Development of a Subunit Vaccine against Duck Hepatitis A Virus Serotype 3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DHAV-3 Virus Culture
2.2. Recombinant Protein Expression of VP1, VP1-C, and nFliC
2.3. Vaccine Preparation and Immunization of Ducklings
2.4. Analysis of Humoral Immune Response
2.5. Analysis of Cellular Immune Response
2.6. Analysis of Cytokine mRNA Levels
2.7. Duck Hepatitis A Virus Serotype 3 Challenge Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
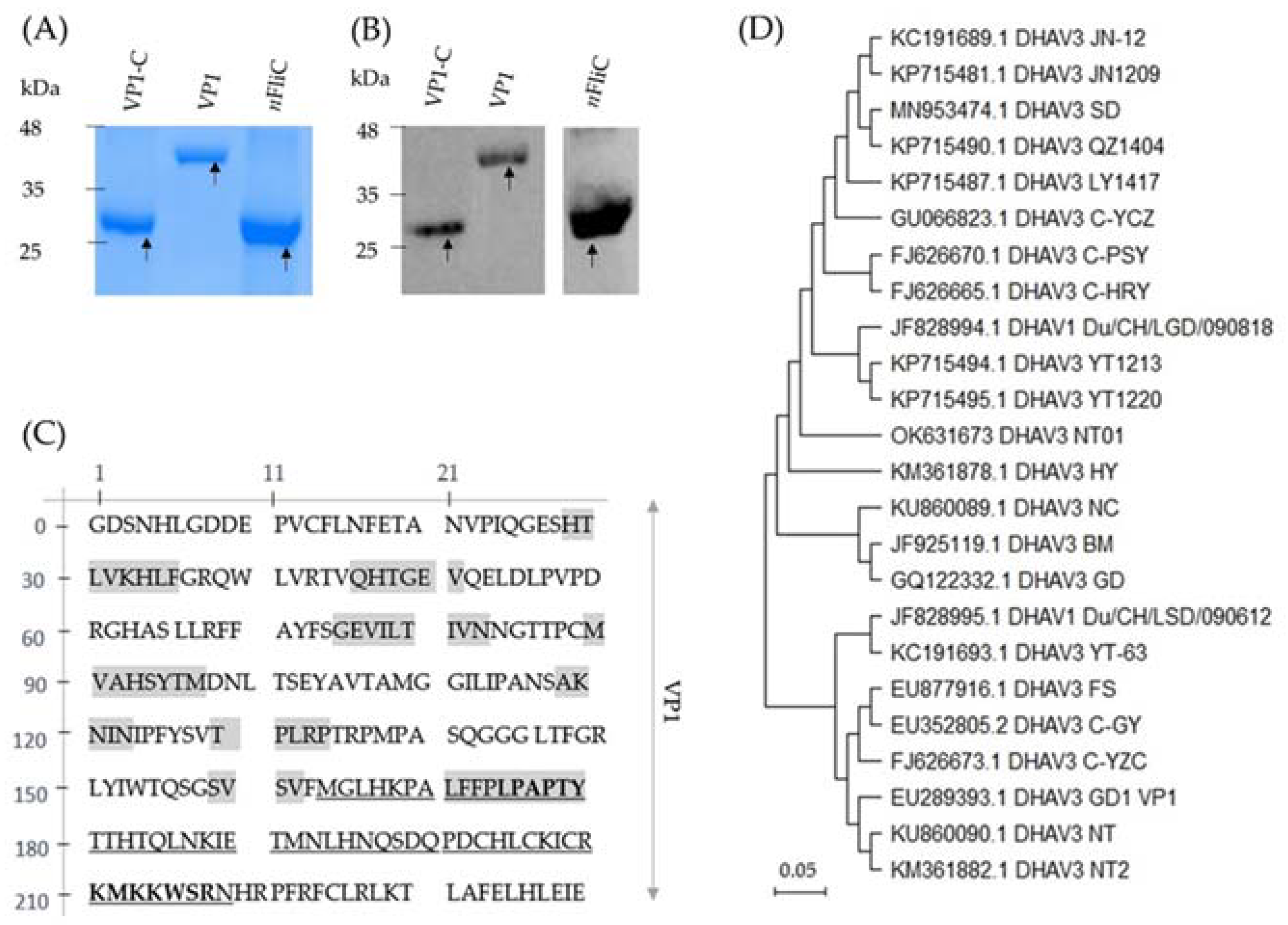
3.1. Recombinant VP1 and VP1-C Were Formulated as Vaccines
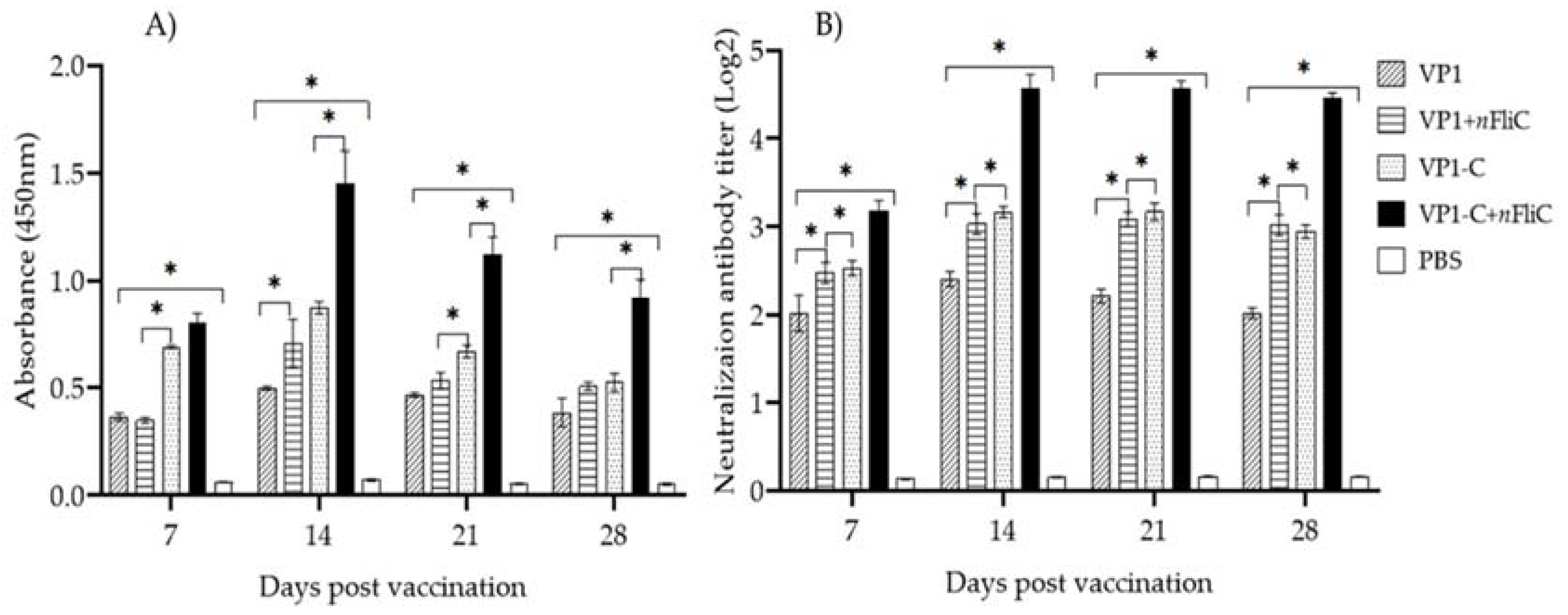
3.2. VP-1C + nFliC Elicited the Highest Level of Virus-Specific Antibody and Neutralization Titer
3.3. VP-1C + nFliC Elicited the Highest Level of T Cell Immune Response
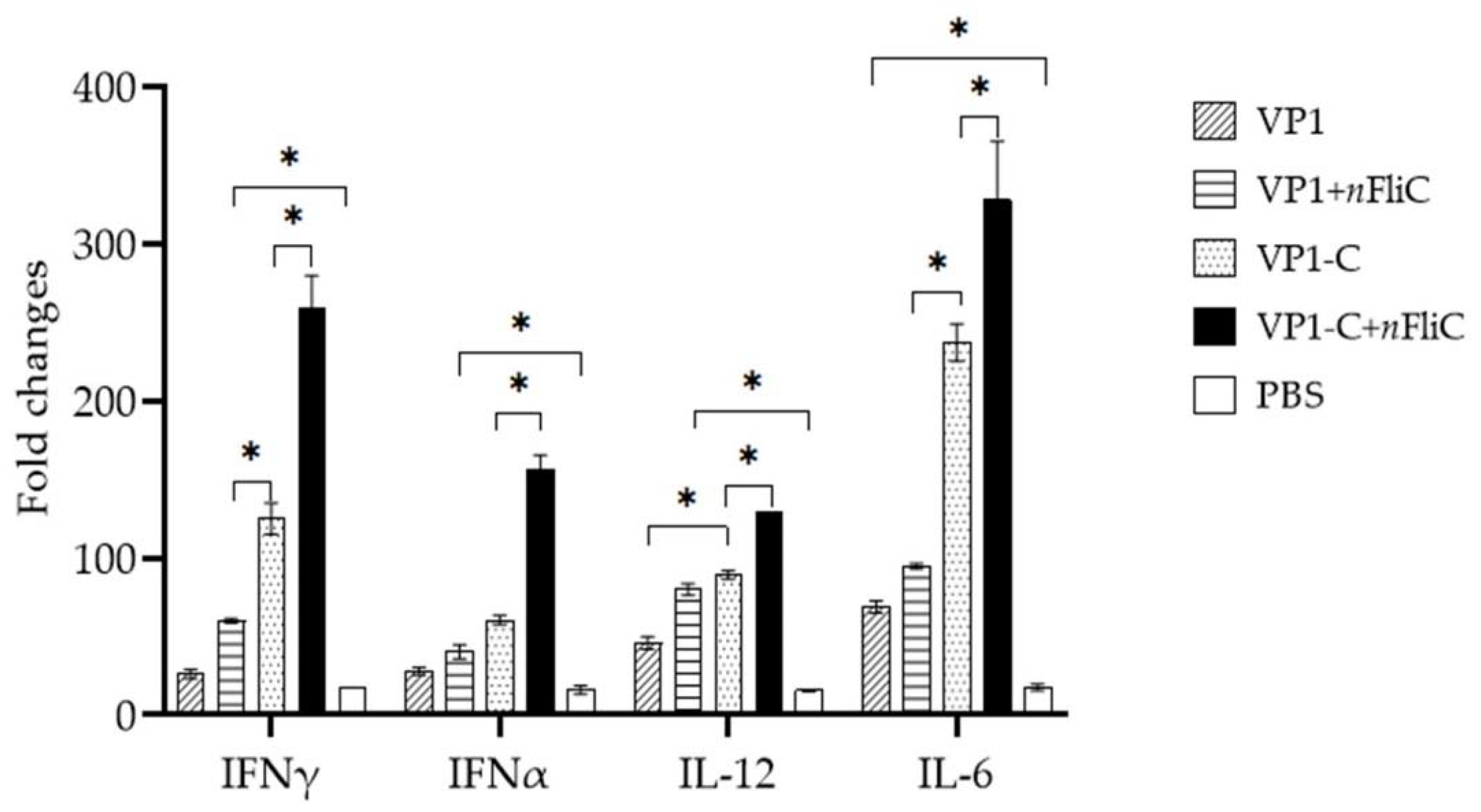
3.4. VP1-C + nFliC Elicited the Highest Level of ProInflammatory Cytokine Expression
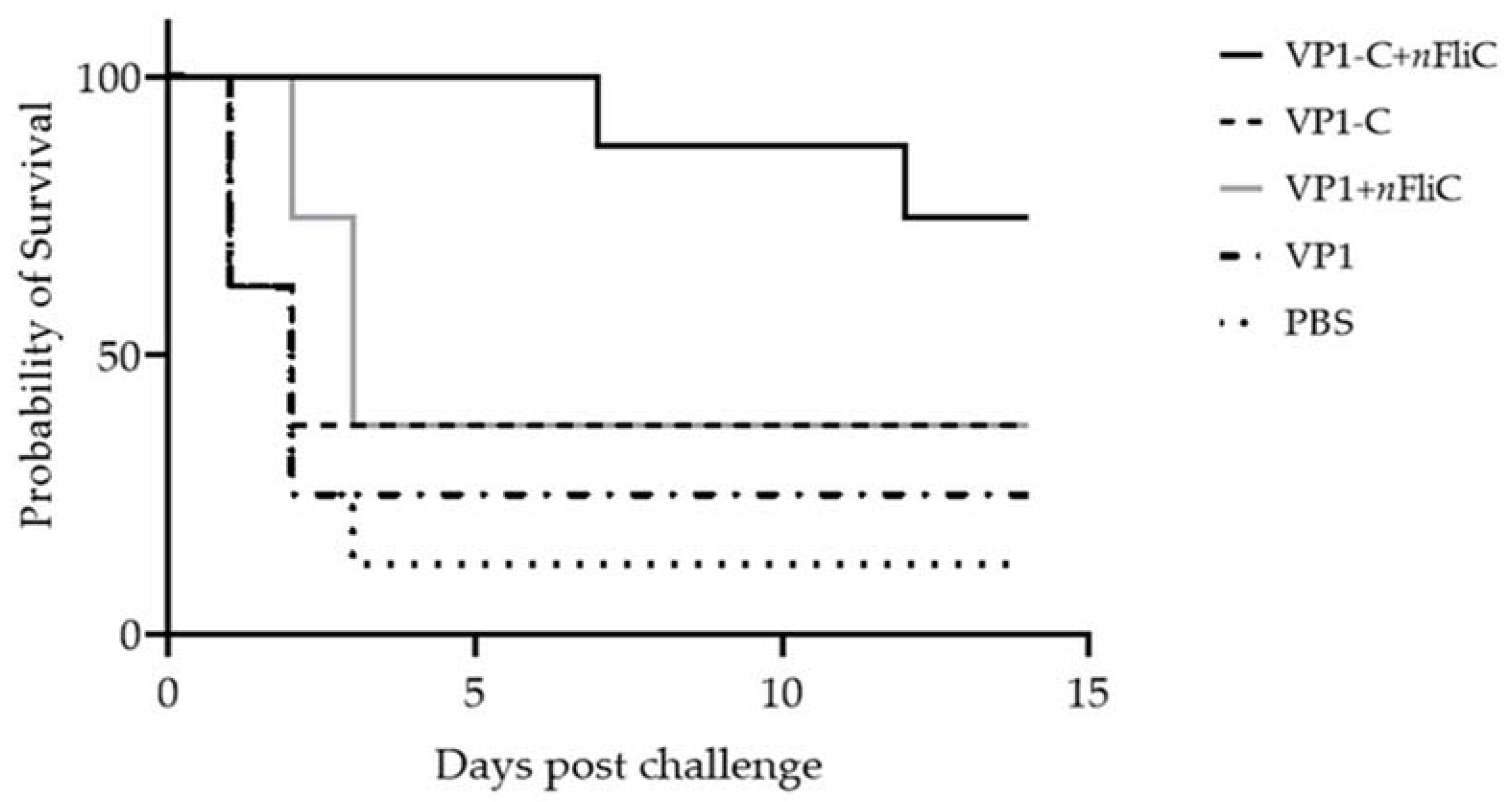
3.5. VP1-C + nFliC Provided 75% Protection Rate in a Challenge Experiment versus 25% for VP1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Lin, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Meng, F.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Evidence of VP1 of Duck Hepatitis A Type 1 Virus as a Target of Neutralizing Antibodies and Involving Receptor-Binding Activity. Virus Res. 2017, 227, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yugo, D.M.; Hauck, R.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Meng, X.-J. Hepatitis Virus Infections in Poultry. Avian Dis. 2016, 60, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Lan, J.; Lin, S.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, S. A Novel Peptide Isolated from a Phage Display Peptide Library Modeling Antigenic Epitope of DHAV-1 and DHAV-3. Vaccines 2020, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wulin, S.; Bai, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Identification of a Conserved B-Cell Epitope on Duck Hepatitis a Type 1 Virus VP1 Proteine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118041. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.C.; Kim, M.J.; Kwon, Y.K.; Lindberg, A.M.; Joh, S.J.; Kwon, H.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Kwon, J.H. Development of Duck Hepatitis A Virus Type 3 Vaccine and Its Use to Protect Ducklings against Infections. Vaccine 2009, 27, 6688–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Pan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D. Molecular Detection and Typing of Duck Hepatitis A Virus Directly from Clinical Specimens. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 131, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Guo, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, M.; Cao, D.; Cheng, A.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; et al. Mutations in VP0 and 2C Proteins of Duck Hepatitis a Virus Type 3 Attenuate Viral Infection and Virulence. Vaccines 2019, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, M.; Yang, X.; Du, J.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, H. Recovery of Duck Hepatitis A Virus 3 from a Stable Full-Length Infectious CDNA Clone. Virus Res. 2011, 160, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, H.; Doan, T.; Thi, X.; Le, K.; Thi, R.; Thi, K.; Thanh, N.; Le, H. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis Reveal the Prevalence of Duck Hepatitis A Virus Genotype-3 in Vietnam. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2017, 23, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Meng, C.; Li, L.; Liu, G. High Yield Expression of Duck Hepatitis A Virus VP1 Protein in Escherichia Coli, and Production and Characterization of Polyclonal Antibody. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 191, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H.; Knowles, N.J.; Tsai, H.J. Molecular Analysis of Duck Hepatitis Virus Type 1 Indicates That It Should Be Assigned to a New Genus. Virus Res. 2007, 123, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.C.; Kwon, Y.K.; Joh, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Tolf, C.; Kim, J.H.; Sung, H.W.; Lindberg, A.M.; Kwon, J.H. Recent Korean Isolates of Duck Hepatitis Virus Reveal the Presence of a New Geno- and Serotype When Compared to Duck Hepatitis Virus Type 1 Type Strains. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, V.; Bashiruddin, J.B.; Belsham, G.J.; Stenfeldt, C.; Bøtner, A.; Knowles, N.J.; Bankowski, B.; Parida, S.; Barnett, P. Characteristics of a Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus with a Partial VP1 G-H Loop Deletion in Experimentally Infected Cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, N.; Semler, B.L.; Rothberg, P.G.; Larsen, G.R.; Adler, C.J.; Dorner, A.J.; Emini, E.A.; Hanecak, R.; Lee, J.J.; Van Der Werf, S.; et al. Primary Structure, Gene Organization and Polypeptide Expression of Poliovirus RNA. Nature 1981, 291, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Wang, M.; Wen, X.; Cheng, A.; Jia, R.; Sun, K.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; et al. Cleavage of poly(A)-binding Protein by Duck Hepatitis A Virus 3C Protease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.G.; Jo, Y.J.; Sung, J.H.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, K.N.; Park, S.G. Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies Specific for Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Type A and Type O VP1. Hybridoma 2012, 31, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Kwon, Y.K.; Joh, S.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.J. Molecular Analysis of Duck Hepatitis Virus Type 1 Reveals a Novel Lineage Close to the Genus Parechovirus in the Family Picornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3307–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, T.; Belsham, G.J. Identification of Plasticity and Interactions of a Highly Conserved Motif within a Picornavirus Capsid Precursor Required for Virus Infectivity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.