Protective Immunization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) against Salmon Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) Infestation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Facility and Ethics
2.2. Vaccine Preparation
2.3. Fish and Design of the Trial
2.4. Lice Challenge Procedures
2.5. Lice Counts
2.6. Fish Sampling
2.7. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.8. RT-qPCR Protocol
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
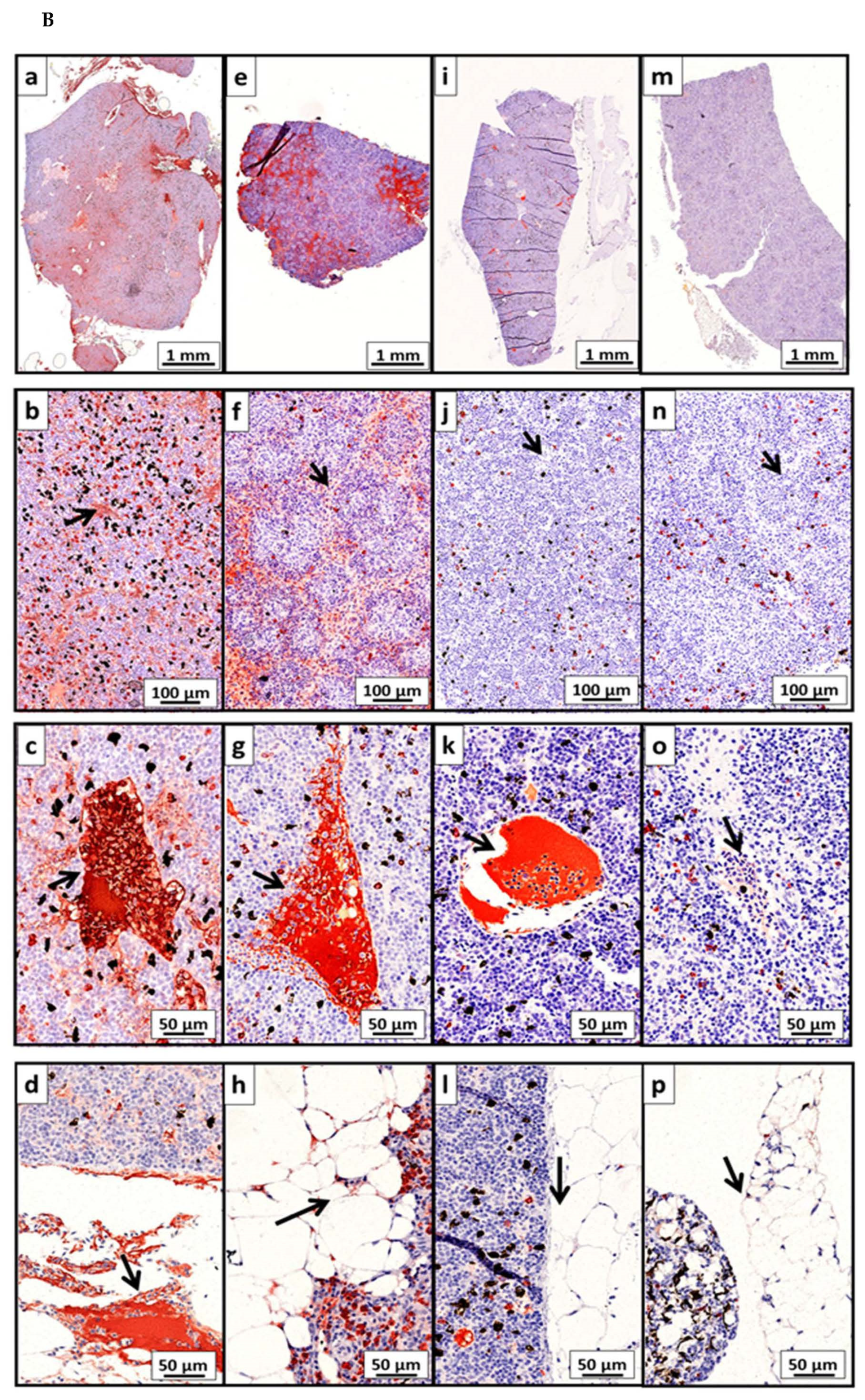
2.10.1. Analysis of Total IgM and Production of IgM Positive Cells
2.10.2. Analysis of P33-Specific Antibodies In Situ in Spleen
3. Results
3.1. P33 Vaccination Reduces Salmon Lice Counts on Atlantic Salmon
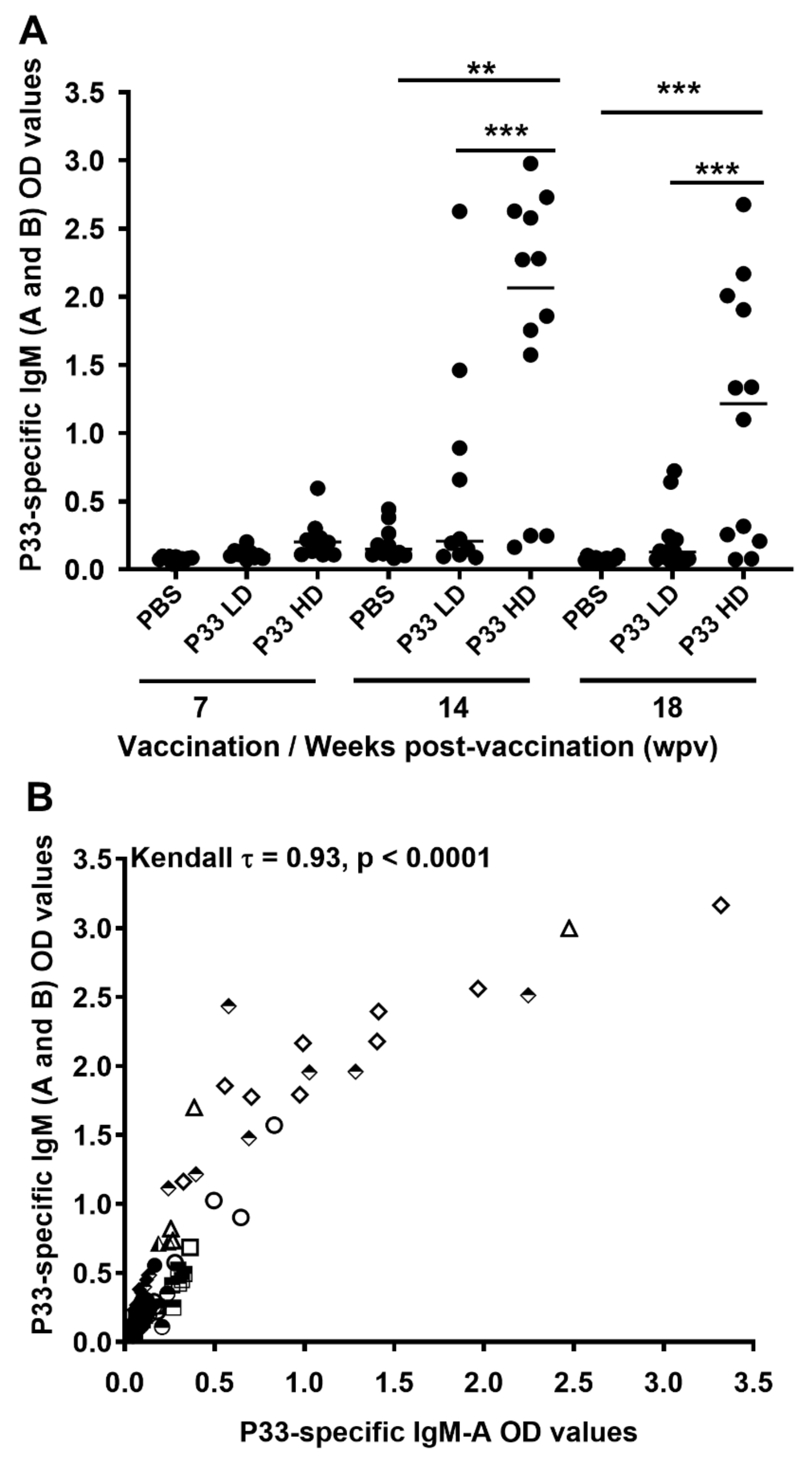
3.2. P33 Vaccination Induces P33-Specific IgM Antibodies
3.2.1. Quantification of P33-Specific IgM in Plasma
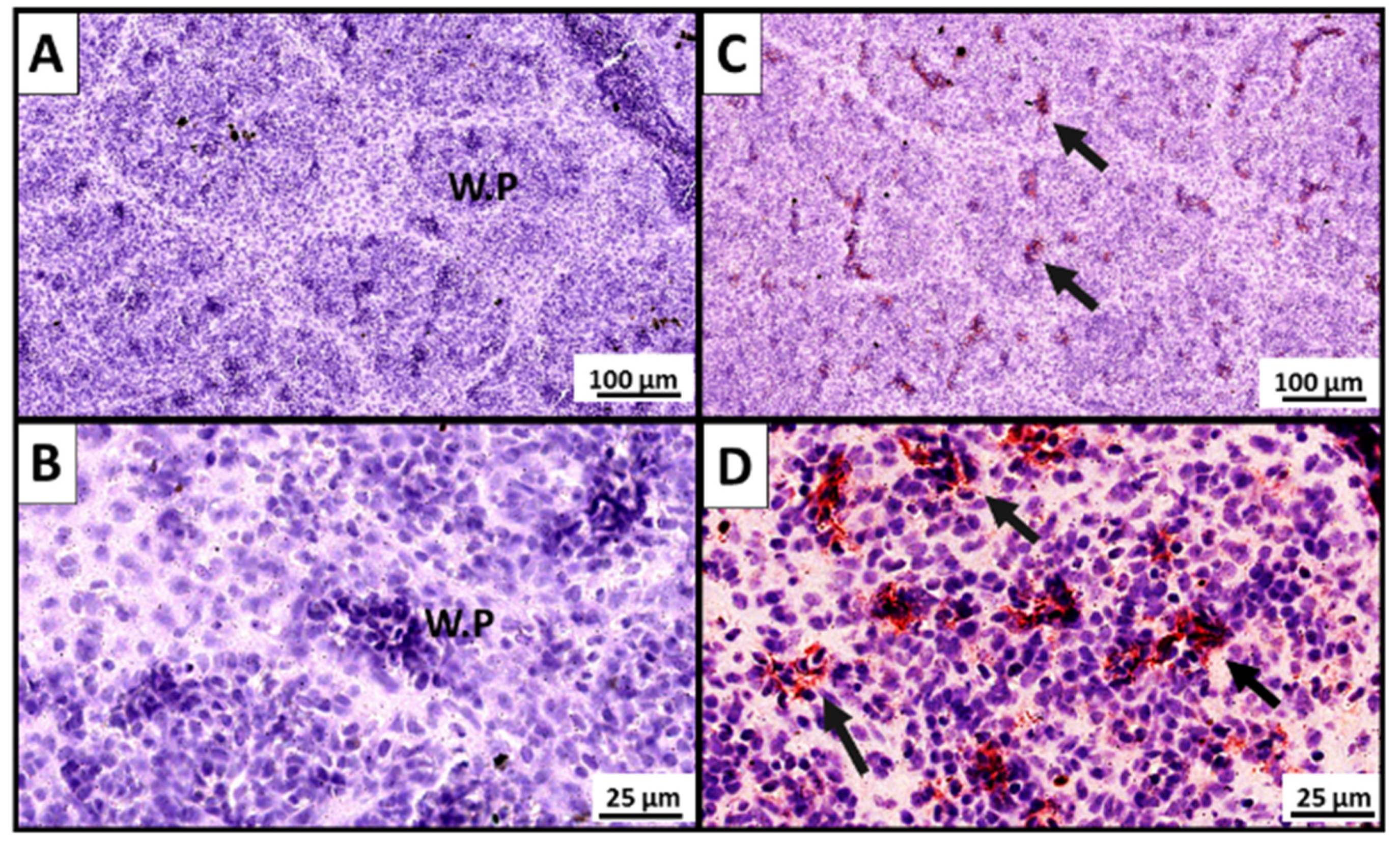
3.2.2. Demonstration of P33-Specific Antibodies In Situ in the Spleen of Vaccinated Fish
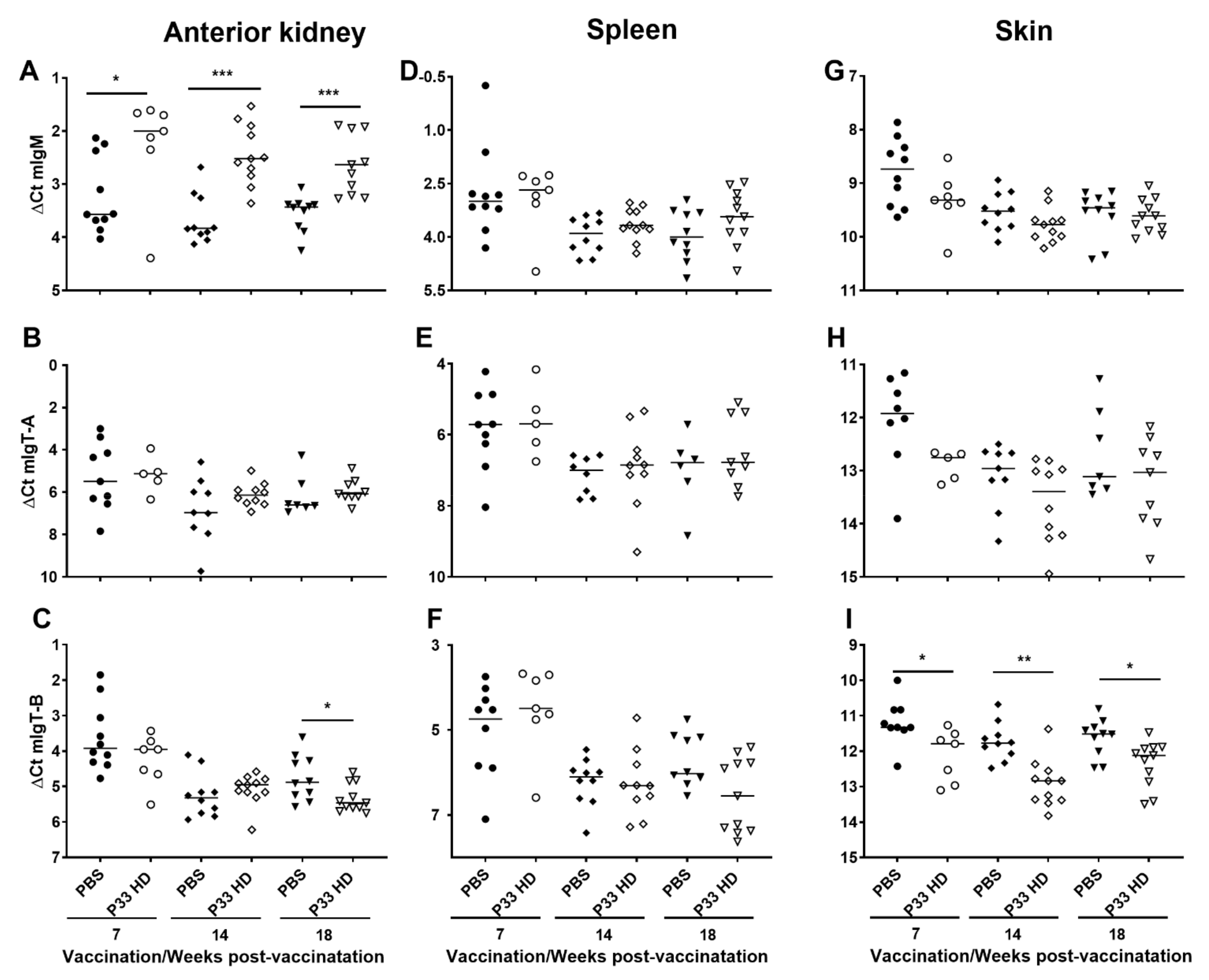
3.3. Immunoglobulin Kinetics Are Altered after P33 Vaccination
3.3.1. P33 Vaccine Modifies Immunoglobulin Gene Expression in Vaccinated Fish
3.3.2. IgM Production in Fish Immune Tissues Is Modulated after P33 Vaccination
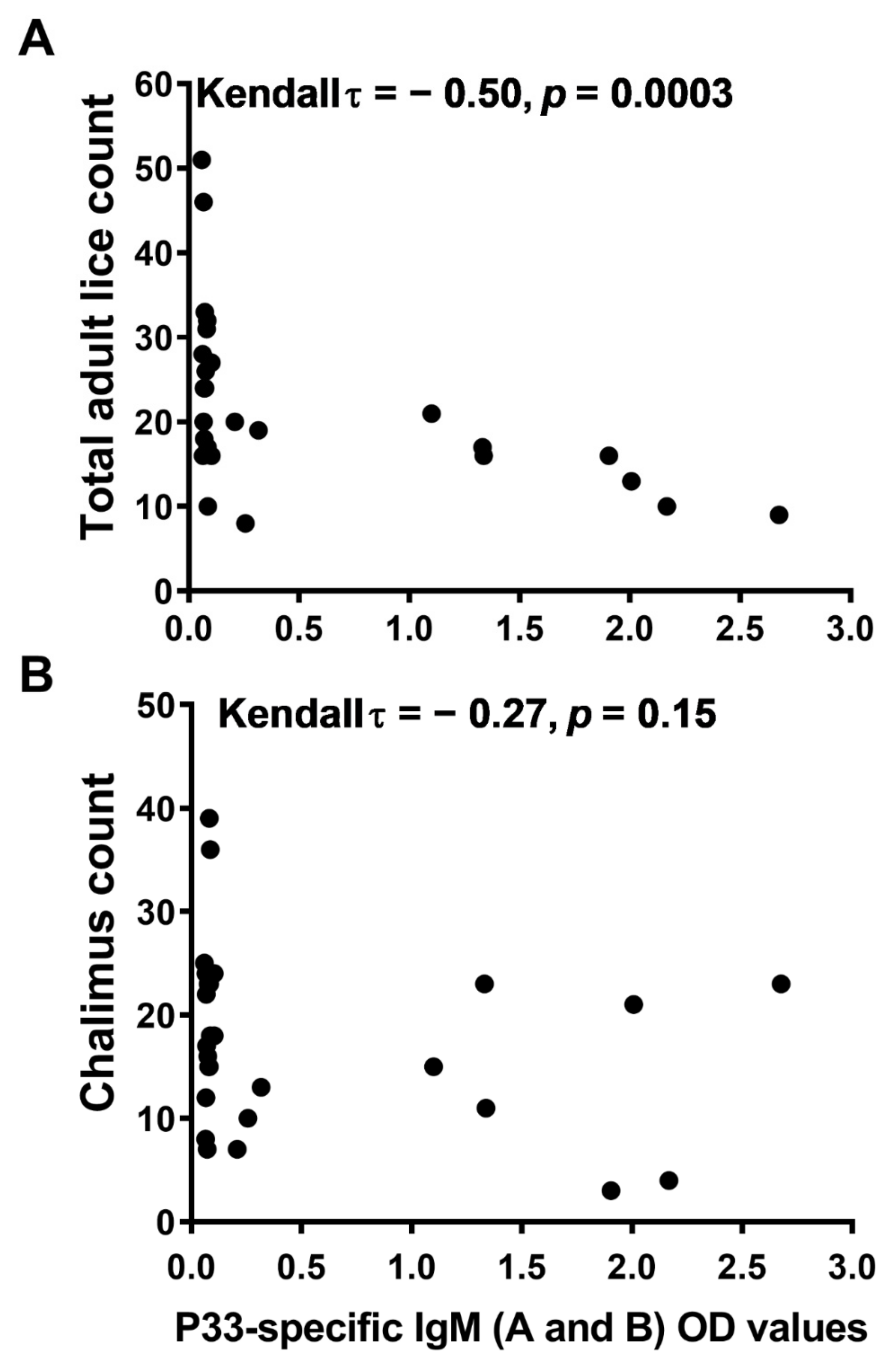
3.4. Vaccine-Induced Protection against Salmon Lice Correlates with the P33-Specific IgM in Fish Plasma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costello, M.J. Ecology of sea lice parasitic on farmed and wild fish. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsdottir, H.; Bron, J.; Wootten, R.; Turnbull, J. The histopathology associated with the pre-adult and adult stages of Lepeophtheirus salmonis on the Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 1992, 15, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, S. Sea lice in Chilean salmon farms. Bull.-Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2003, 23, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Torrissen, O.; Jones, S.; Asche, F.; Guttormsen, A.; Skilbrei, O.T.; Nilsen, F.; Horsberg, T.E.; Jackson, D. Salmon lice–impact on wild salmonids and salmon aquaculture. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plant, K.P.; LaPatra, S.E. Advances in fish vaccine delivery. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECURED. Gavac. Vacuna Recombinante Contra la Garrapata. Available online: https://www.ecured.cu/Gavac (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Leong, J.-A.C. Molecular and biotechnological approaches to fish vaccines. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1993, 4, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Redondo, M.; Montero, C.; García-García, J.; Méndez, L.; Serrano, E.; Valdés, M.; Enriquez, A.; Canales, M. Field studies and cost-effectiveness analysis of vaccination with Gavac™ against the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Vaccine 1998, 16, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, K.N.; Moore, T.; Sriskantha, A.; Spring, K.; Tellam, R.; Willadsen, P.; Cobon, G.S. Cloning and expression of a protective antigen from the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9657–9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crompton, P.D.; Pierce, S.K.; Miller, L.H. Advances and challenges in malaria vaccine development. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4168–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, V.M.; Meeusen, E.N.; Young, A.R.; Andrews, A.E.; Nash, A.D.; Brandon, M.R. Vaccination of sheep against larvae of the sheep blowfly (Lucilia cuprina). Vaccine 1996, 14, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.T.; Nunn, F.; Nath, M.; Frew, D.; Wells, B.; Marr, E.J.; Huntley, J.F.; McNeilly, T.N.; Nisbet, A.J. A recombinant subunit vaccine for the control of ovine psoroptic mange (sheep scab). Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, J. Host resistance to ectoparasites. Rev. Sci. Tech.-Off. Int. Des. Epizoot. 1994, 13, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, J.; Sommerville, C.; Rae, G. The functional morphology of the alimentary canal of larval stages of the parasitic copepod Lepeophtheirus salmonis. J. Zool. 1993, 230, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxaspen, K. A review of the biology and genetics of sea lice. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rae, G.H. Sea louse control in Scotland, past and present. Pest Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, Y.; Basabe, L.; Acosta, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Mendoza, A.; Lisperger, A.; Zamorano, E.; González, M.; Rivas, M.; Contreras, S. Novel gene isolated from Caligus rogercresseyi: A promising target for vaccine development against sea lice. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, Y.; García, C.; Pons, T.; Haussmann, D.; Rodríguez-Ramos, T.; Basabe, L.; Acosta, J.; Estrada, M.P. Akirins in sea lice: First steps towards a deeper understanding. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute, N.V. Louse Off 2-Cost Effective Sea Lice Vaccine; Development and Efficacy Evaluation. Available online: https://wwweng.vetinst.no/research-and-innovation/ongoing-research-projects/louse-off-2-cost-effective-sea-lice-vaccine-development-and-efficacy-evaluation (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Leal, Y.V.J.; García, C.; Takizawa, F.; Sunyer, O.; Purcell, S.; Fast, M.; Estrada, M.P.; Carpio, Y. Efficacy Evaluation of an Immunogenic Peptide Derived from the Lepeophtheirus Salmonis in Controlled Immunization-Challenge Experiment in Salmo salar. Available online: https://az659834.vo.msecnd.net/eventsairwesteuprod/production-happening-public/ec2a2f9ae0ea493bbb0fb44cf43ee0b9 (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Swain, J.K.; Johansen, L.-H.; González, Y.C. Validating a salmon lice vaccine candidate as a preventive measure against salmon lice at the lab-scale. Nofima Rapp. 2018, 32, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Animal., T.S. Providean Aquatec Sea Lice. Available online: http://www.tecnovax.com.ar/productos/providean-aquatec-sea-lice/ (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Swain, J.K.; Carpio, Y.; Johansen, L.-H.; Velazquez, J.; Hernandez, L.; Leal, Y.; Kumar, A.; Estrada, M.P. Impact of a candidate vaccine on the dynamics of salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) infestation and immune response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.; Karlsen, M.; Villar, M.; Olsen, R.H.; Leknes, L.M.; Furevik, A.; Yttredal, K.L.; Tartor, H.; Grove, S.; Alberdi, P. Vaccination with Ectoparasite Proteins Involved in Midgut Function and Blood Digestion Reduces Salmon