Hydrogen Sulfide Regulates Irisin and Glucose Metabolism in Myotubes and Muscle of HFD-Fed Diabetic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Dietary Treatment
2.2. Cell Culture, Gene Silencing, and Treatments
2.3. Analysis of mRNA Expression Using Quantitative PCR and Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Hydrogen Sulfide Measurements
2.5. Glucose Uptake Assays
2.6. GSH, Protein Carbonyl, MDA, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Irisin Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
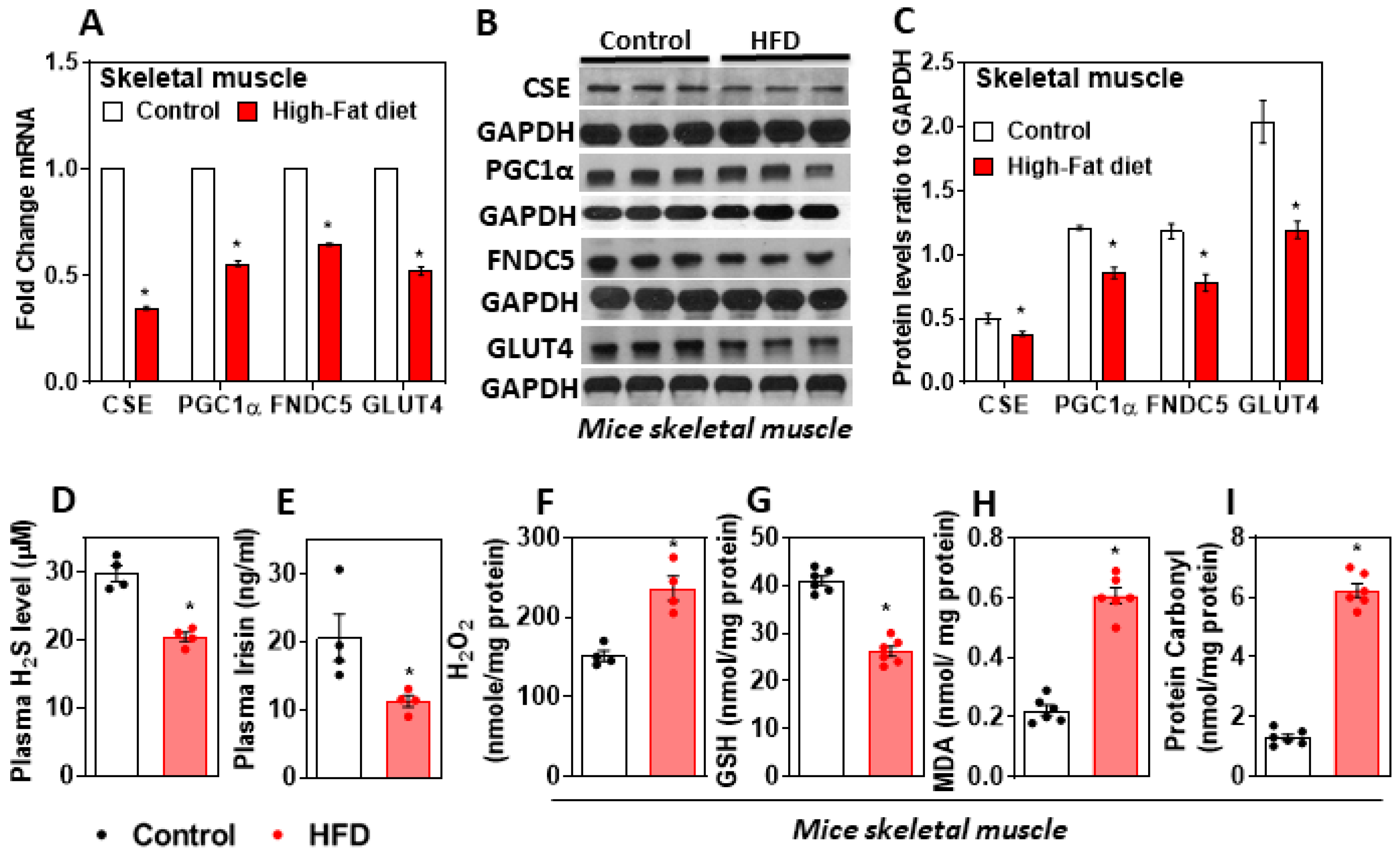
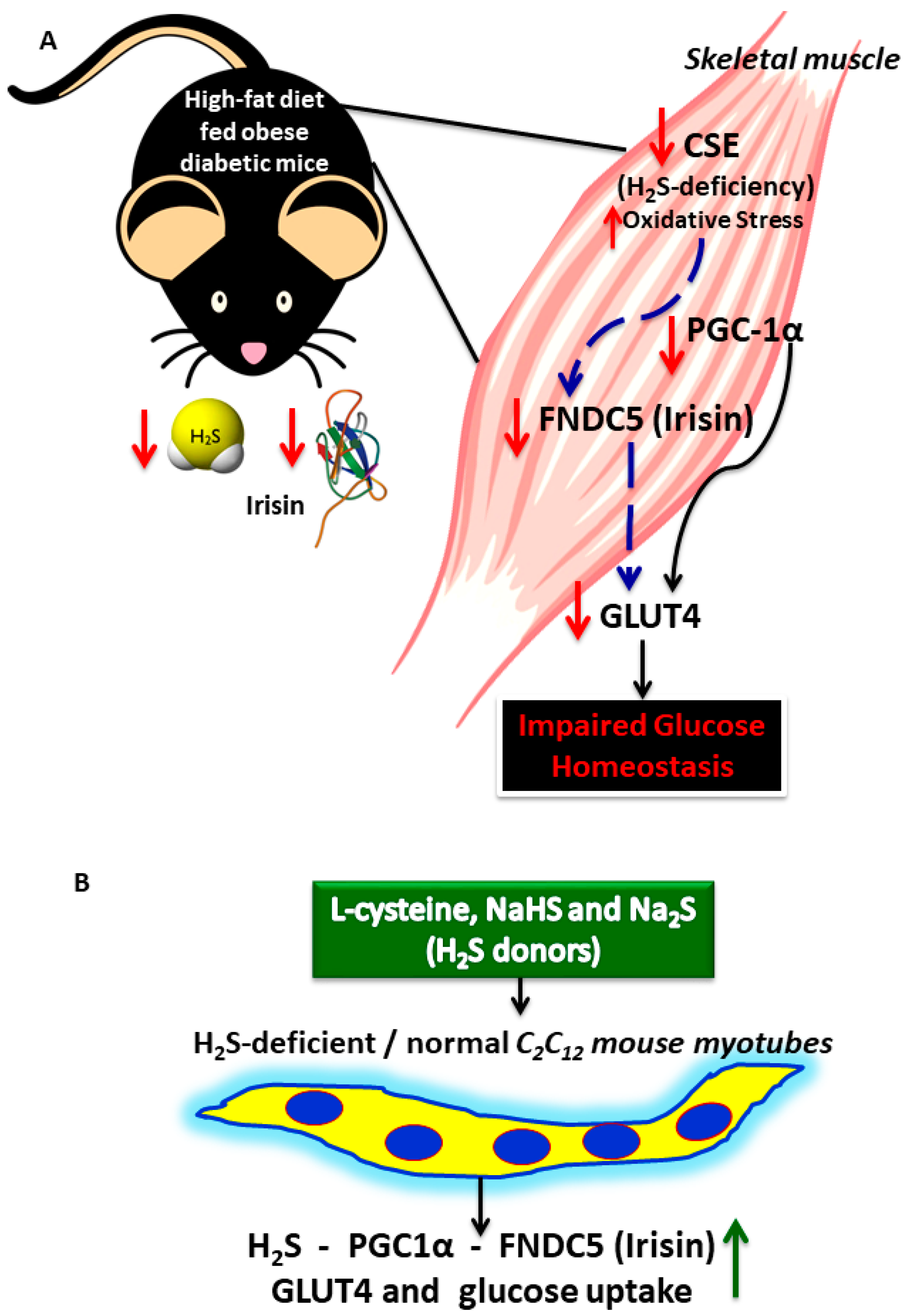
3.1. H2S Deficiency Impairs FNDC5/Irisin in the Skeletal Muscle of HFD-Fed Mice
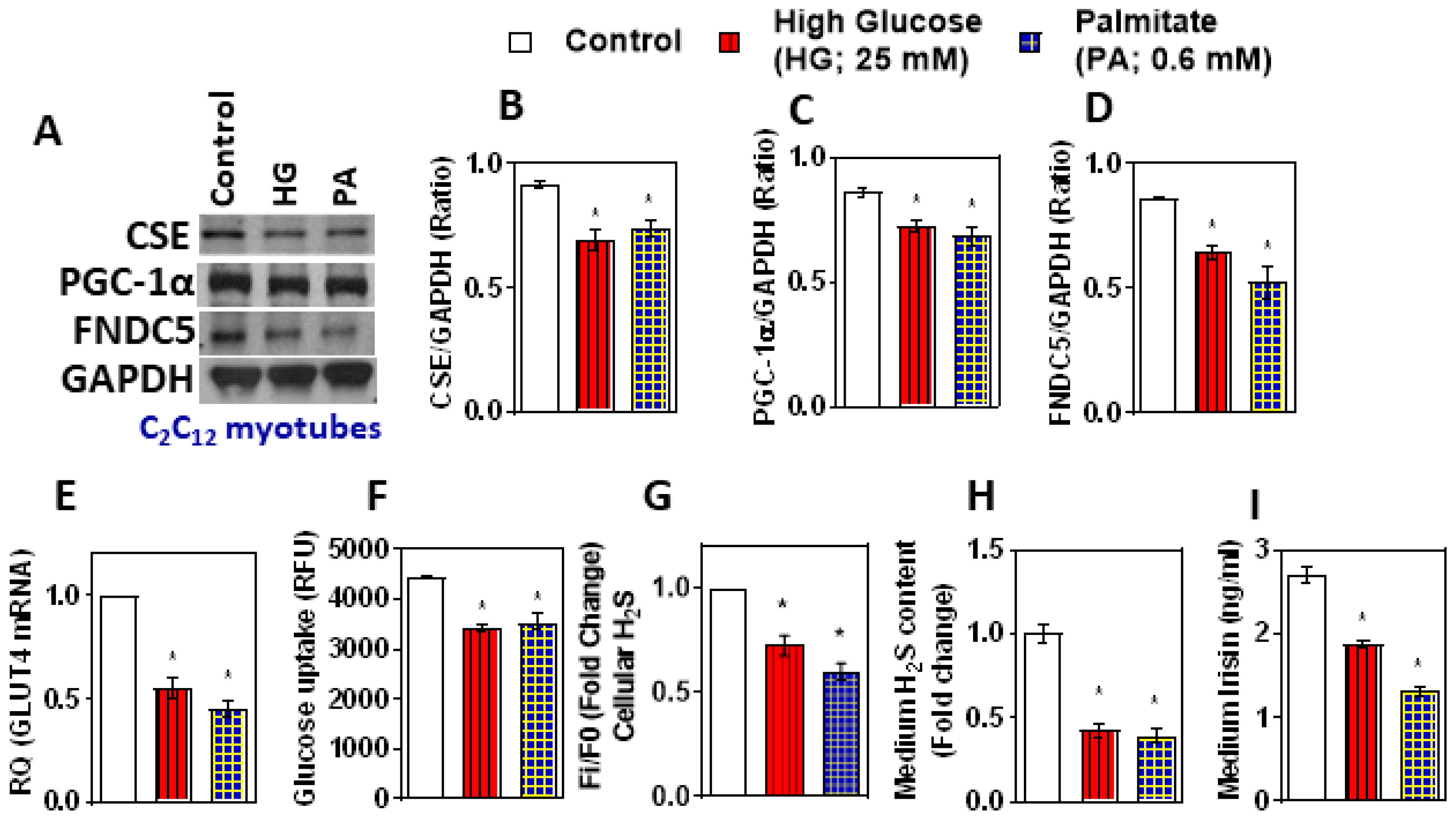
3.2. Treatment with High Glucose and Palmitate Affects H2S Levels and FNDC5/Irisin Expression and Secretion in In Vitro myotubes
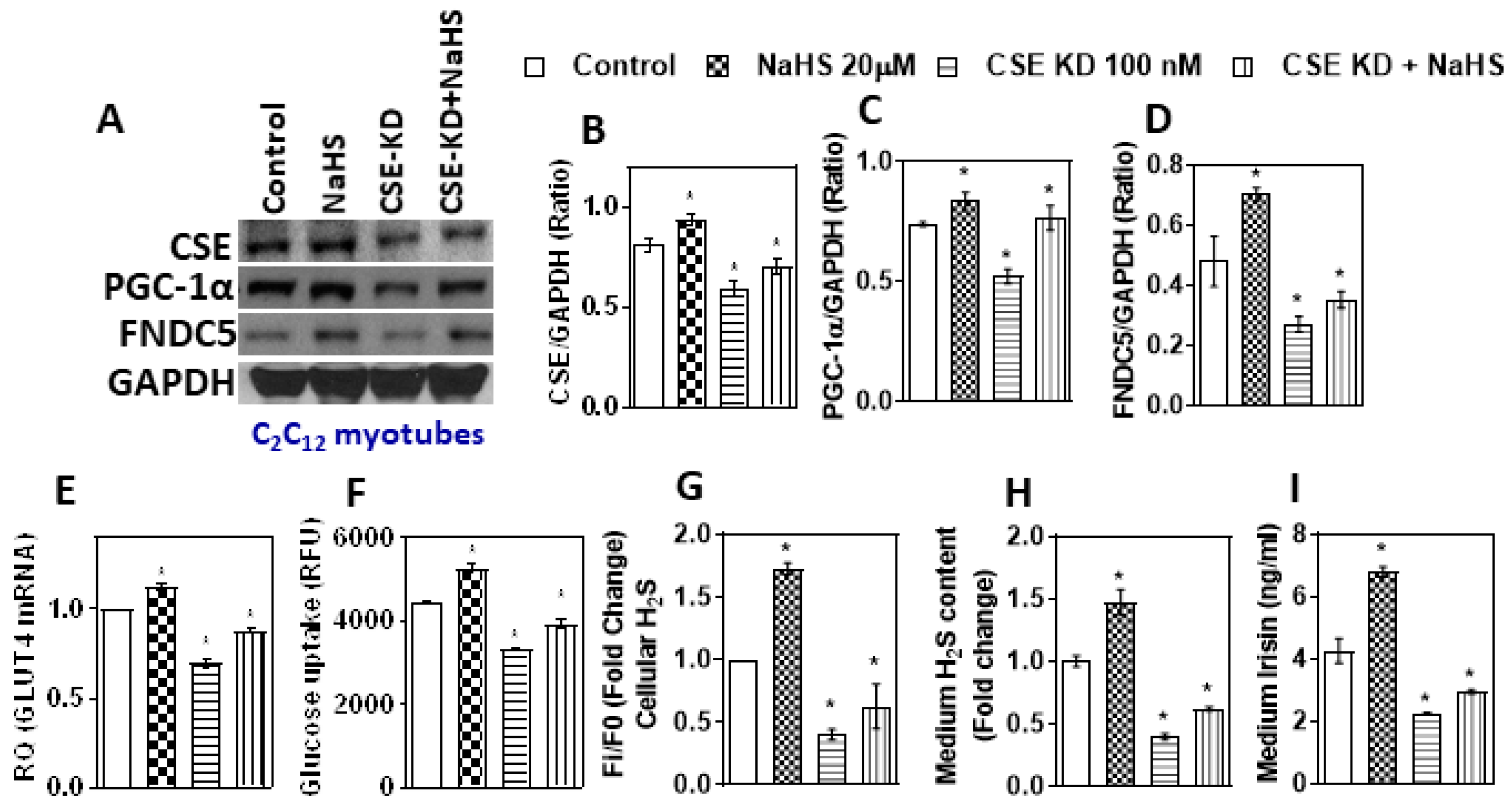
3.3. Inhibition of H2S Production Reduces Irisin and Glucose Uptake
3.4. CSE Knockdown Affects the PGC-1α Mediated Uptake of Irisin, GLUT4, and Glucose
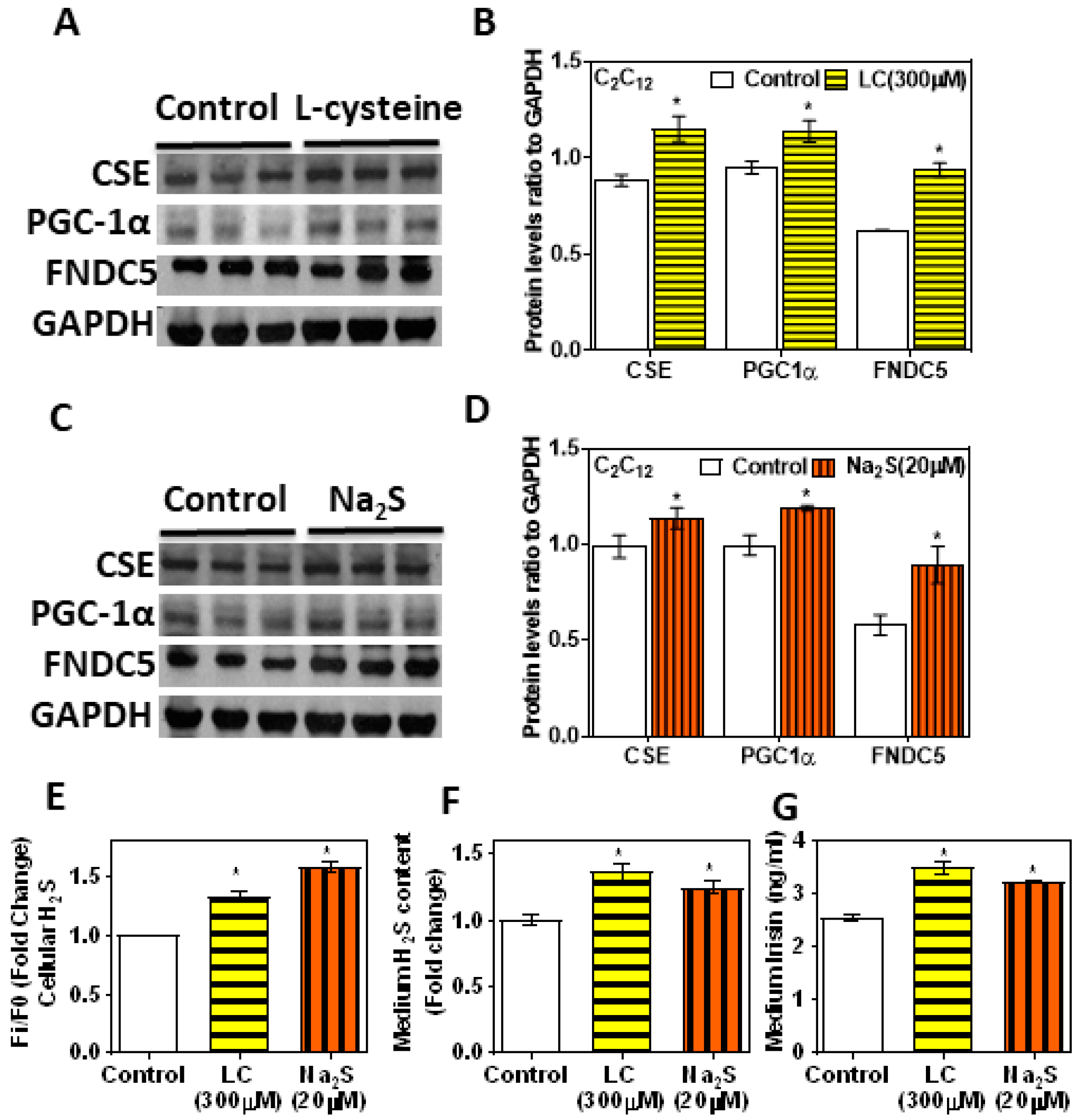
3.5. H2S Donors/Precursor (NaHS/Na2S/LC) Positively Regulate PGC-1α, Irisin, and GLUT4 Mediated Glucose Uptake in Myoblasts
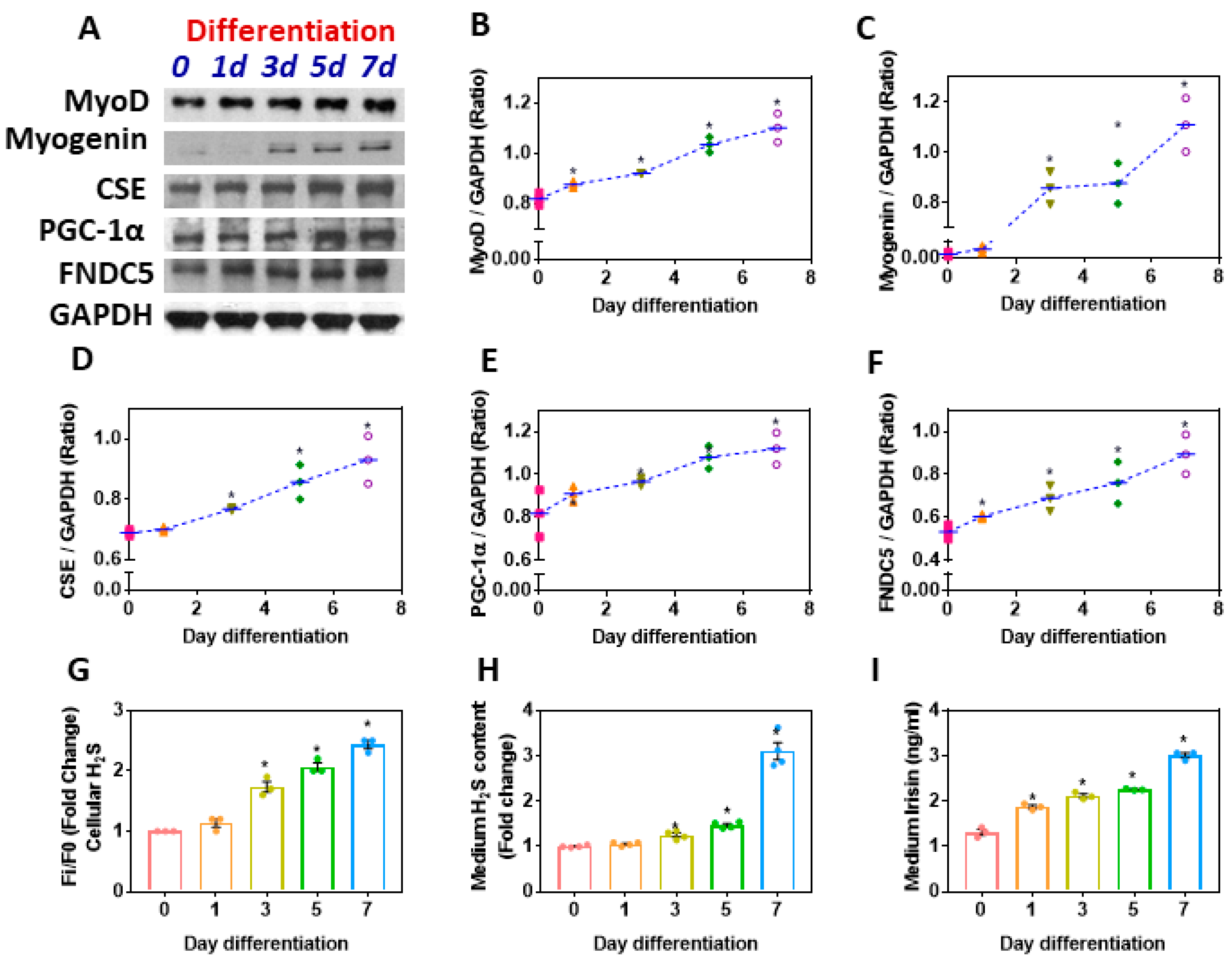
3.6. Myoblast Differentiation Synergistically Upregulates CSE-H2S and the PGC-1α-FNDC5/Irisin Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, P.; Balasubramanian, K. Phthalate exposure in utero causes epigenetic changes and impairs insulin signalling. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Seshasai, S.R.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubak, M.P.; Heesch, M.W.; Shute, R.J.; Dinan, N.E.; Laursen, T.L.; La Salle, D.T.; Slivka, D.R. Irisin and Fibronectin Type III Domain-Containing 5 Responses to Exercise in Different Environmental Conditions. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 10, 666–680. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, Y.; Gleitsmann, K.; Mangner, N.; Werner, S.; Fischer, T.; Bowen, T.S.; Kricke, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kurabayashi, M.; Schuler, G.; et al. Fibronectin type III domain containing 5 expression in skeletal muscle in chronic heart failure-relevance of inflammatory cytokines. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Wong, M.D.; Toy, W.C.; Tan, C.S.; Liu, S.; Ng, X.W.; Tavintharan, S.; Sum, C.F.; Lim, S.C. Lower circulating irisin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2013, 27, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-K.; Kim, M.-K.; Bae, K.H.; Seo, H.-A.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Lee, W.-K.; Kim, J.-G.; Lee, I.-K.; Park, K.-G. Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 100, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdiova, T.; Balaz, M.; Vician, M.; Maderova, D.; Vlcek, M.; Valkovic, L.; Srbecky, M.; Imrich, R.; Kyselovicova, O.; Belan, V.; et al. Effects of obesity, diabetes and exercise on Fndc5 gene expression and irisin release in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: In vivo and in vitro studies. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Liu, S.; Wong, M.D.; Tan, C.S.; Tavintharan, S.; Sum, C.F.; Lim, S.C. Relationship between circulating irisin, renal function and body composition in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2014, 28, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, P.; Chen, S.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, Q.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Cao, X.-H.; Ren, M.; Wang, J.-K. The association of new inflammatory markers with type 2 diabetes mellitus and macrovascular complications: A preliminary study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Chen, P.; Jin, H.; Xie, X.; Gao, T.; Yang, L.; Yu, X. Circulating levels of irisin in middle-aged first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus—correlation with pancreatic β-cell function. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.J.; Serrano, M.; Guerra, E.; Pardo, G.; Tinahones, F.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Irisin Is Expressed and Produced by Human Muscle and Adipose Tissue in Association with Obesity and Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E769–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Rose, P.; Moore, P.K. Hydrogen Sulfide and Cell Signaling. