Argan Oil: A Natural Bioactive Lipid Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Argan Oil
2.1. Extraction Methods
2.2. Composition of Argan Oil
2.2.1. Saponifiable Fraction:
2.2.2. Unsaponifiable Fraction:
- Tocopherols:
- Polyphenols:
- Phytosterols:
- Other minor compounds
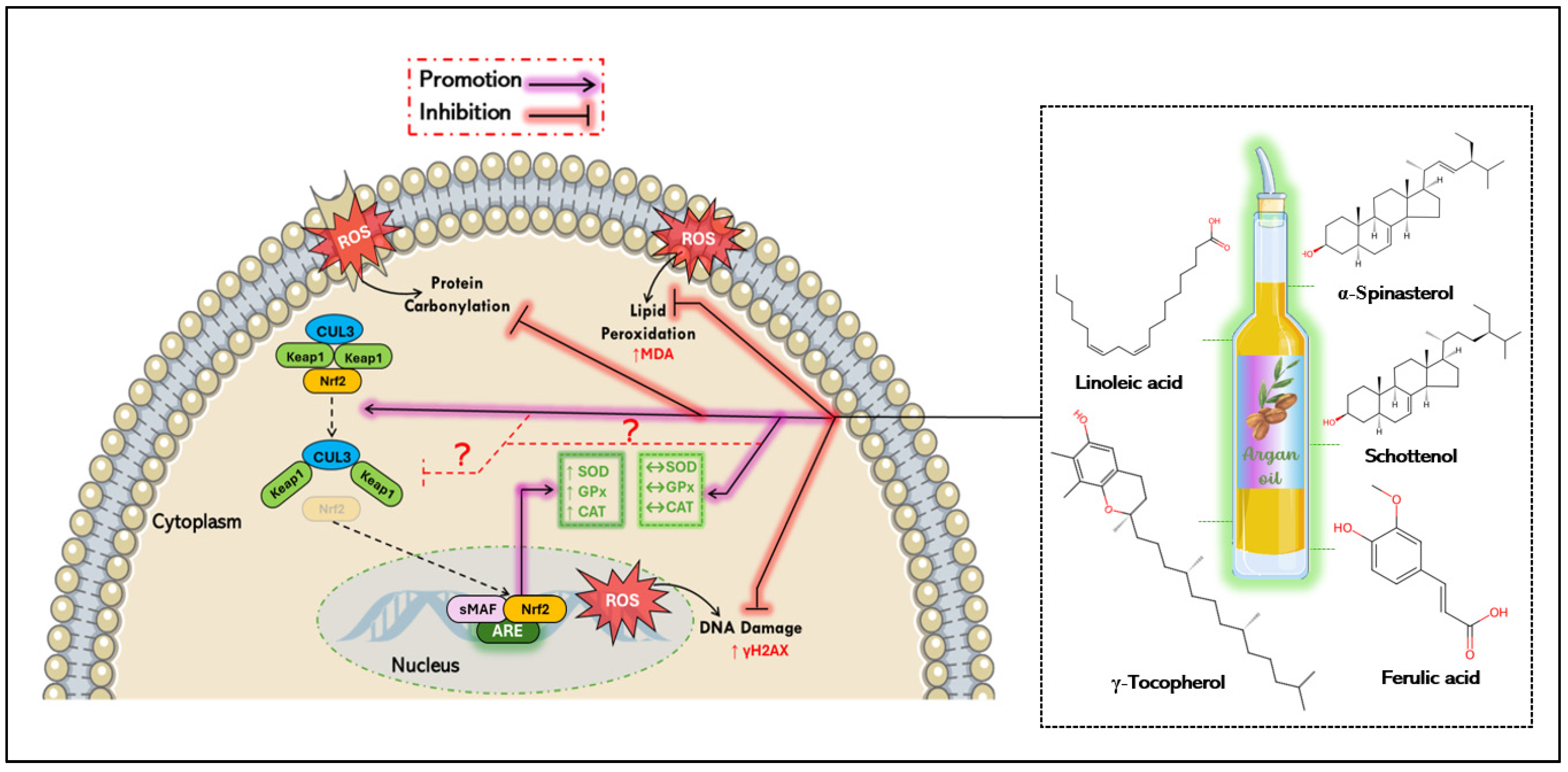
3. Antioxidant Potential of Argan Oil
3.1. In Vitro Studies
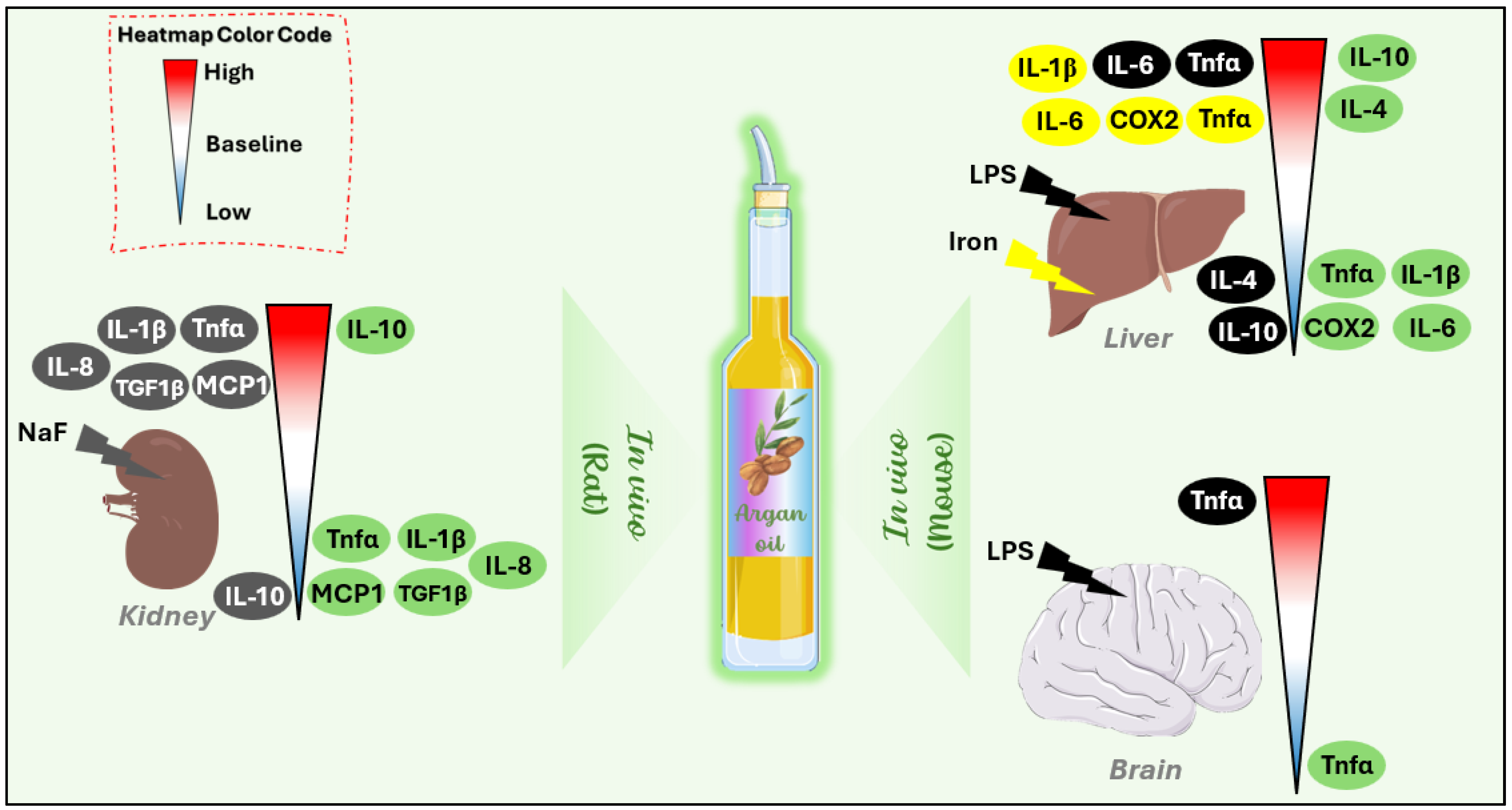
3.2. In Vivo Studies
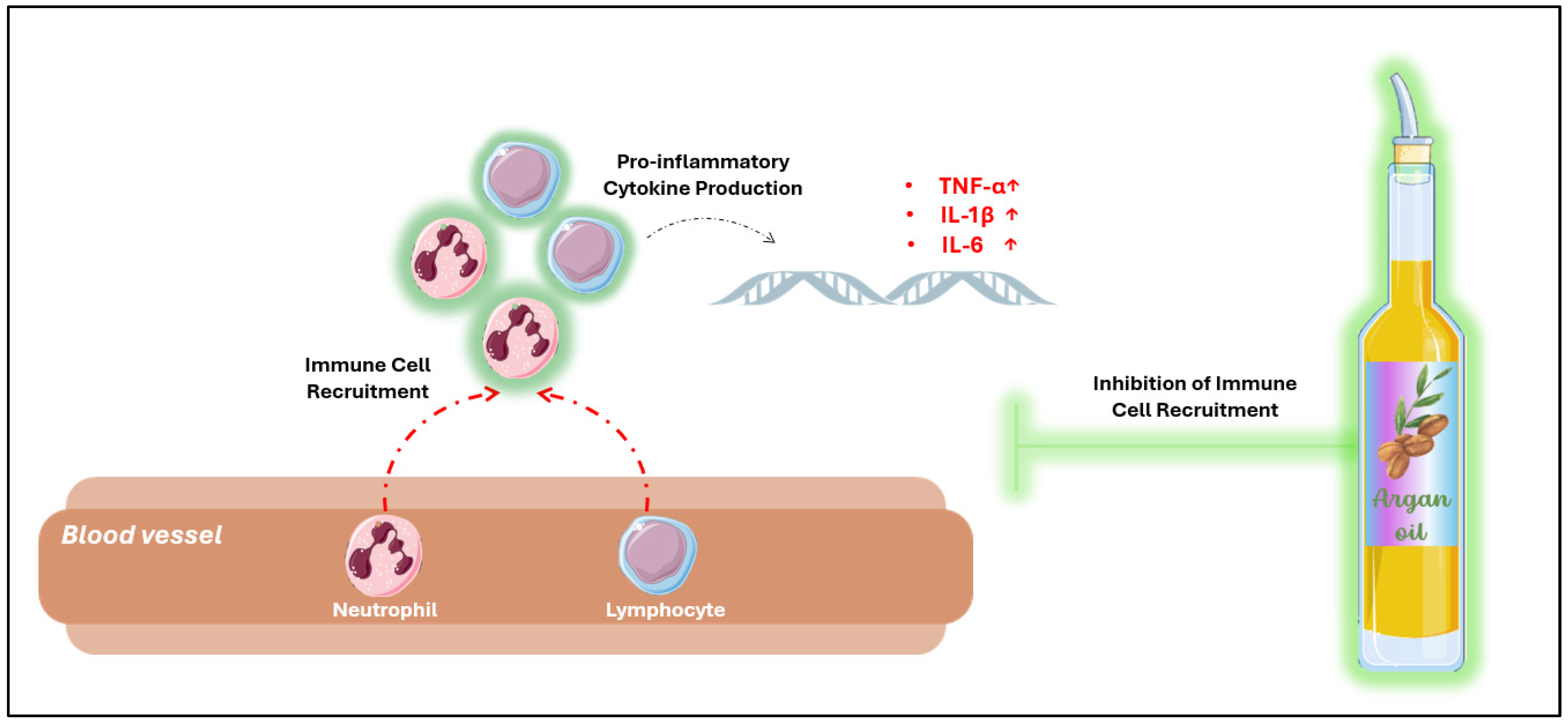
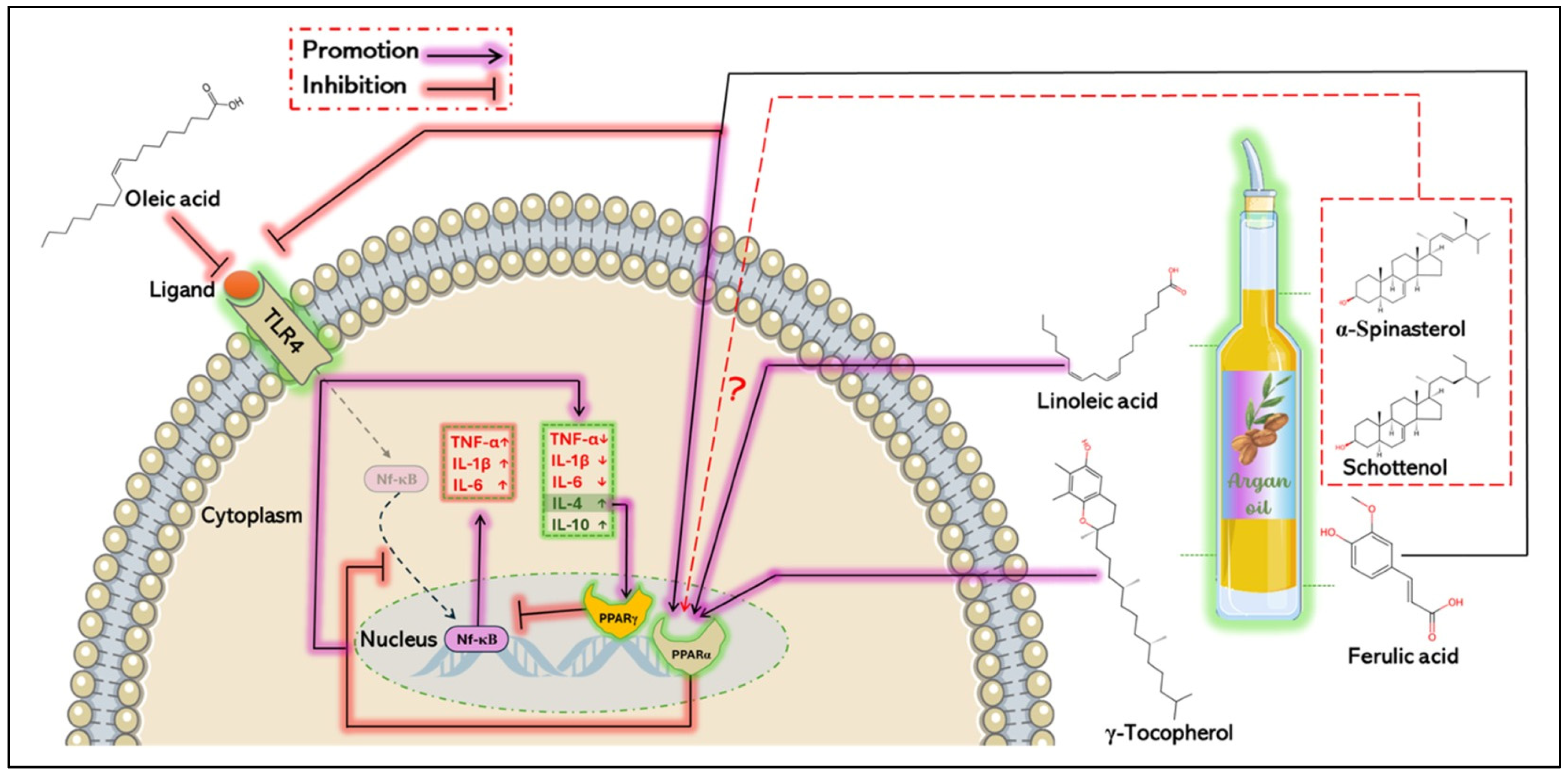
4. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Argan Oil
4.1. Effect of Argan Oil on Modulation of Inflammatory Markers
4.2. Effect of Argan Oil on Tissue Protection
5. Discussion: Molecular Mechanisms of Argan Oil
5.1. Antioxidant Mechanisms of Argan Oil
5.2. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Argan Oil
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mostafa, K.; El Kharrassi, Y.; Badreddine, A.; Andreoletti, P.; Vamecq, J.; El Kebbaj, M.S.; Latruffe, N.; Lizard, G.; Nasser, B.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M. Nopal Cactus (Opuntia Ficus-Indica) as a Source of Bioactive Compounds for Nutrition, Health and Disease. Mol. Basel Switz. 2014, 19, 14879–14901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free Radicals, Antioxidants and Functional Foods: Impact on Human Health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesci, S.; Spagnoletta, A.; Oppedisano, F. Inflammation, Mitochondria and Natural Compounds Together in the Circle of Trust. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.A.; Desai, T.R.; Tirgar, P.R. Evaluation of Iron Chelating and Antioxidant Potential of Epilobium Hirsutum for the Management of Iron Overload Disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabolacci, C.; Forni, C.; Jadeja, R.N.; Facchiano, F. Natural Compounds against Cancer, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9495628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchab, H.; Ishaq, A.; Limami, Y.; Saretzki, G.; Nasser, B.; El Kebbaj, R. Antioxidant Effects of Cactus Seed Oil against Iron-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mouse Liver, Brain and Kidney. Molecules 2024, 29, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badreddine, A.; Zarrouk, A.; Karym, E.M.; Debbabi, M.; Nury, T.; Meddeb, W.; Sghaier, R.; Bezine, M.; Vejux, A.; Martine, L.; et al. Argan Oil-Mediated Attenuation of Organelle Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress and Cell Death Induced by 7-Ketocholesterol in Murine Oligodendrocytes 158N. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kharrassi, Y.; Maata, N.; Mazri, M.A.; El Kamouni, S.; Talbi, M.; El Kebbaj, R.; Moustaid, K.; Essamadi, A.K.; Andreoletti, P.; El Mzouri, E.H.; et al. Chemical and Phytochemical Characterizations of Argan Oil (Argania spinosa L. Skeels), Olive Oil (Olea Europaea L. Cv. Moroccan Picholine), Cactus Pear (Opuntia Megacantha Salm-Dyck) Seed Oil and Cactus Cladode Essential Oil. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kebbaj, R.; Andreoletti, P.; El Hajj, H.I.; El Kharrassi, Y.; Vamecq, J.; Mandard, S.; Saih, F.-E.; Latruffe, N.; El Kebbaj, M.S.; Lizard, G.; et al. Argan Oil Prevents Down-Regulation Induced by Endotoxin on Liver Fatty Acid Oxidation and Gluconeogenesis and on Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator-1α, (PGC-1α), Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α (PPARα) and Estrogen Related Receptor α (ERRα). Biochim. Open 2015, 1, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kamouni, S.; El Kebbaj, R.; Andreoletti, P.; El Ktaibi, A.; Rharrassi, I.; Essamadi, A.; El Kebbaj, M.S.; Mandard, S.; Latruffe, N.; Vamecq, J.; et al. Protective Effect of Argan and Olive Oils against LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mice Livers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchab, H.; Ishaq, A.; EL Kebbaj, R.; Nasser, B.; Saretzki, G. Protective Effect of Argan Oil on DNA Damage in Vivo and in Vitro. Biomarkers 2021, 26, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellahcen, S.; Hakkou, Z.; Ziyyat, A.; Legssyer, A.; Mekhfi, H.; Aziz, M.; Bnouham, M. Antidiabetic and Antihypertensive Effect of Virgin Argan Oil in Model of Neonatal Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic and l-Nitroarginine Methylester (l-NAME) Hypertensive Rats. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2013, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennani, H.; Drissi, A.; Giton, F.; Kheuang, L.; Fiet, J.; Adlouni, A. Antiproliferative Effect of Polyphenols and Sterols of Virgin Argan Oil on Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2007, 31, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msanda, F.; Mayad, E.H.; Furze, J.N. Floristic Biodiversity, Biogeographical Significance, and Importance of Morocco’s Arganeraie Biosphere Reserve. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 64156–64165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zougagh, M.; Salghi, R.; Dhair, S.; Rios, A. Nanoparticle-Based Assay for the Detection of Virgin Argan Oil Adulteration and Its Rapid Quality Evaluation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrouf, Z.; Guillaume, D. Argan Oil: Occurrence, Composition and Impact on Human Health. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhifi, W.; Miguel, M.; Mnif, W. Argan Oil: Extraction, Categories, Chemical Composition and Health Benefits. In Seed Oil: Production, Uses and Benefits; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 175–188. ISBN 978-153613561-9/978-153613560-2. [Google Scholar]
- El Maouardi, M.; Kharbach, M.; Cherrah, Y.; De Braekeleer, K.; Bouklouze, A.; Vander Heyden, Y. Quality Control and Authentication of Argan Oils: Application of Advanced Analytical Techniques. Molecules 2023, 28, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, R.; Kharbach, M.; Vander Heyden, Y.; Doukkali, Z.; Ghchime, R.; Bouklouze, A.; Cherrah, Y.; Alaoui, K. In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Response and Bioactive Compounds’ Profile of Polyphenolic Extracts from Edible Argan Oil (Argania spinosa L.), Obtained by Two Extraction Methods. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, D.; Pioch, D.; Charrouf, Z. Argan [Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels] Oil. In Fruit Oils: Chemistry and Functionality; Fawzy, R.M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 317–352. ISBN 978-3-030-12472-4. [Google Scholar]
- El Kebbaj, R.; El Kamouni, S.; El Hajj, H.I.; Andreoletti, P.; Gresti, J.; Latruffe, N. Modulation of Peroxisomes Abundance by Argan Oil and Lipopolysaccharides in Acyl-CoA Oxidase 1-Deficient Fibroblasts. Health 2013, 5, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khallouki, F.; Younos, C.; Soulimani, R.; Oster, T.; Charrouf, Z.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Bartsch, H.; Owen, R.W. Consumption of Argan Oil (Morocco) with Its Unique Profile of Fatty Acids, Tocopherols, Squalene, Sterols and Phenolic Compounds Should Confer Valuable Cancer Chemopreventive Effects. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2003, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueda, A.; Samaniego-Sánchez, C.; Olalla, M.; Giménez, R.; Cabrera-Vique, C.; Seiquer, I.; Lara, L. Combination of Analytical and Chemometric Methods as a Useful Tool for the Characterization of Extra Virgin Argan Oil and Other Edible Virgin Oils. Role of Polyphenols and Tocopherols. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampi, A.-M.; Kataja, L.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Vieno, P. Antioxidant Activities of α- and γ-Tocopherols in the Oxidation of Rapeseed Oil Triacylglycerols. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, G.G.; McPhail, D.B.; Morrice, P.C.; Arthur, J.R. Antioxidant Effectiveness of Tocopherol Isomers. In Lipid-Soluble Antioxidants: Biochemistry and Clinical Applications; Ong, A.S.H., Packer, L., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 76–84. ISBN 978-3-0348-7432-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Ames, B.N. Gamma-Tocopherol, but Not Alpha-Tocopherol, Decreases Proinflammatory Eicosanoids and Inflammation Damage in Rats. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2003, 17, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Blachier, F.; Tossou, M.C.B.; Rahu, N. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7432797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, R. Chemistry and Biochemistry of Dietary Polyphenols. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechqoq, H.; El Yaagoubi, M.; El Hamdaoui, A.; Momchilova, S.; Guedes da Silva Almeida, J.R.; Msanda, F.; El Aouad, N. Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry and Biological Properties of Argan Tree (Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels) (Sapotaceae)—A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Vique, C.; Marfil, R.; Giménez, R.; Martínez-Augustin, O. Bioactive Compounds and Nutritional Significance of Virgin Argan Oil—An Edible Oil with Potential as a Functional Food. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M. Composition chimique de l’huile d’argane « vierge ». Cah. Agric. 2005, 14, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Benz, C.C.; Yau, C. Ageing, Oxidative Stress and Cancer: Paradigms in Parallax. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashima, R.; Witting, P.K.; Stocker, R. Oxidants and Antioxidants in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2001, 12, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T.D. Metals, Toxicity and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free Radicals, Metals and Antioxidants in Oxidative Stress-Induced Cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.S.; Woodside, J.V. Antioxidants in Health and Disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Biochemistry of Oxidative Stress. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, R.; Aydın, B.; Şekeroğlu, V.; Atlı Şekeroğlu, Z. Protective Effect of Argan Oil on Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress against Acrylamide-Induced Liver and Kidney Injury in Rats. Biomark. Biochem. Indic. Expo. Response Susceptibility Chem. 2020, 25, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, B. Effects of Argan Oil on the Mitochondrial Function, Antioxidant System and the Activity of NADPH- Generating Enzymes in Acrylamide Treated Rat Brain. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şekeroğlu, Z.A.; Aydın, B.; Şekeroğlu, V. Argan Oil Reduces Oxidative Stress, Genetic Damage and Emperipolesis in Rats Treated with Acrylamide. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orabi, S.H.; Abd Eldaium, D.; Hassan, A.; Sabagh, H.S.E.; Abd Eldaim, M.A. Allicin Modulates Diclofenac Sodium Induced Hepatonephro Toxicity in Rats via Reducing Oxidative Stress and Caspase 3 Protein Expression. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 74, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necib, Y.; Bahi, A.; Zerizer, S.; Abdennour, C.; Boulakoud, M.S.; Chettoum, A.; Abdelkader, H. Effect of Argan Oil (Argania spinosa L.) on Kidney Function Impairment and Oxidative Stress Induced by Mercuric Chloride in Rats. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2013, 22, 144. [Google Scholar]
- El Mostafi, H.; Elhessni, A.; Touil, T.; Ouichou, A.; Laaziz, A.; Doumar, H.; Mesfioui, A. Argan Oil Supplementation Attenuates Voluntary Ethanol Consumption and Withdrawal Syndrome Promoted by Adolescent Intermittent Ethanol in Rat. Alcohol 2020, 87, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakour, M.; Soulo, N.; Hammas, N.; Fatemi, H.; Aboulghazi, A.; Taroq, A.; Abdellaoui, A.; Al-Waili, N.; Lyoussi, B. The Antioxidant Content and Protective Effect of Argan Oil and Syzygium Aromaticum Essential Oil in Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Biochemical and Histological Changes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimeur, A.; Meskini, N.; Mimouni, V.; Ulmann, L.; Messaouri, H.; Pineau-Vincent, F.; Abouakil, N.; Tremblin, G. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Argan Oil versus Fish Oil on Risk Factors for Cardio-Vascular Disease in High-Fat-Fed Rats. Nutrition 2019, 57, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Midaoui, A.; Haddad, Y.; Couture, R. Beneficial Effects of Argan Oil on Blood Pressure, Insulin Resistance, and Oxidative Stress in Rat. Nutrition 2016, 32, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, A.M.; Kuru, S.; Kismet, K.; Cavusoglu, T.; Bag, Y.M.; Senes, M.; Cihan, N.; Celepli, P.; Unal, Y.; Hucumenoglu, S. Rectal Application of Argan Oil Improves Healing of Colorectal Anastomosis in Rats1. Acta Cir. Bras. 2018, 33, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sour, S.; Belarbi, M.; Sari, N.; Benammar, C.H.; Baghdad, C.H.; Visioli, F. Argan Oil Reduces, in Rats, the High Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Effects of Obesity. