Radical Scavenging Activity of Olive Oil Phenolic Antioxidants in Oil or Water Phase during the Oxidation of O/W Emulsions: An Oxidomics Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Emulsions Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Oxidative Stability of O/W Emulsions
2.4. Accelerated Oxidation of O/W Emulsions
2.5. Total Phenolic Content
2.6. Antiradical Activity
2.7. Lipid Hydroperoxides
2.8. FTIR Analysis
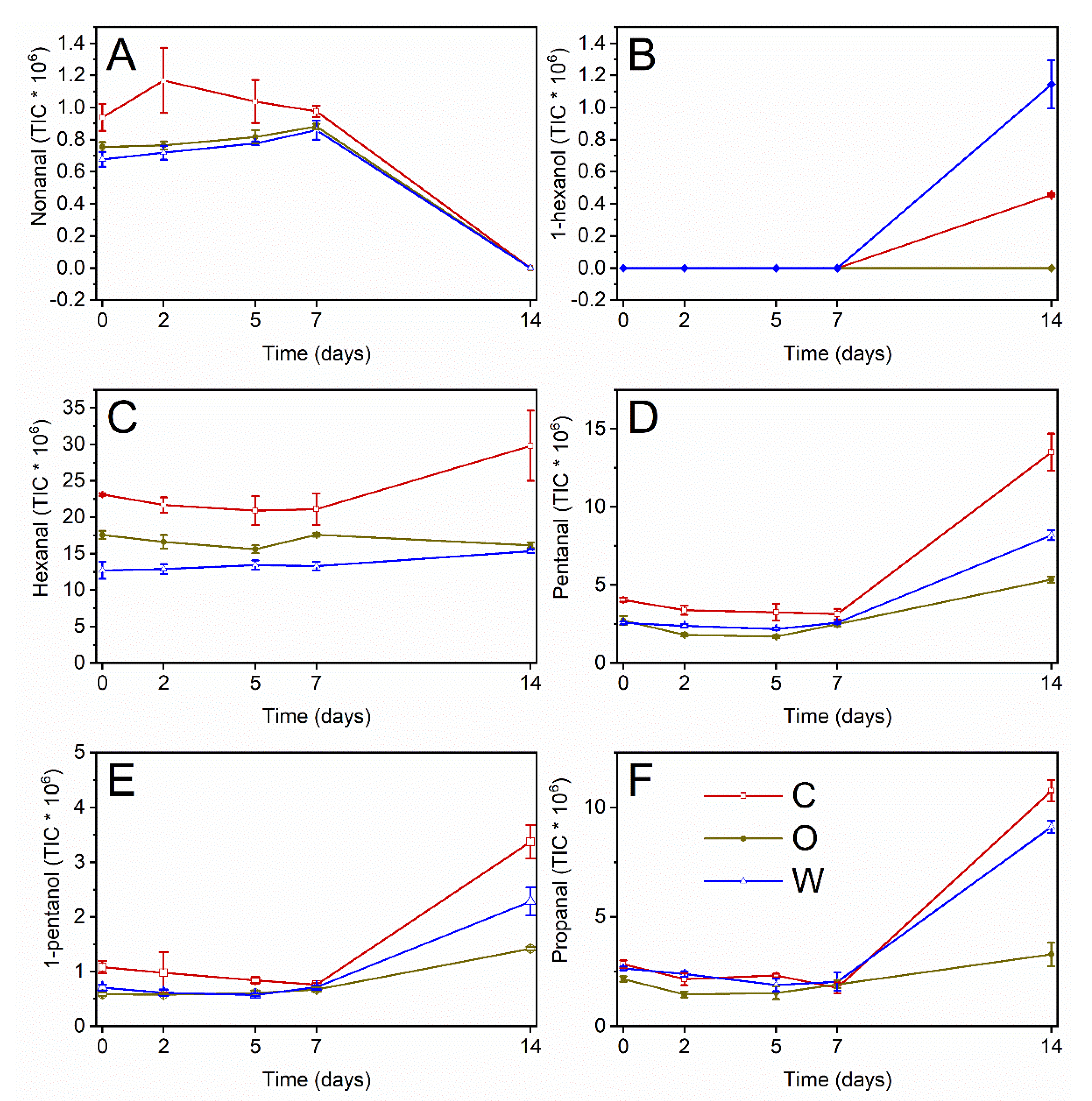
2.9. Volatile Compounds Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
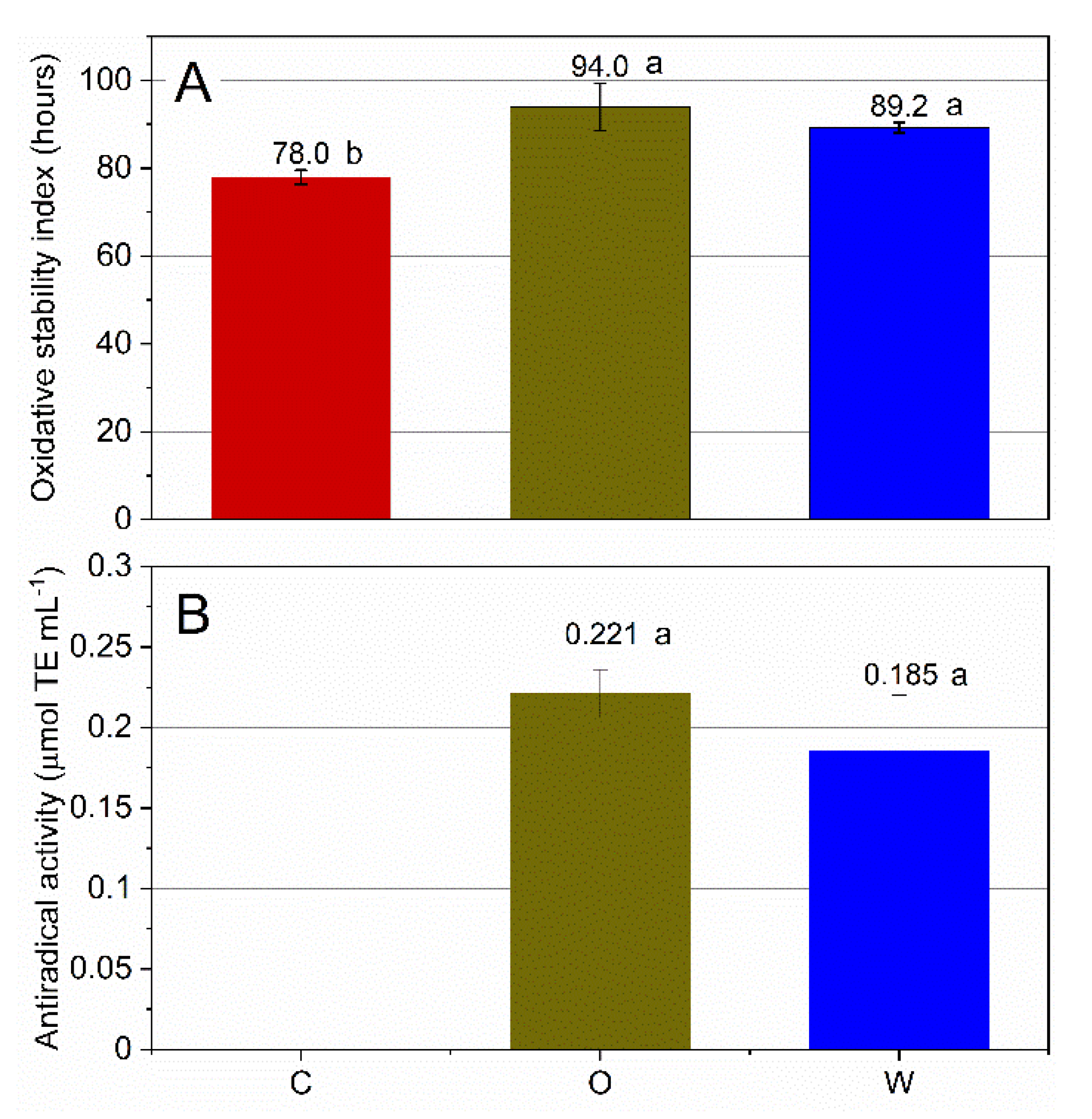
3.1. Oxidative Stability
3.2. Hydroperoxides
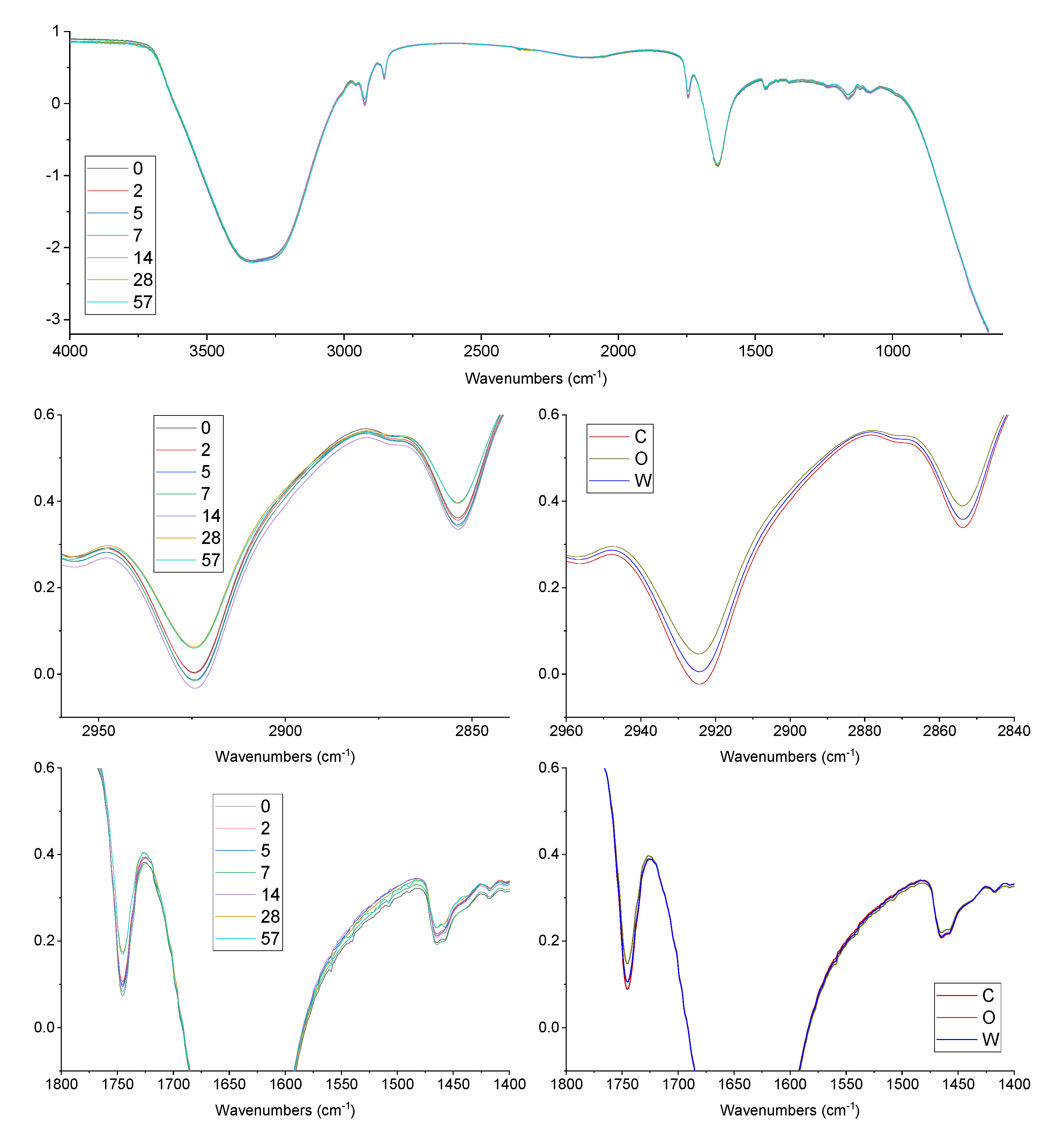
3.3. FTIR Oxidation Features
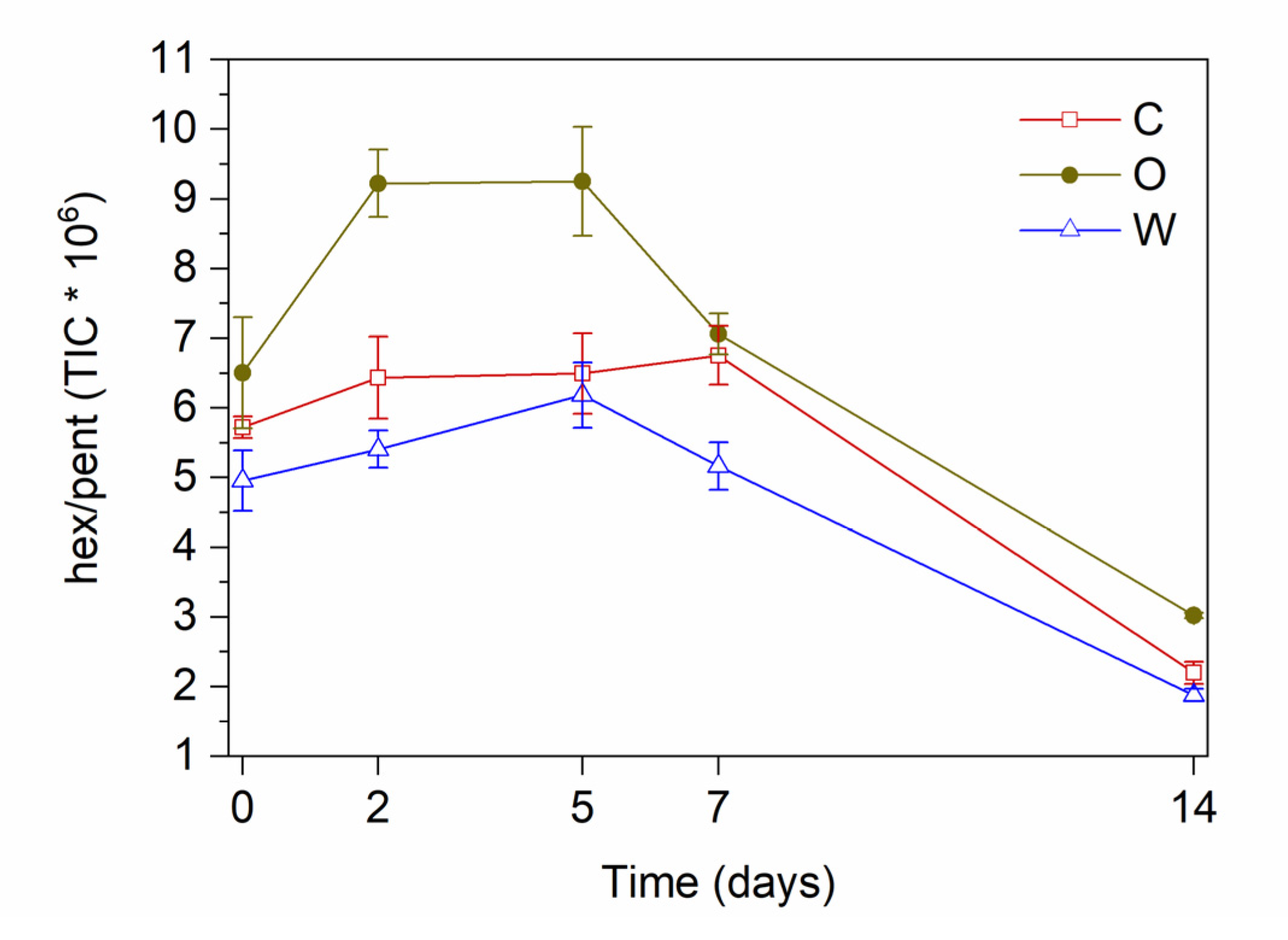
