Targeting Circadian Protein Rev-erbα to Alleviate Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Enhance Functional Recovery Following Brain Trauma
Abstract
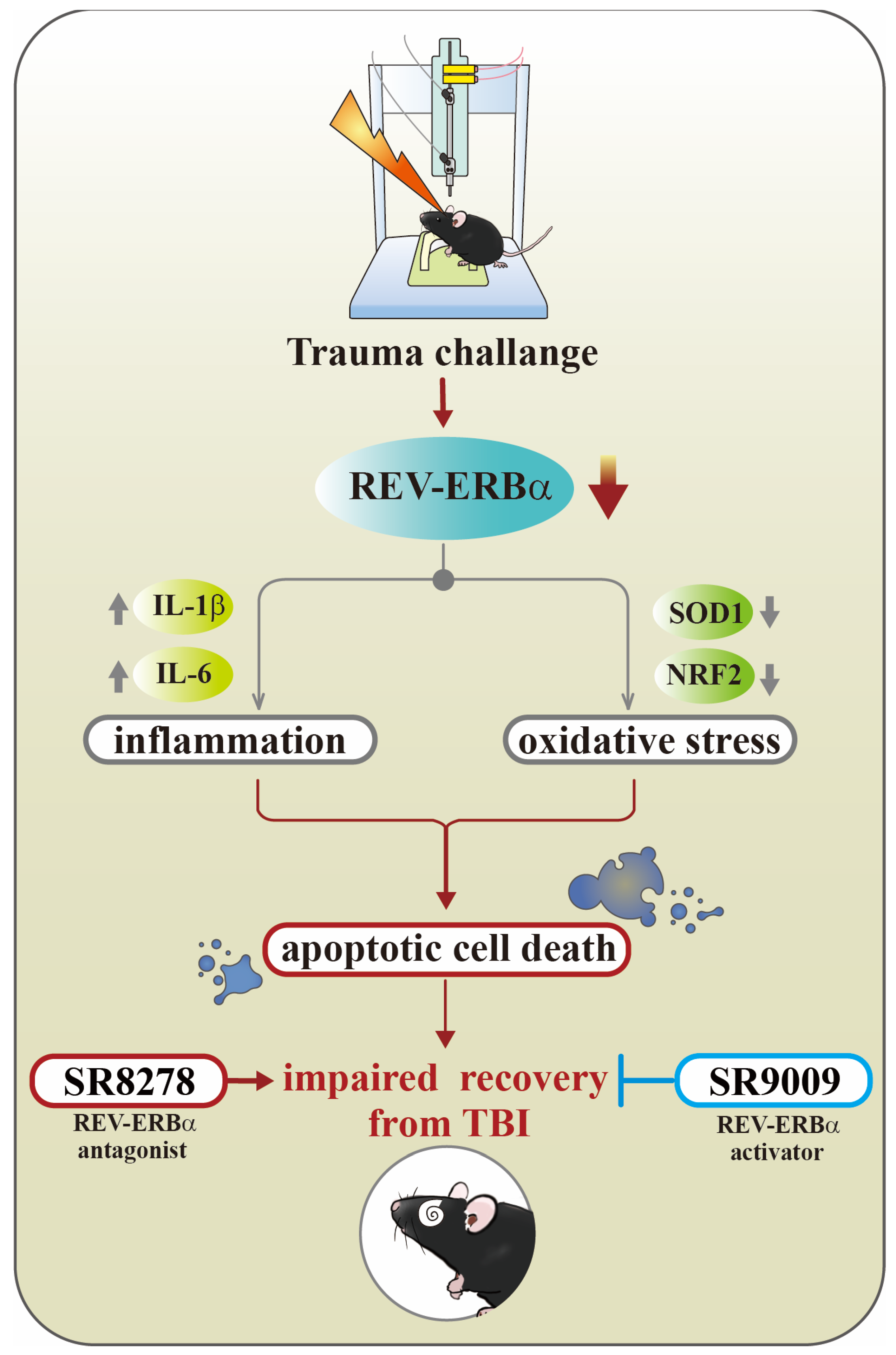
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. The Mouse Model for Traumatic Brain Injury
2.3. Experimental Designs
2.4. Novel Object Recognition Task
2.5. Neurological Severity Score (NSS)
2.6. Grip Strength Test
2.7. Y-Maze Testing
2.8. Histological and Immunofluorescence Analyses
2.9. TUNEL Staining for the Evaluation of Apoptotic Cell Death
2.10. Real-Time PCR Measurement
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
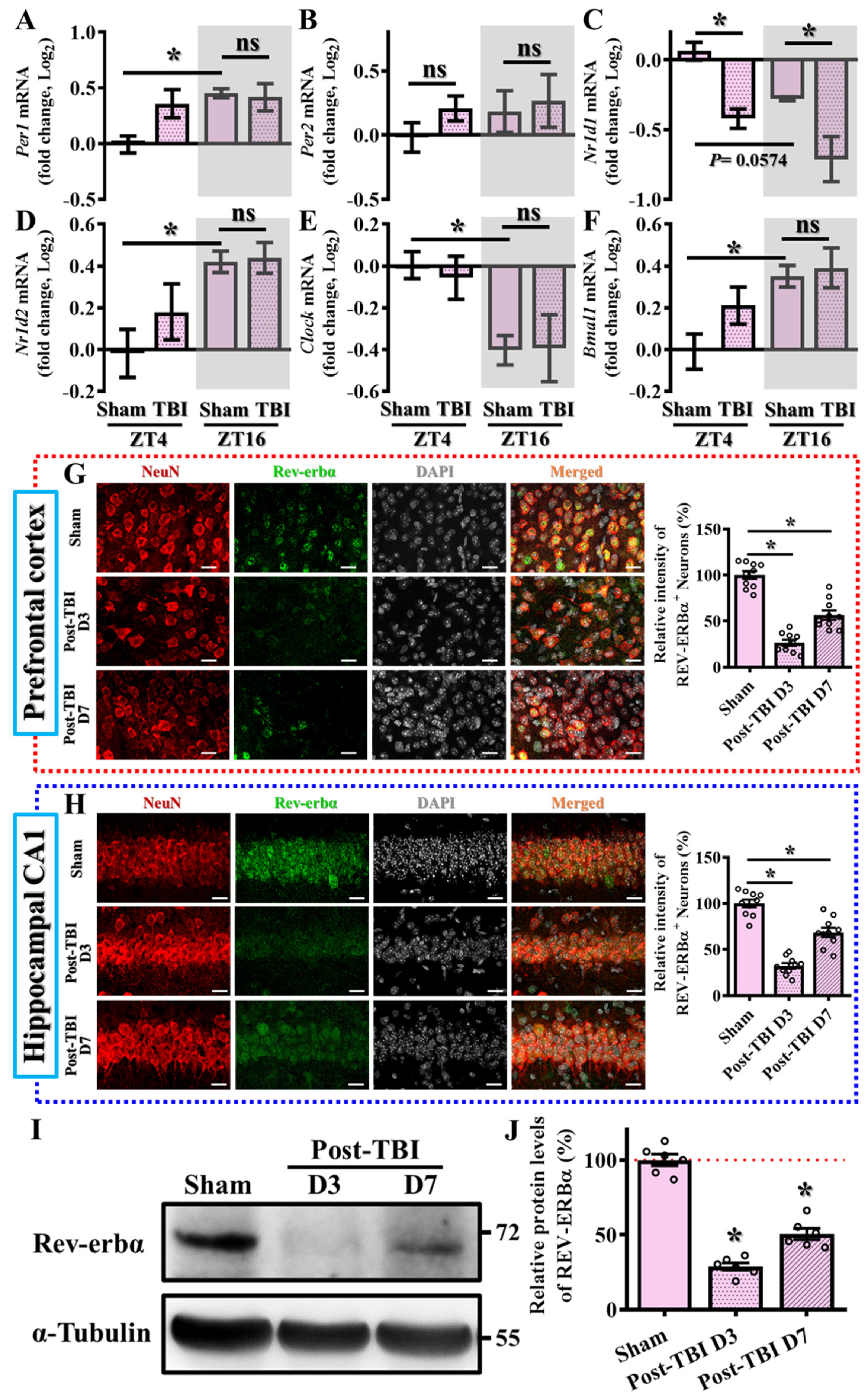
3.1. Alteration in the Levels of Circadian Genes Following TBI
3.2. Levels of Nr1d1 Correlate to TBI Phenotypes
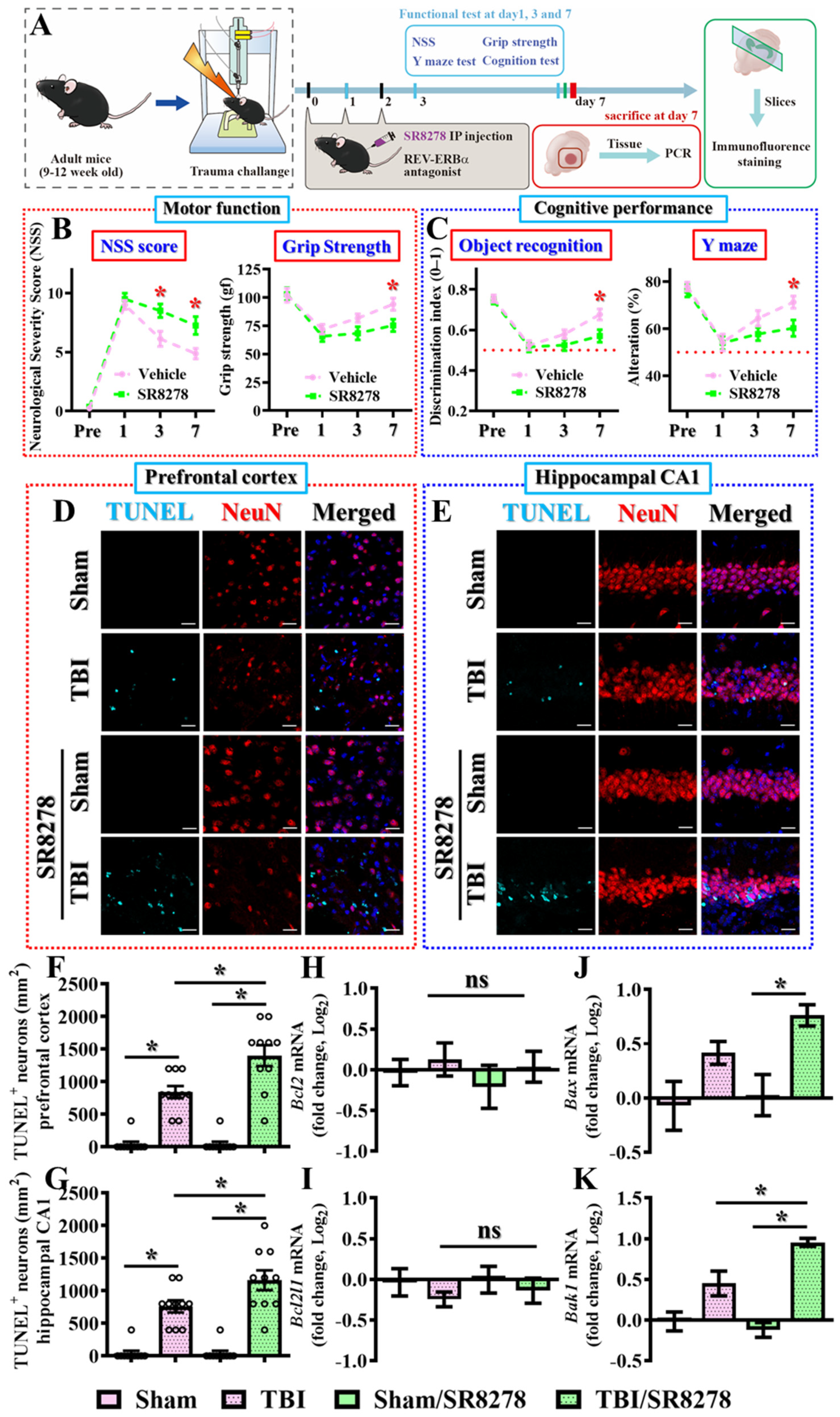
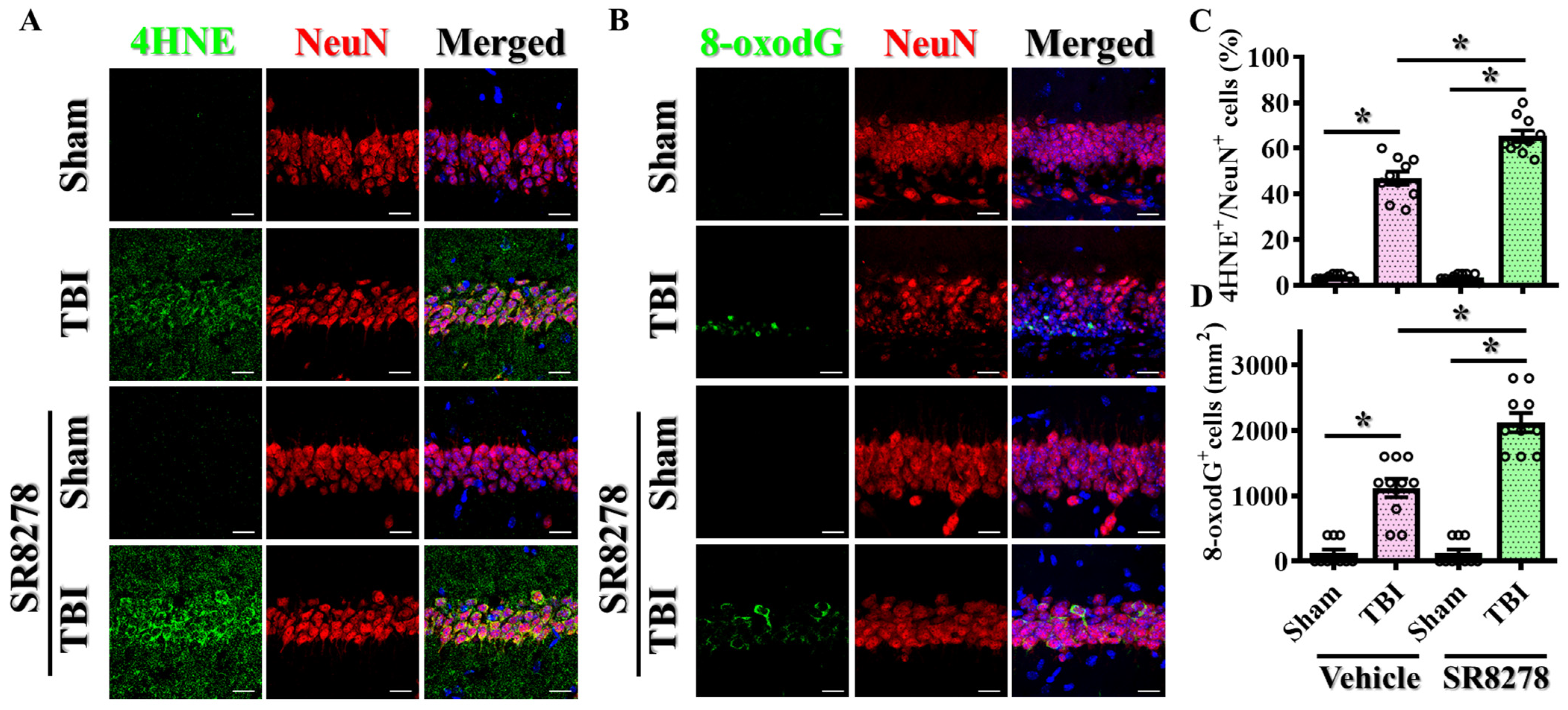
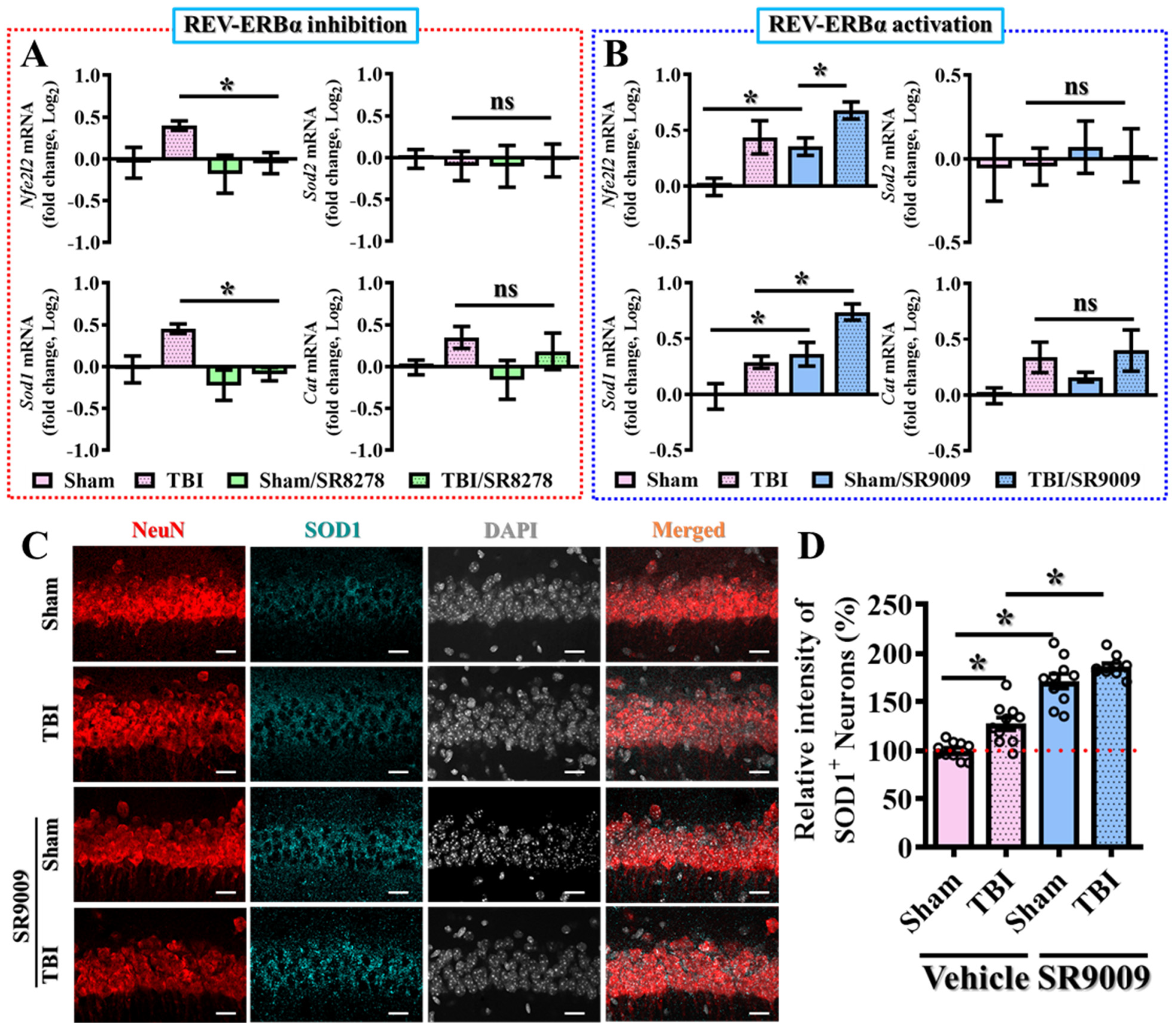
3.3. Pharmacological Inhibition of Rev-Erbα Slows Down Recovery from TBI
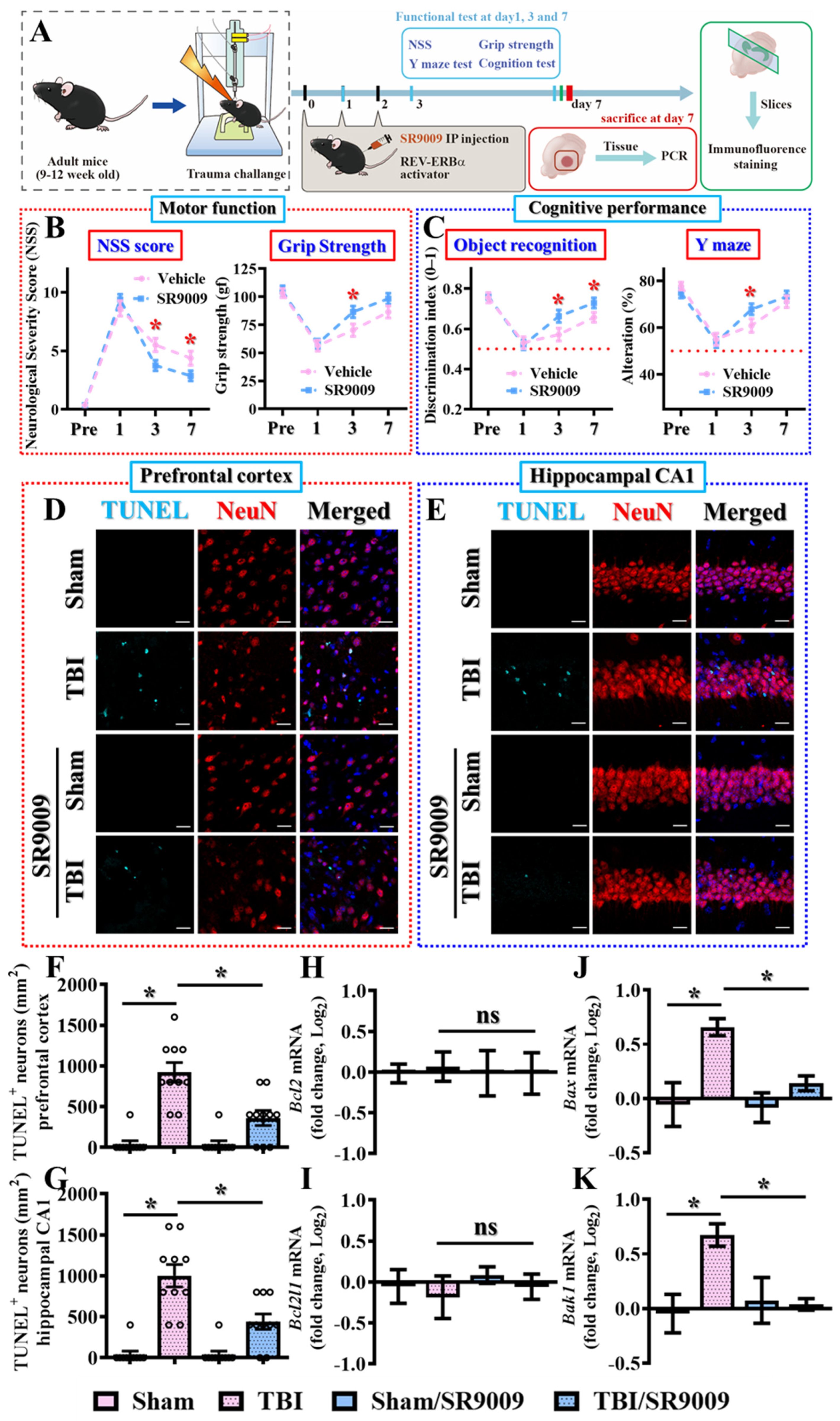
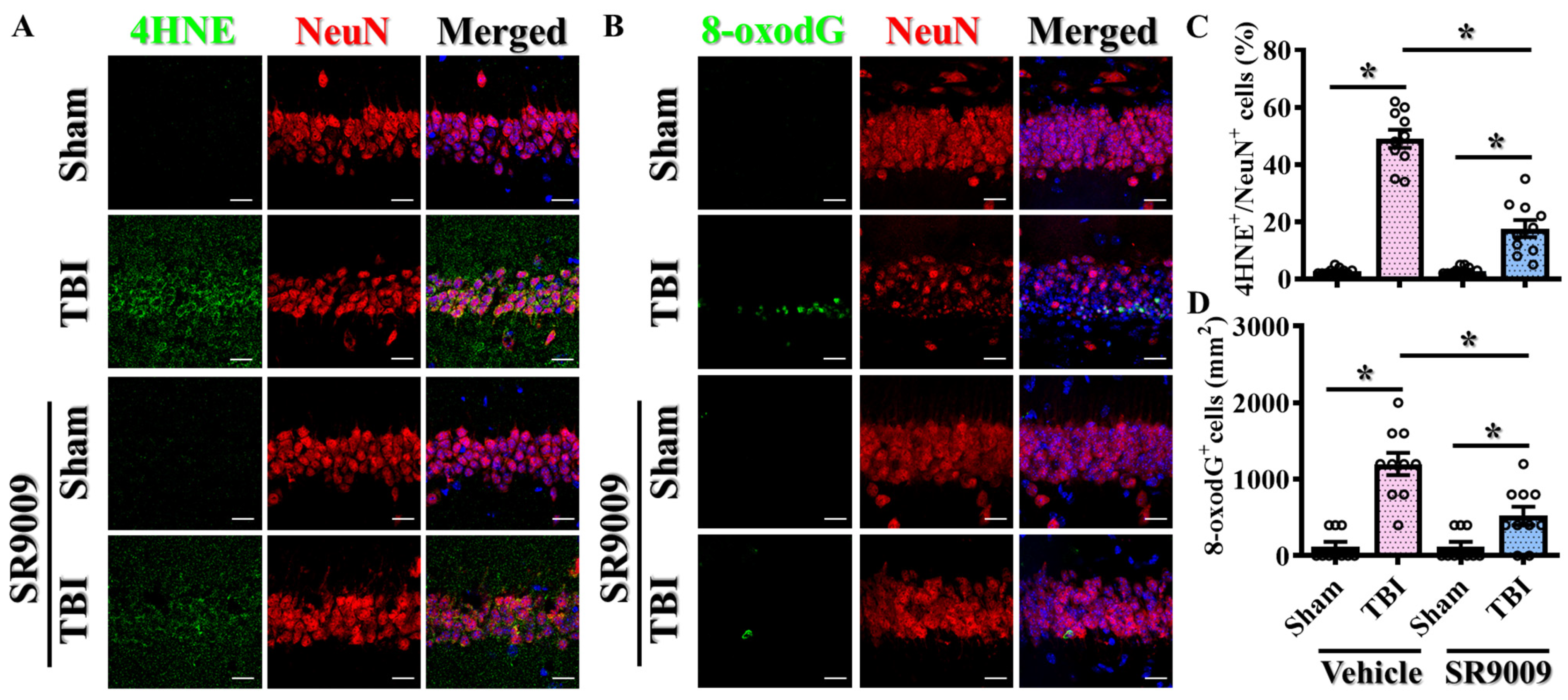
3.4. Pharmacological Activation of Rev-Erbα Promotes Functional Recovery
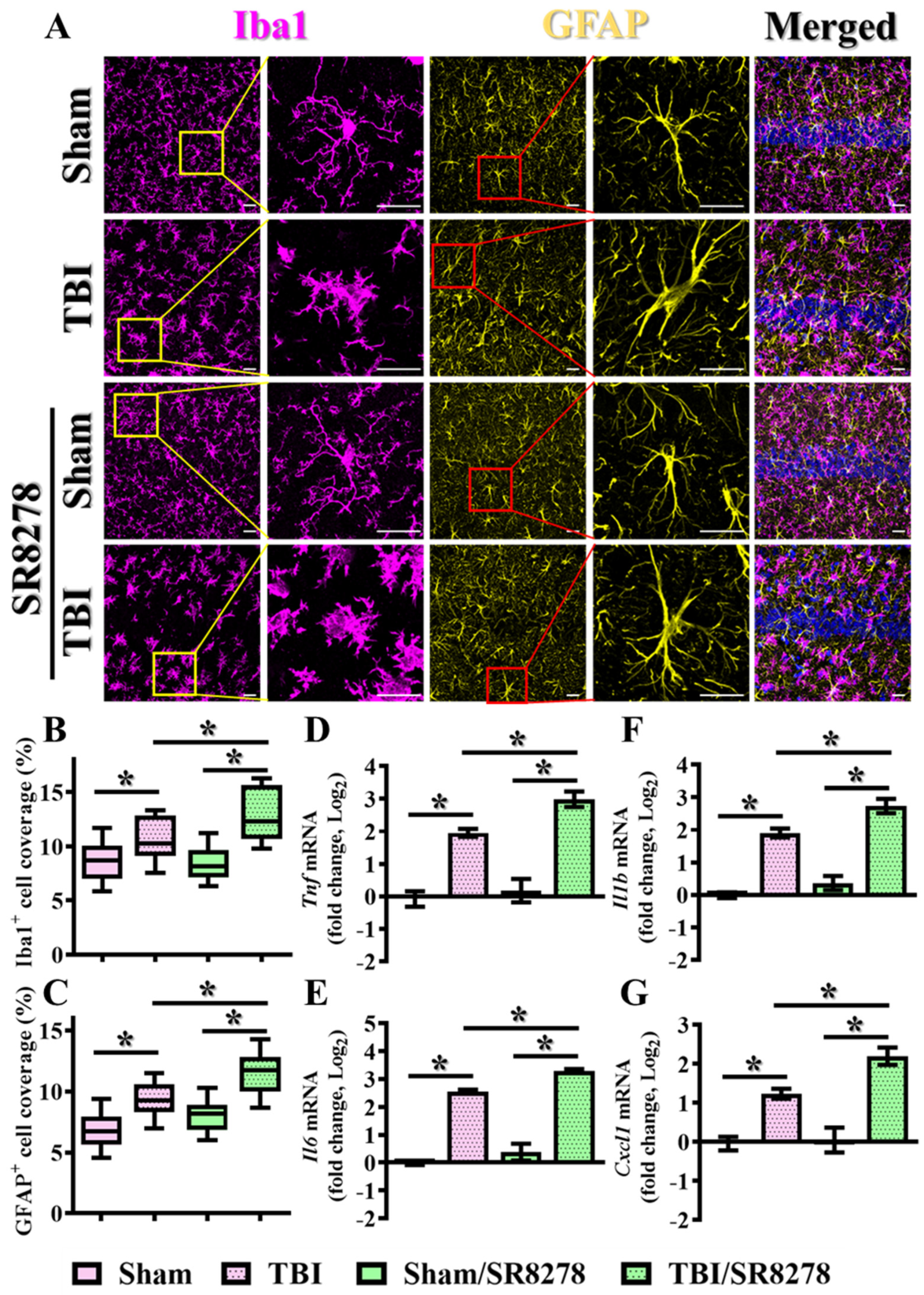
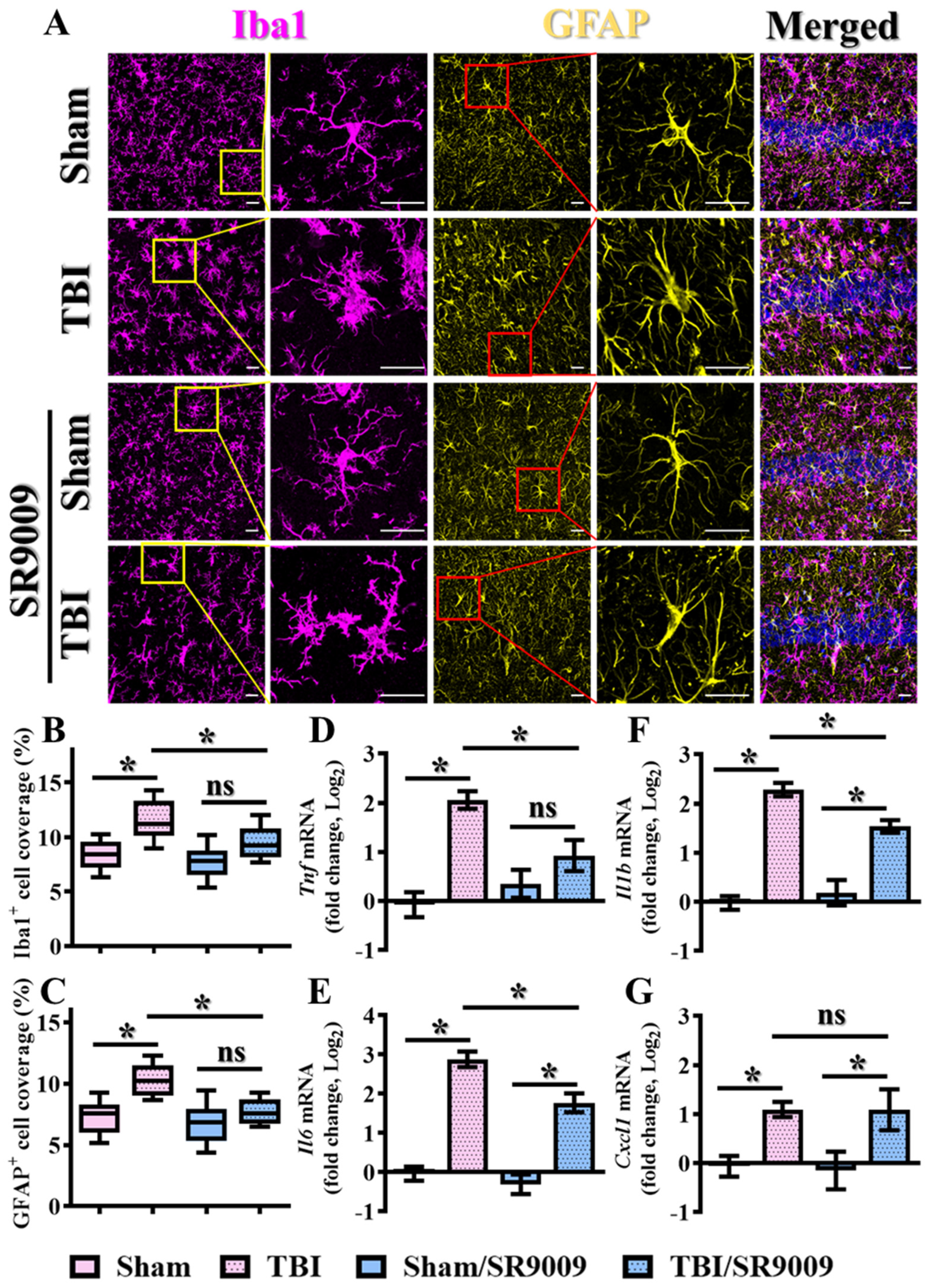
3.5. Modulation of TBI-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Rev-Erbα
3.6. Modulation of TBI-Induced Excessive Oxidative Stress by Rev-erbα
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanisms of Rev-erbα’s Action in TBI
4.2. Potential Mechanisms of Rev-erbα Reduction Following TBI
4.3. Corroborating Evidence for Rev-erbα Agonists in Other Types of Brain Damage
4.4. Targeting Rev-erbα in Susceptible Populations
4.5. Therapeutic Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Adelson, P.D.; Andelic, N.; Bell, M.J.; Belli, A.; Bragge, P.; Brazinova, A.; Büki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 987–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, M.C.; Rattani, A.; Gupta, S.; Baticulon, R.E.; Hung, Y.C.; Punchak, M.; Agrawal, A.; Adeleye, A.O.; Shrime, M.G.; Rubiano, A.M.; et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1080–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, J.D.; Selassie, A.W.; Orman, J.A. The