Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers as HIV-1 Vaccine Immunogens
Abstract
:1. Env as a Viral Entry Machine
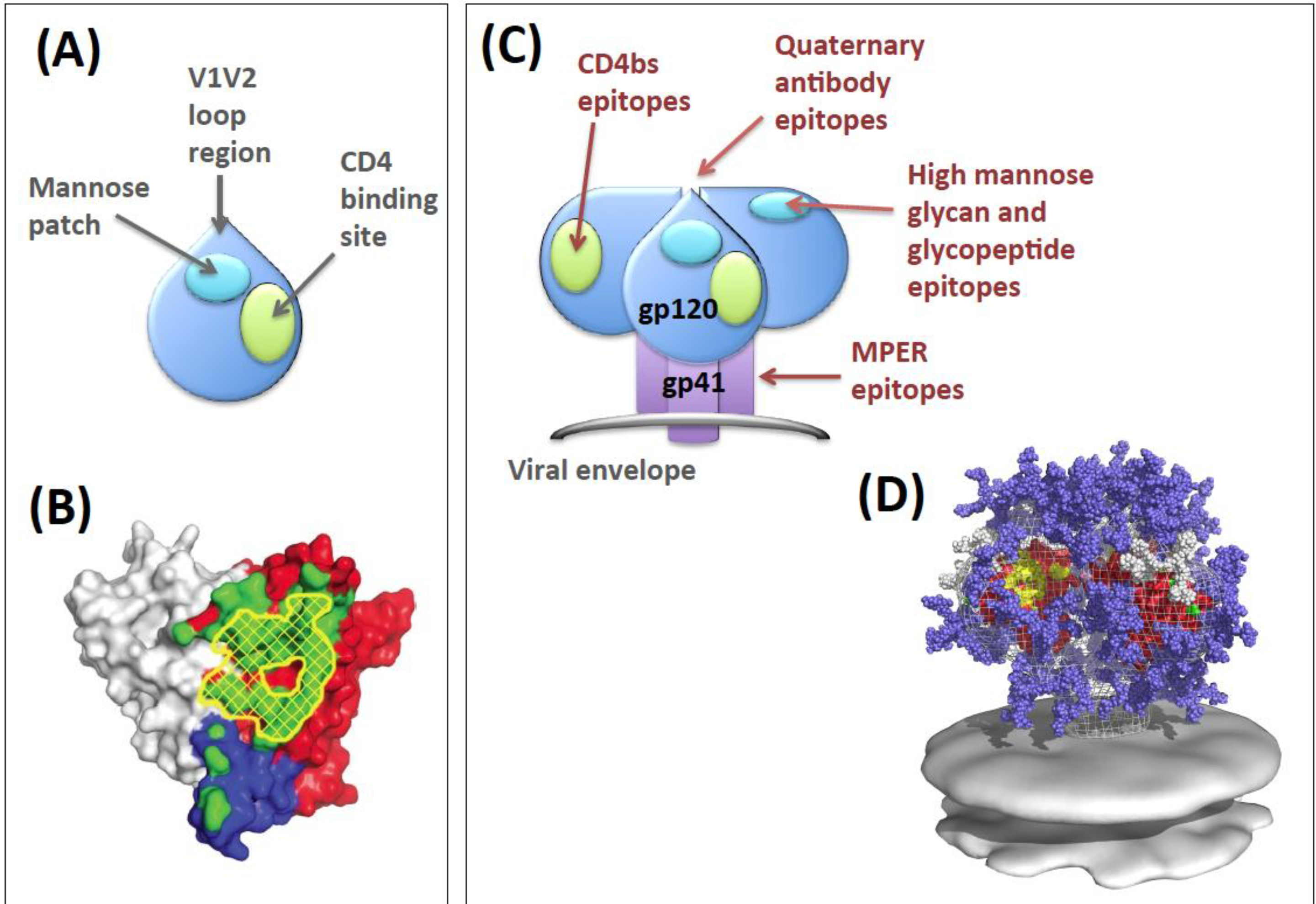
2. Env Antibody Evasion Strategies
3. Env as a Vaccine Antigen
4. Preparation of Membrane-Anchored Trimers
5. Preparation of Soluble Trimers

6. Potential for Success and Current Strategies
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Checkley, M.A.; Luttge, B.G.; Freed, E.O. HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein biosynthesis, trafficking, and incorporation. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 410, 582–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, C.; Welsch, S.; Michor, S.; Sattentau, Q.J. The regulated secretory pathway in CD4+ T cells contributes to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 cell-to-cell spread at the virological synapse. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002226. [Google Scholar]
- Postler, T.S.; Desrosiers, R.C. The tale of the long tail: The cytoplasmic domain of HIV-1 gp41. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Steckbeck, J.D.; Kuhlmann, A.S.; Montelaro, R.C. C-terminal tail of human immunodeficiency virus gp41: Functionally rich and structurally enigmatic. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Sattentau, Q.J. The HIV-1-containing macrophage compartment: A perfect cellular niche? Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Krausslich, H.G. HIV-1 assembly, budding, and maturation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, P.D.; Wyatt, R.; Robinson, J.; Sweet, R.W.; Sodroski, J.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structure of an HIV gp120 envelope glycoprotein in complex with the CD4 receptor and a neutralizing human antibody. Nature 1998, 393, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilen, C.B.; Tilton, J.C.; Doms, R.W. HIV: Cell binding and entry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, R.; Durell, S.; Viard, M. HIV entry and envelope glycoprotein-mediated fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40841–40849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.A.; Bartesaghi, A.; Borgnia, M.J.; Meyerson, J.R.; de la Cruz, M.J.; Bess, J.W.; Nandwani, R.; Hoxie, J.A.; Lifson, J.D.; Milne, J.L.; et al. Molecular architectures of trimeric SIV and HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins on intact viruses: Strain-dependent variation in quaternary structure. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001249. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Liu, J.; Taylor, K.A.; Roux, K.H. Structural comparison of HIV-1 envelope spikes with and without the V1/V2 loop. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2741–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, J.; Julien, J.P.; Menis, S.; Ota, T.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; McGuire, A.; Sok, D.; Huang, P.S.; Macpherson, S.; Jones, M.; et al. Rational HIV immunogen design to target specific germline B Cell Receptors. Science 2013, 340, 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Georgiev, I.; Wu, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Dai, K.; Finzi, A.; Kwon, Y.D.; Scheid, J.F.; Shi, W.; Xu, L.; et al. Structural basis for broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by antibody VRC01. Science 2010, 329, 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Schief, W.R.; Ban, Y.E.; Stamatatos, L. Challenges for structure-based HIV vaccine design. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2009, 4, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, N.; Sattentau, Q. Cell-to-cell HIV-1 spread and its implications for immune evasion. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2009, 4, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Trkola, A. Humoral immunity to HIV-1: Neutralization and beyond. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 262, 5–25. [Google Scholar]
