Myeloid GRK2 Regulates Obesity-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Modulating Inflammatory Responses in Perivascular Adipose Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Animal Experimental Design
2.3. Vascular Reactivity Studies
2.4. RNA Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. GRK2 Expression Positively Correlates with Myeloid and Lymphoid Markers and Leptin in Perivascular Adipose Tissue from Patients with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
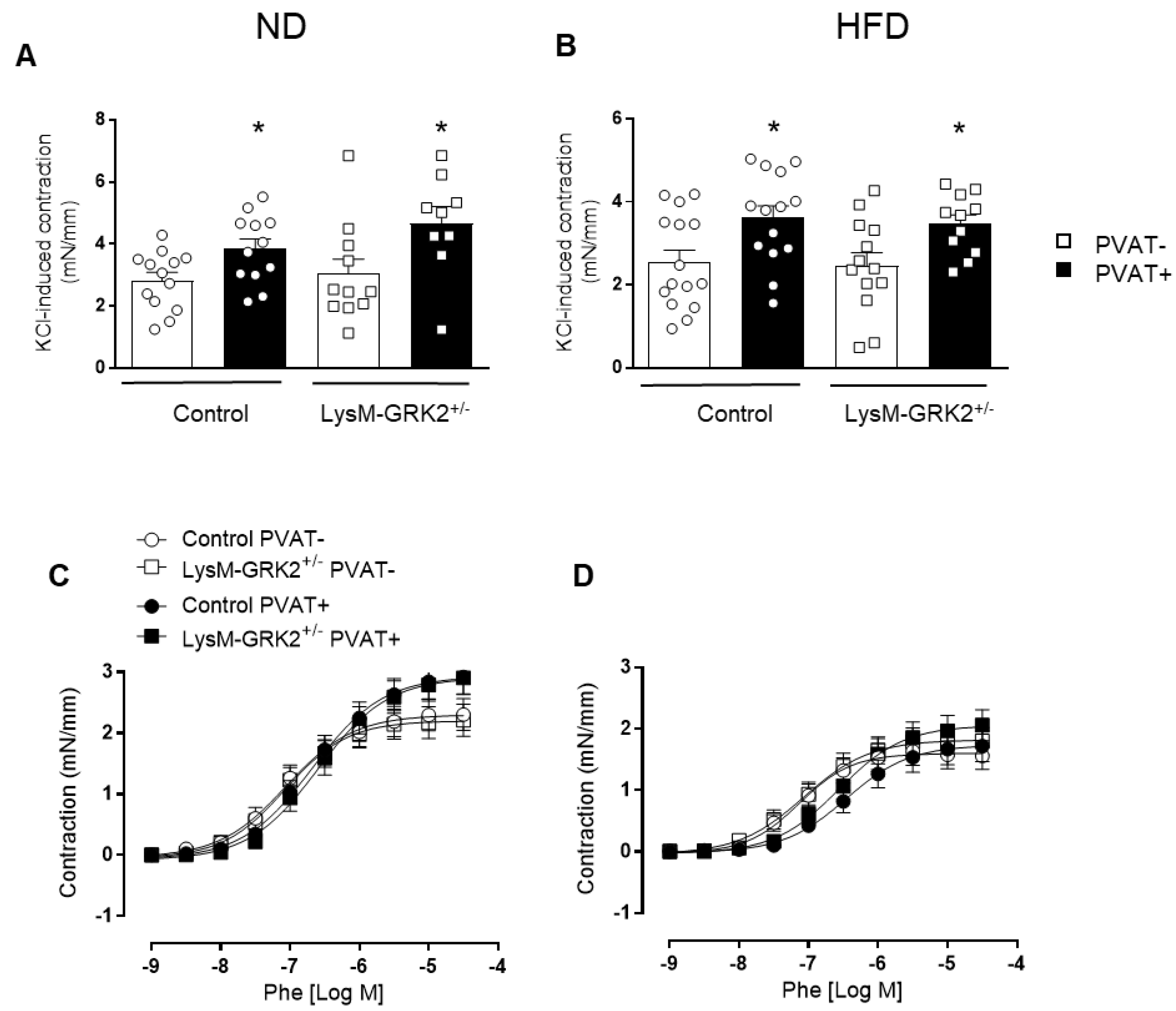
3.2. GRK2 Downregulation in Myeloid Cells Preserves Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation in Arteries with PVAT from Obese Animals
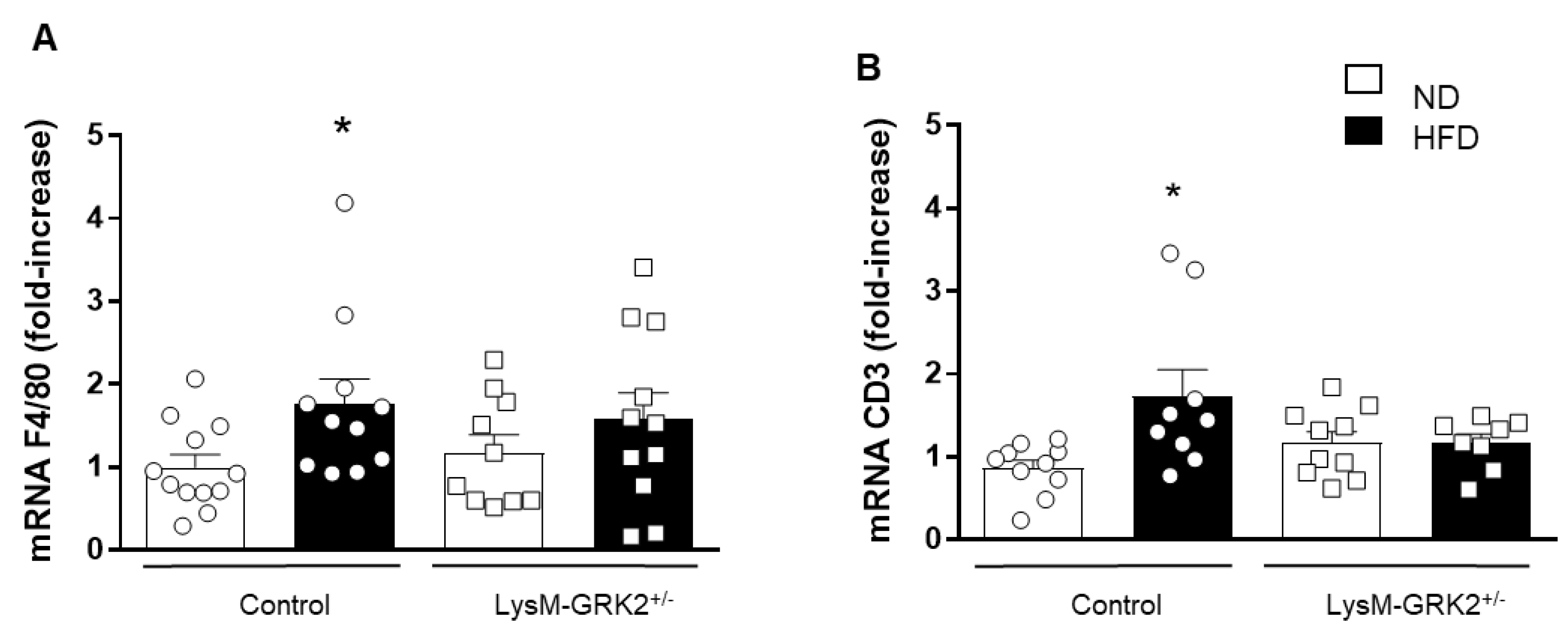
3.3. GRK2 Deficiency in Myeloid Cells Prevents Infiltration of Immune Cells and Upregulation of TNFα and Nox1 in PVAT from Obese Animals and Blockade of These Pathways Rescues Vasodilator Responses to Insulin in Arteries with PVAT from HFD-Fed Animals
3.4. The Expression of TNFα in PVAT from Patients with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Positively Correlates with Obesity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Redondo, A.B.; Esteban, V.; Briones, A.M.; Díaz del Campo, L.S.; González-Amor, M.; Méndez-Barbero, N.; Campanero, M.R.; Redondo, J.M.; Salaices, M. Regulator of calcineurin 1 modulates vascular contractility and stiffness through the upregulation of COX-2-derived prostanoids. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 133, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avendaño, M.S.; García-Redondo, A.B.; Zalba, G.; González-Amor, M.; Aguado, A.; Martínez-Revelles, S.; Beltrán, L.M.; Camacho, M.; Cachofeiro, V.; Alonso, M.J.; et al. mPGES-1 (Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1) Mediates Vascular Dysfunction in Hypertension Through Oxidative Stress. Hypertension 2018, 72, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agabiti-Rosei, C.; Paini, A.; De Ciuceis, C.; Withers, S.; Greenstein, A.; Heagerty, A.M.; Rizzoni, D. Modulation of Vascular Reactivity by Perivascular Adipose Tissue (PVAT). Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.G.; O’Malley, E.J.; Ho, W.S.V. Pro-contractile effects of perivascular fat in health and disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 3482–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang Cao, Z.F.; Stoffel, E.; Cohen, P. Role of Perivascular Adipose Tissue in Vascular Physiology and Pathology. Hypertension 2017, 69, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Duranti, E.; Rossi, C.; Dell’Agnello, U.; Santini, E.; Anselmino, M.; Chiarugi, M.; Taddei, S.; Solini, A. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha participates on the endothelin-1/nitric oxide imbalance in small arteries from obese patients: Role of perivascular adipose tissue. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gustafson, B.; Hammarstedt, A.; Andersson, C.X.; Smith, U. Inflamed Adipose Tissue. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2276–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Alfonso, M.S.; Somoza, B.; Tsvetkov, D.; Kuczmanski, A.; Dashwood, M.; Gil-Ortega, M. Role of Perivascular Adipose Tissue in Health and Disease. In Comprehensive Physiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 23–59. [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein, A.S.; Khavandi, K.; Withers, S.B.; Sonoyama, K.; Clancy, O.; Jeziorska, M.; Laing, I.; Yates, A.P.; Pemberton, P.W.; Malik, R.A.; et al. Local Inflammation and Hypoxia Abolish the Protective Anticontractile Properties of Perivascular Fat in Obese Patients. Circulation 2009, 119, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghamohammadzadeh, R.; Greenstein, A.S.; Yadav, R.; Jeziorska, M.; Hama, S.; Soltani, F.; Pemberton, P.W.; Ammori, B.; Malik, R.A.; Soran, H.; et al. Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Human Small Artery Function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateri, D.L.; Moorleghen, J.J.; Balakrishnan, A.; Owens, A.P.; Howatt, D.A.; Subramanian, V.; Poduri, A.; Charnigo, R.; Cassis, L.A.; Daugherty, A. Endothelial Cell–Specific Deficiency of Ang II Type 1a Receptors Attenuates Ang II–Induced Ascending Aortic Aneurysms in LDL Receptor −/− Mice. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milewicz, D.M.; Trybus, K.M.; Guo, D.; Sweeney, H.L.; Regalado, E.; Kamm, K.; Stull, J.T. Altered Smooth Muscle Cell Force Generation as a Driver of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Ren, P.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, G.; Xie, W.; Lloyd, E.E.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Curci, J.A.; et al. NLRP3 (Nucleotide Oligomerization Domain–Like Receptor Family, Pyrin Domain Containing 3)–Caspase-1 Inflammasome Degrades Contractile Proteins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siasos, G.; Mourouzis, K.; Oikonomou, E.; Tsalamandris, S.; Tsigkou, V.; Vlasis, K.; Vavuranakis, M.; Zografos, T.; Dimitropoulos, S.; Papaioannou, T.; et al. The Role of Endothelial Dysfunction in Aortic Aneurysms. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 4016–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor, F., Jr.; Lucas, E.; Jurado-Pueyo, M.; Garcia-Guerra, L.; Nieto-Vazquez, I.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Fernandez-Veledo, S.; Murga, C. G Protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2): A novel modulator of insulin resistance. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 117, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murga, C.; Arcones, A.C.; Cruces-Sande, M.; Briones, A.M.; Salaices, M.; Mayor, F., Jr. G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 (GRK2) as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avendano, M.S.; Lucas, E.; Jurado-Pueyo, M.; Martinez-Revelles, S.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Salaices, M.; Briones, A.M.; Murga, C.; Avendaño, M.S.; et al. Increased nitric oxide bioavailability in adult GRK2 hemizygous mice protects against angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Hypertension 2014, 63, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anis, Y.; Leshem, O.; Reuveni, H.; Wexler, I.; Ben Sasson, R.; Yahalom, B.; Laster, M.; Raz, I.; Ben Sasson, S.; Shafrir, E.; et al. Antidiabetic effect of novel modulating peptides of G-protein-coupled kinase in experimental models of diabetes. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vila-Bedmar, R.; Cruces-Sande, M.; Lucas, E.; Willemen, H.L.D.M.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Murga, C.; Jr, F.M.; Murga, C. Reversal of diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance by inducible genetic ablation of GRK2. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, E.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Arcones, A.C.; Cruces-Sande, M.; Cachofeiro, V.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Murga, C. Obesity-induced cardiac lipid accumulation in adult mice is modulated by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 levels. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruces-Sande, M.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Arcones, A.C.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.; Rada, P.; Gutierrez-de-Juan, V.; Vargas-Castrillon, J.; Iruzubieta, P.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, C.; Formentini, L.; et al. Involvement of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) in the development of non-alcoholic steatosis and steatohepatitis in mice and humans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3655–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroon, A.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. GRKs and arrestins: Regulators of migration and inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vila-Bedmar, R.; Cruces-Sande, M.; Arcones, A.C.; Willemen, H.L.D.M.; Prieto, P.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Díaz-Rodríguez, D.; Francisco, S.; Jaén, R.I.; Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; et al. GRK2 levels in myeloid cells modulate adipose-liver crosstalk in high fat diet-induced obesity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagan, A.; Mikolajczyk, T.P.; Mrowiecki, W.; MacRitchie, N.; Daly, K.; Meldrum, A.; Migliarino, S.; Delles, C.; Urbanski, K.; Filip, G.; et al. T Cells Are Dominant Population in Human Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Their Infiltration in the Perivascular Tissue Correlates With Disease Severity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, T.K.; Stoll, L.L.; Denning, G.M.; Harrelson, A.; Blomkalns, A.L.; Idelman, G.; Rothenberg, F.G.; Neltner, B.; Romig-Martin, S.A.; Dickson, E.W.; et al. Proinflammatory Phenotype of Perivascular Adipocytes. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucas, E.; Cruces-Sande, M.; Briones, A.M.; Salaices, M.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Murga, C.; Vila-Bedmar, R. Molecular physiopathology of obesity-related diseases: Multi-organ integration by GRK2. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 121, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taguchi, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Kobayashi, T. G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and endothelial dysfunction: Molecular insights and pathophysiological mechanisms. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2015, 51, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Takemori, K.; Su, L.; An, W.; Lu, C.; Sharma, A.; Lee, R. Perivascular adipose tissue promotes vasoconstriction: The role of superoxide anion. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 71, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landecho, M.F.; Tuero, C.; Valentí, V.; Bilbao, I.; de la Higuera, M.; Frühbeck, G. Relevance of Leptin and Other Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular Risk. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Withers, S.B.; Agabiti-Rosei, C.; Livingstone, D.M.; Little, M.C.; Aslam, R.; Malik, R.A.; Heagerty, A.M. Macrophage Activation Is Responsible for Loss of Anticontractile Function in Inflamed Perivascular Fat. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Hou, N.; Han, F.; Guo, Y.; Hui, Z.; Du, G.; Zhang, Y. Effect of high free fatty acids on the anti-contractile response of perivascular adipose tissue in rat aorta. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 63, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-J.; Holloway, A.C.; Su, L.-Y.; Takemori, K.; Lu, C.; Lee, R.M.K.W. Effects of fetal and neonatal exposure to nicotine on blood pressure and perivascular adipose tissue function in adult life. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 590, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketonen, J.; Shi, J.; Martonen, E.; Mervaala, E. Periadventitial Adipose Tissue Promotes Endothelial Dysfunction via Oxidative Stress in Diet-Induced Obese C57Bl/6 Mice. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theccanat, T.; Philip, J.L.; Razzaque, A.M.; Ludmer, N.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Akhter, S.A. Regulation of cellular oxidative stress and apoptosis by G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2; The role of NADPH oxidase 4. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aghamohammadzadeh, R.; Unwin, R.D.; Greenstein, A.S.; Heagerty, A.M. Effects of Obesity on Perivascular Adipose Tissue Vasorelaxant Function: Nitric Oxide, Inflammation and Elevated Systemic Blood Pressure. J. Vasc. Res. 2015, 52, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Clinical and Laboratory Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Gender (M/F) | 39/3 |
| Age (Years) | 70.32 ± 1.122 |
| Body weight (Kg) | 85.8 ± 2.257 |
| Height | 1.711 ± 0.011 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 29.31 ± 0.756 |
| Abdominal perimeter (cm) | 109 ± 2.01 |
| Smoking (no/yes/ex) | 4/15/24 |
| Diabetes mellitus (yes/total) | 10/42 |
| Hypertension (yes/total) | 29/42 |
| Hyperlipidemia (yes/total) | 26/42 |
| * Cardiopathies (yes/total) | 19/42 |
| CKD | 12/42 |
| COPD | 13/42 |
| Medication | |
| Antihypertensive | 29/39 (74%) |
| Lipid lowering drugs | 30/39 (77%) |
| Antidiabetic | 9/39 (23%) |
| Antiaggregant | 22/39 (56%) |
| Anticoagulant | 7/39 (18%) |
| Beta blockers | 14/39 (36%) |
| GENE NAME | NCBI Seq | Forward Sequence | Reverse Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mice | |||
| Tnfa | NM_013693 | 5′CCACGCTCTTCTGTCTACTG | 5′TGAGGGTCTGGGCCATAGA |
