Abstract
Quinoa, a globally cultivated “golden grain” belonging to Chenopodium in the Amaranthaceae family, is recognized for being gluten-free, with a balanced amino acid profile and multiple bioactive components, including peptides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, and saponins. The bioactive compounds extracted from quinoa offer multifaceted health benefits, including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, cardiovascular disease (CVD) improvement, gut microbiota regulation, and anti-cancer effects. This review aims to intricately outline quinoa’s nutritional value, functional components, and physiological benefits. Importantly, we comprehensively provide conclusions on the effects and mechanisms of these quinoa-derived bioactive components on multiple cancer types, revealing the potential of quinoa seeds as promising and effective anti-cancer agents. Furthermore, the health-promoting role of quinoa in modulating gut microbiota, maintaining gut homeostasis, and protecting intestinal integrity was specifically emphasized. Finally, we provided a forward-looking description of the opportunities and challenges for the future exploration of quinoa. However, in-depth studies of molecular targets and clinical trials are warranted to fully understand the bioavailability and therapeutic application of quinoa-derived compounds, especially in cancer treatment and gut microbiota regulation. This review sheds light on the prospect of developing dietary quinoa into functional foods or drugs to prevent and manage human diseases.
1. Introduction
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Will.), an ancient grain with a long history, has garnered great attention due to its nutritional and health-promoting properties, making it an excellent choice for individuals with coeliac disease and gluten intolerance. Originating from the Andean region of South America, quinoa has been cultivated and consumed for over 5000 years, being revered as the “golden grain” and “mother grain” [1]. The ability to tolerate drought and cold conditions makes it thrive in high-altitude areas and poor soils. Therefore, quinoa cultivation was present in more than 120 countries by 2018, and almost 110 countries have started to test and produce quinoa in the last 30 years, including South America, North America, Asia, Europe, and other regions [2].
As an ancient grain, quinoa showcases a multitude of varieties and diversities classified based on the color, size, and texture of the grains. The most common classification of quinoa is based on color, which includes white, red, and black [3,4]. Quinoa is the sole pseudocereal recognized by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) as a single crop capable of providing all essential nutrients required by humans and ranks seventh on the list of “Top Ten Healthy Nutritious Foods” globally [5]. Overall, the dietary value of quinoa is higher than other grains such as rice, wheat, and corn, with values of 73%, 56%, 49%, and 36%, respectively, approaching that of beef (74%). Quinoa stands out as a superior plant-based protein source, providing nine essential amino acids, notably lysine (4.8 g/100 g protein), threonine (3.7 g/100 g protein), and methionine (1.9 g/100 g protein), which are typically deficient in conventional grains [6,7]. Furthermore, quinoa is abundant in dietary fiber, which is beneficial for intestinal motility and digestive health, particularly in promoting gut homeostasis [1]. Quinoa also serves as a rich mineral source, containing considerable amounts of magnesium, zinc, iron, calcium, potassium, and other essential minerals, with approximately four times higher calcium and iron content compared to other crops [8]. Furthermore, quinoa contains diverse secondary metabolites such as polyphenolic compounds, polysaccharides, saponins, and other bioactive compounds, making quinoa a valuable food source for both humans and animals [9].
As a highly nutritious and gluten-free pseudocereal, quinoa has gained more and more attention due to its high-quality protein, palatable taste, and balanced nutritional profile [10]. To recognize quinoa’s nutritional value, the FAO designated 2013 as the “International Year of Quinoa” and listed it among the top 10 most nourishing foods globally [11]. This review aims to provide an in-depth analysis of quinoa’s nutritional composition and multiple bioactive effects on human health. The remarkable properties and health-promoting benefits of quinoa make it a compelling candidate for inclusion in diverse diets, offering a sustainable and nutritious solution for addressing global nutritional challenges. Without specific emphasis, “quinoa” in this review refers to “quinoa seeds”.
2. Nutritional Profile and Functional Components of Quinoa Seeds
2.1. Protein and Bioactive Peptides
The protein content of quinoa ranges from 12% to 22%, surpassing that of rice at 7.5%, barley at 11%, and corn at 13.4%. The quality of dietary protein is determined by the ratio of essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained from diet. The proteins in grains can be categorized into four types: albumins, globulins, prolamins, and glutelins. Unlike other cereal crops that primarily store prolamin proteins, quinoa contains very little prolamin protein (0.5–7%) and glutelin protein (18%). Instead, the main storage protein of quinoa is globulin (37%) and albumin (35%), stabilized by disulfide bonds [6,12]. The low concentration of prolamin in quinoa makes it a suitable alternative for individuals with celiac disease and an attractive option for gluten-free products. The main component of quinoa globulin is 11S globulin, also known as globular globulin. It has a hexameric structure and is composed of six pairs of small, basic polypeptides and larger, acidic polypeptides with molecular masses of 22–23 and 32–39 kDa, respectively [13]. 11S globulin has herein become the reference source for FAO amino acids leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, and tyrosine [1]. The secondary structure of quinoa albumin consists of 4% α-helices, 50% β-sheets, and 46% aperiodic structure [14]. Compared to globulins, quinoa albumin is characterized by high levels of cysteine, arginine, histidine, and lysine. Quinoa protein fulfills over 180% of the histidine requirement estimated by the FAO/WHO/UNU, as well as 274% for isoleucine, 338% for lysine, 212% for methionine+cysteine, 320% for phenylalanine+tyrosine, 331% for threonine, 228% for tryptophan, and 323% for valine [15,16]. The lysine content in quinoa is twice as high as in wheat or corn [17]. Therefore, quinoa serves as a high-quality plant-based protein with a well-balanced amino acids profile, addressing deficiencies in lysine and histidine, particularly beneficial for pregnant women and infants. Studies have shown that quinoa protein is highly digestible in animals (about 95.3%), compared to 101.5% for casein; raw quinoa protein is absorbed at a rate of 91.6%, and heat treatment, such as cooking, further increases protein absorption capacity up to 95.3%, making quinoa a suitable food option for individuals with dyspepsia [18]. Due to its high digestibility and superior amino acid profile, the nutritional value of quinoa is comparable to that of beef and far surpasses rice, wheat, and corn [16].
Bioactive peptides (BAPs) are short protein fragments with biological activity derived from specific regions of proteins through enzymatic hydrolysis or proteolytic processes, exhibiting various physiological effects in living organisms [19]. Recent investigations have focused on isolating and characterizing bioactive hydrolysates and BAPs obtained from quinoa proteins with advanced techniques and functional trials [7,20]. The BAPs and protein hydrolysates derived from quinoa have displayed numerous bioactive effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects, especially in terms of hypoglycemic, hypotensive, and hypolipidemic activities, which have been widely studied in vitro and in vivo [21,22,23]. Table 1 summarizes several BAPs derived from quinoa protein, along with their sources and analytical methods.

Table 1.
Typical peptides isolated from quinoa samples.
2.2. Carbohydrates and Dietary Fiber
Carbohydrates represent the largest proportion of macronutrients in quinoa seeds, accounting for 58–64% of the seed dry matter (DM), lower than that of wheat, corn, or rice (ranging from 78% to 81%) [30]. Polysaccharides are high-molecular-weight carbohydrates bound by glycosidic bonds with biological functions. Quinoa polysaccharides include starch polysaccharides and non-starch polysaccharides. In quinoa, starch serves as the most important carbohydrate (accounting for 60%), characterized by high solubility and digestibility with small granules of approximately 1.5 μm in diameter [1]. Quinoa has a higher content of amylopectin starch than amylose starch, and such a unique amylopectin structure gives quinoa starch special physicochemical properties such as low gelatinization temperatures and slow retrogradation [31]. Quinoa has low levels of free sugars, primarily sucrose, glucose, fructose, arabinose, and maltose, making it a low glycemic index grain particularly advantageous for individuals with diabetes.
Dietary fiber is the indigestible portion of plant-based foods that is digested and metabolized by microorganisms in the large intestine, mostly concentrated in the bran layers of the grains. According to the prebiotic property, dietary fiber can be classified as resistant oligosaccharides, non-starch polysaccharides, resistant starches, and associated substances [32]. Non-starch polysaccharides are the major components of quinoa fiber. The content of quinoa fiber ranges from 14% to 20%, higher than that of other cereals and more similar to fruits. Additionally, the content of insoluble fiber ranges from 10% to 14%, while soluble fiber ranges from 3.7% to 5.9% [12]. The composition of quinoa fiber was pectins (4.7%), hemicellulose (41%), lignins (1.7%), and cellulose (52%) [33]. The insoluble fiber in quinoa primarily comprises homogalacturonans interspersed with rhamnogalacturonan I units, which include galactans and arabinans as sidechains (55%), xyloglucans (30%) primarily with di- and trisaccharide sidechains, and cellulose. The soluble fiber mainly consists of arabinans and homogalacturonans [34]. It was reported that the soluble dietary fiber (SDF) of quinoa had higher hydroxyl radical scavenging ability compared to wheat SDF, with red quinoa SDF exhibiting superior functional characteristics such as higher thermal stability, gel-forming capacity, bile acid-binding capacity, and water-holding capacity than that of white and black varieties [35,36]. In addition to genetic factors, the composition of quinoa fiber is also influenced by processing methods and growing conditions [37].
2.3. Lipids
The content of lipids in quinoa ranges from 4.4% to 8.8%, surpassing traditional grains like corn, rice, and millet, making it a potential resource for oil extraction. The content of fatty acid (FA) in the embryo of quinoa is higher than that in the endosperm, pericarp, and seed coat. The average lipid level in quinoa is 5.3%, with 85% comprising FA. Approximately 11% of FA were saturated, with palmitic acid predominating [38]. The unsaturated FA of quinoa mainly includes oleic acid (19.7–29.5%), linoleic acid (49.0–56.4%), and α-linolenic acid (8.7–11.7%), similar to soybean composition [1,17,38]. Compared to light-colored varieties, dark-colored quinoa seeds had higher FA content, with unsaturated FA reaching 89.42% and an omega-6/omega-3 FA ratio of ca.6/1 [39]. The lipid profile of quinoa altered throughout the growth stages. With growth, α-linolenic acid was the predominant FA, ranging from 385 to 473 g/kg of total, whereas linoleic acid gradually decreased until the shoot stage then increased. Palmitic acid, oleic acid, and stearidonic acid showed consistent content during the process [40]. Moreover, processing methods and climate change also influence the FA content, composition, and proportions [41]. In one study, the content of polyunsaturated FA in quinoa irradiated by an electron beam increased by 3% at 1 kGy, and the value of omega-3/omega-6 (0.21) increased by 5% [42]. Quinoa lipids are known for their relative stability and resistance to oxidation, even after heating or exposure to oxygen. The high oxidative stability of quinoa lipids and seed oil may be attributed to the presence of vitamin E, especially γ-tocopherol, as natural antioxidants [39,43,44].
2.4. Vitamins and Minerals
Quinoa seeds contain bioavailable vitamins, including vitamin C, vitamin B6, vitamin B5, thiamine, and folate. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient with antioxidant capacity that must be acquired exogeneously from food. The vitamin C content in 100 g of quinoa leaves ranges from 70 to 230 mg, 40–52 mg for 4-day-old sprouts, 37–70 mg for 20-day-old seedlings, and 16 mg for seeds, which is undetectable in wheat, corn, or rice [45]. Additionally, 100 g quinoa contains high levels of vitamin B6 and folic acid, basically meeting the daily requirements of an adult. In particular, riboflavin in 100 g of quinoa meets 80% of children’s and 40% of adults’ needs [12]. Furthermore, quinoa is a good source of vitamin B2, fulfilling approximately 40% of the daily recommended intake for an adult [46]. Quinoa’s ash content (3.4%) is higher than that of rice (0.5%), wheat (1.8%), and most other grains. With regard to meeting the recommended daily intake of minerals, 100 g of quinoa is capable of fulfilling the daily needs of adults for magnesium, manganese, copper, and iron, while phosphorus and zinc provide 40–60% of the daily requirements [12]. Moreover, the mineral of quinoa was found in biologically appropriate forms for better absorption [16]. Importantly, during germination, the iron, calcium, and zinc contents of quinoa can be further enhanced, increasing by approximately 39.43%, 49.04%, and 20.25%, respectively [47]. Such a process is due to the germination activating enzymes within the seeds (α-amylase, proteases, pullulanase, phytase, and other glucosidases), which degrade antinutritional factors and break down complex macronutrients to release more minerals [48,49]. Additionally, antinutritional factors like phytic acid and tannin, which usually bind minerals and reduce their bioavailability, are significantly reduced during germination, thereby increasing mineral availability [50,51]. Finally, cell wall hydrolysis and new metabolic activities during germination also enhance mineral release or synthesis [52].
2.5. Polyphenols
Polyphenols are a diverse group of bioactive secondary metabolites produced by plants, characterized by the presence of one or more aromatic rings and hydroxyl groups. Polyphenols have two general classes: one is flavonoids, and the other is phenolic acids [53]. Among these, flavonoids are further divided into flavones, flavononse, flavonols, flavanols, isoflavones, anthocyanins, and phenolic acids are generally classified into hydroxybenzoic and hydroxycinnamic acids. Different colors and varieties of quinoa exhibit variations in the composition and content of polyphenols [54]. In red, white, and black quinoa, the total phenolic content (TPC) and total flavonoid content (TFC) ranged from 514.03 to 1409.54 mg gallic acid equivalent (GAE)/100 g and 177.49 to 407.75 mg rutin equivalent (RE)/100 g, respectively. Red quinoa showed the highest TPC and TFC with the best ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging activity. TPC in red and black quinoa are predominantly present in bound form, with protocatechuic acid being the most abundant phenolic acid but in free form in white quinoa [55]. At least 23 polyphenols were identified in quinoa, with the majority being phenolic acids, primarily including vanillic acid, ferulic acid, and their derivatives, as well as dominant flavonoids quercetin, kaempferol, and their glycosides. Notably, darker-colored quinoa seeds exhibited higher phenolic concentrations and antioxidant activity [56]. The anthocyanin content in quinoa was approximately 120.4 ± 7.2 mg cyanidine-3-glucoside equivalent (CGE) per 100 g DW, much higher than that of jasmine rice, Amaranthus hybridus, and soybean [57,58]. Generally, germination could further increase the TPC and antioxidant activity of quinoa [58,59]. Moreover, the environmental factors and variety of quinoa greatly influence the types and levels of polyphenols. Numerous studies have shown that fermentation of quinoa or its extracts with Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium species significantly increased the TPC, bioavailability, and antioxidant capacity, suggesting a promising formulation for future health-promoting fermented foods [60,61,62,63]. Importantly, quinoa leaf extracts were another valuable source of polyphenolic compounds, with considerable amounts of ferulic, sinapinic, and gallic acids, as well as flavonoids like kaempferol, isorhamnetin, and rutin [64,65,66].
2.6. Saponins
Quinoa saponins, a typical antinutritional factor, serve a crucial function in shielding seeds from birds and insects due to their bitter taste and toxic effects. The basic structural formula of quinoa saponin is CnH2n−8O10 (n ≥ 5), which results from the glycosidic chain linking the carbohydrate chain to hydrophobic aglycones [67]. Quinoa-derived saponins are triterpene glycosides formed by the attachment of hydrophilic oligosaccharides at C-3 and C-28 positions of hydrophobic aglycone. Glucose, galactose, arabinose, glucuronic acid, and xylose are the common oligosaccharide sugars [68]. Saponins are the primary secondary metabolites in quinoa, mainly found in the outer layer of the seeds, with total content ranging from 3.81 to 27.1 mg/g [69]. Lim et al. found that quinoa seeds had significantly higher sapogenin content than stems, leaves, and roots, which were mainly composed of phytolaccagenic acid. Notably, quinoa roots had the highest amount of total saponin (13.39 g/100 g), followed by quinoa bran [70]. At least 40 saponin with eight different aglycones from quinoa have been isolated in the past 30 years, with the derived molecular entities essentially being phytolaccagenic, oleanolic, and serjanic acids; hederagenin; 3β,23,30 trihydroxy olean-12-en-28-oic acid; 3β-hydroxy-27-oxo-olean-12en-28-oic acid; and 3β,23,30 trihydroxy olean-12-en-28-oic acid [71,72]. The most common extraction methods for quinoa saponins include maceration, extraction by reflux, and Soxhlet, which rely on the solubility of solutes in solvents. Ethanol and methanol are considered optimal solvents for saponin extraction due to their high solubilizing capacity, with ultrasound and microwave assistance further enhancing extraction efficiency [73]. Key information on multiple saponins derived from quinoa is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Contents of saponin in various quinoa samples.
