Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccine among Pregnant Women in Real-World Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
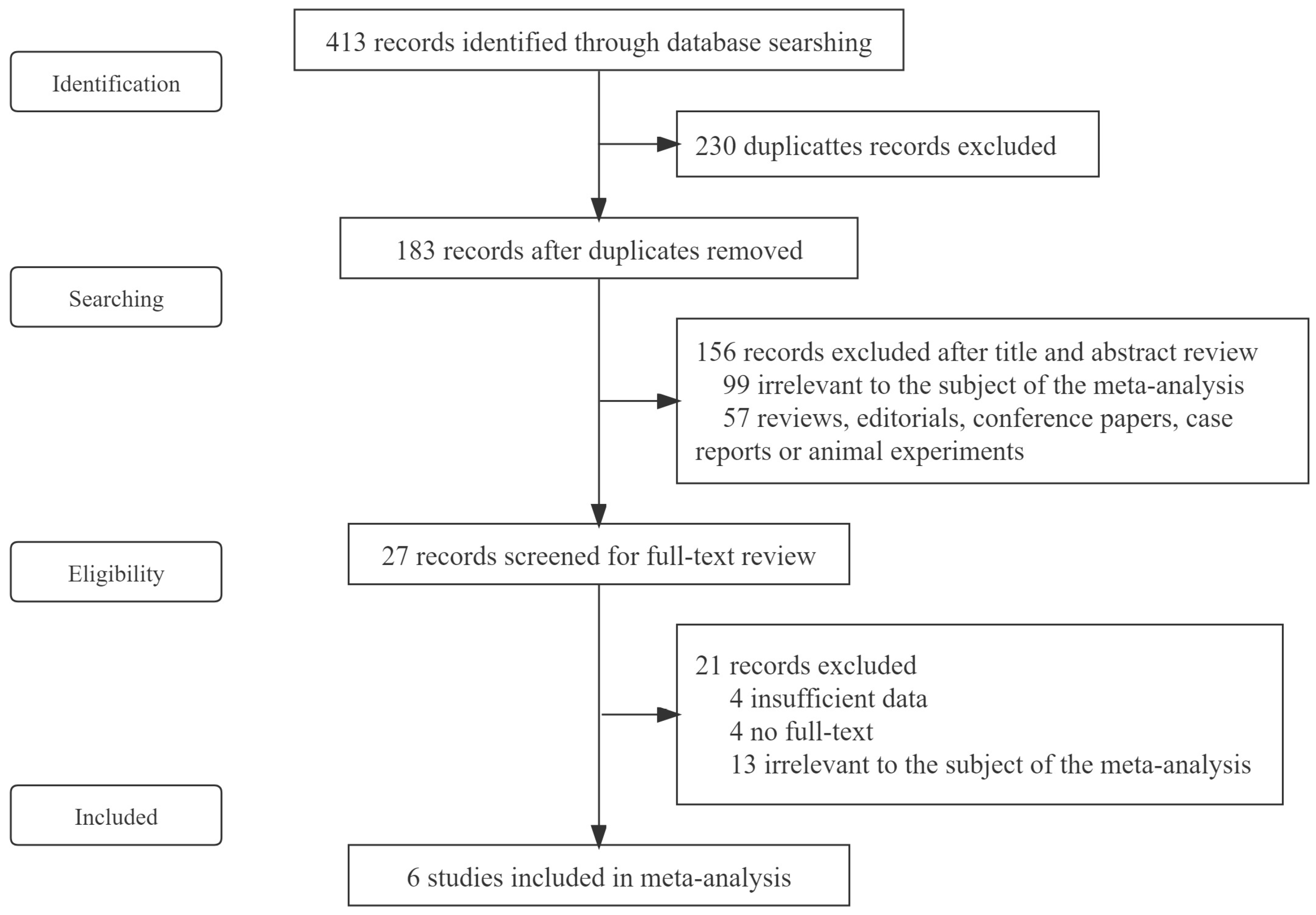
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics
3.2. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines among Pregnant Women
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
3.4. Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Pregnant Women
3.5. Quality Evaluation and Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/table (accessed on 22 December 2021).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data on COVID-19 during Pregnancy: Severity of Maternal Illness. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#pregnant-population (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Science Brief: Evidence Used to Update the List of Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with Higher Risk for Se-vere COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/underlying-evidence-table.html (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Pregnant People at Increased Risk for Severe Illness from COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/pregnant-people.html (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- World Health Organization. Draft Landscape of COVID-19 Candidate Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines.. (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. WHO Issues Emergency Use Listing for Eighth COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/03-11-2021-who-issues-emergency-use-listing-for-eighth-covid-19-vaccine (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Han, X.; Xu, P.; Ye, Q. Analysis of COVID-19 vaccines: Types, thoughts, and application. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsaperla, R.; Leone, G.; Familiari, M.; Ruggieri, M. COVID-19 vaccination in pregnant and lactating women: A systematic review. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Sivajohan, B.; McClymont, E.; Albert, A.; Elwood, C.; Ogilvie, G.; Money, D. Systematic review of the safety, immunogenicity, and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant and lactating individuals and their infants. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2021, 156, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, I.; Shekhar, R.; Sheikh, A.B.; Pal, S. COVID-19 Vaccine in Pregnant and Lactating Women: A Review of Existing Evidence and Practice Guidelines. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 13, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillo, E.; Tosto, V.; Gerli, S.; Buonomo, E. COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy and postpartum. The journal of maternal-fetal & neonatal medicine. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Perinat. Med. Fed. Asia Ocean. Perinat. Soc. Int. Soc. Perinat. Obs. 2021, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Lee, W.L.; Yang, S.T.; Tsui, K.H.; Chang, C.C.; Lee, F.K. The impact of COVID-19 in pregnancy: Part II. Vaccination to pregnant women. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. JCMA 2021, 84, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.; Moodley, J.; Moran, N. Perspectives on COVID-19 vaccination for pregnant women in South Africa. Afr. J. Prim. Health Care Fam. Med. 2021, 13, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Interim recommendations for use of the ChAdOx1-S [recombinant] vaccine against COVID-19 (AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine AZD1222 Vaxzevria™, SII COVISHIELD™). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE_recommendation-AZD1222-2021.1 (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Interim Recommendations for Use of the Bharat Biotech BBV152 COVAXIN® Vaccine Against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE-recommendation-bbv152-covaxin (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Annexes to the Recommendations for Use of the Pfizer–BioNTech Vaccine BNT162b2 Against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE-recommendation-BNT162b2-GRADE-ETR-annexes (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Interim Recommendations for Use of the Moderna mRNA-1273 Vaccine Against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/interim-recommendations-for-use-of-the-moderna-mrna-1273-vaccine-against-covid-19 (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Interim Recommendations for the Use of the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S (COVID-19) Vaccine. