Abstract
In this work, we evaluated the physical and oxidative stabilities of 5% w/w fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with 1%wt Tween20 and containing 2 mg/mL of protein hydrolysates from olive seed (OSM–H), sunflower (SFSM–H), rapeseed (RSM–H) and lupin (LUM–H) meals. To this end, the plant-based substrates were hydrolyzed at a 20% degree of hydrolysis (DH) employing a mixture 1:1 of subtilisin: trypsin. The hydrolysates were characterized in terms of molecular weight profile and in vitro antioxidant activities (i.e., DPPH scavenging and ferrous ion chelation). After incorporation of the plant protein hydrolysates as water-soluble antioxidants in the emulsions, a 14-day storage study was conducted to evaluate both the physical (i.e., ζ-potential, droplet size and emulsion stability index) and oxidative (e.g., peroxide and anisidine value) stabilities. The highest in vitro DPPH scavenging and iron (II)-chelating activities were exhibited by SFSM–H (IC50 = 0.05 ± 0.01 mg/mL) and RSM–H (IC50 = 0.41 ± 0.06 mg/mL). All the emulsions were physically stable within the storage period, with ζ-potential values below −35 mV and an average mean diameter D[4,3] of 0.411 ± 0.010 μm. Although LUM–H did not prevent lipid oxidation in emulsions, OSM–H and SFSM–H exhibited a remarkable ability to retard the formation of primary and secondary lipid oxidation products during storage when compared with the control emulsion without antioxidants. Overall, our findings show that plant-based enzymatic hydrolysates are an interesting alternative to be employed as natural antioxidants to retard lipid oxidation in food emulsions.
1. Introduction
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), and more specifically, those belonging to the omega-3 family such as eicosapentaenoic (C20:5n-3, EPA) and docosahexaenoic (C22:6n-3, DHA) acids, have attracted growing interest over the past decades as functional ingredients for food formulations. Several studies support the health benefits associated with a regular intake of omega-3 fatty acids, such as the prevention of cardiovascular disease [1], diabetes [2] and inflammatory diseases (e.g., asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases and Alzheimer) [3,4], among others. EPA and DHA are semi-essential fatty acids since their natural conversion from α- linolenic acid is insufficient to meet human dietary requirements [5]. Therefore, both fatty acids should be supplied by diet. To this regard, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recommends an adequate daily intake of 250–500 mg of EPA plus DHA for the maintenance of general cardiovascular health among healthy adults and children [6].
Among the different dietary sources for omega-3 PUFAs, fish oil is commonly used for food enrichment due to its unique composition and high digestibility. The incorporation of lipid ingredients, particularly PUFAs, into food matrices is hindered by their poor solubility and tendency to undergo oxidation. The oxidation of PUFAs results in undesirable fishy and rancid off-flavors, as well as reducing their potential health benefits [7]. To this regard, delivery systems such as oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions or capsules can provide a physical barrier between the lipids and oxygen or other pro-oxidant species. Although O/W emulsions are widely employed for liquid or meat-based foodstuffs fortified with fish oil [8,9,10,11], their oxidative deterioration during processing and storage (e.g., due to the increased specific surface area) still poses a major challenge. This drawback is commonly overcome by the use of antioxidant compounds, which are able to inhibit lipid oxidation by different mechanisms such as radical scavenging, metal ion chelation, reduction or singlet oxygen quenching, among others. Synthetic antioxidants (e.g., butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, propyl gallate and tertbutyl hydroquinone) have been widely used in the food industry due to their strong antioxidant activity, availability and low cost. Nevertheless, their consumption presents several adverse side effects such as skin allergies, gastrointestinal disorders or even increased risk of cancer associated with long-term consumption. All these safety issues have promoted more stringent regulations restricting their use in favor of natural alternative compounds [12].
In general, antioxidant peptides are sequences containing 2–15 amino acids, which are inactive when encrypted within the pattern protein but display their biological activity when released by enzymatical hydrolysis, digestion or microbial fermentation. They share common features such as the presence of hydrophobic amino residues (i.e., Leu, Ile and Pro), aromatic amino acids such as Tyr or Trp or amino acids with nucleophilic sulfur-containing side chains (Cys and Met) [13]. These peptides find application as additives for food preservation, retarding the oxidation of food components, mainly lipids, during food processing and storage. Agro-industrial by-products are cheap and sustainable protein sources for antioxidant peptides. They present a variable protein content, ranging from 2% (e.g., potato peel) to more than 50% (e.g., soybean meal or pumpkin seed) in a dry weight basis [14]. Such materials have been extensively studied as substrates for releasing antioxidant peptides by enzymatic hydrolysis, employing commercial proteases such as alcalase, Flavourzyme, Protamex or papain. Enzymatic hydrolysis is a common method employed in the food industry to improve the nutritional and technological properties of proteins, as well as to obtain hydrolysates or peptides with biological activity. Compared with chemical hydrolysis, enzymes are specific catalysts which operate under moderate conditions of pH and temperature without generation of salts or other toxic by-products. These advantages make enzymatic hydrolysis the preferred treatment to produce bioactive peptides intended for food or feed applications. Indeed, antioxidant peptides have been identified in protein hydrolysates from a wide variety of plant substrates such as seeds [15,16], beans [17,18] or leaves [19,20], among others.
This work aims at investigating the potential use of plant protein hydrolysates (PPH) from sustainable sources as natural antioxidants for fish oil-in-water emulsions. To this end, four dried meals from olive seed, rapeseed, sunflower seed and lupin meals were hydrolyzed at 20% degree of hydrolysis (DH) by a mixture 1:1 of commercial proteases (i.e., subtilisin and trypsin). Most of these materials are generated as by-products from agriculture (i.e., lupin) or vegetal oil industry (i.e., olive, sunflower and rapeseed) and normally reduced to dried meals for animal feeding. The plant protein hydrolysates were characterized by their molecular weight distribution and in vitro antioxidant properties (i.e., radical scavenging and ferrous chelation activity) prior to their incorporation as natural antioxidants into 5% fish oil-in-water emulsions. The physical (i.e., droplet size distribution, zeta potential and creaming) and oxidative (peroxide and anisidine values) stability of the emulsions stabilized with Tween20 and containing the hydrolysates were monitored during a storage period of 14 days, with a special focus on the effect of PPH addition to retard oxidation of fish oil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Meals and Enzymes
This study employs four plant-based meals, obtained from local companies. Lupin (Lupinus albus) and olive (Olea europaea) seed meals were obtained from Dayelet (Barcelona, Spain) and Q’omer (Valencia, Spain), respectively. Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seed and rapeseed (Brassica napus) meals were purchased from Bernabé Campal (Salamanca, Spain). All these plant substrates were analyzed for their protein content, reporting average values of 28.4, 20.9, 24.6 and 34.5%wt for lupin, olive seed, sunflower and rapeseed, respectively. According to the suppliers, the plant meals employed in this work presented a variable lipid content. While rapeseed and sunflower meal are by-products from oil extraction, so their fat content is below 4%wt, olive seed meal presented a reported lipid content between 8–14%wt, followed by lupin meal (7.2%wt). The plant protein hydrolysates were produced employing two commercial endoproteases, Alcalase 2.4 L (subtilisin EC 3.4.21.62) and PTN 6.0S (trypsin 3.4.21.4), both purchased from Novozymes (Bagsvaerd, Denmark). All the analytical-grade chemicals employed for analysis were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merk, New York, NY, USA).
2.2. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
The enzymatic treatments were carried out in a jacketed glass reactor at a laboratory scale. To this end, samples were homogenized in distilled water at a ratio 2.5% protein w/v. This suspension was transferred to a 250 mL jacketed reactor heated at 50 °C under magnetic stirring. After that, pH 8.0 was adjusted and maintained throughout the reaction, employing 0.5 M sodium hydroxide by means of a pH-stat titrine (718 STAT Titrino, Metrohm, Switzerland). An enzymatic mixture containing Alcalase 2.4 L and PTN (1:1, w/w) was employed as catalyst, employing an enzyme-to-substrate ratio of 5% (w/w). All the hydrolysis reactions were performed in duplicate to confirm the reproducibility of the hydrolysis curves. The enzymatic reactions were allowed until attaining a degree of hydrolysis of 20%. At this point, the hydrolysis was stopped by heating the reaction mixture at 90 °C for 10 min, to inactivate enzymes. Finally, the final hydrolysates were vacuum-filtered and then freeze-dried in a LyoMicron lyophilizer (Coolvacuum Technologies, Barcelone, Spain). The dried powders obtained from two replicated hydrolysis were mixed and stored at −20 °C prior to analysis.
The degree of hydrolysis (DH) can be related to the amount of 0.5 N NaOH added to the reaction mixture to keep pH constant during the enzymatic treatment, according to the pH-Stat method [21] (pp. 122–123) as shown in Equation (1):
where Vb (mL) and Nb (eq/L) are the volume and normality of the base employed for the titration, respectively. The term mp stands for the mass of the protein present in the reaction mixture (g), htot represents the number of peptide bonds per mass of protein and was assumed as 8.6 milliequivalents of peptide bonds per gram of protein [21] (pp. 146–147). The average degree of dissociation of the α-amino groups (α) at pH 8.0 and 50 °C was estimated as 88.5%, as reported in the literature [21] (p. 142).
2.3. Plant Meal Solubilization and Protein Recovery
After enzyme inactivation, all hydrolysates were vacuum-filtered through 8 mm cellulose paper, and the solids retained were dried in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h. The percentage of solubilization of the plant meals in water after the enzymatic treatment was calculated by Equation (2):
where mR (g) represents the mass of dried solids retained on the filter paper, and m0 (g) is the mass of plant meal dissolved in distilled water at the start of the reaction.
