A Melanin-Related Phenolic Polymer with Potent Photoprotective and Antioxidant Activities for Dermo-Cosmetic Applications
Abstract
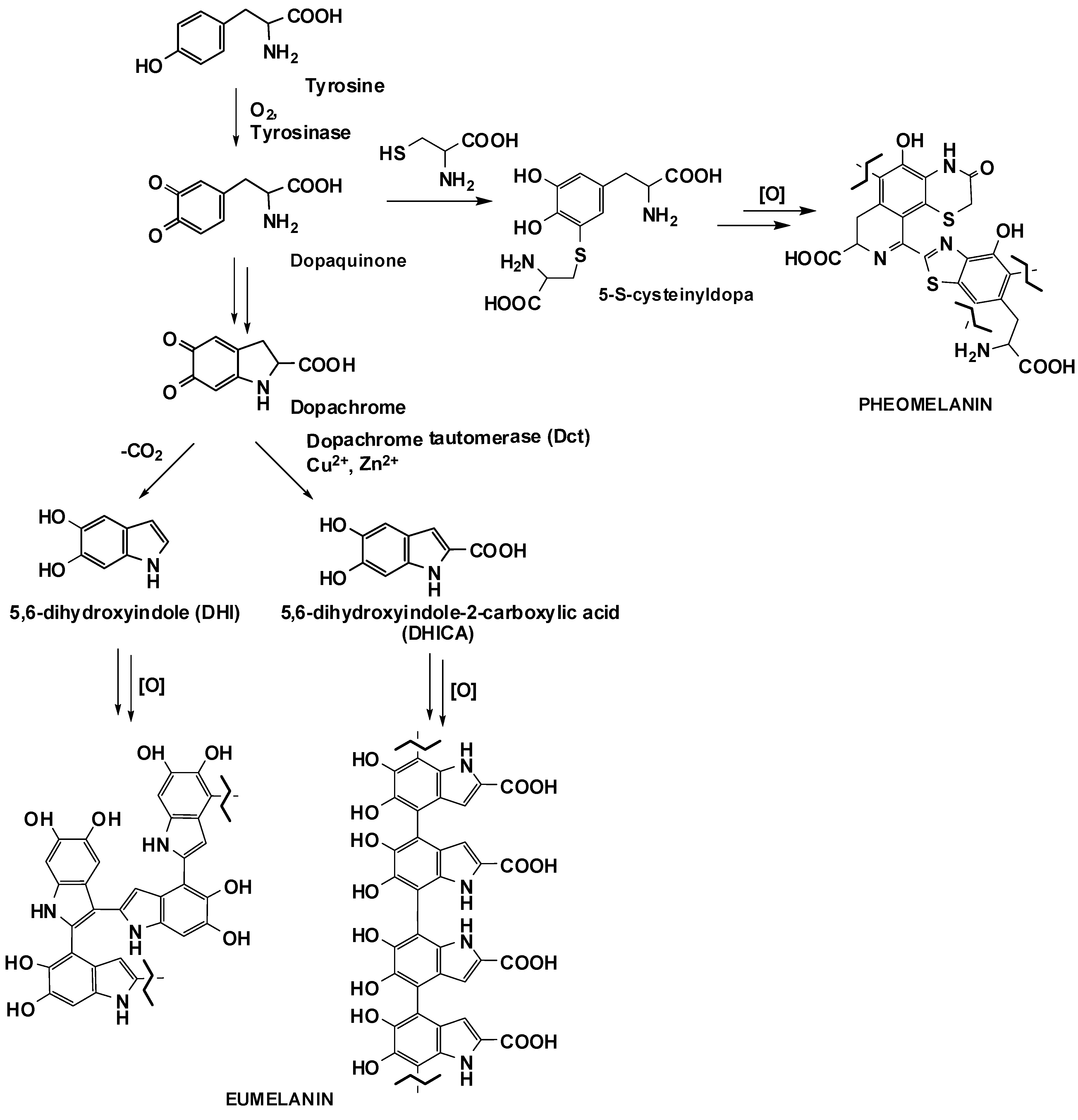
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Analysis of Cell Viability
2.4. UVA irradiation and H2DCFDA Assay
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Catalase Assay
2.7. Determination of Intracellular Glutathione (GSH) Levels
2.8. Analysis of Lipid Peroxidation Levels
2.9. Quantification of Internalized Melanin
2.10. HPLC and LC-MS Analysis of Cell Lysate
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biocompatibility of MeDHICA-Melanin on Keratinocytes
3.2. Inhibition of UVA-Induced Damage on HaCaT Cells by MeDHICA-Melanin
3.3. Induction of Nrf-2 Nuclear Translocation by MeDHICA-melanin
3.4. Cellular Uptake of MeDHICA-Melanin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Micillo, R.; Panzella, L.; Koike, K.; Monfrecola, G.; Napolitano, A.; D’Ischia, M. “Fifty shades” of black and red or how carboxyl groups fine tune eumelanin and pheomelanin properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvan, I.; Solano, F. Bird integumentary melanins: Biosynthesis, forms, function and evolution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Bino, S.; Duval, C.; Bernerd, F. Clinical and biological characterization of skin pigmentation diversity and its consequences on UV impact. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyamura, Y.; Coelho, S.G.; Wolber, R.; Miller, S.A.; Wakamatsu, K.; Zmudzka, B.Z.; Ito, S.; Smuda, C.; Passeron, T.; Choi, W.; et al. Regulation of human skin pigmentation and responses to ultraviolet radiation. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Diversity of human hair pigmentation as studied by chemical analysis of eumelanin and pheomelanin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugumaran, M.; Barek, H. Critical analysis of the melanogenic pathway in insects and higher animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meredith, P.; Sarna, T. The physical and chemical properties of eumelanin. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 572–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Pakdel, E.; Liang, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Liu, D.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. Natural eumelanin and its derivatives as multifunctional materials for bioinspired applications: A review. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 4312–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzella, L.; Ebato, A.; Napolitano, A.; Koike, K. The late stages of melanogenesis: Exploring the chemical facets and the application opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Ischia, M. Melanin-based functional materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solano, F. Melanin and melanin-related polymers as materials with biomedical and biotechnological applications-cuttlefish ink and mussel foot proteins as inspired biomolecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Huang, H.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Recent advances and progress on melanin-like materials and their biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra, M.; Bonadies, I.; Carfagna, C.; Cassinese, A.; Cimino, F.; Crescenzi, O.; Criscuolo, V.; D’Ischia, M.; Maglione, M.G.; Manini, P.; et al. Eumelanin-based organic bioelectronics: Myth or reality? MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ischia, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Cicoira, F.; Di Mauro, E.; Garcia-Borron, J.C.; Commo, S.; Galvan, I.; Ghanem, G.; Kenzo, K.; Meredith, P.; et al. Melanins and melanogenesis: From pigment cells to human health and technological applications. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 520–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longo, D.L.; Stefania, R.; Aime, S.; Oraevsky, A. Melanin-based contrast agents for biomedical optoacoustic imaging and theranostic applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Ischia, M.; Napolitano, A.; Pezzella, A.; Meredith, P.; Buehler, M.J. Melanin biopolymers: Tailoring chemical complexity for materials design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A. Natural and bioinspired phenolic compounds as tyrosinase inhibitors for the treatment of skin hyperpigmentation: Recent advances. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; D’Ischia, M.; Napolitano, A.; Pezzella, A. Structure of Melanins. In Melanins and Melanosomes; Borovansky, J., Riley, P.A., Eds.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 167–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Chemistry of mixed melanogenesis—Pivotal roles of dopaquinone. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, A.; Panzella, L.; Leone, L.; D’Ischia, M. Red hair benzothiazines and benzothiazoles: Mutation-inspired chemistry in the quest for functionality. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kim, E.; Temocin, Z.; Li, J.; Dadachova, E.; Wang, Z.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A.; Bentley, W.E.; Payne, G. Reverse engineering to characterize redox properties: Revealing melanin’s redox activity through mediated electrochemical probing. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 5814–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A.; Payne, G.F. Redox activities of melanins investigated by electrochemical reverse engineering: Implications for their roles in oxidative stress. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Panzella, L.; Monfrecola, G.; D’Ischia, M. Pheomelanin-induced oxidative stress: Bright and dark chemistry bridging red hair phenotype and melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, A.M.; Lo, J.; Fisher, D.E. How does pheomelanin synthesis contribute to melanomagenesis? Two distinct mechanisms could explain the carcinogenicity of pheomelanin synthesis. BioEssays 2013, 35, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Malek, Z.A.; Ito, S. Being in the red: A no-win situation with melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Sarna, T. Photodegradation of eumelanin and pheomelanin and its pathophysiological implications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A.; D’Ischia, M. Is DHICA the key to dopachrome tautomerase and melanocyte functions? Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2011, 24, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, D.; Flori, E.; Maresca, V.; Ottaviani, M.; Aspite, N.; Dell’Anna, M.L.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A.; Picardo, M.; D’Ischia, M. The eumelanin intermediate 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid is a messenger in the cross-talk among epidermal cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, X.M.; Dai, X.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, T.C.; Beermann, F.; Wakamatsu, K.; Xu, S.Z. Regulation of DHICA-mediated antioxidation by dopachrome tautomerase: Implication for skin photoprotection against UVA radiation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzella, L.; Gentile, G.; D’Errico, G.; Della Vecchia, N.F.; Errico, M.E.; Napolitano, A.; Carfagna, C.; D’Ischia, M. Atypical structural and π-electron features of a melanin polymer that lead to superior free-radical-scavenging properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12684–12687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blarzino, C.; Mosca, L.; Foppoli, C.; Coccia, R.; De Marco, C.; Rosei, M.A. Lipoxygenase/H2O2-catalyzed oxidation of dihydroxyindoles: Synthesis of melanin pigments and study of their antioxidant properties. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 26, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, B.; Vitiello, G.; Luciani, G.; Calcagno, V.; Costantini, A.; Gallo, M.; Parisi, S.; Paladino, S.; Iacomino, M.; D’Errico, G.; et al. Probing the eumelanin-silica interface in chemically engineered bulk hybrid nanoparticles for targeted subcellular antioxidant protection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37615–37622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchi, T.; Pezzella, A.; Di Mauro, E.; Cestola, S.; Ginsburg, D.; Luzi, M.; Rigucci, A.; Santato, C. On the antioxidant activity of eumelanin biopigments: A quantitative comparison between free radical scavenging and redox properties. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-M.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, S.-Z.; Wakamatsu, K.; Lei, T.-C. Maintenance of immune hyporesponsiveness to melanosomal proteins by DHICA-mediated antioxidation: Possible implications for autoimmune vitiligo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanuja, S.K.; Iswarya, S.; Gnanamani, A. Marine fungal DHICA as a UVB protectant: Assessment under in vitro and in vivo conditions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 179, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanuja, S.K.; Iswarya, S.; Rajasekaran, S.; Dinesh, M.G.; Gnanamani, A. Pre-treatment of extracellular water soluble pigmented secondary metabolites of marine imperfect fungus protects HDF cells from UVB induced oxidative stress. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 17, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, Y.; Corre, S.; Mouchet, N.; Vaulont, S.; Prince, S.; Galibert, M.D. USF-1 is critical for maintaining genome integrity in response to UV-induced DNA photolesions. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marabini, L.; Melzi, G.; Lolli, F.; Dell’Agli, M.; Piazza, S.; Sangiovanni, E.; Marinovich, M. Effects of Vitis vinifera L. leaves extract on UV radiation damage in human keratinocytes (HaCaT). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 204, 111810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, A.E.; Eveleigh, J.F. Mechanisms of DNA oxidation. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999, 222, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, G.; Zadlo, A.; Sarna, M.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Sarna, T. Aerobic photoreactivity of synthetic eumelanins and pheomelanins: Generation of singlet oxygen and superoxide anion. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Kikuta, M.; Koike, S.; Szewczyk, G.; Sarna, M.; Zadlo, A.; Sarna, T.; Wakamatsu, K. Roles of reactive oxygen species in UVA-induced oxidation of 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid-melanin as studied by differential spectrophotometric method. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micillo, R.; Iacomino, M.; Perfetti, M.; Panzella, L.; Koike, K.; D’Errico, G.; D’Ischia, M.; Napolitano, A. Unexpected impact of esterification on the antioxidant activity and (photo)stability of a eumelanin from 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Alam, M.B.; Lee, S.H. Protection of UVB-induced photoaging by fuzhuan-brick tea aqueous extract via MAPKs/Nrf2-mediated down-regulation of MMP-1. Nutrients 2018, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kostyuk, V.; Potapovich, A.; Albuhaydar, A.R.; Mayer, W.; De Luca, C.; Korkina, L. Natural substances for prevention of skin photoaging: Screening systems in the development of sunscreen and rejuvenation cosmetics. Rejuvenation Res. 2018, 2, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruk, G.; Illiano, A.; Del Giudice, R.; Raiola, A.; Amoresano, A.; Rigano, M.M.; Piccoli, R.; Monti, D.M. Malvidin and cyanidin derivatives from açai fruit (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) counteract UV-A-induced oxidative stress in immortalized fibroblasts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 172, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galano, E.; Arciello, A.; Piccoli, R.; Monti, D.M.; Amoresano, A. A proteomic approach to investigate the effects of cadmium and lead on human primary renal cells. Metallomics 2014, 6, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, R.F.; Sizer, I.W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice, R.; Petruk, G.; Raiola, A.; Barone, A.; Monti, D.M.; Rigano, M.M. Carotenoids in fresh and processed tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruits protect cells from oxidative stress injury. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, R.; Rogge, F.; Lee, M. Protein, lipid, and DNA radicals to measure skin UVA damage and modulation by melanin. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidrus, E.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Fehér, P.; Hegedűs, C.; Janka, E.A.; Paragh, G.; Vasas, G.; Bácskay, I.; Remenyik, E. Silymarin: Friend or foe of UV exposed keratinocytes? Molecules 2019, 24, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aquilano, K.; Baldelli, S.; Ciriolo, M.R. Glutathione: New roles in redox signaling for an old antioxidant. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobeh, M.; El-Raey, M.; Rezq, S.; Abdelfattah, M.A.O.; Petruk, G.; Osman, S.; El-Shazly, A.M.; El-Beshbishy, H.A.; Mahmoud, M.F.; Wink, M. Chemical profiling of secondary metabolites of Eugenia uniflora and their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, pain killing and anti-diabetic activities: A comprehensive approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 240, 111939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobeh, M.; Mahmoud, M.F.; Petruk, G.; Rezq, S.; Ashour, M.L.; Youssef, F.S.; El-Shazly, A.M.; Monti, D.M.; Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Wink, M. Syzygium aqueum: A polyphenol- rich leaf extract exhibits antioxidant, hepatoprotective, pain-killing and anti-inflammatory activities in animal models. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, H.; Li, H.; Ho, Z.Y.; Dai, X.Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, R.; Liang, B.; Zhu, H. Pterostilbene’s protective effects against photodamage caused by UVA/UVB irradiation. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q. Role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yue, X.; Proetto, T.; Jones, Y.; Gianneschi, N.C. Mimicking melanosomes: Polydopamine nanoparticles as artificial microparasols. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulms, D.; Schwarz, T. Molecular mechanisms of UV-induced apoptosis. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2000, 16, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.-C.; Chou, C.W.; Senthil Kumar, K.J.; Fu, K.T.; Wang, H.M.; Hsu, L.S.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wu, C.R.; Chen, S.C.; Yang, H.L. Ellagic acid protects human keratinocyte (HaCaT) cells against UV-A-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through the upregulation of the HO-1 and Nrf-2 antioxidant genes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreiras, H.; Lopes-da-Silva, M.; Seabra, M.C.; Barral, D.C. Melanin processing by keratinocytes: A non-microbial type of host-pathogen interaction? Traffic 2019, 20, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiberg, M.; Paine, C.; Sharlow, E.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Costanzo, M.; Eisinger, M.; Shapiro, S.S. The protease-activated receptor 2 regulates pigmentation via keratinocyte-melanocyte interactions. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 254, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liberti, D.; Alfieri, M.L.; Monti, D.M.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A. A Melanin-Related Phenolic Polymer with Potent Photoprotective and Antioxidant Activities for Dermo-Cosmetic Applications. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040270
Liberti D, Alfieri ML, Monti DM, Panzella L, Napolitano A. A Melanin-Related Phenolic Polymer with Potent Photoprotective and Antioxidant Activities for Dermo-Cosmetic Applications. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(4):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040270
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiberti, Davide, Maria Laura Alfieri, Daria Maria Monti, Lucia Panzella, and Alessandra Napolitano. 2020. "A Melanin-Related Phenolic Polymer with Potent Photoprotective and Antioxidant Activities for Dermo-Cosmetic Applications" Antioxidants 9, no. 4: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040270
APA StyleLiberti, D., Alfieri, M. L., Monti, D. M., Panzella, L., & Napolitano, A. (2020). A Melanin-Related Phenolic Polymer with Potent Photoprotective and Antioxidant Activities for Dermo-Cosmetic Applications. Antioxidants, 9(4), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040270








