Functional and Structural Insights into the Human PPARα/δ/γ Targeting Preferences of Anti-NASH Investigational Drugs, Lanifibranor, Seladelpar, and Elafibranor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PPAR Activation Assay 1: Transactivation Assay
2.2. Recombinant PPARα/δ/γ-LBD Expression and Purification
2.3. PPAR Activation Assay 2: PGC1α/SRC1 Coactivator Recruitment Assay
2.4. PPAR Activation Assay 3: Thermal Stability Assay Using Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
2.5. Cocrystallization of PPARα/δ/γ-LBD with Lanifibranor, Seladelpar, or Elafibranor
2.5.1. PPARα Cocrystals
2.5.2. PPARδ Cocrystals
2.5.3. PPARγ Cocrystals
2.6. X-ray Diffraction: Data Collection and Model Refinement
2.7. Evaluation of Molecular Interactions between PPAR-LBD Amino Acids and Ligands
3. Results
3.1. Transactivation of Gene Expression via PPARα/δ/γ-LBD
3.2. PGC1α/SRC1 Coactivator Recruitment via PPARα/δ/γ-LBD
3.3. Thermal Stability of PPARα/δ/γ-LBD
3.4. Structures of the PPARα/δ/γ-LBD–Lanifibranor Complexes
3.5. Structures of the PPARα/δ/γ-LBD–Seladelpar Complexes
3.6. Structures of the PPARα-LBD–Elafibranor Complex
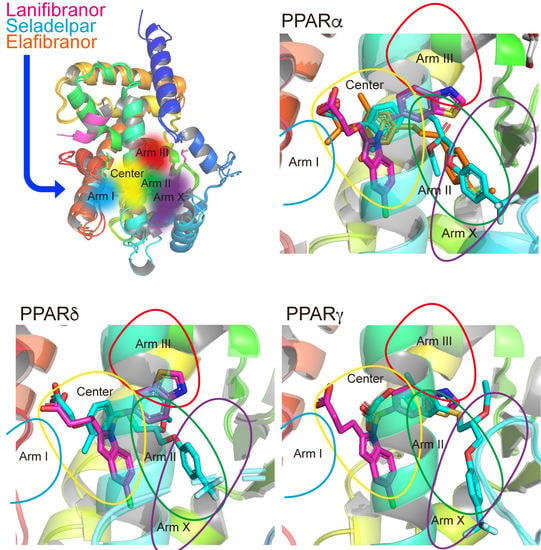
3.7. LBP Regional Localization of the Five PPAR Ligands in PPARα/δ/γ-LBD
3.8. Molecular Interactions between PPARα/δ/γ-LBD Amino Acids and the Ligands
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lee, G.; Heo, S.Y.; Roh, Y.S. Oxidative stress is a key modulator in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheka, A.C.; Adeyi, O.; Thompson, J.; Hameed, B.; Crawford, P.A.; Ikramuddin, S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppalanchi, R.; Noureddin, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Sanyal, A.J. Therapeutic pipeline in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.; Szabo, G.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Byrne, C.D.; Cusi, K.; Dufour, J.F.; Roden, M.; Sacks, F.; Tacke, F. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S.; Tan, W.R.; Low, Z.S.; Marvalim, C.; Lee, J.Y.H.; Tan, N.S. Exploration and development of PPAR modulators in health and disease: An update of clinical evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CymaBay Therapeutics Press Release. CymaBay Therapeutics Halts Clinical Development of Seladelpar. 25 November 2019. Available online: https://ir.cymabay.com/press-releases/detail/476/cymabay-therapeutics-halts-clinical-development-of-seladelpar (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- GENFIT Press Release (11 May 2020). GENFIT: Announces Results from Interim Analysis of RESOLVE-IT Phase 3 Trial of Elafibranor in Adults with NASH and Fibrosis. Available online: https://ir.genfit.com/news-releases/news-release-details/genfit-announces-results-interim-analysis-resolve-it-phase-3/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Lehmann, J.M.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Wilkison, W.O.; Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12953–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, T.; Fairall, L.; Amin, K.; Inaba, Y.; Szanto, A.; Balint, B.L.; Nagy, L.; Yamamoto, K.; Schwabe, J.W. Structural basis for the activation of PPARgamma by oxidized fatty acids. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Martins, T.; Sadowski, I. Wild type GAL4 binds cooperatively to the GAL1-10 UASG in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9629–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, A.; Kamata, S.; Akahane, M.; Machida, Y.; Uchii, K.; Shiiyama, Y.; Habu, Y.; Miyawaki, S.; Kaneko, C.; Oyama, T.; et al. Functional and structural insights into human PPARα/δ/γ subtype selectivity of bezafibrate, fenofibric acid, and pemafibrate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, S.; Oyama, T.; Saito, K.; Honda, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Suda, K.; Ishikawa, R.; Itoh, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Shibata, T.; et al. PPARα ligand-binding domain structures with endogenous fatty acids and fibrates. iScience 2020, 23, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, S.; Oyama, T.; Ishii, I. Preparation of co-crystals of human PPARα-LBD and ligand for high-resolution X-ray crystallography. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, A.; Kamata, S.; Satta, C.; Machida, Y.; Uchii, K.; Terasawa, K.; Nemoto, A.; Oyama, T.; Ishii, I. Structural basis for anti-non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetic dyslipidemia drug saroglitazar as a PPARα/γ dual agonist. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, P.R.; Murshudov, G.N. How good are my data and what is the resolution? Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Reddy, J.K. Transcription coactivators for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1771, 936–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feige, J.N.; Auwerx, J. Transcriptional coregulators in the control of energy homeostasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchiroud, L.; Eichner, L.J.; Shaw, R.J.; Auwerx, J. Transcriptional coregulators: Fine-tuning metabolism. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefere, S.; Puengel, T.; Hundertmark, J.; Penners, C.; Frank, A.K.; Guillot, A.; de Muynck, K.; Heymann, F.; Adarbes, V.; Defrêne, E.; et al. Differential effects of selective- and pan-PPAR agonists on experimental steatohepatitis and hepatic macrophages. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouno, T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Kisseleva, T.; Cable, E.E.; Schnabl, B. Selective PPARδ agonist seladelpar suppresses bile acid synthesis by reducing hepatocyte CYP7A1 via the fibroblast growth factor 21 signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattenberg, J.M.; Pares, A.; Kowdley, K.V.; Heneghan, M.A.; Caldwell, S.; Pratt, D.; Bonder, A.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Levy, C.; Vierling, J.; et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of elafibranor in patients with primary biliary cholangitis and incomplete response to UDCA. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Sattar, M.A.; Johns, E.J.; Eseyin, O.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist (pioglitazone) with exogenous adiponectin ameliorates arterial stiffness and oxidative stress in diabetic Wistar Kyoto rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 907, 174218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boubia, B.; Poupardin, O.; Barth, M.; Binet, J.; Peralba, P.; Mounier, L.; Jacquier, E.; Gauthier, E.; Lepais, V.; Chatar, M.; et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a novel series of indole sulfonamide peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) α/γ/δ triple activators: Discovery of lanifibranor, a new antifibrotic clinical candidate. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2246–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Muccio, D.D.; Melo, N.; Atigadda, V.R.; Renfrow, M.B. Stability of the retinoid X receptor-α homodimer in the presence and absence of rexinoid and coactivator peptide. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Luo, H.; Chen, J.; Cheng, F.; Gui, C.; Zhang, R.; Shen, J.; Chen, K.; Jiang, H.; et al. Binding analyses between human PPARgamma-LBD and ligands. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzio, G.; Barrera, G.; Pizzimenti, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and oxidative stress in physiological conditions and in cancer. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.J.; Yu, W.Q.; Yang, T.M.; Guo, S.D. Targeting PPARs for therapy of atherosclerosis: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tan, H.; Wan, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, X. PPAR-γ signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 245, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.Y.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.G. Transactivation of the PPAR-responsive enhancer module in chemopreventive glutathione S-transferase gene by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and retinoid X receptor heterodimer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3701–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruzehaji, N.; Frantz, C.; Ponsoye, M.; Avouac, J.; Pezet, S.; Guilbert, T.; Luccarini, J.M.; Broqua, P.; Junien, J.L.; Allanore, Y. Pan PPAR agonist IVA337 is effective in prevention and treatment of experimental skin fibrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouac, J.; Konstantinova, I.; Guignabert, C.; Pezet, S.; Sadoine, J.; Guilbert, T.; Cauvet, A.; Tu, L.; Luccarini, J.M.; Junien, J.L.; et al. Pan-PPAR agonist IVA337 is effective in experimental lung fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer-Diaz, Z.; Aristu-Zabalza, P.; Andrés-Rozas, M.; Robert, C.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Broqua, P.; Junien, J.L.; Wettstein, G.; Bosch, J.; et al. Pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor improves portal hypertension and hepatic fibrosis in experimental advanced chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.M.; Bedossa, P.; Ratziu, V.; Anstee, Q.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Harrison, S.A.; Balabanska, R.; Mateva, L.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of the pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor in NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dougherty, E.J.; Danner, R.L. PPARγ signaling and emerging opportunities for improved therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artis, D.R.; Lin, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Mehra, U.; Perreault, M.; Erbe, D.; Krupka, H.I.; England, B.P.; Arnold, J.; et al. Scaffold-based discovery of indeglitazar, a PPAR pan-active anti-diabetic agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlus, C.L.; Galambos, M.R.; Aspinall, R.J.