3.4. Focus on the Hydroperoxide Decay Phase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Ropers, M.-H.; Genot, C. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Involvement of the Interfacial Layer. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 945–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Revisiting the polar paradox theory: A critical overview. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3499–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, W.L. Recent Trends in Food Applications of Antioxidants. In Autoxidation in Food and Biological Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 295–365. ISBN 978-1-4757-9351-2. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Durand, E.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Hurdles in Predicting Antioxidant Efficacy in Oil-in-water emulsions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüneis, V.; Fruehwirth, S.; Zehl, M.; Ortner, J.; Schamann, A.; König, J.; Pignitter, M. Simultaneous Analysis of Epoxidized and Hydroperoxidized Triacylglycerols in Canola Oil and Margarine by LC-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10174–10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüneis, V.; Pignitter, M. Epoxide Value—A Novel Marker for the Quality Assessment of Food Lipids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5039–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignitter, M.; Zaunschirm, M.; Lach, J.; Unterberger, L.; Kopic, A.; Keßler, C.; Kienesberger, J.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Riegger, C.; et al. Regioisomeric distribution of 9- and 13-hydroperoxy linoleic acid in vegetable oils during storage and heating. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Pasqualone, A.; Summo, C.; Caponio, F. Everything Should Be as Simple as It Can Be. But Not Simpler. Does Food Lipid Oxidation Require an Omics Approach? Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1800103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, P.; Durand, E.; Decker, E.A. The Need for a New Step in the Study of Lipid Oxidation in Heterophasic Systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8433–8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguerre, M.; Tenon, M.; Bily, A.; Birtić, S. Toward a Spatiotemporal Model of Oxidation in Lipid Dispersions: A Hypothesis-Driven Review. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Pasqualone, A.; Summo, C.; Caponio, F. An “Omics” Approach for Lipid Oxidation in Foods: The Case of Free Fatty Acids in Bulk Purified Olive Oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1800102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Cortés, P.; Camiña, J.M. Oxidomics on the omega-3 volatile degradation pattern to determine differences between vegetable and marine oils. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro-Sierra, J.; Tolkach, A.; Kulozik, U. Fractionation of α-Lactalbumin and β-Lactoglobulin from Whey Protein Isolate Using Selective Thermal Aggregation, an Optimized Membrane Separation Procedure and Resolubilization Techniques at Pilot Plant Scale. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Olive Council. COI/T.20/Doc No 29—Determination of Biophenols in Olive Oils by HPLC; International Olive Council: Madrid, Spain, 2009.
