Insect–Antioxidants Symbiotic Nexus—Pathway for Sustainable and Resilient Aquaculture: A Case Study for Evaluating Koi Carp Growth and Oxidative Stress Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- Develop innovative fish feeds for the production of koi carp in a recirculating aquaculture system, based on alternative protein sources (insect flour) and phytogenic additives (Curcuma longa—turmeric and Beta vulgaris—beetroot) as antioxidants;
- (b)
- Evaluate and characterize the innovative feeds in regards to the amino acid content;
- (c)
- Conduct a comparative analysis to evaluate the growth performance, hematological and biochemical profile, and metabolic rate of the experimental fish biomass.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Amino Acid Analysis from the Innovative Feeds
2.4. Fish Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, and Condition Factor
2.5. Fish Oxygen Consumption—Respirometry
2.6. Hematological Profile and Blood Biochemical Indicator Analysis
2.7. Oxidative Stress
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Amino Acid Content in Innovative Fish Feeds
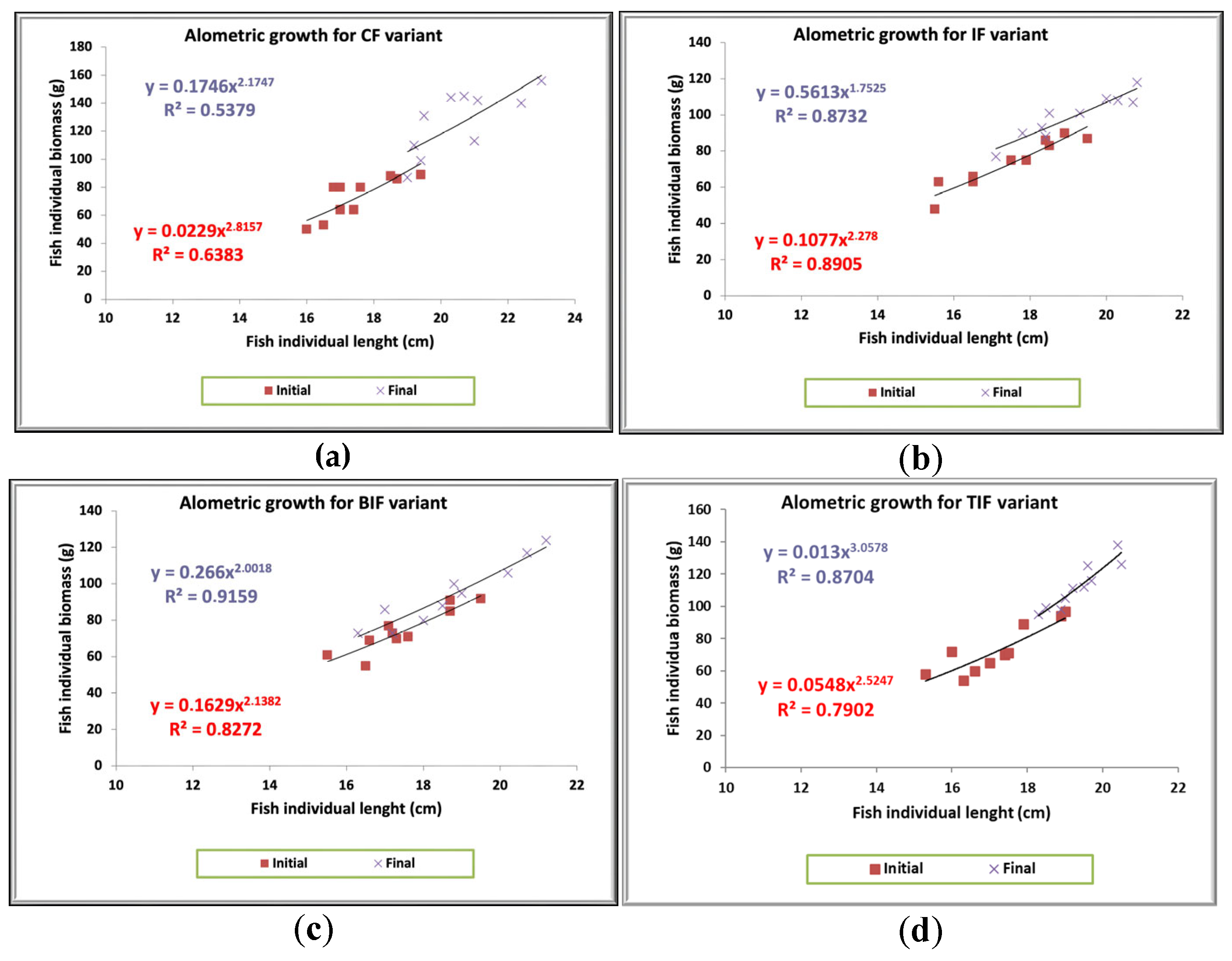
3.2. Fish Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, and Condition Factor
3.3. Fish Oxygen Consumption—Respirometry
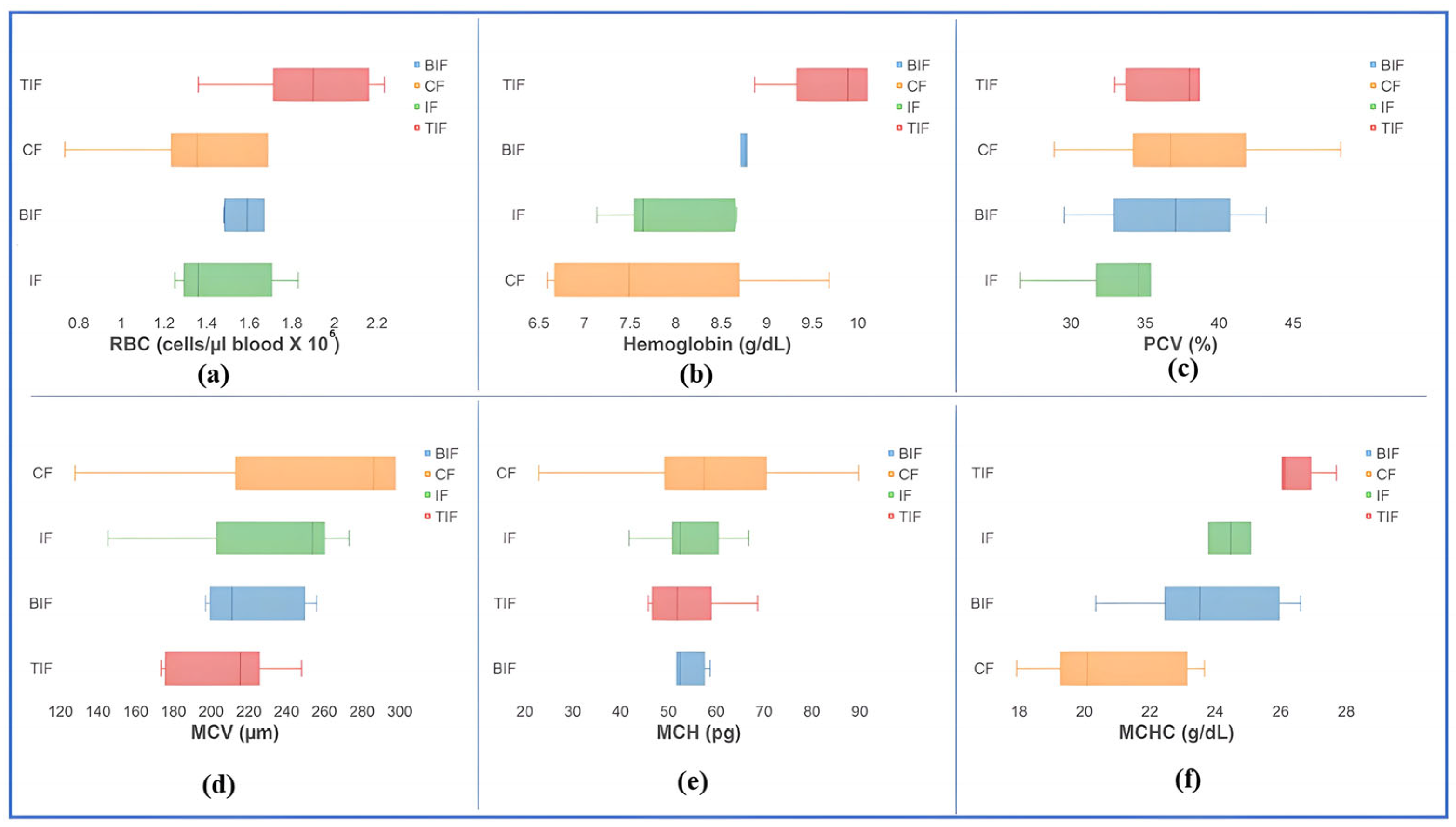
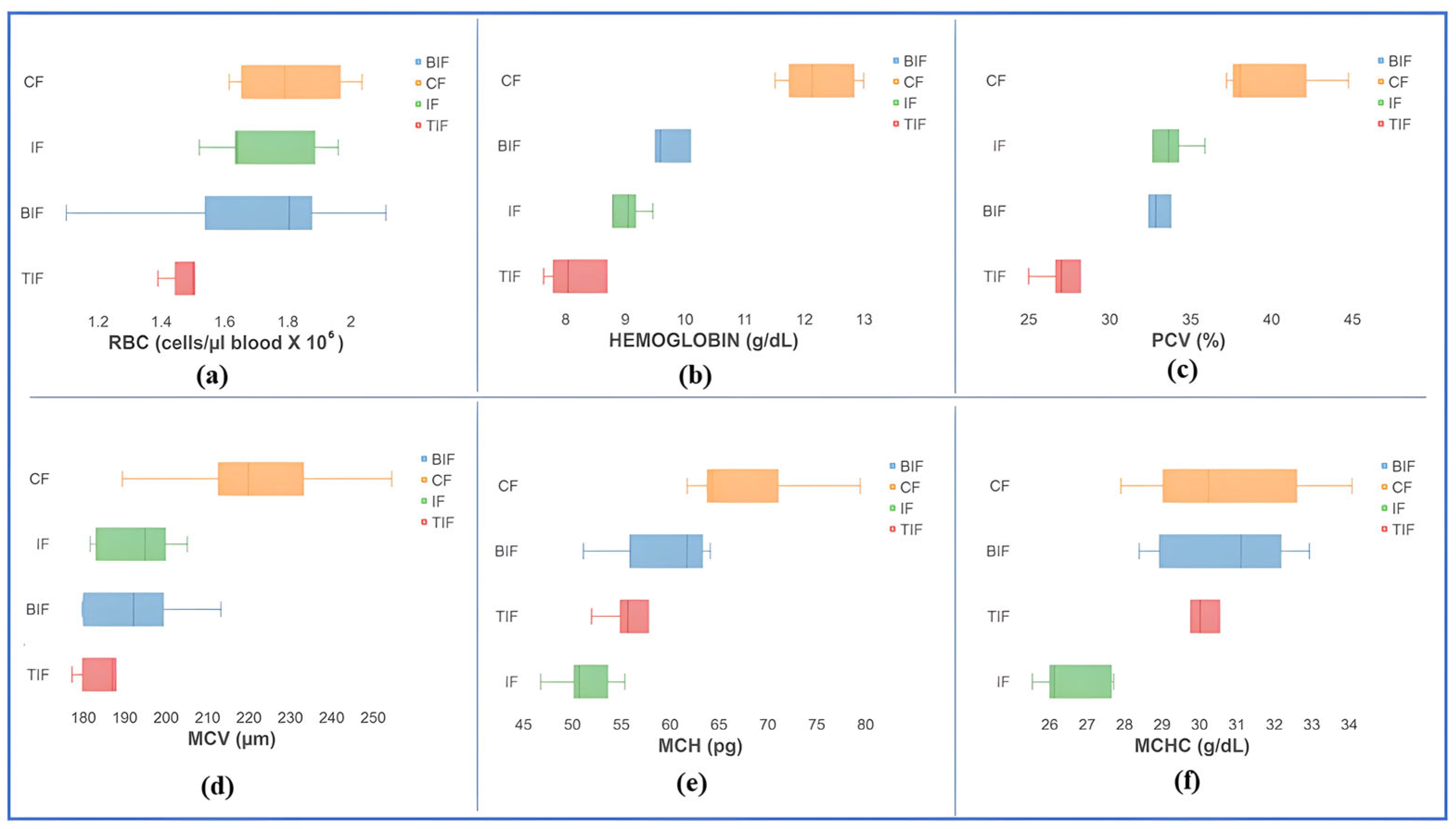
3.4. Hematological Profile and Blood Biochemical Indices
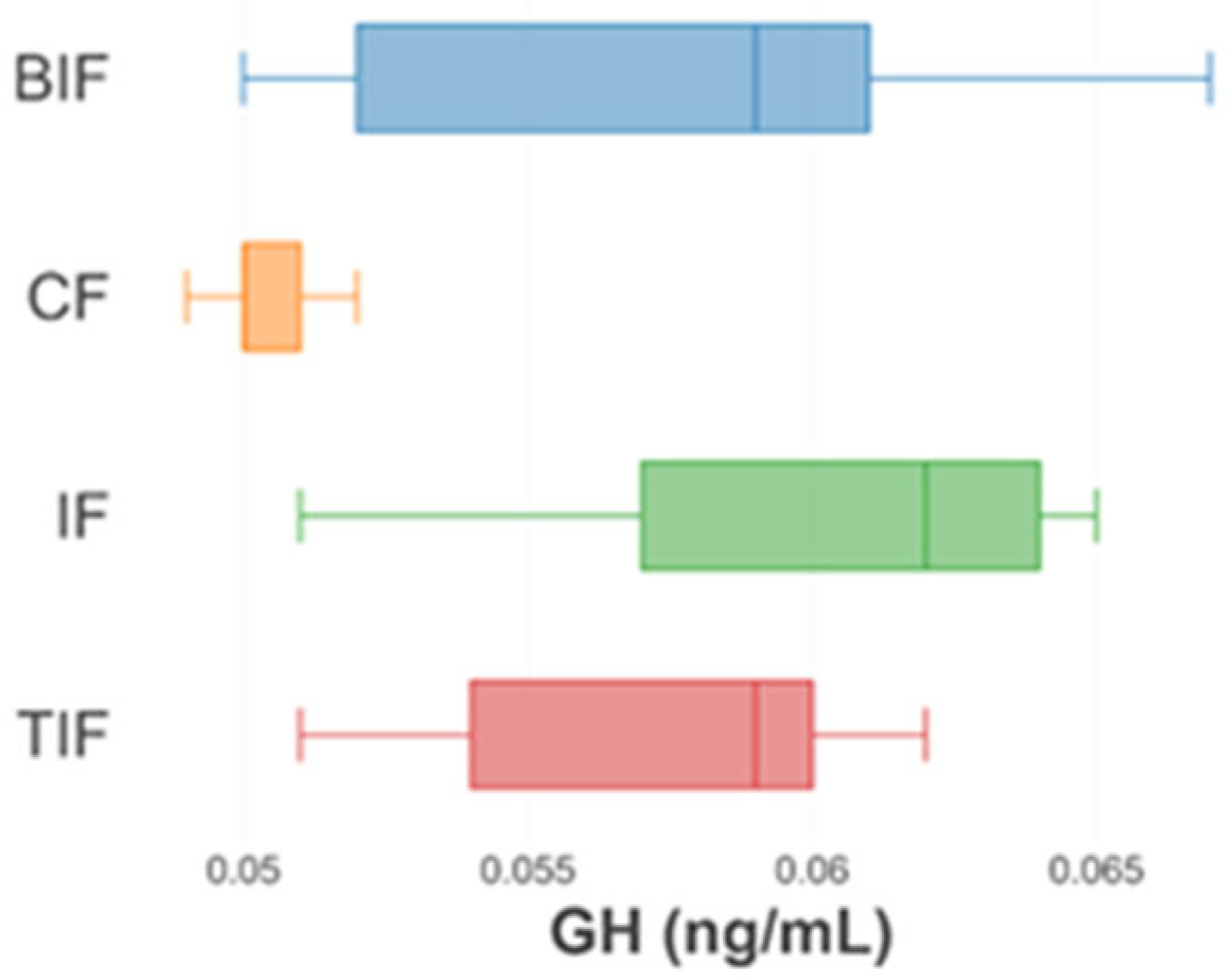
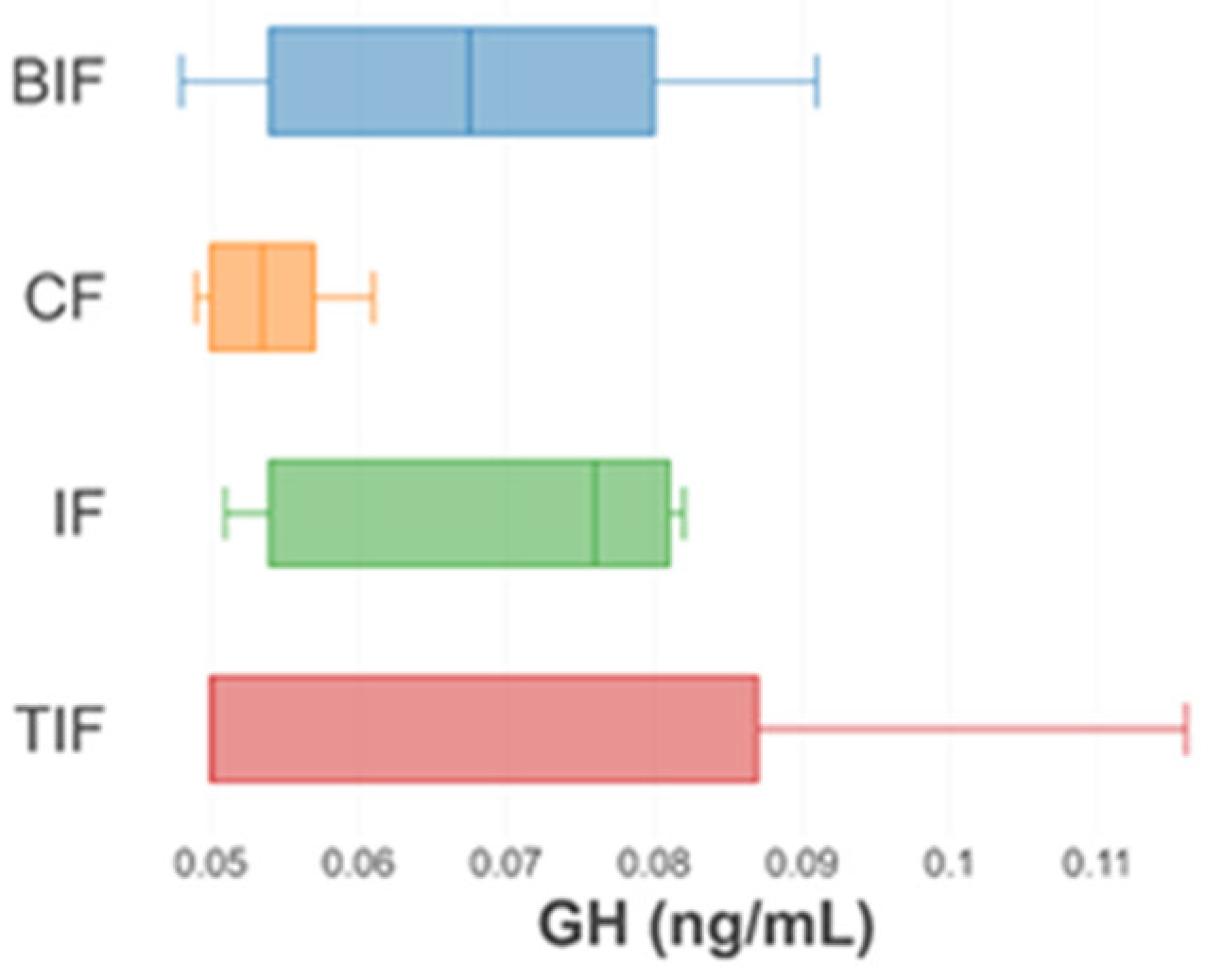
3.5. Oxidative Stress
4. Discussion
- A relatively small sample size—This sample size number may be considered adequate for preliminary insights. However, a larger sample can minimize variability. Future studies could consider using a larger fish population to improve the level of confidence in our results;
- Species specificity—The results obtained within this study should be extrapolated cautiously for other species due to differences in species feeding ecologies, nutritional requirements, development stages, lifecycles, and rearing systems.
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Market Research Intellect. Koi Market Size And Projection. Available online: https://www.marketresearchintellect.com/blog/koi-fish-market-the-rising-tide-of-demand-for-colorful-carp-in-aquaculture/ (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Luo, X.-L.; Rauan, A.; Xing, J.-X.; Sun, J.; Wu, W.-Y.; Ji, H. Influence of Dietary Se Supplementation on Aquaponic System: Focusing on the Growth Performance, Ornamental Features and Health Status of Koi Carp (Cyprinus carpio Var. Koi), Production of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Water Quality. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market Data Forecast, Ltd. Koi Market Size, Share, Analysis & Trends, 2032. Available online: https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/koi-market (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Nuwansi, K.K.T.; Verma, A.K.; Chandrakant, M.H.; Prabhath, G.P.W.A.; Peter, R.M. Optimization of Stocking Density of Koi Carp (Cyprinus carpio Var. Koi) with Gotukola (Centella asiatica) in an Aquaponic System Using Phytoremediated Aquaculture Wastewater. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 735993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisingkorn, W.; Rinthong, P.; Kamolrat, N.; Wiriyapattanasub, P.; Wongmaneeprateep, S.; Suriyaphan, J.; Pholoeng, A.; Wangkahart, E. Impact of Dietary Mulberry (Morus alba) Fruit Extract on the Growth Performance, Skin Color, and Immune Response of Fancy Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquac. Rep. 2025, 40, 102611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.H.L.; Davies, S.J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Fitzgerald, R.; Johnson, M.P. Macroalgae as a Sustainable Aquafeed Ingredient. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 458–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilami, S.K.; Turek, J.; Červený, D.; Lepič, P.; Kozák, P.; Burkina, V.; Sakalli, S.; Tomčala, A.; Sampels, S.; Mráz, J. Insect Meal as a Partial Replacement for Fish Meal in a Formulated Diet for Perch Perca fluviatilis. TrJFAS 2020, 20, 867–878. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, F.A.; Guldhe, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Rawat, I.; Bux, F. Improving the Feasibility of Aquaculture Feed by Using Microalgae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43234–43257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale Saba, A.; Fakoya, K.A.; Elegbede, I.O.; Olayiwola Amoo, Z.; Moruf, R.O.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Akere, T.H.; Muhammad Dadile, A.; Adewolu, M.A.; Ojewole, A.E.; et al. Replacement of Fishmeal in the Diet of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JTAS 2023, 46, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Mitra, S.; Khan, M.A. Technical and Cost Efficiency of Pond Fish Farms: Do Young Educated Farmers Bring Changes? J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wen, X.; Rong, H.; Xiao, L.; Lin, F. Effects of Fish Meal Replacement with Composite Proteins Source on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Capacity and Swim Bladder Quality of Chu’s Croaker (Nibea Coibor). Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Dai, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Lou, B.; Guo, S. Evaluation of Common Housefly Musca Domestica Maggot Meal as Partial Substitution of Fish Meal and Fish Oil in Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir Sinensis Diets. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 41, 102709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Ginés, R.; Martín, I.; Zamorano, M.J.; Acosta, F.; Fontanillas, R.; Torrecillas, S.; Montero, D. Genetic Selection for High Growth Improves the Efficiency of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) in Using Novel Diets with Insect Meal, Single-Cell Protein and a DHA Rich-Microalgal Oil. Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawski, M.