, J.S.; Chen, H.H. Alpha-tocopherol downregulates the expression of GPIIb promoter in HEL cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, D.; De Franco, F.; Torquato, P.; Marinelli, R.; Cerra, B.; Ronchetti, R.; Schon, A.; Fallarino, F.; De Luca, A.; Bellezza, G.; et al. Garcinoic Acid Is a Natural and Selective Agonist of Pregnane X Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 3701–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podszun, M.C.; Jakobi, M.; Birringer, M.; Weiss, J.; Frank, J. The Long Chain α-tocopherol Metabolite α13′-COOH and γ-tocotrienol Induce P-glycoprotein Expression and Activity by Activation of the Pregnane X Receptor in the Intestinal Cell Line LS 180. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 61, 1600605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comitato, R.; Leoni, G.; Canali, R.; Ambra, R.; Nesaretnam, K.; Virgili, F. Tocotrienols Activity in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells: Involvement of ERbeta Signal Transduction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire-Ewing, S.; Desrumaux, C.; Néel, D.; Lagrost, L. Vitamin E Transport, Membrane Incorporation and Cell Metabolism: Is α-Tocopherol in Lipid Rafts an Oar in the Lifeboat? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, J.M. Vitamin E: A Role in Signal Transduction. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 135–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, A.; Arita, M.; Sato, Y.; Kiyose, C.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, O.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Affinity for α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein as a Determinant of the Biological Activities of Vitamin E Analogs. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaempf-Rotzoll, D.E.; Traber, M.G.; Arai, H. Vitamin E and transfer proteins. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, N.O.; Ohto, U.; Hiramatsu, T.; Urabe, M.; Uchida, Y.; Satow, Y.; Arai, H. Impaired α-TTP-PIPs Interaction Underlies Familial Vitamin E Deficiency. Science 2013, 340, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerflinger, N.; Linder, C.; Ouahchi, K.; Gyapay, G.; Weissenbach, J.; Le Paslier, D.; Rigault, P.; Belal, S.; Hamida, C.B.; Hentati, F. Ataxia with Vitamin E Deficiency: Refinement of Genetic Localization and Analysis of Linkage Disequilibrium by Using New Markers in 14 Families. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 56, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ouahchi, K.; Arita, M.; Kayden, H.; Hentati, F.; Ben Hamida, M.; Sokol, R.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K.; Mandel, J.L.; Koenig, M. Ataxia with Isolated Vitamin E Deficiency Is Caused by Mutations in the α–Tocopherol Transfer Protein. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalier, L.; Ouahchi, K.; Kayden, H.J.; Di Donato, S.; Reutenauer, L.; Mandel, J.L.; Koenig, M. Ataxia with Isolated Vitamin E Deficiency: Heterogeneity of Mutations and Phenotypic Variability in a Large Number of Families. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 62, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traber, M.G.; Lane, J.C.; Lagmay, N.R.; Kayden, H.J. Studies on the Transfer of Tocopherol between Lipoproteins. Lipids 1992, 27, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmölz, L.; Birringer, M.; Lorkowski, S.; Wallert, M. Complexity of Vitamin E Metabolism. World J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 7, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Kluge, S.; Schmölz, L.; Wallert, M.; Galli, F.; Birringer, M.; Lorkowski, S. Long-Chain Metabolites of Vitamin E: Metabolic Activation as a General Concept for Lipid-Soluble Vitamins? Antioxidants 2018, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traber, M.G.H.; Head, B. Vitamin E: How Much Is Enough, Too Much and Why! Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 177, 212–225. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, F.; Polidori, M.C.; Stahl, W.; Mecocci, P.; Kelly, F.J. Vitamin E Biotransformation in Humans. Vitam. Horm. 2007, 76, 263–280. [Google Scholar]