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Minkler, P.; Grove, D.; Wang, R.; Willard, B.; Dweik, R.; Hine, C. Non-enzymatic hydrogen sulfide production from cysteine in blood is catalyzed by iron and vitamin B6. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.K.; Micinski, D.; Lieblong, B.J.; Stapleton, T. Relationship between hydrogen sulfide levels and HDL-cholesterol, adiponectin, and potassium levels in the blood of healthy subjects. Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichette, J.; Fynn-Sackey, N.; Gagnon, J. Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfate Prebiotic Stimulates the Secretion of GLP-1 and Improves Glycemia in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3416–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsanathan, R.; Jain, S.K. Hydrogen sulfide increases glutathione biosynthesis, and glucose uptake and utilisation in C2C12 mouse myotubes. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padiya, R.; Khatua, T.N.; Bagul, P.K.; Kuncha, M.; Banerjee, S.K. Garlic improves insulin sensitivity and associated metabolic syndromes in fructose fed rats. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsanathan, R.; Jain, S.K. Glutathione deficiency alters the vitamin D-metabolizing enzymes CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 in human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells and kidney of HFD-fed mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 131, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Cai, B.; Liao, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Fan, X.; Gong, Y.; Yang, J.; Cui, Q.H.; Tang, C.; et al. Increase or Decrease Hydrogen Sulfide Exert Opposite Lipolysis, but Reduce Global Insulin Resistance in High Fatty Diet Induced Obese Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Peh, M.T.; Feng, W.; Dymock, B.W.; Moore, P.K. Hydrogen Sulfide Promotes Adipogenesis in 3T3L1 Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Feng, W.; Peh, M.T.; Peh, K.; Dymock, B.W.; Moore, P.K. A novel slow-releasing hydrogen sulfide donor, FW1256, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in mouse macrophages and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsouda, A.; Szabo, C.; Papapetropoulos, A. Reduced adipose tissue H2S in obesity. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, M.; Terzuoli, E.; Ziche, M.; Morbidelli, L. H2S dependent and independent anti-inflammatory activity of zofenoprilat in cells of the vascular wall. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longen, S.; Beck, K.-F.; Pfeilschifter, J. H2S-induced thiol-based redox switches: Biochemistry and functional relevance for inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcicka, G.; Jamroz-Wiśniewska, A.; Atanasova, P.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Chylińska-Kula, B.; Bełtowski, J. Differential effects of statins on endogenous H2S formation in perivascular adipose tissue. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Suguro, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhu, Y.Z. Hydrogen sulfide stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, C.K.; Calvert, J.W. Hydrogen sulfide and ischemia–reperfusion injury. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichette, J.; Gagnon, J. Implications of Hydrogen Sulfide in Glucose Regulation: How H2S Can Alter Glucose Homeostasis through Metabolic Hormones. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3285074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ates, I.; Kaplan, M.; Yuksel, M.; Mese, D.; Alisik, M.; Erel, Ö.; Yilmaz, N.; Guler, S. Determination of thiol/disulphide homeostasis in type 1 diabetes mellitus and the factors associated with thiol oxidation. Endocrine 2015, 51, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, I.; Kaplan, M.; Inan, B.; Alısık, M.; Erel, O.; Yilmaz, N.; Guler, S. How does thiol/disulfide homeostasis change in prediabetic patients? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 110, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Han, J.; Lu, H.; Cui, C.; Yang, J.; Cui, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, C.; Xu, G.; et al. Cystathionine beta synthase-hydrogen sulfide system in paraventricular nucleus reduced high fatty diet induced