Epidemiology of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2010, 25, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteneck, G.G.; Cuthbert, J.P.; Corrigan, J.D.; Bogner, J.A. Risk of Negative Outcomes after Traumatic Brain Injury: A Statewide Population-Based Survey. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2016, 31, E43–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, E.I.; Andelic, N.; Fure, S.C.R.; Røe, C.; Søberg, H.L.; Hellstrøm, T.; Spjelkavik, Ø.; Enehaug, H.; Lu, J.; Ugelstad, H.; et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of combined cognitive and vocational rehabilitation in patients with mild-to-moderate TBI: Results from a randomized controlled trial. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, M.A.M.; Rocha, G.S.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Falcao, D.; Lima, R.R.; Cavalcanti, J.R.L.P. Cellular and Molecular Pathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: What Have We Learned So Far? Biology 2023, 12, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, F.; Ji, W. Ginkgolide A attenuated apoptosis via inhibition of oxidative stress in mice with traumatic brain injury. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesharaki-Zadeh, A. Oxidative Stress in Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclos, C.; Dumont, M.; Paquet, J.; Blais, H.; Van der Maren, S.; Menon, D.K.; Bernard, F.; Gosselin, N. Sleep-wake disturbances in hospitalized patients with traumatic brain injury: Association with brain trauma but not with an abnormal melatonin circadian rhythm. Sleep 2019, 43, zsz191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, N.A.; Ponsford, J.L.; St Hilaire, M.A.; Mansfield, D.; Rajaratnam, S.M. Circadian Melatonin Rhythm Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2016, 30, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ma, S.; Guo, D.; Cheng, T.; Li, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Guan, F.; Yang, B.; Wang, J. Environmental Circadian Disruption Worsens Neurologic Impairment and Inhibits Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Adult Rats after Traumatic Brain Injury. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, D.R.; Sell, S.L.; Micci, M.A.; Crookshanks, J.M.; Parsley, M.; Uchida, T.; Prough, D.S.; DeWitt, D.S.; Hellmich, H.L. Traumatic brain injury-induced dysregulation of the circadian clock. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, D.; Ni, H.; Liu, C.; Xiong, J.; Liu, H.; Gao, R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G. The circadian clock regulator Bmal1 affects traumatic brain injury in rats through the p38 MAPK signalling pathway. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 178, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, A.D.; Greenough, E.K. Circadian Rhythms Regulate Neuroinflammation after Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury. In Biological Implications of Circadian Disruption: A Modern Health Challenge; Fonken, L.K., Nelson, R.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 183–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang-Sun, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.-Z.; Escames, G.; Lei, W.-R.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.-Z.; Tian, Y.; Ren, Y.-N.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Yang, Y. Targeting NR1D1 in organ injury: Challenges and prospects. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, L.J.; Lazar, M.A. Nuclear receptor Rev-erbα: Up, down, and all around. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liao, F.; Luo, G.; Qian, Y.; He, X.; Xu, W.; Ding, S.; Pu, J. NR1D1 Deletion Induces Rupture-Prone Vulnerable Plaques by Regulating Macrophage Pyroptosis via the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5217572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qi, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C.; Tao, T.; Zhou, C.; Sun, X.; et