- Torquato, P.; Giusepponi, D.; Alisi, A.; Galarini, R.; Bartolini, D.; Piroddi, M.; Goracci, L.; Di Veroli, A.; Cruciani, G.; Crudele, A.; et al. Nutritional and Lipidomics Biomarkers of Docosahexaenoic Acid-Based Multivitamin Therapy in Pediatric NASH. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Im, S.; Wagner, J.G.; Hernandez, M.L.; Peden, D.B. Gamma-tocopherol, a major form of vitamin E in diets: Insights into antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, mechanisms, and roles in disease management. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 178, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.Y.; Im, S.; Jiang, Q. Different forms of vitamin E and metabolite 13′-carboxychromanols inhibit cyclooxygenase-1 and its catalyzed thromboxane in platelets, and tocotrienols and 13′-carboxychromanols are competitive inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 100, 108884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Natural forms of vitamin E: Metabolism, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities and their role in disease prevention and therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallert, M.; Schmölz, L.; Galli, F.; Birringer, M.; Lorkowski, S. Regulatory Metabolites of Vitamin E and Their Putative Relevance for Atherogenesis. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 495–503. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolini, D.; Torquato, P.; Barola, C.; Russo, A.; Rychlicki, C.; Giusepponi, D.; Bellezza, G.; Sidoni, A.; Galarini, R.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Impairs the Cytochrome P-450-Dependent Metabolism of α-Tocopherol (Vitamin E). J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 47, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Im, S.; Nakatsu, C.; Jones-Hall, Y.; Jiang, Q. Vitamin E Delta-Tocotrienol and Metabolite 13′-Carboxychromanol Inhibit Colitis-Associated Colon Tumorigenesis and Modulate Gut Microbiota in Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 89, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.; Neytchev, O.; Witasp, A.; Kublickiene, K.; Stenvinkel, P.; Shiels, P.G. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease and Dialysis Patients. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 1426–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Gallieni, M.; Rizzo, M.A.; Stucchi, A.; Delanaye, P.; Cavalier, E.; Moysés, R.M.A.; Jorgetti, V.; Iervasi, G.; Giannini, S.; et al. Vitamin K Plasma Levels Determination in Human Health. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Crepaldi, G.; Maggi, S.; Galli, F.; D’Angelo, A.; Calò, L.; Giannini, S.; Miozzo, D.; Gallieni, M. Vitamin K, Bone Fractures, and Vascular Calcifications in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Important but Poorly Studied Relationship. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2011, 34, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huish, S.A.; Jenkinson, C.; Dunn, J.A.; Meredith, D.J.; Bland, R.; Hewison, M. Low Serum 1,25(Oh)2D3 in End-Stage Renal Disease: Is Reduced 1α-Hydroxylase the Only Problem? Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Varga, Z.; Balla, J.; Ferraro, B.; Canestrari, F.; Floridi, A.; Kakuk, G.; Buoncristiani, U. Vitamin E, lipid profile, and peroxidation in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2001, 78, S148–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Floridi, A.G.; Floridi, A.; Buoncristiani, U. Accumulation of Vitamin E Metabolites in the Blood of Renal Failure Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E. Lipid Oxidation That Is, and Is Not, Inhibited by Vitamin E: Consideration about Physiological Functions of Vitamin E. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 176, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Pierantonelli, I.; Torquato, P.; Marinelli, R.; Ferreri, C.; Chatgilialoglu, C.; Bartolini, D.; Galli, F. Lipidomic Biomarkers and Mechanisms of Lipotoxicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 144, 293–309. [Google Scholar]
- Torquato, P.; Bartolini, D.; Giusepponi, D.; Piroddi, M.; Sebastiani, B.; Saluti, G.; Galarini, R.; Galli, F. Increased Plasma Levels of the Lipoperoxyl Radical-Derived Vitamin E Metabolite α-Tocopheryl Quinone Are an Early Indicator of Lipotoxicity in Fatty Liver Subjects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 131, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrass, C.K. Lipid metabolism and renal disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2006, 151, 106–121. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.X.; Hong, Q.; Peng, D.H.; Yang, Y.; Yu, W.L.; Shui, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.M. Evaluation of Serum Free Fatty Acids in Chronic Renal Failure: Evidence from a Rare Case with Undetectable Serum Free Fatty Acids and Population Data. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, L.F.; Shintani, A.; Ikizler, T.A.; Himmelfarb, J. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Are Associated with Adiposity in Moderate to Severe CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, T.; Schmidt, E.B.; Christensen, J.H. The effect of n-3 fatty acids on C-reactive protein levels in patients with chronic renal failure. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusepponi, D.G.; Galarini, R.; Barola, C.; Torquato, P.; Bartolini, D.; Moretti, S.; Saluti, G.; Gioiello, A.; Libetta, C.; Galli, F. LC-MS/MS Assay for the Simultaneous Determination of Tocopherols, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Metabolites in Human Plasma and Serum. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 144, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Ikizler, T.A.; Hakim, R.M. Perspectives in Renal Medicine: The Elephant in Uremia: Oxidant Stress as a Unifying Concept of Cardiovascular Disease in Uremia. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1524–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Piroddi, M.; Annetti, C.; Aisa, C.; Floridi, E.; Floridi, A. Oxidative Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species. Cardiovasc. Disord. Hemodial. Contrib. Nephrol. 2005, 149, 240–260. [Google Scholar]
- Libetta, C.S.; Sepe, V.; Esposito, P.; Galli, F.; Dal Canton, A. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Implications in Uremia and Hemodialysis. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canestrari, F.G.; Galli, F.; Giorgini, A.; Albertini, M.C.; Galiotta, P.; Pascucci, M.; Bossù, M. Erythrocyte Redox State in Uremic Anemia: Effects of Hemodialysis and Relevance of Glutathione Metabolism. Acta Haematol. 1994, 91, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Rovidati, S.; Benedetti, S.; Buoncristiani, U.; Covarelli, C.; Floridi, A.; Canestrari, F. Overexpression of Erythrocyte Glutathione S-Transferase in Uremia and Dialysis. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Piroddi, M.; Bartolini, D.; Ciffolilli, S.; Buoncristiani, E.; Ricci, G.; Buoncristiani, U. Blood Thiol Status and Erythrocyte Glutathione-S-Transferase in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients on Treatment with Frequent (Daily) Hemodialysis. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, D.; Sumino, K.; Yokoyama, M. Analysis of 7-ketocholesterol in low density lipoprotein and fatty acid composition in erythrocyte membranes of patients on maintenance hemodialysis and healthy controls. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 295, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canestrari, F.B.; Buoncristiani, U.; Galli, F.; Giorgini, A.; Albertini, M.C.; Carobi, C.; Pascucci, M.; Bossù, M. Redox State, Antioxidative Activity and Lipid Peroxidation in Erythrocytes and Plasma of Chronic Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 1995, 234, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzetta, O.; Cominacini, L.; Garbin, U.; Fratta Pasini, A.; Gammaro, L.; Bianco, F.; Davoli, A.; Campagnola, M.; De Santis, A.; Pastorino, A.M.; et al. Increased Susceptibility of LDL to in Vitro Oxidation in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis: Effects of Fish Oil and Vitamin E Administration. Clin. Nephrol. 1995, 44, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro, B.; Galli, F.; Frei, B.; Kingdon, E.; Canestrari, F.; Rice-Evans, C.; Buoncristiani, U.; Davenport, A.; Moore, K.P. Peroxynitrite-Induced Oxidation of Plasma Lipids Is Enhanced in Stable Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamprea-Montealegre, J.A.; Katz, R.; Scharnagl, H.; Silbernagel, G.; März, W.; Drechsler, C.; Wanner, C.; De Boer, I.H. Triglyceride–Rich Lipoproteins, Apolipoproteins, and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Events among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and End–Stage Renal Disease on Hemodialysis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2021, 152, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Davies, K.J.; Ursini, F. How do nutritional antioxidants really work: Nucleophilic tone and para-hormesis versus free radical scavenging in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosch, A.; Müller, R.; Freytag, C.; Borgmann, S.; Kraus, J.; Dierkes, J.; Neumann, K.H.; König, W. Small-Sized Low-Density Lipoproteins of Subclass B from Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease Effectively Augment Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Adhesive Properties in Human Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F. Protein damage and inflammation in uraemia and dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22 (Suppl. S5), v20–v36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroddi, M.; Depunzio, I.; Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C.; Aisa, C.M.; Binaglia, L.; Minelli, A.; Butterfield, A.D.; Galli, F. Oxidatively-Modified and Glycated Proteins as Candidate pro-Inflammatory Toxins in Uremia and Dialysis Patients. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Rovidati, S.; Chiarantini, L.; Campus, G.; Canestrari, F.; Buoncristiani, U. Bioreactivity and Biocompatibility of a Vitamin E-Modified Multilayer Hemodialysis Filter. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhitkovich, A. Ascorbate: Antioxidant and biochemical activities and their importance for in vitro models. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 3623–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, G.; Lecour, S.; Lahet, J.J.; Siohan, P.; Vergely, C.; Chevet, D.; Rifle, G.; Rochette, L. Alteration in Plasma Antioxidant Capacities in Chronic Renal Failure and Hemodialysis Patients: A Possible Explanation for the Increased Cardiovascular Risk in These Patients. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 47, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, G.; Lecour, S.; Cabanne, J.F.; Motte, G.; Guilland, J.C.; Chevet, D.; Rochette, L. Vitamin E-Coated Dialyzer Reduces Oxidative Stress in Hemodialysis Patients. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusepponi, D.; Torquato, P.; Bartolini, D.; Piroddi, M.; Birringer, M.; Lorkowski, S.; Libetta, C.; Cruciani, G.; Moretti, S.; Saluti, G.; et al. Determination of Tocopherols and Their Metabolites by Liquid-Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Human Plasma and Serum. Talanta 2017, 170, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, D.; Marinelli, R.; Giusepponi, D.; Galarini, R.; Barola, C.; Stabile, A.M.; Sebastiani, B.; Paoletti, F.; Betti, M.; Rende, M.; et al. Alpha-Tocopherol Metabolites (the Vitamin E Metabolome) and Their Interindividual Variability during Supplementation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torquato, P.; Ripa, O.; Giusepponi, D.; Galarini, R.; Bartolini, D.; Wallert, M.; Pellegrino, R.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; Birringer, M.; et al. Analytical Strategies to Assess the Functional Metabolome of Vitamin E. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 124, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquato, P.; Giusepponi, D.; Galarini, R.; Bartolini, D.; Piroddi, M.; Galli, F. Chapter 15: Analysis of Vitamin E Metabolites. In Food Chemistry, Function and Analysis; CPI Group: Croydon, UK, 2019; Volume 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Kane, J.; McMonagle, E.; Zaltas, E.; Bobzin, S.; Boddupalli, S.; Phinney, S.; Miller, G. Alpha and Gamma Tocopherol Metabolism in Healthy Subjects and Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Metabolism of natural forms of vitamin E and biological actions of vitamin E metabolites. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 179, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.; Leist, M.; Petrzika, M.; Gassmann, B.; Brigelius-Flohe, R. Novel Urinary Metabolite of α-Tocopherol, 2,5,7,8-Tetramethyl-2(2’- Carboxyethyl)-6-Hydroxychroman, as an Indicator of an Adequate Vitamin E Supply? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 1527S–1534S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Lee, R.; Dunster, C.; Atkinson, J.; Floridi, A.; Kelly, F.J. γ-Tocopherol Metabolism and Its Relationship with α-Tocopherol in Humans: A Stable Isotope Supplementation Study. BioFactors 2001, 15, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Lee, R.; Dunster, C.; Kelly, F.J. Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Carboxyethyl-Hydroxychroman Metabolites of α- and γ-Tocopherol in Human Plasma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usberti, M.; Gerardi, G.M.; Bufano, G.; Tira, P.; Micheli, A.; Albertini, A.; Floridi, A.; Di Lorenzo, D.; Galli, F. Effects of Erythropoietin and Vitamin E-Modified Membrane on Plasma Oxidative Stress Markers and Anemia of Hemodialyzed Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 40, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Lonn, E.M.; Yi, Q.; Gerstein, H.C.; Hoogwerf, B.J.; Pogue, J.