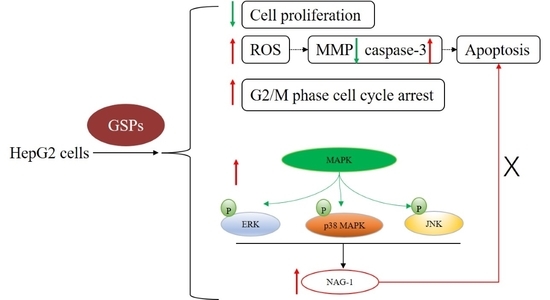
Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of HepG2 Cells Accompanied by Induction of the MAPK Pathway and NAG-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. MTT Assay for Cell Viability and Colony Formation Assay
2.4. Apoptosis Analysis Using Flow Cytometry
2.5. Determination of ROS Production
2.6. Measurement of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
2.7. Determination of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 Activity
2.8. Cell Cycle Analysis Using Flow Cytometry
2.9. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Plasmid and Transfection
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
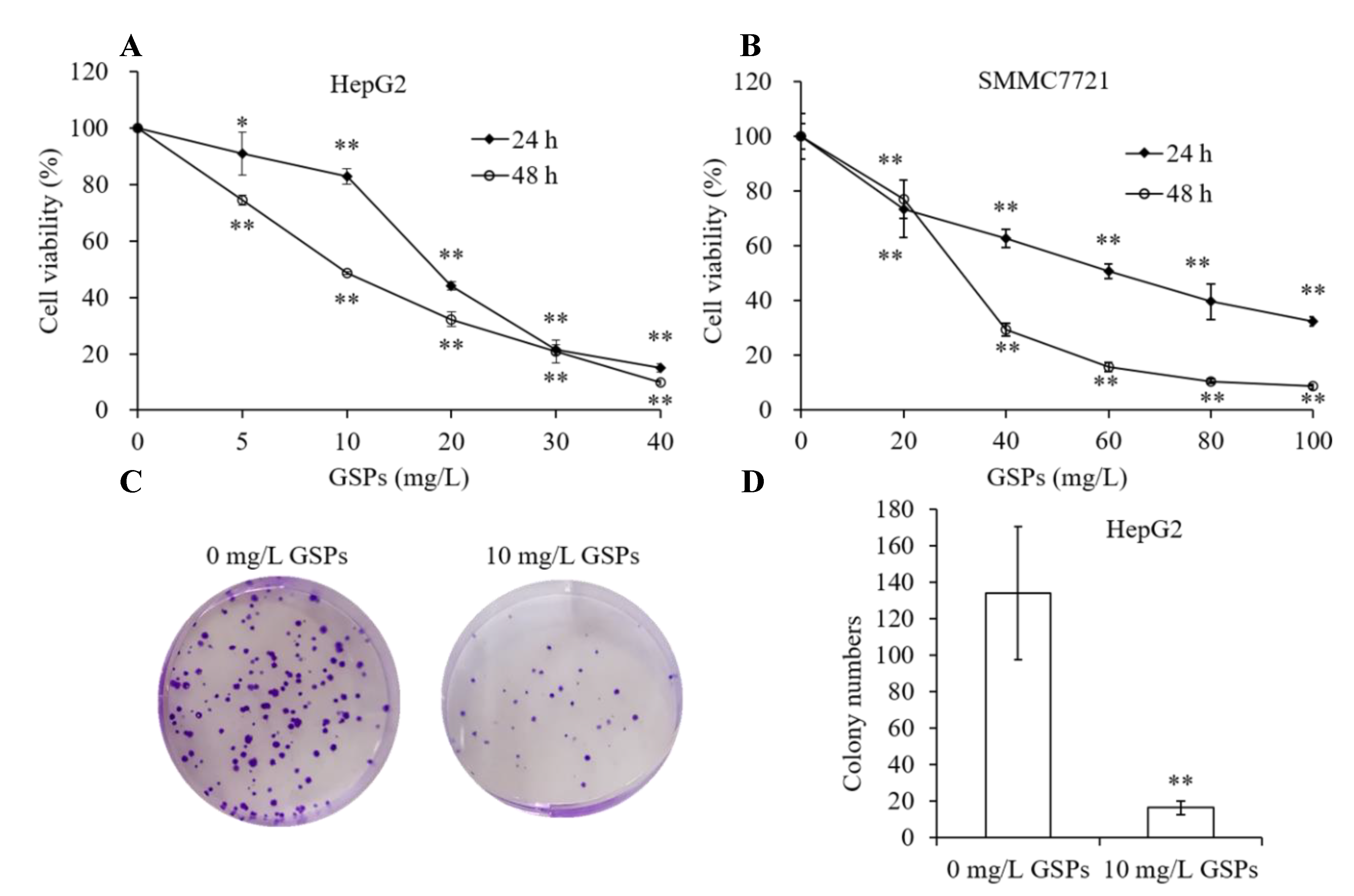
3.1. GSPs Inhibit Proliferation of HepG2 Cells
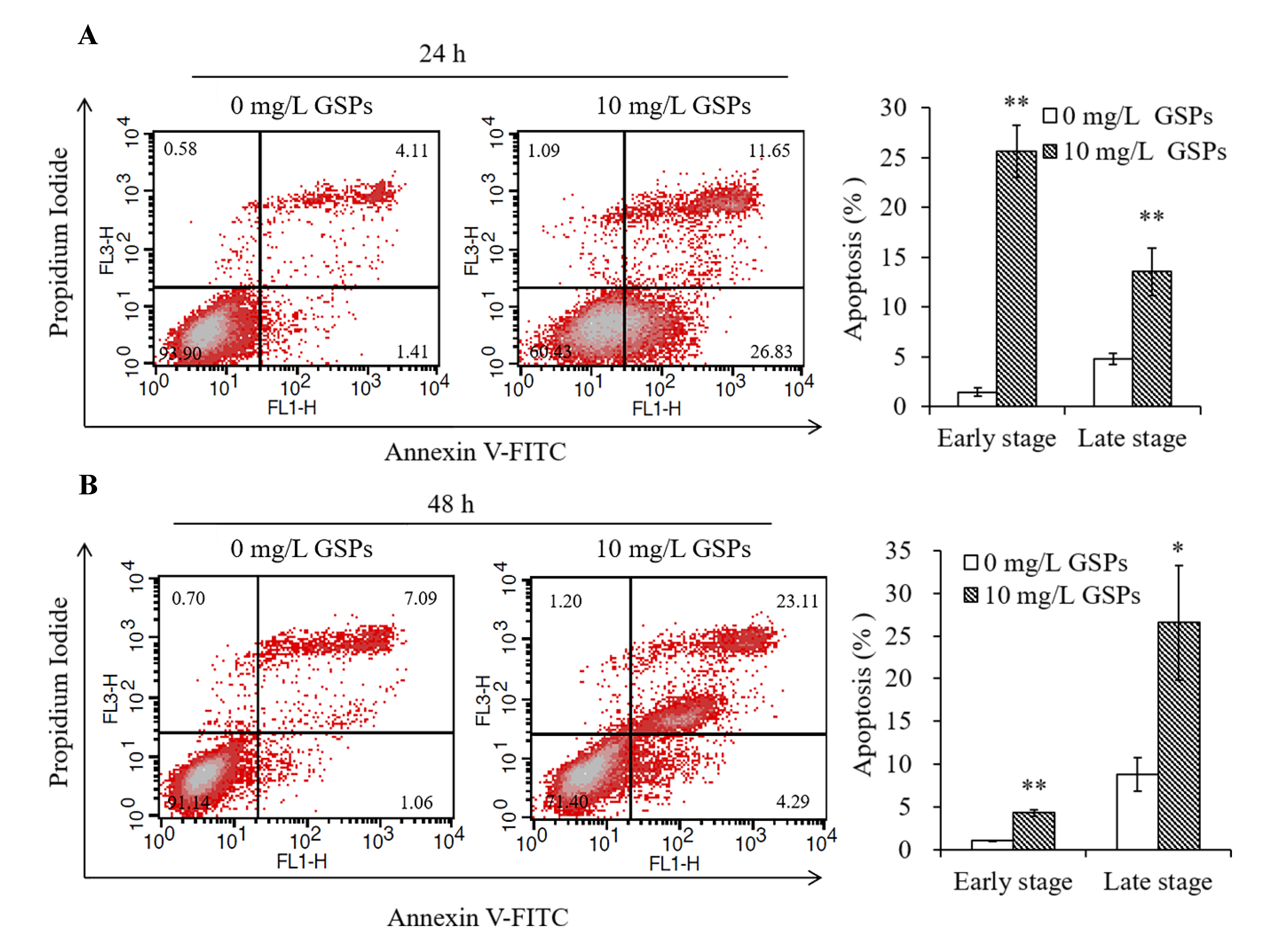
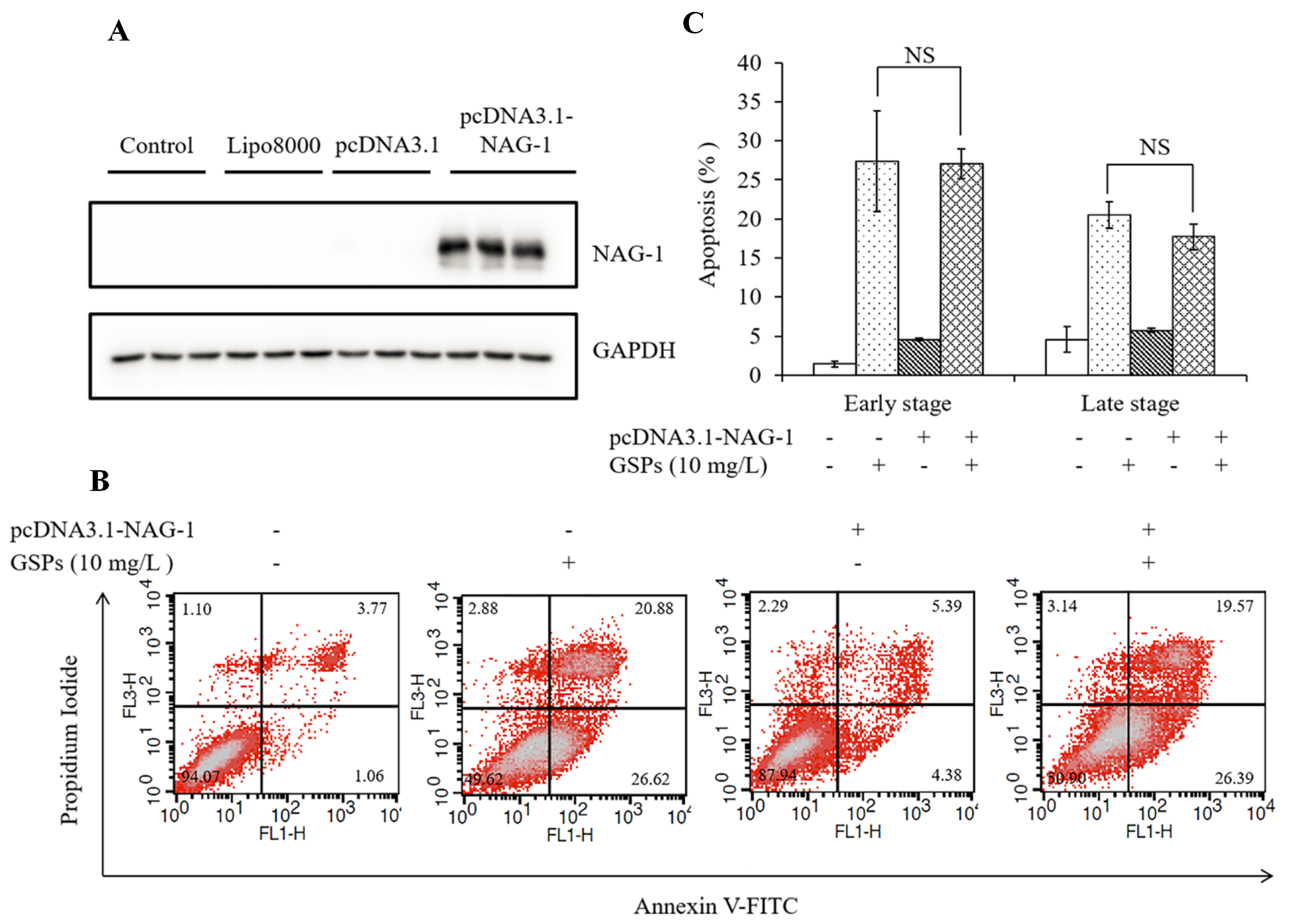
3.2. GSPs Induce the Apoptosis of HepG2 Cells
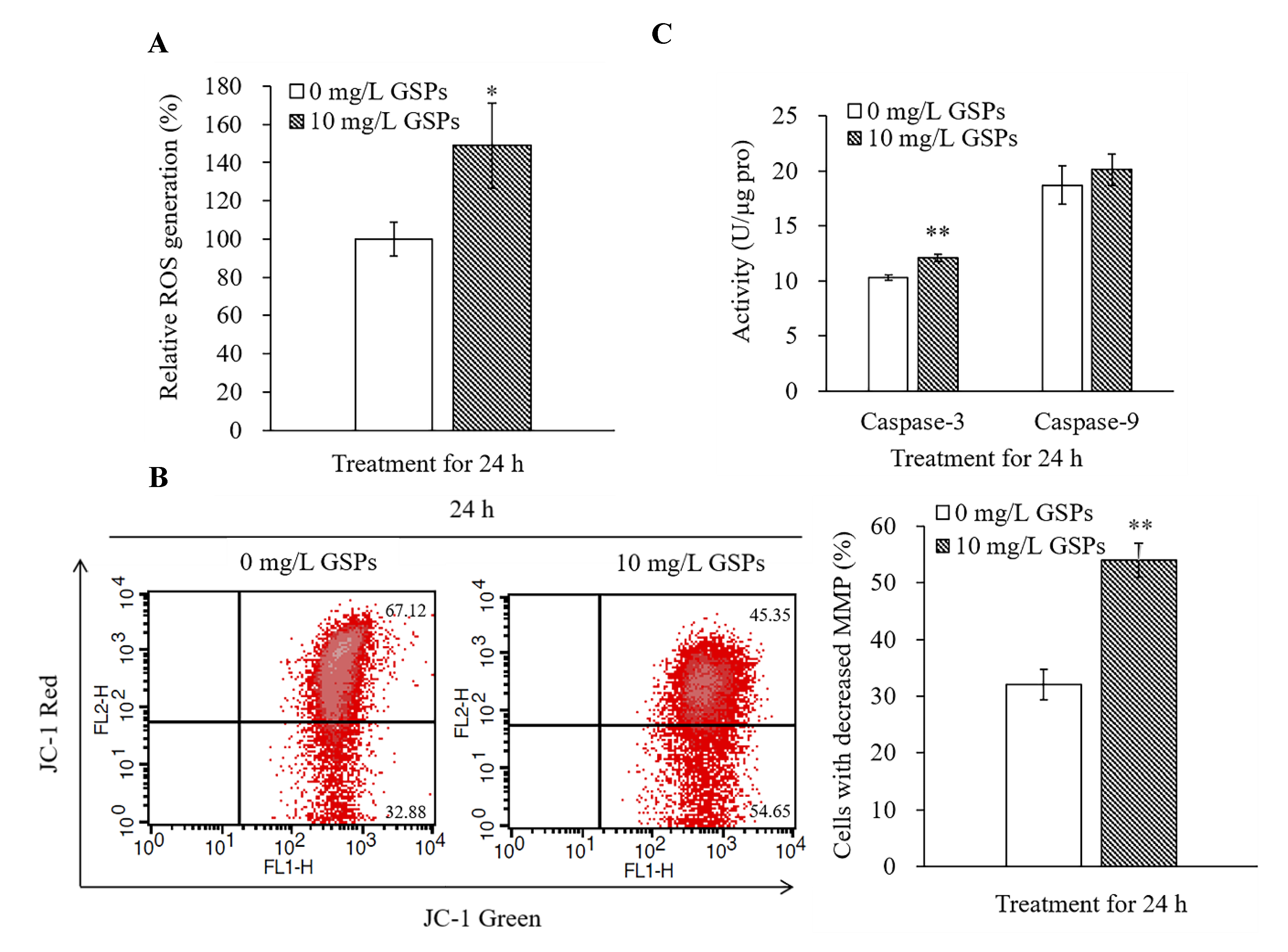
3.3. GSPs Trigger ROS Production, Decrease the MMP, and Increase the Caspase-3 Activity of HepG2 Cells
3.4. GSPs Induce G2/M Phase Cell Cycle Arrest of HepG2 Cells
3.5. Effects of GSPs on Cell Cycle-Related Proteins of HepG2 Cells
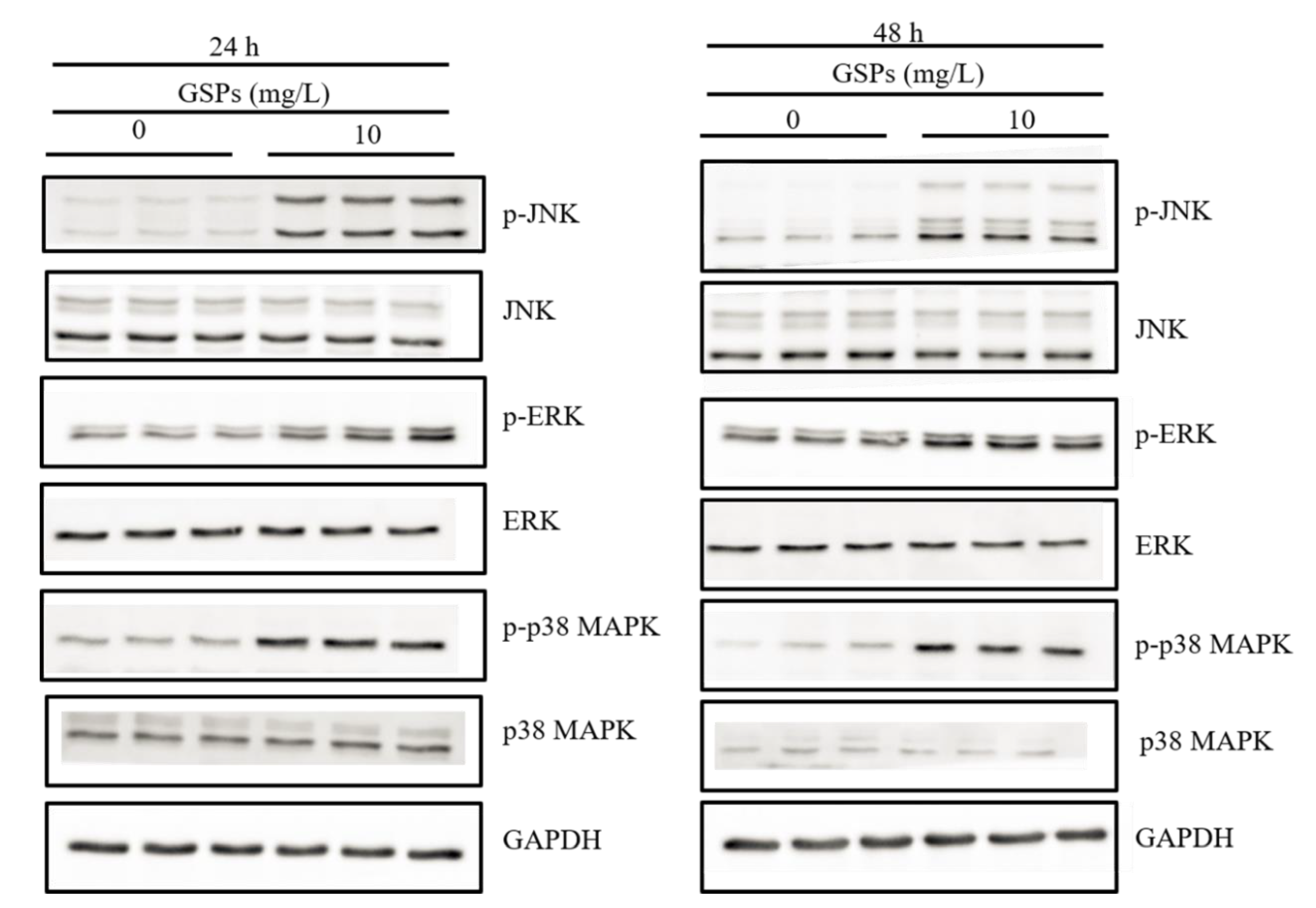
3.6. GSPs Induce the Phosphorylation of the MAPK Pathway-Related Proteins
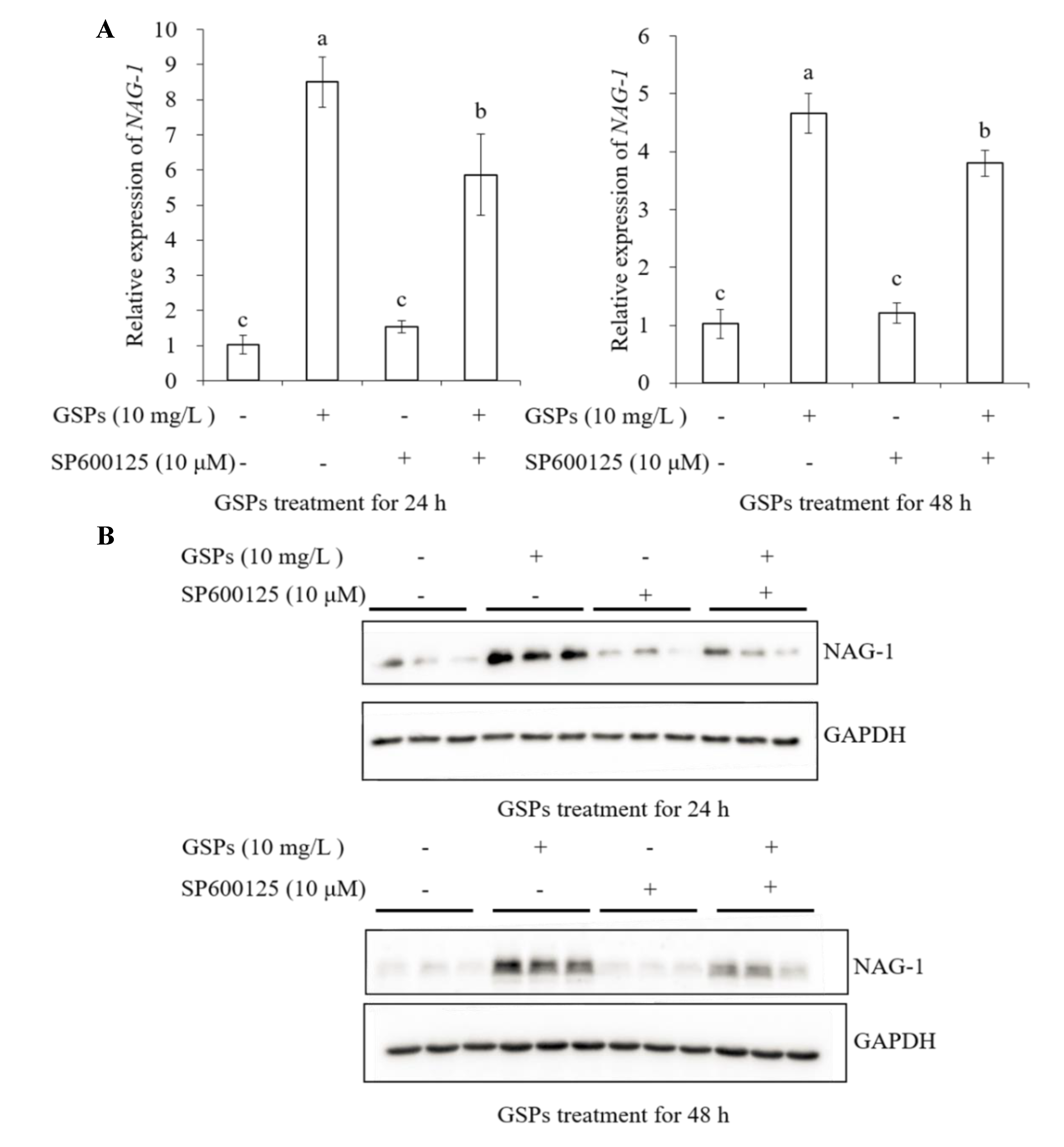
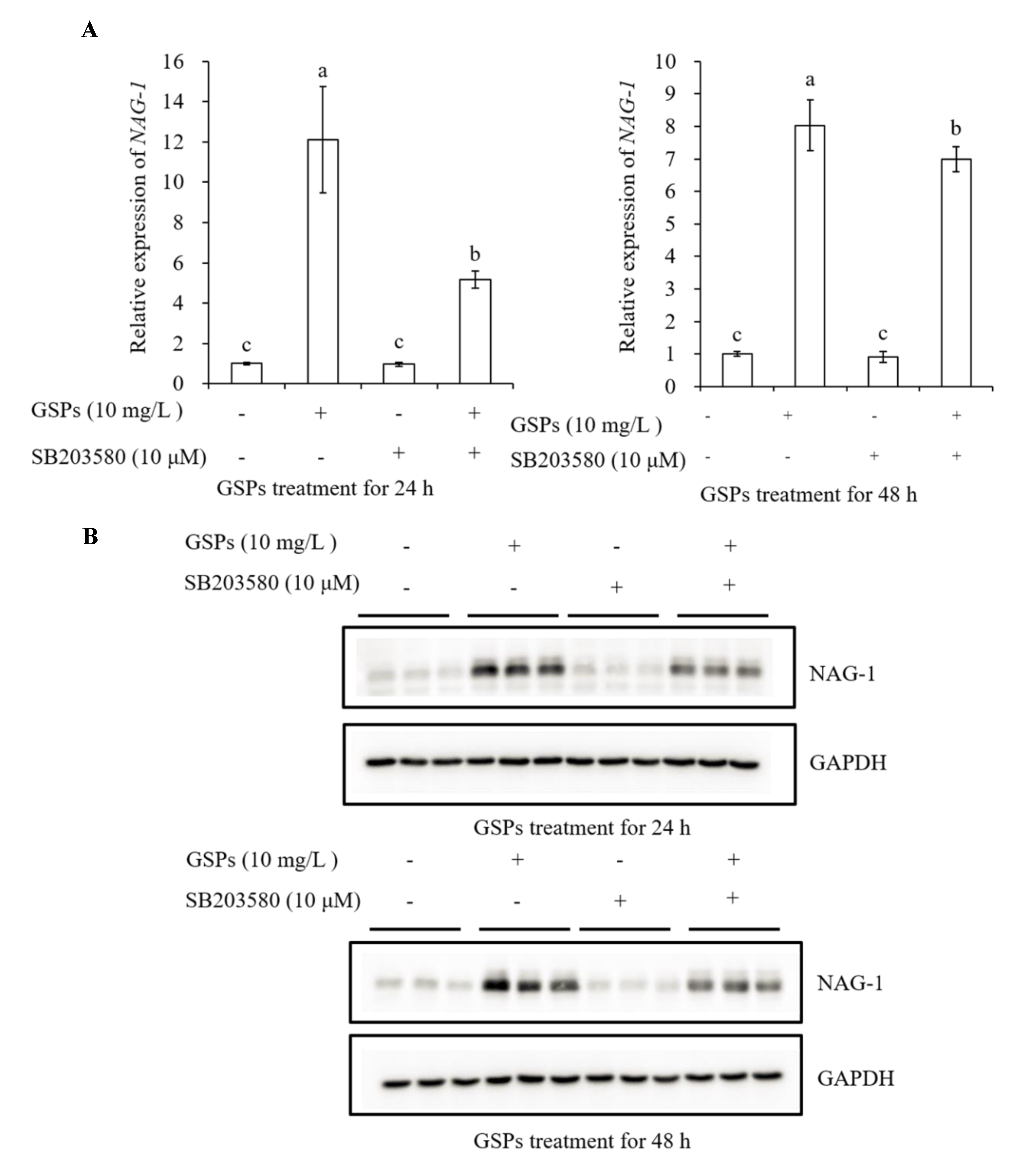
3.7. GSPs Induce Expression of NAG-1 of HepG2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsim, N.C.; Frampton, A.E.; Habib, N.A.; Jiao, L.R. Surgical treatment for liver cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, J.; Victor, D.; Asham, E.H.; Burroughs, S.G.; Boktour, M.; Saharia, A.; Li, X.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Monsour, H.P. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2016, 3, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daher, S.; Massarwa, M.; Benson, A.A.; Khoury, T. Current and future treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An updated comprehensive review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mccormick, F. Cancer gene therapy: Fringe or cutting edge? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, V.; Singh, T.; Katiyar, S.K. Multi-targeted prevention and therapy of cancer by proanthocyanidins. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, R.; Katiyar, S.K. Bioactive phytochemical proanthocyanidins inhibit growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting multiple signaling molecules. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.D.; Meeran, S.M.; Katiyar, S.K. Proanthocyanidins inhibit in vitro and in vivo growth of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting the prostaglandin E-2 and prostaglandin E-2 receptors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, T.; Sharma, S.D.; Katiyar, S.K. Grape proanthocyanidins induce apoptosis by loss of mitochondrial membrane potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, R.P.; Gu, M.; Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, C. Grape seed extract inhibits in vitro and in vivo growth of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6194–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, M.; Mandair, R.; Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, C. Grape seed extract induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamza, A.A.; Heeba, G.H.; Elwy, H.M.; Murali, C.; El-Awady, R.; Amin, A. Molecular characterization of the grape seeds extract’s effect against chemically induced liver cancer: In vivo and in vitro analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upanan, S.; Yodkeeree, S.; Thippraphan, P.; Punfa, W.; Wongpoomchai, R.; Limtrakul, P. The Proanthocyanidin-rich fraction obtained from red rice germ and bran extract induces HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis. Molecules 2019, 24, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, R.; Vaid, M.; Katiyar, S.K. Grape proanthocyanidin inhibit pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo through induction