- Reboredo-Rodríguez, P.; Valli, E.; Bendini, A.; Di Lecce, G.; Simal-Gándara, J.; Gallina Toschi, T. A widely used spectrophotometric assay to quantify olive oil biophenols according to the health claim (EU Reg. 432/2012). Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A., Jr.; Rossi, J.A., Jr. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantha, N.C.; Decker, E.A. Rapid, sensitive, iron-based spectrophotometric methods for determination of peroxide values of food lipids. J. AOAC Int. 1994, 77, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mattia, C.D.; Paradiso, V.M.; Andrich, L.; Giarnetti, M.; Caponio, F.; Pittia, P. Effect of Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds and Maltodextrins on the Physical Properties and Oxidative Stability of Olive Oil O/W Emulsions. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciutelli, M.; Marconi, S.; Boarelli, M.C.; Caprioli, G.; Sagratini, G.; Ballini, R.; Fiorini, D. Olive oil polyphenols: A quantitative method by high-performance liquid-chromatography-diode-array detection for their determination and the assessment of the related health claim. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1481, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellumori, M.; Cecchi, L.; Innocenti, M.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Corbo, F.; Mulinacci, N. The EFSA health claim on olive oil polyphenols: Acid hydrolysis validation and total hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol determination in Italian virgin olive oils. Molecules 2019, 24, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaver, J.; Law, A.J.R.; Brechany, E.Y.; McCrae, C.H. Chemical changes in β-lactoglobulin structure during ageing of protein-stabilized emulsions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 34, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaver, J.; Law, A.J.R.; Brechany, E.Y. Covalent modification of emulsified β-casein resulting from lipid peroxidation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 210, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal-Eldin, A. Lipid Oxidation Pathways; Kamal-Eldin, A., Ed.; AOCS Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-893997-43-1. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, A.F.; Nielsen, N.S.; Jensen, L.S.; Horsewell, A.; Jacobsen, C. The choice of homogenisation equipment affects lipid oxidation in emulsions. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.K. A Simple Method of Fitting the Regression Curve y = α+ δx + βρ x. Biometrics 1961, 17, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragao, G.M.F.; Corradini, M.G.; Peleg, M. A phenomenological model of the peroxide value’s rise and fall during lipid oxidation. JAOCS, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, N.; Skopelitis, Y.; Psaroudaki, M.; Konstantinidou, V.; Chatzilazarou, A.; Tegou, E. Applications of Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy to edible oils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573–574, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, I.N.; Man, Y.B.C.; Tan, C.P.; Aini, I.N. Monitoring peroxide value in oxidized emulsions by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2005, 107, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, S.; Bou-maroun, E.; Dujourdy, L.; Waschatko, G.; Billecke, N.; Cayot, P. Fast and direct analysis of oxidation levels of oil-in-water emulsions using ATR-FTIR. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forss, D.A. Odor and flavor compounds from lipids. In Progress in the Chemistry of Fats and Other Lipids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1973; Volume 13, pp. 177–258. ISBN 0079-6832. [Google Scholar]
- Schaich, K.M. Lipid Oxidation: Theoretical Aspects. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 269–355. ISBN 9780471678496. [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Di Mattia, C.; Giarnetti, M.; Chiarini, M.; Andrich, L.; Caponio, F. Antioxidant Behavior of Olive Phenolics in Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5877–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynier, A.; Rampon, V.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Genot, C. Hexanal and t-2-hexenal form covalent bonds with whey proteins and sodium caseinate in aqueous solution. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, O.; Leus, M.; Everett, D.W. Static headspace analysis of volatile compounds released from β-lactoglobulin-stabilized emulsions determined by the phase ratio variation method. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavel, L.; Andriot, I.; Moreau, C.; Guichard, E. Interactions between β-lactoglobulin and aroma compounds: Different binding behaviors as a function of ligand structure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10208–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ruth, S.M.; King, C.; Delarue, M.; Giannouli, P. Release of volatile compounds from emulsions: Influence of β-lactoglobulin and pH. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2002, 14, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Guichard, E.; Langourieux, S. Interactions between β-lactoglobulin and flavour compounds. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuchi, C.D.; Hernandez, P.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Ability of Lipid Hydroperoxides To Partition into Surfactant Micelles and Alter Lipid Oxidation Rates in Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5445–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharasch, E.D.; Novak, R.F. Mitoxantrone and ametantrone inhibit hydroperoxide-dependent initiation and propagation reactions in fatty acid peroxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 10645–10652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Cerretani, L.; Bendini, A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Del Carlo, M.; Gallina-Toschi, T.; Lercker, G.; Compagnone, D.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of individual phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8918–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimi, H.; Cillard, J.; Cillard, P.; Rahmani, M. Peroxyl and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of some natural phenolic antioxidants. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1991, 68, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva-Martins, F.; Gordon, M.H. Effects of pH and ferric ions on the antioxidant activity of olive polyphenols in oil-in-water emulsions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Difonzo, G.; Pasqualone, A.; Silletti, R.; Cosmai, L.; Summo, C.; Paradiso, V.M.; Caponio, F. Use of olive leaf extract to reduce lipid oxidation of baked snacks. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