2.7. Other Compounds
Quinoa contains minimal amounts of phytic acid, oxalates, betanin, phytosterols, and phytoecdysteroids. Phytic acid, a prevalent anti-nutrient compound in plant-derived foods, demonstrates robust chelating activity against minerals and other cationic molecules. Excessive consumption of phytic acid can reduce the absorption of divalent minerals, including iron, calcium, magnesium, and zinc. The phytic acid content in three colors of quinoa ranged from 1.03 to 1.22 g/100 g, which was decreased by enhanced phytase activity after germination [76]. Oxalate is another anti-nutrient factor that binds to essential minerals, thereby hindering nutrient availability. The total content of oxalates in quinoa seeds and roots ranges from 143 to 232 mg/100 g, while in leaves and stems, the content ranges from 874 to 1959 mg/100 g. Prolonged consumption of soluble oxalates reduces the bioavailability of minerals and trace elements, increasing the risk of developing calcium oxalate stones in the kidneys [77]. Betanin is a hydrophilic, water-soluble plant pigment with potent bioactive properties. Quinoa was found with higher amounts of betanin than other pseudocereals, approximately 3930 μg/g. Betacyanins, mainly betanin and isobetanin, were confirmed for the first time to be the pigments of red and black quinoa seeds instead of anthocyanins [56]. Plant phytosterols are a type of sterol that serve as crucial components of plant cell membranes and are known for anti-cholesterol functionality. It was reported that 100 g quinoa seeds contained 118 mg phytosterols, primarily consisting of β-sitosterol, campesterol, brassicasterol, and stigmasterol, surpassing barley, rye, millet, and corn in content [78]. Moreover, the level of phytosterols in quinoa seed oil reached 45.0 mg/g, with β-sitosterol being the most abundant (19.6–46.6 mg/g), followed by stigmasterol (8.7–20.1 mg/g) and campesterol (0.4–2.0 mg/g). However, the phytosterol content in quinoa flour was only 0.80 mg/g [78,79]. Quinoa also belongs to sources of phytoecdysteroids, with total content ranging from 138 to 570 μg/g, demonstrating potential pharmacological and metabolic bioactivities. At least 13 different phytoecdysteroids have been identified and isolated from quinoa seeds, with the most common being 20-hydroxyecdysone (20-HE), comprising 60–90% of the total phytoecdysteroids [80,81].
3. Bioactive Activities of Quinoa
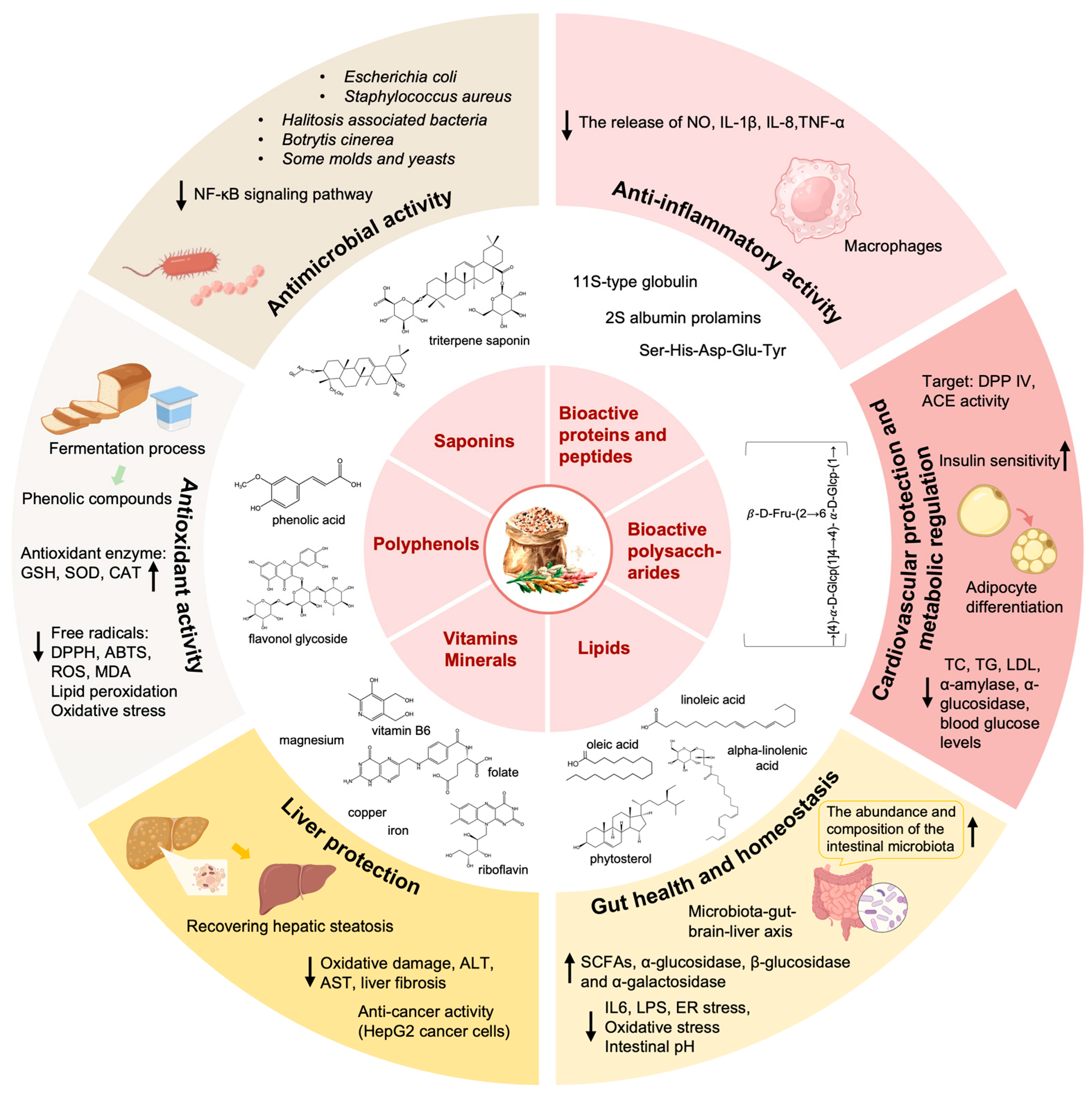
Quinoa possesses remarkable nutritional value, gluten-free characteristics, and therapeutic potential with possible nutraceutical benefits. Numerous studies have highlighted the multiple health-promoting benefits associated with quinoa consumption, attributed to its BAPs, polysaccharides, and unsaturated fatty acids, especially phytochemicals. Here, we comprehensively summarized the health benefits and molecular mechanisms of bioactive components derived from quinoa both in vivo and in vitro, providing theoretical support for developing quinoa as a novel functional food in the future (Figure 1).
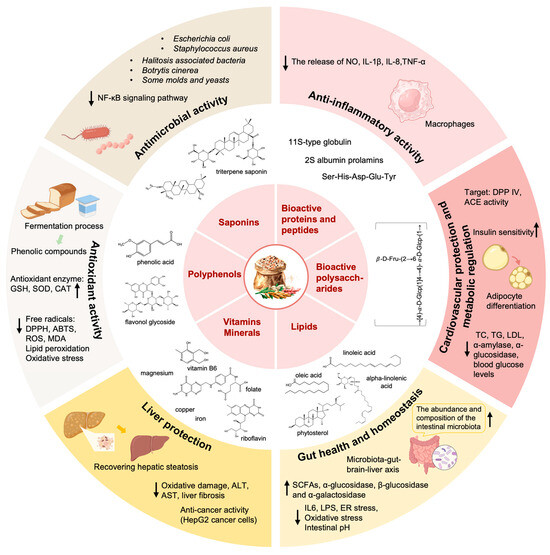
Figure 1.
The bioactive activities of functional components derived from quinoa. Quinoa has various physiological functions. The bioactive proteins and peptides, polysaccharides, lipids, vitamins and minerals, polyphenols, and saponins in quinoa play different physiological functions, including but not limited to antioxidant activity, antimicrobial activity, anti-inflammatory activity, liver protection, CVD protection, metabolic regulation, and impact on gut health and homeostasis (↑: increase; ↓: decrease).
3.1. Antioxidant Activity
In fact, all parts of the quinoa plant exhibit antioxidant activity, not just the seeds. A comprehensive comparison of total saponins, sapogenins, polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidant activity in different parts of quinoa plants was conducted and found that quinoa roots and sprouts had the highest content of flavonoids and phenolic acids, exerting stronger antioxidant activity than other parts [70]. In line with this, quinoa sprouts showed a higher level of total phenolic content and flavonoids and stronger antioxidant capacity compared to seed extracts [82]. Different quinoa varieties also exhibit varying levels of antioxidant capacity. In 25 yellow-seeded quinoa varieties, Temuco and Rainbow were identified as the most effective varieties in scavenging free radicals, while Baer and Temuco had the highest reducing power, indicating their capacity to donate electrons to ROS [83]. Many studies have unveiled that darker varieties of quinoa, like black quinoa, showed stronger antioxidant ability due to their higher level of total polyphenols and flavonoids. Moreover, free phenolics contributed the most (50–83%) to total phenolic content compared with conjugated or bound forms. Consistently, compared to white quinoa, extracts from black and red quinoa exhibited higher antioxidant activity, effectively reducing oxidative stress in HMEC-1 cells [84]. The latest research showed that the antioxidant activity and polyphenol content of quinoa was closely associated with the variety, as the darkest quinoa varieties, Negra and Pasankalla, exhibited the most favorable bioactive features regardless of their origin zone [85]. Interestingly, despite lower levels of total antioxidants compared to red quinoa, white quinoa’s richer content of bound phenolics demonstrated better DPPH and ABTS scavenging abilities, emphasizing the influence of polyphenol forms on antioxidant activity [55,56,74]. A recent study again confirmed that the darkest quinoa cultivars had the best functional properties and bioactive profile, underlining that genetic variability was more important than geographic factors [85]. Notably, the seed oil of black quinoa also exhibited the strongest antioxidant activity with the highest level of phytosterols, followed by red and white varieties [86].
The antioxidant capacity of quinoa is the integrated result of multiple bioactive components, especially BAPs, polysaccharides, unsaturated fatty acids, and polyphenolic compounds. In addition, vitamin C, vitamin E, and small amounts of carotenoids synergistically contribute to antioxidants. Daliri et al. reported that the DPPH radical scavenging capacity increased in the quinoa protein hydrolysate treated with trypsin digestion due to the expansion of protein molecules and availability of electron donor amino acids [20]. Further, quinoa peptides obtained by alkaline enzyme showed better antioxidant activity compared to trypsin hydrolysis [87]. Betanin-loaded nanocarriers based on 11S globulin from quinoa displayed stronger antioxidant efficacy than whole grains [88]. In detail, the albumin components of quinoa protein showed better antioxidant ability than globulins [89]. Lunasin, a representative BAP detected in quinoa, demonstrated strong ABTS radical scavenging activity (IC50 = 1.45 g/L) and oxygen radical scavenging activity [22]. Additionally, quinoa polysaccharide SQAP-2 exhibited outstanding capabilities for scavenging free radicals, including DPPH, ABTS, hydroxyl, superoxide radicals, and ferric iron reduction [90]. Another polysaccharide isolated from quinoa with high content and low molecular weight (8852 Da) purified by column chromatography exhibited a significant antioxidant effect against DPPH and ABTS [91]. Ethanol extraction of red quinoa bran yielded higher levels of rutin and total antioxidants. In vivo experiments indicated that feeding such extracts suppressed the expression of fatty acid synthesis enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase by increasing superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity while reducing alcohol-induced ALT and AST [92]. The hydrolysates from red quinoa improved renal oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats by reducing MDA levels and alleviating reduced SOD and glutathione (GSH) levels [93]. Al Qabba et al. found that ferulic acid and quercetin were the major phenolic acids and flavonoids in red quinoa and yellow quinoa sprouts, and more polyphenols were detected after germination. Importantly, quinoa sprout extracts markedly reduced MDA and efficiently enhanced the reduced GSH and SOD activities in oxidative stress-induced rats [94]. In the fructose-fed rat model, dietary supplementation of quinoa dramatically reduced oxidative stress levels in plasma, kidneys, liver, and lungs, manifested by a large decrease in blood MDA levels and lipid peroxidation biomarkers [95].
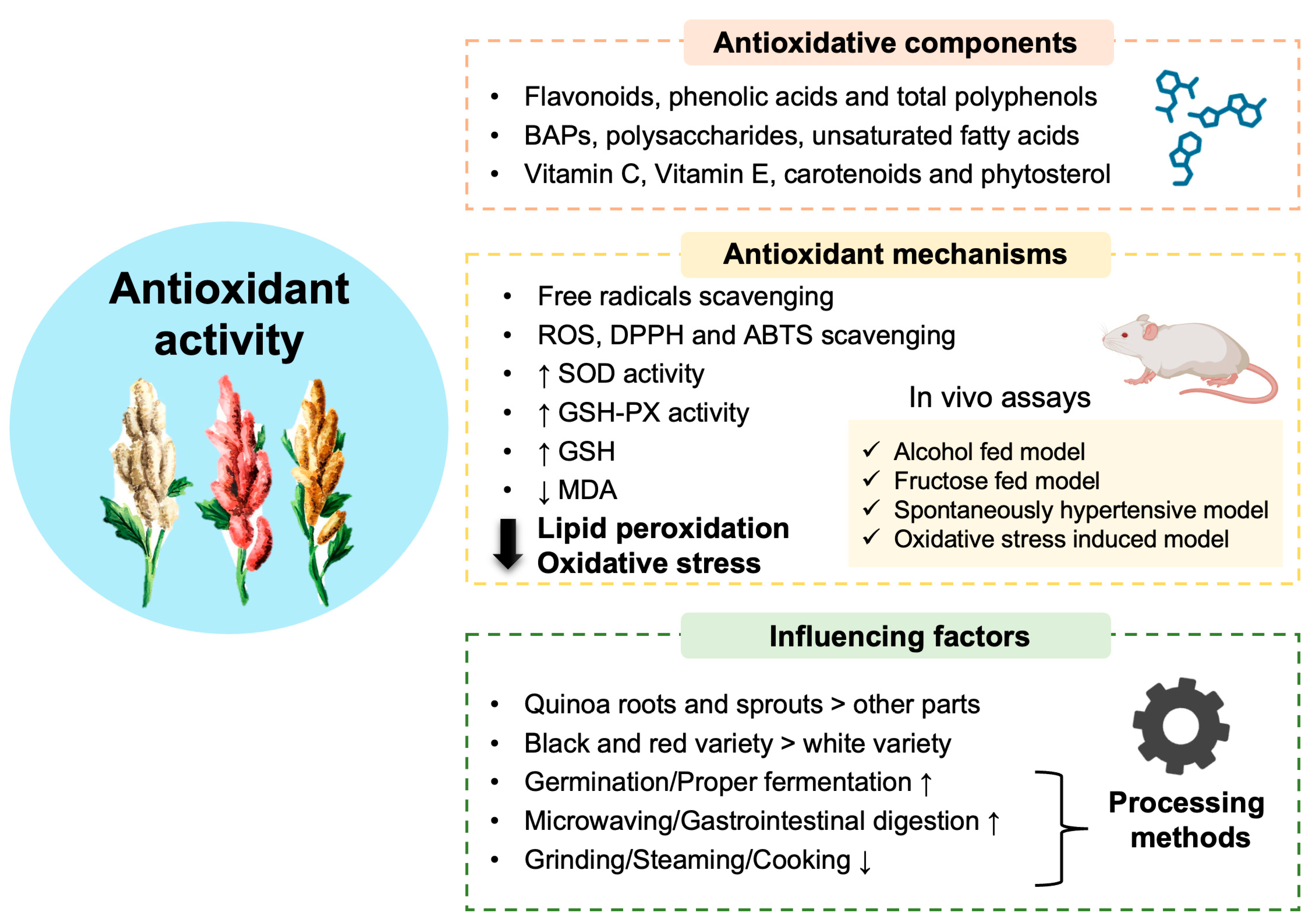
Different processing methods bring about changes in the antioxidant activity of quinoa. Grinding, steaming, and cooking led to reduced antioxidant activity due to the loss of total polyphenols and flavonoids by 31.5% and 41.4%, highlighting the importance of maintaining grain integrity [96]. Interestingly, microwaving released more polyphenols from black quinoa and enhanced the overall antioxidant activity [97]. Furthermore, gastrointestinal digestion of quinoa flavonoids led to a twofold increase in its antioxidant profile [98]. Importantly, germination and proper fermentation have been solidly confirmed to promote the antioxidant bioactivity of quinoa in multiple ways, especially by producing more BAPs and phytochemicals [62,99,100,101,102,103]. This section is illustrated in Figure 2.