obesity and insulin resistance by brain-adipose axis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3281–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Ju, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Racine, M.; Baath, S.; Merritt, T.J.; Wang, R.; Wu, L. Cystathionine gamma-lyase/hydrogen sulfide system is essential for adipogenesis and fat mass accumulation in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, A.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, G.; Gupta, A.; Keshri, G.K.; Bharti, B.; Meena, R.N.; Prabhakar, A.K.; Singh, D.; Bhargava, K.; et al. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is critical for suppression of cardiac hypertrophy by H2S. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Sun, X.; Yu, M.; Dong, S.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W.; et al. Exogenous H2S Protects Against Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Activating Autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1168–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Untereiner, A.; Wu, L. Hydrogen Sulfide and Glucose Homeostasis: A Tale of Sweet and the Stink. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 1463–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.; Gungor, N.; McVie, R.; Jain, S.K. Decreased Cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE) Activity in Livers of Type 1 Diabetic Rats and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) of Type 1 Diabetic Patients. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11767–11778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. L-cysteine and hydrogen sulfide increase PIP3 and AMPK/PPARγ expression and decrease ROS and vascular inflammation markers in high glucose treated human U937 monocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 2334–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Kahlon, G.; Morehead, L.; Lieblong, B.; Stapleton, T.; Hoeldtke, R.; Bass, P.F.; Levine, S.N. The Effect of Sleep Apnea and Insomnia on Blood Levels of Leptin, Insulin Resistance, IP-10, and Hydrogen Sulfide in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2012, 10, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.K.; Bull, R.; Rains, J.L.; Bass, P.F.; Levine, S.N.; Reddy, S.; McVie, R.; Bocchini, J.A. Low Levels of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Blood of Diabetes Patients and Streptozotocin-Treated Rats Causes Vascular Inflammation? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteman, M.; Gooding, K.M.; Whatmore, J.L.; Ball, C.I.; Mawson, D.; Skinner, K.; Tooke, J.E.; Shore, A.C. Adiposity is a major determinant of plasma levels of the novel vasodilator hydrogen sulphide. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manna, P.; Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Vitamin D supplementation inhibits oxidative stress and upregulate SIRT1/AMPK/GLUT4 cascade in high glucose-treated 3T3L1 adipocytes and in adipose tissue of high fat diet-fed diabetic mice. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 615, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsanathan, R.; Jain, S.K. Hydrogen sulfide regulates circadian-clock genes in C2C12 myotubes and the muscle of high-fat-diet-fed mice. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 672, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsanathan, R.; Jain, S.K. Glutathione deficiency induces epigenetic alterations of vitamin D metabolism genes in the livers of high-fat diet-fed obese mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Ho, P.; Loke, Y.Y.; Huang, S.H.; Tan, C.S.; Whiteman, M.; Lu, J.; Moore, P.K. Hydrogen sulfide and its possible roles in myocardial ischemia in experimental rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.-W.; Ha, H.-H.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Y.-T.; Williams, D.R. Novel use of fluorescent glucose analogues to identify a new class of triazine-based insulin mimetics possessing useful secondary effects. Mol. BioSyst. 2010, 7, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giuffrè, A.; Vicente, J.B. Hydrogen Sulfide Biochemistry and Interplay with Other Gaseous Mediators in Mammalian Physiology. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6290931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizaw, M.; Anandakumar, P.; Debela, T. A Review on the Role of Irisin in Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Pharmacopunct. 