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE-recommendation-Ad26.COV2.S-2021.1 (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Annexes to WHO Interim Recommendations for Use of the COVID-19 Vaccine BIBP. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE-recommendation-BIBP-annexes (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Interim Recommendations for Use of the Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine, CoronaVac, Developed by Sinovac. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE_recommendation-Sinovac-CoronaVac-2021.1 (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Overview of the Implementation of COVID-19 Vaccination Strategies and Deployment Plans in the EU/EEA. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/overview-implementation-covid-19-vaccination-strategies-and-deployment-plans (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- UK Government. COVID-19 Vaccination: A Guide on Pregnancy and Breastfeeding—GOV.UK. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-vaccination-women-of-childbearing-age-currently-pregnant-planning-a-pregnancy-or-breastfeeding/covid-19-vaccination-a-guide-for-women-of-childbearing-age-pregnant-planning-a-pregnancy-or-breastfeeding (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Queation&Answer on COVID-19 Vaccination (updated 31 March 2021). Available online: https://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/zl/szkb_11803/jszl_12208/202104/t20210401_225334.html (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Shimabukuro, T.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Myers, T.R.; Moro, P.L.; Oduyebo, T.; Panagiotakopoulos, L.; Marquez, P.L.; Olson, C.K.; Liu, R.; Chang, K.T.; et al. Preliminary Findings of mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine Safety in Pregnant Persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Tao, L.; Liu, J. The Association Between Risk Perception and COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy for Children Among Reproductive Women in China: An Online Survey. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 741298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Wang, R.; Han, N.; Liu, J.; Yuan, C.; Deng, L.; Han, C.; Sun, F.; Liu, M.; Liu, J. Acceptance of a COVID-19 vaccine and associated factors among pregnant women in China: A multi-center cross-sectional study based on health belief model. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, R.N.; Wick, M.; Mehta, R.; Weaver, A.L.; Virk, A.; Swift, M. Pregnancy and birth outcomes after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2021, 3, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.A.; Chemaitelly, H.; Al Khal, A.; Coyle, P.V.; Saleh, H.; Kaleeckal, A.H.; Latif, A.N.; Bertollini, R.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Abu-Raddad, L.J. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectiveness in preventing confirmed infection in pregnant women. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e153662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, A.Y.; McMahan, K.; Yu, J.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Aguayo, R.; Ansel, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Patel, S.; Apraku Bondzie, E.; Sellers, D.; et al. Immunogenicity of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines in Pregnant and Lactating Women. Jama 2021, 325, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagan, N.; Barda, N.; Biron-Shental, T.; Makov-Assif, M.; Key, C.; Kohane, I.S.; Hernán, M.A.; Lipsitch, M.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.; Reis, B.Y.; et al. Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in pregnancy. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1693–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakeway, H.; Prasad, S.; Kalafat, E.; Heath, P.T.; Ladhani, S.N.; Le Doare, K.; Magee, L.A.; O’Brien, P.; Rezvani, A.; von Dadelszen, P.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy: Coverage and safety. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 226, 236.e1–236.