al. NR1D1 modulates synovial inflammation and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lananna, B.V.; Musiek, E.S. The wrinkling of time: Aging, inflammation, oxidative stress, and the circadian clock in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 139, 104832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Britton, W.R.; Blomfield, A.K.; Kamenecka, T.M.; Dunaief, J.L.; Solt, L.A.; Chen, J. REV-ERBalpha regulates age-related and oxidative stress-induced degeneration in retinal pigment epithelium via NRF2. Redox Biol. 2022, 51, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Yang, G.; O’Donnell, J.C.; Hinson, M.D.; McCormack, S.E.; Falk, M.J.; La, P.; Robinson, M.B.; Williams, M.L.; Yohannes, M.T.; et al. The circadian gene Rev-erbalpha improves cellular bioenergetics and provides preconditioning for protection against oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 93, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, T.L.; Chang, C.C.; Chung, C.L.; Ko, W.C.; Yang, C.H.; Hsieh, C.Y. Neuroprotective Effects of Platonin, a Therapeutic Immunomodulating Medicine, on Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice after Controlled Cortical Impact. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, F.; Xu, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Guo, L.; Zhou, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; et al. Dysregulation of REV-ERBalpha impairs GABAergic function and promotes epileptic seizures in preclinical models. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Kou, J.; Chen, G. Rev-erbalpha agonist SR9009 protects against cerebral ischemic injury through mechanisms involving Nrf2 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-S.; Tsai, P.-Y.; Yang, L.-Y.; Lecca, D.; Luo, W.; Kim, D.S.; Hoffer, B.J.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Greig, N.H.; Wang, J.-Y. 3,6′-Dithiopomalidomide Ameliorates Hippocampal Neurodegeneration, Microgliosis and Astrogliosis and Improves Cognitive Behaviors in Rats with a Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, D.; Lu, M.; Chopp, M. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellu, F.; Mayo, W.; Cherkaoui, J.; Le Moal, M.; Simon, H. A two-trial memory task with automated recording: Study in young and aged rats. Brain Res. 1992, 588, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solt, L.A.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Hughes, T.; Kojetin, D.J.; Lundasen, T.; Shin, Y.; Liu, J.; Cameron, M.D.; Noel, R.; et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists. Nature 2012, 485, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, P.; Dimitry, J.M.; Sheehan, P.W.; Lananna, B.V.; Guo, C.; Robinette, M.L.; Hayes, M.E.; Cedeno, M.R.; Nadarajah, C.J.; Ezerskiy, L.A.; et al. Circadian clock protein Rev-erbalpha regulates neuroinflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5102–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Roberts, K.N.; Scheff, S.W. A time course of contusion-induced oxidative stress and synaptic proteins in cortex in a rat model of TBI. J. Neurotrauma 2008, 25, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shao, C.; Zhang, L.; Siedlak, S.L.; Meabon, J.S.; Peskind, E.R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Perry, G.; Cook, D.G.; et al. Oxidative Stress Signaling in Blast TBI-Induced Tau Phosphorylation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, M.Q.; Hodgson, N.; Lee, H.H.C.; Pascual-Leone, A.; MacMullin, P.C.; Jannati, A.; Dhamne, S.C.; Hensch, T.K.; Rotenberg, A. N-acetylcysteine treatment mitigates loss of cortical parvalbumin-positive interneuron and perineuronal net integrity resulting from persistent oxidative stress in a rat TBI model. Cereb. Cortex 2023, 33, 4070–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhao, Z.; Lang, J.