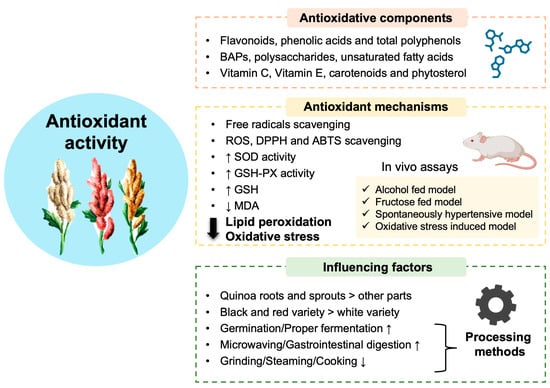
Figure 2.
Quinoa exhibits excellent antioxidant capabilities. Quinoa is rich in various antioxidant components, most notably total polyphenols, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. Additionally, bioactive peptides (BAPs), polysaccharides, and unsaturated fatty acids also possess antioxidant functions. The vitamin family, including vitamin C (VC) and vitamin E (VE), along with small amounts of carotenoids and phytosterols, show antioxidant potential as well. These bioactive components exert their antioxidant effects by scavenging various free radicals like ROS and enhancing the activities of antioxidant-related enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) while reducing the levels of oxidative product malondialdehyde (MDA). In vivo assays induced by multiple models have shown that quinoa and its bioactive components effectively alleviate lipid peroxidation and systemic oxidative stress, consistent with the aforementioned indicators. The overall antioxidant activity of quinoa is significantly influenced by variety, plant parts, and different processing methods (↑: increase; ↓: decrease).
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Grains containing gluten, especially wheat, have been shown to possess a strong ability to activate TLR4 receptors, thereby increasing intestinal inflammation through the activation of intestinal and mesenteric lymph node myeloid cells [104]. Quinoa, in addition to being a gluten-free grain that does not trigger inflammatory responses, exhibits excellent anti-inflammatory activity both in vitro and in vivo due to its rich content of various active components such as BAPs, polyphenols, polysaccharides, and saponins, making it particularly beneficial for individuals with gluten intolerance and digestive diseases [105]. Herein, we mainly focused on the latest advancements in the anti-inflammatory field regarding quinoa and its functional components.
Saponins are the primary antinutritional factors in quinoa and represent strong anti-inflammatory properties. Four saponin components isolated from quinoa dose-dependently reduced the production of nitric oxide (NO), a typical inflammatory factor, and inhibited the release of inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW264.7 cells [106]. It is well known that long-term consumption of high-fat diet (HFD), especially saturated and trans-fats, leads to inflammation and various chronic diseases. Total saponins extracted from quinoa bran significantly reduced IL-6 and LPS levels in HFD-induced obese rats while mitigating weight gain and visceral fat accumulation [107]. Lin et al. identified 11 saponins from quinoa bran, with the main components being hederagenin and oleanolic acid, which alleviated renal inflammation and kidney damage in hyperuricemic mice via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB inflammatory signaling, restoring serum parameters to normal levels [108]. Franceschelli et al. identified 4′-geranyloxyferulic acid as the only phytochemical product found belonging to quinoa secondary metabolites, which effectively inhibited NOS, IL-6, and TNF-α release in HCT-116 cells [109]. A plethora of research has demonstrated that BAPs derived from quinoa possess potent anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial for vegetarians and individuals with celiac disease [110]. Capraro et al. described a novel bioactive peptide, chenopodin, derived from quinoa, which effectively inhibited NF-κB activation and IL-8 expression in Caco-2 cells under IL-1β-induced inflammation [91]. Further, feeding chenopodin reduced mice paw edema and neutrophil recruitment in carrageenan-induced inflammation in vivo [111]. Lunasin is a novel cancer-preventive peptide initially identified from soybean protein [112]. Purified lunasin isolated from various quinoa varieties significantly inhibited the production of NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells, with inhibition rates of 44.77%, 39.81%, and 33.50%, respectively [22]. However, another study pointed out that hydrolysates of quinoa protein prepared using papain, gastric protease, and pancreatin exhibited anti-inflammatory levels similar to those of total protein [113]. Capraro et al. found that none of the quinoa proteins or peptides induced inflammation in Caco-2 cells, but all protein components, especially albumin fraction, showed strong protection against inflammation induced by IL-1β [114]. Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are chronic inflammatory conditions that lead to the disruption of the colonic mucus barrier. A novel quinoa protein peptide, TPGAFF, was found to mitigate colitis in mice by restoring damaged mucus barrier and intestinal permeability, inhibiting activation of inflammatory signals and inflammatory cytokines. Interestingly, TPGAFF also affected the abundance and composition of inflammation-related gut microbiota [115]. The white albumin extracted from quinoa, with a molecular weight of less than 30 kDa, increased macrophage TLR4 expression in vitro and promoted CD68/CD206 ratio, demonstrating its impact on inflammation [116]. Consistently, quinoa ameliorated HFD-induced hepatocarcinoma severity by alleviating immune mediators in the intestinal under the pro-tumor microenvironment, including CD68/CD206 ratio [117]. In addition, four quinoa polysaccharides showed the activity to inhibit the level of TNF-α and IL-6 induced by LPS. Notably, polysaccharides extracted with water had better anti-inflammatory activity than that of alkali [118]. Another purified novel polysaccharide promoted the proliferation of RAW264.7 macrophages in vitro but inhibited the production of nitric oxide in a dose- and time-dependent manner [91]. Moreover, an in vivo assay showed that QPS1, a purified quinoa polysaccharide, improved the inflammatory response induced by cyclophosphamide via reducing the levels of IFN-γ, IL-6, and IFN-α in serum, as well as enhancing the phagocytic function of mononuclear macrophages [119].
Extracts from sprouted seeds of red and yellow quinoa, at a dose of 30 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE) per kg, administered to CCL4-induced rat models significantly alleviated liver inflammation and restored serum indicators [94]. In an ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury rat model, quinoa water extracts attenuated inflammation and repaired the damaged gastric mucosa via inhibiting Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling. Additionally, it also reduced the levels of inflammatory factors in H2O2-induced oxidative stress in GES-1 cells [120]. Red quinoa extracts, rich in antioxidants, counteracted oxidative stress and inflammation induced by CCl4 by inhibiting the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) in vivo, whose effectiveness surpassed the rutin [121]. Chronic metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity have been proven to be closely associated with inflammation, which is viewed as a central homeostatic mechanism [122]. Feeding db/db mice supplemented with quinoa remarkedly reduced protein carbonyls and IL-6, alleviating hepatic steatosis and total liver c accumulation that was presumed to be attributed to dietary fiber and phytochemicals [123]. In mice with HFD/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes (T2DM), feeding quinoa yogurt effectively downregulated the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β) while increasing the release of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, alleviating systemic inflammation mediated by lipid dysregulation [124]. Apart from its active components, quinoa is promising to be utilized for anti-inflammatory applications for other drugs. Hydrolyzed quinoa protein as a carrier micelle stabilized anti-inflammatory drugs through the gastrointestinal tract and prolonged drug release. Animal experiments further confirmed that these micelles effectively accumulated in the inflamed colon region [125]. Collectively, the above findings suggest that quinoa may be used as a functional food component for the prevention and treatment of inflammation.
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity
The antimicrobial activity of quinoa is mainly due to its bioactive compounds like phenolics, saponins, and BAPs from seeds, leaves, roots, and inflorescences. Saponins, a class of secondary metabolites present in quinoa, were identified as major antimicrobial components. Alkali-treated quinoa saponin extracts exerted a noticeable inhibition on mycelial growth and spore germination of Botrytis cinerea due to increased affinity between saponin derivatives and sterols in the cell membrane [126]. Six saponins derived from quinoa husk strongly inhibited the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, with MIC values of 0.0625 mg/mL and 0.125 mg/mL, achieved through inducing bacterial biofilm system collapse [127]. Sun et al. evaluated the inhibitory activity of quinoa saponins against several bacteria associated with halitosis and found that alkaline-converted quinoa saponins exhibited stronger inhibitory effects than resin-obtained quinoa saponin, particularly against Fusobacterium nucleatum, with a low MIC of 31.3 μg/mL [128]. Farajzadeh et al. evaluated the antibacterial activity of ethanol extracts from quinoa seeds of Giza1, Red Carina, and Sajama. The results indicate that Giza1 extract had the highest antibacterial effects. The MIC of Giza1 against L. monocytogenes and E. coli bacteria were 10 and 5 mg/mL, respectively [129]. The antimicrobial properties of quinoa’s abundant polyphenols are well-known, and fermentation further enhanced such activity by releasing more compounds [130]. Crude polysaccharide extracts of quinoa inhibited the growth of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli [131]. Moreover, the quinoa hydrolyzed protein peptides obtained using pepsin and alkali exhibited extremely high antibacterial activity against Gram-positive Streptococcus pyogenes and Gram-negative Escherichia coli [132]. Interestingly, the extract from quinoa inflorescences also contained various effective bioactive components that exhibited antibacterial effects, suggesting the potential optimization for utilizing different parts of the quinoa plant [133].
Microbial spoilage that occurs during food processing, storage, and transportation poses significant challenges to food safety, hygiene, and economic loss. Recently, the antibacterial and health-promoting activity of quinoa has led to its use as a natural food preservative. The active biofilm prepared from quinoa starch and gold nanoparticles exhibited strong antibacterial activity against multiple foodborne pathogens, with an inhibition rate of 99% against Escherichia coli and 98% against Staphylococcus aureus [134]. During a 12-day frozen period, the total counts of Staphylococcus aureus, molds, and yeast in hamburgers encapsulated with quinoa peptide liposomes were significantly reduced by over 50% compared to the control [135]. Another type of edible coating containing chitosan and quinoa protein greatly inhibited the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella species [136]. Chitosan-nanoencapsulated extracts from red quinoa and ginseng have been shown to reduce the counts of various test bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Salmonella, Escherichia coli) [137]. Robledo et al. prepared nano-emulsions coated with quinoa and found it potently inhibited Botrytis cinerea growth in tomatoes after 7 days [138]. The antimicrobial properties of bioactive components within quinoa make it promising to be used as a novel packaging material for the maintenance of food safety and extension of shelf life.
3.4. Cardiovascular Protection and Metabolic Regulation
Excess body weight, hypertension, and dyslipidemia are regarded as the most potent established risk factors for CVD. Quinoa possesses a well-balanced amino acid profile and is abundant in unsaturated fatty acids, dietary fiber, micronutrients, and phytochemicals. These nutritional components collectively contribute to its potential to promote cardiovascular health and prevent CVD. The latest human intervention studies and animal experiments indicated that quinoa consumption partially alleviated metabolic stress and protected cardiovascular health. However, such effectiveness was found to be insufficient, and the molecular mechanisms behind it required further investigation [139]. A recent randomized parallel clinical trial involving 138 participants showed that postprandial blood sugar, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and body mass index were significantly lower in the quinoa group, particularly increasing high-density lipoproteins (HDL) [140]. A clinical study based on elderly prediabetic subjects revealed that an 8-week intake of quinoa lowered postprandial blood glucose levels, which was accompanied by reduced body weight [141]. Another randomized-controlled, double-blind crossover trial demonstrated that healthy older adults consuming 15 g quinoa cookies daily for 4 weeks experienced significant reductions in total and LDL cholesterol concentrations, weight, and BMI compared to the control. However, no significant changes were observed in TG, HDL, or PUFA [142]. The dietary intervention study based on 37 healthy overweight men showed that compared to refined wheat bread, daily consumption of bread containing 20 g quinoa flour demonstrated regulation of blood glucose levels but had minimal impact on other CVD risk biomarkers [143]. A prospective and double-blind study was conducted on 35 women with weight excess who consumed 25 g of quinoa flakes or corn flakes daily for four weeks. Surprisingly, the reduction of TC, LDL, and the increase in GSH occurred only in the quinoa group [144]. Furthermore, several meta-analyses based on randomized controlled trials have demonstrated that quantitatively consuming quinoa effectively intervened in blood glucose and lipid metabolism, particularly significantly reducing serum TG and TC levels [145,146,147].
Numerous in vivo experiments demonstrated quinoa’s activity in regulating lipid metabolism to reduce the risk of CVD. Consuming quinoa significantly reduced TC, LDL, and oxidized LDL levels in obese db/db mice, alleviating hepatic steatosis to levels similar to the control group [123]. In a Wistar rat model, feeding sprouted or fermented quinoa reduced food intake, blood glucose, and plasma lipid levels, as well as the accumulation of epididymal adipose tissue [148]. A recent study showed that quinoa reduced obesity, abnormal glucose, and lipid metabolism in a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced mouse model, possibly by modulating gut microbiota including Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Desulfovibrio [149]. Many studies have indicated a link between dysbiosis of gut microbiota and metabolic syndromes. Saponins from quinoa bran or BAPs from quinoa protein reduced lipid levels, blood glucose, body weight, and hepatic lipid accumulation in vivo via regulating the gut microbiota abundance and composition, which involved molecular mechanisms such as PPAR signaling and inflammatory indicators [107,150]. Supplementation with quinoa extract rich in 20-HE reduced fat tissue accumulation and insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice by reducing adipocyte size and fat storage [80]. Further, 20-HE globally increased energy expenditure and caused a shift in glucose metabolism toward oxidation to the detriment of lipogenesis. In addition, 20-HE also reduced the accumulation of AGE pigments, ROS, and fat deposits in Caenorhabditis elegans [151]. Additionally, a bioactive polysaccharide, SQWP-2, isolated and purified from quinoa greatly inhibited adipocyte differentiation by suppressing PPARγ, C/EBPα, C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ, SREBP1C, and AP2 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, suggesting a direct biofunction on adipocytes [152,153]. Quinoa extracts had little inhibitory effect on human platelet aggregation, suggesting that quinoa’s cardiovascular regulatory function may be independent of such effect [154]. Moreover, soluble and insoluble dietary fiber extracted from quinoa bran also improved lipid metabolism in mice with antioxidant capacity [155].
Postprandial hyperglycemia has been recognized as an important risk factor for CVD and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In preclinical models of Lepdb/+ pregnant mice, administration of quinoa protein hydrolysate alleviated glucose intolerance, improved liver insulin signaling, and several peptides exhibited anti-dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-IV) activity, a key enzyme involved in blood glucose control [156]. In Wistar rats, feeding quinoa for 15 weeks improved glucose intolerance, pancreatic β-cell dysfunction, insulin resistance, and lipid accumulation [157]. Another in vivo assay revealed that quinoa yogurt intake lowered fasting blood glucose levels while elevated hepatic glycogen content in T2DM mice, possibly via Akt/AMPK/PI3K signaling [124]. Based on bioinformatic analysis and computer-aided simulations, globulins in quinoa had the potential to inhibit DPP-IV and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) [158]. Furthermore, four BAPs exhibited the highest DPP-IV inhibitory activity in Caco-2 cells, suggesting that quinoa protein could serve as a promising source of DPP-IV targeted peptides [28]. Moreover, polyphenols and polysaccharides extracted from sprouted quinoa yogurt upregulated GLP-1 release and showed anti-DPP-IV in NCI-H716 cells [159]. In line with this, the phenolic constituents from black quinoa alleviated insulin resistance in HepG2 cells via IRS1/PI3K/Akt/GLUTs signaling [160]. Feeding HFD-induced obese mice with quinoa extracts reduced body weight and fasting blood glucose levels while improving lipid profiles. In particular, the flavonoid rutin plays a key role in blood sugar regulation [161,162]. α-amylase and α-glucosidase are crucial enzymes in metabolizing dietary carbohydrates. The bound polyphenols in quinoa extract, composed of ferulic acid and its derivatives, significantly inhibited α-glucosidase activity in vitro, effectively delaying starch digestion. In vivo experiments showed that feeding ICR mice with 50 mg/kg BP reduced postprandial glucose increases, equivalent to 20 mg/kg of acarbose [163]. It was reported that five crude polysaccharides derived from quinoa exhibited inhibitory activity against α-amylase and α-glucosidase in vitro and that solid-state fermented with Bifidobacterium spp. further enhanced such bioactivity [164,165].