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2015, 25, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essadek, S.; Bouchab, H.; El Kebbaj, R.; Gondcaille, C.; El Kamouni, S.; Savary, S.; Vamecq, J.; Essamadi, A.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; Nasser, B.; et al. Effects of a Short-Term Lipopolysaccharides Challenge on Mouse Brain and Liver Peroxisomal Antioxidant and β-Oxidative Functions: Protective Action of Argan Oil. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchab, H.; Essadek, S.; El Kamouni, S.; Moustaid, K.; Essamadi, A.; Andreoletti, P.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; El Kebbaj, R.; Nasser, B. Antioxidant Effects of Argan Oil and Olive Oil against Iron-Induced Oxidative Stress: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches. Molecules 2023, 28, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, T.M.; Mansour, M.F.; Abdelaziz, A.S.; Mohamed, R.M.S.; Fouad, R.A.; Arisha, A.H. Argan Oil Ameliorates Sodium Fluoride–Induced Renal Damage via Inhibiting Oxidative Damage, Inflammation, and Intermediate Filament Protein Expression in Male Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30426–30436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaniego Sánchez, C.; Troncoso González, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.C.; Quesada Granados, J.J.; López García de la Serrana, H.; López Martínez, M.C. Different Radical Scavenging Tests in Virgin Olive Oil and Their Relation to the Total Phenol Content. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 593, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiquer, I.; Rueda, A.; Olalla, M.; Cabrera-Vique, C. Assessing the Bioavailability of Polyphenols and Antioxidant Properties of Extra Virgin Argan Oil by Simulated Digestion and Caco-2 Cell Assays. Comparative Study with Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamero-Sandemetrio, E.; Gómez-Pastor, R.; Aranda, A.; Matallana, E. Validation and Biochemical Characterisation of Beneficial Argan Oil Treatment in Biomass Propagation for Industrial Active Dry Yeast Production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 51, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Go, P.; Diboh, E.; Sylla, I.; Ahami, A.; Aboussaleh, Y.; Azzaoui, F.-Z.; Boulbaroud, S. Comparison of the Effects of Argan and Nigella Oils on Malathion-Induced Cognitive-Behavioral Alterations and Brain Histopathology in Male Wistar Rats. Curr. Top. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerale, S.; Lucas, L.J.; Keast, R.S.J. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Phenolic Activities in Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakiche, H.; Khali, M.; Boutoumi, H. Phytochemical Characterization and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory and Wound-Healing Activities of Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels Seed Oil. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2017, 11, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lizard, G.; Filali-Zegzouti, Y.; El Midaoui, A. Benefits of Argan Oil on Human Health—4–6 May 2017, Errachidia, Morocco. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, H.B.; Belarbi, M.; Menni, D.B.; Bendiab, H.; Kherraf, Y.; Ksouri, R.; Djebli, N.; Visioli, F. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Argan Oil and Its Minor Components. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Galli, C. The Role of Antioxidants in the Mediterranean Diet. Lipids 2001, 36, S49–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kebbaj, R.; Bouchab, H.; Tahri-Joutey, M.; Rabbaa, S.; Limami, Y.; Nasser, B.; Egbujor, M.C.; Tucci, P.; Andreoletti, P.; Saso, L.; et al. The Potential Role of Major Argan Oil Compounds as Nrf2 Regulators and Their Antioxidant Effects. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebay, L.E.; Robertson, H.; Durant, S.T.; Vitale, S.R.; Penning, T.M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Hayes, J.D. Mechanisms of Activation of the Transcription Factor Nrf2 by Redox Stressors, Nutrient Cues, and Energy Status and the Pathways through Which It Attenuates Degenerative Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 108–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, Z.; Samarghandian, S.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: Implications in Disease Therapy and Protection against Oxidative Stress. Life Sci. 2020, 244, 117329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Collaborative Power of Nrf2 and PPAR γ Activators against Metabolic and Drug-Induced Oxidative Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1378175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrouk, A.; Martine, L.; Grégoire, S.; Nury, T.; Meddeb, W.; Camus, E.; Badreddine, A.; Durand, P.; Namsi, A.; Yammine, A.; et al. Profile of Fatty Acids, Tocopherols, Phytosterols and Polyphenols in Mediterranean Oils (Argan Oils, Olive Oils, Milk Thistle Seed Oils and Nigella Seed Oil) and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Activities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1791–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, F.; Ding, J.; Hu, N.; Dong, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H. Kaempferol and Kaempferide Attenuate Oleic Acid-Induced Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress in HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kern, J.T.; Goodfriend, T.L.; Ball, D.L.; Luesch, H. Activation of the Antioxidant Response Element by Specific Oxidized Metabolites of Linoleic Acid. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2009, 81, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Niu, Z.; Wu, S.; Shan, S. Protective Mechanism of Sulforaphane in Nrf2 and Anti-Lung Injury in ARDS Rabbits. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4911–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Qi, Y.; Li, W.; Han, M.; Muhammad, I.; Zhang, X. High Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic 18-Carbon Fatty Acids Accumulation Up-Regulates CYP2A5/CYP2A6 via NF-E2-Related Factor. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.-L.; Yu, B.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.-X.; Jiang, J.-D.; Kong, W.-J. Gastrodin Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Proinflammatory Response in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through the AMPK/Nrf2 Pathway. Phytother. Res. PTR 2016, 30, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catino, S.; Paciello, F.; Miceli, F.; Rolesi, R.; Troiani, D.; Calabrese, V.; Santangelo, R.; Mancuso, C. Ferulic Acid Regulates the Nrf2/Heme Oxygenase-1 System and Counteracts Trimethyltin-Induced Neuronal Damage in the Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line SH-SY5Y. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 6, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-L.; Zhao, X.-M.; Niu, Y.-C. Ferulic Acid Protects Against Lead Acetate-Induced Inhibition of Neurite Outgrowth by Upregulating HO-1 in PC12 Cells: Involvement of ERK1/2-Nrf2 Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6489–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-T.; Yen, G.-C. Induction of Hepatic Antioxidant Enzymes by Phenolic Acids in Rats Is Accompanied by Increased Levels of Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 3 mRNA Expression. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, S.; Leonard, S.; Traber, M.G.; Jialal, I. Gamma-Tocopherol Supplementation Alone and in Combination with Alpha-Tocopherol Alters Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, M.; Piekut, T.; Prendecki, M.; Sodel, A.; Kozubski, W.; Dorszewska, J. Mitochondrial and Nuclear DNA Oxidative Damage in Physiological and Pathological Aging. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Eo, H.; Lim, Y. Similarities and Differences between Alpha-Tocopherol and Gamma-Tocopherol in Amelioration of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Pre-Fibrosis in Hyperglycemia Induced Acute Kidney Inflammation. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossi, C.G.; González Mañán, D.A.; Romero, N.; Silva, D.; Videla Cabrera, L.; Tapia Opazo, G. Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rosa Mosqueta Oil Supplementation in Rat Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4847–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, G.; Silva, D.; Romero, N.; Pettinelli, P.; Dossi, C.G.; de Miguel, M.; González-Mañán, D. Role of Dietary α- and γ-Tocopherol from Rosa Mosqueta Oil in the Prevention of Alterations Induced by High-Fat Diet in a Murine Model. Nutrition 2018, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarek, A.K.; So, J.Y.; Thomas, P.E.; Lee, H.J.; Paul, S.; Dombrowski, A.; Wang, C.-X.; Saw, C.L.-L.; Khor, T.O.; Kong, A.-N.T.; et al. Dietary Tocopherols Inhibit Cell Proliferation, Regulate Expression of ERα, PPARγ, and Nrf2, and Decrease Serum Inflammatory Markers during the Development of Mammary Hyperplasia. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Sai, B.; Wahnou, H.; Benayad, S.; Rabbaa, S.; Laaziouez, Y.; El Kebbaj, R.; Limami, Y.; Duval, R.E. Gamma-Tocopherol: A Comprehensive Review of Its Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anticancer Properties. Molecules 2025, 30, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essadek, S.; Gondcaille, C.; Savary, S.; Samadi, M.; Vamecq, J.; Lizard, G.; Kebbaj, R.E.; Latruffe, N.; Benani, A.; Nasser, B.; et al. Two Argan Oil Phytosterols, Schottenol and Spinasterol, Attenuate Oxidative Stress and Restore LPS-Dysregulated Peroxisomal Functions in Acox1−/− and Wild-Type BV-2 Microglial Cells. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kharrassi, Y.; Samadi, M.; Lopez, T.; Nury, T.; El Kebbaj, R.; Andreoletti, P.; El Hajj, H.I.; Vamecq, J.; Moustaid, K.; Latruffe, N.; et al. Biological Activities of Schottenol and Spinasterol, Two Natural Phytosterols Present in Argan Oil and in Cactus Pear Seed Oil, on Murine Miroglial BV2 Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badreddine, A.; Karym, E.M.; Zarrouk, A.; Nury, T.; El Kharrassi, Y.; Nasser, B.; Cherkaoui Malki, M.; Lizard, G.; Samadi, M. An Expeditious Synthesis of Spinasterol and Schottenol, Two Phytosterols Present in Argan Oil and in Cactus Pear Seed Oil, and Evaluation of Their Biological Activities on Cells of the Central Nervous System. Steroids 2015, 99, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB Signaling in Inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, N.; Van Hecke, A.; Remue, E.; Van Den Bussche, K.; Moore, Z.; Gefen, A.; Verhaeghe, S.; Beeckman, D. Physiological Processes of Inflammation and Edema Initiated by Sustained Mechanical Loading in Subcutaneous Tissues: A Scoping Review. Wound Repair Regen. 2020, 28, 242–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantacuzzi, M.; De Filippis, B.; Amoroso, R.; Giampietro, L. PPAR Ligands Containing Stilbene Scaffold. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, K.; Inoue, N.; Suzuki, K.; Shimizu, T.; Yanagita, T. The Cholesterol Metabolite Cholest-5-En-3-One Alleviates Hyperglycemia and Hyperinsulinemia in Obese (Db/Db) Mice. Metabolites 2021, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, R.; Kharbach, M.; Eljemli, M.; Bouklouze, A.; Cherrah, Y.; Alaoui, K. Activité anti-inflammatoire in vivo de l’huile d’argan. Phytothérapie 2020, 18, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, K.; Kamijo, Y.; Hora, K.; Takahashi, K.; Higuchi, M.; Kiyosawa, K.; Shigematsu, H.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Aoyama, T. PPAR{alpha} Attenuates the Proinflammatory Response in Activated Mesangial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009, 296, F328–F336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, A.; Gervois, P.; Pauletto, P.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Staels, B. Modulation of Hepatic Inflammatory Risk Markers of Cardiovascular Diseases by PPAR-Alpha Activators: Clinical and Experimental Evidence. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.N.; Fisher, D.R.; Bielinski, D.F.; Cahoon, D.S.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Walnut-Associated Fatty Acids Inhibit LPS-Induced Activation of BV-2 Microglia. Inflammation 2020, 43, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-Y.; Jiang, W.-D.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.-Y.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.-N.; Zhang, Y.