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Q. Nrf2 loss of function exacerbates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in TBI mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 770, 136400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Chen, F.; Wu, Y. Recombinant PEP-1-SOD1 improves functional recovery after neural stem cell transplantation in rats with traumatic brain injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 2929–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; D’Mello, V.; Caruso, D.; Abdul-Muneer, P.M. Traumatic brain injury-induced downregulation of Nrf2 activates inflammatory response and apoptotic cell death. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 1627–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Muneer, P.M. Nrf2 as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tastan, B.; Arioz, B.I.; Genc, S. Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome with Nrf2 Inducers in Central Nervous System Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Sun, Y.; Cai, P.; Jing, Q. Identification of a small molecule SR9009 that activates NRF2 to counteract cellular senescence. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jeon, Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, H. NR1D1 deficiency in the tumor microenvironment promotes lung tumor development by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wright, C.J.; Hinson, M.D.; Fernando, A.P.; Sengupta, S.; Biswas, C.; La, P.; Dennery, P.A. Oxidative stress and inflammation modulate Rev-erbalpha signaling in the neonatal lung and affect circadian rhythmicity. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2014, 21, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Xu, F.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Lin, H.; Ding, Y.; Du, M. Pharmacological activation of rev-erbalpha suppresses LPS-induced macrophage M1 polarization and prevents pregnancy loss. BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, V.T.; Cross, C.E.; Gohil, K. Nr1d1, an important circadian pathway regulatory gene, is suppressed by cigarette smoke in murine lungs. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.S.; Park, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.Y. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Formation: A Concise Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roby, D.A.; Ruiz, F.; Kermath, B.A.; Voorhees, J.R.; Niehoff, M.; Zhang, J.; Morley, J.E.; Musiek, E.S.; Farr, S.A.; Burris, T.P. Pharmacological activation of the nuclear receptor REV-ERB reverses cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-β burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Chi, X.; Sun, Y.; Han, C.; Wan, F.; Hu, J.; Yin, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. The circadian clock protein Rev-erbalpha provides neuroprotection and attenuates neuroinflammation against Parkinson’s disease via the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, C.A.; Gutierrez-Monreal, M.A.; Meng, L.; Zhang, X.; Douma, L.G.; Costello, H.M.; Douglas, C.M.; Ebrahimi, E.; Pham, A.; Oliveira, A.C.; et al. Defining the age-dependent and tissue-specific circadian transcriptome in male mice. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 111982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Manley, G.T.; Abrams, M.; Akerlund, C.; Andelic, N.; Aries, M.; Bashford, T.; Bell, M.J.; Bodien, Y.G.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Forward (Sense) | Reverse (Antisense) |
|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant-Related Genes | ||
| Cat | CGGCACATGAATGGCTATGGATC | AAGCCTTCCTGCCTCTCCAACA |
| Sod1 | GGTGAACCAGTTGTGTTGTCAGG | ATGAGGTCCTGCACTGGTACAG |
| Sod2 | TAACGCGCAGATCATGCAGCTG | AGGCTGAAGAGCGACCTGAGTT |
| Nfe2l2 (Nrf2) | CAGCATAGAGCAGGACATGGAG | GAACAGCGGTAGTATCAGCCAG |
| Inflammatory-related genes | ||
| TNF | GGTGCCTATGTCTCAGCCTCTT | GCCATAGAACTGATGAGAGGGAG |
| IL-6 | TACCACTTCACAAGTCGGAGGC | CTGCAAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTC |
| IL-1β | TGGACCTTCCAGGATGAGGACA | GTTCATCTCGGAGCCTGTAGTG |
| Cxcl1 | TCCAGAGCTTGAAGGTGTTGCC | AACCAAGGGAGCTTCAGGGTCA |
| Cell death-related genes | ||
| Bcl-2 | CCTGTGGATGACTGAGTACCTG | AGCCAGGAGAAATCAAACAGAGG |
| Bcl2l1 | GCCACCTATCTGAATGACCACC | AGGAACCAGCGGTTGAAGCGC |
| Bax | AGGATGCGTCCACCAAGAAGCT | TCCGTGTCCACGTCAGCAATCA |