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Kierończyk, B.; Józefiak, D. Black Soldier Fly Full-Fat Larvae Meal Is More Profitable than Fish Meal and Fish Oil in Siberian Sturgeon Farming: The Effects on Aquaculture Sustainability, Economy and Fish GIT Development. Animals 2021, 11, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro dos Santos, D.K.; Rodrigues de Freitas, O.; Oishi, C.A.; Leão da Fonseca, F.A.; Parisi, G.; Uribe Gonçalves, L. Full-Fat Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal in Diet for Tambaqui, Colossoma Macropomum: Digestibility, Growth Performance and Economic Analysis of Feeds. Animals 2023, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Muros, M.-J.; Barroso, F.G.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Insect Meal as Renewable Source of Food for Animal Feeding: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the Use of Insects in the Diet of Farmed Fish: Past and Future. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer Llagostera, P.; Kallas, Z.; Reig, L.; Amores de Gea, D. The Use of Insect Meal as a Sustainable Feeding Alternative in Aquaculture: Current Situation, Spanish Consumers’ Perceptions and Willingness to Pay. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, S.N.; Bollens, S.M. Fish Assemblages across a Vegetation Gradient in a Restoring Tidal Freshwater Wetland: Diets and Potential for Resource Competition. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2014, 97, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, E.-J.; Biancarosa, I.; Gasco, L. Insects as Raw Materials in Compound Feed for Aquaculture. In Edible Insects in Sustainable Food Systems; Halloran, A., Flore, R., Vantomme, P., Roos, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 263–276. ISBN 978-3-319-74010-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, A.; Sandionigi, A.; Panio, A.; Rimoldi, S.; Orizio, F.; Agostinetto, G.; Hasan, I.; Gasco, L.; Terova, G.; Labra, M. Aquaculture Ecosystem Microbiome at the Water-Fish Interface: The Case-Study of Rainbow Trout Fed with Tenebrio Molitor Novel Diets. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Amato, M.; Biasato, I.; Chiesa, S.; Gasco, L. The Potential Role of Insects as Feed: A Multi-Perspective Review. Animals 2019, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapa, M.A.C.; Kallas, Z. Towards More Sustainable Animal-Feed Alternatives: A Survey on Spanish Consumers’ Willingness to Consume Animal Products Fed with Insects. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 41, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Biasato, I.; Dabbou, S.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F. Animals Fed Insect-Based Diets: State-of-the-Art on Digestibility, Performance and Product Quality. Animals 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Féon, S.; Thévenot, A.; Maillard, F.; Macombe, C.; Forteau, L.; Aubin, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Fish Fed with Insect Meal: Case Study of Mealworm Inclusion in Trout Feed, in France. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ellis, J.; Huyben, D. Examining the Dietary Effect of Insect Meals on the Innate Immune Response of Fish: A Meta-Analysis. Comp. Immunol. Rep. 2024, 7, 200169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willora, F.P.; Farris, N.W.; Ghebre, E.; Zatti, K.; Bisa, S.; Kiron, V.; Verlhac-Trichet, V.; Danielsen, M.; Dalsgaard, T.K.; Sørensen, M. Full-Fat Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal and Yellow Mealworm Meal: Impact on Feed Protein Quality, Growth and Nutrient Utilization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Post Smolts. Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosdowech, S.; Chiasson, M.; Ma, D.W.L.; Huyben, D.; Rooney, N. Dietary Inclusion of Black Soldier Fly, Cricket and Superworm in Rainbow Trout Aquaculture: Impacts on Growth and Nutrient Profiles. Available online: https://colab.ws/articles/10.1163%2F23524588-00001393 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Mousavi, S.; Zahedinezhad, S.; Loh, J.Y. A Review on Insect Meals in Aquaculture: The Immunomodulatory and Physiological Effects. Int. Aquat. Res. 2020, 12, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimoldi, S.; Ceccotti, C.; Brambilla, F.; Faccenda, F.; Antonini, M.; Terova, G. Potential of Shrimp Waste Meal and Insect Exuviae as Sustainable Sources of Chitin for Fish Feeds. Aquaculture 2023, 567, 739256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunji, J.O.; Nimptsch, J.; Wiegand, C.; Schulz, C.; Rennert, B. Effect of Housefly Maggot Meal (Magmeal) Diets on Catalase, and Glutathione S-Transferase in the Liver and Gills of Carp Cyprinus carpio Fingerling. Int. Aquat. Res. 2011, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Taufek, N.M.; Aspani, F.; Muin, H.; Raji, A.A.; Razak, S.A.; Alias, Z. The Effect of Dietary Cricket Meal (Gryllus bimaculatus) on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Enzyme Activities, and Haematological Response of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Chen, Y.; Yu, W.; Lin, M.; Yang, G.; Qin, C.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.; Nie, G. Defatted Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal Can Replace Soybean Meal in Juvenile Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) Diets. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, O.K.; Holen, E.; Piemontese, L.; Liland, N.S.; Lock, E.-J.; Espe, M.; Belghit, I. Effect of Dietary Replacement of Fish Meal with Insect Meal on in Vitro Bacterial and Viral Induced Gene Response in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Head Kidney Leukocytes. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 91, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, C.E.; Powell, M.S.; Gaylord, T.G.; Conley, Z.B.; Sealey, W.M. Investigation of the Suitability of 3 Insect Meals as Protein Sources for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, G.S.C.; Bhujel, R.C. Replacement of Fishmeal by House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) and Field Cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus) Meals: Effect for Growth, Pigmentation, and Breeding Performances of Guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Tey, H.C.; Wendy, W.; Wan Zahari, M. The Effect of House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) Meal on Growth Performance of Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis Sp.). Int. J. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 8, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Taufek, N.M.; Muin, H.; Raji, A.A.; Md Yusof, H.; Alias, Z.; Razak, S.A. Potential of Field Crickets Meal (Gryllus bimaculatus) in the Diet of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, A.; Magnotti, C.; Tsuzuki, M.Y.; Sousa, E.M.d.O.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Martins, M.L.; Lopes, R.G.; Derner, R.B.; Owatari, M.S. Pivotal Roles of Fish Nutrition and Feeding: Recent Advances and Future Outlook for Brazilian Fish Farming. Fishes 2025, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Maradonna, F.; Faheem, M.; Harikrishnan, R.; Devi, G.; Ringø, E.; Van Doan, H.; Ashouri, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O. Sustainable Ornamental Fish Aquaculture: The Implication of Microbial Feed Additives. Animals 2023, 13, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; Le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I.; et al. Review of Alternatives to Antibiotic Use in Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, E.M.; de Souza, R.C.; Melo, J.F.B.; da Costa, M.M.; de Souza, A.M.; Copatti, C.E. Evaluation of the Effects of Ocimum Basilicum Essential Oil in Nile Tilapia Diet: Growth, Biochemical, Intestinal Enzymes, Haematology, Lysozyme and Antimicrobial Challenges. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, D.K.; Sahu, N.P.; Sardar, P.; Deo, A.D.; Bedekar, M.K.; Singha, K.P.; Maiti, M.K. Feeding Turmeric in Combination with Ginger or Garlic Enhances the Digestive Enzyme Activities, Growth and Immunity in Labeo Rohita Fingerlings. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 277, 114964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekani, R.; Akrami, R.; Ghiasvand, Z.; Chitsaz, H.; Jorjani, S. Effect of Dietary Dehydrated Lemon Peel (Citrus limon) Supplementation on Growth, Hemato-Immunolological and Antioxidant Status of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under Exposure to Crowding Stress. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Kim, S.G.; Saha, S.; Kim, H.J.; Jun, J.W.; Chi, C.; Venkatachalam, S.; Park, S.C. Impact of Dietary Piperine on Growth Performance, Immune Response, Antioxidant Status, and Immune-Related Gene Expression in Pathogen-Aggravated Cyprinus carpio. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2023, 141, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyo, M.; Sangarun, P.; Wangkahart, E.; Sujipuri, K. Effects of Banana Flower Powder (Musa sp.) Supplementation on Growth Performance, Whole Body Composition, Antioxidant and Immune Responses, Gene Expression and Liver Histology in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2024, 308, 115882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antache, A.; Petrea, S.-M.; Simionov, I.-A.; Nica, A.; Cristea, V.; Georgescu, P.L.; Iticescu, C.; Ciobîcă, A. Effect of dietary supplementation of nile tilapia with sea. Sci. Pap. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2023, LXVI, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Elnesr, S.S.; Dhama, K. Curcumin and Its Different Forms: A Review on Fish Nutrition. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, N.; Kushwaha, K.; Sharma, P.; Gat, Y.; Panghal, A. Bioactive Compounds of Beetroot and Utilization in Food Processing Industry: A Critical Review. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Effects of Bioactive Substance from Turmeric on Growth, Skin Mucosal Immunity and Antioxidant Factors in Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 92, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haetami, K.; Erdiasari, E.; Herman, R.G.; Pratama, R. A Few Potential of Turmeric as Feed Additive on Fish Growth. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2023, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.J.G.; Velasco, R.R.; Doctolero, J.S. Young Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Tuber as Feed Additive for the Growth and Survival of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019, 7, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Anene, A.; Okorie, E.O.; Ajima, M.N.O.; Onyemaonwu, J. Dietary Supplement of Tumeric (Curcuma longa) Powder: Impact on Haematological and Biochemical Responses in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) Fingerlings. Aquac. Stud. 2021, 22, AQUAST714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, N.; Aberoumand, A.; Ziaei-Nejad, S. Effect of Beta vulgaris L. as Feed Ingredient on Muscle Growth, Nutritional Factors, and Quality of Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 5388–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, N.; Aberoumand, A.; Nejad, S.Z. Effects of Beta vulgaris Powder on Growth and Survival of Common Carp Cyprinus carpio. J. Fish. 2019, 7, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, F.S.; Bhat, F.A.; Shah, T.H.; Asimi, O.; Bhat, B.A.; Abubakr, A.; Chesti, A. Dietary Beta vulgaris Enhances Growth and Improves Hemato-Physiological Responses in Common Carp Cyprinus carpio Var. Communis. Pharma Innov. 2023, 12, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, P.-L.; Barbuta-Misu, N.; Zlati, M.L.; Fortea, C.; Antohi, V.M. Quantifying the Performance of European Agriculture Through the New European Sustainability Model. Agriculture 2025, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari Aqmasjed, S.; Sajjadi, M.M.; Falahatkar, B.; Safari, R. Effects of Dietary Ginger (Zingiber officinale) Extract and Curcumin on Growth, Hematology, Immunity, and Antioxidant Status in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 32, 101714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Ge, K.