-A.; et al. Dietary Alpha-Linolenic Acid/Linoleic Acid Ratios Modulate Intestinal Immunity, Tight Junctions, Anti-Oxidant Status and mRNA Levels of NF-κB P65, MLCK and Nrf2 in Juvenile Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon Idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 51, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Le, D.D.; Bae, C.-S.; Park, J.W.; Lee, M.; Cho, S.-S.; Park, D.-H. Oleic Acid Attenuates Asthma Pathogenesis via Th1/Th2 Immune Cell Modulation, TLR3/4-NF-κB-Related Inflammation Suppression, and Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway Induction. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1429591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Nie, H. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Rui, Y.-X.; Guo, S.-D.; Luan, F.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Derivatives. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jing, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, S.; Gao, L.; Zhao, G. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Sciatica by Inhibiting Neuroinflammation and Promoting Nerve Repair via the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lin, L.; Wu, H. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Lung Injury through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Han, J.-S. Improving the Effect of Ferulic Acid on Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Regulating the JNK/ERK and NF-κB Pathways in TNF-α-Treated 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; Xin, Y.; Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Carp Brain Damage and Growth Inhibition Caused by Avermectin by Modulating the Nrf2/Keap1 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 196, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, W.; Xu, F.; Dai, X.; Shi, L.; Cai, W.; Mu, H.; Hitchens, T.K.; Foley, L.M.; Liu, X.; et al. The Interleukin-4/PPARγ Signaling Axis Promotes Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Remyelination after Brain Injury. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, M.; Kowalski, M.L.; Pawliczak, R. [Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-gamma (PPAR-gamma) and their role in immunoregulation and inflammation control]. Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw. Online 2005, 59, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in Immunoregulation and Therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamorano, J.; Mora, A.L.; Boothby, M.; Keegan, A.D. NF-κB Activation Plays an Important Role in the IL-4-Induced Protection from Apoptosis. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiser, J.; Alexis, N.E.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, W.; Robinette, C.; Roubey, R.; Peden, D.B. In Vivo Gamma Tocopherol Supplementation Decreases Systemic Oxidative Stress and Cytokine Responses of Human Monocytes in Normal and Asthmatic Subjects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Fu, S.; Yang, R.; Yang, K.; Lei, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Advances in the Study of Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Immune Skin Diseases. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpathiou, G.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Ferrand, E.; Dumollard, J.M.; Peoc’h, M. STAT6: A Review of a Signaling Pathway Implicated in Various Diseases with a Special Emphasis in Its Usefulness in Pathology. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2021, 223, 153477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Retinal Neovascularization by Modulating Microglia/Macrophage Polarization through the ROS/NF-κB Axis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 976729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Argan Oil | Olive Oil | |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty Acids (%) | ||
| References | [9] | [22] |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 11.80 | 11.66 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1 n-7) | 0.18 | 0.89 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 6.00 | 3.02 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1n-9) | 45.90 | 76.89 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2n-6) | 34.10 | 6.13 |
| Tocopherols (mg/kg oil) | ||