| Bak1 | GGAATGCCTACGAACTCTTCACC | CAAACCACGCTGGTAGACGTAC |
| Circadian-related genes | ||
| Per1 | GAAACCTCTGGCTGTTCCTACC | AGGCTGAAGAGGCAGTGTAGGA |
| Per2 | CTGCTTGTTCCAGGCTGTGGAT | CTTCTTGTGGATGGCGAGCATC |
| Nr1d1 | CAGGCTTCCGTGACCTTTCTCA | TAGGTTGTGCGGCTCAGGAACA |
| Nr1d2 | CAGTGAGAAGCTGAATGCCCTC | TGCACGGATGAGTGTTTCCTGC |
| Clock | GGCTGAAAGACGGCGAGAACTT | GTGCTTCCTTGAGACTCACTGTG |
| Bmal1 | ACCTCGCAGAATGTCACAGGCA | CTGAACCATCGACTTCGTAGCG |
| Internal controls | ||
| Gapdh | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darmanto, A.G.; Jan, J.-S.; Yen, T.-L.; Huang, S.-W.; Teng, R.-D.; Wang, J.-Y.; Taliyan, R.; Sheu, J.-R.; Yang, C.-H. Targeting Circadian Protein Rev-erbα to Alleviate Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Enhance Functional Recovery Following Brain Trauma. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080901
Darmanto AG, Jan J-S, Yen T-L, Huang S-W, Teng R-D, Wang J-Y, Taliyan R, Sheu J-R, Yang C-H. Targeting Circadian Protein Rev-erbα to Alleviate Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Enhance Functional Recovery Following Brain Trauma. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(8):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080901
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarmanto, Arief Gunawan, Jing-Shiun Jan, Ting-Lin Yen, Shin-Wei Huang, Ruei-Dun Teng, Jia-Yi Wang, Rajeev Taliyan, Joen-Rong Sheu, and Chih-Hao Yang. 2024. "Targeting Circadian Protein Rev-erbα to Alleviate Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Enhance Functional Recovery Following Brain Trauma" Antioxidants 13, no. 8: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080901
APA StyleDarmanto, A. G., Jan, J.-S., Yen, T.-L., Huang, S.-W., Teng, R.-D., Wang, J.-Y., Taliyan, R., Sheu, J.-R., & Yang, C.-H. (2024). Targeting Circadian Protein Rev-erbα to Alleviate Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Enhance Functional Recovery Following Brain Trauma. Antioxidants, 13(8), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13080901