Hypertension is the leading cause of CVD, and ACE is an essential enzyme involved in the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure and electrolyte balance. ACE inhibitors are commonly prescribed medications for the management of hypertension and heart failure. Therefore, ACE inhibition is widely used as an in vitro index to evaluate anti-hypertensive properties. The latest research suggested that utilizing the high-pressure-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis method released the most potent ACE-inhibitory peptides from quinoa [166]. Orally administered hydrolysate of red quinoa (1000 mg/kg/day) for 8 weeks effectively alleviated hypertension indicators in rats without affecting body weight and food intake [93]. Four tripeptides derived from quinoa were identified through PeptideRanker as promising novel ACE-inhibitory bioactive peptides [158]. Consumption of cooked red or black quinoa altered the ACE condition and oxidative stress in hypertension-induced rats, attributed to the presence of phenolic compounds [167]. Quinoa active ingredients, particularly BAPs, have been shown to exert ACE inhibitory activity, which is affected by fermentation or hydrolysis. In contrast to non-fermented quinoa, Lactobacillus plantarum fermented quinoa exhibited increased ACE inhibition, indicating more release of active components in quinoa [164]. Germinated quinoa ferments inoculated with Lactobacillus casei yielded protein peptides LAHMIVAGA and VAHPVF, demonstrating notable inhibitory effects against α-glucosidase and ACE [168]. Chirinos et al. showed that quinoa protein hydrolysate inhibited ACE-1 activity by 89.2% without change after simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro [169]. A novel BAP extracted from quinoa bran albumin, RGQVIYVL, exhibited excellent ACE-suppressing activity (IC50 = 38.16 μM) in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, molecular docking simulations indicated the potential binding between RGQVIYVL and ACE active sites with high affinity [23]. Furthermore, another BAP isolated from quinoa bran globulin hydrolysate was found to bind non-competitively to the active site of ACE at Pro519 and Ser461 [170]. Feeding quinoa protein effectively reduced blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Analysis of gastrointestinal contents and gut microbiota composition revealed promising precursor peptides [171,172]. Interestingly, incorporating quinoa into bread or plant-based milk has shown multifaceted metabolic regulation and CVD protective effects, again underlying the significance of quinoa as a functional food in preventing hypertension [173,174,175].
3.5. Protective Effects on Liver Function
The liver plays a critical role in numerous metabolic reactions, during which ROS, free radicals, and toxic metabolites are produced. Quinoa possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, highlighting its potential as a hepatoprotective agent. Firstly, active components from quinoa reduce non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through various molecular mechanisms such as antioxidation, anti-inflammation, and transcriptional regulation. Many in vivo studies have demonstrated that regular consumption of quinoa, quinoa extracts, or quinoa yogurt markedly alleviated multiple liver-related physiological indicators, including hepatic steatosis, lipid accumulation, hepatic inflammatory factors, liver function parameters (AST/ALT) and alcohol-induced liver damage, and systemic oxidative stress [92,176,177,178]. Interestingly, a study suggested that quinoa mediated the improvement of liver function through potential microbiota–gut–brain–liver interactions. Quinoa was found to modulate metabolism in the colon and liver by reducing ER stress and oxidative stress [149]. Quinoa and its extracts demonstrated preventive effects against hepatic steatosis, positively affecting the hepatic gene transcription program [123,155,179]. Indeed, quinoa was found to effectively upregulate lipid metabolism-related genes (Apoa5, Apoa4, Apoc2) and downregulate immune response-related genes (Irf5, Tlr6, Tlr10, Tlr11, Tlr12) to improve hepatic steatosis in rats [177]. Notably, the activation of ER stress markers eIF2α, GRP78, and CHOP mRNA expression in the liver is one of the potential mechanisms by which quinoa improves HFD-induced obesity in mice [180]. Moreover, the supplements of quinoa polysaccharides contributed to liver health by reversing HFD-induced hepatic steatosis in rats [160]. On the other hand, quinoa prevents the liver from various acute or chronic injuries and exerts a protective function. In the toxic model induced by CCl4, quinoa significantly alleviated liver toxicity by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation response, involving the molecular mechanisms of TGF-β1 signaling and ER stress pathway [94,121,177,181].
3.6. Regulative Effects on Gut Homeostasis and Microbiota
Observational findings achieved during the past two decades suggest that gut microbiota may contribute to the metabolic health of the human host and, when aberrant, to the pathogenesis of various common metabolic disorders, including obesity, T2DM, NAFLD, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), cardio-metabolic diseases, and malnutrition [182]. Dietary interventions offer a direct or indirect means of altering gut microbiota to generate positive, beneficial effects on host health. Quinoa, with its abundance of nutrients and bioactive compounds, has been shown to exert positive effects on intestinal health and gut homeostasis. Numerous in vivo experiments have revealed that quinoa or its bioactive components alleviated intestinal disorder by modulating the composition and abundance of gut microbiota, aiding in the production of probiotics like Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus-enterococcus [60,183,184,185]. Herein, we mainly introduced the effects and mechanisms of quinoa bioactive components, including polysaccharides, saponins, and BAPs, on intestinal health and gut microbiota.
Polysaccharides are crucial for maintaining gut homeostasis and promoting the production of probiotics, particularly the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate. Fecal fermentation of mixed grains (wheat combined with quinoa) yielded the highest level of propionate and butyrate compared with other formulations [186]. An in vitro fermentation with human fecal microbiota showed that quinoa substrates enhanced the growth of certain beneficial bacteria such as Prevotella and Bacteroides. Further, quinoa polysaccharides could be considered prebiotic due to their bioactivity to increase Bifidobacterium and Collinsella [187]. After 4 weeks of red quinoa polysaccharides intake, obese mice exhibited enhanced SCFAs and abundance in beneficial microbes Akkermansia [188]. Moreover, quinoa soluble fiber recovered the intestinal barrier and the abundance of Lactobacillus populations via increasing the number of goblet cells and Paneth cells [189]. Moreover, it was also found to reduce pathogenic varieties (Bacteroidetes and Helicobacter pylori) and enhance SCFAs, particularly acetate and butyrate, to improve ulcerative colitis [190]. Oral administration of quinoa polysaccharides increased the relative abundance and community structure of gut microbiota in rats, reducing the ratio of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, as well as decreasing the abundance of Proteobacteria, Desulfovibrio, and Allobaculum, which has been confirmed to be low in the gut of healthy human [191,192].
Saponins typically regulate intestinal function by exerting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects. Supplementation of quinoa saponins in HFD-induced obese rats resulted in an altered composition of gut microbiota compared to the control. Specifically, there was a decrease in the relative abundance of Firmicutes phylum and an increase in Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Bifidobacterium, Roseburia, and Coprococcus, correlating with distinct metabolites [193]. Moreover, saponin-rich extracts of quinoa have shown evidence to be converted into sapogenin by human gut microbiota and exhibited a modulatory effect on the growth of gut microbes and α-diversity [194,195]. Compared to the HFD group, mice consuming saponin-containing quinoa upregulated the abundance of Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Desulfovibrio in the colon while reducing the abundance of Blautia. Additionally, quinoa increased the expression of TGR5 and GLP-1 in multiple tissues while downregulated the expression of TLR4 in the colon and liver, exerting the potential microbiota–gut–brain–liver interaction mechanisms [149].
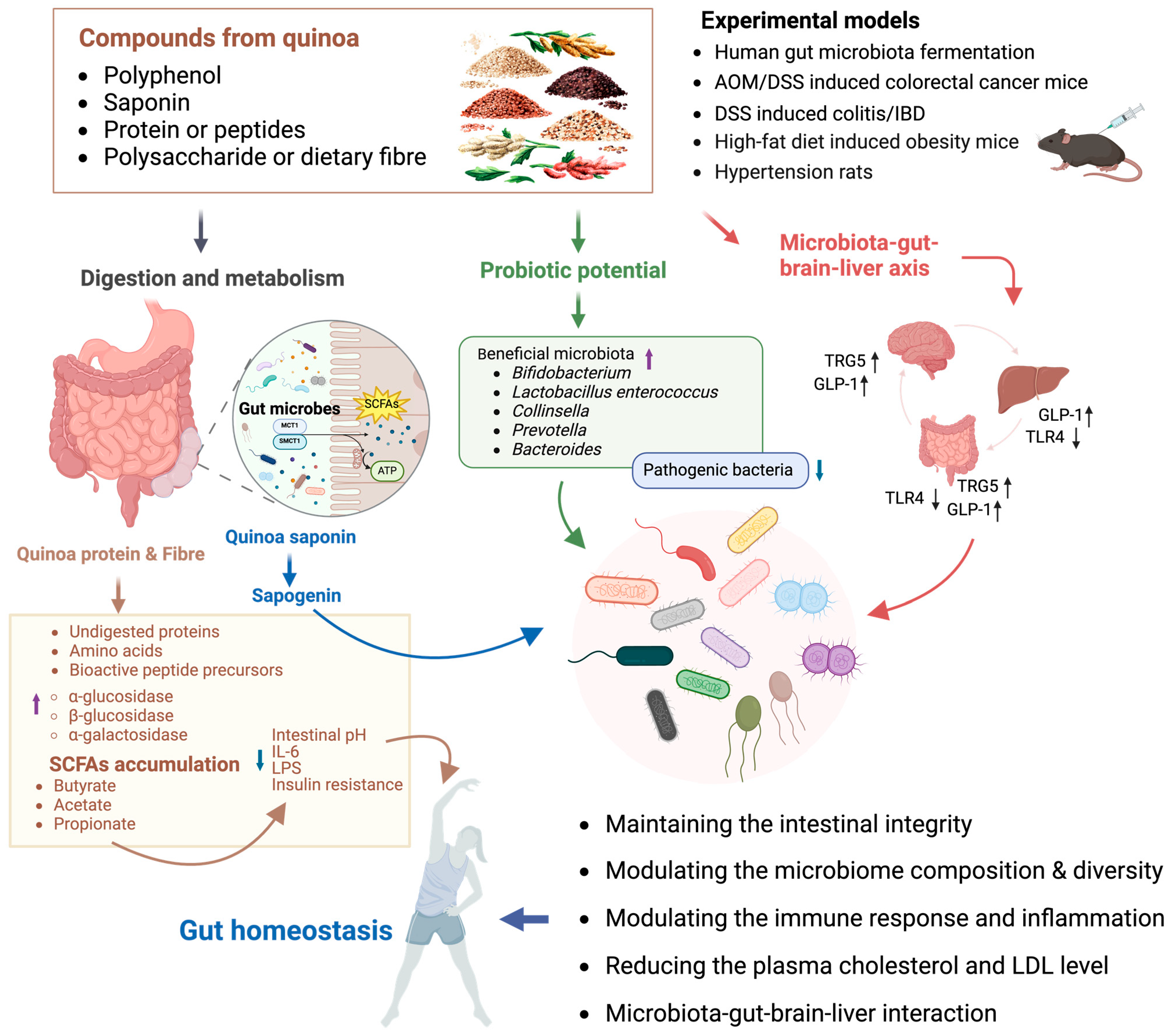
Quinoa protein, when digested in the hindgut, yielded undigested proteins and amino acids that can be used to produce SCFAs in the colon, lowering the intestinal pH and regulating microbiota growth in vivo [183]. Interestingly, the fecal microbiota in quinoa protein-treated spontaneously hypertensive rats shared more features in the composition of genera with non-hypertension rats than that of the captopril-treated group [171]. Multiple in vivo experiments have shown that supplementation with quinoa-derived BAPs restored intestinal barrier damage and inflammation induced by AOM/DSS or HFD by increasing SCFA levels and altering gut microbiota composition and abundance, particularly the ratio of probiotics to harmful bacteria, with involvement of molecular mechanisms PPAR-α/γ and TLR4/IκB-α/NF-κB signaling [150,196,197]. Moreover, the gastrointestinal process of quinoa protein provided further support for its active regulation of gut microbiota composition. In hypertensive rats consuming quinoa protein, there was a significant increase in the α-diversity of fecal microbiota, along with an enhanced abundance of probiotic bacteria Turicibacter and Allobaculum [171]. A novel quinoa peptide, TPGAFF, was identified and proven to alleviate colitis in vivo by reducing the composition of inflammatory-associated gut microbiota through NF-κB-TRPV1 signaling [115]. Several studies suggest that quinoa and its bioactive components have the potential to regulate the potential microbiota–gut–brain–liver axis to alleviate various metabolic disorders and intestinal mucosal damage [149,176]. The protective effects of quinoa on intestinal health can be attributed to its prebiotic properties, modulation of gut microbiota composition, and recovery of the intestinal barrier (Figure 3).
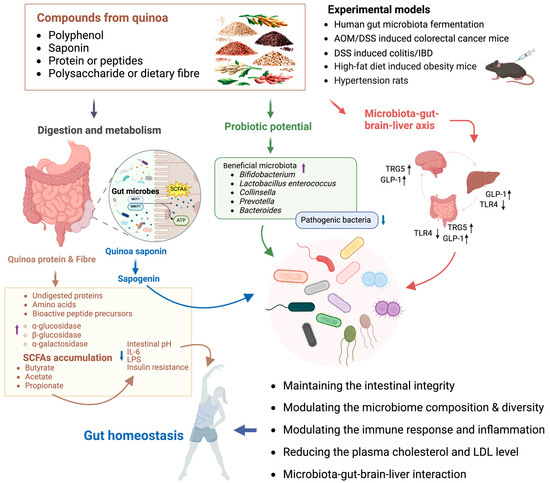
Figure 3.
The potential mechanism of quinoa on human gut microbiota and intestinal homeostasis. Quinoa maintains intestinal homeostasis through multiple mechanisms. Its bioactive substances improve intestinal homeostasis by maintaining intestinal integrity, modulating the microbiome composition and diversity, modulating the immune response and inflammation, reducing the plasma cholesterol and LDL levels, and regulating the microbiota–gut–brain–liver interaction. Quinoa’s bioactive substances increase the activity of relevant enzymes in human body, breaking down complex carbohydrates into more easily absorbed forms, promoting the accumulation of short-chain fatty acids such as butyrate, stabilizing intestinal pH, regulating immunity and inflammation, and modulating insulin resistance, thereby regulating intestinal homeostasis. Additionally, quinoa’s bioactive substances show potential as probiotics, promoting the proliferation of beneficial bacteria, inhibiting the abundance of pathogenic bacteria, and maintaining intestinal homeostasis. Quinoa’s bioactive compounds also maintain intestinal homeostasis through the gut–brain–liver axis, specifically via promoting the increase in TRG5 and GLP-1, inhibiting TRL4, improving intestinal inflammation, and reducing liver fat accumulation (↑: increase; ↓: decrease; AOM/DSS: azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids; MCT1: monocarboxylate transporter 1; SMCT1: sodium-coupled monocarboxylate transporter 1; TRG5: Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide-1; TRL4: Toll-like receptor 4; IL-6: interleukin-6; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; LDL: low-density lipoprotein).