Similarly, protein recovery, defined as the ratio of protein present in the hydrolysate to that in the original substrate, was estimated by Equation (3). This variable is an index of the protein solubilization attained after the enzymatic treatment.
where m0 and mH stand for the mass of plant meal and freeze-dried hydrolysate, which present protein weight fractions (g of protein/g of dried sample) denoted by c0 and cH, respectively.
2.4. Characterization of the Hydrolysates
2.4.1. Proximate Composition of the Hydrolysates
The freeze-dried hydrolysates were analyzed for their protein, lipid and moisture content. A Flash 2000 CHNS/O elemental analyzer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was employed to determine the protein content of meals and hydrolysates. Here, the samples are subjected to complete combustion, and a thermal conductivity detector identified the electrical signal of combustion products (CO2, H2O, N2 and SO2), which is proportional to each elemental concentration (C, H, N and S). The nitrogen-to-protein content factor was assumed to be 5.3, following the work of Rhee K [4].
The lipid content of the PPH was determined after four sequential extractions with a hexane and 2-propanol mixture (1: v/v). Briefly, a certain amount of hydrolysate (between 0.2 and 1.0 g) was mixed with 5 mL distilled water, 20 mL of solvent mixture and then vortexed for 5 min. After that, it was centrifugated at 1200× g for 5 min. The supernate phase was taken to evaporate solvent, and the oil content was quantified by dividing oil mass per hydrolysate mass used.
The moisture content of the PPH was determined by means of an infrared moisture analyzer (AD-4714A, A&D Company, Oxford, UK).
2.4.2. Molecular Weight Distribution of the Hydrolysates
The molecular weight distribution of the hydrolysates was obtained by size exclusion chromatography (SEC). To this end, the hydrolysates were dissolved in distilled water at 10 mg/mL, and 500 μL of each sample was injected into a Superdex Peptide 10/300 GL column (GE Health-care, Uppsala, Sweden) for elution using distilled water as a mobile phase at 0.5 mL/min. The absorbance of the eluted sample was measured at 280 nm. The calibration curve was prepared using different standards with broad weight size distributions (L-Tyrosine (217.7 Da), Vitamin B12 (1355.4 Da), Aprotinin (6512 Da), Cytochrome C (12,384 Da) and Ribonuclease A (13,700 Da).
2.4.3. Antioxidant In Vitro Activity of Hydrolysates
Two antioxidant properties were investigated in the plant protein hydrolysates, namely the ability to sequestrate 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals and the ferrous ion chelating activity.
The DPPH scavenging activity was determined by the method of Picot et al. [22] with slight modifications. Briefly, each hydrolysate aqueous solution was mixed and shaken with the same volume of 0.1 mM DPPH methanolic dissolution. The mixtures were kept for 30 min at room temperature in the dark before measuring absorbance at 515 nm. A series of control samples were prepared by mixing 1 volume of hydrolysate solution with 1 volume of methanol. The blank solution, which displays the minimum radical scavenging, was a mixture 1:1 of DPPH and distilled water. The radical scavenging inhibition was calculated as follows:
where Asample, Acontrol and Ablank denote the absorbances for the sample, the control samples (without addition of DPPH) and the blank solution (DPPH plus distilled water), respectively.
This procedure was repeated for a serial dilution of hydrolysates (0.1–20 mg protein/mL), allowing the calculation of the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50, mg/mL) for each hydrolysate.
Ferrous ion chelating capacity is related to the ability of the plant protein hydrolysates to chelate free metal cations, which catalyze lipid oxidation reactions. This property was determined by the method reported by Decker and Welch [23]. Each aqueous hydrolysate dissolution was mixed with distilled water (1:3.7, v/v) and 0.1 mL of 2 mM ferrous chloride aqueous dissolution. After 3 min, 0.2 mL of 2 mM Ferrozine aqueous dissolution was added to all samples except those used as control, and the blank was analyzed using distilled water instead of hydrolysate dissolution. After incubation for 10 min, the absorbance was read at 562 nm. The iron (II)-chelating activity was then calculated according to Equation (5):
where Asample, Acontrol and Ablank denote the absorbances for the sample, the control sample without addition of Ferrozine and the blank solution where the hydrolysate was replaced by distilled water, respectively.
For comparison purposes, the in vitro chelation of the hydrolysates was expressed as half-maximal concentration (IC50, mg/L).
2.5. Preparation of Emulsions
Six emulsions were prepared to contain 5.0% (w/w) of refined fish oil (BASF Personal Care and Nutrition GmbH, Illertissen, Germany) and stabilized with 1.0% (w/w) Tween 20TM. Four emulsions were produced by incorporating the plant protein hydrolysates as antioxidants into the aqueous phase at a concentration of 2 mg/mL. They were coded as LUM–H (lupin meal hydrolysate), OSM–H (olive seed meal hydrolysate), SFSM–H (sunflower seed meal hydrolysate) and RSM–H (rapeseed meal hydrolysate). Additionally, a positive control emulsion was prepared with whey protein hydrolysate at DH 10% (WPC–H) instead of plant protein hydrolysate. We confirmed by previous studies [24,25] the ability of whey protein hydrolysates to retard lipid oxidation, supporting their use as natural antioxidants in fish oil-in-water emulsions. Finally, a negative control emulsion was produced without the addition of any antioxidant.
Firstly, the aqueous phase containing the protein hydrolysate and the emulsifier Tween 20TM was brought to pH 8.0 and left stirring overnight at 4 °C to allow solubilization and rehydration of the protein. Pre-emulsions were prepared by dispersing the fish oil in the aqueous phase by means of an Ultra Turrax mixer (IKEA Werke GmbH & Co., Staufen, Germany) at 15,000 rpm for 2 min. Then, homogenization was conducted in a high-pressure laboratory homogenizer (Panda Plus 2000, GEA Niro Soavi., Lübeck, Germany) at 450/75 bar, running 3 passes. To accelerate lipid oxidation, 100 µM of FeSO4 7 H2O was added to the emulsions. Additionally, 0.05% (w/w) of sodium azide was incorporated into the emulsions to avoid microbial growth. The emulsion samples were stored in amber glass jars at 25 °C in the dark for 14 days. To evaluate lipid oxidation in the emulsions (i.e., peroxide and anisidine value), sampling was carried out on days 0, 1, 3, 7 and 14. As for the physical stability, samples were drawn on days 0 and 14 for measuring droplet size distribution, creaming and Turbiscan Stability Index (TSI), while zeta potential was measured on day 1.
2.6. Physical Stability of the Emulsions
The droplet surface charge was determined by measuring the zeta potential (ζ, mV). To this end, the emulsions were diluted 1:500 v/v in distilled water, and then pH was adjusted to 8. The zeta potential was measured at room temperature by means of a Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Worcestershire, UK) with a DTS-1060C cell. The zeta was set in the range between −100 and 50 mV, conducting three replicated measurements.
The oil droplet size distribution of the emulsions was obtained by means of laser diffraction equipment, employing a Mastersizer 3000 (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Worcestershire, UK), where samples were scattered in recirculating water at 3000 rpm until reaching an obscuration in the range of 12–15%, and the refractive indices employed for fish oil and water were 1.481 and 1.330, respectively. The results are reported as surface area D3.2 and volume mean D4,3 diameter. The physical stability of the emulsions was additionally evaluated by multiple light scattering in a TurbiscanTM LAB analyzer (Formulaction., Toulouse, France). To this end, 25 mL of each emulsion were reserved in a glass cell to perform measurements of the TSI. Finally, the emulsion destabilization during storage was further evaluated by placing 10 mL of each emulsion in graduated glass tubes and calculating the creaming index as the percentage of phase separation [26].
2.7. Oxidative Stability of the Emulsions
2.7.1. Determination of the Peroxide Value
Firstly, the lipid fraction from emulsions was extracted according to Padial-Domínguez et al. [24] with minor changes. As extraction agents, 20 mL of 1:1 v/v of hexane and 2-propanol were employed. Circa 0.5 g of emulsion (containing around 20 mg of fish oil) was homogenized with 5 mL of distilled water, vortexed for 5 min and then centrifugated at 1200× g for 4 min. Two extractions were made from each emulsion.
The Peroxide Value (PV) was determined according to the standard method described by Shantha N. and Decker E. [27] with minor modifications. In short, oil extracted from emulsions was mixed with 5 mL of 2-propanol, 50 µL of ammonium thiocyanate and 50 µL of iron (II) dissolution. The samples were vortexed and incubated for 5 min at 25 °C. After, absorbance was measured at 485 nm in a GenesysTM 30 visible spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Whalham, MA, USA). Four replicates were performed, and results are presented in milliequivalents of peroxide per kilogram of oil.