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.R.; Yusuf, S. Effects of Vitamin E on Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Mild-to-Moderate Renal Insufficiency: Results of the HOPE Study. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L.F.; Kane, J.; McMonagle, E.; Le, P.; Wu, P.; Shintani, A.; Ikizler, T.A.; Himmelfarb, J. Effects of Combination Tocopherols and Alpha Lipoic Acid Therapy on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, K.; Naghibi, M.; Shabestari, M.; Sharifipour, F.; Dalooee, M.K.; Raeesi, V.; Nik, S.M.; Samadi, M. Evaluation the Effects of Alpha-Tocopherol in Comparison with n-Acetylcystein for Prevention of Contrast Induced Nephropathy (CIN) in CKD Patients. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 14, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolignano, D.; Cernaro, V.; Gembillo, G.; Baggetta, R.; Buemi, M.; D’Arrigo, G. Antioxidant Agents for Delaying Diabetic Kidney Disease Progression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koay, Y.Y.; Tan, G.C.J.; Phang, S.C.W.; Ho, J.I.; Chuar, P.F.; Ho, L.S.; Ahmad, B.; Kadir, K.A. A Phase Iib Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating the Effects of Tocotrienol-Rich Vitamin E on Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, A.; Tana, C.; El Hadi, H.; Pagano, C.; Vettor, R.; Rossato, M. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Metabolic Properties of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols: Clinical Implications for Vitamin E Supplementation in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asleh, R.; Briasoulis, A.; Berinstein, E.M.; Wiener, J.B.; Palla, M.; Kushwaha, S.S.; Levy, A.P. Meta-Analysis of the Association of the Haptoglobin Genotype with Cardiovascular Outcomes and the Pharmacogenomic Interactions with Vitamin E Supplementation. Pharm. Pers. Med. 2018, 11, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Ames, B.N. γ-Tocopherol, but Not α-tocopherol, Decreases Proinflammatory Eicosanoids and Inflammation Damage in Rats. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, K.; Benaksas, E.J.; Bolli, R.; Comp, P.; Grammas, P.; Hamdheydari, L.; Mou, S.; Pye, Q.N.; Stoddard, M.F.; Wallis, G.; et al. New Perspectives on Vitamin E: γ-Tocopherol and Carboxyethylhydroxychroman Metabolites in Biology and Medicine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaz, M.; Smetana, S.; Weinstein, T.; Matas, Z.; Gafter, U.; Iaina, A.; Knecht, A.; Weissgarten, Y.; Brunner, D.; Fainaru, M.; et al. Secondary Prevention with Antioxidants of Cardiovascular Disease in Endstage Renal Disease (SPACE): Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2000, 356, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, P.; Leggett, A.; Cardwell, C.R.; Woodside, J.V.; Thakkinstian, A.; Maxwell, A.P.; McKay, G.J. The Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation on Malondialdehyde as a Biomarker of Oxidative Stress in Haemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.U.; Yeom, J.H.; Kim, W. Beneficial Effects of Vitamin e Supplementation on Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, M.; Pieroni, L.; Di Liberato, L.; Sirolli, V.; Urbani, A. Examining Hemodialyzer Membrane Performance Using Proteomic Technologies. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlová, M.; Amorim, C.G.; Araújo, A.; Santos-Silva, A.; Solich, P.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. The Biocompatibility and Bioactivity of Hemodialysis Membranes: Their Impact in End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 22, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Ou, S.-M.; Lin, C.-C. Influence of Dialysis Membranes on Clinical Outcomes: From History to Innovation. Membranes 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroddi, M.; Pilolli, F.; Aritomi, M.; Galli, F. Vitamin E as a Functional and Biocompatibility Modifier of Synthetic Hemodialyzer Membranes: An Overview of the Literature on Vitamin E-Modified Hemodialyzer Membranes. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 35, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomo, T. Biocompatibility of Hemodiafilters. Contrib. Nephrol. 