3.7. Anti-Cancer Effect
Cancer, a complex and devastating disease, is characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. Quinoa is a highly promising edible and medicinal plant due to its diverse functional components. Here, we reviewed the inhibitory effects of quinoa and its bioactive anti-cancer components in vitro and in vivo, providing a theoretical basis for the functional value of quinoa as an adjunct dietary approach in cancer management. Initially, numerous studies found that extracts of quinoa could inhibit cancer cell viability. An earlier study demonstrated the efficacy of quinoa extracts in inhibiting the in vitro proliferation of human acute leukemia lymphocytes [198]. Next, people compared the anti-cancer activities of several pseudocereals and found quinoa extracts had the strongest cytotoxic activity against multiple human cervical cancer cell lines (C4-I, HTB-35, HTB-34) due to the high level of phenolic components and antioxidant activity [199]. Moreover, the ethanol extracts of quinoa inhibited the proliferation of colorectal cancer cell line (HCT-116) by reducing inflammation-related NO production and decreasing cellular arginine uptake [109]. Another study conducted by Stikić characterized the polyphenolic profiles of two quinoa varieties, Puno and Titicaca, and identified seven new phenolic and flavonoid compounds exerting anti-cancer activity against HCT-116 cells [200]. In A549 lung cancer cells, quinoa extracts at a concentration of 1.92 mg/mL demonstrated potent anti-cancer activity by upregulating BAX and downregulating Bcl2 levels to promote apoptosis [201]. Another study demonstrated the cytotoxicity of quinoa extracts against liver cancer cell line HepG2 in a dose- and time-dependent manner with IC50 of 14.6 μg/mL [202]. The extracts of black quinoa exhibited strong cytotoxicity against breast cancer cell line MCF-7, which is attributed to its high antioxidant content [203]. In summary, extracts from quinoa exhibit remarkable anti-cancer activity against various cancer cell lines, making it a promising source for cancer prevention as part of a novel healthy diet.
With the development of techniques for the identification and separation of bioactive ingredients, more and more studies are beginning to unveil the cytotoxic mechanisms of individual functional components isolated from quinoa against cancer cells. Here, we mainly focused on polyphenols, BAPs, polysaccharides, and saponins. It has been reported that quinoa contains at least 23 phenolic compounds, significantly higher than other grains [54]. Continuous research is revealing newly identified polyphenolic compounds in quinoa, with the highest level found in black varieties [204]. Overall, the anti-cancer effect of most phenolic compounds is attributed to their robust antioxidant activity, which disrupts the oxidative balance within cancer cells, activating signaling pathways such as oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy, ultimately leading to cell death [205]. With a high level of antioxidant capacity, phenolic compounds from red and black quinoa demonstrated anti-tumor bioactivity via dramatically downregulating NO production and inhibiting the proliferation of MCF-7 cells [55]. Besides the seeds, quinoa leaves represent a valuable resource of polyphenolic compounds, which act synergistically in chemoprevention and anti-cancer therapy by modulating oxidative stress and ROS-dependent intracellular signaling pathways. The extract of quinoa leaves was found to contain a considerable amount of ferulic, sinapinic, and gallic acids; kaempferol; isorhamnetin; and rutin, demonstrating potent anti-proliferative, motility-inhibitory, and gap junction communication-suppressing effects against prostate cancer cells in vitro [64]. Moreover, metal-based nanoparticles with quinoa leaf extracts exhibited promising anti-cancer activity against HepG2 cells at very low concentrations [206]. Moreover, the lowest MCF-7 cell line viability percentage (13.92%) was observed in the leaf extracts of the black quinoa at 1000 mg/mL concentration [203]. Notably, compared to red and white varieties, the seed oil of black quinoa, with the highest content of phytosterols, had the best antioxidant and anti-proliferation effect on HCT-116 cells by inducing severe apoptosis [86]. In vivo, feeding breast cancer rats with nano-encapsulated quinoa seed oil inhibited tumor proliferation, activated cell apoptosis, and suppressed the expression of TNF-α, MYC, and PIK3CA, with no hepatorenal toxicity observed [207].
BAPs of quinoa have gained popularity among researchers as a potential source of anti-cancer inhibitors in recent years. After in vitro gastrointestinal digestion, the portion of quinoa peptides with molecular weights >5 kDa exhibited potent anti-cancer activity against various cancer cell lines, including Caco-2, HT-29, and HCT-116 cells, suggesting its role in reducing gene mutations and chromosomal rearrangements [26]. Lunasin is a novel cancer-preventive peptide that was first isolated and purified from soybean protein. For the first time, Ren et al. detected the presence of lunasin in 15 quinoa samples and found it inhibited the production of ROS, NO, TNF-α and IL-6 in vitro, exhibiting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential anti-tumor activity [22]. Interestingly, a study found that compared to using olive leaf polyphenol extract (QLE) alone, the complex of digested quinoa peptides and QLE exhibited stronger inhibition of cell viability in MKN-45 human gastric cancer cells [208]. Fan et al. further identified several novel BAPs with highly anti-cancer bioactivity from quinoa protein digestion, which inhibited the proliferation of colon cancer Caco-2 cells by suppressing the expression of oncogenic genes NF-κB, IL-6, and Bcl-2 [209]. In an in vivo assay, supplementation with quinoa protein and its hydrolysate alleviated the progression of AOM/DSS-induced colon cancer by reversing the reduced SCFAs and dysregulated gut microbiota in colon tissue [196]. A recent study conducted by Galindo Luján utilized label-free mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics to obtain the proteome map of 1211 identified quinoa proteins, which was employed to identify quinoa proteins with potential immunonutritional bioactivities, including those associated with cancer [210].
Previous research has uncovered the anti-cancer efficacy of various plant-based polysaccharides. Two crude polysaccharide extracts of quinoa (Q-40 and Q-60) showed potent antioxidant abilities and inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines at very low concentrations [131]. Another purified quinoa polysaccharide constituted by galacturonic acid and glucose displayed cytotoxicity against liver cancer SMMC-7721 and breast cancer MCF-7 cells without inhibition on normal cells [91]. The terpenoids derived from quinoa bran (TQB) significantly promoted the death of colorectal cancer cell line DLD-1 and HCT-8, with IC50 values of 0.42 ± 0.02 and 0.54 ± 0.05 mg/mL, which was also validated in vivo. Mechanistically, TQB upregulated the level of pro-apoptotic effectors Caspase-3 and Bax while decreasing the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and mitochondrial membrane potential [211]. Further, three saponin components, namely ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, and hederagenin derived from quinoa, inhibited the growth of A549, SH-SY5Y, HepG2, and HeLa cells in vitro, promoting apoptosis via Caspase-3 and cleaved-PARP [212]. Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) are present in several edible plants, and numerous studies have highlighted their potential in anti-cancer therapy. Quinoin, a new RIP isolated from quinoa, strongly inhibited the growth of glioblastoma cells and exhibited synergistic sensitization with temozolomide [213].
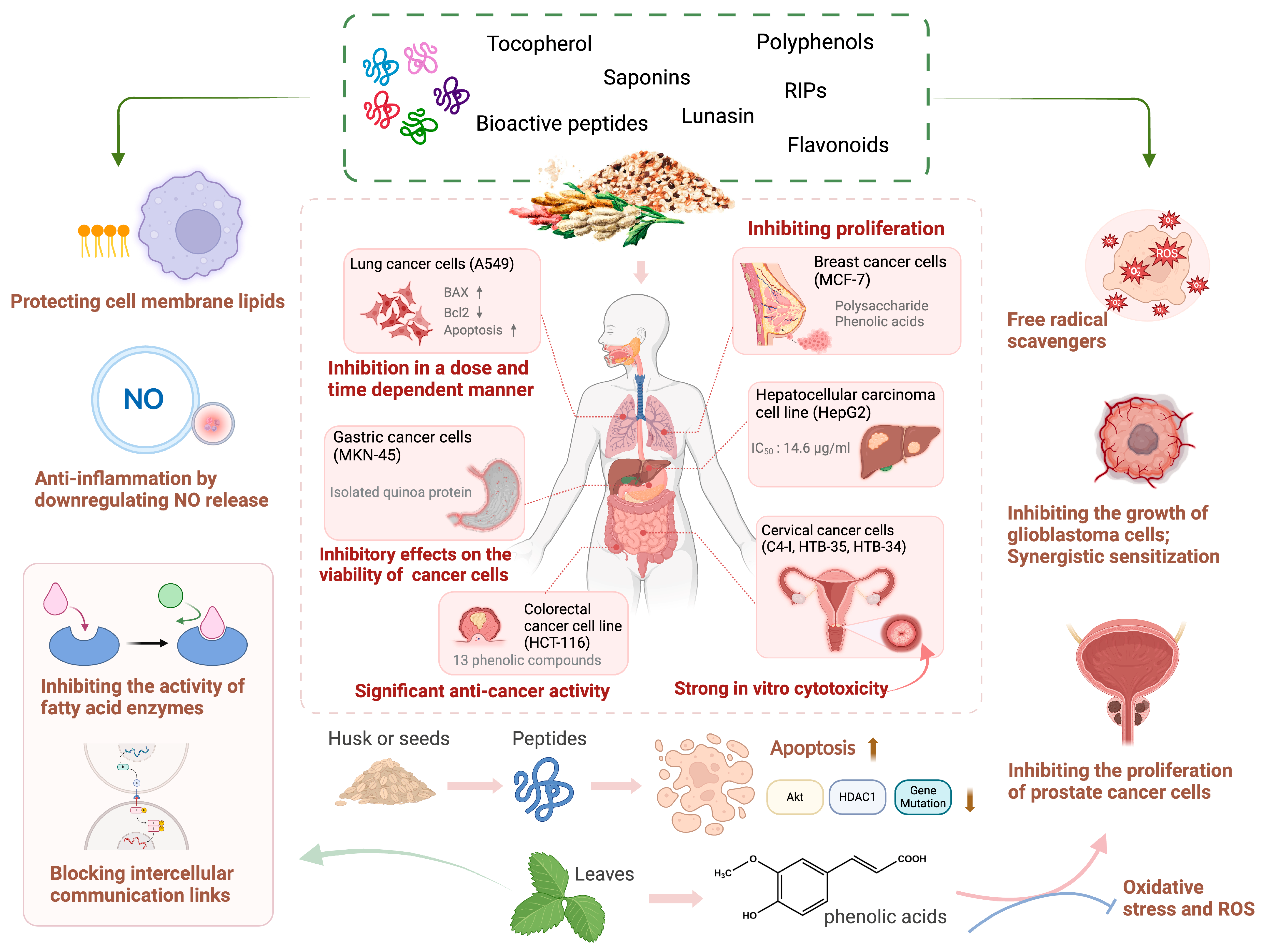
Collectively, the above studies demonstrate that quinoa and its bioactive components possess strong inhibitory effects on multiple cancer cells, making it a promising natural product with great potential for cancer treatment. However, in vivo studies and human clinical trials are limited, and the precise target of quinoa needs to be explored and verified in the future (Figure 4) (Table 3).
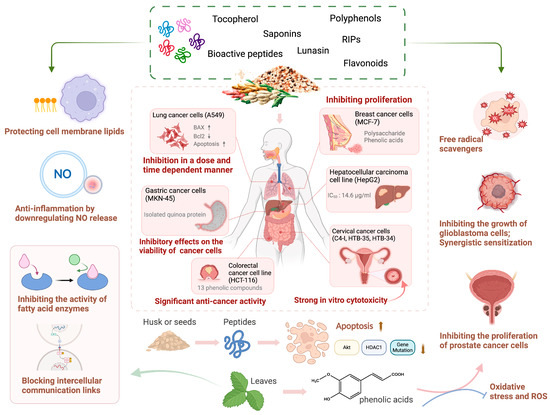
Figure 4.
The inhibitory effect of bioactive components derived from quinoa on various cancer cells. Quinoa exerts anti-cancer effect via various mechanisms. Quinoa-derived bioactive components have strong inhibitory effects on the proliferation of multiple cancer cells, including lung cancer cells (A549), gastric cancer cells (MKN-45), breast cancer cells (MCF-7), liver cancer cells (HepG2), cervical cancer cells (C4-1, HTB-34, HTB-35), and colorectal cancer cells (HCT-116). Such inhibitory effect is primarily achieved by promoting cell apoptosis, inhibiting cell division, downregulating NO release to exert anti-inflammatory effects, scavenging free radicals, and inhibiting signaling pathways such as Akt and HDAC1. Additionally, the active components of quinoa promote cancer cell death through synergistic effects with clinical drugs (↑: increase; ↓: decrease; NO: nitric oxide; ROS: reactive oxygen species; O2−: superoxide anion; BAX: bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma 2; Akt: protein kinase B; HDAC1: histone deacetylase 1).

Table 3.
The effects of bioactive components derived from quinoa on multiple cancer cells.
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
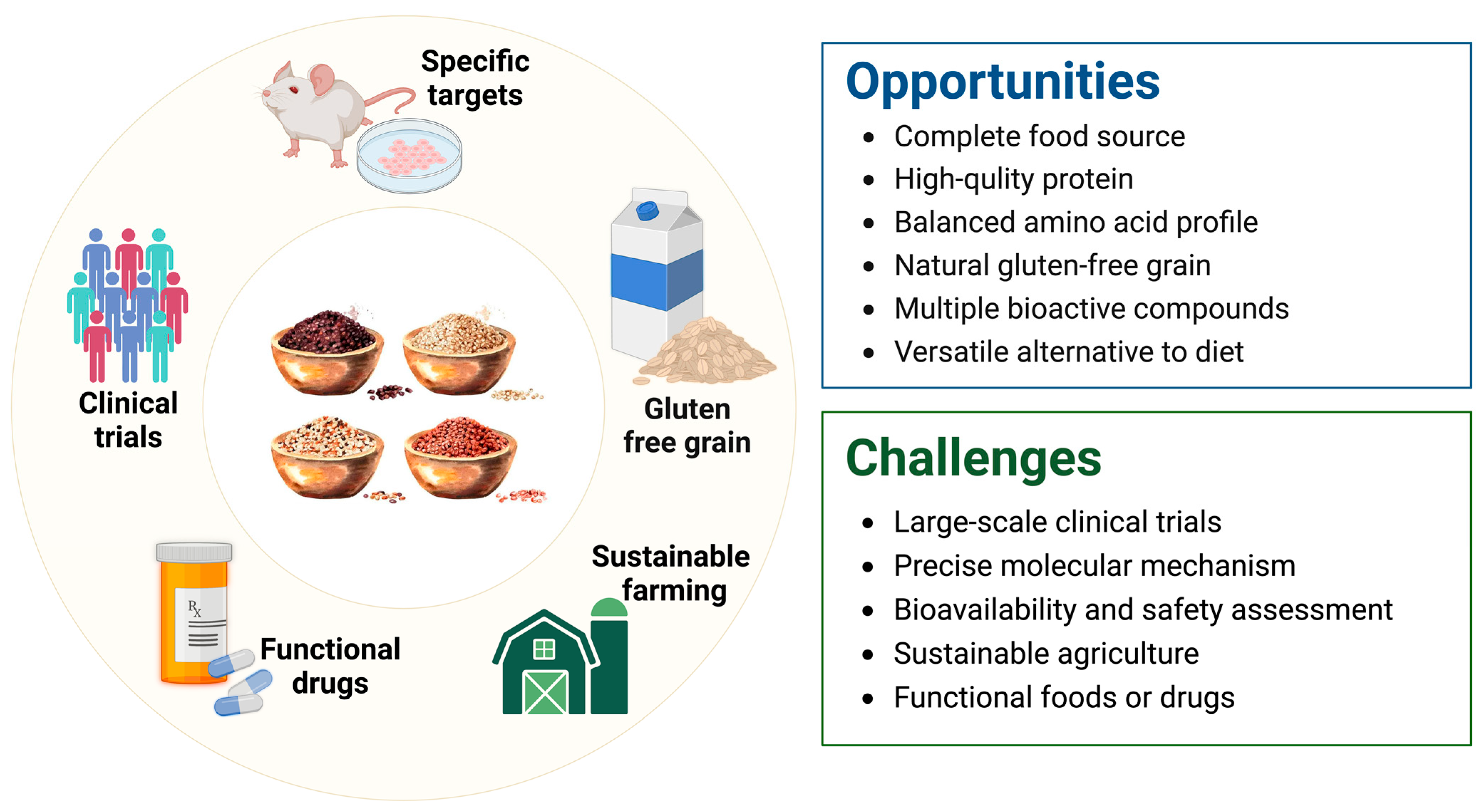
Quinoa has gained popular attention not only for its rich and balanced nutritional profile but also for its various bioactive compounds, such as polysaccharides, BAPs, polyphenols, and saponins. Many in vitro and in vivo experiments have confirmed that quinoa and its bioactive components have preventative or therapeutic effects on multiple human diseases, including CVD, metabolic syndromes, gastrointestinal disorders, and cancer. As a result, quinoa holds immense potential for development into functional foods with many health-promoting benefits. Despite the positive functional value of quinoa, there remains a significant gap in research regarding its specific targets in cell experiments, particularly in human clinical trials. Although there are a few results from dietary intervention studies focusing on obesity and hyperglycemia, research in areas of cancer prevention and gut regulation is virtually absent. Therefore, further well-designed clinical trials should be conducted to confirm the health benefits of quinoa and its derivatives. Furthermore, the deep exploration of protein targets interacting with quinoa bioactive components within cells using advanced technologies such as human proteome microarray technology, computer-aided drug design system, and DARTS assays is quite necessary for elucidating mechanisms and advancing new drug development (Figure 5).