2.7.2. Anisidine Value Assay
The p-anisidine method was carried out according to the ISO 6885:2006 method [28] with slight modifications. In brief, the lipid extract was mixed with 10 mL of hexane, vortexed and distributed into two PyrexTM tubes with screw caps at equal volumes. In the first tube, 1 mL of anisidine dissolution (2.5 mg/mL) in glacial acetic acid was added, while 1 mL of hexane was incorporated in the other one as the control sample. All of them were covered and left in the dark for 10 min before measuring absorbance at 350 nm in a 10 mm cell.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The software RStudio 2022.02.1 (RStudio Team, Boston, MA, USA) was employed to conduct one-way analysis of variance in the data. The significant differences among samples and treatments were computed according to Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Differences between means were considered significant at a level of confidence of 95% (i.e., p-value below 0.05).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Hydrolysates
The proximate composition of all the plant protein hydrolysates, reported in terms of protein, lipid and moisture content, is shown in Table 1. The plant meals employed as substrate for the hydrolysis presented an average protein content between 20.9%wt (olive seed meal) and 34.5%wt (rapeseed meal), which make them suitable as substrate to produce protein hydrolysates. All these substrates were chosen based on their protein content and the previous literature supporting their functional properties. For instance, white lupin is a legume with a reported protein content between 28 and 44%wt, which could promote health benefits due to its bioactive compounds, such as anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, antioxidant and antihypertensive peptides [29,30]. Likewise, oilseed by-products, with a raw protein content of over 20%wt, have been gaining importance as a source of phytosterols, tocopherols and phenolic compounds, as well as peptides with biological activity [31]. In addition to protein, plant-derived meals are sources for a variety of compounds such as alkaloids, polyphenols, vitamins and minerals, as well as lipids, starch and fiber. The latter is usually present as the major component in plant meals [32,33], being responsible for their limited water solubility ([34,35], p. 364). The enzymatic treatment led to improved solubilization of the plant meals, with observed values ranging from 57.9% (lupin) to 75.5% (rapeseed) (Table 1). The limited solubility of plant meals could restrain their use as functional ingredients in food and nutraceutical preparations [31,36]. To this regard, Nissen, A. ([21], pp. 102–103) and Mokni, G. et al. [37] concluded that the enzymatic hydrolysis with alcalase significantly improved protein solubilization. The cleavage of peptide bonds leads to higher exposure of polar groups, and therefore higher solubility of the hydrolysate compared with the native protein. Similar to alcalase, trypsin cleaves preferably the C-terminus of Arg or Lys residues, releasing positive-charged peptides with improved solubility [38,39]. This is reflected in average values of protein recovery for the hydrolysates, as well as their protein content compared with the plant flours, which suggests that enzymatic reaction was effective to solubilize protein in the reaction medium. Sunflower seed meal hydrolysate presented the highest protein recovery in the experimental series (82.2%), similar to rapeseed meal hydrolysate. These results are in agreement with Vioque et al. [40], which mention that the use of oilseed proteins is frequently limited by their low solubility but could be offset by enzymatic hydrolysis.

Table 1.
Percentage solubilization and proximate composition of the plant protein hydrolysates.
Moreover, these results are in agreement with other protein-content sources of different origins. For example, Rivero-Pino et al. [41] studied proteins from Tenebrio Molitor as a source of bioactive peptides. They found that enzymatic hydrolysis improved protein solubility in contrast with unhydrolyzed protein. Over all treatments, alcalase–flavourzyme led to highest protein recovery, obtaining 46% at DH 20%.
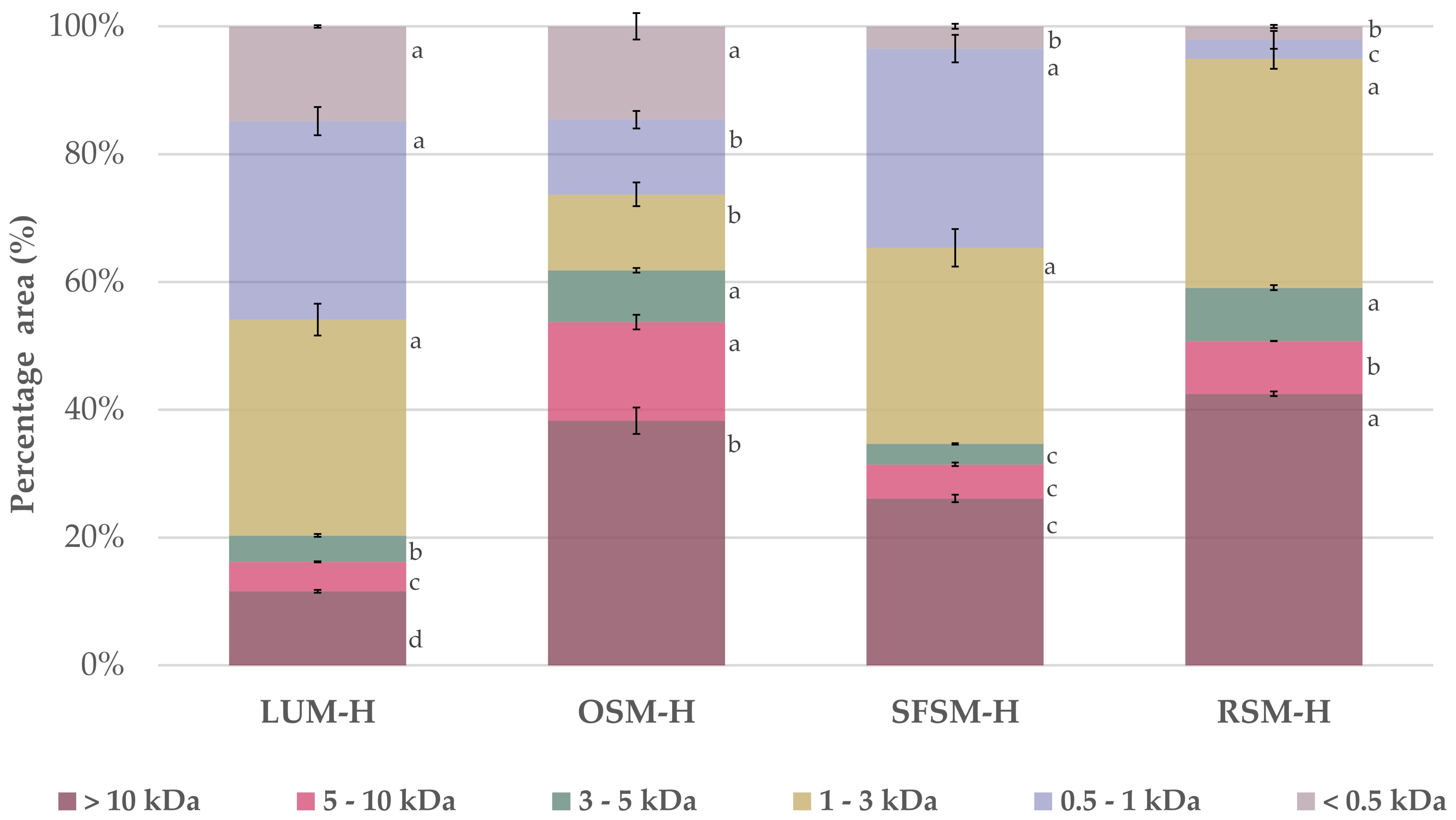
The molecular weight (MW) profile distribution of the four hydrolysates (Figure 1) confirms that the enzymatic treatment with alcalase and PTN was effective to hydrolysate the plant proteins, releasing a distribution of peptides. Alcalase is a broad-spectrum endoprotease, which is widely reported in the literature as a catalyst for the production of food protein hydrolysates [42]. Overall, we found a high presence of low MW peptides below 3 kDa in LUM–H and SFSM–H with a relative proportion of 79.7 and 65.3%, respectively. Additionally, RSM–H and OSM–H exhibited a major proportion of peptides above 5 kDa with 50.7 and 53.7%, respectively. As stated by Ying X., et al. [43], most of the bioactive peptides identified so far have 2–20 amino acid residues, with an average molecular weight under 6 kDa. More specifically, it has been observed that bioactive peptides displaying antioxidant capacity have short chains with a low molecular weight within 0.4 and 2 kDa [43].
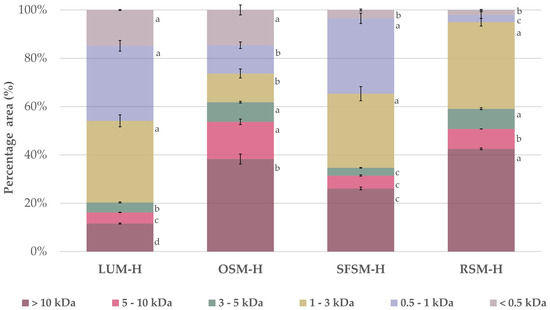
Figure 1.
Relative molecular weight distribution for the four plant protein hydrolysates. LUM–H: lupin meal hydrolysate; OSM–H: olive seed meal hydrolysate; SFSM–H: sunflower seed meal hydrolysate; RSM–H: rape-seed meal hydrolysate. All the data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of triplicate measurements. Different superscript letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) among plant protein hydrolysates.
3.2. Antioxidant In Vitro Activity of Hydrolysates
The antioxidant characteristics of peptides have been related to their ability to scavenge free radicals, chelate metal ions, or act as physical shieldings [44,45]. In the first case, peptides can act as radical inhibitors by donating electrons while holding their stability through the resonance of their structure. Meanwhile, peptides with carboxyl and amino groups on their side chains have a chelating function of metal ions as they can dissociate and be proton donors, inhibiting the production of free radicals through stabilizing metallic pro-oxidants. In addition, they can also act as a physical barrier or membrane to inhibit lipid peroxidation due to their surfactant properties, reducing direct contact between lipids and radicals and other oxidizing species [45].