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshtein, I.; Nevo, D.; Steinberg, D.M.; Rotem, R.S.; Gorfine, M.; Chodick, G.; Segal, Y. Association Between BNT162b2 Vaccination and Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnant Women. Jama 2021, 326, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccines While Pregnant or Breastfeeding. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/pregnancy.html (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Australian Government, Department of Health. COVID-19 Vaccine Weekly Safety Report—05-08-2021. Available online: https://www.tga.gov.au/periodic/covid-19-vaccine-weekly-safety-report-05-08-2021 (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Government of Canada. Vaccination and Pregnancy: COVID-19. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/immunization-vaccines/vaccination-pregnancy-covid-19.html (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Ministère des Solidarités et de la Santé. La Stratégie Vaccinale et la Liste des Publics Prioritaires. Available online: https://solidarites-sante.gouv.fr/grands-dossiers/vaccin-covid-19/publics-prioritaires-vaccin-covid-19 (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.J.; Moreira, E.D., Jr.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Polack, F.P.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine through 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sahly, H.M.; Baden, L.R.; Essink, B.; Doblecki-Lewis, S.; Martin, J.M.; Anderson, E.J.; Campbell, T.B.; Clark, J.; Jackson, L.A.; Fichtenbaum, C.J.; et al. Efficacy of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine at Completion of Blinded Phase. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qin, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, J. Effectiveness and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in real-world studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2021, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.J.; Bordt, E.A.; Atyeo, C.; Deriso, E.; Akinwunmi, B.; Young, N.; Baez, A.M.; Shook, L.L.; Cvrk, D.; James, K.; et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine response in pregnant and lactating women: A cohort study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 225, 303.e301–303.e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beharier, O.; Plitman Mayo, R.; Raz, T.; Nahum Sacks, K.; Schreiber, L.; Suissa-Cohen, Y.; Chen, R.; Gomez-Tolub, R.; Hadar, E.; Gabbay-Benziv, R.; et al. Efficient maternal to neonatal transfer of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e150319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Qestion and Answer on Booster Shots of COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/zl/szkb_11803/jszl_2275/202111/t20211116_252842.html (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- UK Government. Prime Minister’s Address to the Nation on Booster Jabs: 12 December 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/speeches/prime-ministers-address-to-the-nation-on-booster-jabs-12-december-2021 (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. EMA and ECDC Recommendations on Heterologous Vaccination Courses Against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/ema-and-ecdc-recommendations-heterologous-vaccination-courses-against-covid-19 (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Shots. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/booster-shot.html (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Interim Statement on Booster Doses for COVID-19 Vaccination. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/04-10-2021-interim-statement-on-booster-doses-for-covid-19-vaccination (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Manshan, L.; Shan, Y.; Mei, L.; Haixia, S.; Yan, L.; Hong, L. Influence of age on the outcome of pregnancy and childbirth in 5413 pregnant women. J. Guizhou Med. Univ. 2021, 46, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciabattini, A.; Nardini, C.; Santoro, F.; Garagnani, P.; Franceschi, C.; Medaglini, D. Vaccination in the elderly: The challenge of immune changes with aging. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 40, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhishan, J.; Jianghua, W.; Dilu, F.; Lin, X.; Qingmiao, Z.; Hongbo, W. Analysis of differences in immune function between late pregnancy and non-pregnancy patients during COVID-19 convalescence. Prog. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 30, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Peng, Z. Study changes of immune function before and after pregnancy in pregnant women and the influence of CD4+CD25+regulatory T cells and estradiol on pregnancy. Chin. J. Health Lab. 2011, 21, 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Yangtengyu, L.; Xiaoxia, Z. Characteristics of immune system during pregnancy and pregnancy combined with autoimmune diseases. Chin. J. Obstet. Emerg. 2019, 8, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Turan, O.; Hakim, A.; Dashraath, P.; Jeslyn, W.J.L.; Wright, A.; Abdul-Kadir, R. Clinical characteristics, prognostic factors, and maternal and neonatal outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection among hospitalized pregnant women: A systematic review. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2020, 151, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingyi, H.; Weifeng, C.; Yongshu, D. The difference between prospective and retrospective clinical studies. J. Clin. Hepatol. 2016, 35, 904. [Google Scholar]
- Aranha, C.L.M.; Martins, S.R.P.; Oliveira, M.D.U.D. Research methodology topics: Cohort studies or prospective and retrospective cohort studies. J. Hum. Growth Dev. 2019, 29, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Euser, A.M.; Zoccali, C.; Jager, K.J.; Dekker, F.W. Cohort studies: Prospective versus retrospective. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2009, 113, c214–c217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jivraj, S.; Goodman, A.; Ploubidis, G.B.; de Oliveira, C. Testing Comparability Between Retrospective Life History Data and Prospective Birth Cohort Study Data. J. Gerontology Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2020, 75, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Safety and Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccination during Pregnancy. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/pregnancy.html#anchor_1628692520287 (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Ciapponi, A.; Bardach, A.; Mazzoni, A.; Alconada, T.; Anderson, S.A.; Argento, F.J.; Ballivian, J.; Bok, K.; Comandé, D.; Erbelding, E.; et al. Safety of components and platforms of COVID-19 vaccines considered for use in pregnancy: A rapid review. Vaccine 2021, 39, 5891–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainstock, T.; Yoles, I.; Sergienko, R.; Sheiner, E. Prenatal maternal COVID-19 vaccination and pregnancy outcomes. Vaccine 2021, 39, 6037–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nir, O.; Schwartz, A.; Toussia-Cohen, S.; Leibovitch, L.; Strauss, T.; Asraf, K.; Doolman, R.; Sharabi, S.; Cohen, C.; Lustig, Y.; et al. Maternal-neonatal transfer of SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin G antibodies among parturient women treated with BNT162b2 messenger RNA vaccine during pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2021, 4, 100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelman, N.; Nahshon, C.; Shaked-Mishan, P.; Cohen, N.; Sher, M.L.; Gruber, M.; Marom, I.; Zolotarevsky, A.; Lavie, O.; Damti, A.; et al. Maternal and Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulin G Antibody Levels at Delivery After Receipt of the BNT162b2 Messenger RNA COVID-19 Vaccine During the Second Trimester of Pregnancy. JAMA Pediatrics 2021, 175, e215683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdanowski, W.; Waśniewski, T. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Antibody Titers in Cord Blood after COVID-19 Vaccination during Pregnancy in Polish Healthcare Workers: Preliminary Results. Vaccines 2021, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Record Number | First Author | Published Time | Study Design | Location | Vaccine Type | No. of Dose | Median Age | Median Gestational Age | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with SARS-CoV-2 Infection (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with SARS-CoV-2 Infection (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Hospitalization (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Hospitalization (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Severe Illness or ICU Admission (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Severe Illness or ICU Admission (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Death (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Death (n/N) | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Theiler, R. N. | 2021.8 | Retrospective cohort study | USA | BNT162b2+Moderna+ adenovirus vector vaccine | ≥1 | 31.8 | Last trimester | 2/140 | 210/2862 | - | - | 1/140 | 2/1862 | 0/140 | 0/1862 | Low |
