Selenium Status in Diet Affects Nephrotoxicity Induced by Cisplatin in Mice
Abstract
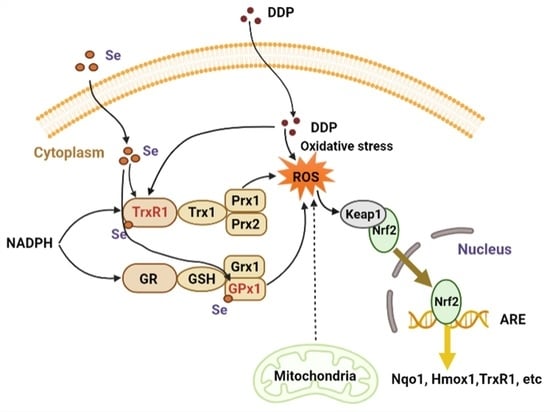
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals and Drug Administration
2.3. Serum AST, ALT, CREA, and UREA Detection
2.4. Histological Analyses
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Measurement of TrxR Activity and GSH Level
2.7. Detection of GPx Activity
2.8. Detection of Elements Content
2.9. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dietary Selenium Altered Serum and Kidney Selenium Levels
3.2. Selenium Status Affected Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity
3.3. Increased Selenoenzyme Activity Mediated Oxidative Stress
3.4. Effect of Selenium Level on Redox Regulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Dasari, S.; Noubissi, F.K.; Ray, P.; Kumar, S. Advances in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of action of cisplatin in cancer therapy. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 13, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, I.A. Cisplatin and oxaliplatin: Our current understanding of their actions. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2018, 18, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, G.P. Cisplatin: Process and future. J. BUON 2013, 18, 564–569. [Google Scholar]
- Marcato, P.D.; Fávaro, W.J.; Durán, N. Cisplatin properties in a nanobiotechnological approach to cancer: A mini-review. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2014, 14, 458–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strojan, P.; Vermorken, J.B.; Beitler, J.J.; Saba, N.F.; Haigentz, M., Jr.; Bossi, P.; Worden, F.P.; Langendijk, J.A.; Eisbruch, A.; Mendenhall, W.M.; et al. Cumulative cisplatin dose in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. S1), E2151–E2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Roth, B.J. Cisplatin in the management of breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 1989, 16, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, M.E.; Davis, L.E.; DeStefano, M.; Abrahm, J. Cisplatin: A clinical review. Part I--Current uses of cisplatin and administration guidelines. Cancer Nurs. 1994, 17, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.D.; Okabe, M.; Shen, D.W.; Liang, X.J.; Gottesman, M.M. The role of cellular accumulation in determining sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 495–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovec, T. Cisplatin and beyond: Molecular mechanisms of action and drug resistance development in cancer chemotherapy. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Ayed, W.; Ben Said, A.; Hamdi, A.; Mokrani, A.; Masmoudi, Y.; Toukabri, I.; Limayem, I.; Yahyaoui, Y. Toxicity, risk factors and management of cisplatin-induced toxicity: A prospective study. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F. Advances in toxicological research of the anticancer drug cisplatin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1469–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabas, K.; Milner, R.; Lurie, D.; Adin, C. Cisplatin: A review of toxicities and therapeutic applications. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2008, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, M.E.; Davis, L.; Abrahm, J. Cisplatin: A clinical review. Part II--Nursing assessment and management of side effects of cisplatin. Cancer Nurs. 1994, 17, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.A.; Catão, C.S.; Martins, N.M.; Curti, C.; Bianchi, M.L.; Santos, A.C. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is associated with oxidative stress, redox state unbalance, impairment of energetic metabolism and apoptosis in rat kidney mitochondria. Arch. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, R.; Ueda, N.; Walker, P.D.; Shah, S.V. Oxidant mechanisms in toxic acute renal failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1997, 29, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, A.G.; Harvat, M.; Vicente-Vicente, L.; Pellicer-Valero, O.J.; Morales, A.I.; Lopez-Hernandez, F.J.; Martin-Guerrero, J.D. Regression Modeling of the Antioxidant-to-Nephroprotective Relation Shows the Pivotal Role of Oxidative Stress in Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.; Leung, N. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review of the literature. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, R.; Zhang, Z.; Baliga, M.; Ueda, N.; Shah, S.V. Role of cytochrome P-450 as a source of catalytic iron in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Z.W.; Tew, K.D.; Townsend, D.M. Cisplatin chemotherapy and renal function. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 152, 305–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. Glutathione and glutaredoxin act as a backup of human thioredoxin reductase 1 to reduce thioredoxin 1 preventing cell death by aurothioglucose. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38210–38219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fourquet, S.; Guerois, R.; Biard, D.; Toledano, M.B. Activation of NRF2 by nitrosative agents and H2O2 involves KEAP1 disulfide formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8463–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hariharan, S.; Dharmaraj, S. Selenium and selenoproteins: It’s role in regulation of inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 667–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Lin, F.; Liu, L.; Mu, Y.; Yan, G.; Luo, G. Comparison between the effects of 2-selenium bridged β-cyclodextrin and ebselen on treating SHRsp stroke. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2008, 24, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryukov, G.V.; Castellano, S.; Novoselov, S.V.; Lobanov, A.V.; Zehtab, O.; Guigo, R.; Gladyshev, V.N. Characterization of mammalian selenoproteomes. Science 2003, 300, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burk, R.F. Selenium, an antioxidant nutrient. Nutr. Clin. Care 2002, 5, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełczykowska, M.; Kocot, J.; Paździor, M.; Musik, I. Selenium—A fascinating antioxidant of protective properties. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.E.; McCollum, G.W.; Boeglin, M.E.; Burk, R.F. Thioredoxin reductase activity is decreased by selenium deficiency. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotruck, J.T.; Pope, A.L.; Ganther, H.E.; Swanson, A.B.; Hafeman, D.G.; Hoekstra, W.G. Selenium: Biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 1973, 179, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, L. Selenium, selenoproteins and the thyroid gland: Interactions in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 8, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, L.V.; Holmgren, A.; Khanna, K.K. Selenium and selenoproteins in health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T. Functionalized selenium nanoparticles with nephroprotective activity, the important roles of ROS-mediated signaling pathways. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 6365–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Yuan, Z.; He, L.; Chen, T. Facile synthesis of antioxidative nanotherapeutics using a microwave for efficient reversal of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Omidvar, B.; Parsi, A. Protective effect of selenium on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity: A double-blind controlled randomized clinical trial. J. Nephropathol. 2013, 2, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nematbakhsh, M.; Nasri, H. The effects of vitamin E and selenium on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in cancer patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013, 18, 626–627. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, L.M.; Darin, J.D.; Bianchi Nde, L. Effects of the antioxidants curcumin or selenium on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and lipid peroxidation in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 43, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Pi, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zang, S.; Li, X.; Fu, A.; Ren, X.; Xu, J.; et al. Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase 1 correlates with platinum-based chemotherapeutic induced tissue injury. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 175, 113873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnér, E.S.; Holmgren, A. Measurement of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esworthy, R.S.; Chu, F.F.; Doroshow, J.H. Analysis of glutathione-related enzymes. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cheng, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, P.; Han, B.; Ren, X.; Zhong, J.L.; Lloyd, M.D.; Pourzand, C.; Holmgren, A.; et al. Selenium status in diet affects acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via interruption of redox environment. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 34, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biasi, A.R.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Adusumilli, P.S. Cisplatin-induced antitumor immunomodulation: A review of preclinical and clinical evidence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5384–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, D.J.; Molepo, J.M.; Eapen, L.; Montpetit, V.A.; Goel, R.; Wong, P.T.; Popovic, P.; Taylor, K.D.; Raaphorst, G.P. Cisplatin and radiation in the treatment of tumors of the central nervous system: Pharmacological considerations and results of early studies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 28, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, E.E.; Essigmann, J.M. Cisplatin. Essays Biochem. 