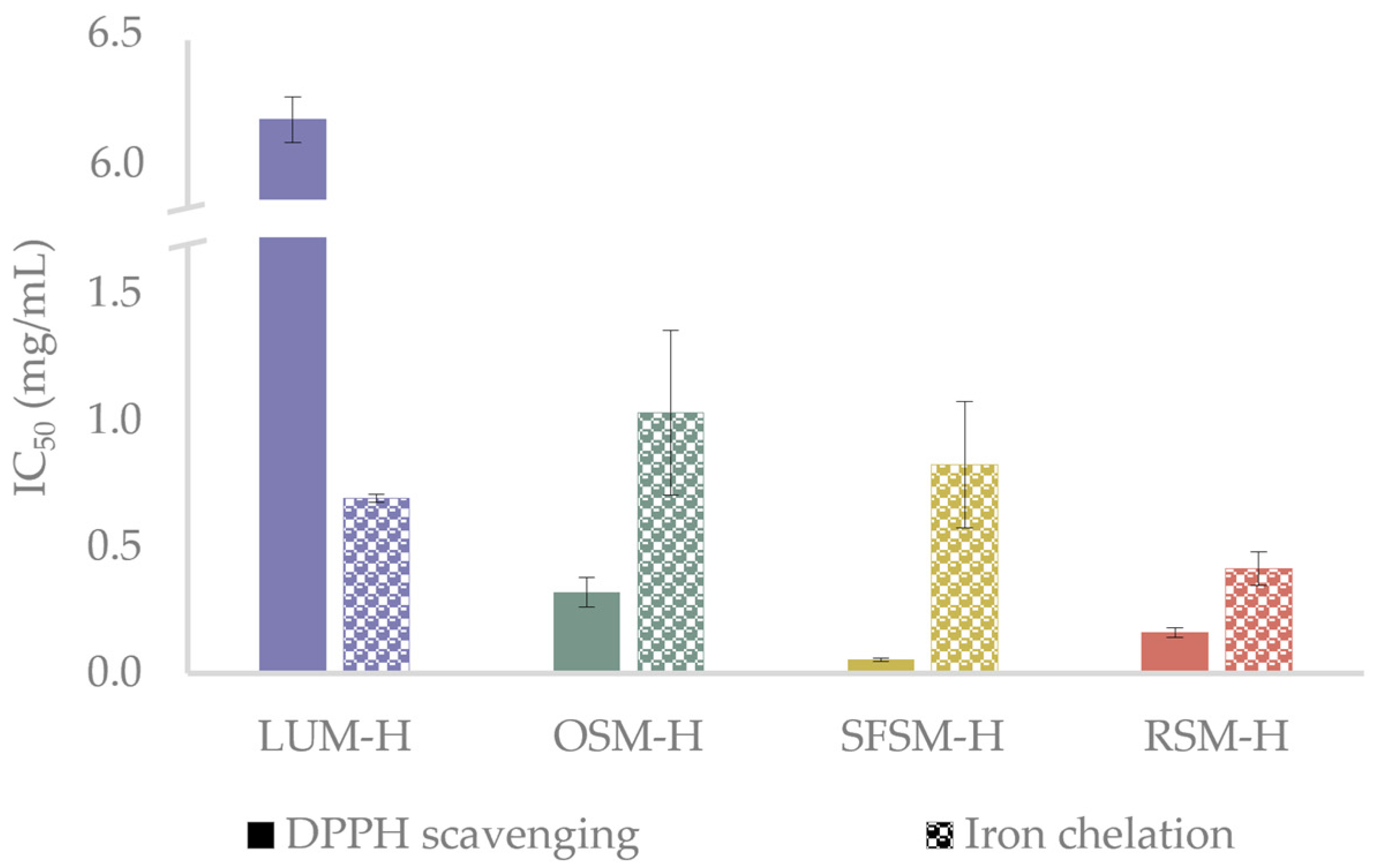
As radical quenching is the primary mechanism employed by antioxidant compounds to inhibit oxidation processes [46], and metals are initiators of undesired oxidative reactions in food products [47], DPPH radical scavenging and iron (II) chelation assays were employed to test the antioxidant in vitro capacity of the hydrolysates (Figure 2). The antioxidant in vitro assays reveals an outstanding capacity of the hydrolysates to scavenge DPPH radicals, with IC50 values ranging from 0.05 to 6.19 mg/mL. SFSM–H and RSM–H exhibit a significantly higher radical scavenging activity over OSM–H and LUM–H, with this last one showing the lowest activity among all samples (p < 0.05). Ying et al. [43] describe Tyr, Lys, Phe, Arg and Met as amino acid residues that could confer strong antioxidant properties. Wang et al. [48] mention that Val, Cys, Phe and Trp have been considered to have a good antioxidant capacity to quench free radicals or reduce metal ions, in agreement with Manzoor et al. [44] and López-García et al. [45], who reported amino acids such as Tyr, His, Trp and Phe as potent radical inhibitors. Bougatef et al. [49] found in their study with Mustelus mustelus muscle protein hydrolysates that the best DPPH radical-scavenging activity was exerted by peptides with MW below 3.5 kDa, with an IC50 close to 0.25 mg/mL. The aminogram results of this fraction revealed an important presence of His, Met, Tyr, Leu, Ile, Gly and Arg. Based on these investigations and the amino acid profiles reported for LUM, OSM, SFSM and RSM, we can suggest that prominent DPPH inhibition activity of oilseed by-products hydrolysates could be conferred due to the presence of some specific amino acids in the raw material. For example, OSM–H may have an important amount of Tyr (25%), Glu (7.5%), Met (6.8%), Arg (5.1%) and Pro (5.1%) [50]; SFSM–H of Arg (8.5%), Leu (7.0%), Gly (6.3%) Val (5.8%), Ile (4.9%) and Pro (4.3%) [51]; and RSM–H of Gly (10.3%), Leu (8.2%) and Arg (6.2%) [52]. Regarding LUM–H results, it is possible to find some presence of Arg (10.7%), Phe + Tyr (8.7%) and Leu (6.8%) [53,54]. Nevertheless, although meals in this work have been reported with amino acids that could confer antioxidant activity, it is important to remark that protein meal solubilization in hydrolysis could change the amino acid profile of all hydrolysates. Additionally, other factors strongly influence the peptide antioxidant activity and should be taken into account, such as the position of some amino acids within the peptidic sequence, peptide chain length and the ability of some hydrophobic amino acids (e.g., Pro, Val, Leu and Tyr) to favor the interaction of peptides with hydrophobic radical species formed at the lipid phase [44,55]. The highest DPPH inhibition performed by SFSM–H, in comparison with the other hydrolysates, could be related to a major presence of peptides below 3 kDa. The low IC50 values for DPPH inhibition reached in our hydrolysates agree with those of He et al. [56], who evaluated the action of different enzymes over antioxidant activities of rapeseed protein isolate. They found that alcalase was one of the most efficient enzymes to produce antioxidant peptides, with DPPH values between 0.4–0.8 mg/mL. However, it should be noted that peptide hydrolysates are not purified, and therefore they contain other compounds that could confer antioxidant activity. For example, Wang et al. [48] studied the fermentation of RSM, finding that DPPH radical scavenging results are not only due to the presence of low MW peptides but the liberation of phenolic compounds that can take place by proteases action. Likewise, González-Hidalgo et al. [57] studied the antioxidant ability of olive by-products, finding that olive seeds showed an interesting amount of phenolic compounds (hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol and oleuropein) which exert high antioxidant activity.
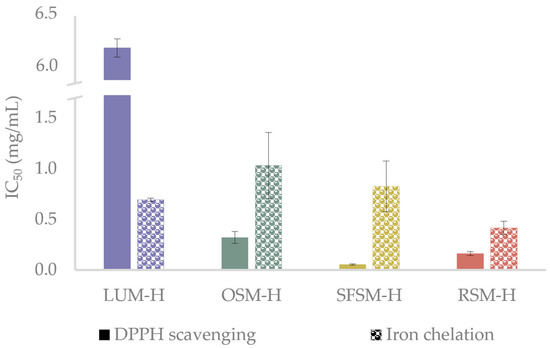
Figure 2.
DPPH scavenging and iron (II)-chelating activity of the hydrolysates, reported as IC50 value (mg/mL). LUM–H: lupin meal hydrolysate; OSM–H: olive seed meal hydrolysate; SFSM–H: sunflower seed meal hydrolysate; RSM–H: rape-seed meal hydrolysate.
The Fe2+ chelating assay showed IC50 values ranging between 0.41 and 0.97 mg/mL. RSM–H displays a significantly higher capacity to chelate Fe2+ over OSM–H, SFSM–H and LUM–H. These IC50 values are similar to those reported for the peptide fractions from Gadus morhua obtained by Sabeena Farvin et al. [58], which exhibited values ranging from 0.15 to 0.75 mg/mL (crude hydrolysate). The further investigations on Gadus morhua hydrolysates [55] suggested that presence of Glu, Gly, Lys, Ala, Arg, His, Tyr, Phe and Pro amino acids may contribute to the iron chelation displayed by the hydrolysates. Other works have reported similar trends, such as those carried out by Zhang et al. [59], which evaluated the antioxidant ability of hydrolysates from chickpea protein and Carrasco-Castilla et al. [60] from bean protein hydrolysates. These studies mention that Glu and Arg, as well as Asp+Asn, Glu+Gln, His and Cys, display an important role when it comes to the chelation of metal ions. Moreover, low MW peptides below 3 kDa could be responsible for the good general performance of SFSM–H and RSM–H among the samples, in agreement with Sabeena Farvin et al. [58], which evaluated the antioxidant activity of cod protein hydrolysates both in vitro and over oil-in-water emulsions with 5% of fish oil. They found that peptides below 3 kDa displayed the lowest IC50 (≈0.15 mg/mL). Based on these investigations, and the reported amino acid composition of our hydrolysates, Glu, Gly and Asp seem to act as important chelating agents in RSM–H. However, Glu and Asp could also be representative inside LUM and SFSM, suggesting that Gly may be responsible for the higher chelating activity of RSM–H, in contrast with the other samples. Nevertheless, OSM–H also exerts important results in this test, which could be due to the high presence of Tyr.
3.3. Physical Stability of Emulsions
The physical stability of the emulsions was studied during 14 days of storage, as shown in the Table 2. All the emulsions produced exhibited high physical stability over storage time. The ζ-potential was measured as an indicator of the charge of the dispersed oil droplets in the emulsion, which is related to its physical stability [51]. High absolute values above 30 mV have been linked with sufficient electrostatic repulsion between droplets that might lead to physically stable emulsions [52]. All the emulsions presented a negative ζ-potential below—40 mV except for the control emulsion NC and WPC–H, which present no significant statistical differences among them. Even if Tween20 is a non-ionic surfactant, Yesiltas et al. [61] suggest that negative ζ-potential values could be due to traces of free fatty acids or other anions present in the buffer. To this regard, we should note the presence of OH- anions added as titration agent (i.e., NaOH) to maintain pH at 8.0 during the hydrolysis. Moreover, the high negative values of zeta potential observed in some the emulsions containing the plant hydrolysates could be related to other natural compounds present in the plant source, such as phenols or gums [62].