of apoptosis and by targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakoshi, J.; Saito, M.; Kataoka, S.; Kikuchi, M. Safety evaluation of proanthocyanidin-rich extract from grape seeds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Buelga, C.; Scalbert, A. Proanthocyanidins and tannin-like compounds - nature, occurrence, dietary intake and effects on nutrition and health. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1094–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.Z.; Ding, L.; Su, Y.L.; Guo, K.; Wang, L.; Kan, H.W.; Ou, Y.R.; Gao, S. Grape seed proanthocyanidins prevent DOCA-salt hypertension-induced renal injury and its mechanisms in rats. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2179–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinicola, S.; Mariggio, M.A.; Morabito, C.; Guarnieri, S.; Cucina, A.; Pasqualato, A.; D’Anselmi, F.; Proietti, S.; Coluccia, P.; Bizzarri, M. Grape seed extract triggers apoptosis in Caco-2 human colon cancer cells through reactive oxygen species and calcium increase: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase involvement. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, W.G.; Miranda, C.L.; Stevens, J.F.; Maier, C.S. Hop proanthocyanidins induce apoptosis, protein carbonylation, and cytoskeleton disorganization in human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells via reactive oxygen species. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hah, Y.S.; Kim, J.G.; Cho, H.Y.; Park, J.S.; Heo, E.P.; Yoon, T.J. Procyanidins from Vitis Vinifera seeds induce apoptotic and autophagic cell death via generation of reactive oxygen species in squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrison, D.K.; Davis, R.J. Regulation of map kinase signaling modules by scaffold proteins in mammals. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003, 19, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baek, S.J.; Kim, K.S.; Nixon, J.B.; Wilson, L.C.; Eling, T.E. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors regulate the expression of a TGF-β superfamily member that has proapoptotic and antitumorigenic activities. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, S.J.; Okazaki, R.; Lee, S.H.; Martinez, J.; Kim, J.S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mishina, Y.; Martin, D.W.; Shoieb, A.; McEntee, M.F.; et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 over expression in transgenic mice suppresses intestinal neoplasia. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekanova, M.; Lee, S.H.; Donnell, R.L.; Sukhthankar, M.; Eling, T.E.; Fischer, S.M.; Baek, S.J. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 expression inhibits urethane-induced pulmonary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shim, M.; Eling, T.E. Vitamin E succinate induces NAG-1 expression in a p38 kinase-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.H.; Woo, S.M.; Min, K.J.; Park, E.J.; Jang, J.H.; Seo, B.R.; Iqbal, T.; Lee, T.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; et al. Rottlerin induces apoptosis of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells through NAG-1 upregulation via an ERK and p38 MAPK-dependent and PKC δ-independent mechanism. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2012, 197, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Kang, Y.; Huo, T.X.; Tao, R.; Wang, X.P.; Li, Z.Y.; Guo, Q.L.; Zhao, L. GL-V9 induced upregulation and mitochondrial localization of NAG-1 associates with ROS generation and cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Jackson, F.R.; Eling, T.E.; McEntee, M.F.; Lee, S.H. Epicatechin gallate-induced expression of NAG-1 is associated with growth inhibition and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2425–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kim, J.S.; Eling, T.E.; Safe, S.; Park, Y.; Baek, S.J. Conjugated linoleic acid stimulates an anti-tumorigenic protein NAG-1 in an isomer specific manner. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiu, S.C.; Wang, M.J.