2016, 189, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Said, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ho, Y.C.; Lim, S.K.; Zainol Abidin, M.N.; Ismail, A.F. A Review of Commercial Developments and Recent Laboratory Research of Dialyzers and Membranes for Hemodialysis Application. Membranes 2021, 11, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitz, M.F.; Martins, M.C.L.; Grabow, N.; Matschegewski, C.; Huang, N.; Chaikof, E.L.; Barbosa, M.A.; Werner, C.; Sperling, C. The Blood Compatibility Challenge. Part 4: Surface Modification for Hemocompatible Materials: Passive and Active Approaches to Guide Blood-Material Interactions. Acta Biomater. 2019, 94, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A. A Critical Review of Recent Advances in Hemodialysis Membranes Hemocompatibility and Guidelines for Future Development. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 122911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridi, A.; Piroddi, M.; Pilolli, F.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aritomi, M.; Galli, F. Analysis Method and Characterization of the Antioxidant Capacity of Vitamin E-Interactive Polysulfone Hemodialyzers. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2974–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F. Vitamin E-Derived Copolymers Continue the Challenge to Hemodialysis Biomaterials. World J. Nephrol. 2012, 1, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Singh, P.; Khurana, S.; Ganguly, N.K.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Rana, D.S.; Taneja, V.; Bhargava, V. Implications of Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Review on Current Concepts and Therapies. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, M.A.; Balk, E.M.; Lau, J.; Liangos, O.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Madias, N.E.; Pereira, B.J.G.; Jaber, B.L. A Systematic Review of the Effect of the Excebrane Dialyser on Biomarkers of Lipid Peroxidation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, G.; Baggetta, R.; Tripepi, G.; Galli, F.; Bolignano, D. Effects of Vitamin E-Coated versus Conventional Membranes in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood Purif. 2017, 43, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelfarb, J. Oxidative Stress in Hemodialysis. In Hemodialysis—From Basic Research to Clinical Trials; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 161, pp. 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, C.C.; Racasan, S.; Kacso, I.M.; Moldovan, D.; Potra, A.; Patiu, I.M.; Vladutiu, D.; Caprioara, M.G. Malondialdehyde Can Predict Survival in Hemodialysis Patients. Clujul Med. 2016, 89, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, L.A.; Naso, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Pagnin, E.; Zanardo, M.; Puato, M.; Rebeschini, M.; Landini, S.; Feriani, M.; Perego, A.; et al. Molecular Biology-Based Assessment of Vitamin E-Coated Dialyzer Effects on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Vascular Remodeling. Artif. Organs 2011, 35, E33–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ribera, L.; Corredor, Z.; Silva, I.; Díaz, J.M.; Ballarín, J.; Marcos, R.; Pastor, S.; Coll, E. Vitamin E-Coated Dialysis Membranes Reduce the Levels of Oxidative Genetic Damage in Hemodialysis Patients. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2017, 815, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, N.; Schinzel, R.; Heidland, A.; Stopper, H. Genotoxicity of Advanced Glycation End Products: Involvement of Oxidative Stress and of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric, P.; Suvakov, S.; Simic, T.; Markovic, D.; Jerotic, D.; Jankovic, A.; Bulatovic, A.; Dragovic, J.T.; Damjanovic, T.; Marinkovic, J.; et al. Vitamin E-Bonded Membranes Do Not Influence Markers of Oxidative Stress in Hemodialysis Patients with Homozygous Glutathione Transferase M1 Gene Deletion. Toxins 2020, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Hung, S.C.; Wei, Y.H.; Tarng, D.C. GST M1 Polymorphism Associates with DNA Oxidative Damage and Mortality among Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.K.; Xiao, L.; Xu, B.; Xu, X.X.; Liu, F.Y.; Sun, L. Effects of Vitamin E-Coated Dialyzer on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Status in Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepe, V.; Gregorini, M.; Rampino, T.; Esposito, P.; Coppo, R.; Galli, F.; Libetta, C. Vitamin E-Loaded Membrane Dialyzers Reduce Hemodialysis Inflammaging. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A New Immune–Metabolic Viewpoint for Age-Related Diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, K.L.; Smith, L.M.; Heires, A.J.; Katafiasz, D.M.; Romberger, D.J.; LeVan, T.D. Aging Leads to Dysfunctional Innate Immune Responses to TLR2 and TLR4 Agonists. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, C. Nitric Oxide Synthase in Innate and Adaptive Immunity: An Update. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kiaii, M.; Aritomi, M.; Nagase, M.; Farah, M.; Jung, B. Clinical Evaluation of Performance, Biocompatibility, and Safety of Vitamin E-Bonded Polysulfone Membrane Hemodialyzer Compared to Non-Vitamin E-Bonded Hemodialyzer. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 22, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torato, T.; Doi, K.; Negishi, K.; Hamasaki, Y.; Satonaka, H.; Hanafusa, N.; Noiri, E. Efficacy of Vitamin E-Bonded Polysulfone Dialyzer and Polysulfone Dialyzer on a Series of Non-Anticoagulant Hemodialysis. ASAIO J. 2013, 59, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hassan, Z.A.; Chalmin, F.; Vido, S.; Berrada, M.; Verhelst, D.; Donnadieu, P.; Moranne, O.; Esnault, V.L.M. Vitamin E–Coated and Heparin-Coated Dialyzer Membranes for Heparin-Free Hemodialysis: A Multicenter, Randomized, Crossover Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, M.; Sasaki, H.; Sekizuka, K.; Sano, H.; Ogawa, K.; Shimizu, C.; Yoshida, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Koremoto, M.; Aritomi, M.; et al. Improved Management of Intradialytic Hypotension (IDH) Using Vitamin E-Bonded Polysulfone Membrane Dialyzer. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2010, 33, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolés, J.; Martín, L.; Broseta, J.J.; Cases, A. Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology and Current Treatments, to Future Agents. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 642296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T. Anemia of Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouridis, I.; Alfayez, M.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Balk, E.M.; Jaber, B.L. Dose of Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents and Adverse Outcomes in CKD: A Metaregression Analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yi, B.; Li, A.M.; Zhang, H. Effects of Vitamin E-Coated Dialysis Membranes on Anemia, Nutrition and Dyslipidemia Status in Hemodialysis Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Andrulli, S.; Viganò, S.M.; Concetti, M.; Urbini, S.; Giacchino, F.; Broccoli, R.; Aucella, F.; Cossu, M.; Conti, P.; et al. Evaluation of the Impact of a New Synthetic Vitamin E-Bonded Membrane on the Hypo-Responsiveness to the Erythropoietin Therapy in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter Study. Blood Purif. 2017, 43, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Ghibelli, L.; Buoncristiani, U.; Bordoni, V.; D’Intini, V.; Benedetti, S.; Canestrari, F.; Ronco, C.; Floridi, A. Mononuclear Leukocyte Apoptosis in Haemodialysis Patients: The Role of Cell Thiols and Vitamin E. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, V.; Piroddi, M.; Galli, F.; De Cal, M.; Bonello, M.; Dimitri, P.; Salvatori, G.; Ranishta, R.; Levin, N.; Tetta, C.; et al. Oxidant and Carbonyl Stress-Related Apoptosis in End-Stage Kidney Disease: Impact of Membrane Flux. Blood Purif. 2006, 24, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X. Abnormal Iron and Lipid Metabolism Mediated Ferroptosis in Kidney Diseases and Its Therapeutic Potential. Metabolites 2022, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engedal, N.; Žerovnik, E.; Rudov, A.; Galli, F.; Olivieri, F.; Procopio, A.D.; Rippo, M.R.; Monsurrò, V.; Betti, M.; Albertini, M.C. From Oxidative Stress Damage to Pathways, Networks, and Autophagy via MicroRNAs. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 4968321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.D.; Santos, S.S.; Meireles, T.; Romero, N.; Glorieux, G.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Zhang, D.D.; Nakao, L.S. Uremic Toxins Promote Accumulation of Oxidized Protein and Increased Sensitivity to Hydrogen Peroxide in Endothelial Cells by Impairing the Autophagic Flux. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bi, X.; Hu, C.; Ding, F.; Ding, W. Therapeutic Approaches in Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Inflammation, and Autophagy in Uremic Cachexia: Role of Aerobic Exercise. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 2789014–2789021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.P.; Han, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.H. Melatonin Rescues Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Senescence Induced by the Uremic Toxin. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooman, J.P.; Kotanko, P.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Shiels, P.G.; Stenvinkel, P. Chronic Kidney Disease and Premature Ageing. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, P.G.; Buchanan, S.; Selman, C.; Stenvinkel, P. Allostatic Load and Ageing: Linking the Microbiome and Nutrition with Age-Related Health. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.; Pawelzik, S.C.; Witasp, A.; Arefin, S.; Hobson, S.; Kublickiene, K.; Shiels, P.G.; Bäck, M.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation and Premature Ageing in Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2020, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
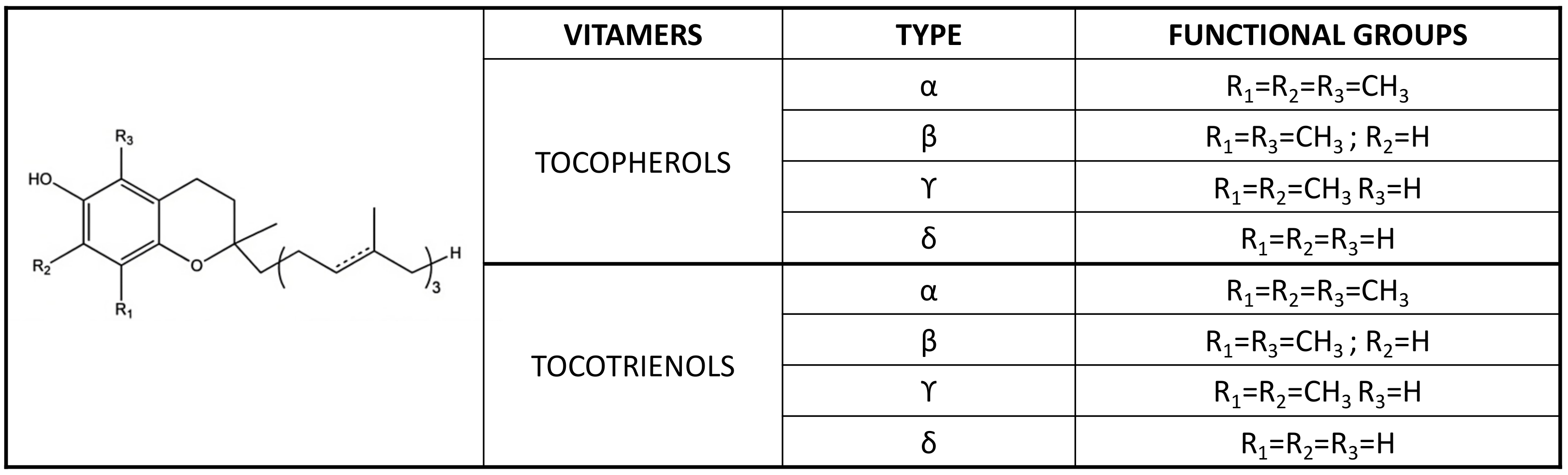

| Biological Function | Tocopherol Effect (Up ↑ or Down ↓ Regulation) | Gene Systems | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immune-inflammatory response and ferroptotic signaling: | α-TOH acetate ↓ | NFkB | [20,21] |
| Non-alpha LCMs ↓ (and to a lower extent α-LCMs) | LOX-5 and COXs | [22,23,24] | |
| α-TOH ↓ (possibly by conversion to α-tocopheryl hydroquinone) | LOX-15 | [25,26,27] | |
| Cholesterol homeostasis | γ-TOH and α-TOH ↑ | PPARγ | [28] |
| α-TOH ↓ | LXR (LXR-regulated receptors: CD36, ABCA1, ABCG1) | [29] | |
| Lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity-related inflammation | γ and α-TOH ↑ | PPARα | [30] |
| Garcinoic acid and α-LCMs ↑ | PPARγ | [31,32,33] | |
| Steroidogenesis | α-TOH ↑ | AP-1 and Ref-1 | [34] |
| Platelet aggregation | α-TOH↓ | GP IIb | [35] |
| Xenobiotic detoxification | T3 ↑ LCMs ↑ (particularly δ-T3-13COOH or garcinoic acid) | PXR (PXR-regulated genes: CYP3A4 Pgp) | [36,37] |
| Estrogen receptor | T3 ↑ | Erβ (Erβ-regulated genes: MIC-1, ECR-1 and cathepsin D) | [38] |
| Parameters | Healthy Controls | CDK Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | pa | |
| α-TOH (nM) | 31,014 | 6535 | 23,873 | 8381 | * |
| α-TQ (nM) | 180 | 73 | 266 | 151 | Ns |
| α-13′-OH (nM) | 3.9 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 0.93 | ** |
| M3 (nM) | 1.8 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 1.1 | Ns |
| Sum 13′-α-OH + M3 (nM) | 4.8 | 1.3 | 4.1 | 1.6 | Ns |
| α-13′-COOH (nM) | 1.8 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.3 | Ns |
| M1 (nM) | 47.8 | 36.6 | 4.5 | 5.7 | ** |
| M2 (nM) | 7.4 | 7.5 | 5.2 | 3.0 | Ns |
| Sum α-13′-COOH + M1 + M2 (nM) | 57.0 | 33.6 | 11.5 | 8.1 | ** |
| α-CEHC (nM) | 25.5 | 12.6 | 288 | 241 | * |
| ϒ-TOH (nM) | 618 | 73 | 862 | 411 | * |
| ϒ-CEHC (nM) | 122 | 59 | 645 | 392 | ** |
| Sum α-LA + ϒ-LA (nM) | 3184 | 1165 | 2851 | 3139 | Ns |
| EPA (nM) | 324 | 202 | 215 | 198 | Ns |
| DHA (nM) | 2363 | 501 | 1842 | 843 | * |
| AA (nM) | 3109 | 498 | 3532 | 1629 | Ns |
| 20-COOH-AA (nM) | 21 | 16 | 8.2 | 8.9 | ** |
| 20-COOH-AA/AA × 1000 | 7.8 | 4.4 | 2.3 | 2.1 | ** |
| EPA/DHA | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.05 | Ns |
| AA/DHA | 1.4 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 0.5 | ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galli, F.; Bonomini, M.; Bartolini, D.; Zatini, L.; Reboldi, G.; Marcantonini, G.; Gentile, G.; Sirolli, V.; Di Pietro, N. Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol) Metabolism and Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050989
Galli F, Bonomini M, Bartolini D, Zatini L, Reboldi G, Marcantonini G, Gentile G, Sirolli V, Di Pietro N. Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol) Metabolism and Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(5):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050989
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalli, Francesco, Mario Bonomini, Desirée Bartolini, Linda Zatini, Gianpaolo Reboldi, Giada Marcantonini, Giorgio Gentile, Vittorio Sirolli, and Natalia Di Pietro. 2022. "Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol) Metabolism and Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease" Antioxidants 11, no. 5: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050989
APA StyleGalli, F., Bonomini, M., Bartolini, D., Zatini, L., Reboldi, G., Marcantonini, G., Gentile, G., Sirolli, V., & Di Pietro, N. (2022). Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol) Metabolism and Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants, 11(5), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050989