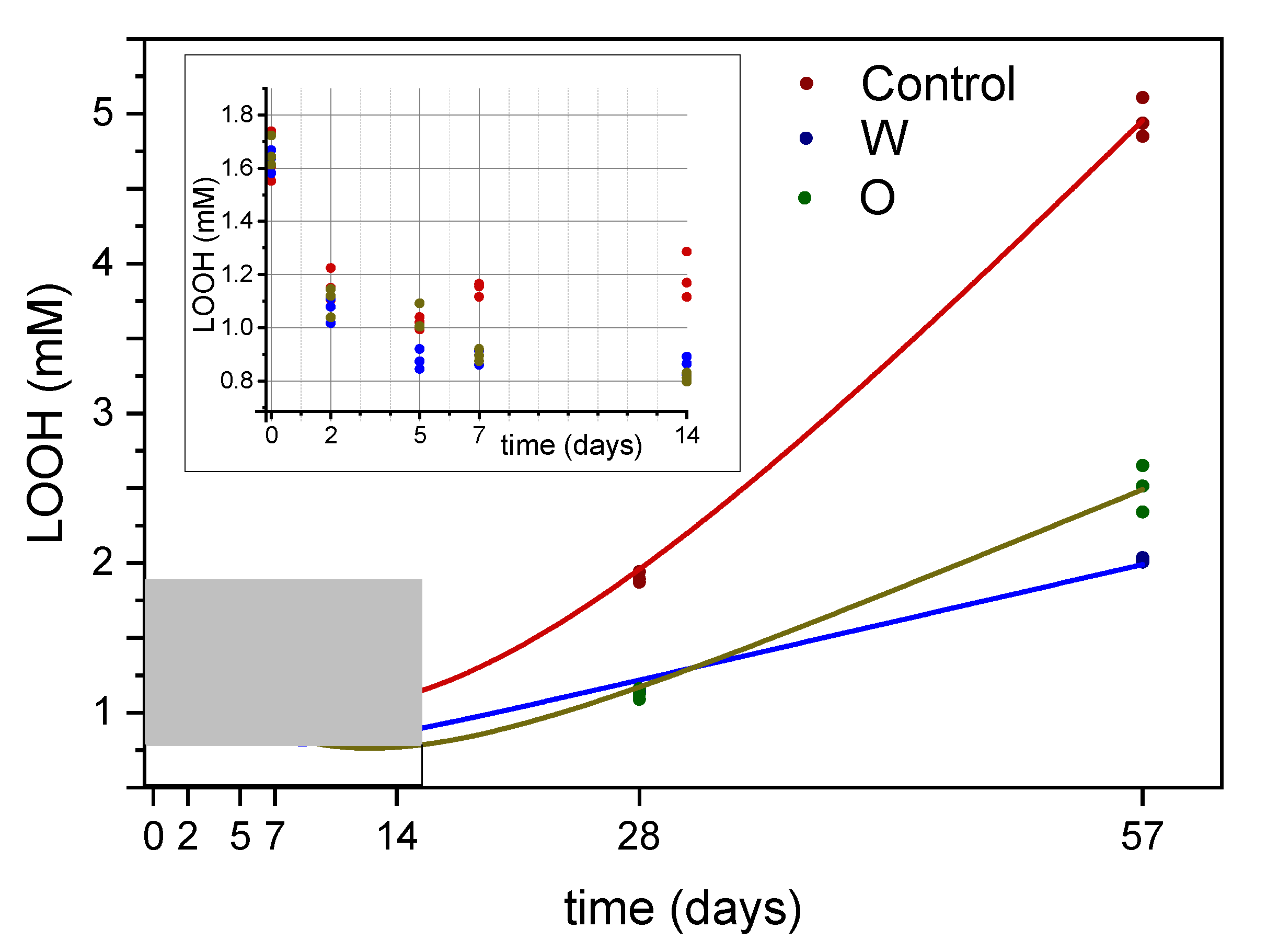

| a | b | c | r | x0 | y0 | Statistics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | S.E. | Value | S.E. | Value | S.E. | Value | S.E. | (days) | (mM) | Red χ2 | Adj. R2 | |
| Control 1 | −1.8437 | 0.65895 | 0.11807 | 0.01079 | 3.34719 | 0.63524 | 0.93408 | 0.01439 | 9.7 | 1.03 | 0.01714 | 0.99996 |
| O | −0.21181 | 0.18694 | 0.04738 | 0.00383 | 1.77902 | 0.18061 | 0.8843 | 0.0187 | 12.4 | 0.76 | 0.01199 | 0.99998 |
| W | 0.47324 | 0.05158 | 0.02661 | 0.00133 | 1.12255 | 0.0606 | 0.7466 | 0.02638 | 8.6 | 0.79 | 0.00464 | 0.99999 |
| Time (d) | Extract | Nonanal | 1-Hexanol | Hexanal | Pentanal | 1-Pentanol | Propanal | Hex/Pent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | A | B | A | A | A | A | B | |
| O | B | C | B | C | C | C | A | |
| W | B | A | C | B | B | B | C | |
| 0 | C | bcd | c | b | d | cd | cd | bcde |
| O | de | c | cde | efg | e | defgh | bcd | |
| W | e | c | f | efg | de | cde | e | |
| 2 | C | a | c | bc | de | cde | defgh | bcd |
| O | cde | c | def | g | e | h | a | |
| W | e | c | ef | efg | e | def | cde | |
| 5 | C | ab | c | bcd | def | de | defg | bcd |
| O | cde | c | ef | g | e | gh | a | |
| W | cde | c | ef | fg | e | efgh | bcde | |
| 7 | C | abc | c | bcd | def | de | fgh | bc |
| O | bcde | c | cde | efg | de | efgh | b | |
| W | bcde | c | ef | efg | de | defgh | de | |
| 14 | C | f | b | a | a | a | a | f |
| O | f | c | ef | c | c | c | f | |
| W | f | a | ef | b | b | b | F |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paradiso, V.M.; Flamminii, F.; Pittia, P.; Caponio, F.; Mattia, C.D. Radical Scavenging Activity of Olive Oil Phenolic Antioxidants in Oil or Water Phase during the Oxidation of O/W Emulsions: An Oxidomics Approach. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100996
Paradiso VM, Flamminii F, Pittia P, Caponio F, Mattia CD. Radical Scavenging Activity of Olive Oil Phenolic Antioxidants in Oil or Water Phase during the Oxidation of O/W Emulsions: An Oxidomics Approach. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(10):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100996
Chicago/Turabian StyleParadiso, Vito Michele, Federica Flamminii, Paola Pittia, Francesco Caponio, and Carla Di Mattia. 2020. "Radical Scavenging Activity of Olive Oil Phenolic Antioxidants in Oil or Water Phase during the Oxidation of O/W Emulsions: An Oxidomics Approach" Antioxidants 9, no. 10: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100996
APA StyleParadiso, V. M., Flamminii, F., Pittia, P., Caponio, F., & Mattia, C. D. (2020). Radical Scavenging Activity of Olive Oil Phenolic Antioxidants in Oil or Water Phase during the Oxidation of O/W Emulsions: An Oxidomics Approach. Antioxidants, 9(10), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100996