- Forthal, D.; Hope, T.J.; Alter, G. New paradigms for functional HIV-specific nonneutralizing antibodies. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Montefiori, D.C.; Morris, L.; Ferrari, G.; Mascola, J.R. Neutralizing and other antiviral antibodies in HIV-1 infection and vaccination. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2007, 2, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Hessell, A.J.; Poignard, P.; Hunter, M.; Hangartner, L.; Tehrani, D.M.; Bleeker, W.K.; Parren, P.W.; Marx, P.A.; Burton, D.R. Effective, low-titer antibody protection against low-dose repeated mucosal SHIV challenge in macaques. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 951–954. [Google Scholar]
- Hessell, A.J.; Rakasz, E.G.; Poignard, P.; Hangartner, L.; Landucci, G.; Forthal, D.N.; Koff, W.C.; Watkins, D.I.; Burton, D.R. Broadly neutralizing human anti-HIV antibody 2G12 is effective in protection against mucosal SHIV challenge even at low serum neutralizing titers. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000433. [Google Scholar]
- Hessell, A.J.; Hangartner, L.; Hunter, M.; Havenith, C.E.; Beurskens, F.J.; Bakker, J.M.; Lanigan, C.M.; Landucci, G.; Forthal, D.N.; Parren, P.W.; et al. Fc receptor but not complement binding is important in antibody protection against HIV. Nature 2007, 449, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, T.W.; Liska, V.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Vlasak, J.; Xu, W.; Ayehunie, S.; Cavacini, L.A.; Posner, M.R.; Katinger, H.; Stiegler, G.; et al. Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Mascola, J.R.; Stiegler, G.; VanCott, T.C.; Katinger, H.; Carpenter, C.B.; Hanson, C.E.; Beary, H.; Hayes, D.; Frankel, S.S.; Birx, D.L.; et al. Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Moldt, B.; Rakasz, E.G.; Schultz, N.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Swiderek, K.; Weisgrau, K.L.; Piaskowski, S.M.; Bergman, Z.; Watkins, D.I.; Poignard, P.; et al. Highly potent HIV-specific antibody neutralization in vitro translates into effective protection against mucosal SHIV challenge in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18921–18925. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, D.R.; Hessell, A.J.; Keele, B.F.; Klasse, P.J.; Ketas, T.A.; Moldt, B.; Dunlop, D.C.; Poignard, P.; Doyle, L.A.; Cavacini, L.; et al. Limited or no protection by weakly or nonneutralizing antibodies against vaginal SHIV challenge of macaques compared with a strongly neutralizing antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11181–11186. [Google Scholar]
- Mascola, J.R.; Montefiori, D.C. The role of antibodies in HIV vaccines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 413–444. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Sattentau, Q.J. Antigenicity and immunogenicity in HIV-1 antibody-based vaccine design. J. AIDS Clin. Res. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, J.P.; Lee, P.S.; Wilson, I.A. Structural insights into key sites of vulnerability on HIV-1 Env and influenza HA. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 250, 180–198. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, D.R.; Poignard, P.; Stanfield, R.L.; Wilson, I.A. Broadly neutralizing antibodies present new prospects to counter highly antigenically diverse viruses. Science 2012, 337, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Decker, J.M.; Wang, S.; Hui, H.; Kappes, J.C.; Wu, X.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Salazar, M.G.; Kilby, J.M.; Saag, M.S.; et al. Antibody neutralization and escape by HIV-1. Nature 2003, 422, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, J.M.; Ban, Y.E.; Crooks, E.T.; Eggink, D.; Osawa, K.; Schief, W.R.; Sanders, R.W. Role of complex carbohydrates in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and resistance to antibody neutralization. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5637–5655. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Sheppard, N.C.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.; Robson, C.L.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; Krashias, G.; Bonomelli, C.; Scanlan, C.N.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Expression-system-dependent modulation of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein antigenicity and immunogenicity. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 403, 131–147. [Google Scholar]