-C.; Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E. Picornavirus Morphogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curry, S.; Fry, E.; Blakemore, W.; Abu-Ghazaleh, R.; Jackson, T.; King, A.; Lea, S.; Newman, J.; Stuart, D. Dissecting the Roles of VP0 Cleavage and RNA Packaging in Picornavirus Capsid Stabilization: The Structure of Empty Capsids of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 9743–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakeel, S.; Westerhuis, B.M.; Ora, A.; Koen, G.; Bakker, A.Q.; Claassen, Y.; Wagner, K.; Beaumont, T.; Wolthers, K.C.; Butcher, S.J. Structural Basis of Human Parechovirus Neutralization by Human Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9571–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sherry, B.; Mosser, A.G.; Colonno, R.J.; Rueckert, R.R. Use of Monoclonal Antibodies to Identify Four Neutralization Immunogens on a Common Cold Picornavirus, Human Rhinovirus 14. J. Virol. 1986, 57, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dill, V.; Eschbaumer, M. Cell Culture Propagation of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus: Adaptive Amino Acid Substitutions in Structural Proteins and Their Functional Implications. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azuma, H.; Yoneda, S. Structure and Dynamics of the GH Loop of the Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Capsid. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2009, 28, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossmann, M.G.; Arnold, E.; Erickson, J.W.; Frankenberger, E.A.; Griffith, J.P.; Hecht, H.J.; Johnson, J.E.; Kamer, G.; Luo, M.; Mosser, A.G.; et al. Structure of a Human Common Cold Virus and Functional Relationship to Other Picornaviruses. Nature 1985, 317, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, S.; Hernéndez, J.; Blakemore, W.; Brocchi, E.; Curry, S.; Domingo, E.; Fry, E.; Ghazaleh, R.A.; King, A.; Newman, J.; et al. The Structure and Antigenicity of a Type C Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus. Structure 1994, 2, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateu, M.G. Antibody Recognition of Picornaviruses and Escape from Neutralization: A Structural View. Virus Res. 1995, 38, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kurnasov, O.; Natarajan, V.; Hong, M.; Gudkov, A.V.; Osterman, A.L. Structural Basis of TLR5-Flagellin Recognition and Signaling. Science 2012, 335, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doan, T.; Wang, H.; Ke, G.; Cheng, L. N-Terminus of Flagellin Fused to an Antigen Improves Vaccine Efficacy against Pasteurella Multocida Infection in Chickens. Vaccines 2020, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. Simple Method of Estimating Fifty Percent Endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Ma, L.; Rao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; He, Q.; Luo, R. Duck Tembusu Virus Infection Promotes the Expression of Duck Interferon-Induced Protein 35 to Counteract RIG-I Antiviral Signaling in Duck Embryo Fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12 (July), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Lin, Y.M.; Yen, T.Y.; Yang, W.J.; Chu, C.Y. CpG Oligodeoxynucleotides Containing GACGTT Motifs Enhance the Immune Responses Elicited by a Goose Parvovirus Vaccine in Ducks. Vaccine 2010, 28, 7956–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, M.; Jiang, B.; Dai, X.; Meng, J. Antigenic Characteristics of the Complete and Truncated Capsid Protein VP1 of Enterovirus 71. Virus Res. 2012, 167, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, D.G.W.; Alonso, S.; Chow, V.T.K.; Poh, C.L. Passive Protection against Lethal Enterovirus 71 Infection in Newborn Mice by Neutralizing Antibodies Elicited by a Synthetic Peptide. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Chou, A.H.; Lien, S.P.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Guo, M.S.; Chow, Y.H.; Yang, W.S.; Chang, K.H.W.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Cross-Neutralization Epitope of Enterovirus 71. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4362–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Gu, L.; Wu, S.; Zhu, S. Duck Hepatitis a Virus Structural Proteins Expressed in Insect Cells Self-Assemble into Virus-like Particles with Strong Immunogenicity in Ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 215, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | Gene-Length (bp) | Annealing Temp. (°C) | GenBank | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VP1 | F | 1 gaattcatgggtgattctaatcatctt | 732 | 53 | OK631673 |