Louse Infestations. Vaccines 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holm, H.; Santi, N.; Kjøglum, S.; Perisic, N.; Skugor, S.; Evensen, Ø. Difference in skin immune responses to infection with salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) of families selected for resistance and susceptibility. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.-A. Identification of another primordial CD80/86 molecule in rainbow trout: Insights into the origin and evolution of CD80 and CD86 in vertebrates. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 89, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingerslev, H.-C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Jakobsen, R.A.; Petersen, C.B.; Wergeland, H.I. Expression profiling and validation of reference gene candidates in immune relevant tissues and cells from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuvander, A.; Fossum, C.; Lorenzen, N. Monoclonal antibodies to salmonid immunoglobulin: Characterization and applicability in immunoassays. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1990, 14, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedfors, I.A.; Bakke, H.; Skjødt, K.; Grimholt, U. Antibodies recognizing both IgM isotypes in Atlantic salmon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, S.; Johansen, R.; Reitan, L.J.; Press, C.M. Immune-and enzyme histochemical characterisation of leukocyte populations within lymphoid and mucosal tissues of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Kania, P.W.; Chettri, J.K.; Skov, J.; Bojesen, A.M.; Dalsgaard, I.; Buchmann, K. Insight from molecular, pathological, and immunohistochemical studies on cellular and humoral mechanisms responsible for vaccine-induced protection of rainbow trout against Yersinia ruckeri. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skugor, S.; Glover, K.A.; Nilsen, F.; Krasnov, A. Local and systemic gene expression responses of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) to infection with the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdenegro-Vega, V.A.; Crosbie, P.B.; Cook, M.T.; Vincent, B.N.; Nowak, B.F. Administration of recombinant attachment protein (r22C03) of Neoparamoeba perurans induces humoral immune response against the parasite in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 38, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, K.D.; Jones, D.R.; Raison, R.L. Characterisation of mucosal and systemic immune responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) using surface plasmon resonance. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2000, 10, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoloki, S.; Reite, O.B.; Brudeseth, B.; Tverdal, A.; Evensen, Ø. A comparative immunopathological study of injection site reactions in salmonids following intraperitoneal injection with oil-adjuvanted vaccines. Vaccine 2006, 24, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabatingan, M.S.; Schmidt, M.R.; Sen, R.; Woodland, R.T. Naive B lymphocytes undergo homeostatic proliferation in response to B cell deficit. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6795–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abos, B.; Estensoro, I.; Perdiguero, P.; Faber, M.; Hu, Y.; Díaz Rosales, P.; Granja, A.G.; Secombes, C.J.; Holland, J.W.; Tafalla, C. Dysregulation of B cell activity during proliferative kidney disease in rainbow trout. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brandal, P.; Egidius, E.; Romslo, I. Host Blood-Major Food Component for Parasitic Copepod Lepeophtheirus-Salmonis Kroyeri, 1838 (Crustacea-Caligidae). Nor. J. Zool. 1976, 24, 341–343. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, M.; Penichet, M.; Mouris, A.; Labarta, V.; Luaces, L.L.; Rubiera, R.; Cordoves, C.; Sanchez, P.; Ramos, E.; Soto, A. Control of Boophilus microplus populations in grazing cattle vaccinated with a recombinant Bm86 antigen preparation. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 57, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Parra, D.; Gomez, D.; Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.A.; von Gersdorff Jorgensen, L.; Heinecke, R.D.; Buchmann, K.; LaPatra, S.; Sunyer, J.O. Teleost skin, an ancient mucosal surface that elicits gut-like immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13097–13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.-Y.; Kong, W.; Yin, Y.-X.; Dong, F.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Yin, G.-M.; Dong, S.; Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.-A.; Xu, Z. Mucosal immunoglobulins protect the olfactory organ of teleost fish against parasitic infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heggland, E.I. Hematophagy in the Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis): Characterization of Genes and Proteins Involved in Parasite Blood-Feedin. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 2020. Available online: https://bora.uib.no/bora-xmlui/handle/1956/21432 (accessed on 1 April 2021).