| References | [20] | [9] |
| α-Tocopherol | 42.23 | 88.01 |
| β-Tocopherol | 3.07 | 7.57 |
| γ-Tocopherol | 715.42 | 4.42 |
| δ-Tocopherol | 103.22 | ND |
| Polyphenols (µg/kg oil) | ||
| References | [23] | [24] |
| Vanillic acid | 67.00 | 1980.00 |
| Syringic acid | 37.00 | 6550.00 |
| Ferulic acid | 3147.00 | 10,500.00 |
| Tyrosol | 12.00 | 21,300.00 |
| Phytosterols (mg/kg oil) | ||
| References | [8] | [8] |
| Campesterol | 16.40 | 11.30 |
| Δ7-avenasterol | 85.80 | 12.30 |
| Spinasterol | 64.40 | ND |
| Schottenol | 849.00 | ND |
| Argan Oil Effects | Studies Design | Prooxidant– Pro-Inflammatory Agent | Outcome Measures | Argan Oil Treatment (Dose) | Outcome Measures | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Preclinical Models | ||||||
| Antioxidant effect | In vivo | Rat (♀) | Acrylamide | Kidney: ↓GPx ↑GSH ↑LP | 6 mL/kg | Kidney: ↔GPx ↓GSH ↔LP | [39,40,41] |
| Brain: ↓GPx ↓GSH ↑LP ↑PC | Brain: ↔GPx ↔GSH ↔LP ↓PC | ||||||
| Liver: ↓SOD ↓GPx ↓GSH ↓ICDH ↓α-KGDH | Liver: ↔SOD ↔GPx ↔GSH ↑ICDH ↑α-KGDH | ||||||
| Thymus: ↑TBARS ↓GSH | Thymus: ↔TBARS ↔GSH | ||||||
| Spleen: ↑PC | Spleen: ↔PC | ||||||
| Bone marrow: ↓GSH | Bone marrow: ↔GSH | ||||||
| Urine: ↑8-OHdG | Urine: ↔8-OHdG | ||||||
| Rat (♂) | Betamethasone | Kidney: ↑MDA | 1 mL/kg | Kidney: ↔MDA | [42] | ||
| Rat (♂) | Mercuric chloride | Kidney: ↓GSH ↑TBARS ↓GPx ↓GST | 5 mL/kg | Kidney: ↔GSH ↔TBARS ↔GPx ↑GST | [43] | ||
| Liver: ↑CAT ↑GST ↑GPx ↑GSH ↑LP | Liver: ↔CAT ↔GST ↔GPx ↔GSH ↔LP | ||||||
| Rat (♂) | Ethanol | Brain: ↑MDA | 10 mL/kg | Brain: ↓MDA | [44] | ||
| Rat (♂) | H2O2 | Liver: Induce binucleation | 10 mL/kg | Liver: Suppress binucleation | [45] | ||
| Rat (♂) | High-fat diet | Liver: ↓GPx | 5% | Liver: ↔GPx | [46] | ||
| Rat (♂) | D-Glucose | Heart: ↑O2•− ↑NADPH oxidase | 5 mL/kg | Heart: ↔O2•− ↔NADPH oxidase | [47] | ||
| Rat (♂) | 0.9% NaCl | Colon: ↑ MDA | 2 mL/kg | Colon: ↔ MDA | [48] | ||
| Rat (♂) | High-fat diet | Plasma: ↑LOOH ↓CAT ↓SOD | 5 g/kg | Plasma: ↓LOOH ↑CAT ↑SOD | [49] | ||
| Mouse (♂) | LPS | Liver: ↑CAT ↑GPx ↑GSH | 6% | Liver: ↔CAT ↔GPx ↔GSH | [11,50] | ||
| Brain: ↑CAT ↑SOD ↓GSH ↑CAT | Brain: ↔CAT ↔SOD ↔GSH ↔CAT | ||||||
| Liver: ↑CAT ↑SOD ↑MDA ↑CAT | Liver: ↔CAT ↔SOD ↔MDA ↔CAT | ||||||
| Mouse (♂) | Iron | Liver: ↓SOD ↓GPx ↑MDA | 6% | Liver: ↑SOD ↑GPx ↔MDA | [12,51] | ||
| Brain: ↓GSH | Brain: ↑GSH | ||||||
| Kidney: ↑SOD ↓GPx | Kidney: ↔SOD ↔GPx | ||||||
| Liver: ↑γH2AX | Liver: ↔γH2AX | ||||||
| In vitro | Tetrahymena pyriformis | Iron | ↑SOD ↑GPx ↑GSH | 0.1% | ↔SOD ↔GPx ↔GSH | [51] | |
| Oligodendrocyte 158N | 7KC | ↑Cell growth ↑O2•− | 0.1% | ↔Cell growth ↔O2•− | [8] | ||
| Fibroblasts MRC-5 | Hyperoxia | ↑γH2AX | 0.1% | ↓γH2AX | [12] | ||
| Anti-inflammatory effect | In vivo | Rat (♂) | NaF | Kidney: ↑Tnf-α ↑IL-1β ↑IL-8 ↑MCP-1 ↑TGF-β1 ↓IL-10 | 6 mg/kg | Kidney: ↓Tnf-α ↓IL-1β ↓IL-8 ↓MCP-1 ↓TGF-β1 ↑IL-10 | [52] |
| Mouse (♂) | LPS | Liver: ↑Tnf-α ↑IL-6 ↓IL-4 ↓IL-10 | 6% | Liver: ↓Tnf-α ↓IL-6 ↑IL-4 ↑IL-10 | [11,50] | ||
| Brain: ↑Tnf-α | Brain: ↓Tnf-α | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabbaa, S.; Bouchab, H.; Laaziouez, Y.; Limami, Y.; Nasser, B.; Andreoletti, P.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; El Kebbaj, R. Argan Oil: A Natural Bioactive Lipid Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050515
Rabbaa S, Bouchab H, Laaziouez Y, Limami Y, Nasser B, Andreoletti P, Cherkaoui-Malki M, El Kebbaj R. Argan Oil: A Natural Bioactive Lipid Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(5):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050515
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabbaa, Soufiane, Habiba Bouchab, Yassir Laaziouez, Youness Limami, Boubker Nasser, Pierre Andreoletti, Mustapha Cherkaoui-Malki, and Riad El Kebbaj. 2025. "Argan Oil: A Natural Bioactive Lipid Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation" Antioxidants 14, no. 5: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050515
APA StyleRabbaa, S., Bouchab, H., Laaziouez, Y., Limami, Y., Nasser, B., Andreoletti, P., Cherkaoui-Malki, M., & El Kebbaj, R. (2025). Argan Oil: A Natural Bioactive Lipid Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants, 14(5), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050515