Table 2.
Surface net charge (on day 1) and droplet size mean diameters (on day 14) for the emulsions studied.
Regarding the droplet size distribution, all the emulsions showed a monomodal distribution centered around 0.4 μm with no significant differences from day 0 to day 14 (Figure S1), indicating high physical stability. The statistical diameters D[3,2] and D[4,3] are listed for day 14 on the Table 2. The surface area mean diameter D[3,2] at day 14 ranged from 0.312 to 0.329 μm among the plant protein hydrolysates, while the volume mean diameter D[4,3] varied from 0.393 to 0.425 μm. According to Tukey’s test, there were not statistical differences between the statistical diameters evaluated at day 0 and 14, presenting slight deviations attributed to the experimental procedure (e.g., emulsion preparation and homogenization). The D[4,3] diameters of our emulsions were higher than those reported by Betül Yesiltas et al. [61], who reported a range between of volume mean diameters between 0.188–0.229 μm. These differences could be explained by the different equipment employed for the homogenization step in the two studies (two-valve homogenizator versus microfluidizer).
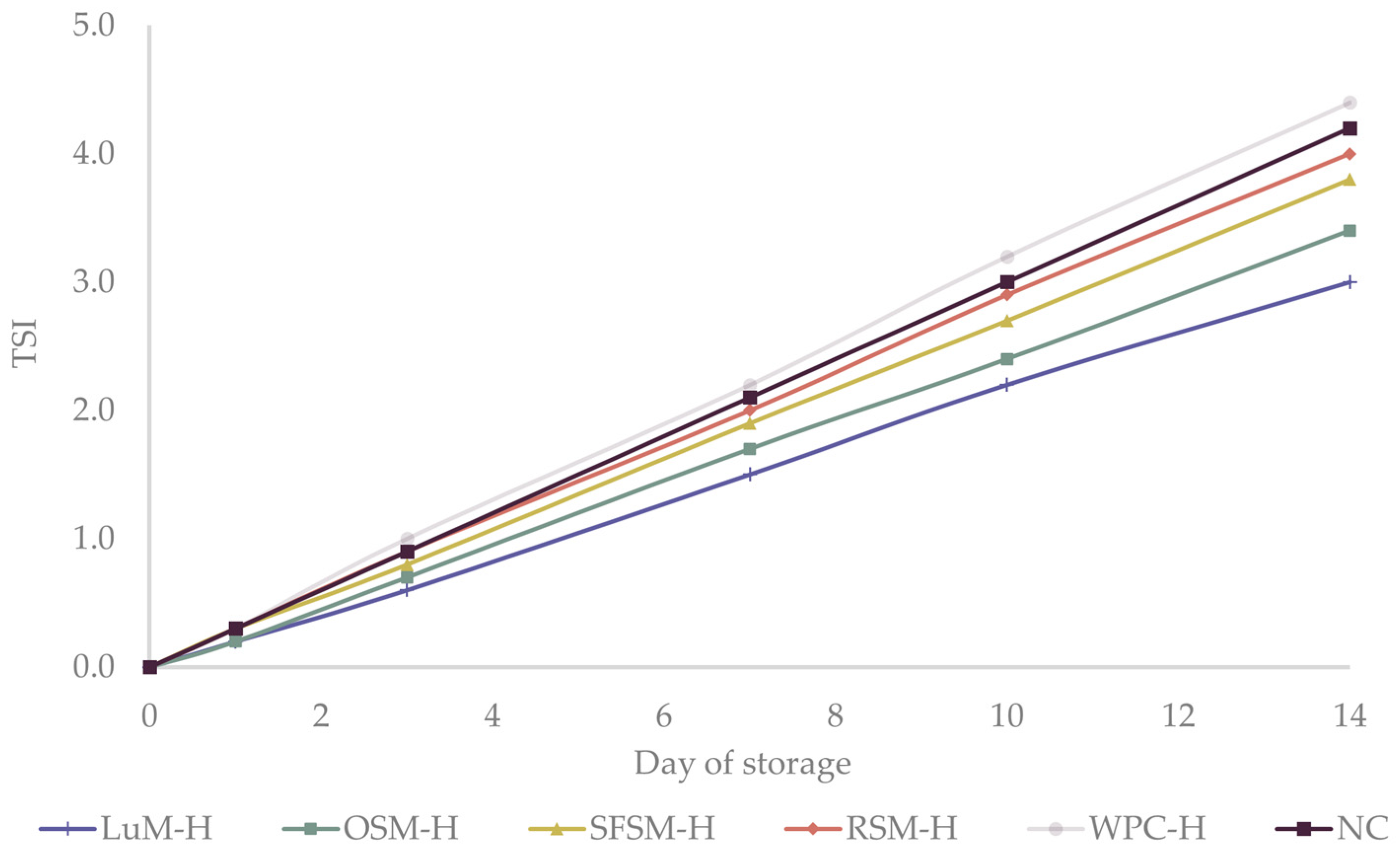
Turbiscan stability index (TSI) is another useful parameter to study the physical destabilization of emulsions over time. TSI values below 3 are an indicator of high physical stability [61]. During the first 7 days of the study, TSI of all emulsions (Figure 3) slightly raised between 1.5–2.2, reaching values between 3.0–4.2 on the last day. These findings are in agreement with creaming experiments, which did not present a visual destabilization through the storage time (data not shown). Additionally, our results are similar to those obtained by Betül Yesiltas et al. [61] for 5%wt fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with 1 %wt Tween20 containing synthetic antioxidant peptides from different sources. Overall, we concluded that the emulsions were physically stable over the storage period, presenting similar droplet sizes. Physically stable emulsions were required in order to explain the differences in oxidative stability among emulsions based on the addition of the plant protein hydrolysates.
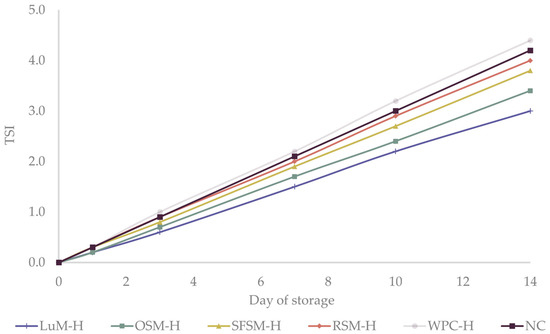
Figure 3.
Turbiscan stability index (TSI) of the six emulsions during storage. LUM–H: lupin meal hydrolysate; OSM–H: olive seed meal hydrolysate; SFSM–H: sunflower seed meal hydrolysate; RSM–H: rapeseed meal hydrolysate; WPC–H: whey protein concentrate hydrolysate; NC: negative control (without hydrolysate).
3.4. Oxidative Stability of Emulsions
3.4.1. Peroxide Value
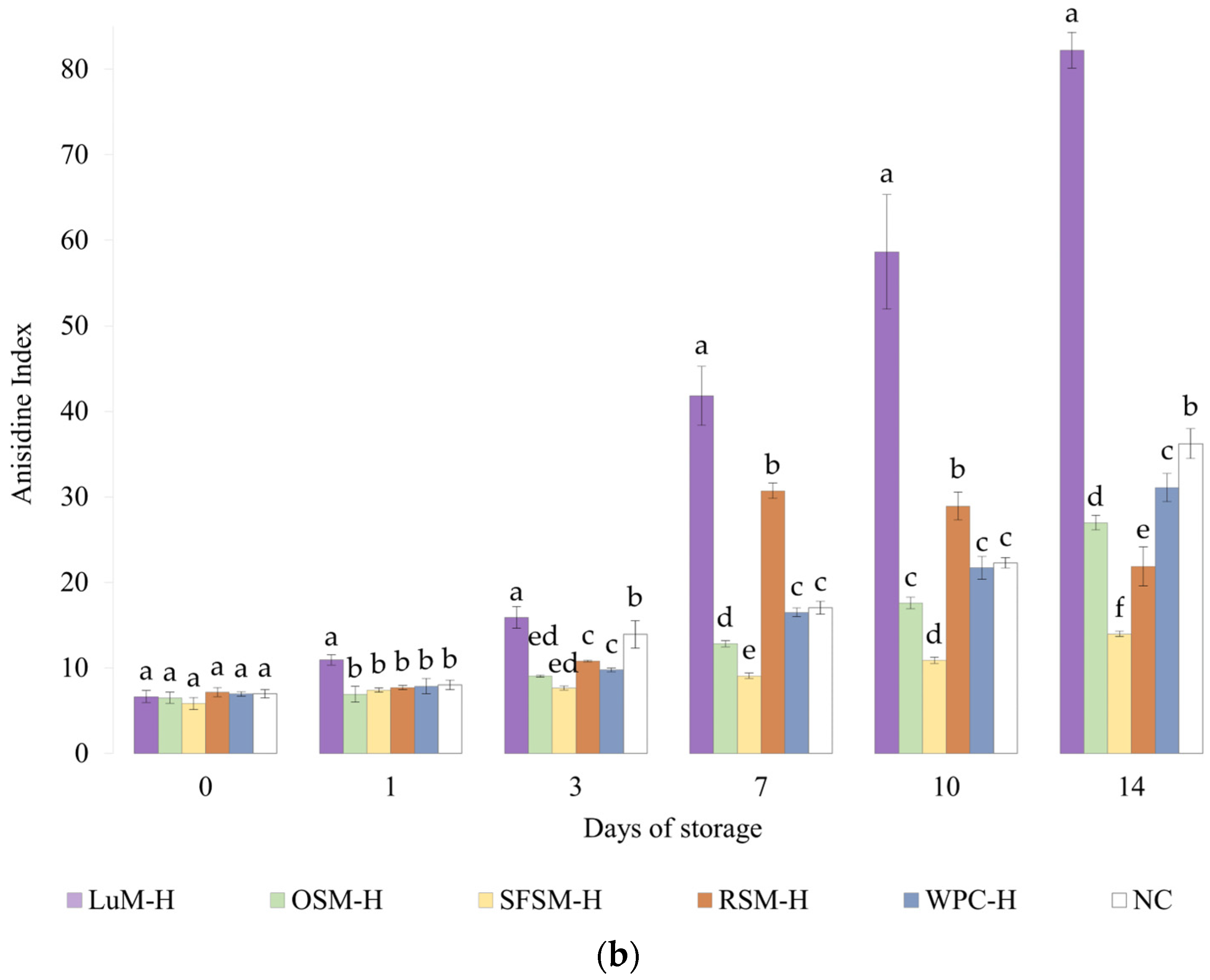
Lipid oxidation critically determines the chemical stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions. Oxidation of fish oil generates a wide variety of compounds, hydroperoxides being the primary oxidation products. As hydroperoxides are highly unstable compounds, they could be decomposed by the action of heat and traces of metals to secondary or final oxidation compounds, which are complex mixtures of volatile, non-volatile and polymeric, among other compounds [61]. Proteins and peptides incorporated into emulsions could inhibit lipid oxidation in different ways: (i) peptides not adsorbed at the interface can bind metal ions and scavenge free radicals in the aqueous phase, whereas (ii) adsorbed peptides could repel cationic metal ions from the interface or bind radicals formed in the proximity of the interfacial layer [43]. A similar droplet size distribution observed for all the emulsions (Table 2 and Figure S1) indicates that the hydrolysates did not show a significant emulsifying activity, denoting that the peptides added to the emulsions were mainly located in the aqueous phase. In this work, the peroxide value and anisidine index were employed to determine primary and secondary (unsaturated aldehydes) oxidation products in the emulsions during 14 days of storage.
