The Role of KEAP1-NRF2 System in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis
Abstract
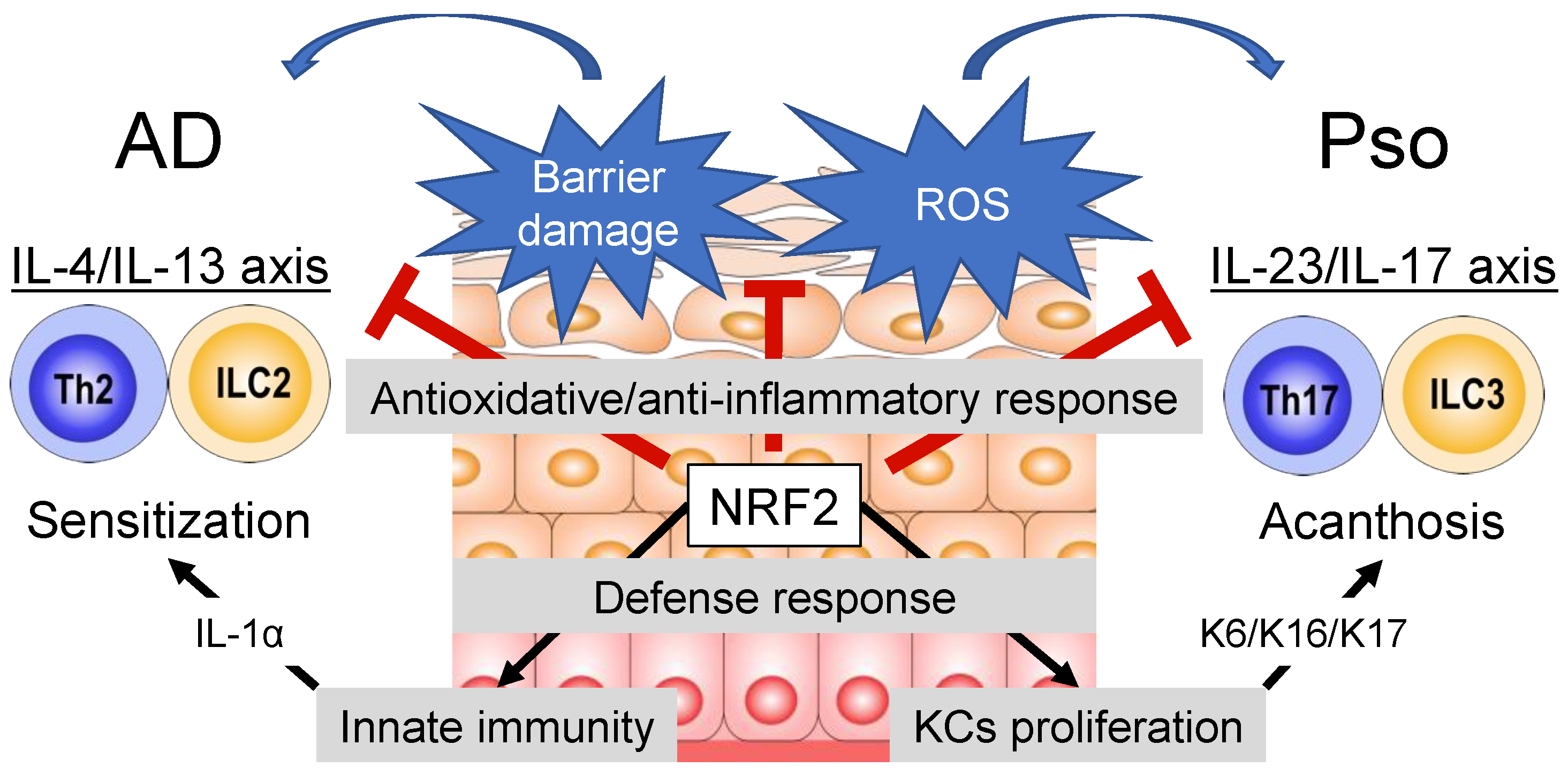
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of the KEAP1-NRF2 System
3. NRF2 as a Critical Regulator of Immune Responses
4. NRF2 as a Driver of Tissue-Repairing Inflammation in the Skin
5. NRF2 as a Regulator of Keratinization
6. Therapeutic Application of NRF2 Activators
7. NRF2 and Atopic Dermatitis
7.1. NRF2 Activators for AD
7.2. NRF2-Mediated Antioxidative Responses in the Epidermis and AD
| Species | Administration Route | Cell Type | Treatment | NRF2 Status | Effect of Treatment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | N/A | AD skin | N/A | Upregulation in skin | N/A | [8] |
| Human | N/A | Peripheral blood of AD | N/A | Downregulation in blood | N/A | [82] |
| Human | In vitro | Organotypic skin models with primary KCs from AD patients | Coal tar | Upregulation in KCs | Induction of epidermal differentiation Inhibition of Th2 cytokine signaling | [66] |
| Human | In vitro | TNF-α and IFN-γ or IL-4-induced AD-like HaCaT cells | Igalan | Upregulation in HaCaT cells | Inhibition of JAK/STAT3 | [67] |
| Mouse | N/A | TNCB-induced AD-like skin | Gene knockout of Nrf2 | Systemic downregulation | Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [8] |
| Mouse | Topical | DNCB-induced AD-like skin | Sulforaphane | Upregulation in skin | Inhibition of JAK1/STAT3 Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [69] |
| Mouse | Topical | OX-induced AD like skin | CPD 14 | Upregulation in HaCaT cells | Inhibition of NF-κB Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [71] |
| Mouse | Topical | OX-induced AD like skin | CPD 6 | Upregulation in macrophages | Inhibition of NF-κB and JAK2/STAT1 Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [72] |
| Mouse | Topical | OX-induced AD like skin | Cardamonin | Upregulation in skin | Downregulation of Th2 cytokines Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [73] |
| Mouse | Subcutaneous | DNCB-induced AD-like skin | Sulforaphane | Upregulation in skin | Inhibition of apoptosis in skin Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [70] |
| Mouse | Oral | DNCB-induced AD-like skin | CKS Platycodin D | Upregulation in HaCaT cells | Inhibition of NF-κB/STAT1 Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [74] |
| Mouse | Oral | DNCB-induced AD-like skin | 6-shogaol | Upregulation in skin | Inhibition of ROS and MAPKs Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [75] |
| Mouse | Oral | DNCB-induced AD-like skin | SST | Upregulation in skin | Downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [76] |
| Mouse | Oral | DNCB-induced AD-like skin | CBT | Upregulation in skin | Downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [77] |
| Mouse | Oral | HDM-induced AD-like skin in NC/Nga transgenic mouse | Quercetin | Upregulation in skin | Inhibition of HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [78] |
| Mouse | Oral | TMA-induced AD like skin | MQL | Upregulation in CD4+ T cells | Inhibition of CD4+ T cells proliferation Amelioration of AD-like skin inflammation | [79] |
8. NRF2 and Psoriasis
8.1. NRF2-Mediated Antioxidative Responses in the Psoriatic Tissues
8.2. NRF2 Activators for In Vitro Models of Psoriasis
8.3. Topical NRF2 Activators for Mouse Models of Psoriasis
8.4. Systemic NRF2 Activators for Mouse Models of Psoriasis
| Species | Administration Route | Cell Type | Treatment | NRF2 Status | Effect of Treatment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | N/A | Psoriatic skin | N/A | Upregulation in skin | N/A | [97] |
| Human | N/A | Psoriatic skin | N/A | Upregulation in skin | N/A | [95] |
| Human | N/A | Psoriatic skin | N/A | Downregulation in skin | N/A | [96] |
| Human | N/A | Psoriatic skin | N/A | Downregulation in skin | N/A | [9] |
| Human | N/A | Psoriatic granulocytes | N/A | Upregulation in granulocytes | N/A | [99] |
| Human | N/A | Psoriatic lymphocytes | N/A | Upregulation in lymphocytes (PsV > PsA) | Exacerbation of pro-oxidative conditionsUpregulation of pro-apoptotic pathway | [100] |
| Human | N/A | Psoriatic fibroblasts | N/A | Upregulation in fibroblasts | N/A | [101] |
| Human | In vitro | HaCaT cells | MET | Downregulation in HaCaT cells | Induction of cell apoptosis Elevation of intracellular ROS | [106] |
| Mouse | N/A | Mice epidermis Cultured mice KCs | Gene knockout of Arpc4 | Upregulation in skin | Development of psoriasis-like disease | [104] |
| Mouse | N/A | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | Nrf2 siRNA | Downregulation in skin | Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [97] |
| Mouse | N/A | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | Gene knockout of Nrf2 | Systemic downregulation | Exacerbation of psoriatic inflammation | [9] |