| Nox1 | NM_172203 | 5′CAACAGCACTCACCAATGCC | 5′ACATCCTCACTGACTGTGCC |
| Il6 | NM_031168 | 5′TGATGGATGCTACCAAACTGG | 5′TTCATGTACTCCAGGTAGCTATGG |
| Ptges | NM_022415 | 5′AGGATGCGCTGAAACGTGGAG | 5′CCGAGGAAGAGGAAAGGATAG |
| Adipoq | NM_009605 | 5′TGATGGCAGAGATGGCACTC | 5′CTGTCTCACCCTTAGGACCA |
| Adgre1 (F4/80) | NM_001256252 | 5′GTTCAGGGCAAACGTCTCG | 5′TGCTCTAACTCTGTGGGAAGC |
| Cd3 | NM_007648 | 5′TATGGCTACTGCTGTCAGGT | 5′TGGCTACTACGTCTGCTACA |
| B2m | NM_009735 | 5′ACCCTGGTCTTTCTGGTGCTT | 5′TAGCAGTTCAGTATGTTCGGCTT |
| Human | |||
| ACTB (β-actin) | NM_009735 | 5′-AGAGCTACGAGCTGCCTGAC | 5′-AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG |
| CD68 | NM_001101 | 5′-TAGCTGGACTTTGGGTGAGG | 5′-CCAGTGCTCTCTGCCAGTA |
| CD3 | NM_001040059 | 5′-TCTACCAGCCCCTCAAGGAT | 5′-AGGAGGAGAACACCTGGACTA |
| CD4 | NM_000073 | Hs00181217 | |
| CD8a | NM_000616.4 | Hs00233520 | |
| GRK2 | NM_001145873 | Hs00176395_m1 | |
| TNFa | NM_001619 | Hs.PT.58.45380900 | |
| NOX5 | NM_024505 | Hs00225846_m1 | |
| RNA18S1 | 106632259 | 4310893E | |
| Parameter | BMI | Ab. Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| BMI | - | p = 0.001 * |
| Ab. Perimeter | p = 0.001 * | - |
| CD68 | p = 0.33 | p = 0.57 |
| CD3 | p = 0.41 | p = 0.32 |
| CD4 | p = 0.46 | p = 0.07 |
| CD8 | p = 0.53 | p = 0.24 |
| TNFα | p = 0.02 * | p = 0.06 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Amor, M.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Rodrigues-Díez, R.; Moreno-Carriles, R.; Arcones, A.C.; Cruces-Sande, M.; Salaices, M.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Briones, A.M.; Murga, C. Myeloid GRK2 Regulates Obesity-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Modulating Inflammatory Responses in Perivascular Adipose Tissue. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100953
González-Amor M, Vila-Bedmar R, Rodrigues-Díez R, Moreno-Carriles R, Arcones AC, Cruces-Sande M, Salaices M, Mayor F Jr., Briones AM, Murga C. Myeloid GRK2 Regulates Obesity-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Modulating Inflammatory Responses in Perivascular Adipose Tissue. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(10):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100953
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Amor, María, Rocío Vila-Bedmar, Raquel Rodrigues-Díez, Rosa Moreno-Carriles, Alba C. Arcones, Marta Cruces-Sande, Mercedes Salaices, Federico Mayor, Jr., Ana M. Briones, and Cristina Murga. 2020. "Myeloid GRK2 Regulates Obesity-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Modulating Inflammatory Responses in Perivascular Adipose Tissue" Antioxidants 9, no. 10: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100953
APA StyleGonzález-Amor, M., Vila-Bedmar, R., Rodrigues-Díez, R., Moreno-Carriles, R., Arcones, A. C., Cruces-Sande, M., Salaices, M., Mayor, F., Jr., Briones, A. M., & Murga, C. (2020). Myeloid GRK2 Regulates Obesity-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Modulating Inflammatory Responses in Perivascular Adipose Tissue. Antioxidants, 9(10), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100953