| 2 | Butt, A. A. | 2021.7 | Prospective cohort study | Qatar | BNT162b2+Moderna | 2 | 32 | Early trimester | 2/407 | 15/407 | - | - | - | - | 0/407 | 0/407 | Low |
| 3 | Collier, A. Y. | 2021.5 | Prospective cohort study | Israel | BNT162b2+Moderna | 2 | 35 | Second trimester | - | - | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | Low |
| 4 | Dagan, N. | 2021.9 | Retrospective cohort study | Israel | BNT162b2 | 2 | 30 | - | 131/10,861 | 235/10,861 | 11/18,061 | 25/18,061 | 0/10,861 | 4/10,861 | 0/10,861 | 0/10,861 | Low |
| 5 | Blakeway, H. | 2021.8 | Retrospective cohort study | England | BNT162b2+Moderna+adenovirus vector vaccine | ≥1 | 35 | Last trimester | 2/140 | 16/1188 | - | - | 8/133 | 16/399 | - | - | Low |
| 6 | Goldshtein, I. | 2021.7 | Retrospective cohort study | Israel | BNT162b2 | ≥1 | 31.1 | - | 118/7530 | 202/7530 | 13/7530 | 23/7530 | - | - | 0/7530 | 0/7530 | Low |
| Record Number | First Author | Published Time | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Uterine Rupture | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Uterine Rupture | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Third- or Fourth-Degree Laceration | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Third- or Fourth-Degree Laceration | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Return to the Operating Room within 72 h of Delivery | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Return to the Operating Room within 72 h of Delivery | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with 5 min Apgar Score < 7 | Unvaccinated PREGNANT Women with 5 min Apgar Score < 7 | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Quantitative Blood Loss >1000 mL | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Quantitative Blood Loss >1000 mL | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Transfusion | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Transfusion | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with postpartum Hemorrhage | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Postpartum Hemorrhage | Risk of Bias |
| (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | ||||
| 1 | Theiler, R. N. | 2021.8 | 0/140 | 1/1862 | 2/140 | 37/1862 | 1/140 | 6/1862 | 3/140 | 38/1862 | 6/140 | 57/1862 | 25/140 | 241/1862 | 1/140 | 5/1862 | low |
| 2 | Butt, A. A. | 2021.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| 3 | Collier, A. Y. | 2021.5 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | low |
| 4 | Dagan, N. | 2021.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| 5 | Blakeway, H. | 2021.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 13/133 | 36/399 | low |
| 6 | Goldshtein, I. | 2021.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| Record Number | First Author | Published Time | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Operative Vaginal Delivery | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Operative Vaginal Delivery | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Cesarean Delivery | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Cesarean Delivery | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Eclampsia or Preeclampsia | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Eclampsia or Preeclampsia | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Pregestational Hypertension | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Pregestational Hypertension | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Thromboembolism | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Thromboembolism | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Stroke | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Stroke | Risk of Bias |
| (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | (n/N) | ||||
| 1 | Theiler, R. N. | 2021.8 | 89/140 | 1238/1862 | 7/140 | 69/1862 | 44/140 | 555/1862 | 1/140 | 23/1862 | 19/140 | 225/1862 | 0/129 | 2/1580 | 0/129 | 2/1581 | low |