| Mouse | Topical | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | TGN | Upregulation in HaCaT cells | Inhibition of NF-κB and STAT3 Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [107] |
| Mouse | Topical | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | Rapamycin | Upregulation in skin | Restoration of suppressed autophagy and increased AHR expression Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [111] |
| Mouse | Topical | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | GAL | Upregulation in skin | Inhibition of NF-κBAmelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [112] |
| Mouse | Topical | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | IDMF | Upregulation in HEK293 | Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [120] |
| Mouse | Topical | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | POH | Upregulation in skin | Inhibition of NF-κB and STAT3 Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [113] |
| Mouse | Topical | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | GA | Downregulation in skin | Downregulation of K16 and K17 Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [121] |
| Mouse | Topical | TPA-induced psoriatic skin | Moringa oleifera seeds | Upregulation in skin | Downregulation of Th17-related cytokines Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [114] |
| Mouse | Intragastric | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | Astilbin | Upregulation in HaCaT cells | Inhibition of ROS and VEGF Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [115] |
| Mouse | Intragastric | IMQ-induced psoriatic skin | DMF | Upregulation in skin | Downregulation of inflammatory cytokines Upregulation of epidermal differentiation markers Amelioration of psoriatic inflammation | [9] |
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| AHR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| Arp2/3 | actin-related protein 2/3 |
| Arpc4 | actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| ca | constitutively active |
| CBT | Chijabyukpi-tang |
| CE | cornified envelope |
| CKS | Changkil saponins |
| CPD 6 | chrysin-derivative |
| CPD 14 | macakurzin C-derivative |
| CUL3 | CULIN3 |
| DAMP | damage-associated molecular pattern |
| DMBA | 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene |
| DMF | dimethyl fumarate |
| DNCB | 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene |
| DNFB | 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene |
| DNTB | 2,4-dinitrothiocyanobenzene |
| FAE | fumaric acid ester |
| FLG | filaggrin |
| GA | gallic acid |
| GAL | galangin |
| GSH | glutathione |
| HDM | house dust mite |
| HEK293 | human embryonic kidney 293 |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| HMGB1 | high-mobility group box 1 |
| IDMF | isosorbide dimethyl fumarate |
| IFN-γ | interferon-gamma |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| IL | interleukin |
| ILC | innate lymphoid cells |
| IMQ | imiquimod |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| K | keratin |
| KC | keratinocyte |
| KEAP1 | Kelch-like erythroid cell-derived protein with cap‘n’collar homology-associated protein 1 |
| LOR | loricrin |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MET | metformin |
| MMF | monomethyl fumarate |
| MQL | miquelianin |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| NHEK | normal human epidermal keratinocytes |
| NLRP3 | nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 |
| NRF2 | nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| OX | oxazolone |
| PAH | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon |
| POH | perillyl alcohol |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| PsA | psoriatic arthritis |
| Pso | psoriasis |
| PsV | psoriasis vulgaris |
| RAGE | receptor for advanced glycation end products |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SC | stratum corneum |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| SPRR2 | small proline-rich protein 2 |
| SST | Soshiho-tang |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TBHQ | tert-butylhydroquinone |
| TGN | tussilagonone |
| Tc | cytotoxic T |
| Th | helper T |
| TMA | trimellitic anhydride |
| TNCB | 2,4,6-trinitro-1-chlorobenzene |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TPA | 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate |
| Treg | regulatory T cell |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 System: A Thiol-Based Sensor-Effector Apparatus for Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schäfer, M.; Werner, S. Nrf2—A regulator of keratinocyte redox signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, J.; Motohashi, H.; Noda, S.; Takahashi, S.; Imakado, S.; Kotsuji, T.; Otsuka, F.; Roop, D.R.; et al. Keap1-null mutation leads to postnatal lethality due to constitutive Nrf2 activation. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Roop, D. The KEAP1/NRF2 Signaling Pathway in Keratinization. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Roop, D.R. The Epidermis: Redox Governor of Health and Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.; Barker, J.N. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Kubota, N.; Saito, A.; Fujisawa, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Okiyama, N.; Suga, Y.; Roop, D.R.; et al. NRF2 Augments Epidermal Antioxidant Defenses and Promotes Atopy. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Inoue, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Saito, A.; Okiyama, N.; Fujisawa, Y.; Furuta, J.; Watanabe, R.; Fujimoto, M. Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Regulates Epidermal Keratinization under Psoriatic Skin Inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmulappa, R.K.; Scollick, C.; Traore, K.; Yates, M.; Trush, M.A.; Liby, K.T.; Sporn, M.B.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Biswal, S. Nrf2-dependent protection from LPS induced inflammatory response and mortality by CDDO-Imidazolide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Rangasamy, T.; Reddy, S.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Biswal, S. Nrf2 is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and survival during experimental sepsis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wruck, C.J.; Fragoulis, A.; Gurzynski, A.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Kan, Y.W.; Chan, K.; Hassenpflug, J.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Varoga, D.; Lippross, S.; et al. Role of oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis: Insights from the Nrf2-knockout mice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, T.; Tian, F.; Zheng, H.; Whitman, S.A.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, D.D. Nrf2 suppresses lupus nephritis through inhibition of oxidative injury and the NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoh, K.; Itoh, K.; Enomoto, A.; Hirayama, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Morito, N.; Koyama, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, S. Nrf2-deficient female mice develop lupus-like autoimmune nephritis11See Editorial by Byrd and Thomas, p. 1606. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Murakami, S.; Biswal, S.S.; Sakaguchi, S.; Harigae, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Motohashi, H. Systemic Activation of NRF2 Alleviates Lethal Autoimmune Inflammation in Scurfy Mice. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 37, e00063-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annunziato, F.; Romagnani, C.; Romagnani, S. The 3 major types of innate and adaptive cell-mediated effector immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gause, W.C.; Wynn, T.A.; Allen, J.E. Type 2 immunity and wound healing: Evolutionary refinement of adaptive immunity by helminths. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, L. Complexity of danger: The diverse nature of damage-associated molecular patterns. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35237–35245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kool, M.; Willart, M.A.; van Nimwegen, M.; Bergen, I.; Pouliot, P.; Virchow, J.C.; Rogers, N.; Osorio, F.; Reis e Sousa, C.; Hammad, H.; et al. An unexpected role for uric acid as an inducer of T helper 2 cell immunity to inhaled antigens and inflammatory mediator of allergic asthma. Immunity 2011, 34, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzaki, H.; Iijima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; O'Grady, S.M.; Kita, H. The danger signal, extracellular ATP, is a sensor for an airborne allergen and triggers IL-33 release and innate Th2-type responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4375–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalli, G.; Colafrancesco, S.; Emmi, G.; Imazio, M.; Lopalco, G.; Maggio, M.C.; Sota, J.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin 1α: A comprehensive review on the role of IL-1α in the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.T.; Briggs, W.H.; Cheng, G.C.; Rossiter, H.B.; Libby, P.; Kupper, T. Mechanical deformation promotes secretion of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 receptor antagonist. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5084–5088. [Google Scholar]