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Jones, D.E.J.; Dörffel, Y.; Gordon, S.C.; Harrison, S.A.; Kremer, A.E.; Mayo, M.J.; et al. A phase II, randomized, open-label, 52-week study of seladelpar in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CymaBay Therapeutics Press Release. FDA Lifts all Clinical Holds on Seladelpar. 23 July 2020. Available online: https://ir.cymabay.com/press-releases/detail/485/fda-lifts-all-clinical-holds-on-seladelpar (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Bays, H.E.; Schwartz, S.; Littlejohn, T., 3rd; Kerzner, B.; Krauss, R.M.; Karpf, D.B.; Choi, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Naim, S.; Roberts, B.K. MBX-8025, a novel peroxisome proliferator receptor-delta agonist: Lipid and other metabolic effects in dyslipidemic overweight patients treated with and without atorvastatin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2889–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kremer, A.E.; Mayo, M.J.; Hirschfield, G.; Levy, C.; Bowlus, C.L.; Jones, D.E.; Steinberg, A.; McWherter, C.A.; Choi, Y.J. Seladelpar improved measures of pruritus, sleep, and fatigue and decreased serum bile acids in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haczeyni, F.; Wang, H.; Barn, V.; Mridha, A.R.; Yeh, M.M.; Haigh, W.G.; Ioannou, G.N.; Choi, Y.J.; McWherter, C.A.; Teoh, N.C.; et al. The selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta agonist seladelpar reverses nonalcoholic steatohepatitis pathology by abrogating lipotoxicity in diabetic obese mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Baiga, T.J.; Downes, M.; La Clair, J.J.; Atkins, A.R.; Richard, S.B.; Fan, W.; Stockley-Noel, T.A.; Bowman, M.E.; Noel, J.P.; et al. Structural basis for specific ligation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2563–E2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratziu, V.; Harrison, S.A.; Francque, S.; Bedossa, P.; Lehert, P.; Serfaty, L.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Boursier, J.; Abdelmalek, M.; Caldwell, S.; et al. Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α and -δ, induces resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis without fibrosis worsening. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1147–1159.e1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cariou, B.; Zaïr, Y.; Staels, B.; Bruckert, E. Effects of the new dual PPAR α/δ agonist GFT505 on lipid and glucose homeostasis in abdominally obese patients with combined dyslipidemia or impaired glucose metabolism. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cariou, B.; Hanf, R.; Lambert-Porcheron, S.; Zaïr, Y.; Sauvinet, V.; Noël, B.; Flet, L.; Vidal, H.; Staels, B.; Laville, M. Dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α/δ agonist GFT505 improves hepatic and peripheral insulin sensitivity in abdominally obese subjects. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamata, S.; Honda, A.; Ishikawa, R.; Akahane, M.; Fujita, A.; Kaneko, C.; Miyawaki, S.; Habu, Y.; Shiiyama, Y.; Uchii, K.; et al. Functional and Structural Insights into the Human PPARα/δ/γ Targeting Preferences of Anti-NASH Investigational Drugs, Lanifibranor, Seladelpar, and Elafibranor. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081523
Kamata S, Honda A, Ishikawa R, Akahane M, Fujita A, Kaneko C, Miyawaki S, Habu Y, Shiiyama Y, Uchii K, et al. Functional and Structural Insights into the Human PPARα/δ/γ Targeting Preferences of Anti-NASH Investigational Drugs, Lanifibranor, Seladelpar, and Elafibranor. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(8):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081523
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamata, Shotaro, Akihiro Honda, Ryo Ishikawa, Makoto Akahane, Ayane Fujita, Chihiro Kaneko, Saeka Miyawaki, Yuki Habu, Yui Shiiyama, Kie Uchii, and et al. 2023. "Functional and Structural Insights into the Human PPARα/δ/γ Targeting Preferences of Anti-NASH Investigational Drugs, Lanifibranor, Seladelpar, and Elafibranor" Antioxidants 12, no. 8: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081523
APA StyleKamata, S., Honda, A., Ishikawa, R., Akahane, M., Fujita, A., Kaneko, C., Miyawaki, S., Habu, Y., Shiiyama, Y., Uchii, K., Machida, Y., Oyama, T., & Ishii, I. (2023). Functional and Structural Insights into the Human PPARα/δ/γ Targeting Preferences of Anti-NASH Investigational Drugs, Lanifibranor, Seladelpar, and Elafibranor. Antioxidants, 12(8), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081523