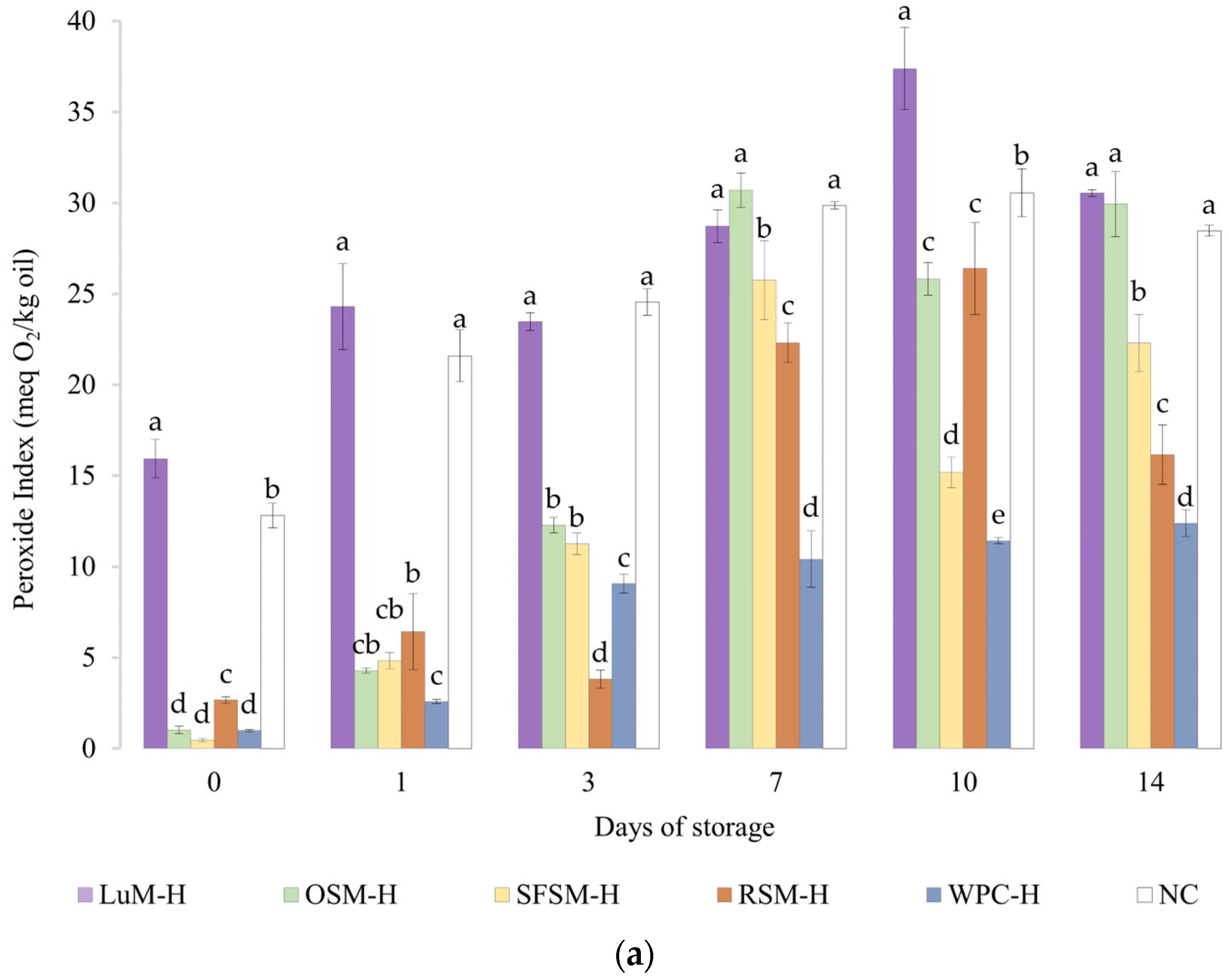
The peroxide value (PV) of emulsions is shown in Figure 4a. The emulsion without antioxidants (NC) had a PV of 12.8 meq O2/kg oil after production, reaching a maximum (36 meq O2/kg oil) on day 7. From this point on, the average values of PV tend to decrease, which implies a lower rate of formation than decomposition of peroxides. These results are comparable with negative control emulsion by Yesiltas et al. [61], which was prepared similarly to ours. In the latter, the first and last (eighth) day of stability had a PV close to 15 and 57 meq O2/kg oil. Moreover, the trends shown by our emulsions were similar to those reported by Cheng et al. [63] in emulsions with 10%wt of soybean oil, 1.13%wt of Tween20 and no antioxidant incorporated.
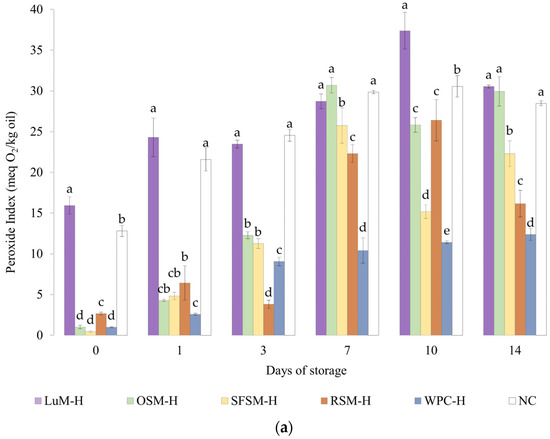
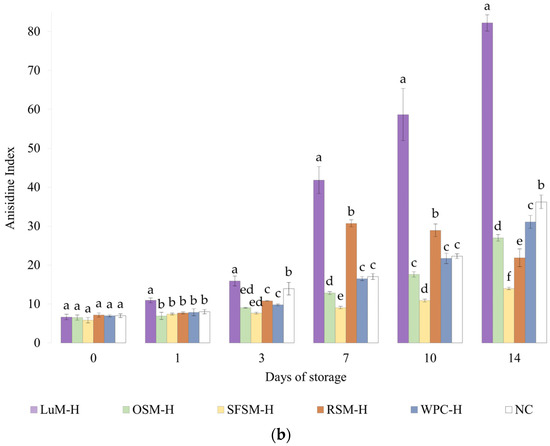
Figure 4.
(a) Peroxide and (b) anisidine value for emulsions prepared with plant-based hydrolysates as antioxidant compounds. LUM–H: lupin meal hydrolysate; OSM–H: olive seed meal hydrolysate; SFSM–H: sunflower seed meal hydrolysate; RSM–H: rapeseed meal hydrolysate; WPC–H: whey protein concentrate hydrolysate; NC: negative control (without hydrolysate). All the data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of triplicate measurements. Different superscript letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) among plant protein hydrolysates.
In contrast, the emulsion containing WPC–H, which was previously reported to exhibit antioxidant activity, had a PV of 1.0 meq O2/kg oil after production. This emulsion showed a 1-day lag phase, and then PV linearly increased to reach its maximum value of 12.4 meq O2/kg oil on day 14. It should be noted that the emulsion containing WPC–H showed significantly lower PV values than the control emulsion without antioxidants. Our results are higher but similar in trend to Padial-Domínguez et al. [24], which produced emulsions using 2%wt of WPC–H as emulsifier instead of Tween20.