2017, 20, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L.; Nagy, P.; Feener, T.D.; Allain, T.; Ditrói, T.; Vaughan, D.J.; Muscara, M.N.; de Nucci, G.; Buret, A.G. A proof-of-concept, Phase 2 clinical trial of the gastrointestinal safety of a hydrogen sulfide-releasing anti-inflammatory drug. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 177, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarević, M.; Battaglia, G.; Jevtić, B.; Djedovic, N.; Bruno, V.; Cavalli, E.; Miljković, Đ.; Nicoletti, F.; Momčilović, M.; Fagone, P. Upregulation of Tolerogenic Pathways by the Hydrogen Sulfide Donor GYY4137 and Impaired Expression of H2S-Producing Enzymes in Multiple Sclerosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Bramanti, P.; Bendtzen, K.; Nicoletti, F. Gasotransmitters and the immune system: Mode of action and novel therapeutic targets. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, C. Exogenous H2S prevents high glucose-induced damage to osteoblasts through regulation of KATP channels. Biochimie 2017, 137, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yang, G.; Jia, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, R. Activation of KATP channels by H2S in rat insulin-secreting cells and the underlying mechanisms. J. Physiol. 2005, 569, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Q.C.; Choo, C.H.; Tan, B.H.; Low, C.-M.; Bian, J.-S. Effect of hydrogen sulfide on intracellular calcium homeostasis in neuronal cells. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munaron, L.; Avanzato, D.; Moccia, F.; Mancardi, D. Hydrogen sulfide as a regulator of calcium channels. Cell Calcium 2013, 53, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrann, C.D.; White, J.P.; Salogiannnis, J.; Laznik-Bogoslavski, D.; Wu, J.; Ma, D.; Lin, J.D.; Greenberg, M.E.; Spiegelman, B.M. Exercise Induces Hippocampal BDNF through a PGC-1α/FNDC5 Pathway. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aslami, H.; Pulskens, W.P.; Kuipers, M.T.; Bos, A.P.; Van Kuilenburg, A.B.P.