Hydroponically Grown Sanguisorba minor Scop.: Effects of Cut and Storage on Fresh-Cut Produce
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Extraction and Untargeted Metabolomics-Based Profiling of Fresh Plant Material Obtained from Two Consecutive Cuts
2.3. Samples Preparation for Phytochemical Analysis of Stored Material
2.4. Pigment Analysis
2.5. Phenol and Flavonoid Extraction
2.6. Total Phenolic Determination
2.7. Flavonoid Determination
2.8. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Analysis
2.9. Ascorbic Acid Extraction
2.10. Total Ascorbic Acid Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. UHPLC-QTOF Mass Spectrometry Untargeted Profiling and Effect of the Two Cuts
3.2. Phytochemical Analyses in Leaves Stored as Fresh-Cut Product
3.2.1. Pigments
3.2.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
3.3.3. Total Flavonoid Content
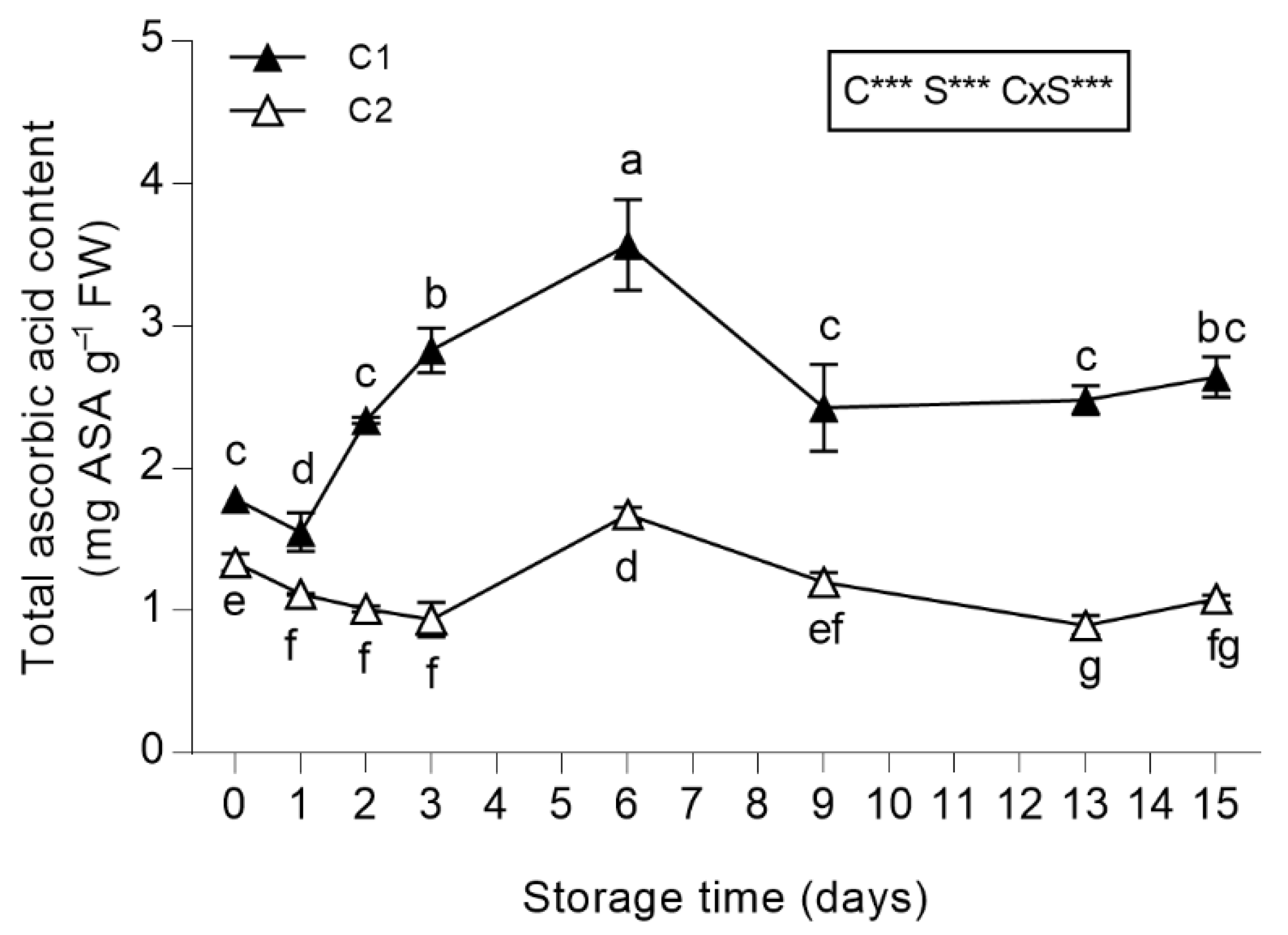
3.3.4. Total Ascorbic Acid (ASA) Content
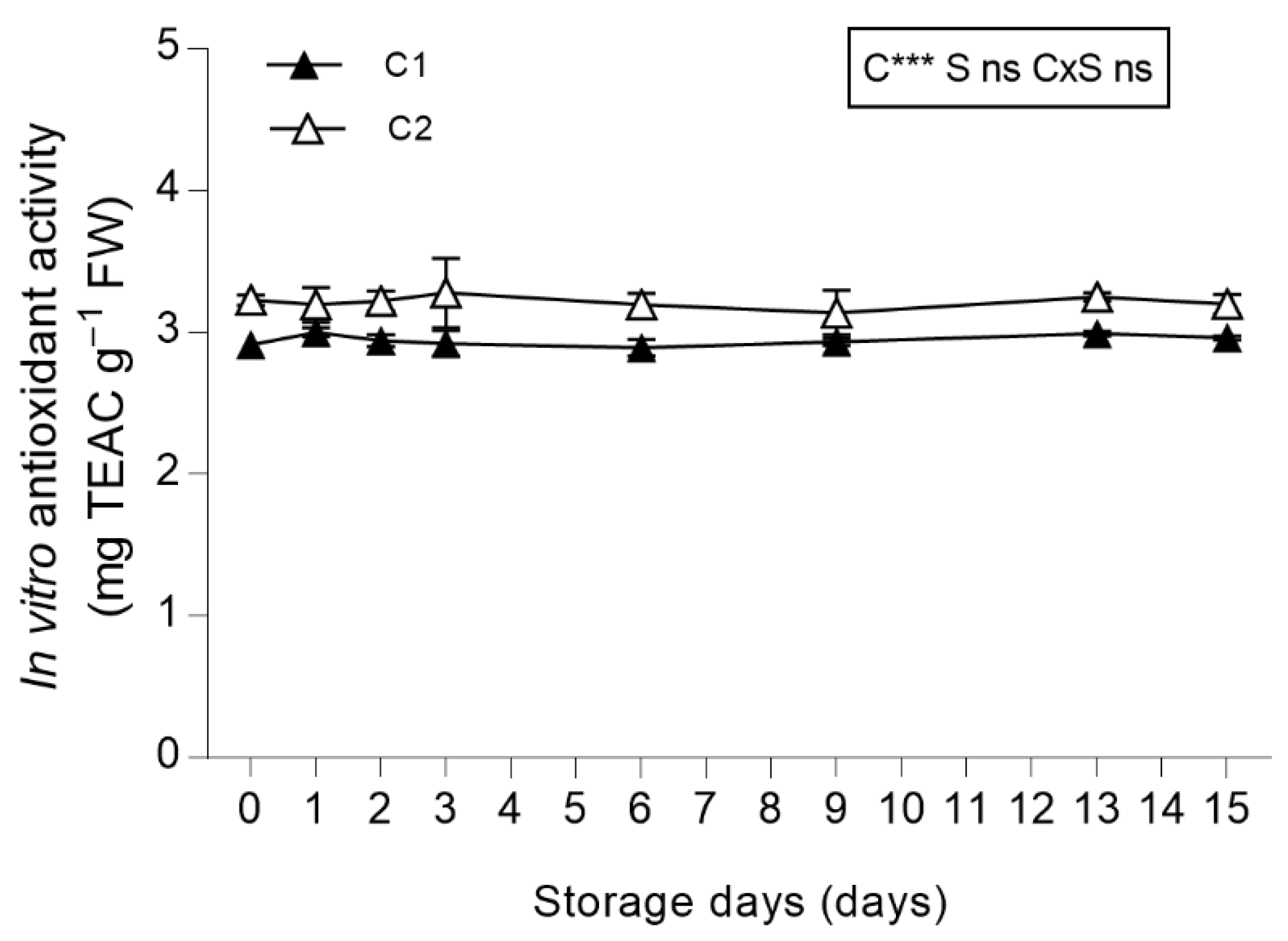
3.3.5. In Vitro Total Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romojaro, A.; Botella, M.A.; Obón, C.; Pretel, M.T. Nutritional and antioxidant properties of wild edible plants and their use as potential ingredients in the modern diet. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.; Carvalho, A.M.; Sánchez-Mata, C.; Cámara, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Pardo-de-Santayana, M.; Tardío, J. Mediterranean non-cultivated vegetables as dietary sources of compounds with antioxidant and biological activity. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccanti, C.; Landi, M.; Benvenuti, S.; Pardossi, A.; Guidi, L. Mediterranean wild edible plants: Weeds or “new functional crops”? Molecules 2018, 23, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Regueiro, J.; Martínez-Huélamo, M.; Rinaldi Alvarenga, J.F.; Leal, L.N.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. A comprehensive study on the phenolic profile of widely used culinary herbs and spices: Rosemary, thyme, oregano, cinnamon, cumin and bay. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Bel, P.; Romojaro, A.; Egea, I.; Pretel, M.T. Wild edible plants as potential antioxidant or nutritional supplements for beverages minimally processed. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, S.A.; Karkanis, A.; Martins, N.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Edible halophytes of the Mediterranean basin: Potential candidates for novel food products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 74, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umate, S.K.; Marathe, V.R. Nutraceutical evaluation of Acalypha indica L.—A potential wild edible plant. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2018, 12, S510–S517. [Google Scholar]