- Barland, C.O.; Zettersten, E.; Brown, B.S.; Ye, J.; Elias, P.M.; Ghadially, R. Imiquimod-induced interleukin-1 alpha stimulation improves barrier homeostasis in aged murine epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.J.; Jung, M.; Kim, M.; Hong, S.P.; Choi, E.H. IL-1α stimulation restores epidermal permeability and antimicrobial barriers compromised by topical tacrolimus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rockwell, C.E.; Zhang, M.; Fields, P.E.; Klaassen, C.D. Th2 skewing by activation of Nrf2 in CD4(+) T cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Brough, D. Understanding the mechanism of IL-1β secretion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.J.; Yen, G.C. The role of Nrf2 in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 1011–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Su, W.; Wan, T.; Yu, J.; Zhu, W.; Tang, F.; Liu, G.; Olsen, N.; Liang, D.; Zheng, S.G. Sodium butyrate regulates Th17/Treg cell balance to ameliorate uveitis via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Biochem. Pharm. 2017, 142, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Scott, E.; Flesch, P. Sulfhydryl and disulfide in keratinization. Science 1954, 119, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K.; Epstein, W.L. Sulfur-containing proteins and epidermal keratinization. J. Cell Biol. 1969, 40, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, Z.; Steinert, P.M. Bricks and mortar of the epidermal barrier. Exp. Mol. Med. 1999, 31, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, A.; Marekov, L.N.; Steinert, P.M. Assembly of the epidermal cornified cell envelope. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3069–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhart, L.; Lippens, S.; Tschachler, E.; Declercq, W. Cell death by cornification. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013, 1833, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrel, T.; Hohl, D.; Rothnagel, J.A.; Longley, M.A.; Bundman, D.; Cheng, C.; Lichti, U.; Bisher, M.E.; Steven, A.C.; Steinert, P.M.; et al. Identification of a major keratinocyte cell envelope protein, loricrin. Cell 1990, 61, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, M.; Dütsch, S.; auf dem Keller, U.; Navid, F.; Schwarz, A.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Werner, S. Nrf2 establishes a glutathione-mediated gradient of UVB cytoprotection in the epidermis. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schäfer, M.; Farwanah, H.; Willrodt, A.H.; Huebner, A.J.; Sandhoff, K.; Roop, D.; Hohl, D.; Bloch, W.; Werner, S. Nrf2 links epidermal barrier function with antioxidant defense. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, M.; Willrodt, A.H.; Kurinna, S.; Link, A.S.; Farwanah, H.; Geusau, A.; Gruber, F.; Sorg, O.; Huebner, A.J.; Roop, D.R.; et al. Activation of Nrf2 in keratinocytes causes chloracne (MADISH)-like skin disease in mice. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawachi, Y.; Xu, X.; Taguchi, S.; Sakurai, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Fujisawa, Y.; Furuta, J.; Takahashi, T.; Itoh, K.; et al. Attenuation of UVB-Induced Sunburn Reaction and Oxidative DNA Damage with no Alterations in UVB-Induced Skin Carcinogenesis in Nrf2 Gene-Deficient Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolfs, F.; Huber, M.; Kuehne, A.; Kramer, S.; Haertel, E.; Muzumdar, S.; Wagner, J.; Tanner, Y.; Böhm, F.; Smola, S.; et al. Nrf2 Activation Promotes Keratinocyte Survival during Early Skin Carcinogenesis via Metabolic Alterations. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4817–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Huang, M.T.; Shen, G.; Yuan, X.; Lin, W.; Khor, T.O.; Conney, A.H.; Kong, A.N. Inhibition of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced skin tumorigenesis in C57BL/6 mice by sulforaphane is mediated by nuclear factor E2-related factor 2. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8293–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Roop, D.R. Loricrin: Past, Present, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huebner, A.J.; Dai, D.; Morasso, M.; Schmidt, E.E.; Schäfer, M.; Werner, S.; Roop, D.R. Amniotic fluid activates the nrf2/keap1 pathway to repair an epidermal barrier defect in utero. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Huebner, A.J.; Rice, R.H.; Koch, P.J.; Speransky, V.V.; Steven, A.C.; Roop, D.R. Lce1 Family Members Are Nrf2-Target Genes that Are Induced to Compensate for the Loss of Loricrin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Okiyama, N.; Fujisawa, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Roop, D.R.; Nomura, T. Loricrin Protects against Chemical Carcinogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 142, 2023–2026.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Zhou, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Nakanishi, H.; Hirose, K.; Oura, H.; Arase, S.