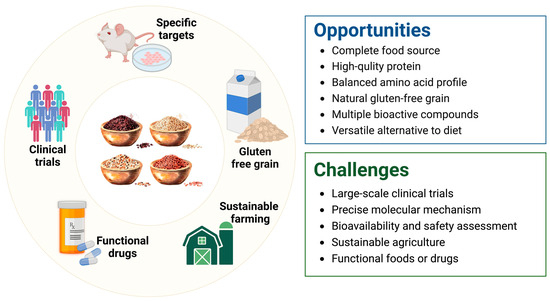
Figure 5.
The challenges and opportunities of quinoa in future applications.
A variety of in vivo experiments have demonstrated the regulatory effects of functional quinoa products, such as yogurt, especially those containing sprouted quinoa, on NAFLD, hypercholesterolemia, intestinal inflammation, and gut microbiota abundance. However, there is limited research on population trials and the impact of processing methods on the bioactive compounds based on these functional foods, highlighting the urgent need for exploration. In addition, further testing and optimization are required to increase the content and stability of bioactive components in quinoa functional foods.
Author Contributions
X.X.: Writing—Original Draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, and Writing—Review and Editing. G.F.: Writing—Original Draft, Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, and Writing—Review and Editing. H.X.: Conceptualization, Investigation, and Visualization. S.P.: Conceptualization, Visualization, and Investigation. W.H.: Conceptualization, Investigation, and Funding Acquisition. J.Z.: Conceptualization, Writing—Review and Editing, Funding Acquisition, and Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number 32272306.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Repo-Carrasco, R.; Espinoza, C.; Jacobsen, S.-E. Nutritional Value and Use of the Andean Crops Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) and Kañiwa (Chenopodium pallidicaule). Food Rev. Int. 2003, 19, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alandia, G.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Jacobsen, S.-E.; Bazile, D.; Condori, B. Global Expansion of Quinoa and Challenges for the Andean Region. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, B.; Wei, X.; Shen, Z.; Su, N. Assessment and Comparison of Nutritional Qualities of Thirty Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seed Varieties. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, J.; Cabanes, J.; Jiménez-Atiénzar, M.; Ibañez-Tremolada, M.; Gómez-Pando, L.R.; García-Carmona, F.; Gandía-Herrero, F. Characterization of Betalains, Saponins and Antioxidant Power in Differently Colored Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) Varieties. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcacundo, R.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Nutritional and Biological Value of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhili, S.; Abdolalizadeh, L.; Hosseini, S.M.; Shojaee-Aliabadi, S.; Mirmoghtadaie, L. Quinoa Protein: Composition, Structure and Functional Properties. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Hao, Y.; Yang, X.; Ren, G.; Richel, A. Exploration on Bioactive Properties of Quinoa Protein Hydrolysate and Peptides: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2896–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamudio, F.V.; Campos, M.R.S. Amaranth, Quinoa and Chia Bioactive Peptides: A Comprehensive Review on Three Ancient Grains and Their Potential Role in Management and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2707–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Han, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Lai, D.; Zhou, L. Quinoa Secondary Metabolites and Their Biological Activities or Functions. Molecules 2019, 24, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Peñas, E.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Pseudocereal Grains: Nutritional Value, Health Benefits and Current Applications for the Development of Gluten-Free Foods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazile, D.; Pulvento, C.; Verniau, A.; Al-Nusairi, M.S.; Ba, D.; Breidy, J.; Hassan, L.; Mohammed, M.I.; Mambetov, O.; Otambekova, M.; et al. Worldwide Evaluations of Quinoa: Preliminary Results from Post International Year of Quinoa FAO Projects in Nine Countries. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, L.E.A. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): Composition, Chemistry, Nutritional, and Functional Properties. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 58, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinegar, C.; Goundan, S. Isolation and Characterization of Chenopodin, the 11S Seed Storage Protein of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewiecki, J.; Delgado-Licon, E.; Haruenkit, R.; Pawelzik, E.; Martin-Belloso, O.; Park, Y.-S.; Jung, S.-T.; Trakhtenberg, S.; Gorinstein, S. Identification and Differences of Total Proteins and Their Soluble Fractions in Some Pseudocereals Based on Electrophoretic Patterns. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7798–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Energy and Protein Requirements: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. In Energy and Protein Requirements: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1985; p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Gálvez, A.; Miranda, M.; Vergara, J.; Uribe, E.; Puente, L.; Martínez, E.A. Nutrition Facts and Functional Potential of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.), an Ancient Andean Grain: A Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcárcel-Yamani, B.; Lannes, S.C.D.S. Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Amaranth (Amaranthus spp.) and Their Influence in the Nutritional Value of Cereal Based Foods. Food Public Health 2012, 2, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Ruales, J.; Grijalva, Y.d.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Nair, B.M. The Nutritional Quality of an Infant Food from Quinoa and Its Effect on the Plasma Level of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in Undernourished Children. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 53, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daliri, E.; Oh, D.; Lee, B. Bioactive Peptides. Foods 2017, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daliri, H.; Ahmadi, R.; Pezeshki, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Mohammadi, M.; Beyrami, H.; Heshmati, M.K.; Ghorbani, M. Quinoa Bioactive Protein Hydrolysate Produced by Pancreatin Enzyme-Functional and Antioxidant Properties. LWT 2021, 150, 111853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, P.; Kilari, B.P.; Kamal, H.; Olalere, O.A.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Multifunctional Bioactive Peptides Derived from Quinoa Protein Hydrolysates: Inhibition of α-Glucosidase, Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV and Angiotensin I Converting Enzymes. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 96, 103130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, J. Detection of Lunasin in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and the in Vitro Evaluation of Its Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Shi, P.; Li, G. Isolation of Novel ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Quinoa Bran Albumin Assisted with an in Silico Approach: Characterization, in Vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular Docking. Molecules 2019, 24, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Safdar, B.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Ying, Z.; Liu, X. Identification of a Novel α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity Peptide from Quinoa Protein Hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Hao, Y.; Richel, A.; Everaert, N.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, X.; Ren, G. Antihypertensive Effect of Quinoa Protein under Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion and Peptide Characterization. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 5569–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcacundo, R.; Miralles, B.; Carrillo, W.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. In Vitro Chemopreventive Properties of Peptides Released from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Protein under Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcacundo, R.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Release of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV, α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) during in Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Wu, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, L. Preparation and Identification of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides from Quinoa Protein. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajayi, F.F.; Mudgil, P.; Jobe, A.; Antony, P.; Vijayan, R.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Novel Plant-Protein (Quinoa) Derived Bioactive Peptides with Potential Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Activities: Identification, Characterization and Molecular Docking of Bioactive Peptides. Foods 2023, 12, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, S.L.; Fernandes, Â.; Pereira, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Sokovic, M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Nutritional Value, Physicochemical Characterization and Bioactive Properties of the Brazilian Quinoa BRS Piabiru. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2969–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, F. Quinoa Starch: Structure, Properties, and Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, E.S.V.; Lima, G.C.; Naves, M.M.V. Dietary Fibers as Beneficial Microbiota Modulators: A Proposed Classification by Prebiotic Categories. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Tan, B.; Zhang, W. Dietary Fibre Extracted from Different Types of Whole Grains and Beans: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Dietary Fiber Polysaccharides of Amaranth, Buckwheat and Quinoa Grains: A Review of Chemical Structure, Biological Functions and Food Uses. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xiong, M.; Bai, T.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Huang, Z.; Qin, W. Comparative Study on the Structure, Physicochemical, and Functional Properties of Dietary Fiber Extracts from Quinoa and Wheat. LWT 2021, 149, 111816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, J. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Different Colored Quinoa Varieties (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Vega-Gálvez, A.; Martínez, E.A.; López, J.; Marín, R.; Aranda, M.; Fuentes, F. Influence of Contrasting Environments on Seed Composition of Two Quinoa Genotypes: Nutritional and Functional Properties. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 73, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.G.; Lawson, L.D.; Fairbanks, D.J.; Robison, L.R.; Andersen, W.R. Seed Lipid Content and Fatty Acid Composition of Three Quinoa Cultivars. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1993, 6, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, P.X.; Zhang, B.; Hernandez, M.; Zhang, H.; Marcone, M.F.; Liu, R.; Tsao, R. Characterisation of Fatty Acid, Carotenoid, Tocopherol/Tocotrienol Compositions and Antioxidant Activities in Seeds of Three Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Genotypes. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiretti, P.G.; Gai, F.; Tassone, S. Fatty Acid Profile and Nutritive Value of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds and Plants at Different Growth Stages. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 183, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matías, J.; Rodríguez, M.J.; Granado-Rodríguez, S.; Cruz, V.; Calvo, P.; Reguera, M. Changes in Quinoa Seed Fatty Acid Profile Under Heat Stress Field Conditions. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 820010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Du, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z. Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation on Phytochemical Composition, Lipase Activity and Fatty Acid of Quinoa. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 98, 103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufari, J.R.; Gorostegui, H.A.; Miranda-Villa, P.P.; Bergesse, A.E.; Calandri, E.L. Oxidative Stability and Characterization of Quinoa Oil Extracted from Wholemeal and Germ Flours. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.-C.; Anderson, A.; Coker, J.; Ondrus, M. Characterization of Lipid Oxidation Products in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). Food Chem. 2007, 101, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Siddiqui, R.A. Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Components in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Greens: A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruales, J.; Nair, B.M. Saponins, Phytic Acid, Tannins and Protease Inhibitors in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa, Willd) Seeds. Food Chem. 1993, 48, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.M.G.; Al-Jumayi, H.A.O.; Elhendy, H.A. Effect of Germination on the Nutritional Profile of Quinoa (Cheopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds and Its Anti-anemic Potential in Sprague–Dawley Male Albino Rats. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Ortiz, F.A.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Rojas-León, A.; Rodríguez-Marín, M.L.; Falfán-Cortés, R.N.; Román-Gutiérrez, A.D. Enzyme Activity during Germination of Different Cereals: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkhata, S.G.; Ayua, E.; Kamau, E.H.; Shingiro, J.-B. Fermentation and Germination Improve Nutritional Value of Cereals and Legumes through Activation of Endogenous Enzymes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2446–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, S.; Pallares Pallares, A.; Vancoillie, F.; Hendrickx, M.; Grauwet, T. Pectin and Phytic Acid Reduce Mineral Bioaccessibility in Cooked Common Bean Cotyledons Regardless of Cell Wall Integrity. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, R.A.; Prakash, J. The Impact of Germination and Dehulling on Nutrients, Antinutrients, in Vitro Iron and Calcium Bioavailability and in Vitro Starch and Protein Digestibility of Some Legume Seeds. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, E.; De Brier, N.; Goos, P.; Smolders, E.; Delcour, J.A. Steeping and Germination of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). I. Unlocking the Impact of Phytate and Cell Wall Hydrolysis on Bio-Accessibility of Iron and Zinc Elements. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 90, 102847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Saeed, F.; Anjum, F.M.; Afzaal, M.; Tufail, T.; Bashir, M.S.; Ishtiaq, A.; Hussain, S.; Suleria, H.A.R. Natural Polyphenols: An Overview. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R.; Hellström, J.K.; Pihlava, J.-M.; Mattila, P.H. Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds in Andean Indigenous Grains: Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa), Kañiwa (Chenopodium pallidicaule) and Kiwicha (Amaranthus caudatus). Food Chem. 2010, 120, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, K.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, H.; Ren, G.; Yang, X.; Li, J. Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, and Antitumor Activities of Phenolic Compounds from White, Red, and Black Chenopodium quinoa Seed. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, P.X.; Liu, R.; Tsao, R. Characterisation of Phenolics, Betanins and Antioxidant Activities in Seeds of Three Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Genotypes. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorinstein, S.; Vargas, O.J.M.; Jaramillo, N.O.; Salas, I.A.; Ayala, A.L.M.; Arancibia-Avila, P.; Toledo, F.; Katrich, E.; Trakhtenberg, S. The Total Polyphenols and the Antioxidant Potentials of Some Selected Cereals and Pseudocereals. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 225, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paśko, P.; Bartoń, H.; Zagrodzki, P.; Gorinstein, S.; Fołta, M.; Zachwieja, Z. Anthocyanins, Total Polyphenols and Antioxidant Activity in Amaranth and Quinoa Seeds and Sprouts during Their Growth. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jubete, L.; Wijngaard, H.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Polyphenol Composition and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Amaranth, Quinoa Buckwheat and Wheat as Affected by Sprouting and Baking. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chu, G.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, S.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y. Benefits of Monascus Anka Solid-State Fermentation for Quinoa Polyphenol Bioaccessibility and the Anti-Obesity Effect Linked with Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2208–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-B.; Nie, P.; Lin, Z.-H.; Zhu, C.; Zhong, L.-Y.; Wei, F.-F.; Wu, Y.; Song, L.-H. The Polyphenols Profile of Co-Fermented Quinoa and Black Barley with Lactobacillus kisonensis and Its In Vitro Bioactivities. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, F.; Melini, V. Impact of Fermentation on Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Quinoa. Fermentation 2021, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Wang, C.; Liu, X. Viscozyme L Hydrolysis and Lactobacillus Fermentation Increase the Phenolic Compound Content and Antioxidant Properties of Aqueous Solutions of Quinoa Pretreated by Steaming with α-Amylase. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Świeca, M.; Sułkowski, M.; Dziki, D.; Baraniak, B.; Czyż, J. Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Chenopodium quinoa Leaves Extracts—In Vitro Study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 57, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoleru, V.; Vitanescu, M.; Teliban, G.-C.; Cojocaru, A.; Vlase, L.; Gheldiu, A.-M.; Mangalagiu, I.; Amăriucăi-Mantu, D.; Burducea, M.; Zheljazkov, V.; et al. Phytosterol and Polyphenol Contents and Quinoa Leave Yields Variation in Relationships to Variety, Density and Harvesting Date. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacrés, E.; Quelal, M.; Galarza, S.; Iza, D.; Silva, E. Nutritional Value and Bioactive Compounds of Leaves and Grains from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Plants 2022, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiallos-Jurado, J.; Pollier, J.; Moses, T.; Arendt, P.; Barriga-Medina, N.; Morillo, E.; Arahana, V.; Torres, M.d.L.; Goossens, A.; Leon-Reyes, A. Saponin Determination, Expression Analysis and Functional Characterization of Saponin Biosynthetic Genes in Chenopodium quinoa Leaves. Plant Sci. 2016, 250, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparg, S.G.; Light, M.E.; Staden, J. van Biological Activities and Distribution of Plant Saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Meza, I.G.; Aluwi, N.A.; Saunders, S.R.; Ganjyal, G.M. GC–MS Profiling of Triterpenoid Saponins from 28 Quinoa Varieties (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Grown in Washington State. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8583–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.G.; Park, H.