Regarding the emulsions containing the plant-based hydrolysates, the emulsion with LUM–H exhibited the highest PV in the experimental series, remaining above NC emulsion all over the storage period. The lower oxidative stability of the emulsion with LUM–H could be explained due to the lowest in vitro antioxidant activity of LUM–H (Figure 2) together with a very negative zeta potential of this emulsion (Table 2). The surface net charge observed on day 1 and mean diameters computed for the droplet distributions could favor the attraction of Fe2+ to the interface catalyzing lipid oxidation [64]. Emulsions containing OSM–H and SFSM–H showed similar PV values during storage, reaching their maximum on day 7 (30.7 and 25.8 meq O2/kg oil, respectively), with considerably lower PV values when compared with the emulsion without antioxidants. Interestingly, the PV of the emulsion containing RSM–H displayed low PV and a lag phase until day 3. Then, the PV rapidly increased and tended to reduce between days 10 and 14. Overall, although emulsions containing hydrolysates from oilseeds by-products were not better in contrast with the emulsion containing WPC–H, they were able to delay the primary oxidation of fish oil by staying below the emulsion without antioxidants in most of the storage days. To the best of our knowledge, there are no works to date that evaluated the oxidative oil-in-water stability of hydrolysates from LUM, OSM, SFSM and RSM, and very few are found from other sources. This is the case of Cheng et al. [63], who studied the oxidative stability of soybean (10%wt) oil-in-water emulsions over 14 days using potato hydrolysates treated with alcalase as natural antioxidants and Tween20 (1.13%wt) as emulsifier. The authors tested different levels of plant protein hydrolysates, reporting minimal oxidation (PV around 20 meq O2/kg oil at day 14) for the emulsion containing 20 mg/mL of hydrolysate. A similar change in PV was observed for SFSM–H (PV ranging from 0.5 to 22.3 meq O2/kg oil) and RSM–H (PV ranging from 2.7 to 16.2 meq O2/kg oil). In contrast, it is noticeable that in our study we used 2 mg/mL of hydrolysate as antioxidant ingredient.
3.4.2. Anisidine Value
The Figure 4b shows the p-anisidine value (AV) of emulsions containing plant-based hydrolysates and the control emulsions. Like the PV results, LUM–H shows the highest AV values, remaining above the NC emulsion during the storage period. These results denote the poor oxidative stability of LUM–H emulsion, which could be explained by its low in vitro antioxidant activity and more negative zeta potential, which favors metal-catalyzed oxidation. Moreover, the lipid content of the lupin hydrolysate (5.9 %wt, Table 1) could also contribute to initiate lipid oxidation [24]. Regarding the RSM–H emulsion, the AV value surpassed the control emulsion WPC–H from the day 7 on, remaining stable until the final storage day. This behavior was unexpected due to the good in vitro DPPH scavenging activity and Fe2+ chelation capacity observed. However, in vitro tests do not represent all complex lipid oxidation mechanisms that take place in the emulsion [65], which could explain the differences between in vitro and emulsion results. Ka et al. [66] evaluated the anti and pro-oxidant properties in vitro and in oil-in-water emulsions of some amino acids, and one of their findings was that some residues (e.g., Cys) exert high antioxidant in vitro capacity but not in oil-in-water emulsions, suggesting that high in vitro antioxidant capacity will not necessarily display similar antioxidant capacities in a real food matrix. By contrast, OSM–H and SFSM–H were able to retard the formation of unsaturated aldehydes in emulsions to greater extent when compared with the control emulsion (NC) or the emulsion containing WPC–H. OSM–H considerably increases the AV after 7 days of storage but without surpassing NC. Shi et al. [67] mention that Tyr, Trp, Met and Cys amino acids confer excellent antioxidant capacities to hazelnut protein peptides, acting as important hydrogen donors for free radicals. Among these amino acid residues, they found that Tyr-containing peptides exert a significant antioxidant activity. In addition, López-García et al. [45] also reported Val as a good electron donor, which could be present in an important amount in OSM–H. Nevertheless, they also mentioned that certain amino acids such as His, Tyr, Trp, Met, Cys and Pro could also avoid lipid peroxidation, which may explain the OSM–H behavior on lipid oxidation tests, as it could be possible to find a big proportion of Tyr and Val in the raw material, as well as some presence of Met. The latter indicates that these hydrolysates possess the ability to reduce the decomposition of peroxides to secondary oxidation products. This was especially the case of SFSM–H since the AV remains quasi-constant, with a slight increment during storage. It is worth noting that SFSM–H was more capable of retarding the secondary oxidation in contrast with WPC–H. The latter could be due to the presence of peptides with antioxidant character but also may be to the presence of other antioxidant compounds (e.g., flavonoids) [68]. In addition, a higher DH in SFSM–H (20%) could lead to the formation of lower peptide chain lengths compared with the DH of WPC–H (10%). This good oxidative stability is in agreement with in vitro results, where SFSM–H displays a remarkable scavenging activity.
4. Conclusions
All plant-based hydrolysates employed in this study, except LUM–H, showed a remarkable in vitro capacity to scavenge DPPH radicals and chelate iron (II) ions. The addition of hydrolysates into 5%wt fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with 1%wt Tween20 did not lead to physical destabilization among all the storage time. The latter was observed as emulsions displayed a moderate negative surface charge of the dispersed oil droplets with an average mean diameter D[4,3] of 0.411 ± 0.010 μm at the end of the storage. Regarding their oxidative stability, LUM–H seems to act as a pro-oxidant, promoting emulsion oxidation, which could be attributed to its lowest in vitro antioxidant activity as well as its more negative zeta potential that may favor the attraction of metal ions to the interface, therefore promoting lipid oxidation. In opposition to this result, OSM–H, SFSM–H and RSM–H were able to delay the formation of first and second oxidation products in the emulsions compared with the negative control. Over them, OSM–H and SFSM–H enhanced the oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions compared with the emulsions with WPC–H and without antioxidants, as shown by AV results. Based on this investigation, enzymatic hydrolysates from vegetable sub-products such as OSM and SFSM could be suitable as bioactive ingredients to incorporate into oil-in-water food emulsions, conferring added value to these substrates from oilseed industries. Additional investigations are needed to study the effect of hydrolysis conditions (e.g., substrate pretreatment, enzymes and degree of hydrolysis) and emulsion preparation (e.g., pH and concentration of hydrolysate) on oxidative stability.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antiox11081612/s1, Figure S1: Image of the fish oil emulsions at day 0; Figure S2: Image of the fish oil emulsions at day 14; Figure S3: Droplet size distribution of the fish oil emulsions at the beginning and end of the storage period.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.J.G.-M., E.M.G., M.d.C.A.-R. and R.P.-G.; data curation, J.L.O.-Q.; investigation, J.L.O.-Q.; resources, E.M.G.; software, A.G.; supervision, P.J.G.-M., E.M.G., M.d.C.A.-R. and R.P.-G.; writing—original draft, J.L.O.-Q.; writing—review and editing, J.L.O.-Q., P.J.G.-M., A.G., M.d.C.A.-R. and R.P.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the project PY20_00021 from the Regional Ministry of Economic Transformation, Industry, Knowledge, and Universities of Andalusia (Spain). J.L. Ospina. acknowledges the grant from the Colombian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation for funding her doctoral studies.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the companie Q’omer and Bernabé Campal for kindly providing some of the plant meals used in this work. We express our thanks to Cristina Coronas for her skillful help with the experiments on physical and oxidative stability.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Elagizi, A.; Lavie, C.J.; Marshall, K.; DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Milani, R.V. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Review. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: A Dose Response Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigaux, J.; Mathieu, S.; Nguyen, Y.; Sanchez, P.; Letarouilly, J.G.; Soubrier, M.; Czernichow, S.; Flipo, R.M.; Sellam, J.; Daïen, C. Impact of Type and Dose of Oral Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Disease Activity in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A.H.R.; Chappell, H.F.; Zulyniak, M.A. Dietary and Supplemental Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids as Moderators of Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdge, G.C.; Calder, P.C. Dietary α-Linolenic Acid and Health-Related Outcomes: A Metabolic Perspective. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2006, 19, 26–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Bresson, J.-L.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Flynn, A.; Golly, I.; Korhonen, H.; Lagiou, P.; Løvik, M.; Marchelli, R.; Martin, A.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA), Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) and Docosapentaenoic Acid (DPA). EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Assessment of Oxidative Stability in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Effect of Emulsification Process, Droplet Size and Storage Temperature. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Simal-Gandara, J. Advantages of Techniques to Fortify Food Products with the Benefits of Fish Oil. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Cui, J.; Taneja, A.; Zhu, X.; Singh, H. Evaluation of Processed Cheese Fortified with Fish Oil Emulsion. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourashouri, P.; Shabanpour, B.; Kordjazi, M.; Jamshidi, A. Characteristic and Shelf Life of Fish Sausage: Fortification with Fish Oil through Emulsion and Gelled Emulsion Incorporated with Green Tea Extract. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4474–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, C.E.; Gharibzahedi, S.M.T. Yogurts Supplemented with Lipid Emulsions Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids: New Insights into the Fortification, Microencapsulation, Quality Properties, and Health-Promoting Effects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.C.; Moldão-Martins, M.; Alves, V.D. Antioxidants of Natural Plant Origins: From Sources to Food Industry Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.-C.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S.; Ee, K.-Y.; Chai, T.-T. Advances on the Antioxidant Peptides from Edible Plant Sources. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgüç, A.; Gençdağ, E.; Yılmaz, F.M. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Plant Origin by-Products: Biological Activities and Techno-Functional Utilizations in Food Developments—A Review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aondona, M.M.; Ikya, J.K.; Ukeyima, M.T.; Gborigo, T.-W.J.A.; Aluko, R.E.; Girgih, A.T. In Vitro Antioxidant and Antihypertensive Properties of Sesame Seed Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysate and Ultrafiltration Peptide Fractions. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozón, B.; Cotabarren, J.; Valicenti, T.; Parisi, M.G.; Obregón, W.D. Chia Expeller: A Promising Source of Antioxidant, Antihypertensive and Antithrombotic Peptides Produced by Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Alcalase and Flavourzyme. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 132185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, A.; Cason, V.G.; Nishide, T.G.; Miranda de Matos, F.; de Castro, R.J.S. Improving the Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Properties of Common Bean Proteins by Enzymatic Hydrolysis Using a Blend of Proteases. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2021, 39, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, L.Y.; Diblan, S.; Aktas, H.; Cakitli, G. Changes in Bioactive Properties of Dry Bean Extracts during Enzymatic Hydrolysis and in Vitro Digestion Steps. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, L.M.; Fan, H.; Zapata, J.E.; Wu, J. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis for Preparing Cassava Leaf Hydrolysate with Antioxidant Activity. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famuwagun, A.A.; Alashi, A.M.; Gbadamosi, O.S.; Taiwo, K.A.; Oyedele, D.; Adebooye, O.C.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant and Enzymes Inhibitory Properties of Amaranth Leaf Protein Hydrolyzates and Ultrafiltration Peptide Fractions. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Nissen, J. Enzymic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins, 1st ed.; Elsevier Applied Science Publishers LTD: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Picot, L.; Ravallec, R.; Fouchereau-Péron, M.; Vandanjon, L.; Jaouen, P.; Chaplain-Derouiniot, M.; Guérard, F.; Chabeaud, A.; Legal, Y.; Alvarez, O.M.; et al. Impact of Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration of an Industrial Fish Protein Hydrolysate on Its Bioactive Properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, E.A.; Welch, B. Role of Ferritin as a Lipid Oxidation Catalyst in Muscle Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial-Domínguez, M.; Espejo-Carpio, F.J.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Jacobsen, C.; Guadix, E.M. Protein Derived Emulsifiers with Antioxidant Activity for Stabilization of Omega-3 Emulsions. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial-Domínguez, M.; Espejo-Carpio, F.J.; Pérez-Gálvez, R.; Guadix, A.; Guadix, E.M. Optimization of the Emulsifying Properties of Food Protein Hydrolysates for the Production of Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Foods 2020, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petursson, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Stabilization of Oil-in-Water Emulsions by Cod Protein Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3996–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shantha, N.C.; Decker, E.A. Rapid, Sensitive, Iron-Based Spectrophotometric Methods for Determination of Peroxide Values of Food Lipids. J. AOAC Int. 1994, 77, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6885:2006; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Determination of Anisidine Value. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/40052.html (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Zafeiriou, I.; Polidoros, A.N.; Baira, E.; Kasiotis, K.M.; Machera, K.; Mylona, P.V. Mediterranean White Lupin Landraces as a Valuable Genetic Reserve for Breeding. Plants 2021, 10, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmidolova, A.; Desseva, I.; Mihaylova, D.; Lante, A. Bioactive Peptides from Lupinus spp. Seed Proteins-State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecka-Majchrzak, K.; Sumara, A.; Fornal, E.; Montowska, M. Oilseed Proteins—Properties and Application as a Food Ingredient. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okagu, I.U.; Ndefo, J.C.; Aham, E.C.; Obeme-Nmom, J.I.; Agboinghale, P.E.; Aguchem, R.N.; Nechi, R.N.; Lammi, C. Lupin-Derived Bioactive Peptides: Intestinal Transport, Bioavailability and Health Benefits. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, D.; Barrionuevo, D.; Bodoira, R.; Zafra, A.; Jiménez-López, J.; Alché, J.d.D. Nutritional Profile and Nutraceutical Components of Olive (Olea europaea L.) Seeds. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4359–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanpit, V.V.; Tajane, S.P.; Mandavgane, S.A. Dietary Fibers from Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Methods of Extraction and Processes of Value Addition. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergio, J.-C.; Serna-Saldívar, O.; Campanella, O.; Editors, V.-O. Science and Technology of Fibers in Food Systems; Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, I.M.; Coelho, J.F.J.; Carvalho, M.G.V.S. Isolation and Valorisation of Vegetable Proteins from Oilseed Plants: Methods, Limitations and Potential. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghribi, A.M.; Gafsi, I.M.; Sila, A.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Bougatef, A.; Besbes, S. Effects of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Conformational and Functional Properties of Chickpea Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.V.; Ong, S.-E.; Mann, M. Trypsin Cleaves Exclusively C-Terminal to Arginine and Lysine Residues. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berraquero-García, C.; Almécija, M.C.; Guadix, E.M.; Pérez-Gálvez, R. Valorisation of Blood Protein from Livestock to Produce Haem Iron-Fortified Hydrolysates with Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vioque, J.; Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Clemente, A.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F. Partially Hydrolyzed Rapeseed Protein Isolates with Improved Functional Properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Medina, R.; Tamm, F.; Guadix, A.M.; Guadix, E.M.; Drusch, S. Functional and Antioxidant Properties of Hydrolysates of Sardine (S. pilchardus) and Horse Mackerel (T. mediterraneus) for the Microencapsulation of Fish Oil by Spray-Drying. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacias-Pascacio, V.G.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Siar, E.H.; Tavano, O.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Use of Alcalase in the Production of Bioactive Peptides: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2143–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Agyei, D.; Udenigwe, C.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, B. Manufacturing of Plant-Based Bioactive Peptides Using Enzymatic Methods to Meet Health and Sustainability Targets of the Sustainable Development Goals. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 769028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.; Singh, J.; Gani, A. Exploration of Bioactive Peptides from Various Origin as Promising Nutraceutical Treasures: In Vitro, in Silico and in Vivo Studies. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, G.; Dublan-García, O.; Arizmendi-Cotero, D.; Oliván, L.M.G. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Food Proteins. Molecules 2022, 27, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Xiong, Y.L.; Kong, B. Antioxidant Activity of Peptide Fractions from Whey Protein Hydrolysates as Measured by Electron Spin Resonance. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rival, S.G.; Boeriu, C.G.; Wichers, H.J. Caseins and Casein Hydrolysates. 2. Antioxidative Properties and Relevance to Lipoxygenase Inhibition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Han, B.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, X.L. Improvement of Nutritional Value, Molecular Weight Patterns (Soluble Peptides), Free Amino Acid Patterns, Total Phenolics and Antioxidant Activity of Fermented Extrusion Pretreatment Rapeseed Meal with Bacillus subtilis YY-1 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae YY-2. LWT 2022, 160, 113280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, A.; Hajji, M.; Balti, R.; Lassoued, I.; Triki-Ellouz, Y.; Nasri, M. Antioxidant and Free Radical-Scavenging Activities of Smooth Hound (Mustelus mustelus) Muscle Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Gastrointestinal Proteases. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Hosseini, F.S.; Reyhane, R.; Rashidi, L. Optimized Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Olive Pomace Proteins Using Response Surface Methodology. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibagon, J.A.; Lee, S.A.; Stein, H.H. Sunflower Expellers Have Greater Ileal Digestibility of Amino Acids than Sunflower Meal, but There Are Only Minor Variations among Different Sources of Sunflower Meal When Fed to Growing Pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vioque, J.; Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Clemente, A.; Pedroche, J.; Bautista, J.; Millan, F. Production and Characterization of an Extensive Rapeseed Protein Hydrolysate. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierlita, D.; Simeanu, D.; Pop, I.M.; Criste, F.; Pop, C.; Simeanu, C.; Lup, F. Chemical Composition and Nutritional Evaluation of the Lupine Seeds (Lupinus albus L.) from Low-Alkaloid Varieties. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelsang-O’Dwyer, M.; Bez, J.; Petersen, I.L.; Joehnke, M.S.; Detzel, A.; Busch, M.; Krueger, M.; Ispiryan, L.; O’Mahony, J.A.; Arendt, E.K.; et al. Techno-Functional, Nutritional and Environmental Performance of Protein Isolates from Blue Lupin and White Lupin. Foods 2020, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farvin, K.H.S.; Andersen, L.L.; Otte, J.; Nielsen, H.H.; Jessen, F.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant Activity of Cod (Gadus morhua) Protein Hydrolysates: Fractionation and Characterisation of Peptide Fractions. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Girgih, A.T.; Malomo, S.A.; Ju, X.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant Activities of Enzymatic Rapeseed Protein Hydrolysates and the Membrane Ultrafiltration Fractions. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hidalgo, I.; Bañón, S.; Ros, J.M. Evaluation of Table Olive by-Product as a Source of Natural Antioxidants. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farvin, K.H.S.; Andersen, L.L.; Nielsen, H.H.; Jacobsen, C.; Jakobsen, G.; Johansson, I.; Jessen, F. Antioxidant Activity of Cod (Gadus morhua) Protein Hydrolysates: In Vitro Assays and Evaluation in 5% Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsion. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Miao, M.; Jiang, B. Purification and Characterisation of a New Antioxidant Peptide from Chickpea (Cicer arietium L.) Protein Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Castilla, J.; Hernández-Álvarez, A.J.; Jiménez-Martínez, C.; Jacinto-Hernández, C.; Alaiz, M.; Girón-Calle, J.; Vioque, J.; Dávila-Ortiz, G. Antioxidant and Metal Chelating Activities of Peptide Fractions from Phaseolin and Bean Protein Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesiltas, B.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Gregersen, S.; Olsen, T.H.; Jones, N.C.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant Peptides Derived from Potato, Seaweed, Microbial and Spinach Proteins: Oxidative Stability of 5% Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh Kenari, R.; Razavi, R. Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Free/Bound Phenolic Compounds of Sesame and Properties of Encapsulated Nanoparticles in Different Wall Materials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J. Antioxidant and Emulsifying Properties of Potato Protein Hydrolysate in Soybean Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Moreno, P.J.; Yang, J.; Gregersen, S.; Jones, N.C.; Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B.; et al. The Structure, Viscoelasticity and Charge of Potato Peptides Adsorbed at the Oil-Water Interface Determine the Physicochemical Stability of Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Ma, J.H.; Luo, H.Y.; Xu, Y.F. Purification and Characterisation of a Novel Antioxidant Peptide Derived from Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Protein Hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ka, H.; Yi, B.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J. Evaluation of Antioxidant or Prooxidant Properties of Selected Amino Acids Using In Vitro Assays and in Oil-in-Water Emulsions Under Riboflavin Sensitization. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C1118–C1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Liu, M.; Zhao, H.; Lv, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhang, B. A Novel Insight into Screening for Antioxidant Peptides from Hazelnut Protein: Based on the Properties of Amino Acid Residues. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petraru, A.; Ursachi, F.; Amariei, S. Nutritional Characteristics Assessment of Sunflower Seeds, Oil and Cake. Perspective of Using Sunflower Oilcakes as a Functional Ingredient. Plants 2021, 10, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).