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Bando, Y.; Izumi, K.; et al. Targeted deletion of the murine corneodesmosin gene delineates its essential role in skin and hair physiology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6720–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kubota, N.; Fujisawa, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Okiyama, N.; Fujimoto, M.; Roop, D.R.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A. Loricrin and NRF2 Coordinate Cornification. JID Innov. 2022, 2, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Hanselmann, C.; Gassmann, M.G.; auf dem Keller, U.; Born-Berclaz, C.; Chan, K.; Kan, Y.W.; Werner, S. Nrf2 transcription factor, a novel target of keratinocyte growth factor action which regulates gene expression and inflammation in the healing skin wound. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 5492–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auf dem Keller, U.; Huber, M.; Beyer, T.A.; Kumin, A.; Siemes, C.; Braun, S.; Bugnon, P.; Mitropoulos, V.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A.; et al. Nrf transcription factors in keratinocytes are essential for skin tumor prevention but not for wound healing. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muzumdar, S.; Koch, M.; Hiebert, H.; Bapst, A.; Gravina, A.; Bloch, W.; Beer, H.D.; Werner, S.; Schäfer, M. Genetic activation of Nrf2 reduces cutaneous symptoms in a murine model of Netherton syndrome. Dis. Model. Mech. 2020, 13, dmm042648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Manda, G.; Hassan, A.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Barbas, C.; Daiber, A.; Ghezzi, P.; León, R.; López, M.G.; Oliva, B.; et al. Transcription Factor NRF2 as a Therapeutic Target for Chronic Diseases: A Systems Medicine Approach. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 348–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robledinos-Antón, N.; Fernández-Ginés, R.; Manda, G.; Cuadrado, A. Activators and Inhibitors of NRF2: A Review of Their Potential for Clinical Development. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9372182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; McKercher, S.R.; Lipton, S.A. Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahidi, F. Antioxidants in food and food antioxidants. Nahrung 2000, 44, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B.G.; Jain, A.D.; Speltz, T.E.; Moore, T.W. Non-electrophilic modulators of the canonical Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sporn, M.B.; Liby, K.T. NRF2 and cancer: The good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, C.; Mann, J. New insights into the epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2014, 69, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarot, S.; Auziere, S.; Gadkari, A.; Girolomoni, G.; Puig, L.; Simpson, E.L.; Margolis, D.J.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Eckert, L. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in adults: Results from an international survey. Allergy 2018, 73, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apfelbacher, C.J.; Diepgen, T.L.; Schmitt, J. Determinants of eczema: Population-based cross-sectional study in Germany. Allergy 2011, 66, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, A.D.; McLean, W.H.I.; Leung, D.Y.M. Filaggrin Mutations Associated with Skin and Allergic Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabashima, K. New concept of the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: Interplay among the barrier, allergy, and pruritus as a trinity. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 70, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, L.A.; Thaçi, D.; Hamilton, J.D.; Graham, N.M.; Bieber, T.; Rocklin, R.; Ming, J.E.; Ren, H.; Kao, R.; Simpson, E.; et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spergel, J.M.; Paller, A.S. Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, S118–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimukai, K.; Morita, K.; Narita, M.; Kondo, M.; Kitazawa, H.; Nozaki, M.; Shigematsu, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Niizeki, H.; Motomura, K.; et al. Application of moisturizer to neonates prevents development of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 824–830.e826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; He, R.; Oyoshi, M.; Geha, R.S. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, C.W.; Later, D.W.; Pelroy, R.A.; Mahlum, D.D.; Wilson, B.W. Comparative chemical and biological analysis of coal tar-based therapeutic agents to other coal-derived materials. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1985, 5, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bogaard, E.H.; Bergboer, J.G.; Vonk-Bergers, M.; van Vlijmen-Willems, I.M.; Hato, S.V.; van der Valk, P.G.; Schroder, J.M.; Joosten, I.; Zeeuwen, P.L.; Schalkwijk, J. Coal tar induces AHR-dependent skin barrier repair in atopic dermatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dao, T.T.P.; Song, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Igalan from Inula helenium (L.) suppresses the atopic dermatitis-like response in stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes via JAK/STAT3 signaling. Inflamm Res. 2020, 69, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Beltrán, C.E.; Calderón-Oliver, M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Chirino, Y.I. Protective effect of sulforaphane against oxidative stress: Recent advances. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Peng, G.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Z.; Han, X. Sulforaphane has a therapeutic effect in an atopic dermatitis murine model and activates the Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alyoussef, A. Attenuation of experimentally induced atopic dermatitis in mice by sulforaphane: Effect on inflammation and apoptosis. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2022, 32, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, M.; Shin, I.; Kim, K.A.; Noh, D.; Baek, S.H.; Chang, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Bae, O.N. A newly synthesized macakurzin C-derivative attenuates acute and chronic skin inflammation: The Nrf2/heme oxygenase signaling as a potential target. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 307, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.H.; Suh, B.; Shin, I.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, D.; Shin, Y.J.; Chang, S.Y.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, H.; Bae, O.N. Inhibitory Effects of a Novel Chrysin-Derivative, CPD 6, on Acute and Chronic Skin Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, O.K.; Choi, W.J.; Keum, Y.S. Cardamonin Inhibits Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis by the Induction of NRF2 and the Inhibition of Th2 Cytokine Production. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Jin, S.W.; Han, E.H.; Park, B.H.; Kim, H.G.; Khanal, T.; Hwang, Y.P.; Do, M.T.; Lee, H.S.; Chung, Y.C.; et al. Platycodon grandiflorum root-derived saponins attenuate atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions via suppression of NF-κB and STAT1 and activation of Nrf2/ARE-mediated heme oxygenase-1. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Oh, D.S.; Lee, M.G.; Lee, C.E.; Kim, Y.U. 6-Shogaol, an active compound of ginger, alleviates allergic dermatitis-like skin lesions via cytokine inhibition by activating the Nrf2 pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 310, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jo, E.H.; Lee, B.; Noh, H.M.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, D.K.; Park, M.C. Soshiho-Tang, a Traditional Herbal Medicine, Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms via Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Lim, J.Y.; Jo, E.H.; Noh, H.M.; Park, S.; Park, M.C.; Kim, D.K. Chijabyukpi-Tang Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines via the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Stimulated HaCaT Cells and Ameliorates 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppagounder, V.; Arumugam, S.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Pitchaimani, V.; Sreedhar, R.; Afrin, R.; Harima, M.; Suzuki, H.; Nomoto, M.; Miyashita, S.; et al. Modulation of HMGB1 translocation and RAGE/NFκB cascade by quercetin treatment mitigates atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga transgenic mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, G.D.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, H.S. Miquelianin Inhibits Allergic Responses in Mice by Suppressing CD4(+) T Cell Proliferation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavanas, S.; Bodemer, C.; Rochat, A.; Hamel-Teillac, D.; Ali, M.; Irvine, A.D.; Bonafé, J.L.; Wilkinson, J.; Taïeb, A.; Barrandon, Y.; et al. Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, S.D.; Goldsmith, L.A. The peeling skin syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1982, 7, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, M.J.; Hwang, S.G.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.A.; Park, M.J.; Song, K.B.; et al. Host-microbial interactions between PTGR2 and Bifidobacterium in the early life gut of atopic dermatitis children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 33, e13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, C.; Louafi, F.; McGuire, C.; Lowings, K.; Kumar, P.; Cooper, H.; Dearman, R.J.; Cumberbatch, M.; Kimber, I.; Healy, E.; et al. The cutaneous biochemical redox barrier: A component of the innate immune defenses against sensitization by highly reactive environmental xenobiotics. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7576–7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez de Agüero, M.; Vocanson, M.; Hacini-Rachinel, F.; Taillardet, M.; Sparwasser, T.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Malissen, B.; Kaiserlian, D.; Dubois, B. Langerhans cells protect from allergic contact dermatitis in mice by tolerizing CD8(+) T cells and activating Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.P.; Stuart, P.E.; Nistor, I.; Hiremagalore, R.; Chia, N.V.C.; Jenisch, S.; Weichenthal, M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Lim, H.W.; Christophers, E.; et al. Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitch, E.; Harper, E.; Skorcheva, I.; Kurtz, S.E.; Blauvelt, A. Pathophysiology of psoriasis: Recent advances on IL-23 and Th17 cytokines. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2007, 9, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Boehncke, S.; Tobin, A.M.; Kirby, B. The ‘psoriatic march’: A concept of how severe psoriasis may drive cardiovascular comorbidity. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Mrowietz, U.; Rostami-Yazdi, M. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrowietz, U.; Christophers, E.; Altmeyer, P. Treatment of psoriasis with fumaric acid esters: Results of a prospective multicentre study. German Multicentre Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 138, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweckendiek, W. Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. Med. Monatsschr. 1959, 13, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mrowietz, U.; Barker, J.; Boehncke, W.H.; Iversen, L.; Kirby, B.; Naldi, L.; Reich, K.; Tanew, A.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.M.; Warren, R.B. Clinical use of dimethyl fumarate in moderate-to-severe plaque-type psoriasis: A European expert consensus. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32 (Suppl. 3), 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linker, R.A.; Lee, D.-H.; Ryan, S.; van Dam, A.M.; Conrad, R.; Bista, P.; Zeng, W.; Hronowsky, X.; Buko, A.; Chollate, S.; et al. Fumaric acid esters exert neuroprotective effects in neuroinflammation via activation of the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Brain 2011, 134, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bomprezzi, R. Dimethyl fumarate in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: An overview. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2015, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.R.; Kang, S.Y.; Jung, M.J.; Heo, N.H.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, A.; Kim, H.O.; Park, C.W.; Chung, B.Y. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Autophagy-Related Protein Microtubule-Associated Protein Light Chain 3 Expression in Psoriasis. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Bae, J.H.; Kang, S.G.; Cho, S.W.; Chun, D.I.; Nam, S.M.; Kim, C.H.; Nam, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Pro-oxidant status and Nrf2 levels in psoriasis vulgaris skin tissues and dimethyl fumarate-treated HaCaT cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fan, X.; Cui, T.; Dang, E.; Wang, G. Nrf2 Promotes Keratinocyte Proliferation in Psoriasis through Up-Regulation of Keratin 6, Keratin 16, and Keratin 17. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Nomura, T. KEAP1 and epidermal differentiation: Psoriatic epidermis as a model. J. Cutan. Immunol. Allergy 2021, 4, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrożewicz, E.; Wójcik, P.; Wroński, A.; Łuczaj, W.; Jastrząb, A.; Žarković, N.; Skrzydlewska, E. Pathophysiological Alterations of Redox Signaling and Endocannabinoid System in Granulocytes and Plasma of Psoriatic Patients. Cells 2018, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wójcik, P.; Gęgotek, A.; Wroński, A.; Jastrząb, A.; Żebrowska, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Effect of redox imbalance on protein modifications in lymphocytes of psoriatic patients. J. Biochem. 2019, 167, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gęgotek, A.; Domingues, P.; Wroński, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Changes in Proteome of Fibroblasts Isolated from Psoriatic Skin Lesions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkus, H.; Mehregan, A.H. The Primary Histologic Lesion of Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis*. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1966, 46, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Kammen, R.; Song, J.Y.; de Rink, I.; Janssen, H.; Madonna, S.; Scarponi, C.; Albanesi, C.; Brugman, W.; Innocenti, M. Knockout of the Arp2/3 complex in epidermis causes a psoriasis-like disease hallmarked by hyperactivation of transcription factor Nrf2. Development 2017, 144, 4588–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Goodman, A.M. Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Multicenter Metformin Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, X.; Yu, X.; Sun, Q. Metformin Promotes HaCaT Cell Apoptosis through Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species via Raf-1-ERK1/2-Nrf2 Inactivation. Inflammation 2018, 41, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Song, K.; Hiebert, P.; Werner, S.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, Y.S. Tussilagonone Ameliorates Psoriatic Features in Keratinocytes and Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Lesions in Mice via NRF2 Activation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1223–1232.e1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, L.M.; Lin, R.Z. Rapamycin and mTOR kinase inhibitors. J. Chem. Biol. 2008, 1, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, D.; Kim, J.; Shaw, R.J.; Guan, K.L. The autophagy initiating kinase ULK1 is regulated via opposing phosphorylation by AMPK and mTOR. Autophagy 2011, 7, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.M.; Shin, D.M.; Yuk, J.M.; Shi, G.; Choi, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Huang, S.M.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Autophagy negatively regulates keratinocyte inflammatory responses via scaffolding protein p62/SQSTM1. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, J.C.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Park, C.W.; Chung, B.Y. Rapamycin Alleviates 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-Induced Aggravated Dermatitis in Mice with Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis by Inducing Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangaraju, R.; Alavala, S.; Nalban, N.; Jerald, M.K.; Sistla, R. Galangin ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in BALB/c mice via down regulating NF-κB and activation of Nrf2 signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudha Yalamarthi, S.; Puppala, E.R.; Abubakar, M.; Saha, P.; Challa, V.S.; Np, S.; Usn, M.; Gangasani, J.K.; Naidu, V.G.M. Perillyl alcohol inhibits keratinocyte proliferation and attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis like skin-inflammation by modulating NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 103, 108436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Tang, Q.; Wu, W.T.; Huang, X.A.; Xu, Q.; Rong, G.L.; Chen, S.; Song, J.P. Three Constituents of Moringa oleifera Seeds Regulate Expression of Th17-Relevant Cytokines and Ameliorate TPA-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions in Mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Yuhai; Wang, H.; Chasuna; Bagenna. Astilbin reduces ROS accumulation and VEGF expression through Nrf2 in psoriasis-like skin disease. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lahti, A.; Maibach, H.I. Contact urticaria from diethyl fumarate. Contact Dermat. 1985, 12, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meding, B. Occupational contact dermatitis from tertiary-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) in a cutting fluid. Contact Dermat. 1996, 34, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, A.P.; Freeborn, R.A.; Duriancik, D.M.; Kennedy, R.C.; Gardner, E.M.; Rockwell, C.E. The Nrf2 activator tBHQ inhibits the activation of primary murine natural killer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turley, A.E.; Zagorski, J.W.; Rockwell, C.E. The Nrf2 activator tBHQ inhibits T cell activation of primary human CD4 T cells. Cytokine 2015, 71, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bojanowski, K.; Ibeji, C.U.; Singh, P.; Swindell, W.R.; Chaudhuri, R.K. A Sensitization-Free Dimethyl Fumarate Prodrug, Isosorbide Di-(Methyl Fumarate), Provides a Topical Treatment Candidate for Psoriasis. JID Innov. 2021, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Han, L.; Lu, C. Gallic acid inhibits the expression of keratin 16 and keratin 17 through Nrf2 in psoriasis-like skin disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogawa, T.; Ishitsuka, Y. The Role of KEAP1-NRF2 System in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071397
Ogawa T, Ishitsuka Y. The Role of KEAP1-NRF2 System in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(7):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071397
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgawa, Tatsuya, and Yosuke Ishitsuka. 2022. "The Role of KEAP1-NRF2 System in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis" Antioxidants 11, no. 7: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071397
APA StyleOgawa, T., & Ishitsuka, Y. (2022). The Role of KEAP1-NRF2 System in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Antioxidants, 11(7), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071397