- Tanase, C.; Mocan, A.; Coșarcă, S.; Gavan, A.; Nicolescu, A.; Gheldiu, A.M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Muntean, D.L.; Crișan, O. Biological and chemical insights of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) bark: A source of bioactive compounds with functional properties. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coșarcă, S.L.; Moacă, E.A.; Tanase, C.; Muntean, D.L.; Pavel, I.Z.; Dehelean, C.A. Spruce and beech bark aqueous extracts: Source of polyphenols, tannins and antioxidants correlated to in vitro antitumor potential on two different cell lines. Wood Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyda, J.H.; Fernandes, Â.; Calhelha, R.C.; Alves, M.J.; Ferreira, F.D.; Barros, L.; Amaral, J.S.; Ferreira, I.C. Nutritional composition and bioactivity of Umbilicus rupestris (Salisb.) Dandy: An underexploited edible wild plant. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pires, T.C.; Barros, L.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C. Edible flowers: Emerging components in the diet. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarrera, P.M.; Savo, V. Wild food plants used in traditional vegetable mixtures in Italy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 185, 202–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, N.A. Unique phenolic carboxylic acids from Sanguisorba minor. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reher, G.; Slijepcevié, M.; Kraus, L. Hypoglycemic activity of triterpenes and tannins from Sarcopoterium spinosum and two Sanguisorba species. Planta Med. 1991, 57, A57–A58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Proença, C.; Serralheiro, M.L.M.; Araújo, M.E.M. The in vitro screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibition and antioxidant activity of medicinal plants from Portugal. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, D.; Herrmann, F.; Wink, M. Extracts from traditional Chinese medical plants inhibit glycogen synthase kinase 3 β activity, a potential Alzheimer target. Z. Phytother. 2009, 30, V16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranfa, A.; Maurizi, A.; Romano, B.; Bodesmo, M. The importance of traditional uses and nutraceutical aspects of some edible wild plants in human nutrition: The case of Umbria (central Italy). Plant Biosyst. 2014, 148, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzani, P.; Rossetto, M.; De Marco, V.; Sacchetti, L.E.; Paoletti, M.G.; Rigo, A. Wild Mediterranean plants as traditional food: A valuable source of antioxidants. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgersma, A.; Søegaard, K.; Jensen, S.K. Fatty acids, α-tocopherol, β-carotene, and lutein contents in forage legumes, forbs, and a grass-clover mixture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11913–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzocco, L.; Foschia, M.; Tomasi, N.; Maifreni, M.; Dalla Costa, L.; Marino, M.; Cortella, G.; Cesco, S. Influence of hydroponic and soil cultivation on quality and shelf life of ready-to-eat lamb’s lettuce (Valerianella locusta L. Laterr). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.; Ruffoni, B.; Salvi, D.; Savona, M.; Guidi, L. Cold storage does not affect ascorbic acid and polyphenolic content of edible flowers of a new hybrid of sage. Agrochimica 2015, 59, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, M.; Ruffoni, B.; Combournac, L.; Guidi, L. Nutraceutical value of edible flowers upon cold storage. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2018, 30, 336–347. [Google Scholar]