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, H.; Miao, L.; Ge, X. Suitable Cottonseed Protein Concentrate Supplementation in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Serves as an Effective Strategy for Fish Meal Sparing Based on Improvement in Intestinal Antioxidant Capacity, Barrier and Microbiota Composition. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Jia, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q. Protective Role of Sulforaphane against Physiological Toxicity of Triphenyltin in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio Haematopterus). Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.M.; Yousefi, M.; Afzali-Kordmahalleh, A.; Pagheh, E.; Taheri Mirghaed, A. Effects of Dietary Lactic Acid Supplementation on the Activity of Digestive and Antioxidant Enzymes, Gene Expressions, and Bacterial Communities in the Intestine of Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio. Animals 2023, 13, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, G.S.C.; Perera, A.D.; Piyavorasakul, C.; Pumpuang, S. Fishmeal Replacement by House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) and Field Cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus) Meals in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Fingerling Feed. Aquac. Stud. 2022, 23, AQUAST1187. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S. Pond Aquaculture Water Quality Management; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4613-7469-5. [Google Scholar]
- Oroian, M.; Dranca, F.; Ursachi, F. Characterization of Romanian Bee Pollen-An Important Nutritional Source. Foods 2022, 11, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocan, D.; Mireșan, V.; Constantinescu, R.; Cenan, R.; Uiuiu, P.; Muntean, C.; Papuc, T.; Ihuț, A.; Răducu, C. Analysis of Meat Quality and Productivity Indices in Fish Species with Different Nutritional Spectrum. Sci. Pap. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2024, LXVII, 526–534. [Google Scholar]
- Chabot, D.; Steffensen, J.F.; Farrell, A.P. The Determination of Standard Metabolic Rate in Fishes. J. Fish. Biol. 2016, 88, 81–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killen, S.S.; Christensen, E.A.F.; Cortese, D.; Závorka, L.; Norin, T.; Cotgrove, L.; Crespel, A.; Munson, A.; Nati, J.J.H.; Papatheodoulou, M.; et al. Guidelines for Reporting Methods to Estimate Metabolic Rates by Aquatic Intermittent-Flow Respirometry. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb242522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosewarne, P.J.; Wilson, J.M.; Svendsen, J.C. Measuring Maximum and Standard Metabolic Rates Using Intermittent-Flow Respirometry: A Student Laboratory Investigation of Aerobic Metabolic Scope and Environmental Hypoxia in Aquatic Breathers. J. Fish. Biol. 2016, 88, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschke, K.; Agüero, J.; Gebauer, P.; Díaz, F.; Mascaró, M.; López-Ripoll, E.; Re, D.; Caamal-Monsreal, C.; Tremblay, N.; Pörtner, H.-O.; et al. Comparison of Aerobic Scope for Metabolic Activity in Aquatic Ectotherms with Temperature Related Metabolic Stimulation: A Novel Approach for Aerobic Power Budget. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, Z. Stress in Fishes (A Review). Bull. Vurh Vodnany 2001, 4, 169–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ispir, Ü.; Yonar, M.E.; Oz, O.B. Effect of Dietary Vitamin E Supplementation on the Blood Parameters of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2011, 21, 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Draper, H.H.; Hadley, M. Malondialdehyde Determination as Index of Lipid Peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, R.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; van den Berg, H.; Bast, A. Applicability of an Improved Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC) Assay for Evaluation of Antioxidant Capacity Measurements of Mixtures. Food Chem. 1999, 66, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, E. Length-Weight Relationship and Well-Being Factors of 33 Fish Species Caught by Gillnets from the Egyptian Mediterranean Waters off Alexandria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2023, 49, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azrita, A.; Syandri, H.; Aryani, N. Length and Weight Relationship, Condition Factor, and Morphometric Characteristics of Eleven Freshwater Fish Species in Koto Panjang Reservoir, Indonesia. Int. J. Zool. 2024, 2024, 9927705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.; Olsen, R.e.; Song, S.k. Use of Chitin and Krill in Aquaculture—The Effect on Gut Microbiota and the Immune System: A Review. Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, I.; Rimoldi, S.; Saroglia, G.; Terova, G. Sustainable Fish Feeds with Insects and Probiotics Positively Affect Freshwater and Marine Fish Gut Microbiota. Animals 2023, 13, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Global Overview on the Use of Fish Meal and Fish Oil in Industrially Compounded Aquafeeds: Trends and Future Prospects. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santigosa, E.; García-Meilán, I.; Valentín, J.M.; Navarro, I.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Gallardo, M.Á. Plant Oils’ Inclusion in High Fish Meal-Substituted Diets: Effect on Digestion and Nutrient Absorption in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata L.). Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhoro, H.; Zhou, J.; Hua, Y.; Ng, W.-K.; Ye, L.; Zhang, J.; Shao, Q. Soy Protein Concentrate as a Substitute for Fish Meal in Diets for Juvenile Acanthopagrus Schlegelii: Effects on Growth, Phosphorus Discharge and Digestive Enzyme Activity. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köprücü, K.; Özdemir, Y. Apparent Digestibility of Selected Feed Ingredients for Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2005, 250, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longvah, T.; Mangthya, K.; Ramulu, P. Nutrient Composition and Protein Quality Evaluation of Eri Silkworm (Samia ricinii) Prepupae and Pupae. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józefiak, A.; Engberg, R.M. Insect Proteins as a Potential Source of Antimicrobial Peptides in Livestock Production. A Review. J. Anim. Feed. Sci. 2017, 26, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, K.; Rajan, D.K.; Ganesan, A.R.; Divya, D.; Johansen, J.; Zhang, S. Chitin, Chitosan and Chitooligosaccharides as Potential Growth Promoters and Immunostimulants in Aquaculture: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-C.; Shiu, Y.-L.; Chiu, S.-T.; Ballantyne, R.; Liu, C.-H. Effects of Chitin from Daphnia Similis and Its Derivative, Chitosan on the Immune Response and Disease Resistance of White Shrimp, Litopenaeus Vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 119, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggink, K.M.; Pedersen, P.B.; Lund, I.; Dalsgaard, J. Chitin Digestibility and Intestinal Exochitinase Activity in Nile Tilapia and Rainbow Trout Fed Different Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal Size Fractions. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5536–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriani, Y.; Pratama, R.I.; Hanidah, I.I. Chitosan Application in Aquatic Feed and Its Impact on Fish and Shrimp Productivity. Asian J. Biol. 2023, 19, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, A.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Habiba, M.M.; El-Zayat, A.; El-Sharnouby, M.E.; Sewilam, H.; Dawood, M.A.O. The Impact of Dietary Curcumin on the Growth Performance, Intestinal Antibacterial Capacity, and Haemato-Biochemical Parameters of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Animals 2021, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahyani, R.; Satyantini, W.H.; Nindarwi, D.D.; Cahyoko, Y. Addition of Turmeric in Feed on Growth and Survival Rate of Nilasa Red Tilapia (Oreochromis sp.). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 679, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, H.; Mahboub, H.H.; Salem, S.M.R.; Abdelwahab, A.M.; Alwutayd, K.M.; Shaalan, M.; Ismail, S.H.; Abdelfattah, A.M.; Khalid, A.; Mansour, A.T.; et al. Nano-Curcumin/Chitosan Modulates Growth, Biochemical, Immune, and Antioxidative Profiles, and the Expression of Related Genes in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fishes 2023, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hong, J.; Fu, Z.; Ma, Z. Effects of Dietary Curcumin on Growth and Digestive Physiology of Seriola Dumerili. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 862379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-R.; Liu, C.-L.; Lee, H.-P.; Chen, J.-K. The Identification and Characterization of Chitotriosidase Activity in Pancreatin from Porcine Pancreas. Molecules 2013, 18, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaconisi, V.; Bonelli, A.; Pupino, R.; Gai, F.; Parisi, G. Mealworm as Dietary Protein Source for Rainbow Trout: Body and Fillet Quality Traits. Aquaculture 2018, 484, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemello, G.; Renna, M.; Caimi, C.; Guerreiro, I.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Biasato, I.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F.; Gasco, L. Partially Defatted Tenebrio Molitor Larva Meal in Diets for Grow-Out Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum): Effects on Growth Performance, Diet Digestibility and Metabolic Responses. Animals 2020, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales-Mérida, S.; Gobbi, P.; Józefiak, D.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Dudek, K.; Rawski, M.; Kierończyk, B.; Józefiak, A. Insect meals in fish nutrition.|EBSCOhost. Available online: https://openurl.ebsco.com/contentitem/doi:10.1111%2Fraq.12281?sid=ebsco:plink:crawler&id=ebsco:doi:10.1111%2Fraq.12281 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Sealey, W.M.; Gaylord, T.G.; Barrows, F.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; McGuire, M.A.; Ross, C.; St-Hilaire, S. Sensory Analysis of Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, Fed Enriched Black Soldier Fly Prepupae, Hermetia illucens. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazoche, P.; Poret, S. Acceptability of Insects in Animal Feed: A Survey of French Consumers. J. Consum. Behav. 2021, 20, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartano, S.; Grasso, S. UK Consumers’ Willingness to Try and Pay for Eggs from Insect-Fed Hens. Future Foods 2021, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-M.; Khosravi, S.; Mauliasari, I.R.; Lee, B.-J.; You, S.-G.; Lee, S.-M. Nutritional Evaluation of Cricket, Meal as Fish Meal Substitute for Olive Flounder, Juveniles. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 52, 859–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulick, S.P.; Jahan, F.; Islam, M.B.; Bashera, M.A.; Hasan, M.S.; Islam, M.J.; Ahmed, S.; Karmakar, D.; Ahmed, F.; Saha, T.; et al. Nutritional Characteristics and Antiradical Activity of Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.), Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), and Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Grown in Bangladesh. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamauag, R.E.P.; Ragaza, J.A. Histidine Requirement of Snubnose Silver Pompano Trachinotus Blochii. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 302, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Sagada, G.; Yan, Y. Methionine in Fish Health and Nutrition: Potential Mechanisms, Affecting Factors, and Future Perspectives. Aquaculture 2023, 568, 739310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.; Pedrosa, R.; Castro, C.; Magalhães, R.; Matos, E.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Peres, H.; Pérez-Jiménez, A. Dietary Tryptophan Supplementation Implications on Performance, Plasma Metabolites, and Amino Acid Catabolism Enzymes in Meagre (Argyrosomus regius). Fishes 2023, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, D.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, K.; Hu, F. Effect of Dietary Tryptophan on Growth, Intestinal Microbiota, and Intestinal Gene Expression in an Improved Triploid Crucian Carp. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 676035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Li, X.; He, J.; Xu, H.; Feng, W.; Chen, Q.; Han, T.; Wang, J. Effects of Arginine Family Amino Acids Supplementation on Growth, Whole-Body Amino Acid Profiles, Antioxidant Capacity, and Gene Expression of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus Salmoides). Aquaculture 2025, 594, 741312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, P.; Murariu, G.; Timofti, M.; Georgescu, L.P. Multivariate statistical analyses of danube river water quality at galati, romania. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2018, 17, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Fatan, N.; Sivajothy, K.; Yossa, R. Comparative Estimation of the Lysine Requirements in Two Generations of Improved Strain of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) at the Grow-out Stage. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millamena, O.M. The Essential Nutrients: Proteins and Amino Acids. In Nutrition in Tropical Aquaculture: Essentials of Fish Nutrition, Feeds, and Feeding of Tropical Aquatic Species; Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center: Bangkok, Thailand, 2002; pp. 7–20. ISBN 978-971-8511-58-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hrubec, T.C.; Cardinale, J.L.; Smith, S.A. Hematology and Plasma Chemistry Reference Intervals for Cultured Tilapia (Oreochromis Hybrid). Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 29, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T.; Romagosa, E.; Ishikawa, C.M. Hematological Parameters of “Cachara”, Pseudoplatystoma Fasciatum Linnaeus, 1766 (Osteichthyes, Pimelodidae), Reared in Captivity. Bol Inst Pesca 2005, 31, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave, J. Haematological Parameters in a Neotropical Fish, Corydoras Paleatus (Jenyns, 1842) (Pisces, Callichthyidae), Captured from Pristine and Polluted Water. Hydrobiologia 2005, 537, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Burgos-Aceves, M.A.; Lionetti, L.; Faggio, C. Multidisciplinary Haematology as Prognostic Device in Environmental and Xenobiotic Stress-Induced Response in Fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Abiado, M.A.; Mbahinzireki, G.; Rinchard, J.; Lee, K.J.; Dabrowski, K. Effect of Diets Containing Gossypol on Blood Parameters and Spleen Structure in Tilapia, Oreochromis Sp., Reared in a Recirculating System. J. Fish Dis. 2004, 27, 359. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, M.M.; Lim, C.; Klesius, P.H. Effect of Soybean Meal Replacement by Cottonseed Meal and Iron Supplementation on Growth, Immune Response and Resistance of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus Puctatus) to Edwardsiella Ictaluri Challenge. Aquaculture 2002, 207, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.W.; Silva-Carrillo, Y.; Hernandez, C.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, B.; Castillo-Vargasmachuca, S. The Effect of Substituting Fish Meal with Soybean Meal on Growth, Feed Efficiency, Body Composition and Blood Chemistry in Juvenile Spotted Rose Snapper Lutjanus Guttatus (Steindachner, 1869). Aquaculture 2012, 364, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunji, J.O.; Kloas, W.; Wirth, M.; Neumann, N.; Pietsch, C. Effect of Housefly Maggot Meal (Magmeal) Diets on the Performance, Concentration of Plasma Glucose, Cortisol and Blood Characteristics of Oreochromis niloticus Fingerlings. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witeska, M.; Lugowska, K.; Kondera, E. Reference Values of Hematological Parameters for Juvenile Cyprinus carpio. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2016, 36, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, Y.; Dhawan, A.; Holeyappa, S.A.; Thammegowda, N.B. Hematological Responses of Common Carp Cyprinus carpio Administered with Neem (Azadirachta indica) Leaf Extraction. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2018, 53, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeili, N. Blood Performance: A New Formula for Fish Growth and Health. Biology 2021, 10, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiekou Lorinczova, H.; Begum, G.; Temouri, L.; Renshaw, D.; Zariwala, M.G. Co-Administration of Iron and Bioavailable Curcumin Reduces Levels of Systemic Markers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Placebo-Controlled Randomised Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madibana, M.J.; Mlambo, V.; Lewis, B.; Fouché, C. Effect of Graded Levels of Dietary Seaweed (Ulva Sp.) on Growth, Hematological and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Dusky Kob, Argyrosomus Japonicus, Sciaenidae. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 43, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.T.; Muhammad, N.O. Effect of Aspergillus Niger Fermented Chrysophyllum Albidum Seed Meal on Growth and Haematological Parameters in Rats. Int. J. Biosci. 2010, 5, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, S.; Desai, P.B.; Hull, V.V.; Math, A.A.K.; Vernekar, S.N.; Kulkarni, S.S. A Review on Laboratory Liver Function Tests. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2009, 3, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khshali, M.S.; Al Hilali, H.A. Some Physiological Changes (Alp, Ast And Alt) Of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Caused By High Salinity. Biochem. Cell. Arch. 2020, 19, 4605–4610. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, R.S. Blood Serum Concentration of Protein, Albumin and Globulin in Locally Available Four Fresh Water Fishes. Int. J. Curr. Adv. Res. 2021, 10, 23613–23615. [Google Scholar]