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, S.P.; Huang, S.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, S.Z.; Harn, H.J.; Pang, C.Y. Activation of NAG-1 via JNK signaling revealed an isochaihulactone-triggered cell death in human LNCaP prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wynne, S.; Djakiew, D. NSAID inhibition of prostate cancer cell migration is mediated by Nag-1 induction via the p38 MAPK-p75NTR pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suganya, M.; Gnanamangai, B.M.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Selvaraj, A.; Govindasamy, C.; Elsadek, M.F.; Ponmurugan, P. Antitumor effect of proanthocyanidin induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer (HT-29) cells and its molecular docking studies. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.S.; Yu, S.J. Lipophilic grape seed proanthocyanidin exerts anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on PC3 human prostate cancer cells and suppresses PC3 xenograft tumor growth in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T.K. Apoptosis: A target for anticancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Fanburg, B.L. Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L1005–L1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, D.R.; Reed, J.C. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 1998, 281, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reers, M.; Smiley, S.T.; MottolaHartshorn, C.; Chen, A.; Lin, M.; Chen, L.B. Mitochondrial membrane potential monitored by JC-1 dye. Mitochondrial Biog. Genet. 1995, 260, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, B.B.; Green, D.R. Suicidal tendencies: Apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20049–20052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Thakur, K.; Hussain, S.S.; Zhang, J.G.; Xiao, G.R.; Wei, Z.J. Licochalcone A from licorice root, an inhibitor of human hepatoma cell growth via induction of cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.; Forman, H.J. Redox signaling and the MAP kinase pathways. Biofactors 2003, 17, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaron, F.; Hermann, S. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 2011, 147, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, X.F.; Zheng, P.S. Grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSPs) inhibit the growth of cervical cancer by inducing apoptosis mediated by the mitochondrial pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.X.; Leung, G.P.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Xiao, J.B.; Lao, L.X.; Feng, F.; Mak, J.C.W.; Wang, Y.; Sze, S.C.W.; Zhang, K.Y.B. Proanthocyanidins from Uncaria rhynchophylla induced apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells while enhancing cytotoxic effects of 5-fluorouracil. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, I.T.N.; Tang, J.C.O.; Chui, C.H.; Cheng, G.Y.M.; Yau, M.Y.C.; Lau, F.Y.; Wong, R.S.M.; Leung, T.W.T.; Cheung, F.; Ho, K.P.; et al. Superoxide anion is involved in the early apoptosis mediated by Gleditsia sinensis fruit extract. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 13, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, M. Cell cycle checkpoints and their inactivation in human cancer. Cell Prolif. 2000, 33, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranathan, P.; Pasham, D.; Balaji, U.; Cardenas, J.; Gu, J.; Toden, S.; Goel, A. Mechanistic insights into anticancer properties of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from grape seeds in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.N.; Chu, S.C.; Chiou, H.L.; Chiang, C.L.; Yang, S.F.; Hsieh, Y.S. Cyanidin 3-glucoside and peonidin 3-glucoside inhibit tumor cell growth and induce apoptosis in vitro and suppress tumor growth in vivo. Nutr. Cancer 2005, 53, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.S.; Liu, Z.M.; Ding, L.; Chang, W.C.; Hsu, P.