- Calarese, D.A.; Scanlan, C.N.; Zwick, M.B.; Deechongkit, S.; Mimura, Y.; Kunert, R.; Zhu, P.; Wormald, M.R.; Stanfield, R.L.; Roux, K.H.; et al. Antibody domain exchange is an immunological solution to carbohydrate cluster recognition. Science 2003, 300, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Lee, J.H.; Doores, K.J.; Murin, C.D.; Julien, J.P.; McBride, R.; Liu, Y.; Marozsan, A.; Cupo, A.; Klasse, P.J.; et al. Supersite of immune vulnerability on the glycosylated face of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 796–803. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, J.S.; Pancera, M.; Carrico, C.; Gorman, J.; Julien, J.P.; Khayat, R.; Louder, R.; Pejchal, R.; Sastry, M.; Dai, K.; et al. Structure of HIV-1 gp120 V1/V2 domain with broadly neutralizing antibody PG9. Nature 2011, 480, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Pejchal, R.; Doores, K.J.; Walker, L.M.; Khayat, R.; Huang, P.S.; Wang, S.K.; Stanfield, R.L.; Julien, J.P.; Ramos, A.; Crispin, M.; et al. A potent and broad neutralizing antibody recognizes and penetrates the HIV glycan shield. Science 2011, 334, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Kwon, Y.D.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; O’Dell, S.; Cavacini, L.; Hessell, A.J.; Pancera, M.; Tang, M.; Xu, L.; et al. Structural basis of immune evasion at the site of CD4 attachment on HIV-1 gp120. Science 2009, 326, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Poignard, P.; Raja, A.; Zwick, M.B.; Delgado, K.; Franti, M.; Binley, J.; Vivona, V.; Grundner, C.; Huang, C.C.; et al. Access of antibody molecules to the conserved coreceptor binding site on glycoprotein gp120 is sterically restricted on primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10557–10565. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.M.; Morelli, M.; Dennison, S.M.; Liao, H.X.; Zhang, R.; Xia, S.M.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Sun, L.; Harrison, S.C.; Haynes, B.F.; et al. Role of HIV membrane in neutralization by two broadly neutralizing antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20234–20239. [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau, Q.J.; Moore, J.P. Conformational changes induced in the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein by soluble CD4 binding. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, R.; Moore, J.; Accola, M.; Desjardin, E.; Robinson, J.; Sodroski, J. Involvement of the V1/V2 variable loop structure in the exposure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 epitopes induced by receptor binding. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 5723–5733. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Gerard, N.P.; Wyatt, R.; Choe, H.; Parolin, C.; Ruffing, N.; Borsetti, A.; Cardoso, A.A.; Desjardin, E.; Newman, W.; et al. CD4-induced interaction of primary HIV-1 gp120 glycoproteins with the chemokine receptor CCR-5. Nature 1996, 384, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Bazick, J.; Sodroski, J. Characterization of the multiple conformational States of free monomeric and trimeric human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins after fixation by cross-linker. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6725–6737. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, A.; Borgnia, M.J.; Shi, D.; Bartesaghi, A.; He, H.; Pejchal, R.; Kang, Y.K.; Depetris, R.; Marozsan, A.J.; Sanders, R.W.; et al. Trimeric HIV-1 glycoprotein gp140 immunogens and native HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins display the same closed and open quaternary molecular architectures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11440–11445. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, E.E.; Borgnia, M.J.; Kuybeda, O.; Schauder, D.M.; Bartesaghi, A.; Frank, G.A.; Sapiro, G.; Milne, J.L.; Subramaniam, S. Structural mechanism of trimeric HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein activation. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002797. [Google Scholar]
