Alleviating Effects of Ethanol Extract from Acremonium terricola Culture on Patulin Toxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Strains
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Extraction of EEAT
2.4. Cultivation, Chunking, and Synchronization of C. elegans
2.4.1. Cultivation and Passaging of C. elegans
2.4.2. Synchronization of C. elegans
2.5. Preparation and Purification of PAT
2.6. Alleviating Effect of EEAT on PAT
2.7. Fluorescent Staining
2.8. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
2.9. EEAT Full Component Analysis
2.10. Molecular Docking of EEAT Active Ingredients with Oxidative Stress Target Proteins
2.11. Experimental Validation of Docking Results
2.12. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
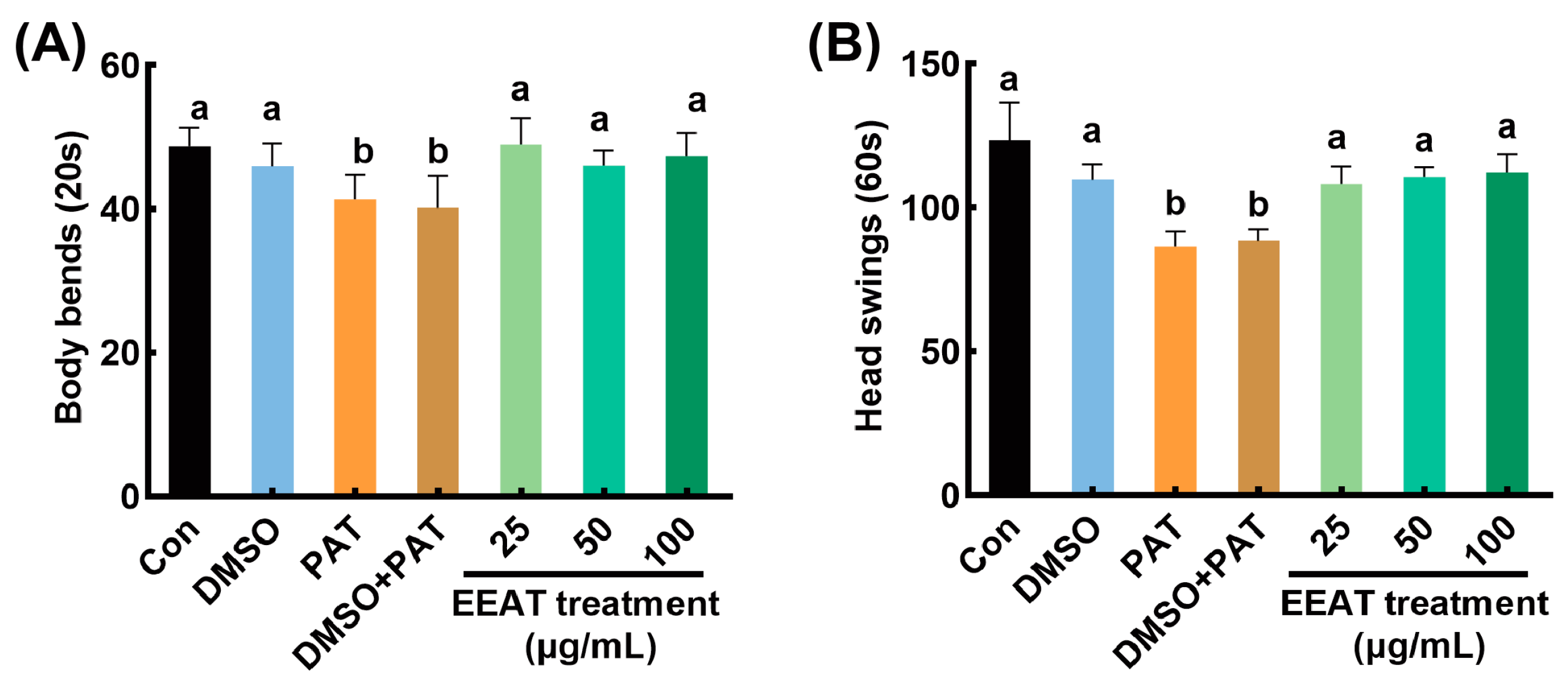
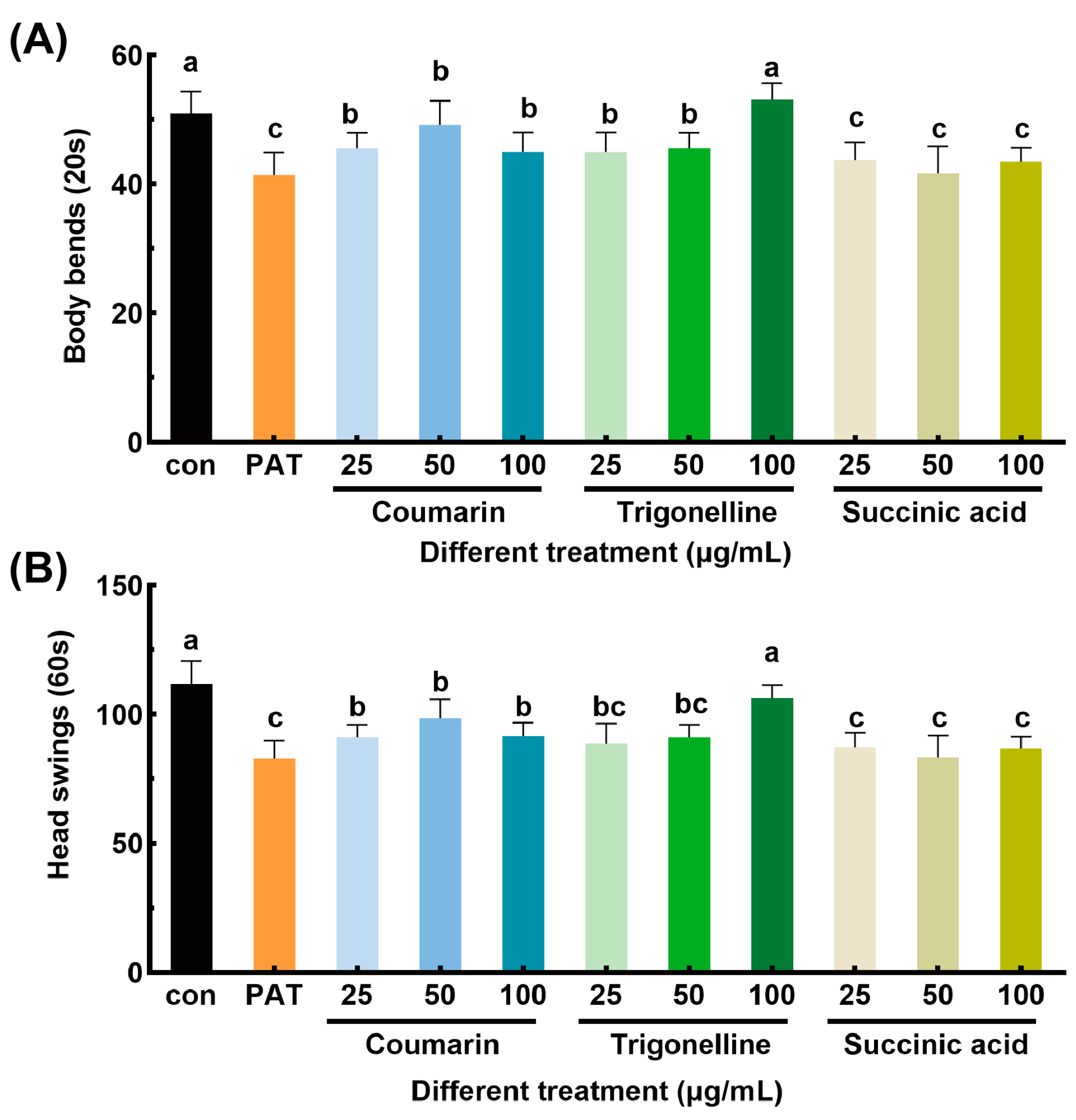
3.1. Alleviating Effects of EEAT on Locomotory Capacity Impairment Induced by PAT in C. elegans
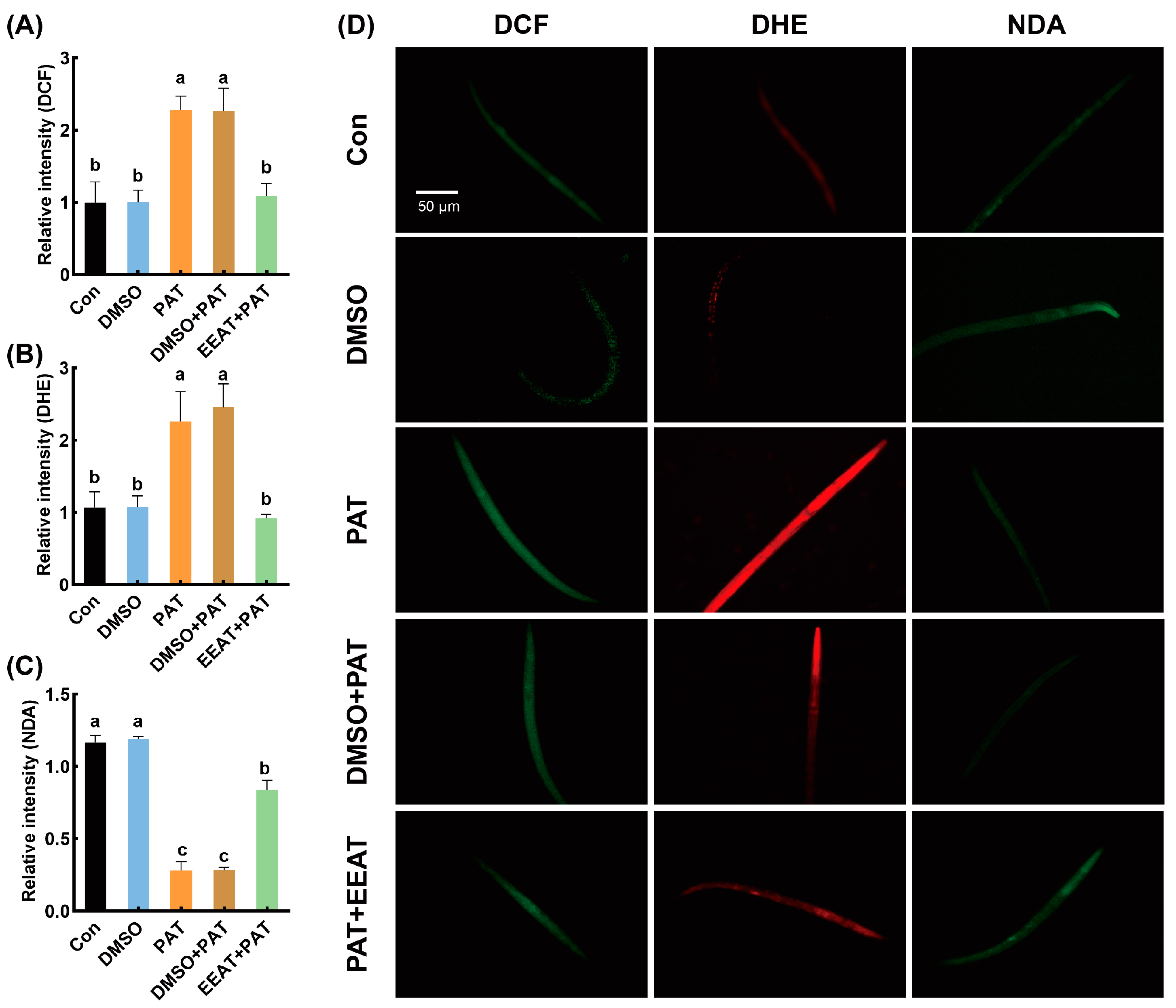
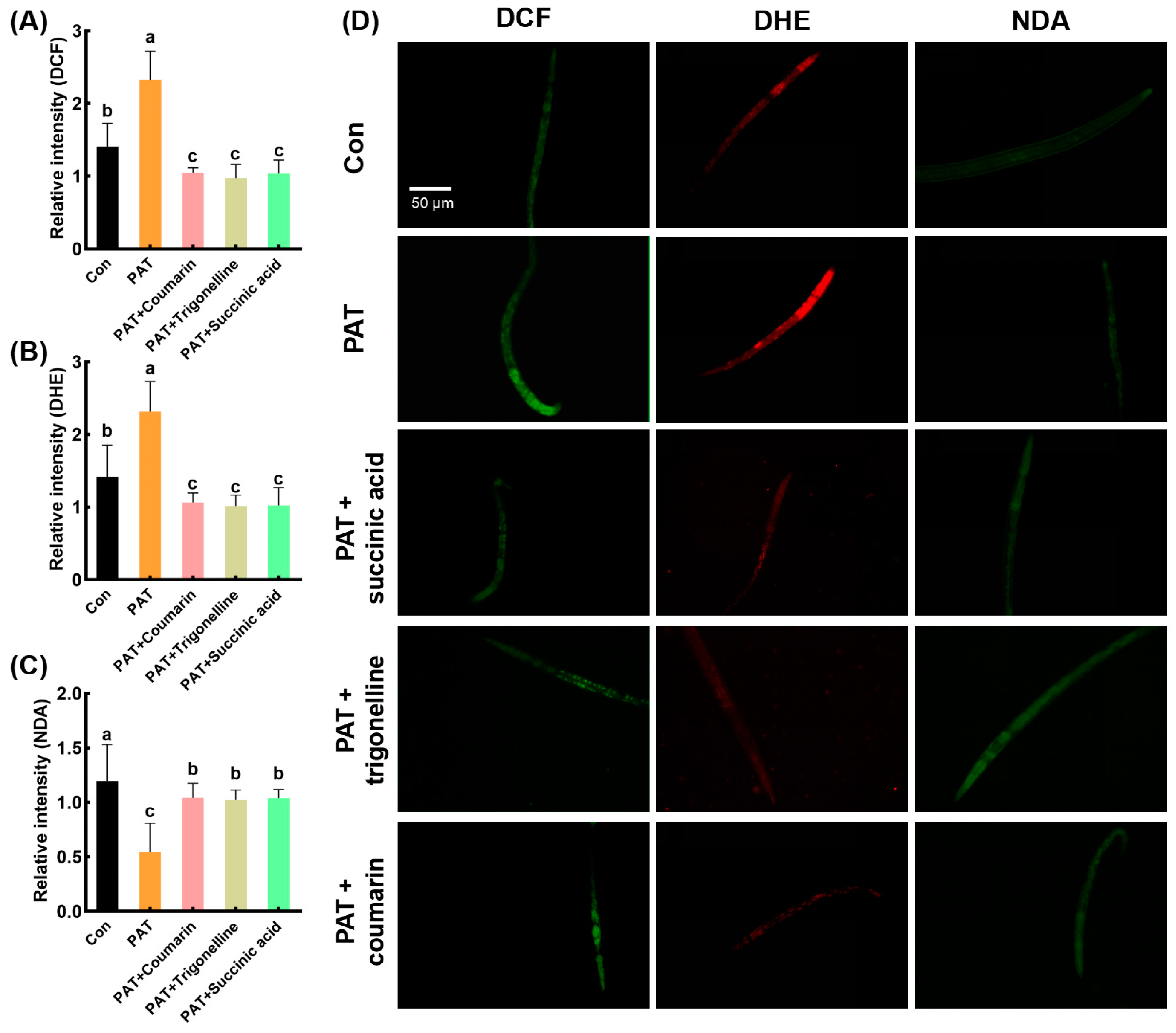
3.2. Alleviating Effects of EEAT on Oxidative Damage Induced by PAT in C. elegans
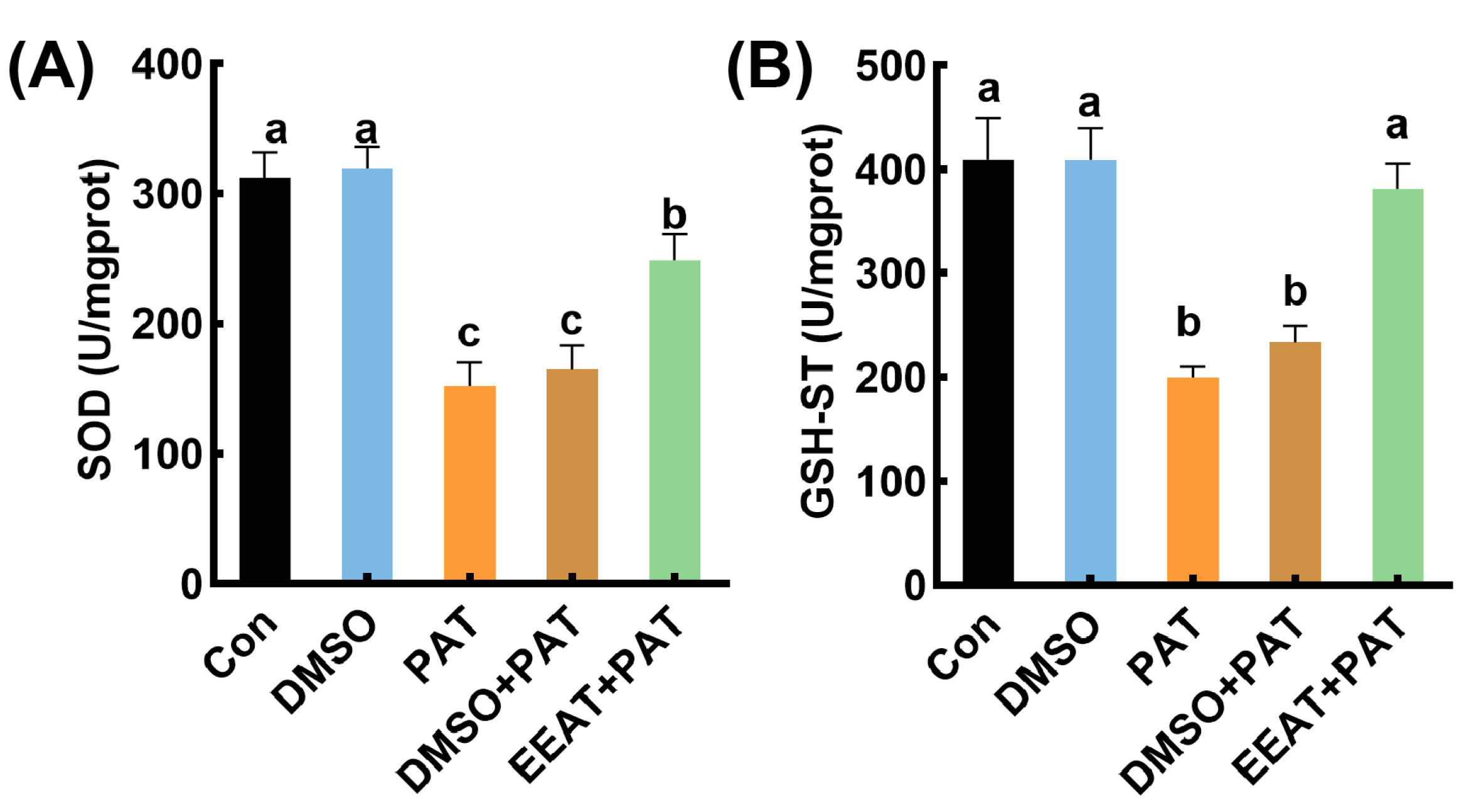
3.3. Effects of EEAT on Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Inhibited by PAT in C. elegans
3.4. The Chemical Composition Analysis of EEAT
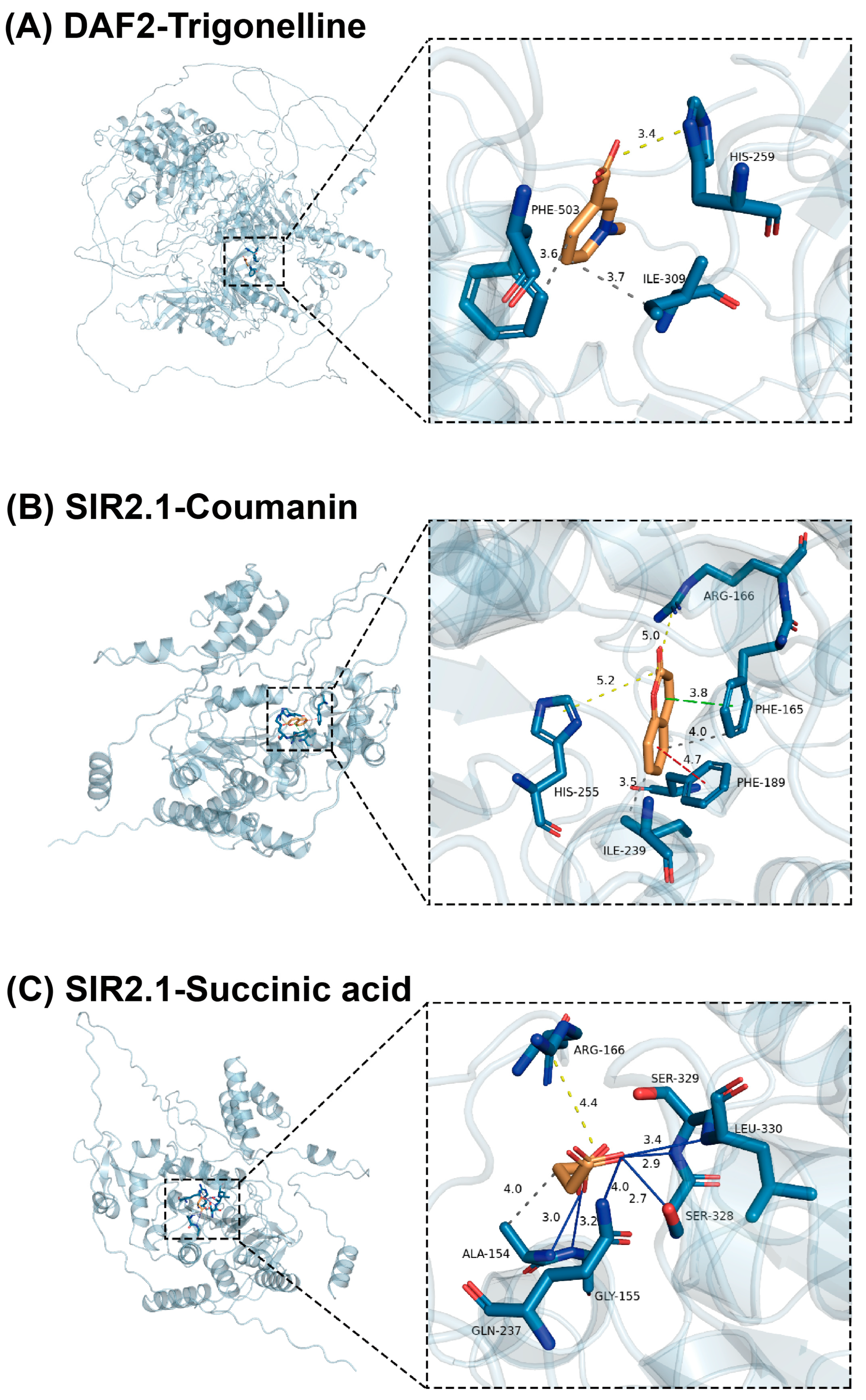
3.5. Docking of EEAT Active Ingredients and Target Proteins
3.6. Verification of Molecular Docking Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puel, O.; Galtier, P.; Oswald, I.P. Biosynthesis and Toxicological Effects of Patulin. Toxins 2010, 2, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioi, J.D.; Zhou, T.; Tsao, R.; Marcone, F.M. Mitigation of Patulin in Fresh and Processed Foods and Beverages. Toxins 2017, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moake, M.M.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I.; Worobo, R.W. Comprehensive Review of Patulin Control Methods in Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2005, 4, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Akbar, M.; Razis, A.F.A.; Waqas, M. Assessment of patulin in different cultivars of apples, juices, and distribution in decay portion. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 104, 3866–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.; Goktepe, I. The characteristics, occurrence, and toxicological effects of patulin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Shan, S.; Mei, G.; Pan, H.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Chen, D. Long-term investigation and analysis of patulin occurrence in juice products in China. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 5551–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, D.; Kamle, M.; Sharma, B.; Pandhi, S.; Devi, S.; Dhawan, K.; Selvakumar, R.; Mishra, D.; Kumar, A.; Arora, S.; et al. Patulin in food: A mycotoxin concern for human health and its management strategies. Toxicon 2021, 198, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, N.; Stopper, H. Patulin: Mechanism of genotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.Y.; Shan, S.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.F.; Liao, W.; Zhao, C.; Chu, Q. Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A patulin degradation candidate both in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Gong, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Tian, F.; Chen, W. Food-borne patulin toxicity is related to gut barrier disruption and can be prevented by docosahexaenoic acid and probiotic supplementation. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Sharma, G.; Liu, G.; Shen, J.; Shao, B.; Hao, Z. Therapeutic detoxification of quercetin for aflatoxin B1-related toxicity: Roles of oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolic enzymes. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tang, S.S.; Peng, X.Y.; Sharma, G.; Yin, S.T.; Hao, Z.H.; Li, J.C.; Shen, J.Z.; Dai, C.S. Lycopene as a Therapeutic Agent against Aflatoxin B1-Related Toxicity: Mechanistic Insights and Future Directions. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Liu, R.M.; Xia, S.; Wei, G.Q.; Ishfaq, M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.Y. Protective role of curcumin on aflatoxin B1-induced TLR4/RIPK pathway mediated-necroptosis and inflammation in chicken liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chang, M.; Hou, X.; Yan, M.; Zhang, S.; Song, W.; Sheng, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Apple polyphenols prevent patulin-induced intestinal damage by modulating the gut microbiota and metabolism of the gut-liver axis. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xiong, Y.; Bi, L.; Zhong, H.; Ren, J.; Zhou, B. Non-antibiotic feed additives production by Acremonium terricola solid-fermented Camellia oleifera meal. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Guo, Y.W.; Lu, Y.; He, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Xie, K.Z. Effects of Acremonium terricola Culture on the Growth, Slaughter Yield, Immune Organ, Serum Biochemical Indexes, and Antioxidant Indexes of Geese. Animals 2022, 12, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.l.; Zhang, Y.J.; Shuo, W.; Cao, Z.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, W.; Lu, N.; Li, S.L. Acremonium terricola Culture’s Dose–Response Effects on Lactational Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, and Ruminal Characteristics in Holstein Dairy Cows. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Peng, Y.Z.; Nie, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Huang, B. Dietary supplementation with Acremonium terricola culture alters the gut microbial structure and improves the growth performance, antioxidant status, and immune function of weaning piglets. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xu, H.; Lv, J.; Zhang, G.; Dou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Acremonium terricola culture plays anti-inflammatory and antioxidant roles by modulating MAPK signaling pathways in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 64, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.R. The C. elegans model in toxicity testing. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, N.P.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, H.M. Caenorhabditis elegans: A model organism in the toxicity assessment of environmental pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 39273–39287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.J.; Pan, M.C.; Chang, C.K.; Chang, S.W.; Hsieh, C.W. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of cordycepin from Cordyceps militaris using orthogonal experimental design. Molecules 2014, 19, 20808–20820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshan, Z.; Ferrante, M.; Tadi, M.; Ansari, F.; Heydari, A.; Hosseini, M.S.; Conti, G.O.; Sadrabad, E.K. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of ethanolic extract of pomegranate peels, juice and seeds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Papalia, T.; Settineri, G.; Mallamaci, C.; Panuccio, M.R. Sulfur bentonite-organic-based fertilizers as tool for improving bio-compounds with antioxidant activities in red onion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Jia, R.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Ye, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Tetrastigma hemsleyanum tubers polysaccharide ameliorates LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages and Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Chen, W.; Jia, R.Y.; Ye, X.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, X.D. Tetrastigma hemsleyanum leaves extract against acrylamide-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells and Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneş, A.; Kordali, Ş.; Turan, M.; Usanmaz Bozhüyük, A. Determination of antioxidant enzyme activity and phenolic contents of some species of the Asteraceae family from medicanal plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, D.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.M. Thermodynamics of π-π Interactions of Benzene and Phenol in Water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Cao, C.; Zhu, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Identification of a TonB-Dependent Siderophore Receptor as a Novel Anti-Biofilm Target and Virtual Screening for Its Inhibitor in Pseudomonas fluorescens PF08. Foods 2025, 14, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Shamim, A.; Azam, S.S.; Wadood, A. Identification of potent inhibitors for chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like through moleculardocking studies. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 2924–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Singh, N.; Ansari, K.M. Toxicological effects of patulin mycotoxin on the mammalian system: An overview. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Gao, X.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, K.; et al. Baicalin protects against zearalenone-induced chicks liver and kidney injury by inhibiting expression of oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and caspase signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Jin, C.; Li, D.; Deng, Y.; Yao, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.L.; Wang, T. Multi-level advances in databases related to systems pharmacology in traditional Chinese medicine: A 60-year review. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1289901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Jin, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Z. A comprehensive application: Molecular docking and network pharmacology for the prediction of bioactive constituents and elucidation of mechanisms of action in component-based Chinese medicine. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2021, 90, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez de Souza, L.; Alseekh, S.; Scossa, F.; Fernie, A.R. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry variants for metabolomics research. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadati, F.; Modarresi Chahardehi, A.; Jamshidi, N.; Jamshidi, N.; Ghasemi, D. Coumarin: A natural solution for alleviating inflammatory disorders. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2024, 7, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; López-Jornet, P.; Lopez, E.P.; Harun, N.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Beyatli, A.; Sytar, O.; Shaheen, S.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Natural Coumarins: Exploring the Pharmacological Complexity and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6492346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zheng, Z.; Lv, J.; Bao, J.; Chang, S.; Jiang, X.; Xin, Y. Shikimic acid (SA) inhibits neuro-inflammation and exerts neuroprotective effects in an LPS-induced in vitro and in vivo model. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1265571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, G.R.; Vasconcelos, A.B.S.; Antony, P.J.; Montalvão, M.M.; de Franca, M.N.F.; Hillary, V.E.; Ceasar, S.A.; Liu, D. Natural sources, biosynthesis, biological functions, and molecular mechanisms of shikimic acid and its derivatives. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2023, 13, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Kaldate, R.; Bisht, A. Chapter4.5—Citric acid, antioxidant effects in health. In Antioxidants Effects in Health; Nabavi, S.M., Silva, A.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilaniu, H.; Gustafsson, L.; Rigoulet, M.; Nyström, T. Asymmetric inheritance of oxidatively damaged proteins during cytokinesis. Science 2003, 299, 1751–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erjavec, N.; Larsson, L.; Grantham, J.; Nyström, T. Accelerated aging and failure to segregate damaged proteins in Sir2 mutants can be suppressed by overproducing the protein aggregation-remodeling factor Hsp104p. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2410–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.Y. Growth phase-dependent roles of Sir2 in oxidative stress resistance and chronological lifespan in yeast. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.D.; Tissenbaum, H.A.; Liu, Y.; Ruvkun, G. daf-2, an insulin receptor-like gene that regulates longevity and diapause in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 1997, 277, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| RT (min) * | Name | m/z | Formula | Mass Errors (ppm) | RA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.811 | Lysine | 104.03537 | C3H7NO3 | 0.50 | 187,777,184.87 |
| 0.815 | 4-Hydroxyproline | 130.05098 | C5H9NO3 | 0.10 | 467,035,200.25 |
| 0.843 | D-(-)quinic acid | 191.05608 | C7H12O6 | −0.65 | 19,110,219.03 |
| 0.912 | Uracil | 111.02004 | C4H4N2O2 | 0.39 | 62,055,885.23 |
| 0.953 | Succinic acid | 117.0194 | C4H6O4 | 0.59 | 2,421,659,365.08 |
| 0.962 | Shikimic acid | 173.04547 | C7H10O5 | −0.72 | 10,718,161.54 |
| 1.014 | Adenine | 134.0473 | C5H5N5 | 0.62 | 67,826,555.72 |
| 1.042 | Citric acid | 191.01973 | C6H8O7 | 0.02 | 174,899,125.03 |
| 1.248 | Leucine | 130.08737 | C6H13NO2 | 0.17 | 2,732,637,408.76 |
| RT (min) * | Name | m/z | Formula | Mass Errors (ppm) | RA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.78 | D-fructose-1,6-Diphosphate sodium | 341.003 | C6H14O12P2 | 0.27 | 8,309,708.86 |
| 0.944 | Acetylcholine | 146.118 | C7H15NO2 | 1.36 | 287,983,209.06 |
| 0.946 | Trigonelline | 138.055 | C7H7NO2 | 0.83 | 232,929,326.28 |
| 1.005 | Guanine | 152.05692 | C5H5N5O | 1.54 | 448,995,412.07 |
| 1.022 | L-Isoleucine | 132.10207 | C6H13NO2 | 1.25 | 1,906,817,715.69 |
| 1.058 | 4-Hydroxyproline | 132.06573 | C5H9NO3 | 1.64 | 1,034,646,396.52 |
| 1.061 | Adenine | 136.06201 | C5H5N5 | 1.78 | 1,162,426,530.13 |
| 1.131 | Galactitol | 183.08659 | C6H14O6 | 1.53 | 759,773,486.42 |
| 1.158 | 2,2-Dimethylsuccinic acid | 147.06535 | C6H10O4 | 1.10 | 521,316,184.20 |
| 1.188 | 4-Guandinobutyric acid | 146.09254 | C5H11N3O2 | 0.92 | 109,412,261.72 |
| 10.414 | Coumarin | 147.04411 | C9H6O2 | 0.39 | 114,026,419.58 |
| 12.834 | Jasmonic acid | 211.1329 | C12H18O3 | 0.16 | 19,143,380.67 |
| 14.444 | Cortisol | 345.2059 | C21H30O5 | −0.20 | 29,494,327.46 |
| 19.314 | Bilirubin | 585.2713 | C33H36N4O6 | 0.92 | 19,929,457.87 |
| 2.658 | Isohexanoic acid | 132.1021 | C6H13NO2 | 1.46 | 1,618,895,399.44 |