1999, 34, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieja, K.; Talerczyk, M. Selenium as an element in the treatment of ovarian cancer in women receiving chemotherapy. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 93, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkoshi, A.; Ishii, R.; Wakamori, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Higashi, K.; Nakanome, A.; Ogawa, T.; Katori, Y. Serum selenium predicts achievement of full-dose cisplatin in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective, observational study. Oral. Oncol. 2021, 121, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Shao, F. Daphnetin protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, R.M.; Abo El Gheit, R.E.; Badawi, G.A. Vincamine protects against cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 and hindering TLR4/ IFN-gamma/CD44 cells inflammatory cascade. Life Sci. 2021, 272, 119224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, N.; Badavi, M.; Mard, S.A.; Dianat, M.; Moghadam, M.T. The renoprotective effects of gallic acid on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammatory effects, and downregulation of lncRNA TUG1. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Pei, C.; Olatunji, O.J.; Tang, J.; Famurewa, A.C.; Wang, H.; Yan, B. Protective Effects of Nucleosides-Rich Extract from Cordyceps cicadae against Cisplatin Induced Testicular Damage. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrill, A.H.; Lin, H.; Tobacyk, J.; Seely, J.C. Mouse population-based evaluation of urinary protein and miRNA biomarker performance associated with cisplatin renal injury. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, A.; Oda, K.; Mori, N.; Murakami, T. Modulated function of multidrug resistance-associated proteins in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure rats. Pharmazie 2017, 72, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Guo, Y.; Huang, T.S.; Zhao, J.; Huang, X.J.; Tang, H.X.; An, N.; Pan, Q.; Xu, Y.Z.; Liu, H.F. Asiatic acid protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jongh, F.E.; van Veen, R.N.; Veltman, S.J.; de Wit, R.; van der Burg, M.E.; van den Bent, M.J.; Planting, A.S.; Graveland, W.J.; Stoter, G.; Verweij, J. Weekly high-dose cisplatin is a feasible treatment option: Analysis on prognostic factors for toxicity in 400 patients. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, D.B.; Cha, M.H.; Won, D.H.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, Y.Y.; Yun, J.W. Transcriptomic analysis of rat kidney reveals a potential mechanism of sex differences in susceptibility to cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 174, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Koizumi, W.; Nishikawa, K.; Gotoh, M.; Fuse, N.; Sugimoto, N.; Nishina, T.; Amagai, K.; Chin, K.; Niwa, Y.; et al. Sex differences in the safety of S-1 plus oxaliplatin and S-1 plus cisplatin for patients with metastatic gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| No. | Gene | Sequence (F) | Sequence (R) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI: 123701799 | Trx1 | CATGCCGACCTTCCAGTTTTA | TTTCCTTGTTAGCACCGGAGA |
| GI: 110224446 | TrxR1 | CCCACTTGCCCCAACTGTT | GGGAGTGTCTTGGAGGGAC |
| GI:1212477963 | TrxR2 | GATCCGGTGGCCTAGCTTG | TCGGGGAGAAGGTTCCACAT |
| GI:1335348593 | Grx1 | GCTCAGGAGTTTGTGAACTGC | AGAAGACCTTGTTTGAAAGGCA |
| GI:1043678440 | GPx1 | AGTCCACCGTGTATGCCTTCT | GAGACGCGACATTCTCAATGA |
| GI:1547242143 | GPx4 | GCCTGGATAAGTACAGGGGTT | CATGCAGATCGACTAGCTGAG |
| GI: 254553443 | Txnip | TCTTTTGAGGTGGTCTTCAACG | GCTTTGACTCGGGTAACTTCACA |
| GI: 195947362 | Hmox-1 | AAGCCGAGAATGCTGAGTTCA | GCCGTGTAGATATGGTACAAGGA |
| GI: 161621259 | Nqo-1 | AGGATGGGAGGTACTCGAATC | AGGCGTCCTTCCTTATATGCTA |
| GI: 576080554 | GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Wen, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Lu, J. Selenium Status in Diet Affects Nephrotoxicity Induced by Cisplatin in Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061141
Liu S, Wen X, Huang Q, Zhu M, Lu J. Selenium Status in Diet Affects Nephrotoxicity Induced by Cisplatin in Mice. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(6):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuang, Xing Wen, Qihan Huang, Minghui Zhu, and Jun Lu. 2022. "Selenium Status in Diet Affects Nephrotoxicity Induced by Cisplatin in Mice" Antioxidants 11, no. 6: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061141
APA StyleLiu, S., Wen, X., Huang, Q., Zhu, M., & Lu, J. (2022). Selenium Status in Diet Affects Nephrotoxicity Induced by Cisplatin in Mice. Antioxidants, 11(6), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061141