-M.; Yoon, K.S. Analysis of Saponin Composition and Comparison of the Antioxidant Activity of Various Parts of the Quinoa Plant (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzam, K.E.; Hafsa, J.; Sobeh, M.; Mhada, M.; Taourirte, M.; Kacimi, K.E.; Yasri, A. An Insight into Saponins from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd): A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuljanabhagavad, T.; Wink, M. Biological Activities and Chemistry of Saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Phytochem. Rev. 2009, 8, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Herrera, T.; García-Risco, M.R.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Bioaccessibility of Saponins from Edible Seeds: Quinoa, Lentil, Fenugreek, Soybean and Lupin. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chi, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Fan, S.; Huang, F.; Xue, K.; Liu, L. Characterization of Saponins and Phenolic Compounds: Antioxidant Activity and Inhibitory Effects on α-Glucosidase in Different Varieties of Colored Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2128–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrosan, M.; Tan, T.-C.; Easa, A.M.; Gammoh, S.; Alu’datt, M.H.; Aleid, G.M.; Alhamad, M.N.; Maghaydah, S. Evaluation of Quality and Protein Structure of Natural Water Kefir-Fermented Quinoa Protein Concentrates. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Alvarado, P.; Pavón-Vargas, D.J.; Abarca-Robles, J.; Valencia-Chamorro, S.; Haros, C.M. Effect of Germination on the Nutritional Properties, Phytic Acid Content, and Phytase Activity of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd). Foods 2023, 12, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siener, R.; Hönow, R.; Seidler, A.; Voss, S.; Hesse, A. Oxalate Contents of Species of the Polygonaceae, Amaranthaceae and Chenopodiaceae Families. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.; Galvin, K.; O’Connor, T.P.; Maguire, A.R.; O’Brien, N.M. Phytosterol, Squalene, Tocopherol Content and Fatty Acid Profile of Selected Seeds, Grains, and Legumes. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2007, 62, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Aluwi, N.A.; Saunders, S.R.; Ganjyal, G.M.; Medina-Meza, I.G. Metabolic Fingerprinting Unveils Quinoa Oil as a Source of Bioactive Phytochemicals. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucault, A.-S.; Mathé, V.; Lafont, R.; Even, P.; Dioh, W.; Veillet, S.; Tomé, D.; Huneau, J.-F.; Hermier, D.; Quignard-Boulangé, A. Quinoa Extract Enriched in 20-hydroxyecdysone Protects Mice from Diet-induced Obesity and Modulates Adipokines Expression. Obesity 2012, 20, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, B.L.; Poulev, A.; Kuhn, P.; Grace, M.H.; Lila, M.A.; Raskin, I. Quinoa Seeds Leach Phytoecdysteroids and Other Compounds with Anti-Diabetic Properties. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso-Roca, E.C.; Aguilar-Felices, E.J.; Tinco-Jayo, J.A.; Arroyo-Acevedo, J.L.; Herrera-Calderon, O. Biomolecules with Antioxidant Capacity from the Seeds and Sprouts of 20 Varieties of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. (Quinoa). Plants 2021, 10, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobota, A.; Świeca, M.; Gęsiński, K.; Wirkijowska, A.; Bochnak, J. Yellow-Coated Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd)—Physicochemical, Nutritional, and Antioxidant Properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, E.S.; Pek, C.J.N.; Tan, J.C.W.; Leo, C.H. Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Effect of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) with Pressurized Hot Water Extraction (PHWE). Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrali, D.; Giupponi, L.; Peña-Armada, R.D.l.; Villanueva-Suárez, M.J.; Mateos-Aparicio, I. The Quinoa Variety Influences the Nutritional and Antioxidant Profile Rather than the Geographic Factors. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 133531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Physicochemical, Antioxidant and Anticancer Characteristics of Seed Oil from Three Chenopodium quinoa Genotypes. Molecules 2022, 27, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, S.; Moslehishad, M.; Salami, M. Antioxidant and Alpha-Glucosidase Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of Hydrolyzed Protein and Bioactive Peptides of Quinoa. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.H.; Velázquez, F.; Burrieza, H.P.; Martínez, K.D.; Rubio, A.P.D.; Ferreira, C.D.S.; Buera, M.D.P.; Pérez, O.E. Betanin Loaded Nanocarriers Based on Quinoa Seed 11S Globulin. Impact on the Protein Structure and Antioxidant Activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capraro, J.; Benedetti, S.D.; Dio, M.D.; Bona, E.; Abate, A.; Corsetto, P.A.; Scarafoni, A. Characterization of Chenopodin Isoforms from Quinoa Seeds and Assessment of Their Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Caco-2 Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, C.; Qin, P.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Yao, Y.; Ren, G. Structural Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Alkali-Extracted Polysaccharides from Quinoa. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zou, L.; Fu, C.; Li, P.; Zhao, G. Chemical Characterization, Antioxidant, Immune-Regulating and Anticancer Activities of a Novel Bioactive Polysaccharide from Chenopodium quinoa Seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-A.; Ke, B.-J.; Cheng, S.-C.; Lee, C.-L. Red Quinoa Bran Extract Prevented Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Increasing Antioxidative System and Repressing Fatty Acid Synthesis Factors in Mice Fed Alcohol Liquid Diet. Molecules 2021, 26, 6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Moreno, M.; Jiménez-Moreno, E.; Márquez Gallego, A.; Vera Pasamontes, G.; Uranga Ocio, J.A.; Garcés-Rimón, M.; Miguel-Castro, M. Red Quinoa Hydrolysates with Antioxidant Properties Improve Cardiovascular Health in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qabba, M.M.; El-Mowafy, M.A.; Althwab, S.A.; Alfheeaid, H.A.; Aljutaily, T.; Barakat, H. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant Activity, and Ameliorating Efficacy of Chenopodium quinoa Sprouts against CCl4-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasko, P.; Barton, H.; Zagrodzki, P.; Izewska, A.; Krosniak, M.; Gawlik, M.; Gawlik, M.; Gorinstein, S. Effect of Diet Supplemented with Quinoa Seeds on Oxidative Status in Plasma and Selected Tissues of High Fructose-Fed Rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Chi, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Fan, S.; Dong, L.; Huang, F.; Liu, L. Changes in Saponins, Phenolics and Antioxidant Activity of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) during Milling Process. LWT 2019, 114, 108381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, K.; Li, S.; Cao, H.; Guan, X. Microwaving Released More Polyphenols from Black Quinoa Grains with Hypoglycemic Effects Compared with Traditional Cooking Methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 5948–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Schneider, R.G. Quinoa Flavonoids and Their Bioaccessibility during in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıkardeş, E.; Güzel, N. Impact of Germination Pre-Treatments on Buckwheat and Quinoa: Mitigation of Anti-Nutrient Content and Enhancement of Antioxidant Properties. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhinder, S.; Kumari, S.; Singh, B.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Impact of Germination on Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Properties, Antinutritional Factors, Mineral Content and Maillard Reaction Products of Malted Quinoa Flour. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciochi, R.A.; Galván-D’Alessandro, L.; Vandendriessche, P.; Chollet, S. Effect of Germination and Fermentation Process on the Antioxidant Compounds of Quinoa Seeds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 71, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-B.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.-J.; Li, Y.-C.; Wang, M.; Zou, L.-H.; Liu, D.-Y.; Chen, W.-J. The Combined Effect of Protein Hydrolysis and Lactobacillus Plantarum Fermentation on Antioxidant Activity and Metabolomic Profiles of Quinoa Beverage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñuel, L.; Boeri, P.; Zubillaga, F.; Barrio, D.A.; Torreta, J.; Cruz, A.; Vásquez, G.; Pinto, A.; Carrillo, W. Production of White, Red and Black Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd Var. Real) Protein Isolates and Its Hydrolysates in Germinated and Non-Germinated Quinoa Samples and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation. Plants 2019, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zevallos, V.F.; Raker, V.; Tenzer, S.; Jimenez-Calvente, C.; Ashfaq-Khan, M.; Rüssel, N.; Pickert, G.; Schild, H.; Steinbrink, K.; Schuppan, D. Nutritional Wheat Amylase-Trypsin Inhibitors Promote Intestinal Inflammation via Activation of Myeloid Cells. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1100–1113.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Tsao, R. Phytochemicals in Quinoa and Amaranth Grains and Their Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, and Potential Health Beneficial Effects: A Review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Shi, Z.; Ren, G. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Saponins from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages Cells. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, H1018–H1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Song, Y.; Cao, Y.-N.; Zhang, L.-L.; Zhao, G.; Wu, D.-T.; Zou, L. Total Saponins from Quinoa Bran Alleviate High-fat Diet-induced Obesity and Systemic Inflammation via Regulation of Gut Microbiota in Rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3876–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.; Han, X.; Cheng, X.; Wu, M.; Lv, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) Bran Saponins Alleviate Hyperuricemia and Inhibit Renal Injury by Regulating the PI3K/AKT/NFκB Signaling Pathway and Uric Acid Transport. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6635–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschelli, S.; Gatta, D.M.P.; Pesce, M.; Ferrone, A.; Quiles, J.L.; Genovese, S.; Epifano, F.; Fiorito, S.; Taddeo, V.A.; Patruno, A.; et al. Modulation of CAT-2B-Mediated l-Arginine Uptake and Nitric Oxide Biosynthesis in HCT116 Cell Line Through Biological Activity of 4′-Geranyloxyferulic Acid Extract from Quinoa Seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orona-Tamayo, D.; Valverde, M.E.; Paredes-López, O. Bioactive Peptides from Selected Latin American Food Crops—A Nutraceutical and Molecular Approach. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1949–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeu, D.G.; Cordeiro, H.G.; Tonelli, F.C.P.; Godin, A.M.; Melo, I.S.F.d.; Matsui, T.C.; Rodrigues, F.F.; da Silva, J.A.; Coelho, M.d.M.; Machado, R.R.; et al. Chenopodin as an Anti-Inflammatory Compound. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 4435–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Hsieh, C.-C.; de Lumen, B.O. Lunasin, a Novel Seed Peptide for Cancer Prevention. Peptides 2009, 30, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Hao, Y.; Teng, C.; Yao, Y.; Ren, G. Functional Properties and Adipogenesis Inhibitory Activity of Protein Hydrolysates from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capraro, J.; Benedetti, S.D.; Heinzl, G.C.; Scarafoni, A.; Magni, C. Bioactivities of Pseudocereal Fractionated Seed Proteins and Derived Peptides Relevant for Maintaining Human Well-Being. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, T.; Xiong, L.; Wang, F.; Song, H.; Zhou, J.; Wei, S.; Ren, B.; Shen, X. A Quinoa Peptide Protects Impaired Mucus Barriers in Colitis Mice by Inhibiting NF-κB-TRPV1 Signaling and Regulating the Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srdić, M.; Ovčina, I.; Fotschki, B.; Haros, C.M.; Llopis, J.M.L. C. quinoa and S. hispanica L. Seeds Provide Immunonutritional Agonists to Selectively Polarize Macrophages. Cells 2020, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laparra Llopis, J.M.; Brown, D.; Saiz, B. Chenopodium quinoa and Salvia hispanica Provide Immunonutritional Agonists to Ameliorate Hepatocarcinoma Severity under a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Ren, G. Antioxidant and Immunoregulatory Activity of Polysaccharides from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19307–19318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Li, J.; Bai, B. Purification, Structural Elucidation and in Vivo Immunity-Enhancing Activity of Polysaccharides from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, D. The Protective Effect of Quinoa on the Gastric Mucosal Injury Induced by Absolute Ethanol. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-A.; Ke, B.-J.; Cheng, C.-S.; Wang, J.-J.; Wei, B.-L.; Lee, C.-L. Red Quinoa Bran Extracts Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury and Fibrosis in Mice via Activation of Antioxidative Enzyme Systems and Blocking TGF-Β1 Pathway. Nutrients 2019, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noratto, G.D.; Murphy, K.; Chew, B.P. Quinoa Intake Reduces Plasma and Liver Cholesterol, Lessens Obesity-Associated Inflammation, and Helps to Prevent Hepatic Steatosis in Obese Db/Db Mouse. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaroakpo, J.U.; Nan, W.; Hao, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Pang, X.; Lv, J. The Hyperglycemic Regulatory Effect of Sprouted Quinoa Yoghurt in High-Fat-Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8354–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, Q.-M.; Pan, L.-H.; Luo, J.-P.; Zha, X.-Q. Hydrolytic Quinoa Protein and Cationic Lotus Root Starch-Based Micelles for Co-Delivery of Quercetin and Epigallo-Catechin 3-Gallate in Ulcerative Colitis Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15189–15201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuardo, M.; Martín, R.S. Antifungal Properties of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) Alkali Treated Saponins against Botrytis cinerea. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2008, 27, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Hou, Z.; Xue, P. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action Saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Husks against Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 149, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Xue, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, G. Improved Antibacterial Effects of Alkali-Transformed Saponin from Quinoa Husks against Halitosis-Related Bacteria. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajzadeh, Z.; Shakerian, A.; Rahimi, E.; Bagheri, M. Chemical, Antioxidant, Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Components and Antimicrobial Effects of Different Species of Quinoa Seeds. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 51, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelshafy, A.M.; El-Naggar, E.A.; Kenawi, M.N. Enhancing the Antibacterial Activity of Quinoa Fermented by Probiotics: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. J. Adv. Microbiol. 2022, 22, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, B. Physicochemical Properties, Structural Characterization and Biological Activities of Polysaccharides from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi-Yekta, M.; Reihani, S.F.S.; Mohammadi, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Quinoa Protein Hydrolysate against Streptococcus pyogenes and Escherichia coli. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, e9993241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.H.; Javaid, A. Anticancer, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Compounds of Quinoa Inflorescence. Adv. Life Sci. 2020, 8, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pagno, C.H.; Costa, T.M.H.; Menezes, E.W.d.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Hertz, P.F.; Matte, C.R.; Tosati, J.V.; Monteiro, A.R.; Rios, A.O.; Flôres, S.H. Development of Active Biofilms of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa W.) Starch Containing Gold Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yekta, M.M.; Rezaei, M.; Nouri, L.; Azizi, M.H.; Jabbari, M.; Eş, I.; Khaneghah, A.M. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Burgers with Quinoa Peptide-loaded Nanoliposomes. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-García, M.; Ríos-Romo, R.A.; Melgarejo-Mancilla, A.; Díaz-Ramírez, M.; Hernández-Hernández, H.M.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Pierro, P.D.; Regalado-González, C. Rheological and Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan and Quinoa Protein Filmogenic Suspensions with Thyme and Rosemary Essential Oils. Foods 2020, 9, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziminezhad, H.; Esmaeilzadeh Kenari, R.; Raftani Amiri, Z. The Effect of Antimicrobial Properties of Nano-Encapsulated Red Quinoa and Ginseng Extracts on the Shelf Life of Cream. Food Res. J. 2024, 33, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, N.; Vera, P.; López, L.; Yazdani-Pedram, M.; Tapia, C.; Abugoch, L. Thymol Nanoemulsions Incorporated in Quinoa Protein/Chitosan Edible Films; Antifungal Effect in Cherry Tomatoes. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lietz, G.; Seal, C.J. Effects of Quinoa Intake on Markers of Cardiovascular Risk: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Cai, X.; Qiu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Huang, L. Glucolipid Metabolism Improvement in Impaired Glucose Tolerance Subjects Consuming a Quinoa-Based Diet: A Randomized Parallel Clinical Trial. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1179587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rizzolo, D.A.; Acar-Denizli, N.; Kostov, B.; Roura, E.; Sisó-Almirall, A.; Delicado, P.; Gomis, R. Glycaemia Fluctuations Improvement in Old-Age Prediabetic Subjects Consuming a Quinoa-Based Diet: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshahidi, L.K.; Caballero, E.; Osses, A.; Hyland, B.W.; Ternan, N.G.; Gill, C.I.R. Modest Improvement in CVD Risk Markers in Older Adults Following Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Consumption: A Randomized-Controlled Crossover Study with a Novel Food Product. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3313–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lietz, G.; Bal, W.; Watson, A.; Morfey, B.; Seal, C. Effects of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Consumption on Markers of CVD Risk. Nutrients 2018, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.G.D.; Ovídio, P.P.; Padovan, G.J.; Junior, A.A.J.; Marchini, J.S.; Navarro, A.M. Metabolic Parameters of Postmenopausal Women after Quinoa or Corn Flakes Intake—A Prospective and Double-Blind Study. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atefi, M.; Mirzamohammadi, S.; Darand, M.; Tarrahi, M.J. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) Interventions on Blood Lipids. J. Herb. Med. 2022, 34, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, J.; Abedi, S.; Shirinbakhshmasoleh, M.; Moodi, F.; Moodi, V.; Ghavami, A. The Effects of Quinoa Seed Supplementation on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials. Phytother. Res. PTR 2021, 35, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Perez, D.; Radcliffe, J.; Tierney, A.; Jois, M. Quinoa Seed Lowers Serum Triglycerides in Overweight and Obese Subjects: A Dose-Response Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2017, 1, e001321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.d.O.; Barcelos, M.d.F.P.; Vieira, C.N.d.G.; Abreu, W.C.d.; Ferreira, E.B.; Pereira, R.C.; de Angelis-Pereira, M.C. Effects of Sprouted and Fermented Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) on Glycemic Index of Diet and Biochemical Parameters of Blood of Wistar Rats Fed High Carbohydrate Diet. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-Y.; Tao, S.-Y.; Wu, Y.-X.; An, T.; Lv, B.-H.; Liu, J.-X.; Liu, Y.-T.; Jiang, G.-J. Quinoa Reduces High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice via Potential Microbiota-Gut-Brain-Liver Interaction Mechanisms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00329-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wu, T.; You, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Ding, L. Quinoa Peptides Alleviate Obesity in Mice Induced by a High-Fat Diet via Regulating of the PPAR-α/γ Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 2300258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucault, A.S.; Even, P.; Lafont, R.; Dioh, W.; Veillet, S.; Tomé, D.; Huneau, J.F.; Hermier, D.; Quignard-Boulangé, A. Quinoa Extract Enriched in 20-Hydroxyecdysone Affects Energy Homeostasis and Intestinal Fat Absorption in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 128, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Shi, Z.; Yao, Y.; Ren, G. Structural Characterization of Quinoa Polysaccharide and Its Inhibitory Effects on 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Differentiation. Foods 2020, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ren, G. Suppressive Effects of Saponin-Enriched Extracts from Quinoa on 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Differentiation. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3282–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón, M.; Bustos, M.; Mendez, D.; Fuentes, E.; Palomo, I.; Lutz, M. In Vitro Assay of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Lupin (Lupinus spp.) Extracts on Human Platelet Aggregation. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wei, C.; Uthamapriya, R.A.; Wu, Y.; Cao, L. The Effects of Quinoa Bran Dietary Fiber on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Transcriptome in Obese Rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busso, D.; González, A.; Santander, N.; Saavedra, F.; Quiroz, A.; Rivera, K.; González, J.; Olmos, P.; Marette, A.; Bazinet, L.; et al. A Quinoa Protein Hydrolysate Fractionated by Electrodialysis with Ultrafiltration Membranes Improves Maternal and Fetal Outcomes in a Mouse Model of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2300047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcaliskan Ilkay, H.; Karabulut, D.; Kamaci Ozocak, G.; Mehmetbeyoglu, E.; Kaymak, E.; Kisioglu, B.; Cicek, B.; Akyol, A. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Supplemented Cafeteria Diet Ameliorates Glucose Intolerance in Rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 6920–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Richel, A.; Hao, Y.; Fan, X.; Everaert, N.; Yang, X.; Ren, G. Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV and Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Released from Quinoa Protein by in Silico Proteolysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaroakpo, J.U.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Pang, X.; Lv, J. In Vitro Modulation of Glucagon-like Peptide Release by DPP-IV Inhibitory Polyphenol-Polysaccharide Conjugates of Sprouted Quinoa Yoghurt. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, L.; Chen, G. Phenolic Constituents from Black Quinoa Alleviate Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Regulating IRS1/PI3K/Akt/GLUTs Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 18780–18791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanisha; Venkategowda, S.; Majumdar, M. Amelioration of Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia in a High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice by Supplementation of a Developed Optimized Polyherbal Formulation. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanisha; Venkategowda, S.; Majumdar, M. Response Surface Methodology Based Development of an Optimized Polyherbal Formulation and Evaluation of Its Anti-Diabetic and Anti-Obesity Potential in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2024, 14, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, B.; Yan, Y.; Liang, J.; Guan, X. Bound Polyphenols from Red Quinoa Prevailed over Free Polyphenols in Reducing Postprandial Blood Glucose Rises by Inhibiting α-Glucosidase Activity and Starch Digestion. Nutrients 2022, 14, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyash, M.; Johnson, S.K.; Liu, S.-Q.; Al-Mheiri, A.; Abushelaibi, A. Cytotoxicity, Antihypertensive, Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Activities of Solid-State Fermented Lupin, Quinoa and Wheat by Bifidobacterium Species: In-Vitro Investigations. LWT 2018, 95, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Chang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Xu, P.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activities of Polysaccharides from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho Oliveira, L.; Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Frias, J.; Elena Cartea, M.; Francisco, M.; Cristianini, M.; Peñas, E. High Pressure-Assisted Enzymatic Hydrolysis Potentiates the Production of Quinoa Protein Hydrolysates with Antioxidant and ACE-Inhibitory Activities. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros-Yupanqui, M.; Lante, A.; Mihaylova, D.; Krastanov, A.I.; Vílchez-Perales, C. Impact of Consumption of Cooked Red and Black Chenopodium quinoa Willd. over Blood Lipids, Oxidative Stress, and Blood Glucose Levels in Hypertension-induced Rats. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaroakpo, J.U.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Pang, X.; Lv, J. α-Glucosidase and ACE Dual Inhibitory Protein Hydrolysates and Peptide Fractions of Sprouted Quinoa Yoghurt Beverages Inoculated with Lactobacillus casei. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 124985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos, R.; Pedreschi, R.; Velásquez-Sánchez, M.; Aguilar-Galvez, A.; Campos, D. In Vitro Antioxidant and Angiotensin I-converting Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa) and Kiwicha (Amaranthus caudatus) Proteins. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Sang, S.; Liu, Y. A Novel Antihypertensive Pentapeptide Identified in Quinoa Bran Globulin Hydrolysates: Purification, In Silico Characterization, Molecular Docking with ACE and Stability against Different Food-Processing Conditions. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hao, Y.; Fan, X.; Richel, A.; Everaert, N.; Yang, X.; Ren, G. Administration with Quinoa Protein Reduces the Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats and Modifies the Fecal Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muñoz, A.; Valle, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Bazinet, L.; Enrione, J. Production of Antihypertensive and Antidiabetic Peptide Fractions from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) by Electrodialysis with Ultrafiltration Membranes. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2022, 11, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.M.S.; Fouda, K.; Mehaya, F.M.; Mohamed, D.A.; Mohammad, A.A.; Abdelgayed, S.S.; Mohamed, R.S. Fortified Vegetarian Milk for Prevention of Metabolic Syndrome in Rats: Impact on Hepatic and Vascular Complications. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selma-Gracia, R.; Haros, C.M.; Laparra Llopis, J.M. Inclusion of Salvia hispanica L. and Chenopodium quinoa into Bread Formulations Improves Metabolic Imbalances Derived from a High-Fat Intake in Hyperglycaemic Mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7994–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marak, N.R.; Das, P.; Das Purkayastha, M.; Baruah, L.D. Effect of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa W.) Flour Supplementation in Breads on the Lipid Profile and Glycemic Index: An in Vivo Study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1341539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Tianqi, F.; Zhang, C.; Deng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. High-Protein Compound Yogurt with Quinoa Improved Clinical Features and Metabolism of High-Fat Diet–Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 5309–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Lv, W.; Li, Y.; Nie, P.; Lu, J.; Geng, Y.; Heng, Z.; Song, L. Alleviating the Effect of Quinoa and the Underlying Mechanism on Hepatic Steatosis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Lyu, W.; Lin, Z.; Lu, J.; Geng, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, H. Quinoa Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Regulates the Gut Microbiota in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats. Foods 2023, 12, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Okbi, S.Y.; Hamed, T.E.; Elewa, T.A.; Ramadan, A.A.; El-Karamany, M.F.; Bakry, B.A. Role of Polar Extracts from Two Quinoa Varieties in Prevention of Steatohepatitis and Cardiovascular Diseases and Improving Glucose Tolerance in Rats. J. Herbmed Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Liu, J.-X.; Yang, X.; Lv, B.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, G. Supplementation of Quinoa Regulates Glycolipid Metabolism and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the High-Fat Diet-Induced Female Obese Mice. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahhab, K.G.; Mannaa, F.A.; Ashry, M.; Khaled, D.M.; Hassan, L.K.; Gomaa, H.F. Chenopodium quinoa Ethanolic Extract Ameliorates Cyclophosphamide®-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Male Rats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 30, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut Microbiota in Human Metabolic Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotschki, B.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Jurgoński, A.; Amarowicz, R.; Opyd, P.; Bez, J.; Muranyi, I.; Petersen, I.L.; Llopis, M.L. Protein-Rich Flours from Quinoa and Buckwheat Favourably Affect the Growth Parameters, Intestinal Microbial Activity and Plasma Lipid Profile of Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Mills, D.; Noratto, G. Molecular Exploration of Fecal Microbiome in Quinoa-Supplemented Obese Mice. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullón, B.; Gullón, P.; Tavaria, F.K.; Yáñez, R. Assessment of the Prebiotic Effect of Quinoa and Amaranth in the Human Intestinal Ecosystem. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3782–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yu, Q.; Ma, L.; Su, T.; Zhang, D.; Yao, D.; Li, Z. In Vitro Simulated Fecal Fermentation of Mixed Grains on Short-Chain Fatty Acid Generation and Its Metabolized Mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 112949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyneb, H.; Pei, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Win, Y.; Gong, L. In Vitro Study of the Effect of Quinoa and Quinoa Polysaccharides on Human Gut Microbiota. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5735–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tang, H. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Red Quinoa Polysaccharide on Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus Mice Induced by Streptozotocin and High-Fat Diet. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1308866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Kolba, N.; Khen, N.; Even, C.; Turjeman, S.; Koren, O.; Tako, E. Quinoa Soluble Fiber and Quercetin Alter the Composition of the Gut Microbiome and Improve Brush Border Membrane Morphology In Vivo (Gallus gallus). Nutrients 2022, 14, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Mai, P.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Quinoa Bran Soluble Dietary Fiber Ameliorates Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Ulcerative Colitis in BALB/c Mice by Maintaining Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zou, L.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Zhao, G.; Hu, Y. Dietary Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia and Modulate Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial Signature of Dysbiosis in Gut Microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Ji, X.; Song, L.; Cao, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, R.; Tao, F.; Zhang, F.; Xue, P. Saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Husks Alleviated High-Fat-Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia via Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Multiple Metabolic Pathways. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierro, J.N.D.; Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The Hydrolysis of Saponin-Rich Extracts from Fenugreek and Quinoa Improves Their Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity and Hypocholesterolemic Effect. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhai, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Hou, Z.; Cao, Y.; Feng, J.; Xue, P. Safety Assessment of Crude Saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Husks: 90-Day Oral Toxicity and Gut Microbiota & Metabonomics Study in Rats. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Guo, H.; Teng, C.; Yang, X.; Qin, P.; Richel, A.; Zhang, L.; Blecker, C.; Ren, G. Supplementation of Quinoa Peptides Alleviates Colorectal Cancer and Restores Gut Microbiota in AOM/DSS-Treated Mice. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tuo, Y.; You, H.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, L. Quinoa Protein and Its Hydrolysate Ameliorated DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibiting Inflammatory Response. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaduri, S. An Assessment of Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities of Super Grain Quinoa. J. Food Process. Technol. 2016, 7, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paśko, P.; Tyszka-Czochara, M.; Namieśnik, J.; Jastrzębski, Z.; Leontowicz, H.; Drzewiecki, J.; Martinez-Ayala, A.L.; Nemirovski, A.; Barasch, D.; Gorinstein, S. Cytotoxic, Antioxidant and Binding Properties of Polyphenols from the Selected Gluten-Free Pseudocereals and Their by-Products: In Vitro Model. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 87, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stikić, R.I.; Milinčić, D.D.; Kostić, A.Ž.; Jovanović, Z.B.; Gašić, U.M.; Tešić, Ž.L.; Djordjević, N.Z.; Savić, S.K.; Czekus, B.G.; Pešić, M.B. Polyphenolic Profiles, Antioxidant, and in Vitro Anticancer Activities of the Seeds of Puno and Titicaca Quinoa Cultivars. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaei, H.; Karimi, F.; Ghorbany, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.S.; Moudi, M.; Mousavi-Kouhi, S.M. Investigating Cytotoxic Effect and Molecular Mechanisms of Quinoa Seed Extract Against Human Lung Cancer Cell Line. Jentashapir J. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2021, 12, e121089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.A.; Fouda, K.A.; Mohamed, R.S. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Quinoa and Safflower Seeds and Their Preventive Effects on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2019, 22, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifati, S.E.; Ranaiezadeh, M.R.; Daneshmand, F.; Karimi Bekr, Z.; Rezaee, M.-B. The Phytochemical Content and Cytotoxic Effects of Quinoa Commercial Cultivars (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) on MCF7 Cell Line of Breast Cancer. J. Med. Plants By-Prod. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, T.; Bai, L.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Guan, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, H. Effects of Variety and Origin on the Metabolic and Texture Characteristics of Quinoa Seeds Based on Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Field Quadrupole-Orbitrap High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.T.; Wong, T.Y.; Wei, C.I.; Huang, Y.W.; Lin, Y. Tannins and Human Health: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 421–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younas, M.; Rizwan, M.; Zubair, M.; Inam, A.; Ali, S. Biological Synthesis, Characterization of Three Metal-Based Nanoparticles and Their Anticancer Activities against Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El makawy, A.I.; Abdel-Aziem, S.H.; Mohammed, S.E.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Abd EL-Kader, H.A.; Sharaf, H.A.; Youssef, D.A.; Mabrouk, D.M. Exploration of Tumor Growth Regression of Quinoa and Chia Oil Nanocapsules via the Control of PIK3CA and MYC Expression, Anti-Inflammation and Cell Proliferation Inhibition, and Their Hepatorenal Safety in Rat Breast Cancer Model. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2024, 48, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyari, M.A.; Motahar, S.F.S.; Salami, M.; Betti, M.; Hosseini, E.; Habibi-Kelishomi, Z.; Goliaei, B.; Ghasemi, A. Structural, Functional, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Conjugates of Quinoa Protein Isolate and Olive Leaf Polyphenolic Extract: Application in Production of Bread. Food Struct. 2022, 33, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Guo, H.; Teng, C.; Zhang, B.; Blecker, C.; Ren, G. Anti-Colon Cancer Activity of Novel Peptides Isolated from in Vitro Digestion of Quinoa Protein in Caco-2 Cells. Foods 2022, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Luján, R.; Pont, L.; Sanz-Nebot, V.; Benavente, F. A Proteomics Data Mining Strategy for the Identification of Quinoa Grain Proteins with Potential Immunonutritional Bioactivities. Foods 2023, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Cui, K.; Yang, R.; Liu, F.; Shan, S.; Israr, G.; Li, Z. Terpenoids of Quinoa Bran Suppresses Colorectal Cancer by Inducing Cell Apoptosis. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio-Paucar, G.N.; Palo-Cardenas, A.I.; Rondón-Ortiz, A.N.; Pino-Figueroa, A.; Gonzales-Condori, E.G.; Villanueva-Salas, J.A. Cytotoxic Activity of Saponins and Sapogenins Isolated from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. in Cancer Cell Lines. Scientifica 2023, 2023, e8846387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, R.; Ragucci, S.; Castaldo, S.; Oliva, M.A.; Landi, N.; Pedone, P.V.; Arcella, A.; Maro, A.D. Cytotoxicity Effect of Quinoin, Type 1 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Quinoa Seeds, on Glioblastoma Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cedrón, M.G.; del Hierro, J.N.; Reguero, M.; Wagner, S.; Bouzas, A.; Quijada-Freire, A.; Reglero, G.; Martín, D.; Molina, A.R. Saponin-Rich Extracts and Their Acid Hydrolysates Differentially Target Colorectal Cancer Metabolism in the Frame of Precision Nutrition. Cancers 2020, 12, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).