| Gene Name | Primers Sequences (5′–3′) | Accession Number | Effeciency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secretory immunoglobulin M (sIgM) | F:CTACAAGAGGGAGACCGGAG R:AGGGTCACCGTATTATCACTAGTT | XM_014203125 | 100.36 |
| Membrane immunoglobulin M (mIgM) | F:CCTACAAGAGGGAGACCGA R:GATGAAGGTGAAGGCTGTTTT | Y12457 | 81.84 |
| Immunoglobulin T isoform C (IgT-C) | F:GCTAAGAGTGTCTGGGAAATGA R:TGGAGGGTTTGAGATTGGTC | HQ379938.1 | 84.9 |
| Immunoglobulin D (IgD) | F:TGAACATCGCTGCTTCAAC R:CCAGCACAGCACTGTCTCC | AF141606.1 | 97.09 |
| Secretory immunoglobulin T isoform A (sIgT-A) | F:CCAAGGATAAGTGGGAGAGAA R:TCACTTGTCTTCACATGAGTTACC | GQ907003 | 80.2 |
| Membrane immunoglobulin T isoform A (mIgT-A) | F:CCAAGGATAAGTGGGAGAGAA R:AGGATGTTCGCCATGGACT | GQ907003 | 103.41 |
| Secretory immunoglobulin T isoform B (sIgT-B) | F:GAATGTTTGGGACACGGAAG R:TCACATATCTTGACATGAGTTACCC | GQ907004.1 | 89.89 |
| Membrane immunoglobulin T isoform B (mIgT-B) | F:GAATGTTTGGGACACGGAAG R:GCTCAGTCAGTGGGATGTTCT | GQ907004.1 | 92.3 |
| Elongation factor-1alpha (EF-1 α) | F:TGCCCCTCCAGGATGTCTAC R:CACGGCCCACAGGTACTG | BG933897 | 106.98 |
| Tissue | Scoring Scale | Score Description |
|---|---|---|
| Spleen and anterior kidney | Abundance of IgM+ cells/microscopic field (10× magnification objective lens) | |
| 0 | No positive cells | |
| 1 | ≤10 cells | |
| 2 | 30–50 cells | |
| 3 | 60–80 cells | |
| 4 | >90 cells | |
| IgM labeling intensity | ||
| 0 | No labeling | |
| 1 | Mild labeling | |
| 2 | Moderate labeling | |
| 3 | Strong labeling | |
| 4 | Heavy labeling | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tartor, H.; Karlsen, M.; Skern-Mauritzen, R.; Monjane, A.L.; Press, C.M.; Wiik-Nielsen, C.; Olsen, R.H.; Leknes, L.M.; Yttredal, K.; Brudeseth, B.E.; et al. Protective Immunization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) against Salmon Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) Infestation. Vaccines 2022, 10, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10010016
Tartor H, Karlsen M, Skern-Mauritzen R, Monjane AL, Press CM, Wiik-Nielsen C, Olsen RH, Leknes LM, Yttredal K, Brudeseth BE, et al. Protective Immunization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) against Salmon Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) Infestation. Vaccines. 2022; 10(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleTartor, Haitham, Marius Karlsen, Rasmus Skern-Mauritzen, Adérito Luis Monjane, Charles McLean Press, Christer Wiik-Nielsen, Rolf Hetlelid Olsen, Lisa Marie Leknes, Karine Yttredal, Bjørn Erik Brudeseth, and et al. 2022. "Protective Immunization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) against Salmon Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) Infestation" Vaccines 10, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10010016
APA StyleTartor, H., Karlsen, M., Skern-Mauritzen, R., Monjane, A. L., Press, C. M., Wiik-Nielsen, C., Olsen, R. H., Leknes, L. M., Yttredal, K., Brudeseth, B. E., & Grove, S. (2022). Protective Immunization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) against Salmon Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) Infestation. Vaccines, 10(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10010016