| 3.869 | L-Phenylalanine | 166.08652 | C9H11NO2 | 1.59 | 246,308,482.14 |
| Affinity (kcal/mol) | Ligand | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession Number | Protein | Coumarin | Trigonelline | Succinic Acid | |
| Receptor | PDB ID: 4JDE | SKN-1 | −5.6 | −4.5 | −3.9 |
| PDB ID: 3DC5 | SOD-3 | −5.2 | −4.5 | −3.9 | |
| PDB ID: 3K62 | GST-4 | −5.9 | −5.0 | −4.4 | |
| PDB ID: 2P32 | HSP-1 | −5.8 | −5.4 | −4.4 | |
| UniProt: O16850 | DAF-16 | −5.1 | −4.2 | −3.6 | |
| UniProt: G5EFT5 | HSF-1 | −5.7 | −4.3 | −4.1 | |
| UniProt: Q968Y9 | DAF-2 | −6.6 | −5.5 | −4.2 | |
| UniProt: Q94125 | AGE-1 | −6.5 | −5.2 | −4.5 | |
| UniProt: P13508 | GLP-1 | −6.2 | −4.9 | −4.5 | |
| UniProt: Q95ZQ4 | AAK-2 | −6.0 | −4.7 | −4.1 | |
| UniProt: Q23272 | ATFS-1 | −5.0 | −4.1 | −3.3 | |
| UniProt: P91302 | UBL-5 | −4.4 | −3.9 | −3.8 | |
| UniProt: Q21921 | SIR-2.1 | −7.0 | −4.4 | −5.2 | |
| UniProt: Q9U298 | EAT-2 | −5.7 | −4.6 | −3.9 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.; Edirisinghe, S.K.; Okolo, I.E.; Chen, Z.; Sun, J.; Hong, W.; Zhu, R. Alleviating Effects of Ethanol Extract from Acremonium terricola Culture on Patulin Toxicity. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050509
Lin H, Edirisinghe SK, Okolo IE, Chen Z, Sun J, Hong W, Zhu R. Alleviating Effects of Ethanol Extract from Acremonium terricola Culture on Patulin Toxicity. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(5):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Haiyan, Savindi Kaushalya Edirisinghe, Ijeoma Esther Okolo, Zhen Chen, Juan Sun, Wei Hong, and Ruiyu Zhu. 2025. "Alleviating Effects of Ethanol Extract from Acremonium terricola Culture on Patulin Toxicity" Antioxidants 14, no. 5: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050509
APA StyleLin, H., Edirisinghe, S. K., Okolo, I. E., Chen, Z., Sun, J., Hong, W., & Zhu, R. (2025). Alleviating Effects of Ethanol Extract from Acremonium terricola Culture on Patulin Toxicity. Antioxidants, 14(5), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050509