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Chi, C.C.; Chuang, C.H. Opposite effect of ERK1/2 and JNK on p53-independent p21WAF1/CIP1 supercript stop activation involved in the arsenic trioxide-induced human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cellular cytotoxicity. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyun, J.W.; Chung, H.S. Cyanidin and malvidin from Oryza sativa cv. Heugjinjubyeo mediate cytotoxicity against human monocytic leukemia cells by arrest of G2/M phase and induction of apoptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2213–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.V.; Herman-Antosiewicz, A.; Singh, A.V.; Lew, K.L.; Srivastava, S.K.; Kamath, R.; Brown, K.D.; Zhang, L.; Baskaran, R. Sulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle 25C. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25813–25822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Kaur, M.; Agarwal, C.; Tecklenburg, M.; Sclafani, R.A.; Agarwal, R. P21 and p27 induction by silibinin is essential for its cell cycle arrest effect in prostate carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2696–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashid, A.; Liu, C.; Sanli, T.; Tsiani, E.; Singh, G.; Bristow, R.G.; Dayes, I.; Lukka, H.; Wright, J.; Tsakiridis, T. Resveratrol enhances prostate cancer cell response to ionizing radiation. Modulation of the AMPK, Akt and mTOR pathways. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weh, K.M.; Aiyer, H.S.; Howell, A.B.; Kresty, L.A. Cranberry proanthocyanidins modulate reactive oxygen species in Barrett’s and esophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines. J. Berry Res. 2016, 6, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.F.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, T.; Chevet, E.; Metrakos, P. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase regulation: Roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 261–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, S.W.G.