- Khayat, R.; Lee, J.H.; Julien, J.P.; Cupo, A.; Klasse, P.J.; Sanders, R.W.; Moore, J.P.; Wilson, I.A.; Ward, A.B. Structural characterization of cleaved, soluble HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein trimers. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9865–9872. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, P.D.; Doyle, M.L.; Casper, D.J.; Cicala, C.; Leavitt, S.A.; Majeed, S.; Steenbeke, T.D.; Venturi, M.; Chaiken, I.; Fung, M.; et al. HIV-1 evades antibody-mediated neutralization through conformational masking of receptor-binding sites. Nature 2002, 420, 678–682. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.P.; McKeating, J.A.; Weiss, R.A.; Sattentau, Q.J. Dissociation of gp120 from HIV-1 virions induced by soluble CD4. Science 1990, 250, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar]
- McKeating, J.A.; McKnight, A.; Moore, J.P. Differential loss of envelope glycoprotein gp120 from virions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates: Effects on infectivity and neutralization. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 852–860. [Google Scholar]
- Parren, P.W.; Burton, D.R.; Sattentau, Q.J. HIV-1 antibody—Debris or virion? Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 366–367. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Bartesaghi, A.; Borgnia, M.J.; Sapiro, G.; Subramaniam, S. Molecular architecture of native HIV-1 gp120 trimers. Nature 2008, 455, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Liu, J.; Bess, J., Jr.; Chertova, E.; Lifson, J.D.; Grise, H.; Ofek, G.A.; Taylor, K.A.; Roux, K.H. Distribution and three-dimensional structure of AIDS virus envelope spikes. Nature 2006, 441, 847–852. [Google Scholar]
- Mouquet, H.; Scheid, J.F.; Zoller, M.J.; Krogsgaard, M.; Ott, R.G.; Shukair, S.; Artyomov, M.N.; Pietzsch, J.; Connors, M.; Pereyra, F.; et al. Polyreactivity increases the apparent affinity of anti-HIV antibodies by heteroligation. Nature 2010, 467, 591–595. [Google Scholar]
- Billich, A. AIDSVAX VaxGen. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2004, 5, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, P.; Wang, M.; Wrin, T.; Petropoulos, C.; Gurwith, M.; Sinangil, F.; D’Souza, P.; Rodriguez-Chavez, I.R.; DeCamp, A.; Giganti, M.; et al. Magnitude and breadth of a nonprotective neutralizing antibody response in an efficacy trial of a candidate HIV-1 gp120 vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 595–605. [Google Scholar]
- Zolla-Pazner, S.; Kong, X.P.; Jiang, X.; Cardozo, T.; Nadas, A.; Cohen, S.; Totrov, M.; Seaman, M.S.; Wang, S.; Lu, S. Cross-clade HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies induced with V3-scaffold protein immunogens following priming with gp120 DNA. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9887–9898. [Google Scholar]
- Bou-Habib, D.C.; Roderiquez, G.; Oravecz, T.; Berman, P.W.; Lusso, P.; Norcross, M.A. Cryptic nature of envelope V3 region epitopes protects primary monocytotropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from antibody neutralization. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6006–6013. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, O.; Klasse, P.J.; Sattentau, Q.J.; Moore, J.P. V3: HIV’s switch-hitter. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2005, 21, 171–189. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.C.; Tang, M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Majeed, S.; Montabana, E.; Stanfield, R.L.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Korber, B.; Sodroski, J.; Wilson, I.A.; et al. Structure of a V3-containing HIV-1 gp120 core. Science 2005, 310, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau, Q.J.; Moore, J.P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization is determined by epitope exposure on the gp120 oligomer. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Parren, P.W.; Mondor, I.; Naniche, D.; Ditzel, H.J.; Klasse, P.J.; Burton, D.R.; Sattentau, Q.J. Neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by antibody to gp120 is determined primarily by occupancy of sites on the virion irrespective of epitope specificity. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar]