- Borgognone, D.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Lucini, L.; Colla, G. Changes in biomass, mineral composition, and quality of cardoon in response to NO3−:Cl− ratio and nitrate deprivation from the nutrient solution. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, K.; Sorrentino, M.; Lucini, L.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Bonini, P.; Moreno, M.B.M.; Reynaud, H.; Canaguier, R.; Trtílek, M.; et al. A combined phenotypic and metabolomic approach for elucidating the biostimulant action of a plant-derived protein hydrolysate on tomato grown under limited water availability. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchetti, G.; Lucini, L.; Chiodelli, G.; Giuberti, G.; Montesano, D.; Masoero, F.; Trevisan, M. Impact of boiling on free and bound phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of commercial gluten-free pasta. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://cosmos-fp7.eu/msi (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- Rocchetti, G.; Bhumireddy, S.R.; Giuberti, G.; Mandal, R.; Lucini, L.; Wishart, D.S. Edible nuts deliver polyphenols and their transformation products to the large intestine: An in vitro fermentation model combining targeted/untargeted metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porra, R.J.; Thompson, W.A.; Kriedemann, P.E. Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: Verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biogenrg. 1989, 975, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanto, V.; Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Li, M.; Ma, F.; Liang, D. Antioxidant capacity and the relationship with polyphenol and vitamin C in Actinidia fruits. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampfenkel, K.; Van Montagu, M.; Inzé, D. Extraction and determination of ascorbate and dehydroascorbate from plant tissue. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 225, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Gupta, S. Apigenin: A promising molecule for cancer prevention. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.S.; Landau, J.M.; Huang, M.T.; Newmark, H.L. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 381–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Prey, J.; Brown, J.; Fleming, J.; Harrison, P.R. Effects of dietary flavonoids on major signal transduction pathways in human epithelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 2075–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wan, J.; He, C.W. Rationale for the use of natural anti-inflammatory agents in cancer chemotherapy. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 3, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.L.; Feng, F.; You, Q.D.; Lu, N.; Guo, Q.L. Flavonoid baicalein suppresses adhesion, migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 279, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Zhu, T. Baicalein inhibits proliferation and collagen synthesis of mice fibroblast cell line NIH/3T3 by regulation of miR-9/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3202–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chokchaisiri, R.; Suaisom, C.; Sriphota, S.; Chindaduang, A.; Chuprajob, T.; Suksamrarn, A. Bioactive flavonoids of the flowers of Butea monosperma. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, J.; Silva, A.M.S.; Marques, M.P.M.; Braga, S.S. Ruthenium(II) trithiacyclononane complexes of 7,3′,4′-trihydroxyflavone, chrysin and tectochrysin: Synthesis, characterisation, and cytotoxic evaluation. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2019, 488, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multari, S.; Pihlava, J.M.; Priscilla Ollennu-Chuasam, P.; Hietaniemi, V.; Yang, B.; Suomela, J.P. Identification and quantification of avenanthramides and free and bound phenolic acids in eight cultivars of husked oat (Avena sativa L.) from Finland. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2900–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escobedo-Flores, Y.; Chavez-Flores, D.; Salmeron, I.; Molina-Guerrero, C.; Perez-Vega, S. Optimization of supercritical fluid extraction of polyphenols from oats (Avena sativa L.) and their antioxidant activities. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 80, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, W.J.C.; van Dinteren, S.; Gruppen, H.; Vincken, J.P. Mass spectrometric characterization of avenanthramides and enhancing their production by germination of oat (Avena sativa). Food Chem. 2019, 277, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, F.W. Oat Phenolics: Avenanthramides, novel substituted N-cinnamoylanthranilate alkaloids from oat groats and hulls. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.O.; Milbury, P.E.; Collins, F.W.; Blumberg, J.B. Avenanthramides are bioavailable and have antioxidant activity in humans after acute consumption of an enriched mixture from oats. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrelli, A.; Goitre, L.; Salzano, A.M.; Moglia, A.; Scaloni, A.; Retta, S.F. Biological activities, health benefits, and therapeutic properties of avenanthramides: From skin protection to prevention and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratt, K.; Sunnerheim, K.; Bryngelsson, S.; Fagerlund, A.; Engman, L.; Andersson, R.E.; Dimberg, L.H. Avenanthramides in oats (Avena sativa L.) and structure-antioxidant activity relationships. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 594–600. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wise, M.L.; Li, F.; Dey, M. Phytochemicals attenuating aberrant activation of β-catenin in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gousiadou, C.; Skaltsa, H. Secondary metabolites from Centaurea orphanidea. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2003, 31, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafakou, M.E.; Djeddi, S.; Tarek, H.; Skaltsa, H. Secondary metabolites from the aerial parts of Centaurea papposa (Coss.) Greuter. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2018, 76, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, D.; Farah, A.; Donangelo, C.M.; de Paulis, T.; Martin, P.R. Comprehensive analysis of major and minor chlorogenic acids and lactones in economically relevant Brazilian coffee cultivars. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, M.R.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Katan, M.B. Chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid are absorbed in humans. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kahle, K.; Huemmer, W.; Kempf, M.; Scheppach, W.; Erk, T.; Richling, E. Polyphenols are intensively metabolized in the human gastrointestinal tract after apple juice consumption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10605–10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ӧksüz, S.; Topcu, G. Guaianolides from Centaurea glastifolia. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.H.; Chen, K.X.; Zhang, L.Q.; Li, Y.M. Advance in biological activities of natural guaiane-type sesquiterpenes. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1339–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinopoulou, M.; Karioti, A.; Skaltsas, S.; Skaltsa, H. Sesquiterpene lactones from Anthemis altissima and their anti-Helicobacter pylori activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucka, I.; Olszówka, K.; Chilczuk, B. Changes in the chlorophyll content in stored lettuce Lactuca sativa L. after pre-harvest foliar application of CaCl2. Acta Agrobot. 2013, 66, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, L.E.; Oliveira, D.A.; Hills, K.; Giacobassi, C.; Johnson, J.; Summerlin, H.; Taylor, T.M.; Gomes, C.L. A Comparative study of natural antimicrobial delivery systems for microbial safety and quality of fresh-cut lettuce. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materska, M.; Olszówka, K.; Chilczuk, B.; Stochmal, A.; Pecio, Ł.; Pacholczyk Sienicka, B.; Piacente, S.; Pizza, C.; Masullo, M. Polyphenolic profiles in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) after CaCl2 treatment and cold storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riga, P.; Benedicto, L.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á.; Collado-González, J.; Ferreres, F.; Medina, S. Diffuse light affects the contents of vitamin C, phenolic compounds and free amino acids in lettuce plants. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degl’Innocenti, E.; Pardossi, A.; Tognoni, F.; Guidi, L. Physiological basis of sensitivity to enzymatic browning in ‘lettuce’, ‘escarole’ and ‘rocket salad’ when stored as fresh-cut products. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunkaya, A.; Gökmen, V. Effect of various inhibitors on enzymatic browning, antioxidant activity and total phenol content of fresh lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, D.M.; Selma, M.V.; Marín, A.; Gil, M.I. Ozonated water extends the shelf life of fresh-cut lettuce. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2005, 53, 5654–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanam, U.K.S.; Oba, S.; Yanase, E.; Murakami, Y. Phenolic acids, flavonoids and total antioxidant capacity of selected leafy vegetables. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimler, D.; Vignolini, P.; Arfaioli, P.; Isolania, L.; Romani, A. Conventional, organic and biodynamic farming: Differences in polyphenol content and antioxidant activity of Batavia lettuce. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-López, U.; Sgherri, C.; Miranda-Apodaca, J.; Micaelli, F.; Lacuesta, M.; Mena-Petite, A.; Quartacci, M.F.; Muñoz-Rueda, A. Concentration of phenolic compounds is increased in lettuce grown under high light intensity and elevated CO2. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry-Ryan, C.; O’Beirne, D. Ascorbic acid retention in shredded iceberg lettuce as affected by minimal processing. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonasia, A.; Lazzizera, C.; Elia, A.; Conversa, G. Nutritional, biophysical and physiological characteristics of wild rocket genotypes as affected by soilless cultivation system, salinity level of nutrient solution and growing period. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viacava, G.E.; Goyeneche, R.; Goñi, M.G.; Roura, S.I.; Agüero, M.V. Natural elicitors as preharvest treatments to improve postharvest quality of Butterhead lettuce. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 228, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampholo, B.M.; Maboko, M.M.; Soundy, P.; Sivakumar, D. Phytochemicals and overall quality of leafy lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) varieties grown in closed hydroponic system. J. Food Qual. 2016, 39, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceccanti, C.; Landi, M.; Rocchetti, G.; Miras Moreno, M.B.; Lucini, L.; Incrocci, L.; Pardossi, A.; Guidi, L. Hydroponically Grown Sanguisorba minor Scop.: Effects of Cut and Storage on Fresh-Cut Produce. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120631
Ceccanti C, Landi M, Rocchetti G, Miras Moreno MB, Lucini L, Incrocci L, Pardossi A, Guidi L. Hydroponically Grown Sanguisorba minor Scop.: Effects of Cut and Storage on Fresh-Cut Produce. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(12):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120631
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeccanti, Costanza, Marco Landi, Gabriele Rocchetti, Maria Begoña Miras Moreno, Luigi Lucini, Luca Incrocci, Alberto Pardossi, and Lucia Guidi. 2019. "Hydroponically Grown Sanguisorba minor Scop.: Effects of Cut and Storage on Fresh-Cut Produce" Antioxidants 8, no. 12: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120631
APA StyleCeccanti, C., Landi, M., Rocchetti, G., Miras Moreno, M. B., Lucini, L., Incrocci, L., Pardossi, A., & Guidi, L. (2019). Hydroponically Grown Sanguisorba minor Scop.: Effects of Cut and Storage on Fresh-Cut Produce. Antioxidants, 8(12), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120631