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyoda, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Horimoto, M.; Toyama, T.; Yakushijin, T.; Sakakibara, M.; Takehara, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Hori, M.; Wands, J.R.; et al. Involvement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.J.; Wilson, L.C.; Eling, T.E. Resveratrol enhances the expression of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene (NAG-1) by increasing the expression of p53. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piyanuch, R.; Sukhthankar, M.; Wandee, G.; Baek, S.J. Berberine, a natural isoquinoline alkaloid, induces NAG-1 and ATF3 expression in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 258, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Krisanapun, C.; Lee, S.-H.; Nualsanit, T.; Sams, C.; Peungvicha, P.; Baek, S.J. Molecular targets of apigenin in colorectal cancer cells: Involvement of p21, NAG-1 and p53. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 3365–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhan, J.; Huang, W. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of HepG2 Cells Accompanied by Induction of the MAPK Pathway and NAG-1. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121200
Wang L, Zhan J, Huang W. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of HepG2 Cells Accompanied by Induction of the MAPK Pathway and NAG-1. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(12):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121200
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lihua, Jicheng Zhan, and Weidong Huang. 2020. "Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of HepG2 Cells Accompanied by Induction of the MAPK Pathway and NAG-1" Antioxidants 9, no. 12: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121200
APA StyleWang, L., Zhan, J., & Huang, W. (2020). Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of HepG2 Cells Accompanied by Induction of the MAPK Pathway and NAG-1. Antioxidants, 9(12), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121200