| 2 | Butt, A. A. | 2021.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| 3 | Collier, A. Y. | 2021.5 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | low |
| 4 | Dagan, N. | 2021.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| 5 | Blakeway, H. | 2021.8 | 71/133 | 221/399 | 21/133 | 42/399 | 41/133 | 136/399 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| 6 | Goldshtein, I. | 2021.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 20/7530 | 21/7530 | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| Record Number | First Author | Published Time | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Abortion (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Abortion (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Preterm Birth (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Preterm Birth (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Term Birth (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Term Birth (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Stillbirth (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Stillbirth (n/N) | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Theiler, R. N. | 2021.8 | 1/140 | 4/1862 | 12/140 | 155/1862 | 127/140 | 1703/1862 | 0/140 | 6/1862 | Low |
| 2 | Butt, A. A. | 2021.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Low |
| 3 | Collier, A. Y. | 2021.5 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | Low |
| 4 | Dagan, N. | 2021.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Low |
| 5 | Blakeway, H. | 2021.8 | - | - | 16/133 | 48/399 | - | - | 0/133 | 1/399 | Low |
| 6 | Goldshtein, I. | 2021.7 | 128/7530 | 118/7530 | 77/1387 | 85/1427 | - | - | 1/7530 | 2/7530 | Low |
| Record Number | First Author | Published Time | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with (Very) Low Birthweight (<2500 g) (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with (Very) Low Birthweight (<2500 g) (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Neonatal Birth Trauma (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Neonatal Birth Trauma (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Admission to the Neonatal ICU (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Admission to the Neonatal ICU (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Neonatal Death (n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Neonatal Death (n/N) | Vaccinated Pregnant Women with Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy(n/N) | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women with Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy(n/N) | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Theiler, R. N. | 2021.8 | 14/140 | 142/1862 | 0/140 | 11/1862 | 1/140 | 11/1862 | 0/140 | 0/1862 | 0/140 | 1/1862 | low |
| 2 | Butt, A. A. | 2021.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| 3 | Collier, A. Y. | 2021.5 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/22 | low |
| 4 | Dagan, N. | 2021.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| 5 | Blakeway, H. | 2021.8 | - | - | - | - | 7/133 | 20/399 | - | - | - | - | low |
| 6 | Goldshtein, I. | 2021.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | low |
| Outcomes | Vaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | I2% | P-Heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infection | 255/19,078 | 678/21,848 | 0.495 | 0.348–0.703 | 0.000 | 57.6 | 0.051 |
| Hospitalization | 24/18,391 | 48/18,391 | 0.501 | 0.306–0.818 | 0.006 | 0 | 0.618 |
| Death | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Location | OR | 95%CI | Weight% | p-Value | I2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 0.114 | 0.028–0.464 | 5.59 | |||
| Qatar | 0.129 | 0.029–0.568 | 5.07 | |||
| Israel | 0.564 | 0.482–0.660 | 84.27 | |||
| England | 1.062 | 0.242–4.666 | 5.08 | |||
| Vaccine type | OR | 95%CI | weight% | p-value | I2 | P |
| BNT162b2 | 0.564 | 0.482–0.660 | 84.27 | |||
| BNT162b2+Moderna | 0.129 | 0.029–0.568 | 5.07 | |||
| mRNA + adenovirus vector vaccine | 0.343 | 0.039–3.057 | 10.66 | |||
| No. Of dose | OR | 95%CI | weight% | p-value | I2 | P |
| ≥1 | 0.441 | 0.160–1.214 | 52.35 | |||
| 2 | 0.324 | 0.082–1.278 | 47.65 | |||
| Population size | OR | 95%CI | weight% | p-value | I2 | P |
| <1000 | 0.370 | 0.047–2.920 | 10.14 | |||
| 1000–10,000 | 0.114 | 0.028–0.464 | 5.59 | |||