- Bhilave, M.P. Amylase Activity of Fingerlings of Freshwater Fish Labeo Rohita Fed on Formulated Feed. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2014, 2, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, S.; Ergün, S.; Çelik, E. Effects of Herbal Supplements on Growth Performance of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): Change in Body Composition and Some Blood Parameters. J. BioSci. Biotechnol. 2012, 1, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Georgieva, K.; Zhelyazkov, G.; Georgiev, D. Effect of Dietary Phytoextracts Supplementation on Biochemical Blood Parameters of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Cultivated in a Recirculation System. Aquacult Int. 2020, 26, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Rains, J.; Jones, K. Effect of Curcumin on Protein Glycosylation, Lipid Peroxidation, and Oxygen Radical Generation in Human Red Blood Cells Exposed to High Glucose Levels. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; Kametani, F.; Cui, X.; Igarashi, Y.; Huo, J.; Miyahara, H.; Mori, M.; Higuchi, K. Curcumin Promotes AApoAII Amyloidosis and Peroxisome Proliferation in Mice by Activating the PPARα Signaling Pathway. Elife 2021, 10, e63538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, N.K.; Latimer, K.S.; Burnley, V.V. Hematologic Reference Intervals for Koi (Cyprinus carpio), Including Blood Cell Morphology, Cytochemistry, and Ultrastructure. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 33, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hamidoghli, A.; Bae, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Min, T.; Bai, S.C. Effect of Four Functional Feed Additives on Growth, Serum Biochemistry, Antioxidant Capacity, Gene Expressions, Histomorphology, Digestive Enzyme Activities and Disease Resistance in Juvenile Olive Flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Seo, B.S.; Park, H.S.; Lee, B.-J.; Hur, S.-W.; Nam, T.-J.; Lee, K.-J.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.H. Effect of Fishmeal Content in the Diet on the Growth and Sexual Maturation of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) at a Typical Fish Farm. Animals 2021, 11, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, J.W.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S.B.; Jung, W.J.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Role of Dietary Curcumin against Waterborne Lead Toxicity in Common Carp Cyprinus carpio. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudneva, I. Biomarkers for Stress in Fish Embryos and Larvae; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-0-367-45218-6. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, M.J.; Svendsen, J.C.; Malte, H.; Carvalho, P.; Pereira, R.; Gonçalves, J.F.M.; Ozório, R.O.A. Diets Supplemented with Seaweed Affect Metabolic Rate, Innate Immune, and Antioxidant Responses, but Not Individual Growth Rate in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, L.A.; Schulte, P.M.; Balfry, S.K.; McKinley, R.S.; LaPatra, S.E. The Association between Metabolic Rate, Immune Parameters, and Growth Performance of Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), Following the Injection of a DNA Vaccine Alone and Concurrently with a Polyvalent, Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, T.; Killen, S.S.; Armstrong, J.D.; Metcalfe, N.B. What Causes Intraspecific Variation in Resting Metabolic Rate and What Are Its Ecological Consequences? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir-Tanoli, S.; Tinsley, M.C. Immune Response Costs Are Associated with Changes in Resource Acquisition and Not Resource Reallocation. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Råberg, L.; Vestberg, M.; Hasselquist, D.; Holmdahl, R.; Svensson, E.; Nilsson, J.-A. Basal Metabolic Rate and the Evolution of the Adaptive Immune System. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, M.J.; Salas-Leitón, E.; Brito, F.; Svendsen, J.C.; Baptista, T.; Pereira, R.; Abreu, H.; Reis, P.A.; Gonçalves, J.F.M.; de Almeida Ozório, R.O. Effects of Dietary Gracilaria Sp. and Alaria Sp. Supplementation on Growth Performance, Metabolic Rates and Health in Meagre (Argyrosomus regius) Subjected to Pathogen Infection. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudneva, I.I.; Shaida, V.G. Metabolic Strategy in the Early Life of Some Black Sea Fish Species Measured by Microcalorimetry Method. In Proceedings of the XIVth Conference The Amber ISBC, Sopot, Poland, 2–6 June 2006; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
| Component | CF | IF | BIF | TIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude protein (%) | 38.00 | 38.00 | 38.00 | 38.00 |
| Crude fat (%) | 10.00 | 17.74 | 17.92 | 18.15 |
| Total carbohydrate (%) | 10.00 | 16.55 | 17.04 | 18.00 |
| Reagent | Ingredients | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Reagent 1 Internal Standard Solution | Norvaline 0.2 mM N-propanol 10% | 50 mL |
| Reagent 2 Sodium Carbonate Solution | Na2CO3 | 90 mL |
| Reagent 3A Eluting Medium Component I | Sodium Hydroxide | 60 mL |
| Reagent 3B Eluting Medium Component II | 3-Picoline N-propanol | 40 mL |
| Regent 4 Organic Solution I | Propyl-chloroformate Chloroform | 4 vials, 6 mL each |
| Reagent 5 Organic Solution II | Iso-octane | 50 mL |
| Reagent 6 Acid Solution | Hydrochloric Acid 1N | 50 mL |
| SD Amino Acid Standard Mixtures | AA Standard Mixture | 2 vials of each SD, 2 mL each |
| Amino Acids | CF | IF | BIF | TIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histidine e | 203.10 a | 168.36 a | 198.38 a | 124.5 b |
| Lysine e | 396.12 b | 308.24 b | 622.98 a | 520.35 a |
| Isoleucine e | 315.09 a | 146.82 b | 302.29 a | 219.21 b |
| Leucine e | 418.63 a | 115.63 b | 220.64 b | 181.72 b |
| Methionine e | 141.16 a | 129.62 a | 116.52 a | 116.03 a |
| Phenylalanine e | 296.31 a | 146.79 b | 224.74 a | 167.6 b |
| Threonine e | 187.11 a | 110.95 a | 171.65 a | 129.88 a |
| Tryptophan e | 129.83 a | 136.63 a | 148.41 a | 135.26 a |
| Valine e | 439.16 a | 246.99 b | 489.82 a | 469.78 a |
| Arginine e | 601.72 b | 409.07 c | 758.76 a | 642.41 b |
| Alanine n | 397.21 c | 353.68 c | 710.35 a | 593.33 b |
| Asparagine n | 145.90 b | 125.98 b | 183.51 a | 159.27 b |
| Aspartic acid n | 907.04 c | 998.40 c | 1521.40 b | 2532.00 a |
| Glutamic acid n | 1219.27 b | 1354.60 b | 1761.20 b | 3575.10 a |
| Glutamine n | 386.14 c | 676.10 b | 1008.00 a | 448.30 c |