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Roelofsen, J.; Roelofs, J.; Kerindongo, R.P.; Beurskens, C.J.P.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Donor NaHS Reduces Organ Injury in a Rat Model of Pneumococcal Pneumosepsis, Associated with Improved Bio-Energetic Status. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.T.; Lerin, C.; Haas, W.; Gygi, S.P.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Puigserver, P. Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1α and SIRT1. Nature 2005, 434, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, A.; De Souza, C.T. Multi-regulatory network of ROS: The interconnection of ROS, PGC-1 alpha, and AMPK-SIRT1 during exercise. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 73, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untereiner, A.A.; Wang, R.; Ju, Y.J.; Wu, L. Decreased Gluconeogenesis in the Absence of Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase and the Underlying Mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mustafa, A.K.; Gadalla, M.M.; Sen, N.; Kim, S.; Mu, W.; Gazi, S.K.; Barrow, R.K.; Yang, G.; Wang, R.; Snyder, S.H. H2S Signals Through Protein S-Sulfhydration. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parsanathan, R.; Jain, S.K. Hydrogen Sulfide Regulates Irisin and Glucose Metabolism in Myotubes and Muscle of HFD-Fed Diabetic Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071369
Parsanathan R, Jain SK. Hydrogen Sulfide Regulates Irisin and Glucose Metabolism in Myotubes and Muscle of HFD-Fed Diabetic Mice. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(7):1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071369
Chicago/Turabian StyleParsanathan, Rajesh, and Sushil K. Jain. 2022. "Hydrogen Sulfide Regulates Irisin and Glucose Metabolism in Myotubes and Muscle of HFD-Fed Diabetic Mice" Antioxidants 11, no. 7: 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071369
APA StyleParsanathan, R., & Jain, S. K. (2022). Hydrogen Sulfide Regulates Irisin and Glucose Metabolism in Myotubes and Muscle of HFD-Fed Diabetic Mice. Antioxidants, 11(7), 1369. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071369