- Fouts, T.R.; Binley, J.M.; Trkola, A.; Robinson, J.E.; Moore, J.P. Neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolate JR-FL by human monoclonal antibodies correlates with antibody binding to the oligomeric form of the envelope glycoprotein complex. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar]
- VanCott, T.C.; Bethke, F.R.; Polonis, V.R.; Gorny, M.K.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Redfield, R.R.; Birx, D.L. Dissociation rate of antibody-gp120 binding interactions is predictive of V3-mediated neutralization of HIV-1. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 449–459. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, L.M.; Huber, M.; Doores, K.J.; Falkowska, E.; Pejchal, R.; Julien, J.P.; Wang, S.K.; Ramos, A.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Moyle, M.; et al. Broad neutralization coverage of HIV by multiple highly potent antibodies. Nature 2011, 477, 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Clapham, P.R.; Lu, S. Vaccinology: Precisely tuned antibodies nab HIV. Nature 2011, 477, 416–417. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, D.R.; Weiss, R.A. AIDS/HIV. A boost for HIV vaccine design. Science 2010, 329, 770–773. [Google Scholar]
- Mouquet, H.; Nussenzweig, M.C. HIV: Roadmaps to a vaccine. Nature 2013, 496, 441–442. [Google Scholar]
- Corti, D.; Lanzavecchia, A. Broadly neutralizing antiviral antibodies. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 705–742. [Google Scholar]
- Mascola, J.R.; Haynes, B.F. HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies: Understanding nature’s pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 254, 225–244. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J. The changing face of HIV vaccine research. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2012, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, G.; Guenaga, F.J.; Schief, W.R.; Skinner, J.; Baker, D.; Wyatt, R.; Kwong, P.D. Elicitation of structure-specific antibodies by epitope scaffolds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17880–17887. [Google Scholar]
- Guenaga, J.; Dosenovic, P.; Ofek, G.; Baker, D.; Schief, W.R.; Kwong, P.D.; Karlsson Hedestam, G.B.; Wyatt, R.T. Heterologous epitope-scaffold prime:boosting immuno-focuses B cell responses to the HIV-1 gp41 2F5 neutralization determinant. PLoS One 2011, 6, e16074. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, B.E.; Ban, Y.E.; Holmes, M.A.; Xu, H.; Ellingson, K.; Kraft, Z.; Carrico, C.; Boni, E.; Sather, D.N.; Zenobia, C.; et al. Computational design of epitope-scaffolds allows induction of antibodies specific for a poorly immunogenic HIV vaccine epitope. Structure 2010, 18, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, B.E.; Ban, Y.E.; Friend, D.J.; Ellingson, K.; Xu, H.; Boni, E.; Bradley-Hewitt, T.; Bruhn-Johannsen, J.F.; Stamatatos, L.; Strong, R.K.; et al. Computational protein design using flexible backbone remodeling and resurfacing: Case studies in structure-based antigen design. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 405, 284–297. [Google Scholar]
- Forsell, M.N.; Schief, W.R.; Wyatt, R.T. Immunogenicity of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein oligomers. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2009, 4, 380–387. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, C.; Wagner, R. Virus-like particles-universal molecular toolboxes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 537–545. [Google Scholar]
- Buonaguro, L.; Tagliamonte, M.; Visciano, M.L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. Developments in virus-like particle-based vaccines for HIV. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Crooks, E.T.; Moore, P.L.; Franti, M.; Cayanan, C.S.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, P.; de Vries, R.P.; Wiley, C.; Zharkikh, I.; Schulke, N.; et al. A comparative immunogenicity study of HIV-1 virus-like particles bearing various forms of envelope proteins, particles bearing no envelope and soluble monomeric gp120. Virology 2007, 366, 245–262. [Google Scholar]