| Glycine n | 320.47 a | 200.18 b | 407.84 a | 0 |
| Serine n | 279.06 b | 237.66 b | 456.97 a | 229.49 b |
| Tyrosine n | 481.09 a | 142.05 b | 204.89 b | 170.74 b |
| α-Aminoadipic acid n | 79.02 a | 75.00 a | 82.00 a | 110.81 a |
| α-Aminopimelic acid n | 1652.81 a | 2003.3 a | 1883.50 a | 1983.20 a |
| 3-hydroxyproline/4-hydroxyproline n | 89.12 a | 94.00 a | 97.52 a | 103.17 a |
| Proline n | 284.60 a | 189.71 b | 352.90 a | 277.49 a |
| Hydroxylysine (2 isomers) n | 91.82 a | 105.05 a | 128.42 a | 109.85 a |
| Sarcosine n | 0 | 30.06 a | 0 | 0 |
| α-Aminobutyric acid n | 0 | 49.00 a | 52.00 a | 0 |
| Ornithine n | 0 | 0 | 69.91 a | 0 |
| Glycyl-proline (dipeptide) n | 0 | 0 | 298.53 a | 0 |
| Technological Indicators | CF | IF | BIF | TIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial stocking density (kg/m3) | 6.67 a | 6.69 a | 6.76 a | 6.64 a |
| Initial average fish weight (g) | 73.4 a | 73.6 a | 74.4 a | 73.0 a |
| Final stocking density (kg/m3) | 11.52 a | 9.02 b | 8.56 b | 10.23 a |
| Final average fish weight (g) | 126.7 a | 99.2 b | 94.2 b | 112.5 a |
| Individual biomass gain (g) | 53.3 a | 25.6 c | 19.8 c | 39.5 b |
| Relative growth rate (g/g/day) | 0.013 a | 0.006 c | 0.005 c | 0.010 b |
| Specific growth rate (%/day) | 1.01 a | 0.55 c | 0.44 c | 0.80 b |
| Feed conversion ratio (g/g) | 1.49 c | 3.11 a | 4.06 a | 2.00 b |
| Protein efficiency ratio (g/g) | 1.77 a | 0.85 c | 0.65 c | 1.32 b |
| Fulton coefficient | 1.46 b | 1.42 b | 1.44 b | 1.54 a |
| Experimental Variant | CF | IF | BIF | TIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMR (mg O2/kg/h) | Mean ± Stdv. | 150.60 ± 8.26 a | 123.23 ± 10.99 c | 147.86 ± 20.51 a | 135.12 ± 14.25 b |
| RMR (mg O2/kg/h) | Mean ± Stdv. | 162.57 ± 8.02 a | 132.71 ± 10.59 b | 161.18 ± 21.85 a | 159.41 ± 31.83 a |
| MMR (mg O2/kg/h) | Mean ± Stdv. | 337.24 ± 46.13 b | 301.41 ± 30.32 c | 412.98 ± 88.35 a | 351.33 ± 58.63 b |
| AS (mg O2/kg/h) | Mean ± Stdv. | 186.65 ± 51.60 b | 178.18 ± 37.63 b | 265.12 ± 69.17 a | 216.21 ± 50.50 b |
| Biochemical Parameter | Experimental Variants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | IF | BIF | TIF | ||
| Albumin (g/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 1.05 ± 0.09 a | 1.12 ± 0.09 a | 1.13 ± 0.16 a | 1.16 ± 0.14 a |
| ALPs (U/L) | Mean ± Stdv. | 9.77 ± 0.45 a | 9.45 ± 0.46 a | 9.14 ± 0.22 a | 9.38 ± 0.55 a |
| TGP (U/L) | Mean ± Stdv. | 6.78 ± 0.20 a | 6.74 ± 0.11 a | 6.77 ± 0.17 a | 6.62 ± 0.34 a |
| TGO (U/L) | Mean ± Stdv. | 264.47 ± 47.72 a | 235.98 ± 126.06 a | 284.03 ± 99.92 a | 212.79 ± 43.21 a |
| Amylase (U/L) | Mean ± Stdv. | 26.58 ± 6.23 a | 23.85 ± 4.03 a | 28.03 ± 8.45 a | 28.31 ± 7.15 a |
| Lipase (U/L) | Mean ± Stdv. | 14.81 ± 1.64 a | 14.28 ± 1.53 a | 14.72 ± 0.89 a | 14.01 ± 1.76 a |
| Ca (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 9.28 ± 0.36 a | 9.50 ± 0.22 a | 9.54 ± 0.39 a | 9.32 ± 0.34 a |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 204.14 ± 26.96 a | 174.74 ± 33.26 a | 177.32 ± 13.53 a | 180.44 ± 27.51 a |
| HDL (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 66.38 ± 10.74 a | 59.26 ± 8.15 a | 60.84 ± 7.89 a | 59.93 ± 9.17 a |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 308.23 ± 41.79 a | 212.84 ± 56.96 b | 247.57 ± 53.50 b | 225.91 ± 15.94 b |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 0.39 ± 0.16 a | 0.26 ± 0.11 a | 0.34 ± 0.14 a | 0.25 ± 0.11 a |
| Urea (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 1.01 ± 0.08 a | 0.82 ± 0.06 a | 0.80 ± 0.07 b | 0.74 ± 0.06 b |
| LDH (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 455.29 ± 70.23 a | 419.17 ± 216.79 a | 417.00 ± 249.86 a | 385.47 ± 264.35 a |
| TB (mg/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.43 ± 0.20 a | 0.38 ± 0.14 a | 0.32 ± 0.19 a |
| TP (g/dL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 2.32 ± 0.18 a | 2.17 ± 0.11 a | 2.26 ± 0.23 a | 2.24 ± 0.17 a |
| Experimental Variant | CF | IF | BIF | TIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA (nmol/mL) | Mean ± Stdv. | 1.83 ± 0.11 a | 1.72 ± 0.11 a | 2.08 ± 0.40 a | 1.70 ± 0.03 a |
| Min. | 1.71 | 1.62 | 1.72 | 1.67 | |
| Max. | 1.94 | 1.84 | 2.51 | 1.74 | |
| TAC (mM Trolox) | Mean ± Stdv. | 3.69 ± 0.88 a | 3.39 ± 0.42 a | 4.04 ± 0.39 a | 3.83 ± 0.16 a |
| Min. | 3.16 | 2.92 | 3.61 | 3.68 | |
| Max. | 4.70 | 3.74 | 4.38 | 4.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antache, A.; Simionov, I.-A.; Petrea, Ș.-M.; Nica, A.; Georgescu, P.-L.; Oprică, L.; Grigore, M.-N.; Oroian, M.; Jitaru, D.; Liteanu, A.; et al. Insect–Antioxidants Symbiotic Nexus—Pathway for Sustainable and Resilient Aquaculture: A Case Study for Evaluating Koi Carp Growth and Oxidative Stress Status. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040371
Antache A, Simionov I-A, Petrea Ș-M, Nica A, Georgescu P-L, Oprică L, Grigore M-N, Oroian M, Jitaru D, Liteanu A, et al. Insect–Antioxidants Symbiotic Nexus—Pathway for Sustainable and Resilient Aquaculture: A Case Study for Evaluating Koi Carp Growth and Oxidative Stress Status. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(4):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040371
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntache, Alina, Ira-Adeline Simionov, Ștefan-Mihai Petrea, Aurelia Nica, Puiu-Lucian Georgescu, Lăcrămioara Oprică, Marius-Nicușor Grigore, Mircea Oroian, Daniela Jitaru, Andreea Liteanu, and et al. 2025. "Insect–Antioxidants Symbiotic Nexus—Pathway for Sustainable and Resilient Aquaculture: A Case Study for Evaluating Koi Carp Growth and Oxidative Stress Status" Antioxidants 14, no. 4: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040371
APA StyleAntache, A., Simionov, I.-A., Petrea, Ș.-M., Nica, A., Georgescu, P.-L., Oprică, L., Grigore, M.-N., Oroian, M., Jitaru, D., Liteanu, A., Ciobîcă, A.-S., & Poroch, V. (2025). Insect–Antioxidants Symbiotic Nexus—Pathway for Sustainable and Resilient Aquaculture: A Case Study for Evaluating Koi Carp Growth and Oxidative Stress Status. Antioxidants, 14(4), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040371