| R | aagcttttcaatttccaaatggagct | ||||
| VP1-C | F | gaattcatgggcaggttgtatatctgg | 222 | 53 | OK631673 |
| R | aagcttattgcgagaccatttctt | ||||
| nFliC | F | gaattcatgaactgcactaaacaaact | 309 | 52 | [29] |
| R | aagcttttcagcctggatggagtc | ||||
| GAPDH | F | atcacaccacacatggcgt | 207 | 59.5 | GCA_015476345.1 |
| R | tttatagccgccgaggctg | ||||
| IFN-γ | F | cagacctactgcttgtttgt | 192 | 53.5 | AJ012254 |
| R | ttcatttctctctgtccagt | ||||
| IFN-α | F | cagccatctacagcgccc | 138 | 60 | AY879230.1 |
| R | ggctgggagccatgttgc | ||||
| IL-12 | F | ctggaggtcattgatgaggtg | 168 | 56 | AJ564201 |
| R | gaaagtcaaagggaagtaggac | ||||
| IL-6 | F | accgtgtgcgagaacagc | 135 | 60 | AB191038 |
| R | gaaaagcccgctggagagt | ||||
| DHAV-1 | F | gccccactctatggaaatttg | 767 | 53 | [9] |
| R | atttggtcagattcaatttcc | ||||
| DHAV-3 | F | atgcgagttggtaaggattttcag | 881 | 56 | [9] |
| R | gatcctgatttaccaacaaccat | ||||
| qVP1 | F | atgaaccagtgtgttttctc | 175 | 53 | OK631673 |
| R | aacagagatgcatgaccc |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Truong, T.-N.; Cheng, L.-T. Development of a Subunit Vaccine against Duck Hepatitis A Virus Serotype 3. Vaccines 2022, 10, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040523
Truong T-N, Cheng L-T. Development of a Subunit Vaccine against Duck Hepatitis A Virus Serotype 3. Vaccines. 2022; 10(4):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040523
Chicago/Turabian StyleTruong, Trang-Nhu, and Li-Ting Cheng. 2022. "Development of a Subunit Vaccine against Duck Hepatitis A Virus Serotype 3" Vaccines 10, no. 4: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040523
APA StyleTruong, T.-N., & Cheng, L.-T. (2022). Development of a Subunit Vaccine against Duck Hepatitis A Virus Serotype 3. Vaccines, 10(4), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040523