- Crooks, E.T.; Tong, T.; Osawa, K.; Binley, J.M. Enzyme digests eliminate nonfunctional Env from HIV-1 particle surfaces, leaving native Env trimers intact and viral infectivity unaffected. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5825–5839. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, T.; Crooks, E.T.; Osawa, K.; Binley, J.M. HIV-1 virus-like particles bearing pure env trimers expose neutralizing epitopes but occlude nonneutralizing epitopes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3574–3587. [Google Scholar]
- Grundner, C.; Li, Y.; Louder, M.; Mascola, J.; Yang, X.; Sodroski, J.; Wyatt, R. Analysis of the neutralizing antibody response elicited in rabbits by repeated inoculation with trimeric HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins. Virology 2005, 331, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Svehla, K.; Mathy, N.L.; Voss, G.; Mascola, J.R.; Wyatt, R. Characterization of antibody responses elicited by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolate trimeric and monomeric envelope glycoproteins in selected adjuvants. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.K.; Andjelic, S.; Binley, J.M.; Crooks, E.T.; Franti, M.; Iyer, S.P.; Donovan, G.P.; Dey, A.K.; Zhu, P.; Roux, K.H.; et al. Structural and immunogenicity studies of a cleaved, stabilized envelope trimer derived from subtype A HIV-1. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5120–5132. [Google Scholar]
- Beddows, S.; Franti, M.; Dey, A.K.; Kirschner, M.; Iyer, S.P.; Fisch, D.C.; Ketas, T.; Yuste, E.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Klasse, P.J.; et al. A comparative immunogenicity study in rabbits of disulfide-stabilized, proteolytically cleaved, soluble trimeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp140, trimeric cleavage-defective gp140 and monomeric gp120. Virology 2007, 360, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Pancera, M.; Wyatt, R. Selective recognition of oligomeric HIV-1 primary isolate envelope glycoproteins by potently neutralizing ligands requires efficient precursor cleavage. Virology 2005, 332, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, C.; Klasse, P.J.; Michael, E.; Kake, S.; Barnes, K.; Kibler, C.W.; Campbell-Gardener, L.; Si, Z.; Sodroski, J.; Moore, J.P.; et al. The impact of envelope glycoprotein cleavage on the antigenicity, infectivity, and neutralization sensitivity of Env-pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particles. Virology 2005, 338, 154–172. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, A.K.; David, K.B.; Lu, M.; Moore, J.P. Biochemical and biophysical comparison of cleaved and uncleaved soluble, trimeric HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins. Virology 2009, 385, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, L.M.; Phogat, S.K.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Wagner, D.; Phung, P.; Goss, J.L.; Wrin, T.; Simek, M.D.; Fling, S.; Mitcham, J.L.; et al. Broad and potent neutralizing antibodies from an African donor reveal a new HIV-1 vaccine target. Science 2009, 326, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, J.M.; Sanders, R.W.; Clas, B.; Schuelke, N.; Master, A.; Guo, Y.; Kajumo, F.; Anselma, D.J.; Maddon, P.J.; Olson, W.C.; Moore, J.P. A recombinant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein complex stabilized by an intermolecular disulfide bond between the gp120 and gp41 subunits is an antigenic mimic of the trimeric virion-associated structure. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 627–643. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, J.M.; Cayanan, C.S.; Wiley, C.; Schulke, N.; Olson, W.C.; Burton, D.R. Redox-triggered infection by disulfide-shackled human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pseudovirions. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5678–5684. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, R.W.; Vesanen, M.; Schuelke, N.; Master, A.; Schiffner, L.; Kalyanaraman, R.; Paluch, M.; Berkhout, B.; Maddon, P.J.; Olson, W.C.; et al. Stabilization of the soluble, cleaved, trimeric form of the envelope glycoprotein complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8875–8889. [Google Scholar]