| >10,000 | 0.564 | 0.482–0.660 | 84.27 | |||
| Study design | OR | 95%CI | weight% | p-value | I2 | P |
| Retrospective cohort study | 0.542 | 0.408–0.722 | 94.93 | |||
| Prospective cohort study | 0.129 | 0.029–0.568 | 5.07 | |||
| Median age | OR | 95%CI | weight% | p-value | I2 | P |
| <35 | 0.471 | 0.325–0.682 | 94.92 | |||
| ≥35 | 1.062 | 0.242–4.666 | 5.08 | |||
| Overall | 0.495 | 0.348–0.703 | 100.00 | <0.05 | 57.6% | 0.051 |
| Outcomes | Source of Data | Vaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | I2 | P-Heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uterine rupture | 1, 3 | 0/140 | 1/1862 | 4.416 | 0.179–108.909 | 0.364 | - | - |
| Third- or fourth-degree laceration | 1, 3 | 2/140 | 37/1862 | 0.715 | 0.170–2.997 | 0.646 | - | - |
| Return to the operating room within 72 h of delivery | 1, 3 | 1/140 | 6/1862 | 2.225 | 0.266–18.615 | 0.460 | - | - |
| 5 min Apgar score < 7 | 1, 3 | 3/140 | 38/1862 | 1.051 | 0.320–3.449 | 0.934 | - | - |
| Quantitative blood loss > 1000 mL | 1, 3 | 6/140 | 57/1862 | 1.418 | 0.600–3.348 | 0.426 | - | - |
| Transfusion | 1, 3 | 25/140 | 241/1862 | 1.462 | 0.929–2.300 | 0.100 | - | - |
| Postpartum hemorrhage with blood transfusion | 1, 3, 5 | 14/273 | 41/2261 | 1.181 | 0.625–2.234 | 0.608 | 0 | 0.437 |
| Spontaneous vaginal delivery | 1, 3, 5 | 160/273 | 1459/2261 | 0.899 | 0.690–1.171 | 0.429 | 0 | 0.861 |
| Operative vaginal delivery | 1, 3, 5 | 28/273 | 111/2261 | 1.514 | 0.955–2.401 | 0.078 | 0 | 0.759 |
| Cesarean delivery | 1, 3, 5 | 85/273 | 691/2261 | 0.979 | 0.741–1.293 | 0.880 | 0 | 0.432 |
| Eclampsia or preeclampsia up to 72 h from delivery | 1, 3, 6 | 21/7670 | 44/9392 | 0.912 | 0.507–1.640 | 0.759 | 0 | 0.638 |
| Gestational hypertension | 1, 3 | 19/140 | 225/2862 | 1.142 | 0.691–1.890 | 0.604 | - | - |
| Thromboembolism within 4 weeks before or after delivery | 1, 3 | 0/129 | 2/1580 | 2.438 | 0.116–51.047 | 0.566 | - | - |
| Stroke within 4 weeks before or after delivery | 1, 3 | 0/129 | 2/2581 | 2.439 | 0.116–51.080 | 0.566 | - | - |
| Outcomes | Vaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | I2 | P-Heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abortion | 129/7670 | 122/9392 | 1.102 | 0.858–1.416 | 0.447 | 0 | 0.319 |
| Preterm birth | 105/1660 | 288/3688 | 0.958 | 0.742–1.237 | 0.743 | 0 | 0.944 |
| Term birth | 127/140 | 1703/1862 | 0.912 | 0.504–1.651 | 0.761 | - | - |
| Stillbirth | 1/7803 | 9/9791 | 0.738 | 0.149–3.651 | 0.710 | 0 | 0.913 |
| Outcomes | Source of Data | Vaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | Unvaccinated Pregnant Women n/N | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | I2 | P-Heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal birth trauma | 1, 3 | 0/140 | 11/1862 | 0.573 | 0.034–9.773 | 0.700 | - | - |
| (Very) low birthweight (<2500 g) | 1, 3 | 14/140 | 142/1862 | 1.346 | 0.755–2.399 | 0.314 | - | - |
| Admission to the neonatal ICU | 1, 3, 5 | 8/273 | 31/2261 | 1.076 | 0.478–2.424 | 0.860 | 0 | 0.903 |
| Neonatal death | 1, 3 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| Neonatal hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy | 1, 3 | 0/140 | 1/1862 | 4.416 | 0.179–108.909 | 0.364 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Deng, J.; Liu, Q.; Du, M.; Liu, M.; Liu, J. Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccine among Pregnant Women in Real-World Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020246
Ma Y, Deng J, Liu Q, Du M, Liu M, Liu J. Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccine among Pregnant Women in Real-World Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vaccines. 2022; 10(2):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020246
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yirui, Jie Deng, Qiao Liu, Min Du, Min Liu, and Jue Liu. 2022. "Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccine among Pregnant Women in Real-World Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Vaccines 10, no. 2: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020246
APA StyleMa, Y., Deng, J., Liu, Q., Du, M., Liu, M., & Liu, J. (2022). Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccine among Pregnant Women in Real-World Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vaccines, 10(2), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020246