- Klasse, P.J.; Depetris, R.S.; Pejchal, R.; Julien, J.P.; Khayat, R.; Lee, J.H.; Marozsan, A.J.; Cupo, A.; Cocco, N.; Korzun, J.; et al. Influences on trimerization and aggregation of soluble, cleaved HIV-1 SOSIP envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9873–9885. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, R.W.; Derking, R.; Cupo, A.; Julien, J.P.; Yasmeen, A.; de Val, N.; Kim, H.J.; Blattner, C.; de la Pena, A.T.; Korzun, J.; et al. A next-generation cleaved, soluble HIV-1 Env trimer, BG505 SOSIP.664 gp140, expresses multiple epitopes for broadly neutralizing but not non-neutralizing antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003618. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, B.F.; Kelsoe, G.; Harrison, S.C.; Kepler, T.B. B-cell-lineage immunogen design in vaccine development with HIV-1 as a case study. Nature Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 423–433. [Google Scholar]
- Guenaga, J.; Wyatt, R.T. Structure-guided alterations of the gp41-directed HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody 2F5 reveal new properties regarding its neutralizing function. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002806. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Ofek, G.; Laub, L.; Louder, M.K.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Longo, N.S.; Imamichi, H.; Bailer, R.T.; Chakrabarti, B.; Sharma, S.K.; et al. Broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by a gp41-specific human antibody. Nature 2012, 491, 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffner, T.; Kong, L.; Duncan, C.J.; Back, J.W.; Benschop, J.J.; Shen, X.; Huang, P.S.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.; Destefano, J.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Immune focusing and enhanced neutralization induced by HIV-1 gp140 chemical cross-linking. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10163–10172. [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel, M.H. Limitations to the structure-based design of HIV-1 vaccine immunogens. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 741–753. [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel, M.H. Requirements for empirical immunogenicity trials, rather than structure-based design, for developing an effective HIV vaccine. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hoot, S.; McGuire, A.T.; Cohen, K.W.; Strong, R.K.; Hangartner, L.; Klein, F.; Diskin, R.; Scheid, J.F.; Sather, D.N.; Burton, D.R.; et al. Recombinant HIV envelope proteins fail to engage germline versions of anti-CD4bs bNAbs. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003106. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J. Broadly neutralizing antibodies and the search for an HIV-1 vaccine: The end of the beginning. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 693–701. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sattentau, Q.J. Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers as HIV-1 Vaccine Immunogens. Vaccines 2013, 1, 497-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines1040497
Sattentau QJ. Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers as HIV-1 Vaccine Immunogens. Vaccines. 2013; 1(4):497-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines1040497
Chicago/Turabian StyleSattentau, Quentin J. 2013. "Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers as HIV-1 Vaccine Immunogens" Vaccines 1, no. 4: 497-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines1040497
APA StyleSattentau, Q. J. (2013). Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers as HIV-1 Vaccine Immunogens. Vaccines, 1(4), 497-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines1040497



